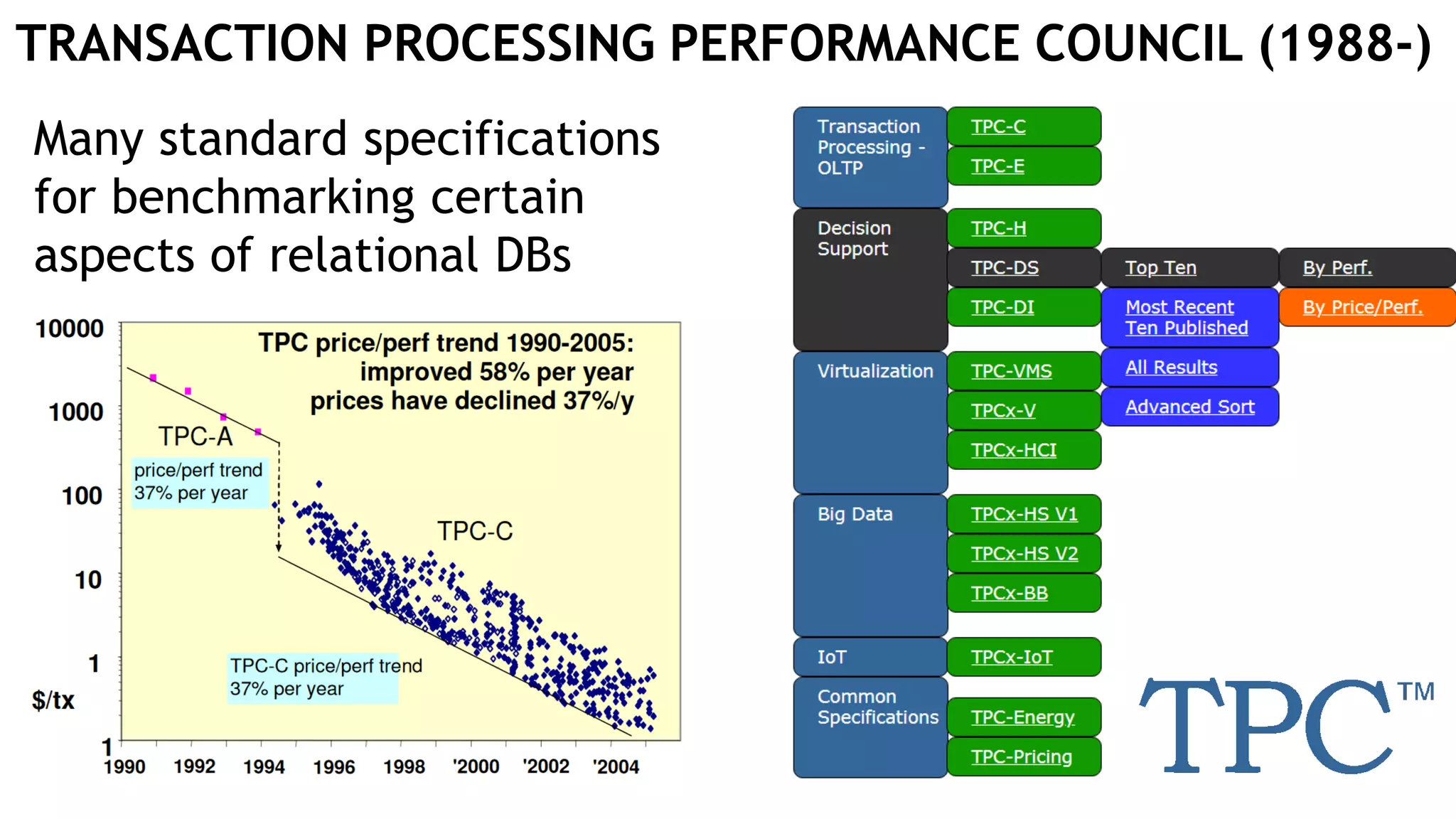
