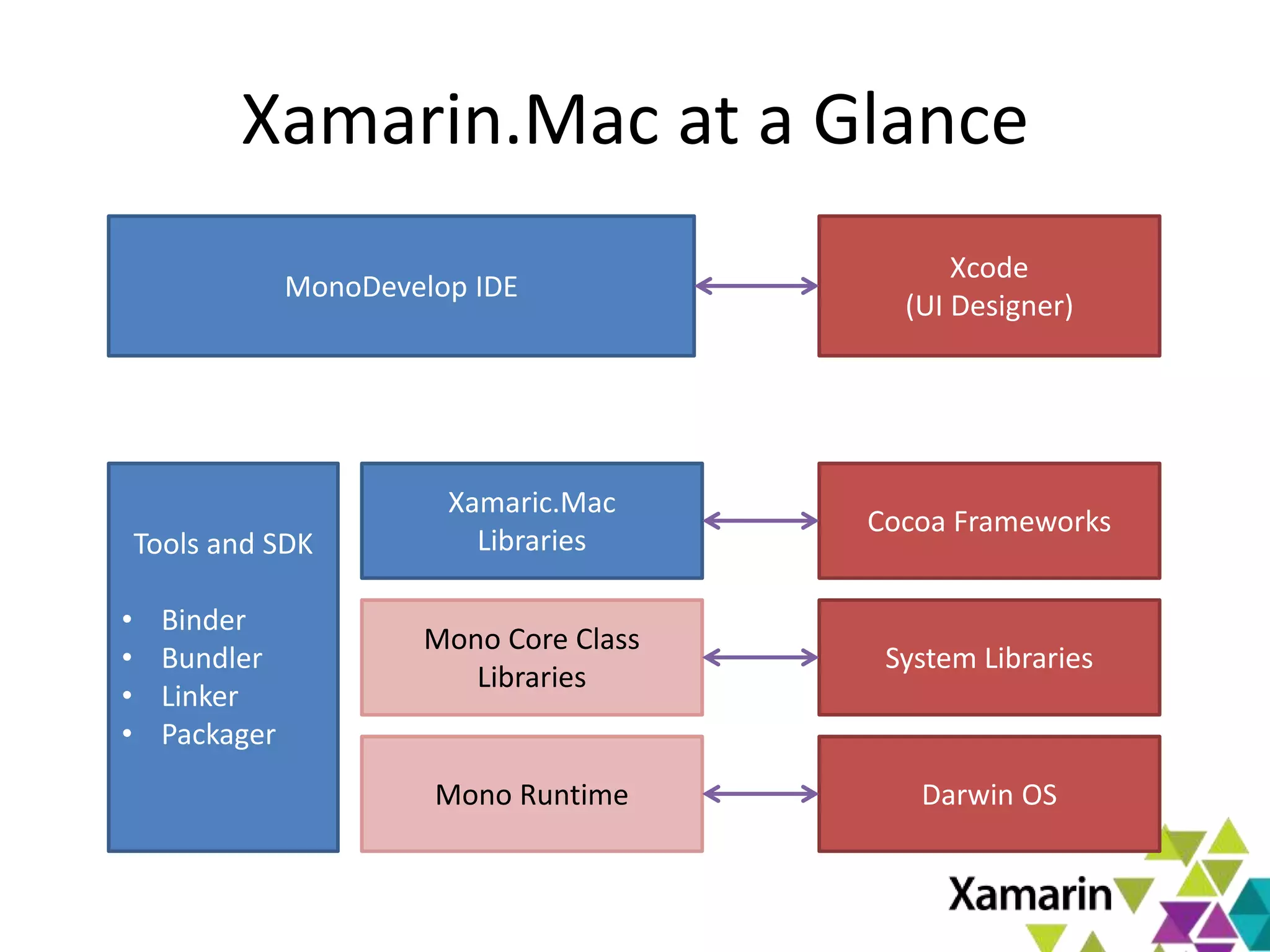
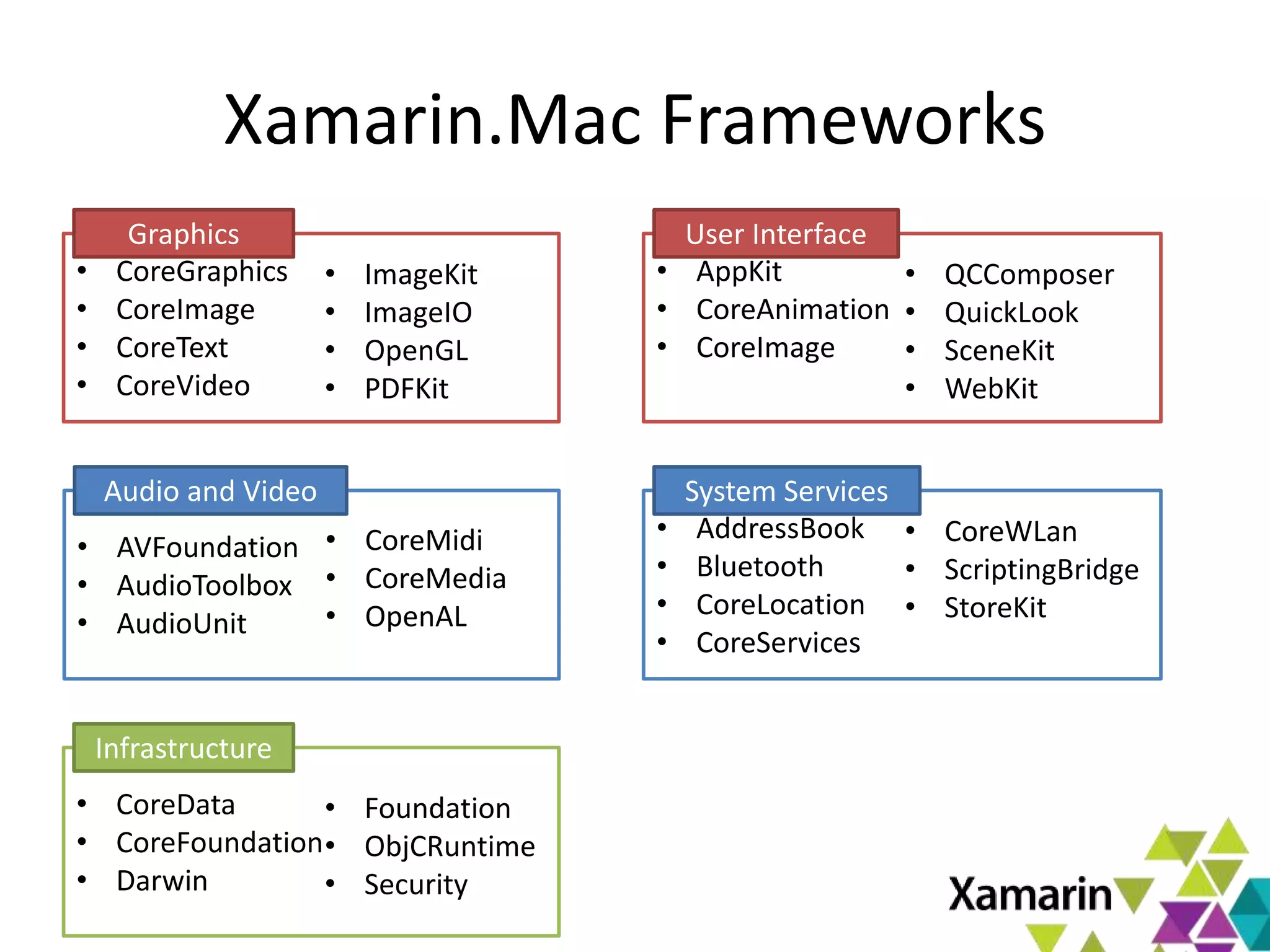
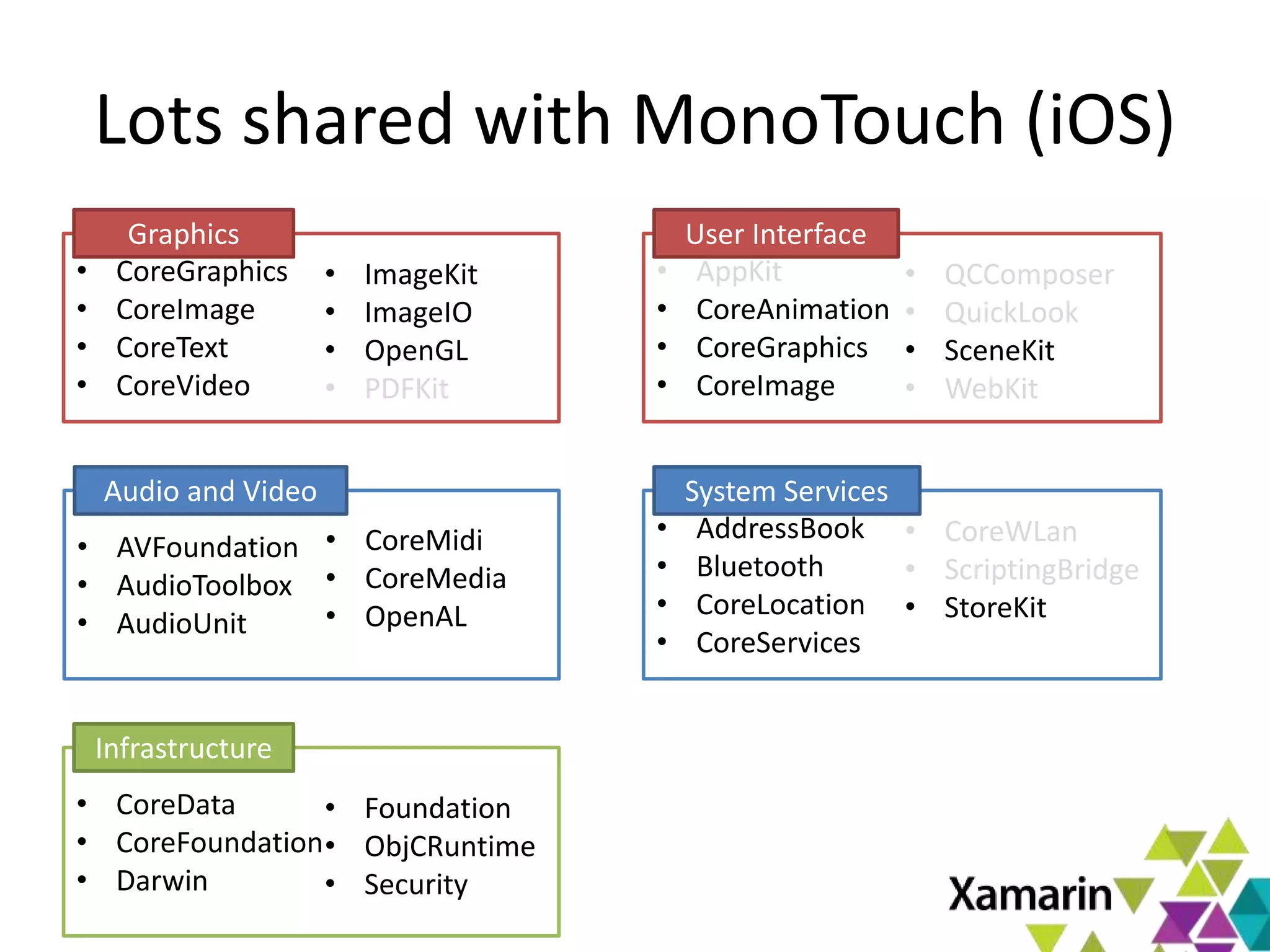
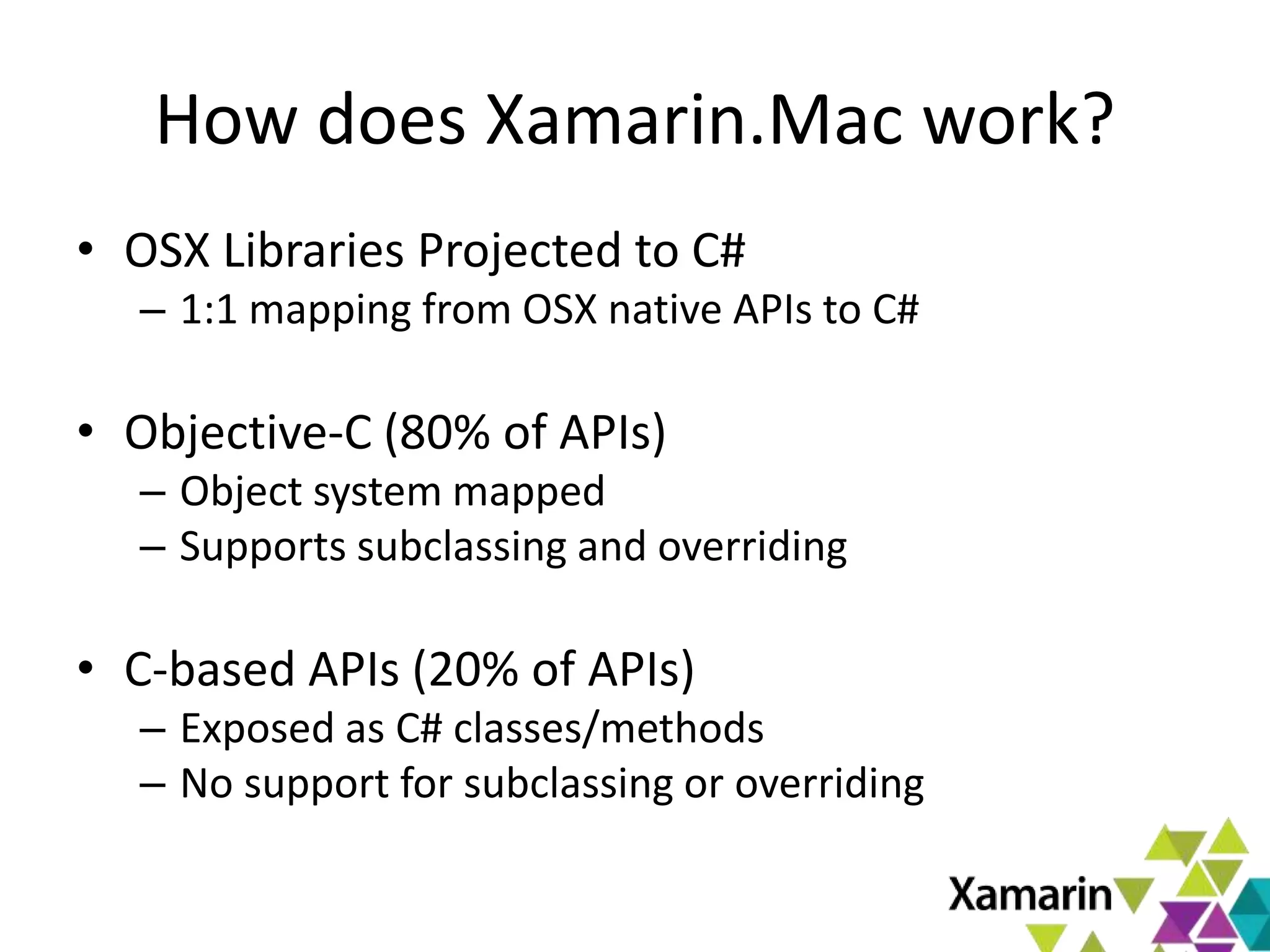
