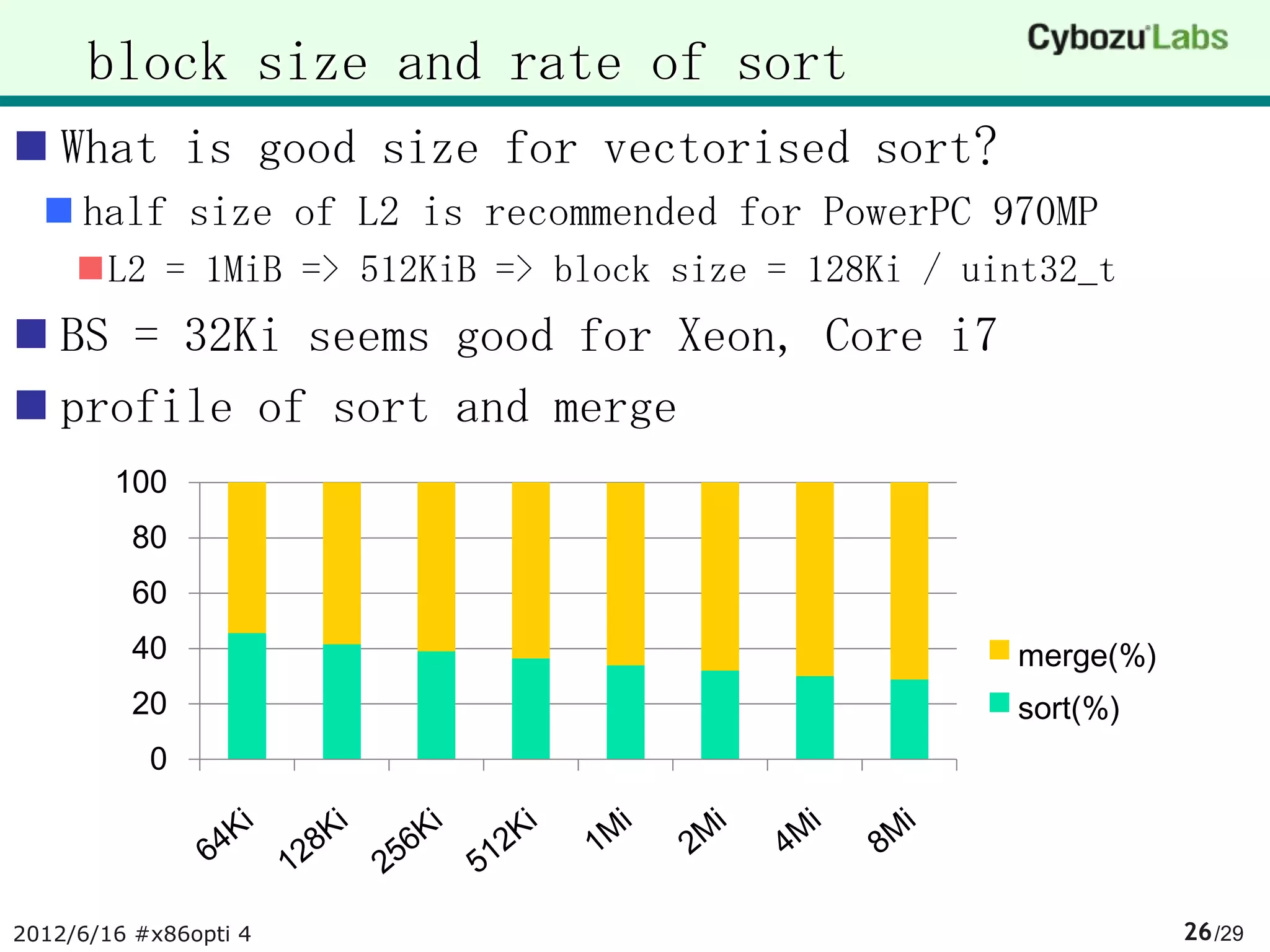
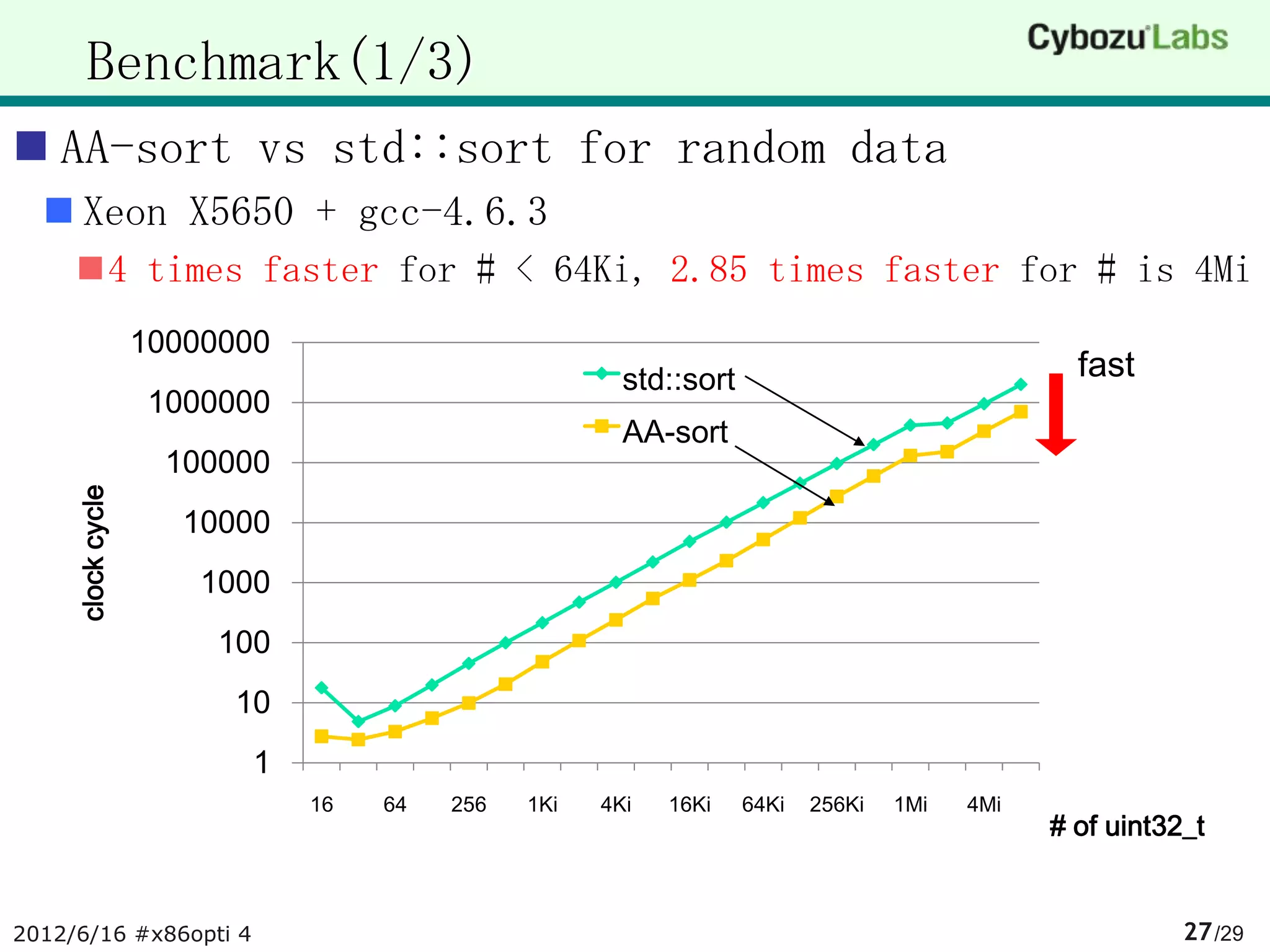
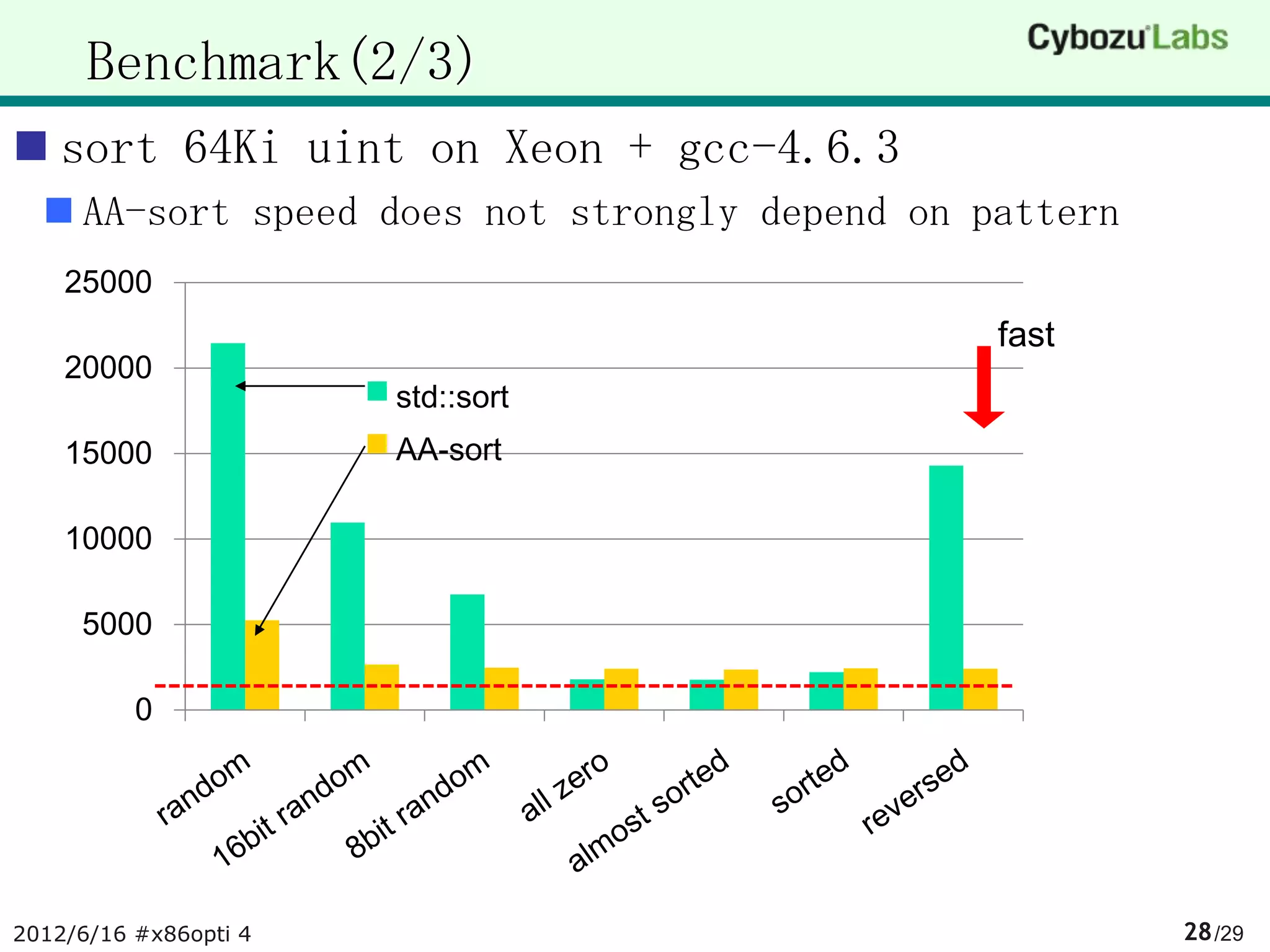
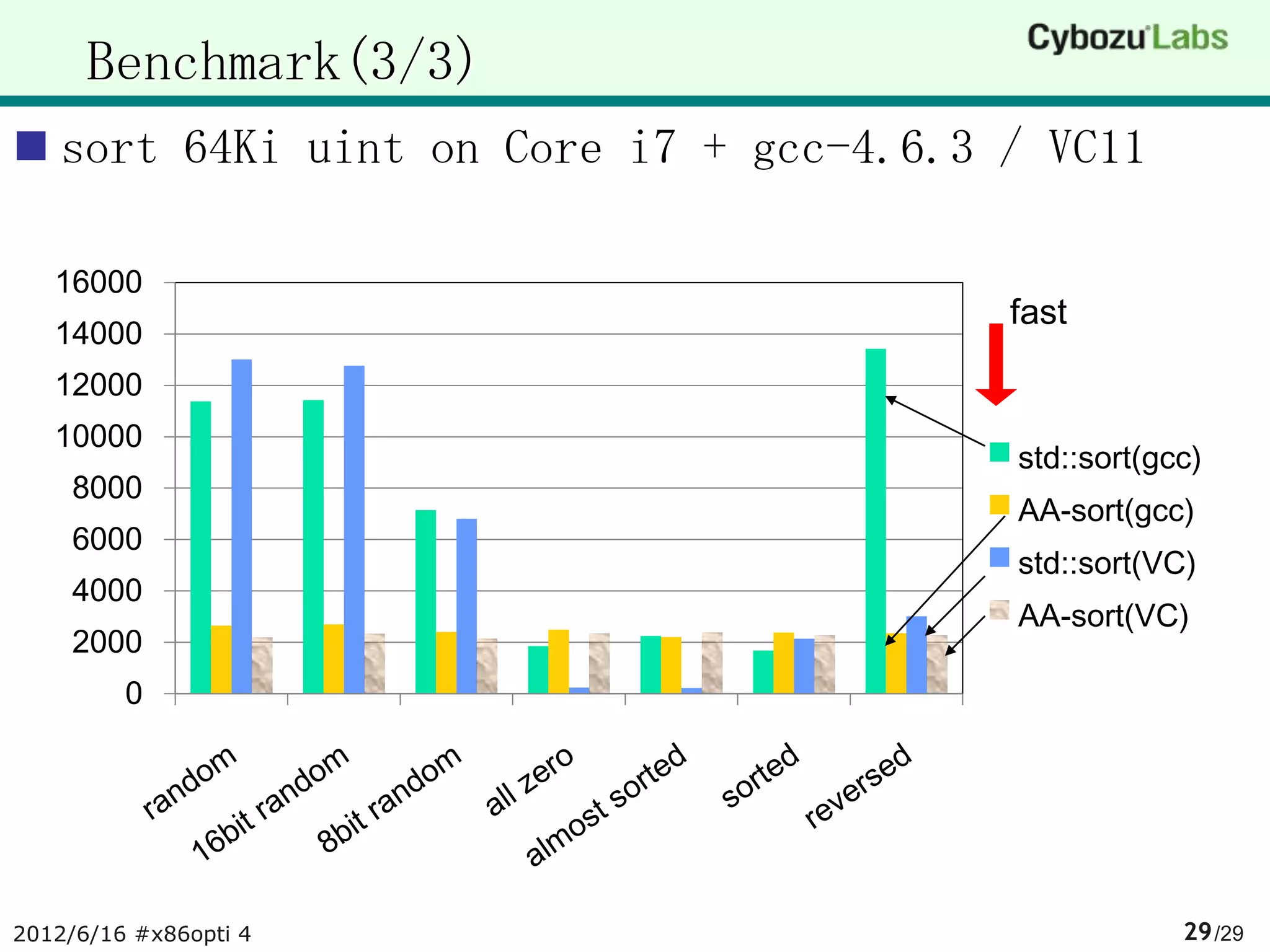
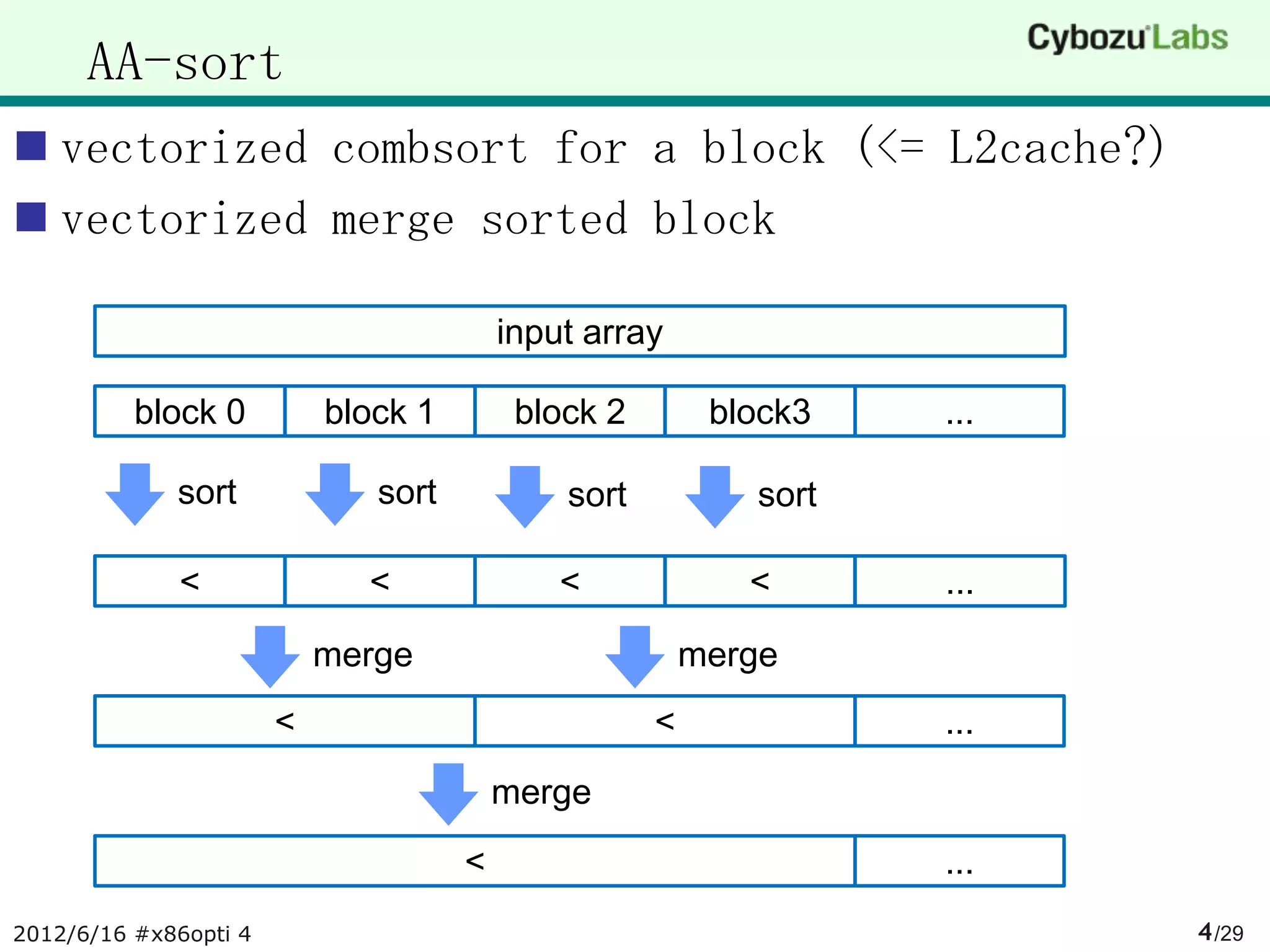
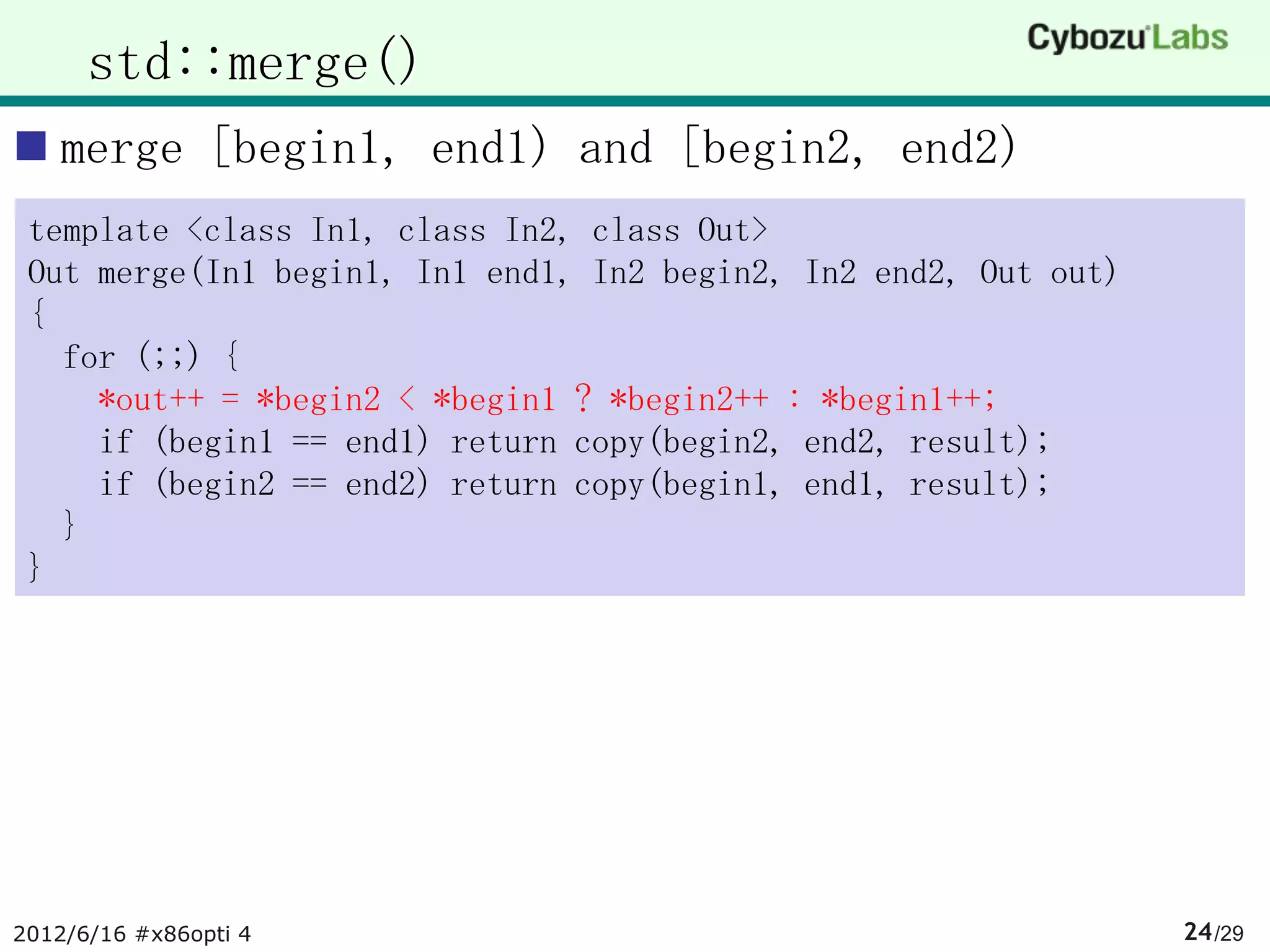
The document summarizes AA-sort, a sorting algorithm optimized for SIMD and multicore processors. AA-sort works by first sorting blocks of data in parallel using vectorized combsort. It then merges the sorted blocks together. Key steps include sorting 4 elements within each SIMD register, transposing the registers, and performing a vectorized version of combsort without conditional branches. The document provides pseudocode for these steps.
![classic combsort(1/2)
improved bubble sort
unstable
O(n log n)
compare two elements having a gap(>=1)
gap is divided by shrink factor (about 1.3)