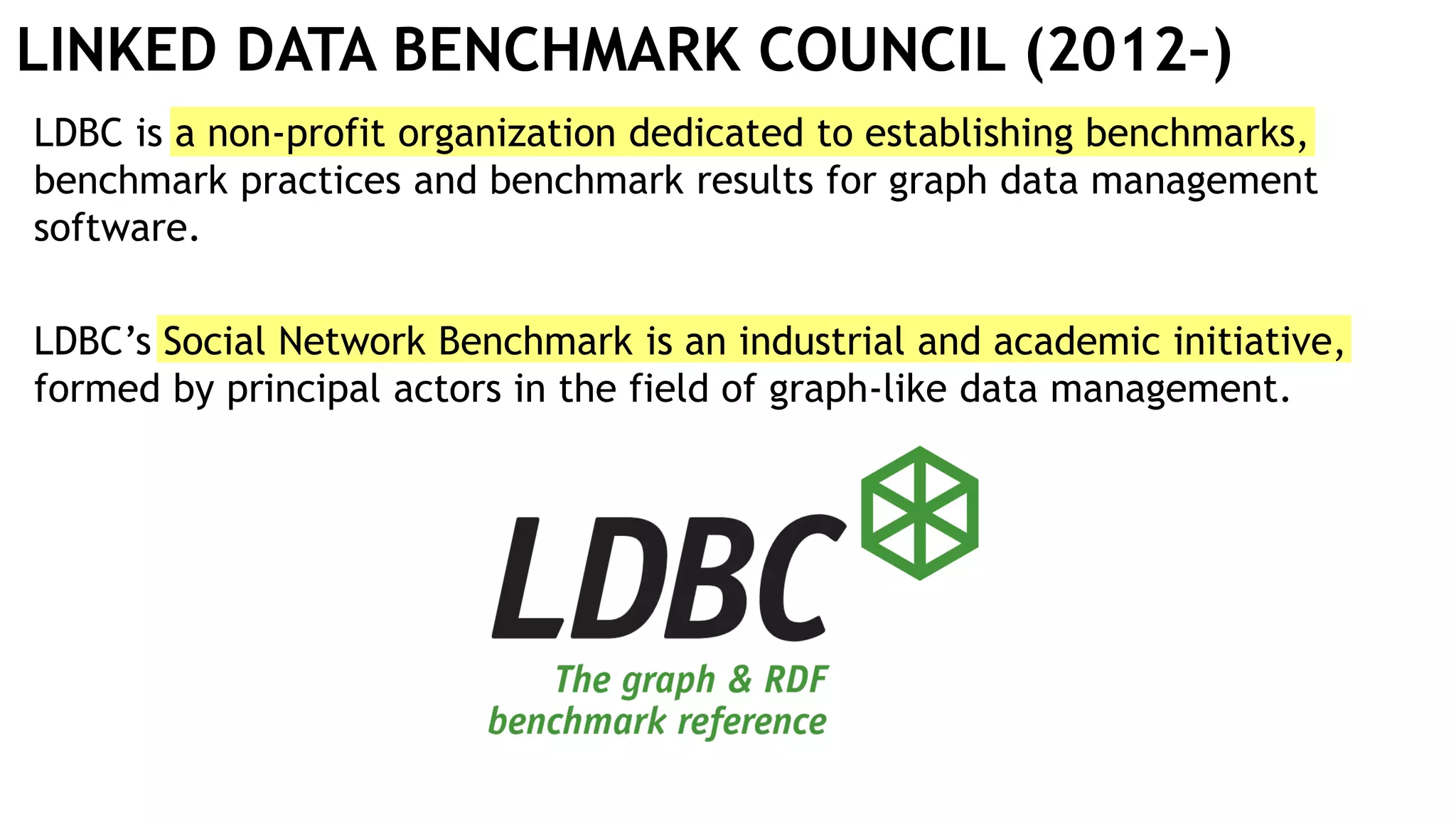
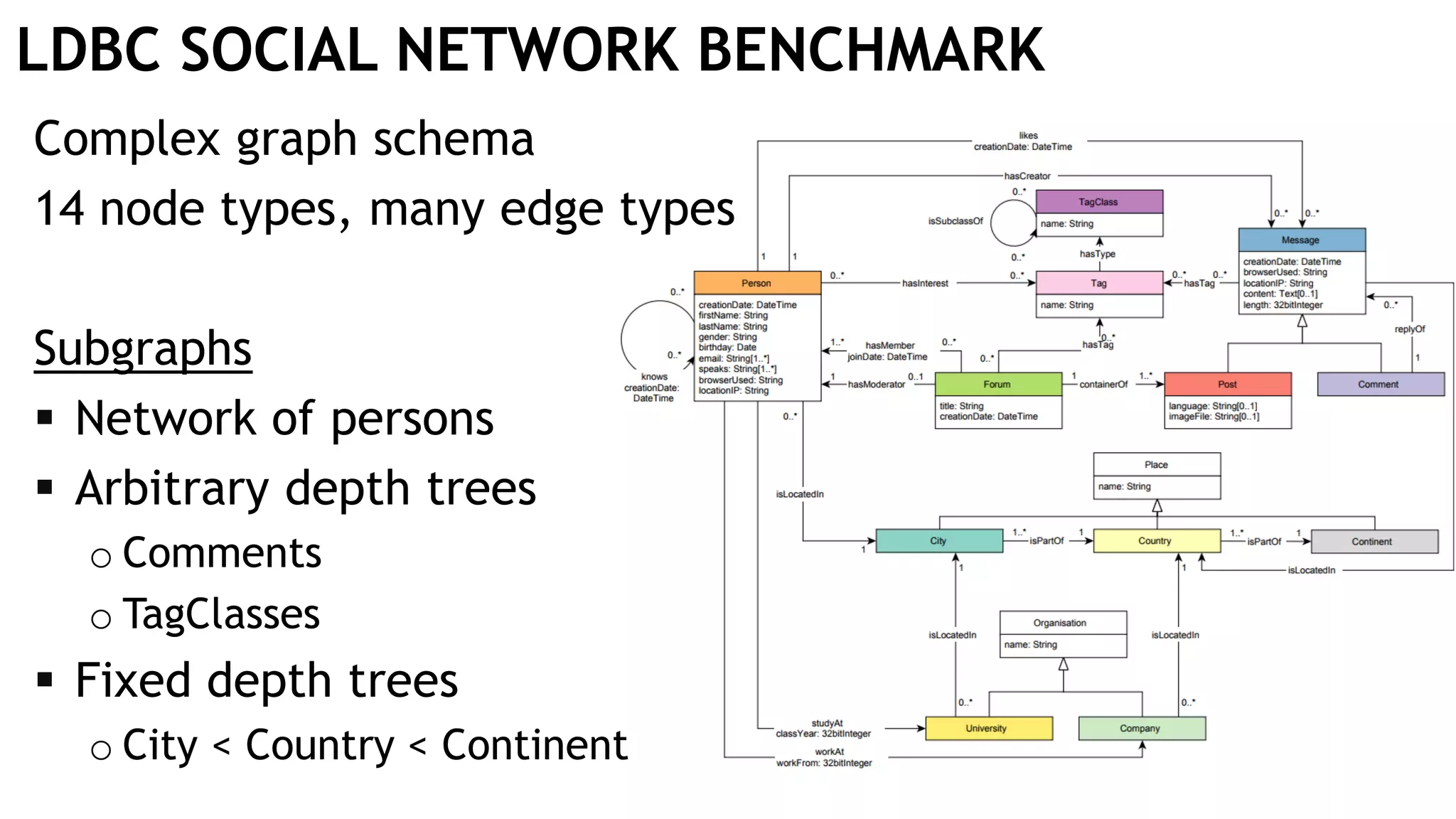