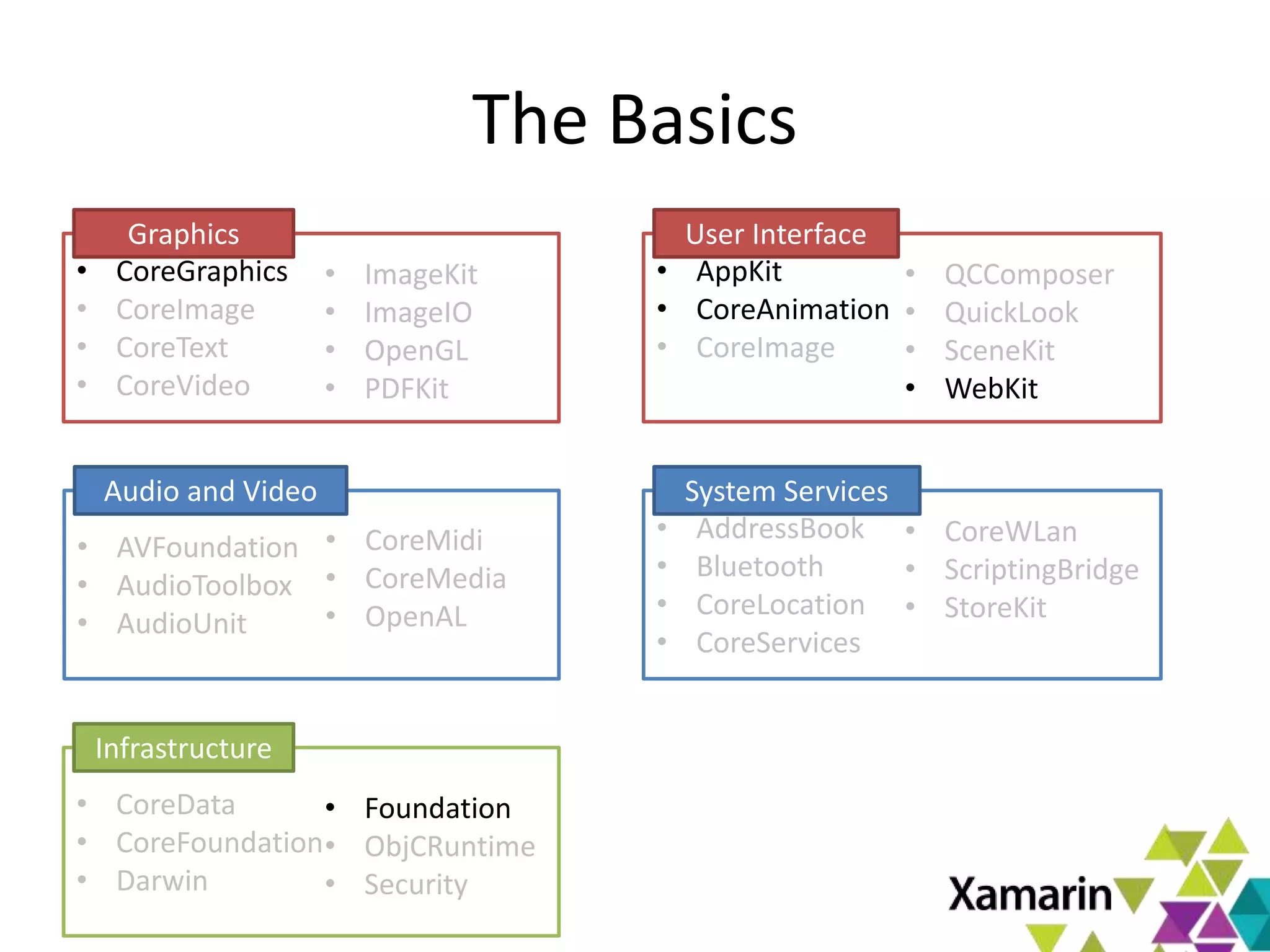
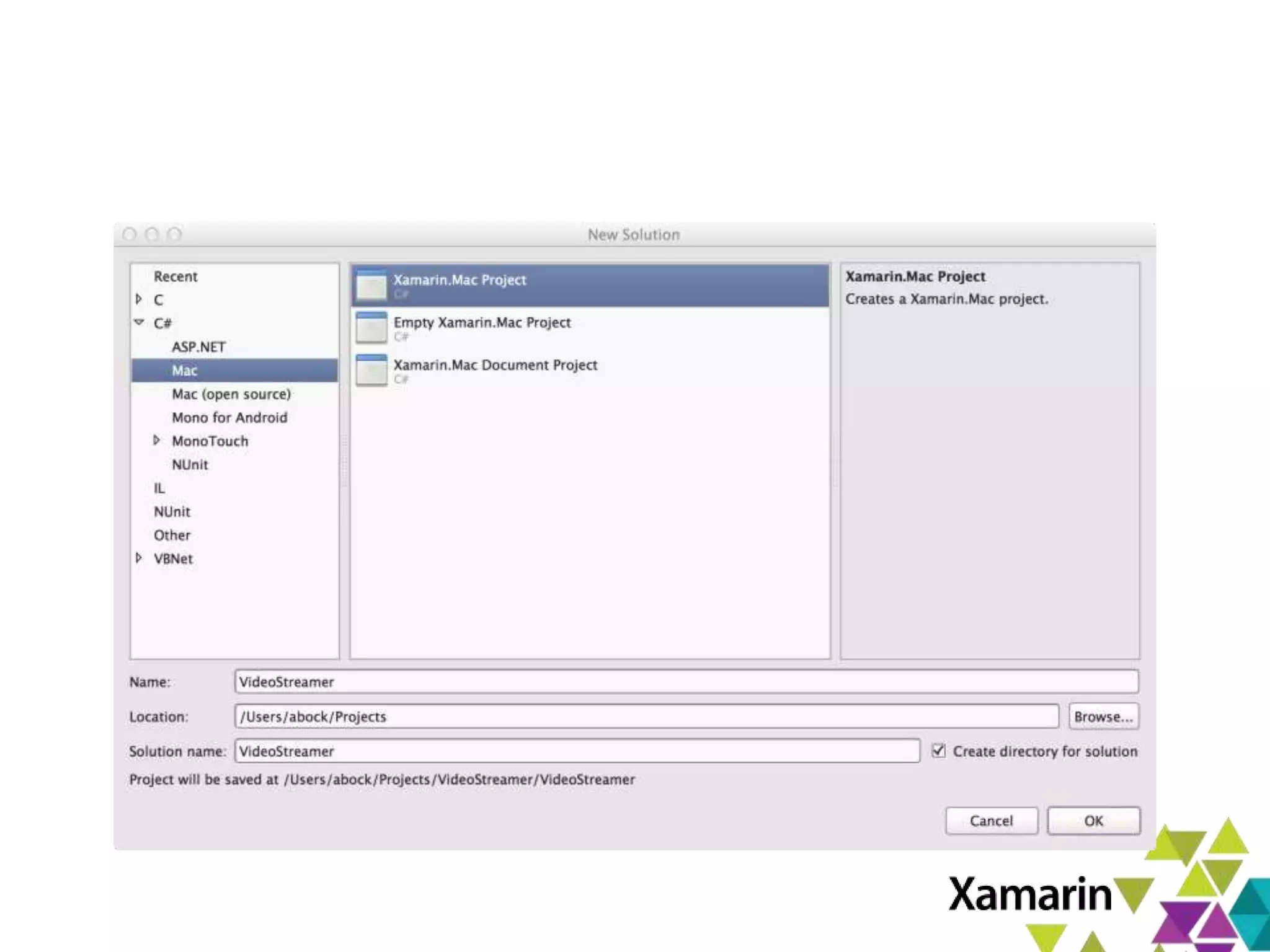
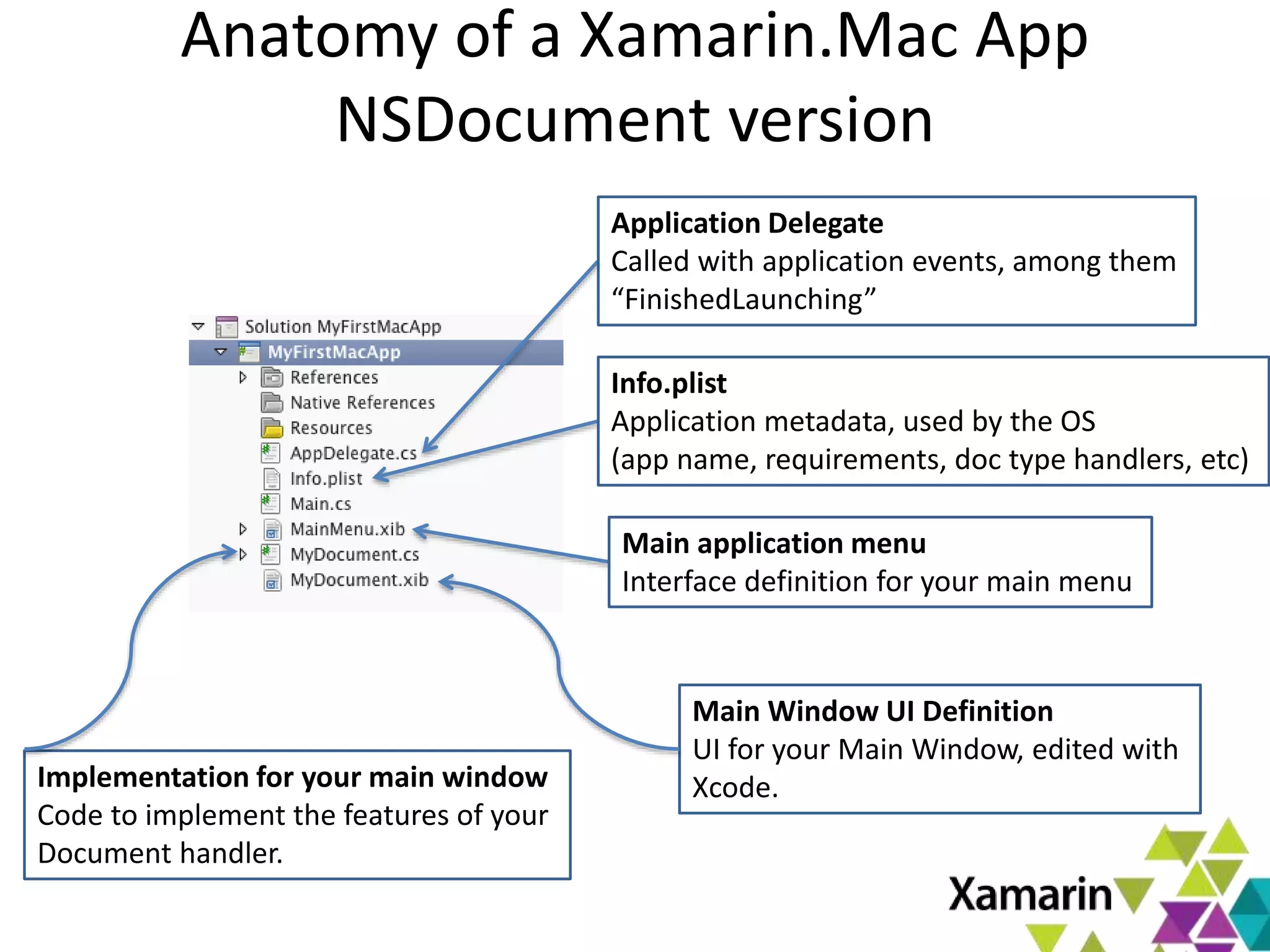
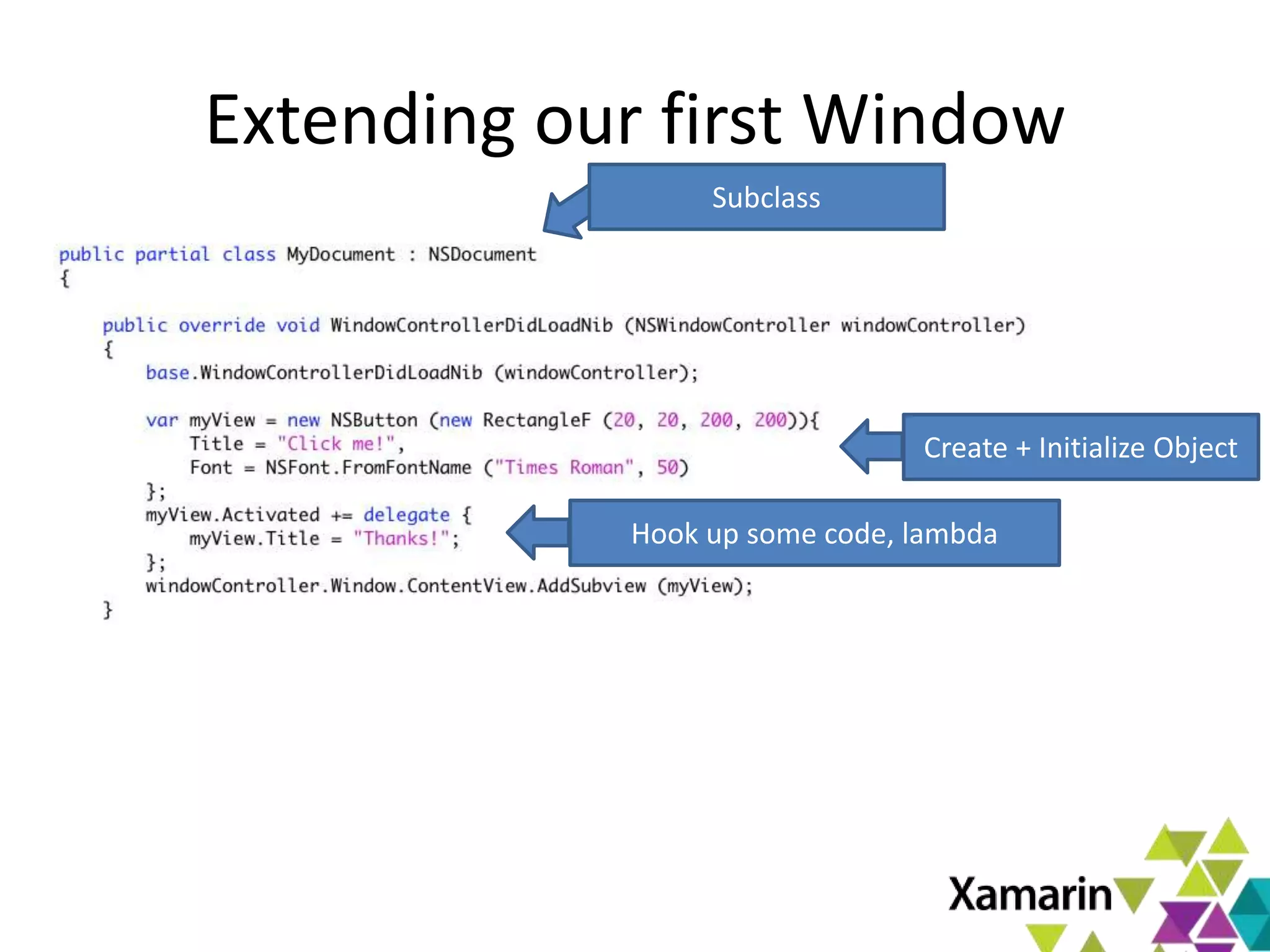