size_t nextGap(size_t N) { return (N * 10) / 13; }
void combsort(uint32_t *a, size_t N) {
size_t gap = nextGap(N);
while (gap > 1) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < N - gap; i++) {
if (a[i] > a[i + gap]) std::swap(a[i], a[i + gap]);
}
gap = nextGap(gap);
}
…
2012/6/16 #x86opti 4 6 /29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/x86opti4-120615233954-phpapp01/75/AA-sort-with-SSE4-1-6-2048.jpg)
![classic combsort(2/2)
gap = 1 means bubble sort
loop until the array is fully sorted
…
for (;;) {
bool isSwapped = false;
for (size_t i = 0; i < N - 1; i++) {
if (a[i] > a[i + 1]) {
std::swap(a[i], a[i + 1]);
isSwapped = true;
}
}
if (!isSwapped) return;
}
}
2012/6/16 #x86opti 4 7 /29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/x86opti4-120615233954-phpapp01/75/AA-sort-with-SSE4-1-7-2048.jpg)
![gap function
Combsort11
last pattern of gap [11, 8, 6, 4, 3, 2, 1] seems good
by http://cs.clackamas.cc.or.us/molatore/cs260Spr03/combsort.htm
size_t nextGap(size_t n) {
n = (n * 10) / 13;
if (n == 9 || n == 10) return 11; // (*)
return n;
}
a little faster if line(*) is appended
2012/6/16 #x86opti 4 8 /29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/x86opti4-120615233954-phpapp01/75/AA-sort-with-SSE4-1-8-2048.jpg)
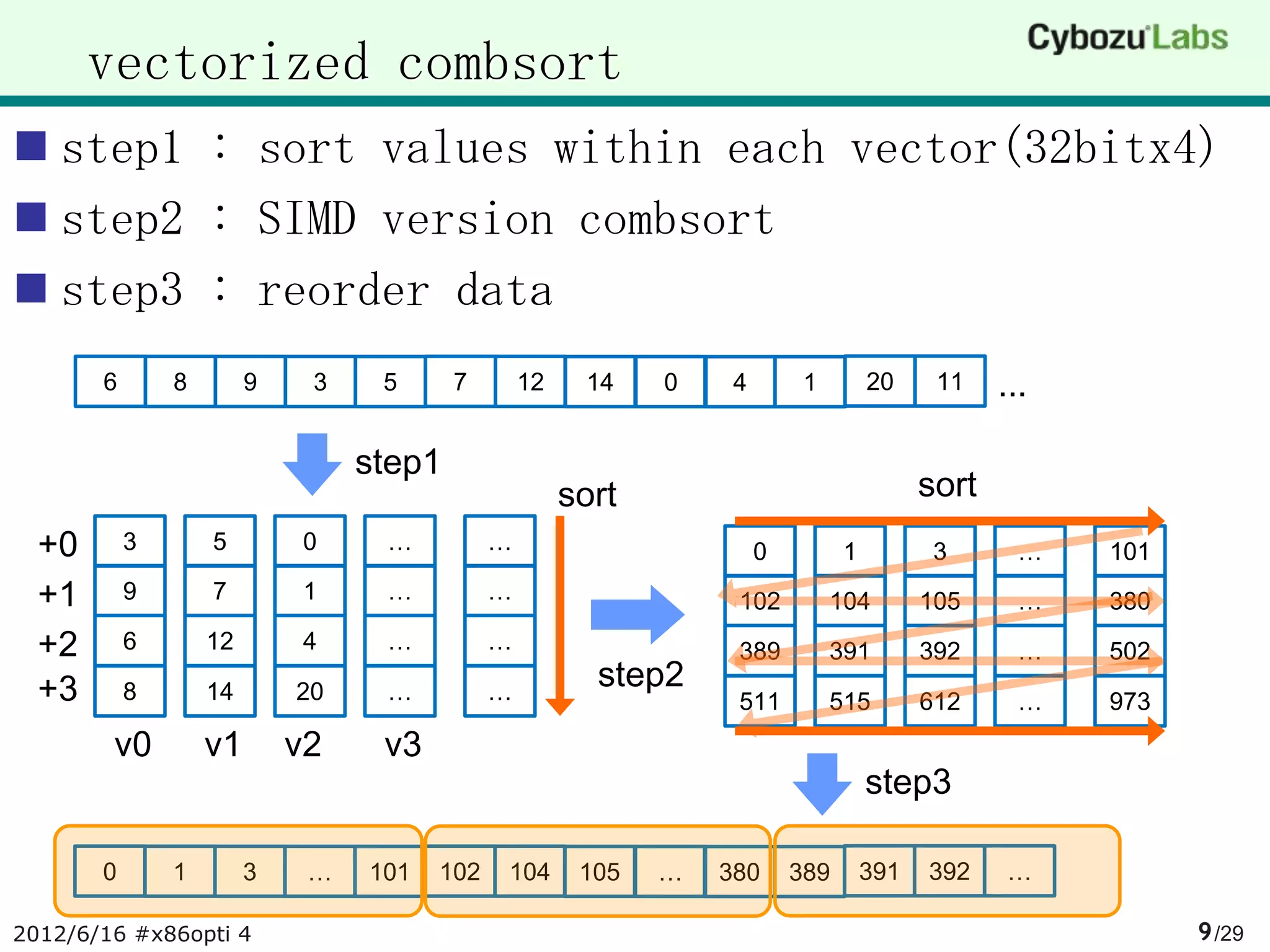
![step1
step1.1 : sort [v[i][j] | i<-[0..3]] for j = 0,
1, 2, 3
step1.2 : transpose
3 5 0 8
2 7 1 2
step1.1
8 12 4 13
9 14 20 15
sort
v0 v1 v2 v3 0 3 5 8
step1.2
1 2 2 7
4 8 12 13
transpose
9 14 15 20
0 1 4 9
3 2 8 14
5 2 12 15
8 7 13 20
2012/6/16 #x86opti 4 10 /29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/x86opti4-120615233954-phpapp01/75/AA-sort-with-SSE4-1-10-2048.jpg)
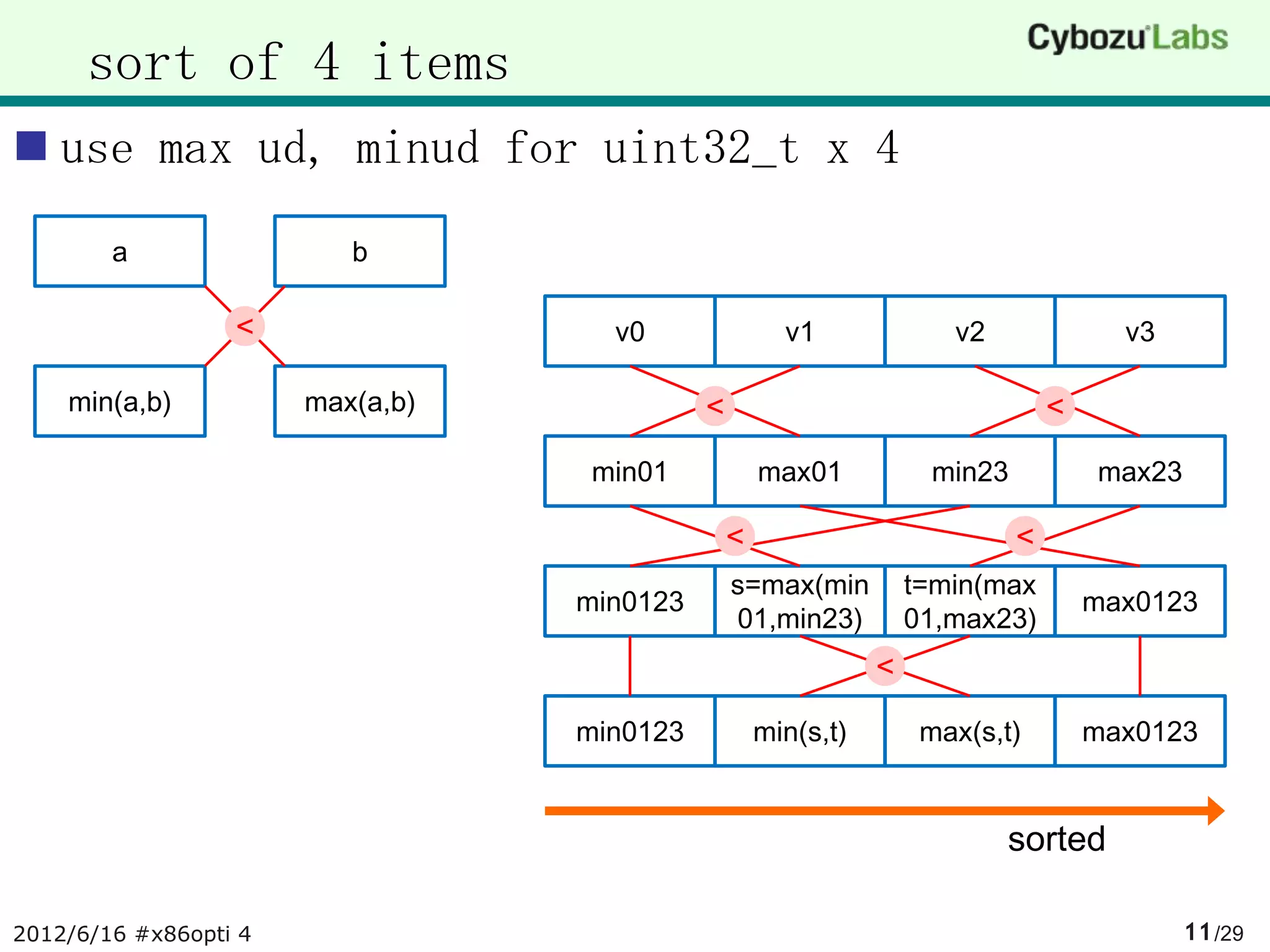