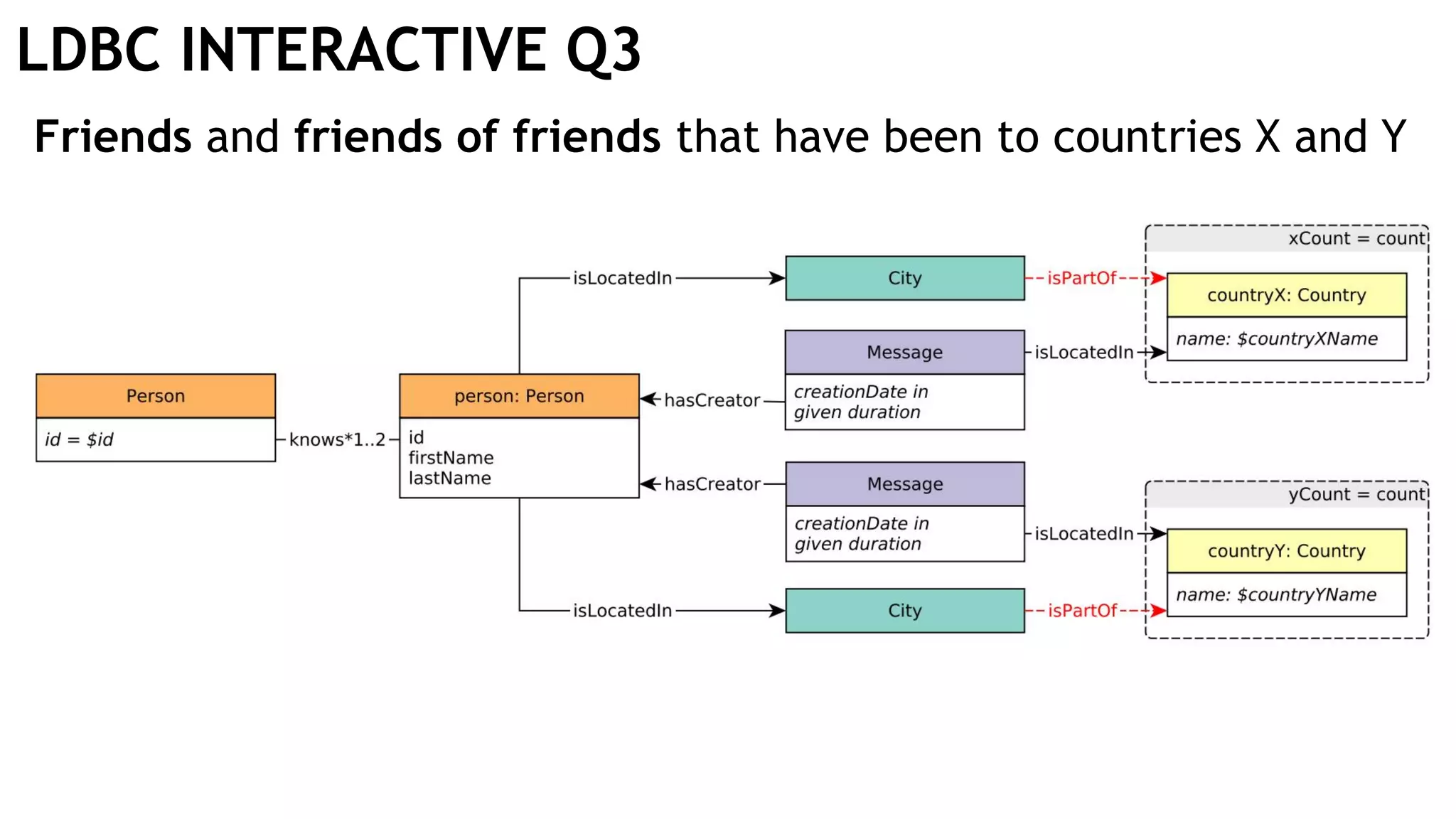