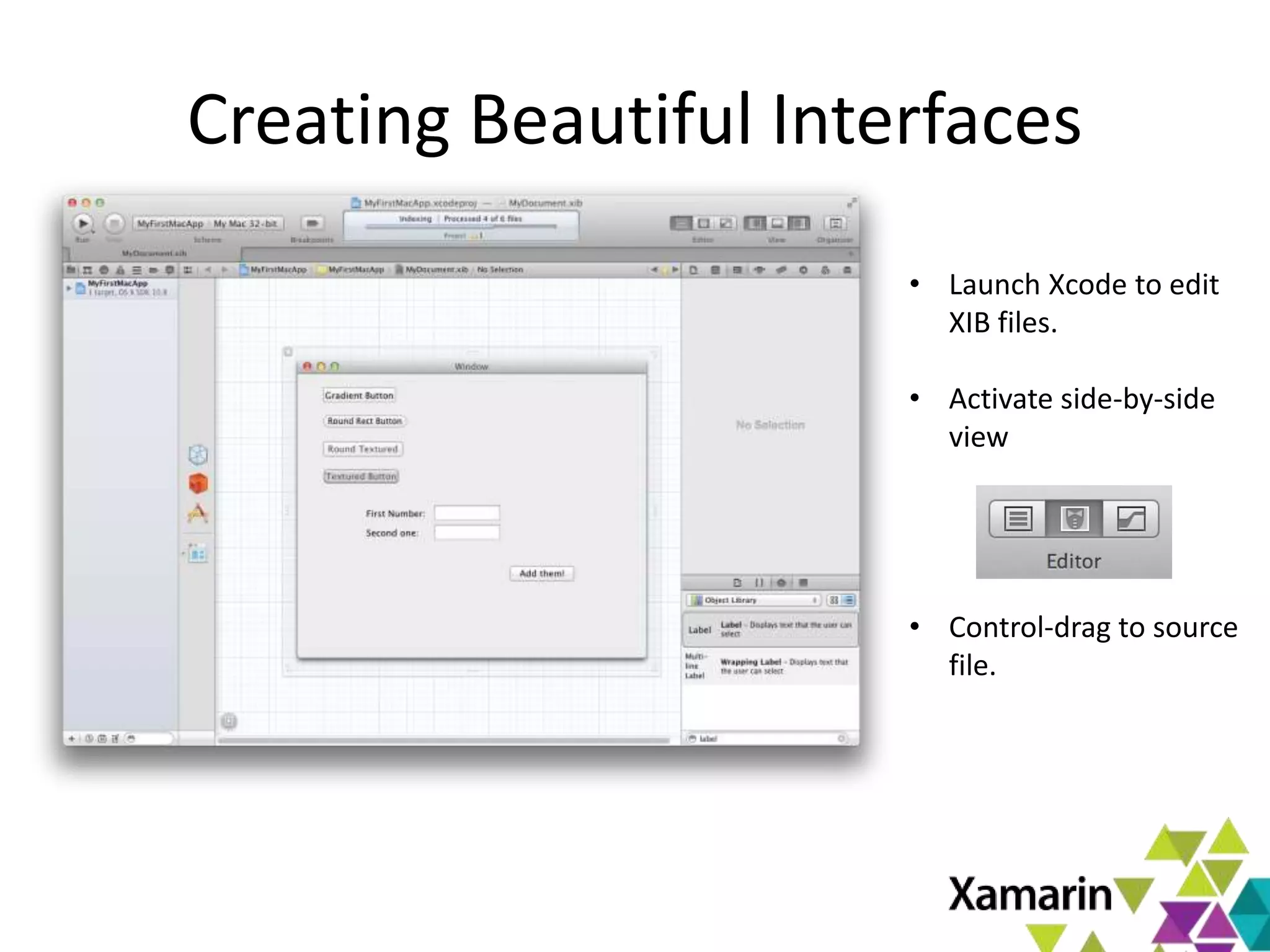
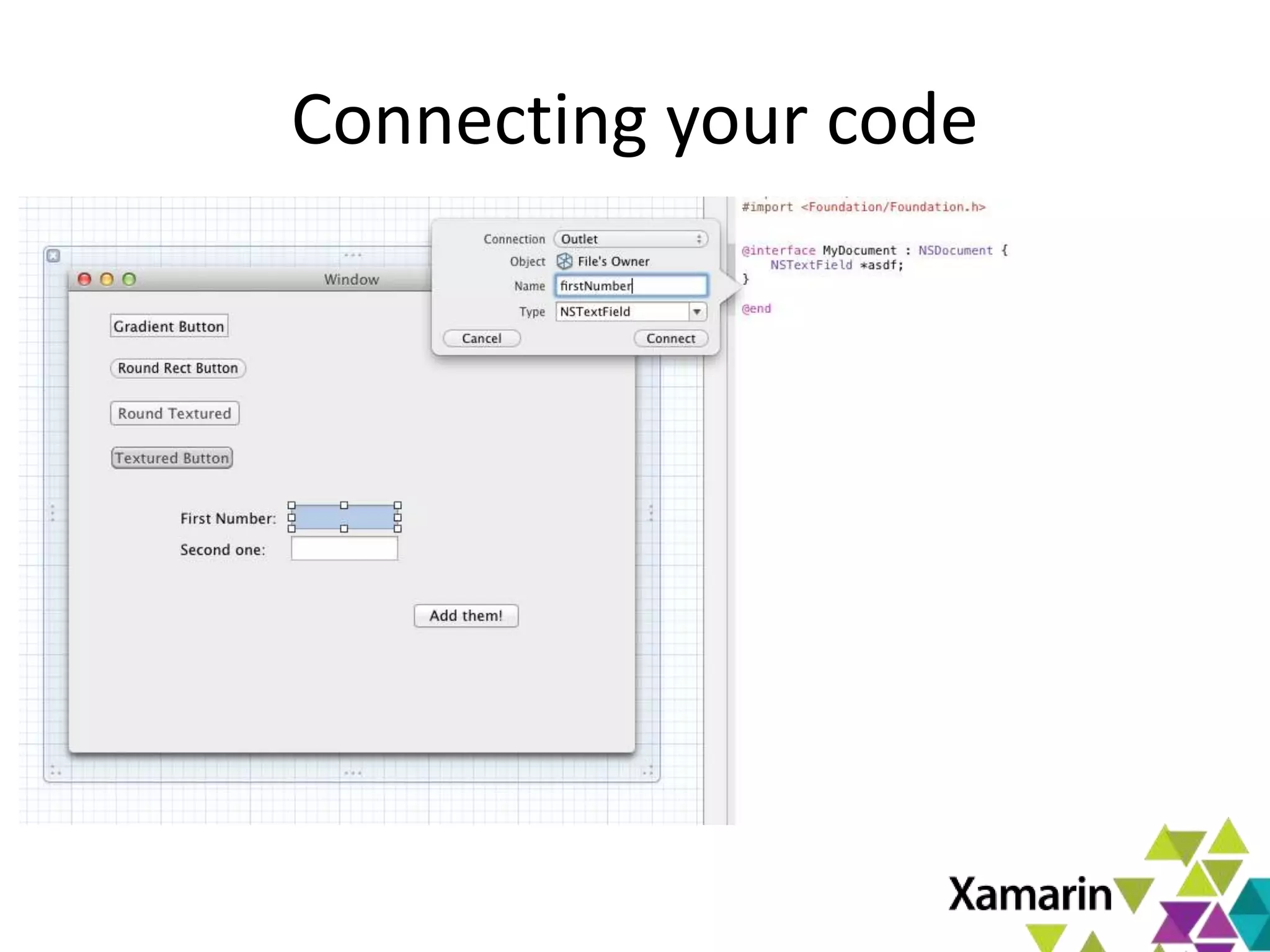
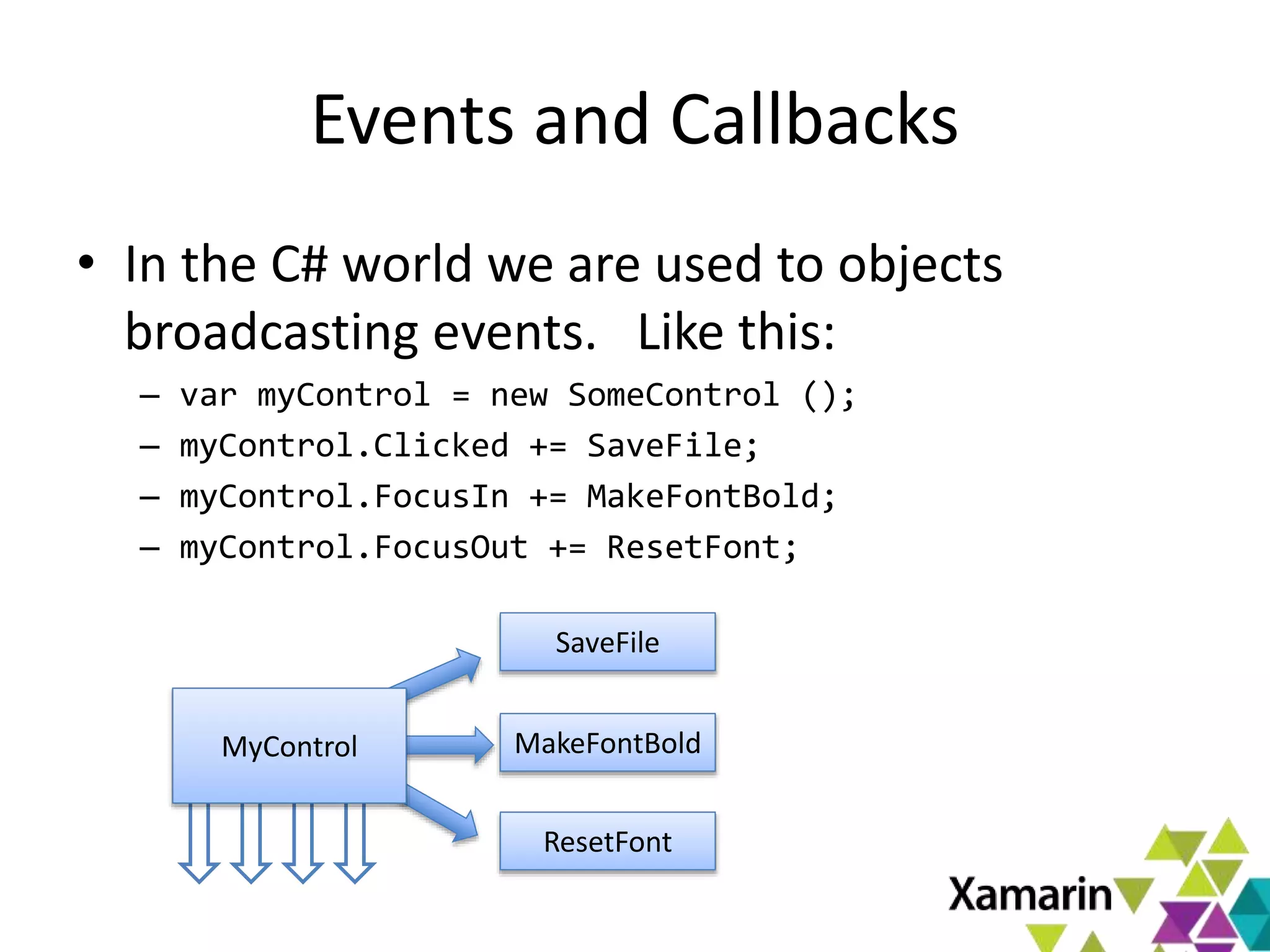