![source of step1.1
V128 is a type of 32-bit integer x 4
pminud(a, b) : min(a_i, b_i) for i = 0, 1, 2, 3
void sort_step1_vec(V128 x[4])
{
V128 min01 = pminud(x[0], x[1]);
V128 max01 = pmaxud(x[0], x[1]);
V128 min23 = pminud(x[2], x[3]);
V128 max23 = pmaxud(x[2], x[3]);
x[0] = pminud(min01, min23);
x[3] = pmaxud(max01, max23);
V128 s = pmaxud(min01, min23);
V128 t = pminud(max01, max23);
x[1] = pminud(s, t);
x[2] = pmaxud(s, t);
}
2012/6/16 #x86opti 4 12 /29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/x86opti4-120615233954-phpapp01/75/AA-sort-with-SSE4-1-12-2048.jpg)
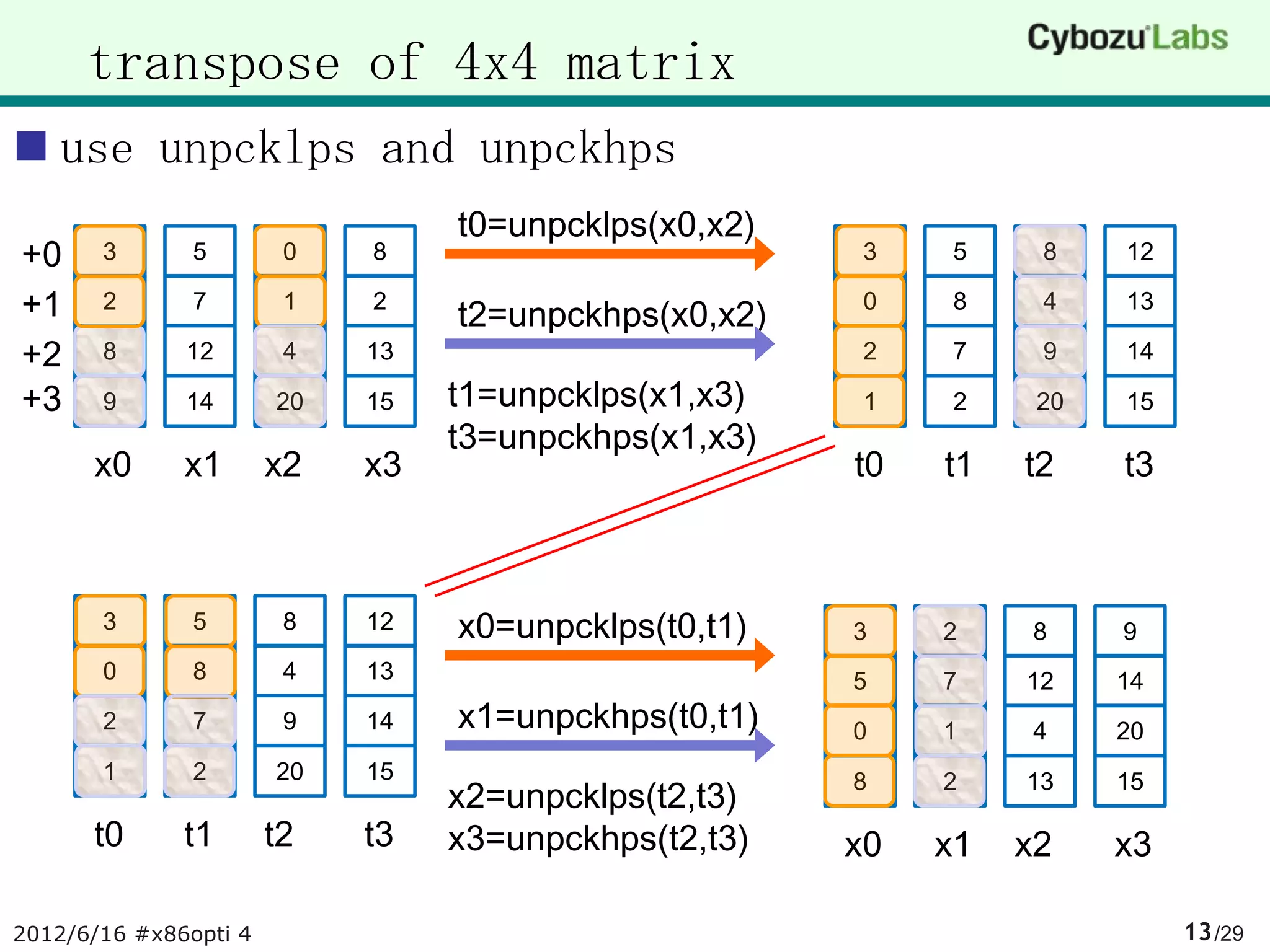
![source of transpose and step1
void transpose(V128 x[4]) void sort_step1(V128 *va, size_t N)
{ {
V128 x0 = x[0]; for(size_t i = 0; i < N; i+= 4) {
V128 x1 = x[1]; sort_step1_vec(&va[i]);
V128 x2 = x[2]; transpose(&va[i]);
V128 x3 = x[3]; }