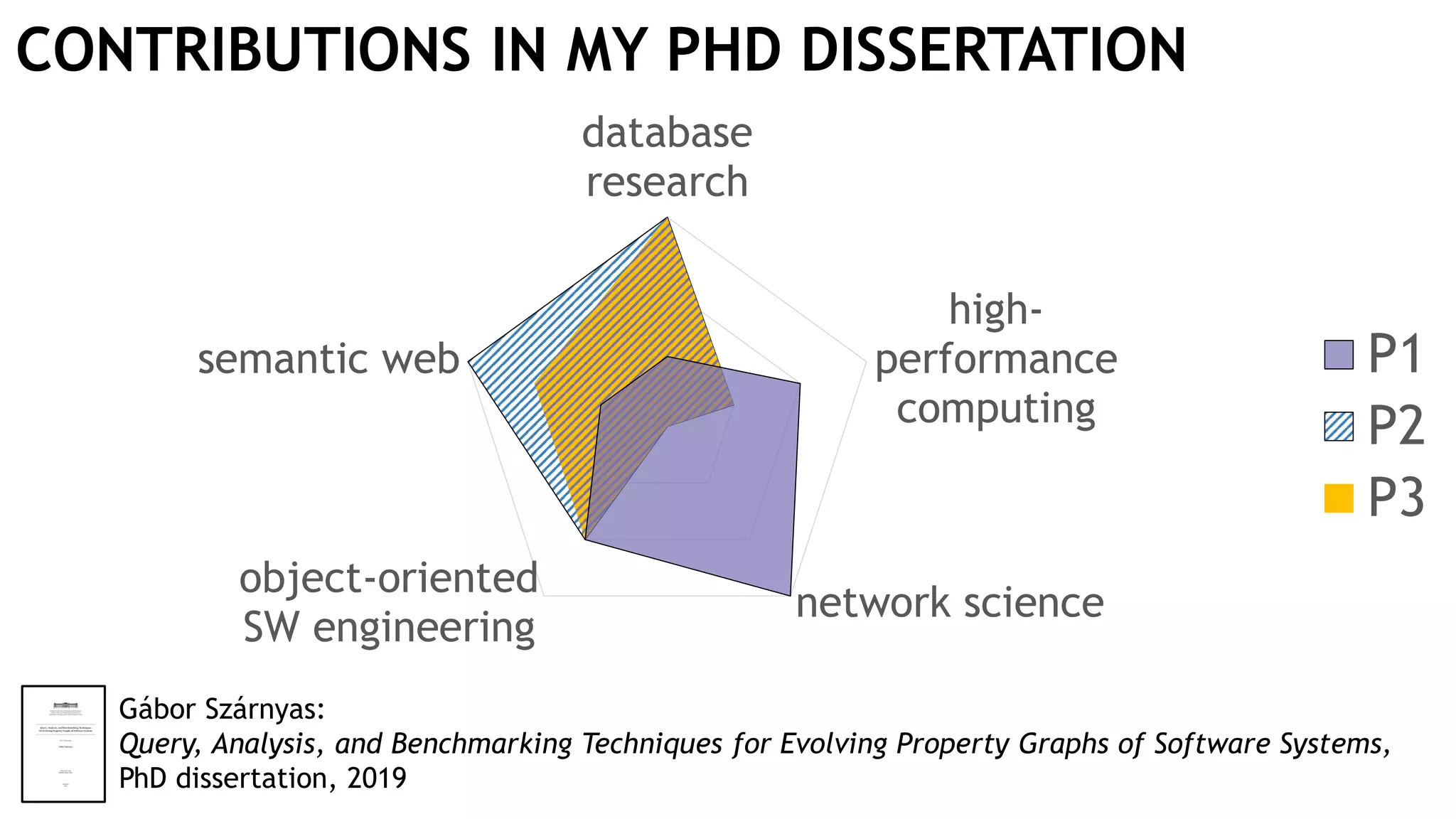
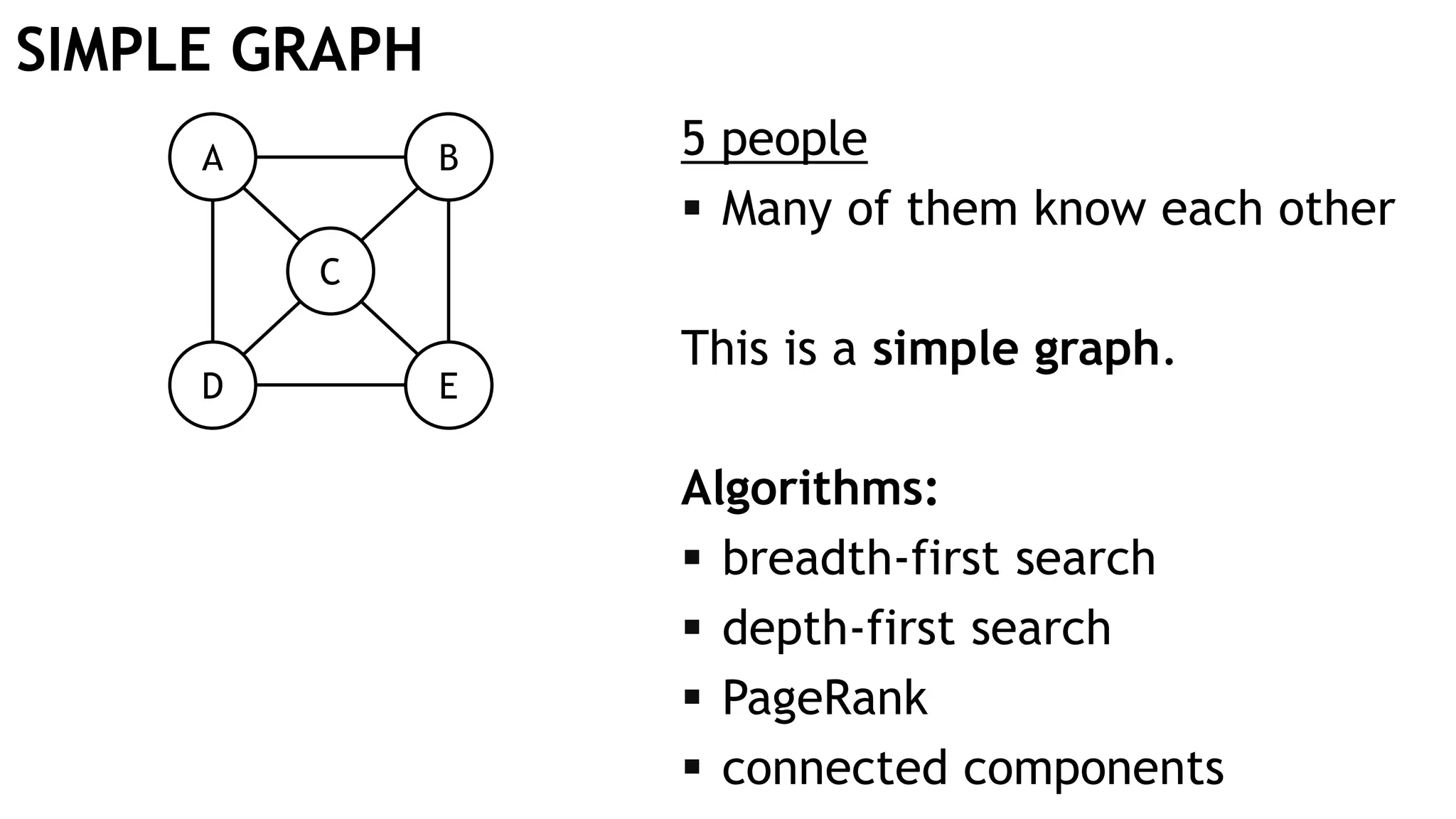