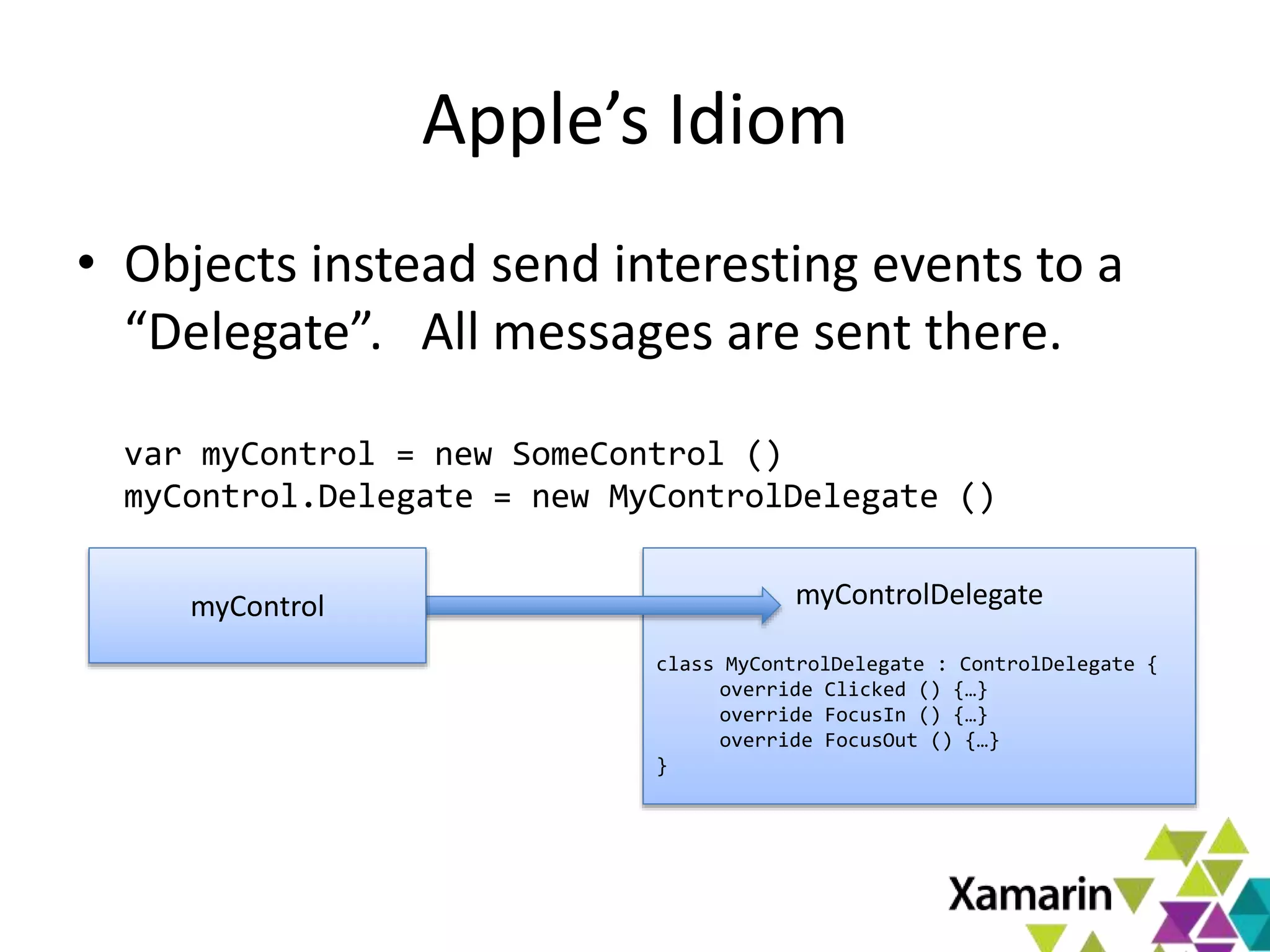
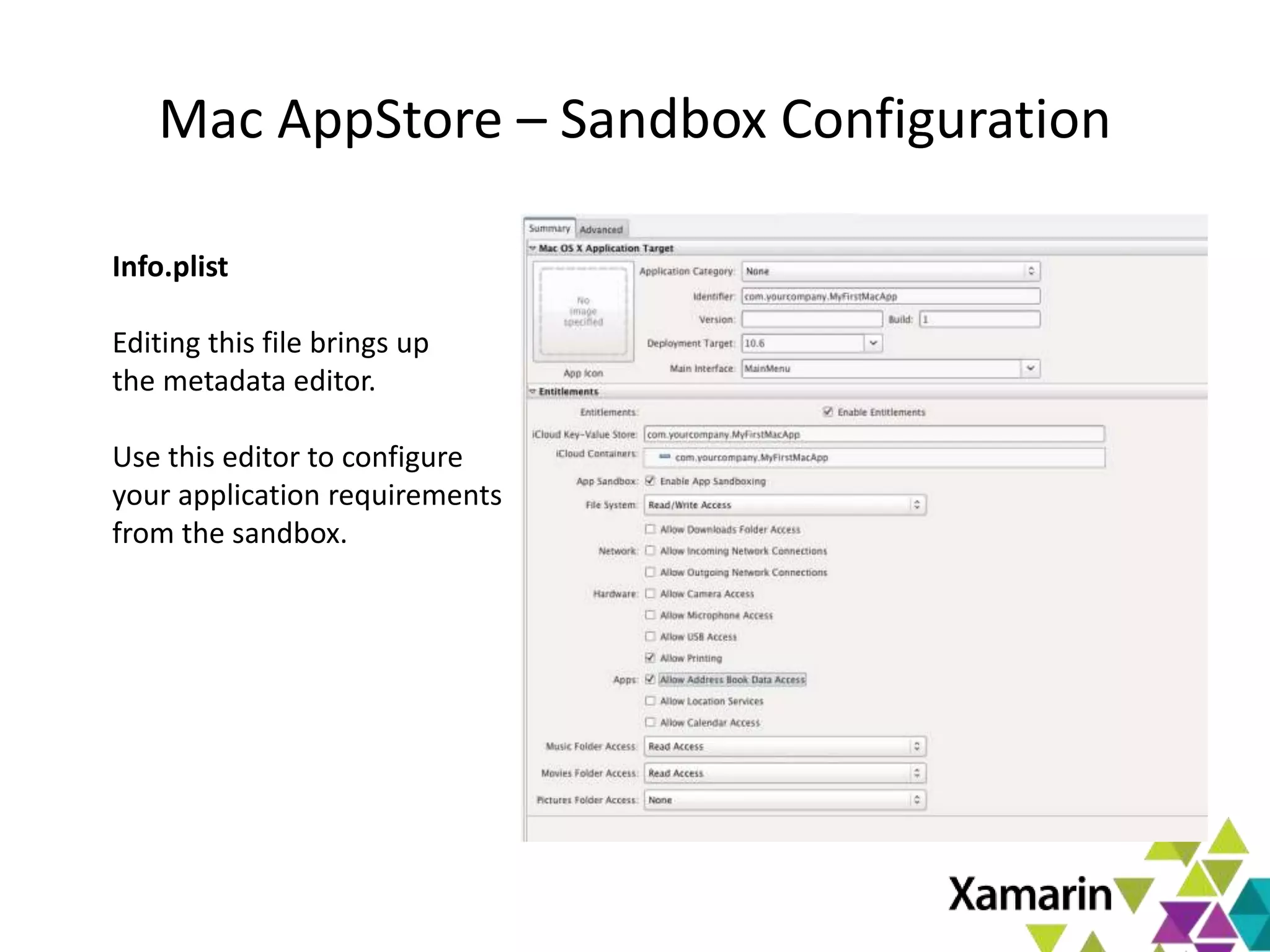
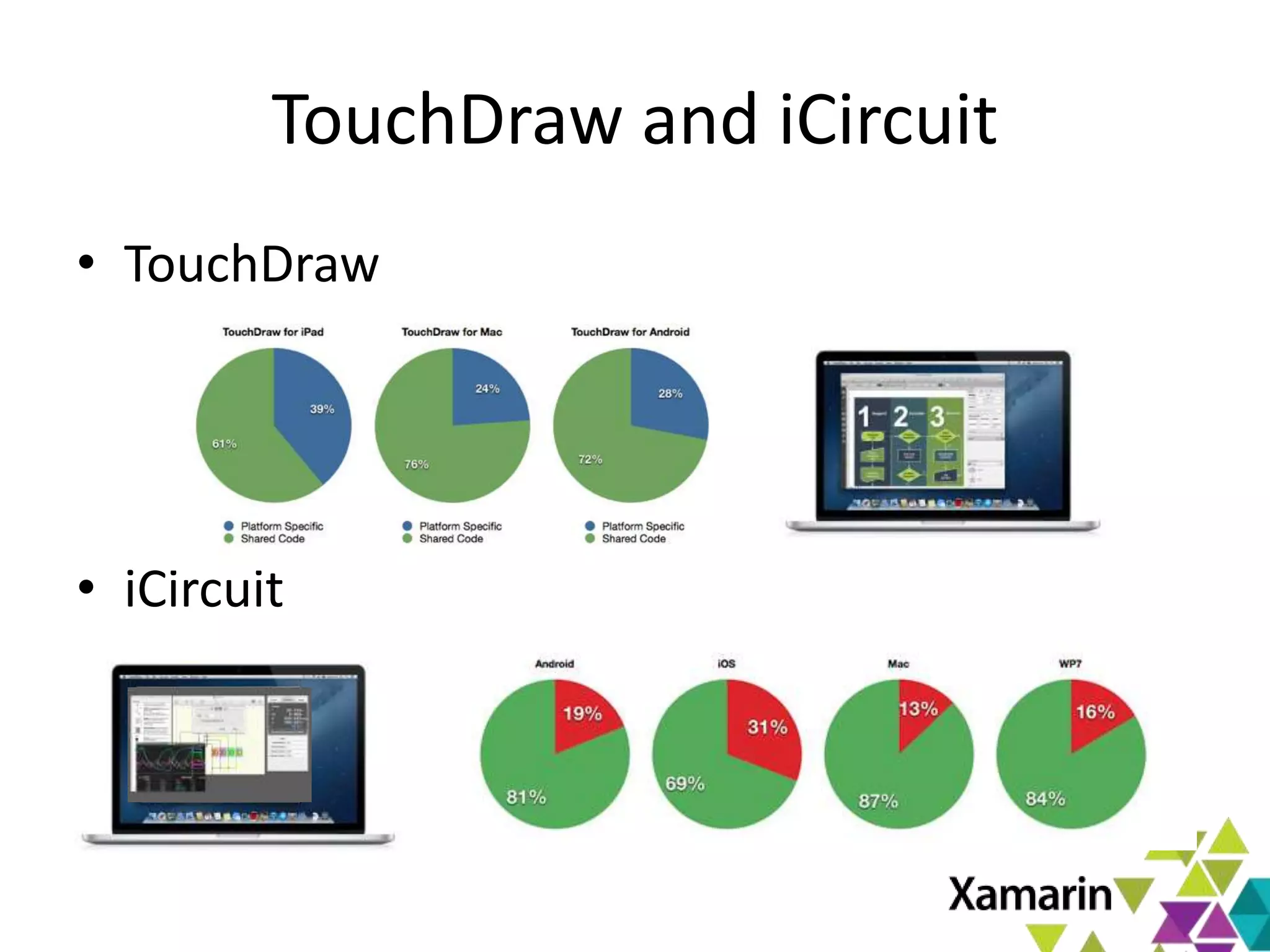
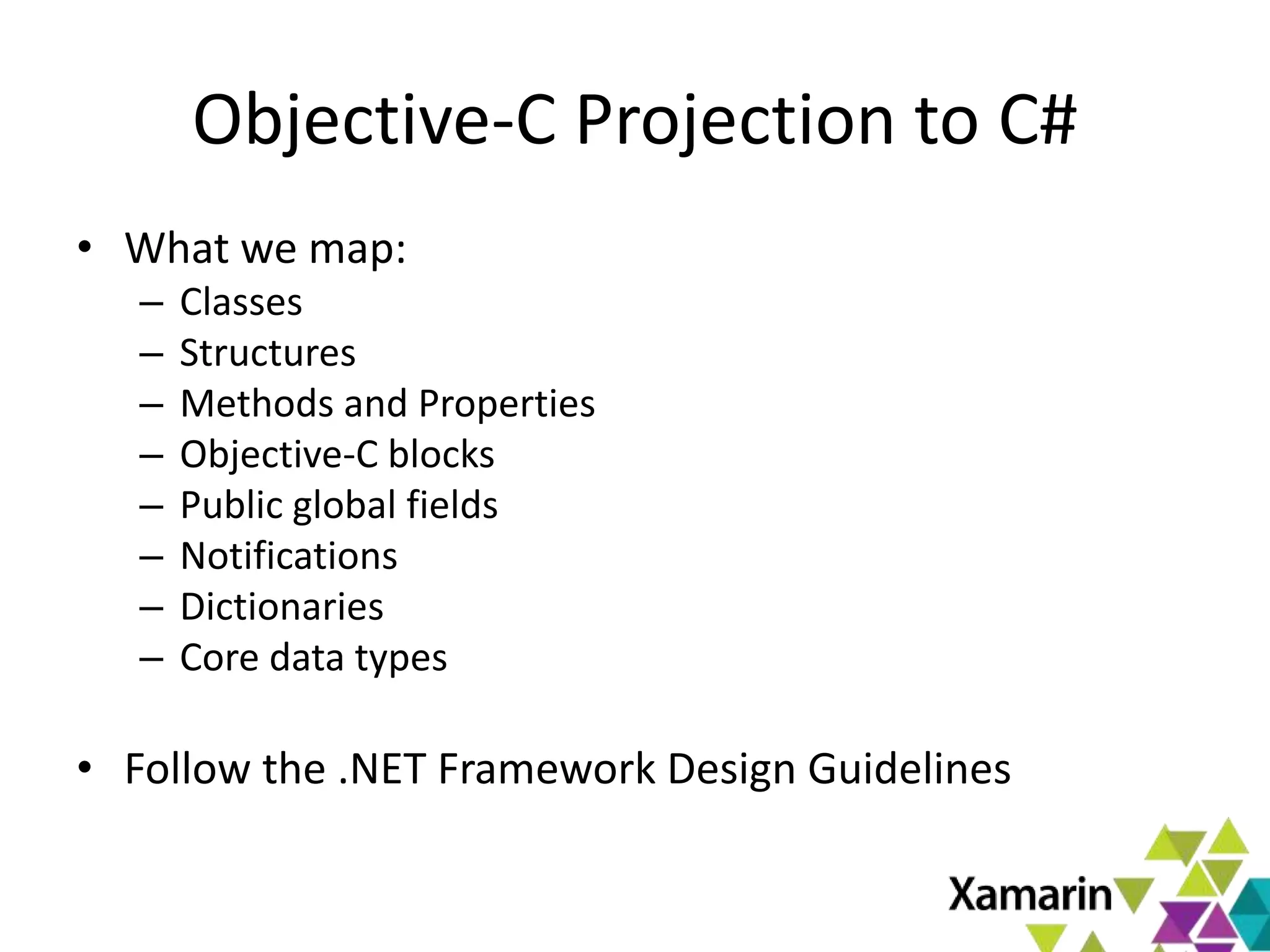