V128 t0 = unpcklps(x0, x2); }
V128 t1 = unpcklps(x1, x3);
V128 t2 = unpckhps(x0, x2);
V128 t3 = unpckhps(x1, x3);
x[0] = unpcklps(t0, t1);
x[1] = unpckhps(t0, t1);
x[2] = unpcklps(t2, t3);
x[3] = unpckhps(t2, t3);
}
2012/6/16 #x86opti 4 14 /29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/x86opti4-120615233954-phpapp01/75/AA-sort-with-SSE4-1-14-2048.jpg)
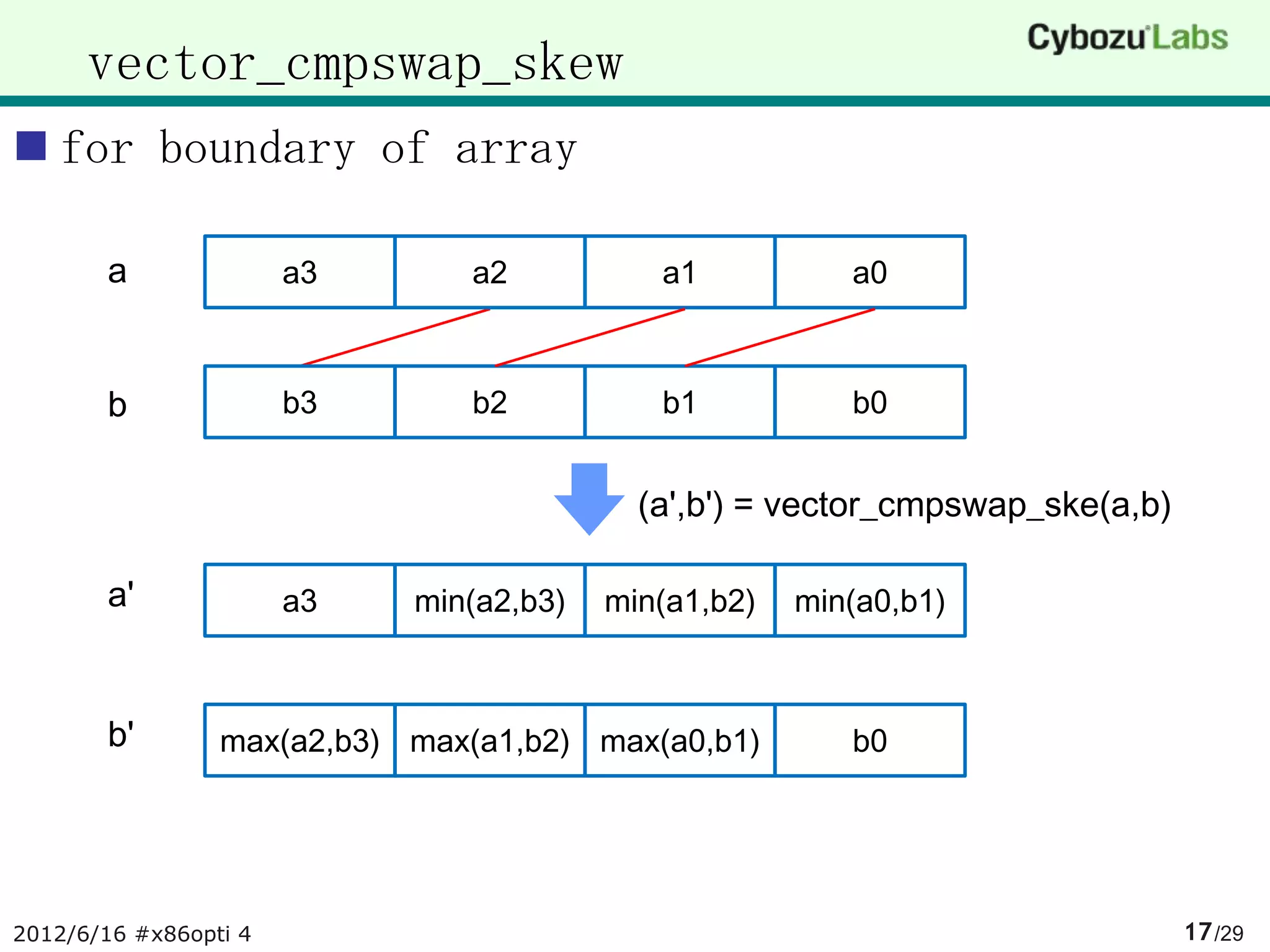
![SIMD version combsort
first half code use
vector_cmpswap
vector_cmpswap_skew
bool sort_step2(V128 *va, size_t N) {
size_t gap = nextGap(N);
while (gap > 1) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < N - gap; i++) {
vector_cmpswap(va[i], va[i + gap]);
}
for (size_t i = N - gap; i < N; i++) {
vector_cmpswap_skew(va[i], va[i + gap - N]);
}
gap = nextGap(gap);
}
...