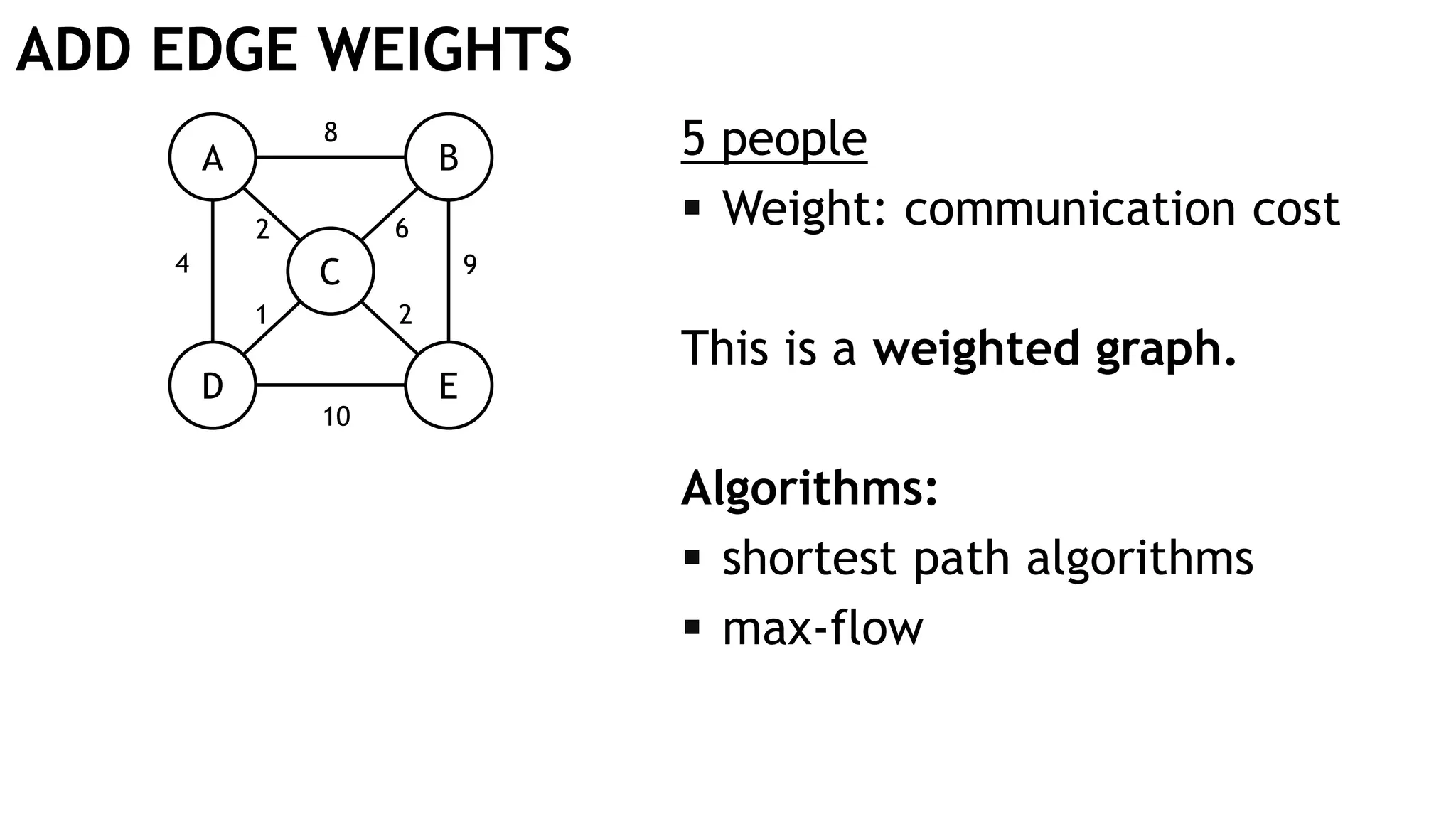