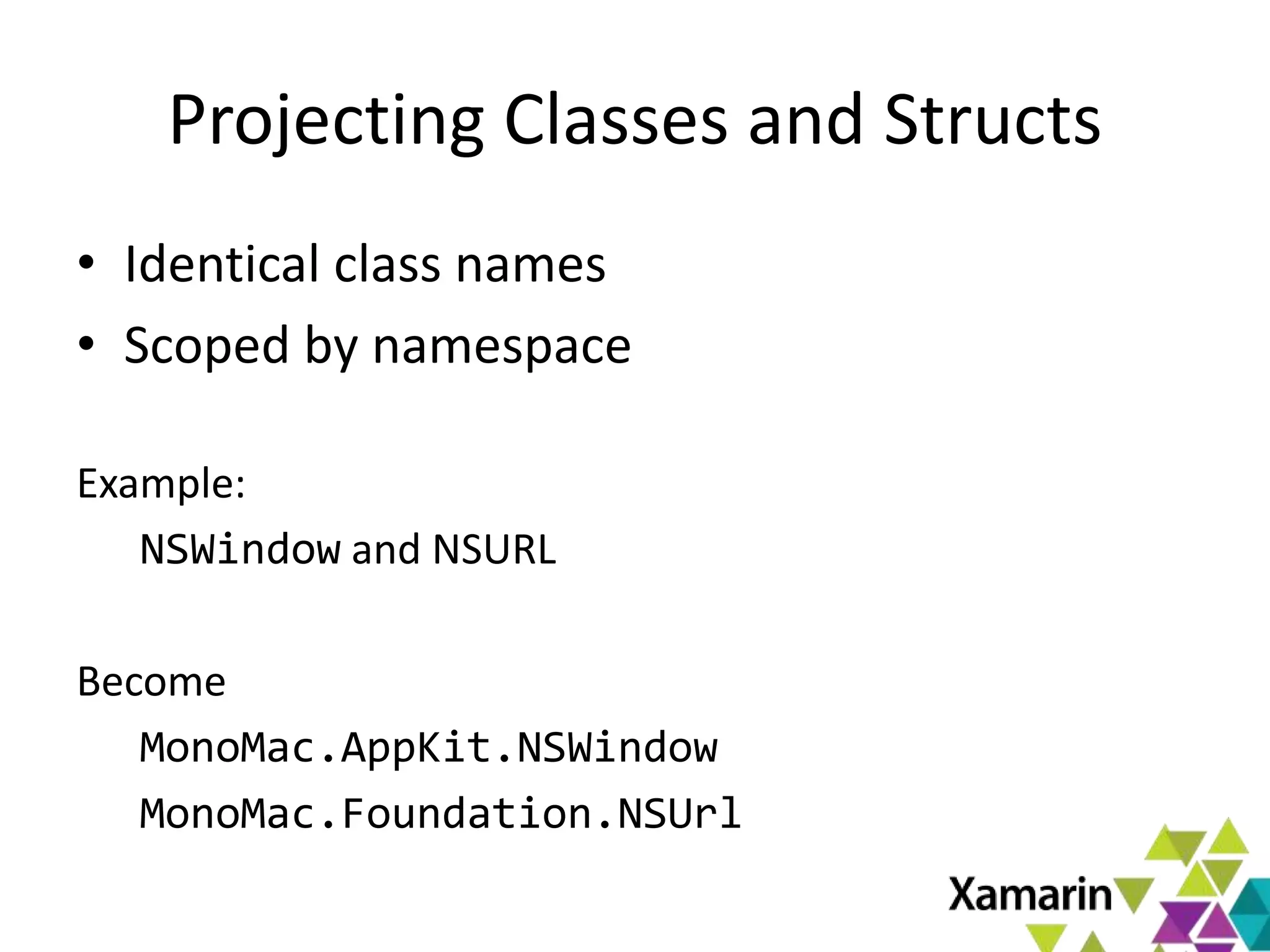
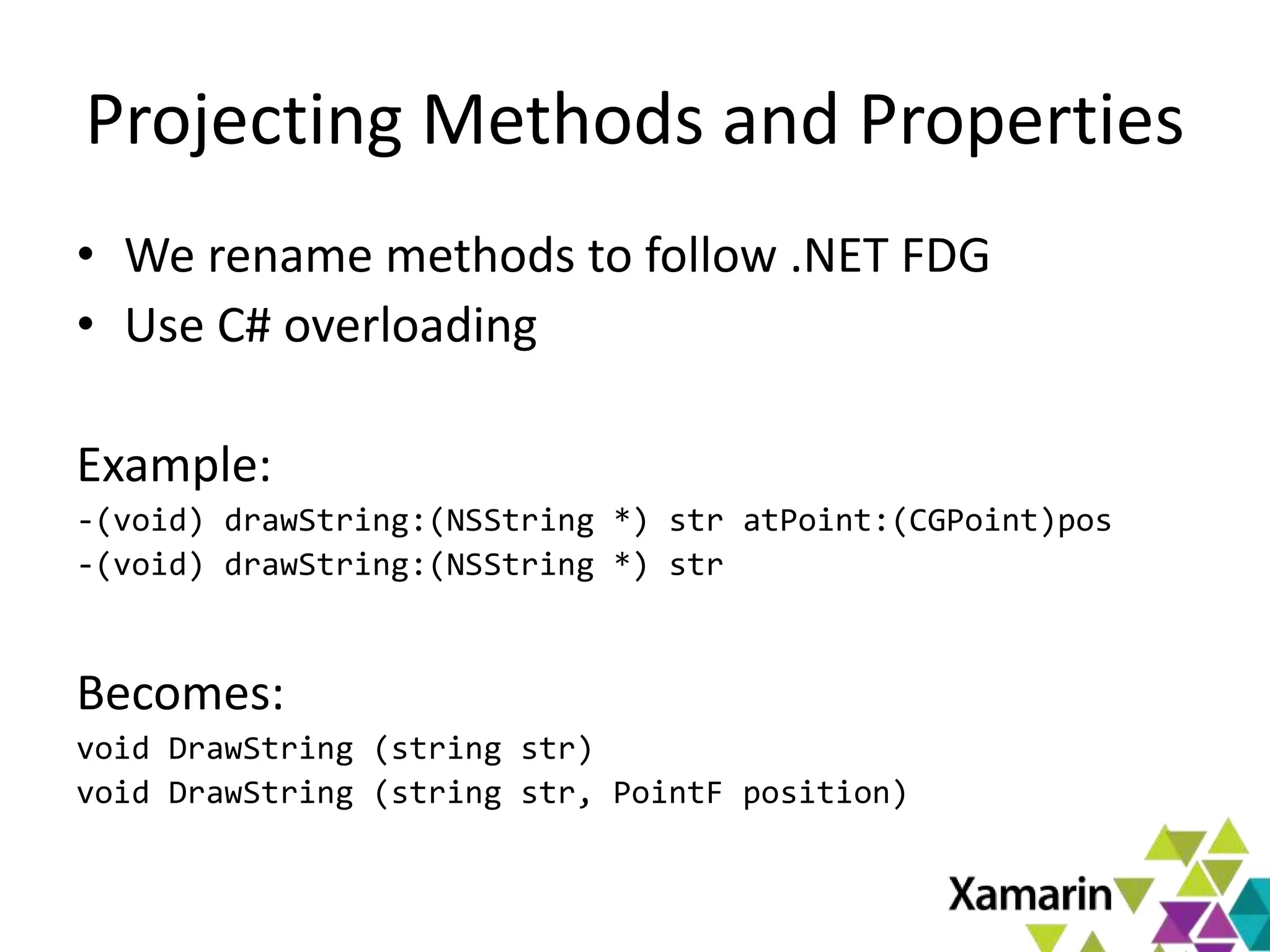
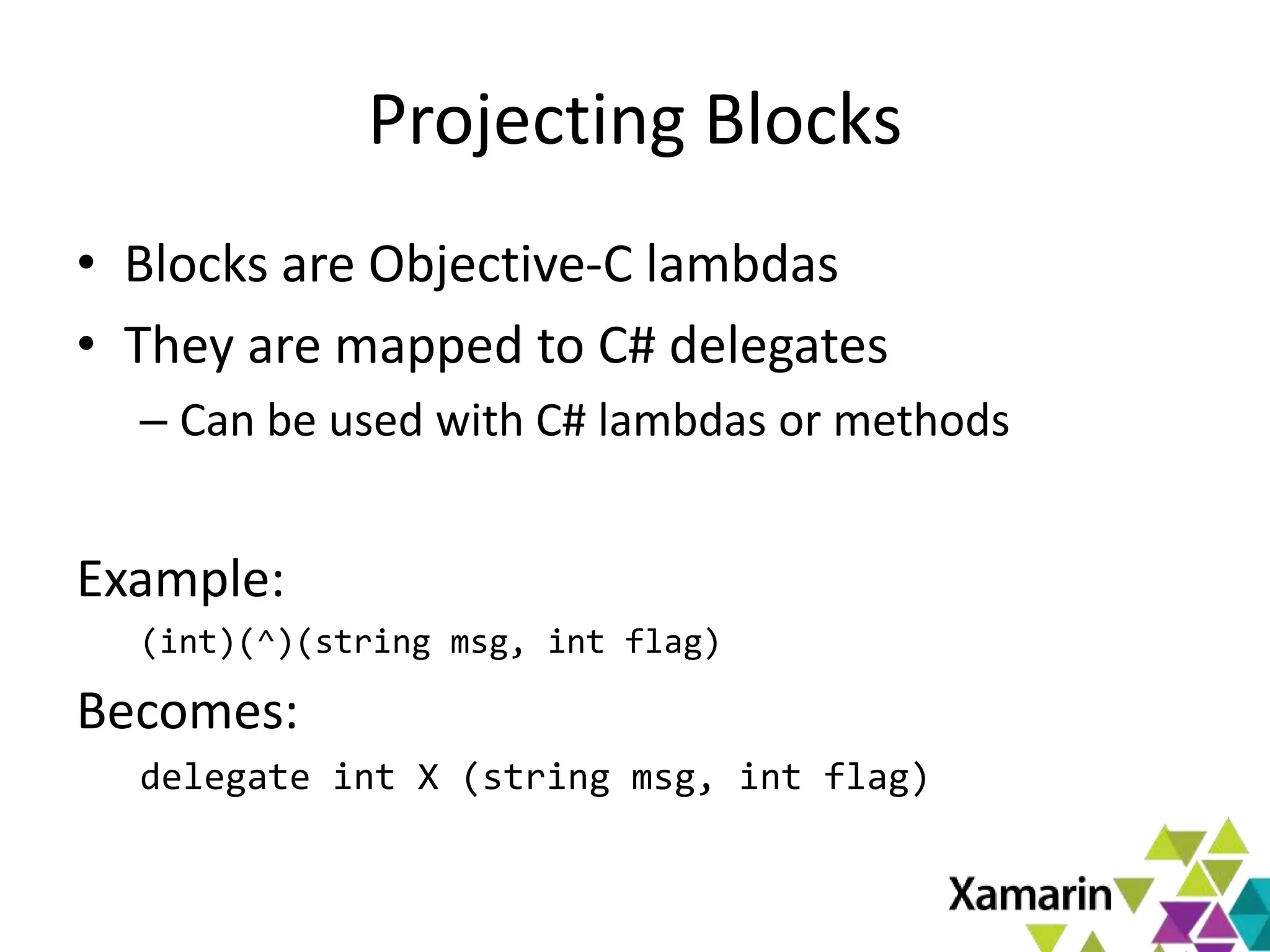
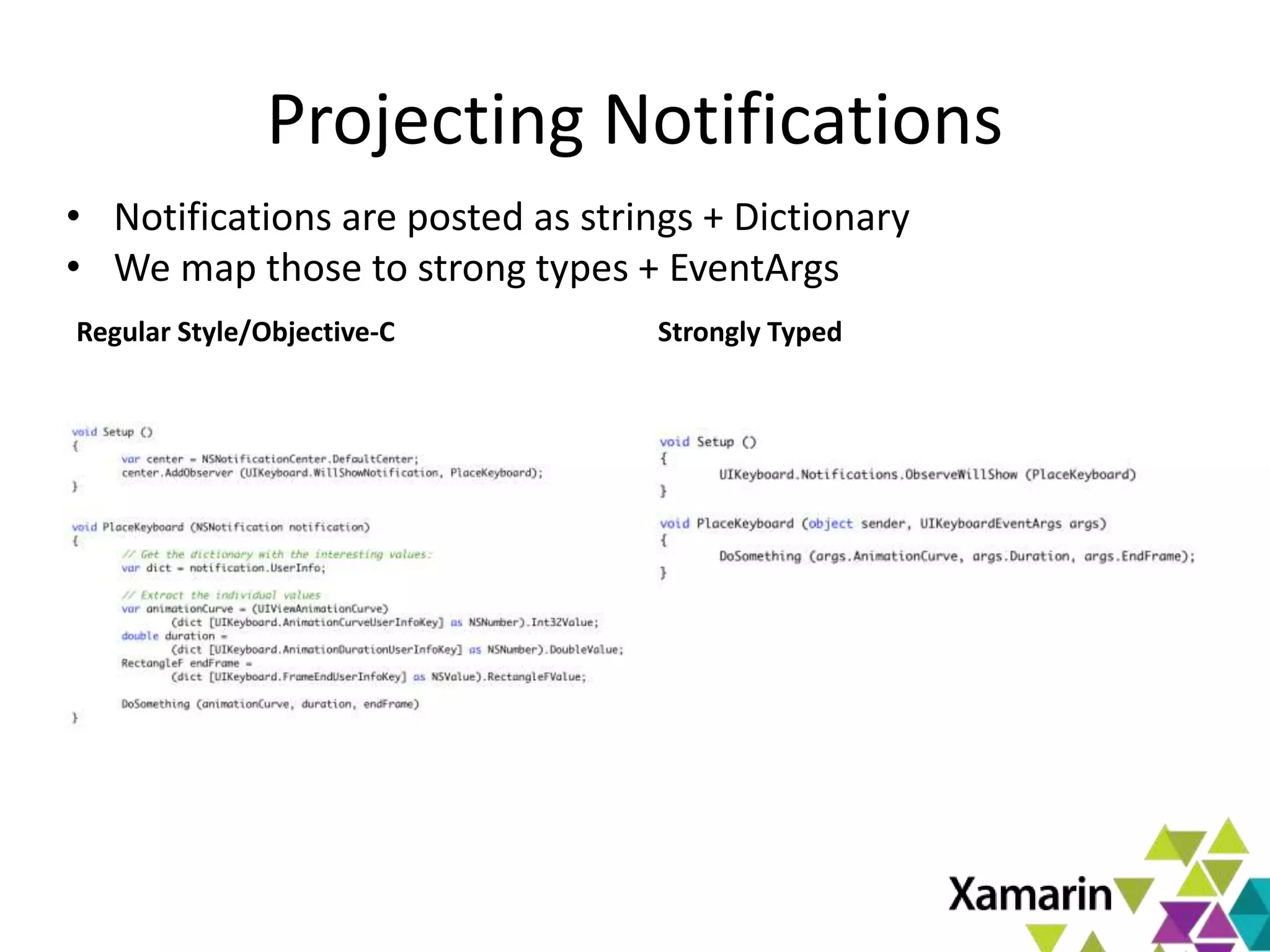