2012/6/16 #x86opti 4 15 /29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/x86opti4-120615233954-phpapp01/75/AA-sort-with-SSE4-1-15-2048.jpg)
![vector_cmpswap
no conditional branch
a b
<
min(a,b) max(a,b)
if (a[i] > a[i + gap]) std::swap(a[i], a[i + gap]);
vectorised
void vector_cmpswap(V128& a, V128& b)
{
V128 t = pmaxud(a, b);
a = pminud(a, b);
b = t;
}
2012/6/16 #x86opti 4 16 /29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/x86opti4-120615233954-phpapp01/75/AA-sort-with-SSE4-1-16-2048.jpg)
![isSortedVec
check whether array is sorted
ptest_zf(a, b) is true if (a & b) == 0
a <= b max(a,b) == b c := max(a,b) – b == 0
pcmpgtd is for int32_t, so we can't use it
bool isSortedVec(const V128 *va, size_t N) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < N - 1; i++) {
V128 a = va[i];
V128 b = va[i + 1];
V128 c = pmaxud(a, b);
c = psubd(c, b);
if (!ptest_zf(c, c)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
2012/6/16 #x86opti 4 18 /29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/x86opti4-120615233954-phpapp01/75/AA-sort-with-SSE4-1-18-2048.jpg)
![loop for gap == 1
vectorised bubble sort for gap == 1
retire if loop count reaches maxLoop
fall to std::sort
almost rare
const int maxLoop = 10;
for (int i = 0; i < maxLoop; i++) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < N - 1; i++) {
vector_cmpswap(va[i], va[i + 1]);
}
vector_cmpswap_skew(va[N - 1], va[0]);
if (isSortedVec(va, N)) return true;
}
2012/6/16 #x86opti 4 19 /29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/x86opti4-120615233954-phpapp01/75/AA-sort-with-SSE4-1-19-2048.jpg)
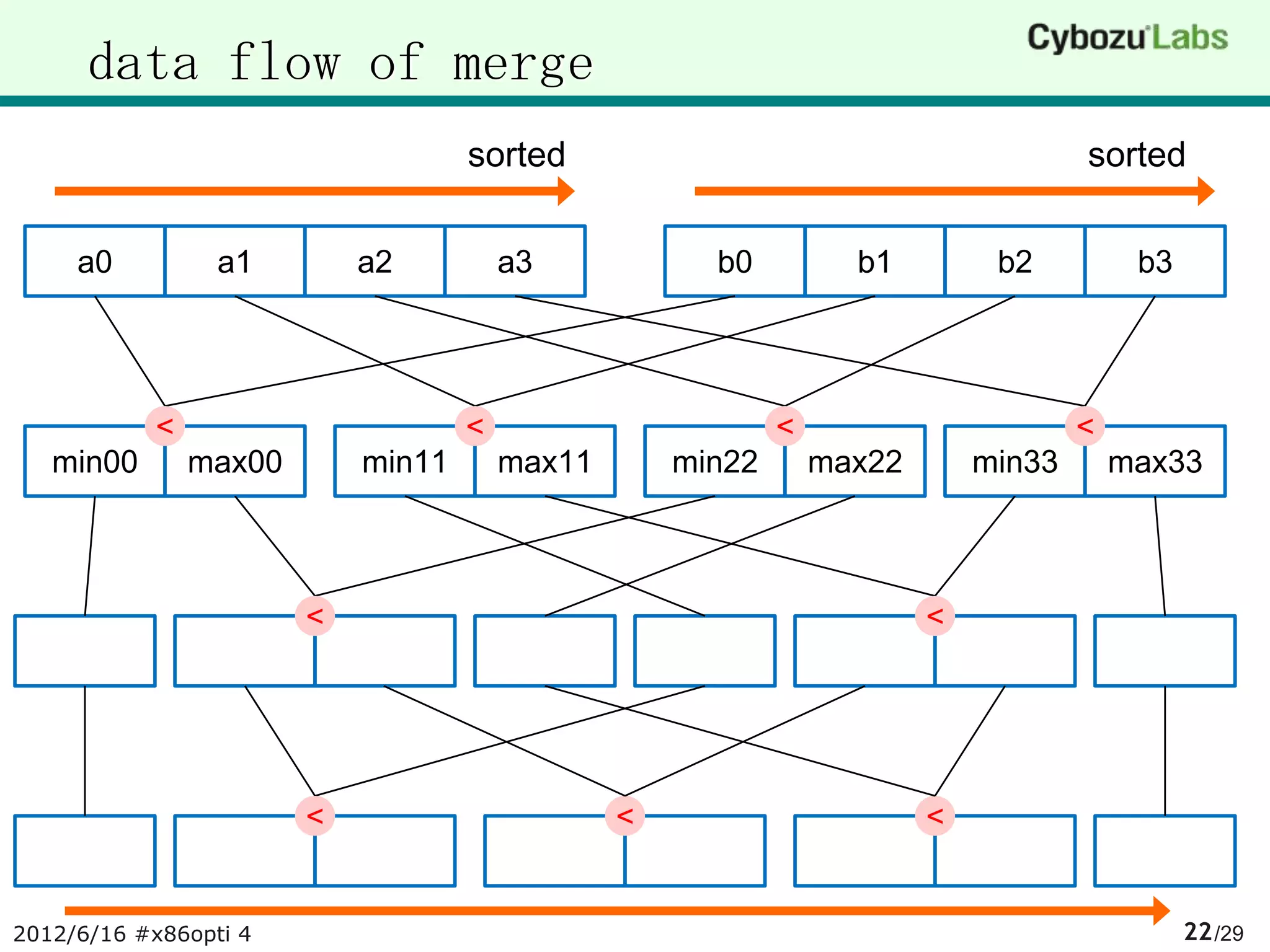
![merge two sorted vector
a = [a3:a2:a1:a0], b = [b3:b2:b1:b0] are soreted
c = [b:a] = merge and sort (a, b)
sorted
a a0 a1 a2 a3
sorted