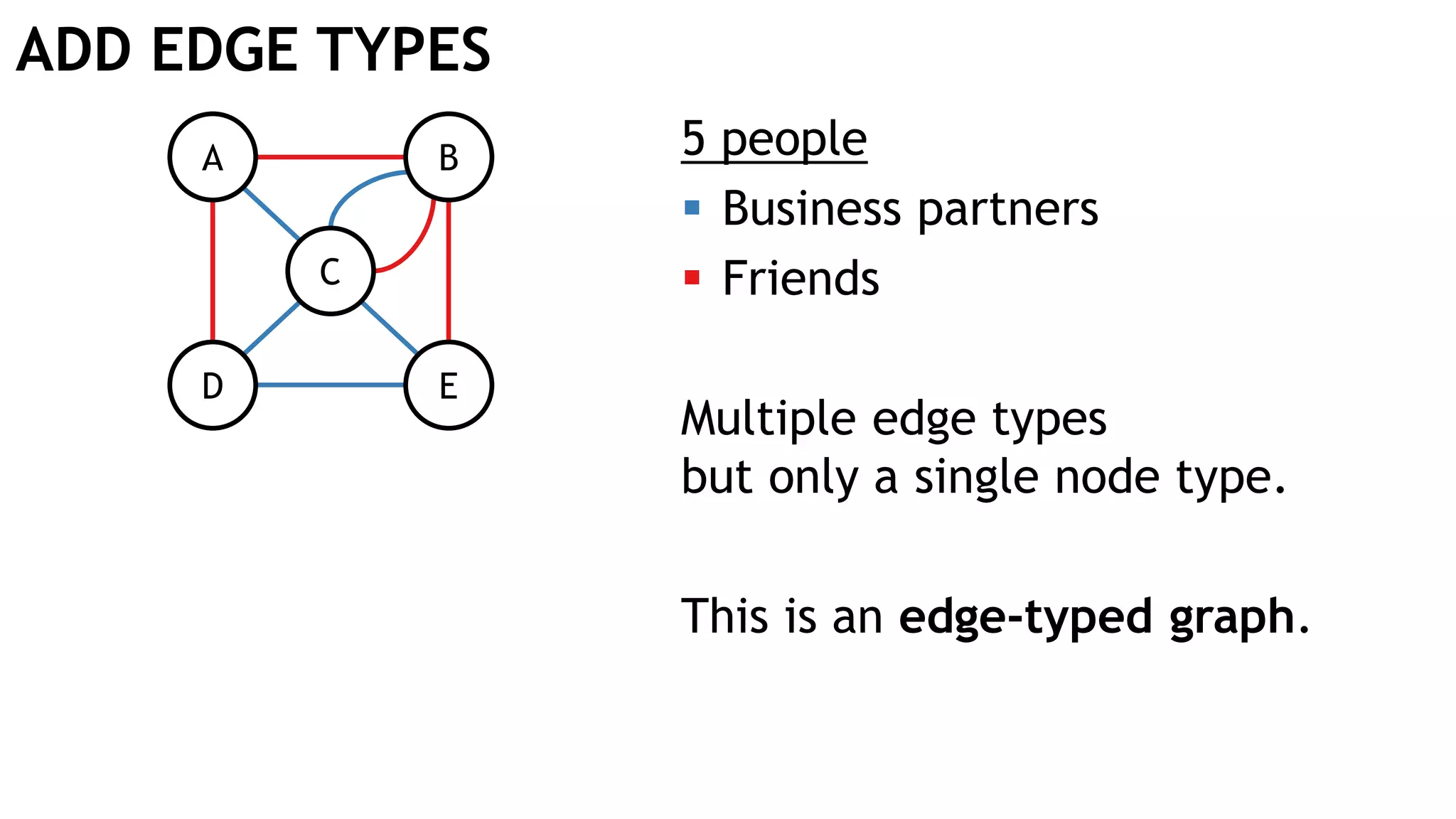