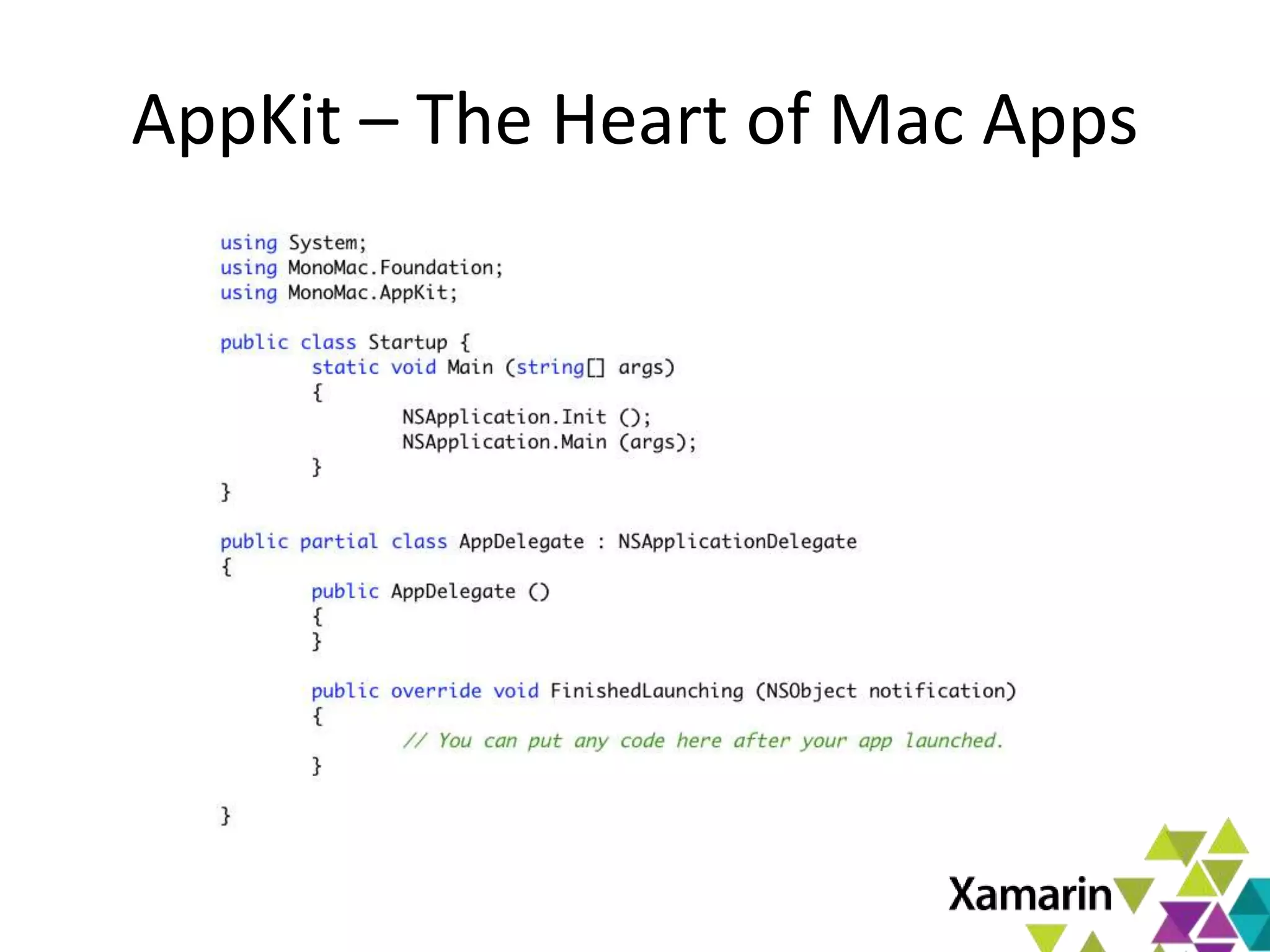
Xamarin.Mac allows developers to create macOS applications using C# and .NET libraries, providing access to native APIs for deep integration with the operating system. The platform includes tools like MonoDevelop and allows for features such as async programming and access to graphics and audio frameworks. Applications can be packaged as bundles, requiring code signing for distribution, especially through the Mac App Store.