b b0 b1 b2 b3
[b:a] = vector_merge(a,b)
c0 c1 c2 c3 c0 c1 c2 c3
sorted
2012/6/16 #x86opti 4 21 /29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/x86opti4-120615233954-phpapp01/75/AA-sort-with-SSE4-1-21-2048.jpg)
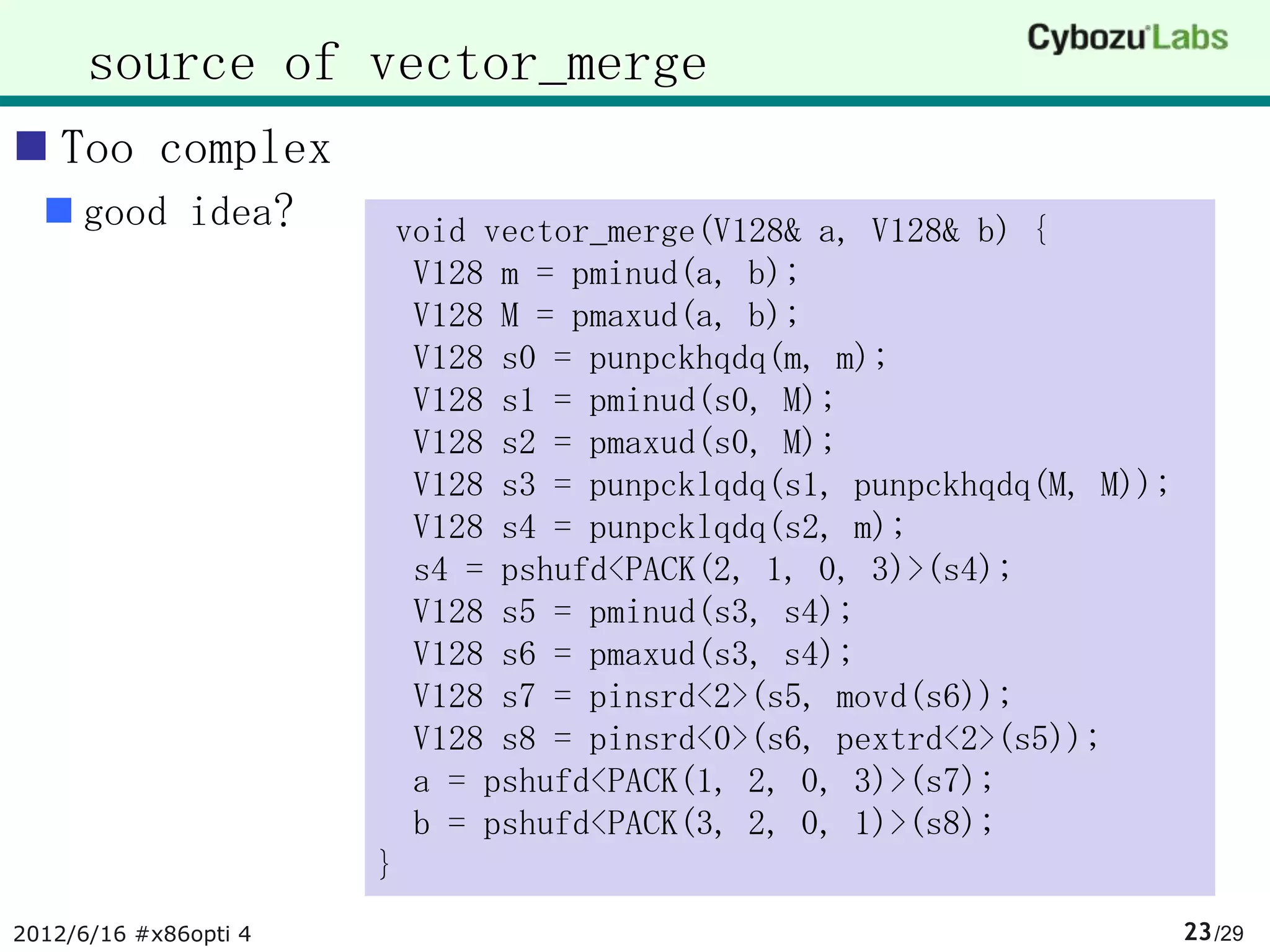
![vectorised merge
merge arrays with vector_merge()
void merge(V128 *vo, const V128 *va, size_t aN, const V128 *vb, size_t bN){
uint32_t aPos = 0, bPos = 0, outPos = 0;
V128 vMin = va[aPos++];
V128 vMax = vb[bPos++];
for (;;) {
vector_merge(vMin, vMax);
vo[outPos++] = vMin;
if (aPos < aN) {
if (bPos < bN) {
V128 ta = va[aPos];
V128 tb = vb[bPos]; ; compare ta0 with tb0
if (movd(ta) <= movd(tb)) {
vMin = ta;
aPos++;
} else {
vMin = tb;
bPos++;
}
2012/6/16 #x86opti 4 25 /29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/x86opti4-120615233954-phpapp01/75/AA-sort-with-SSE4-1-25-2048.jpg)