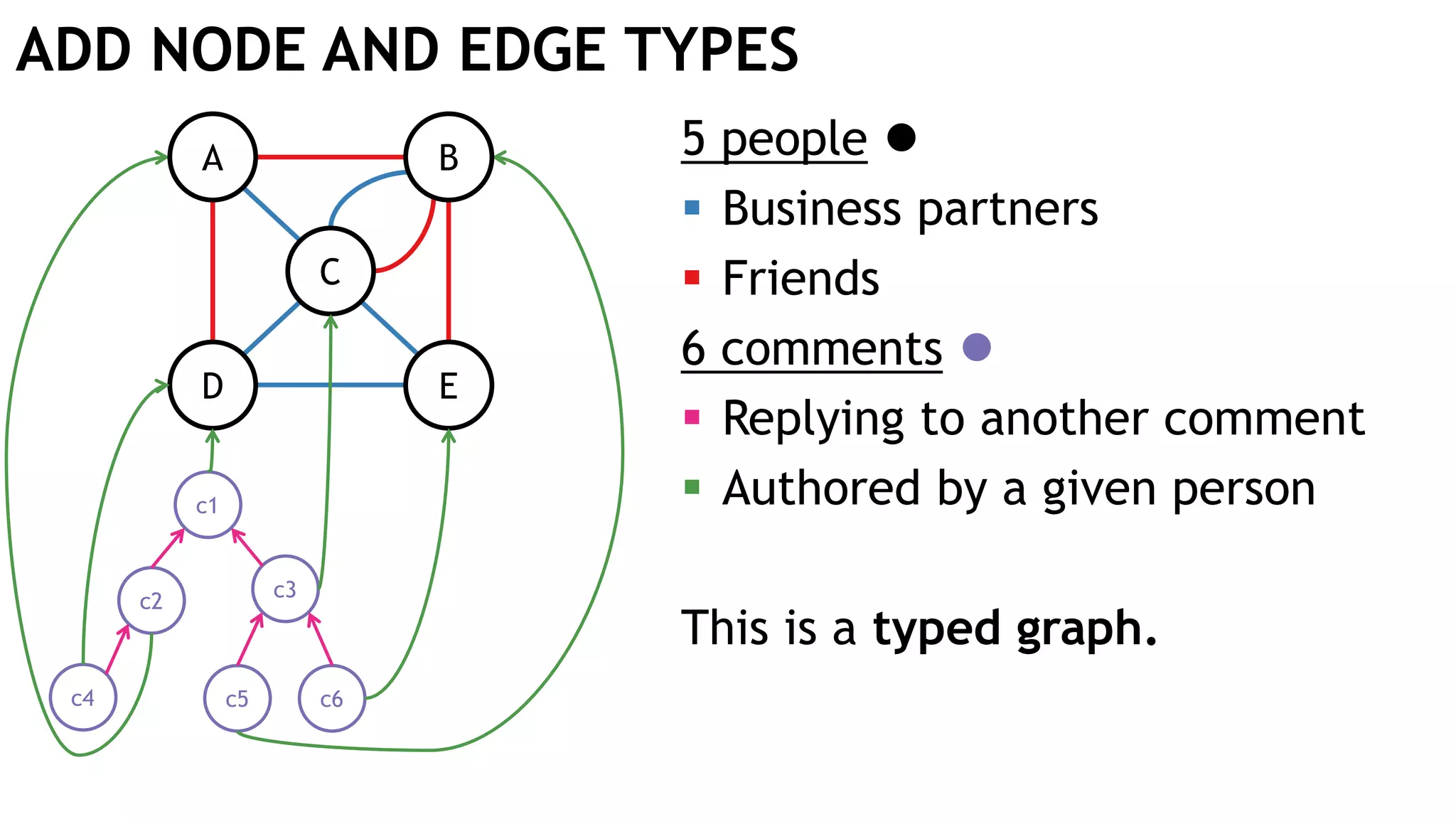
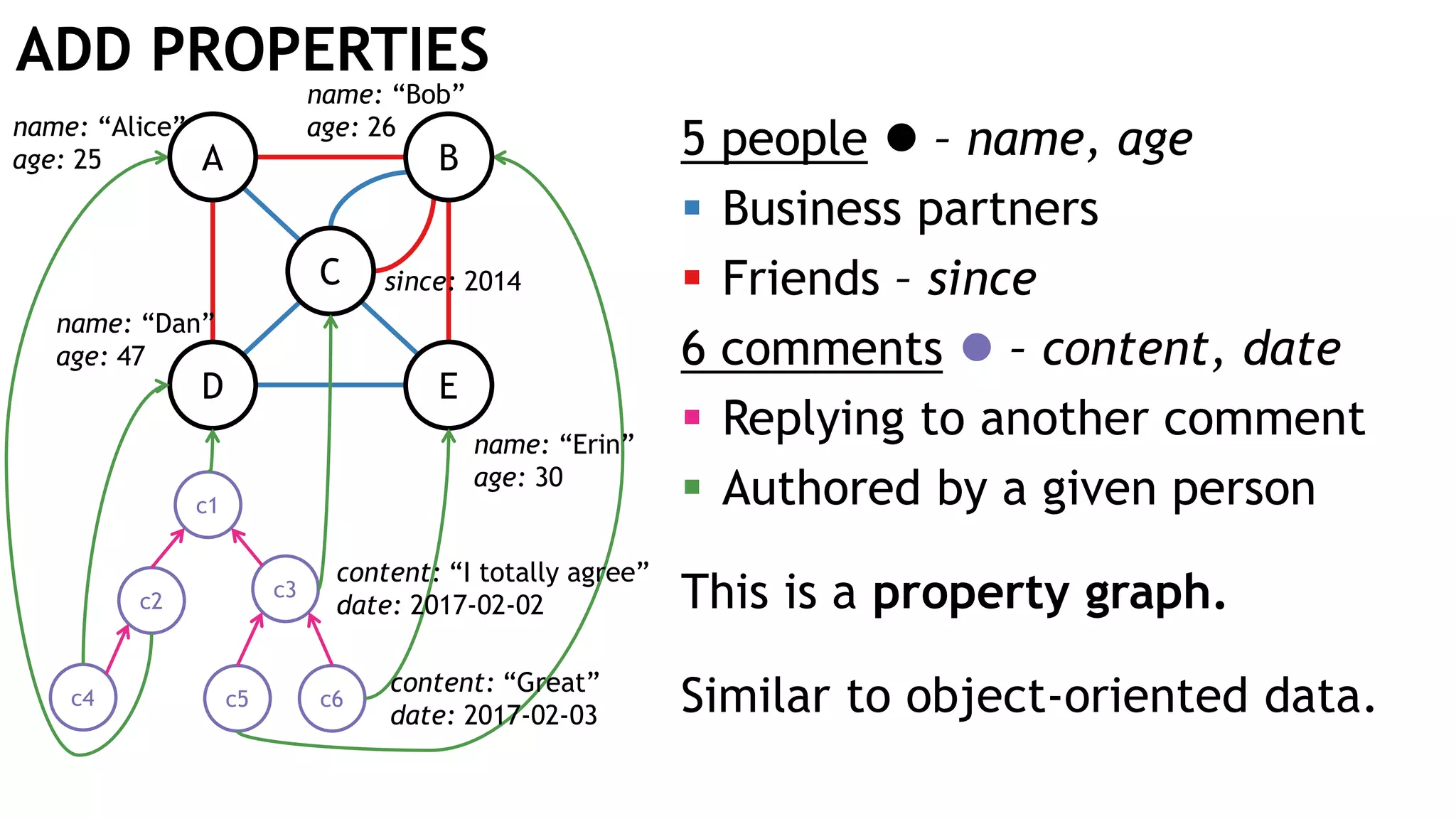
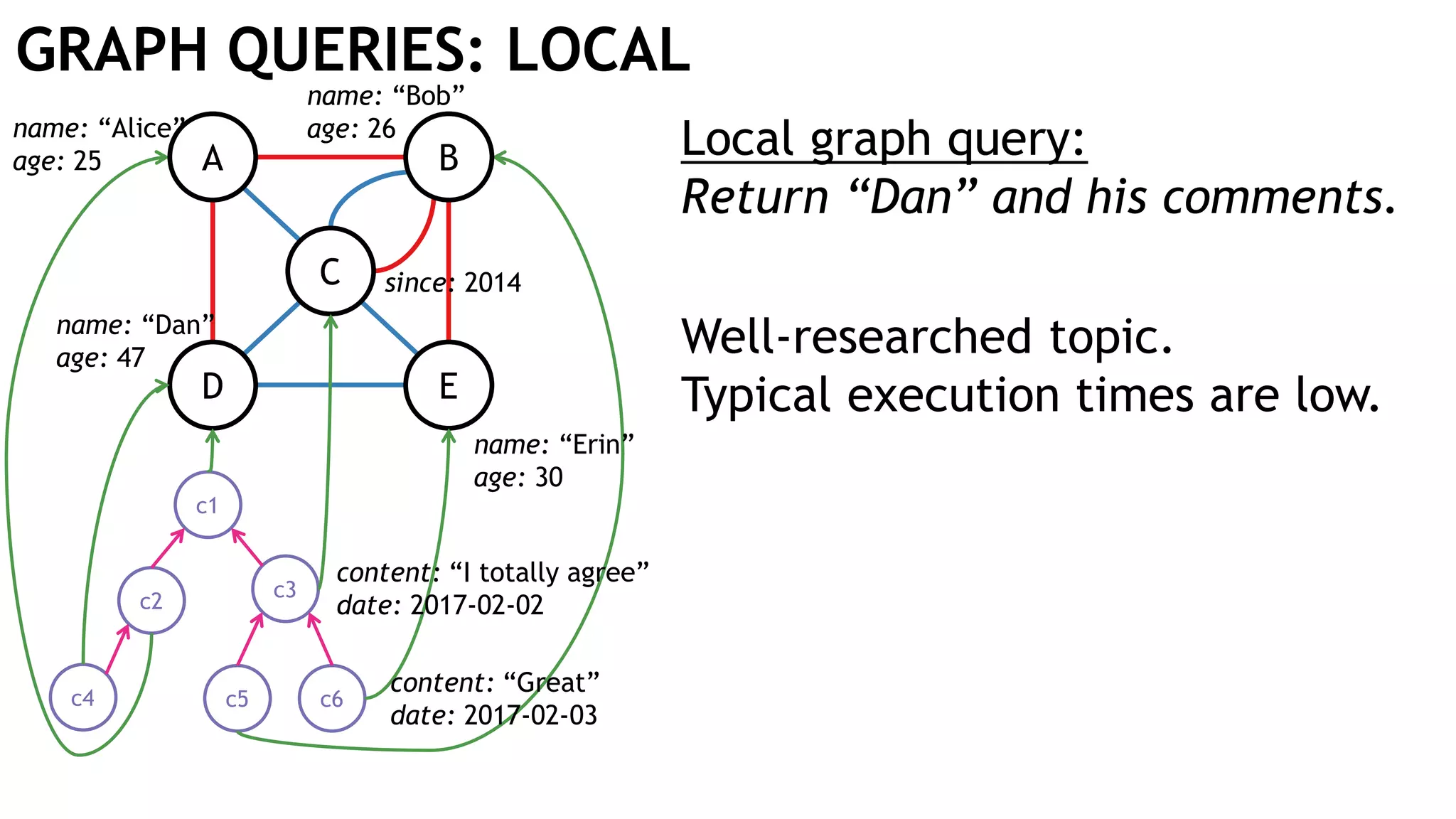
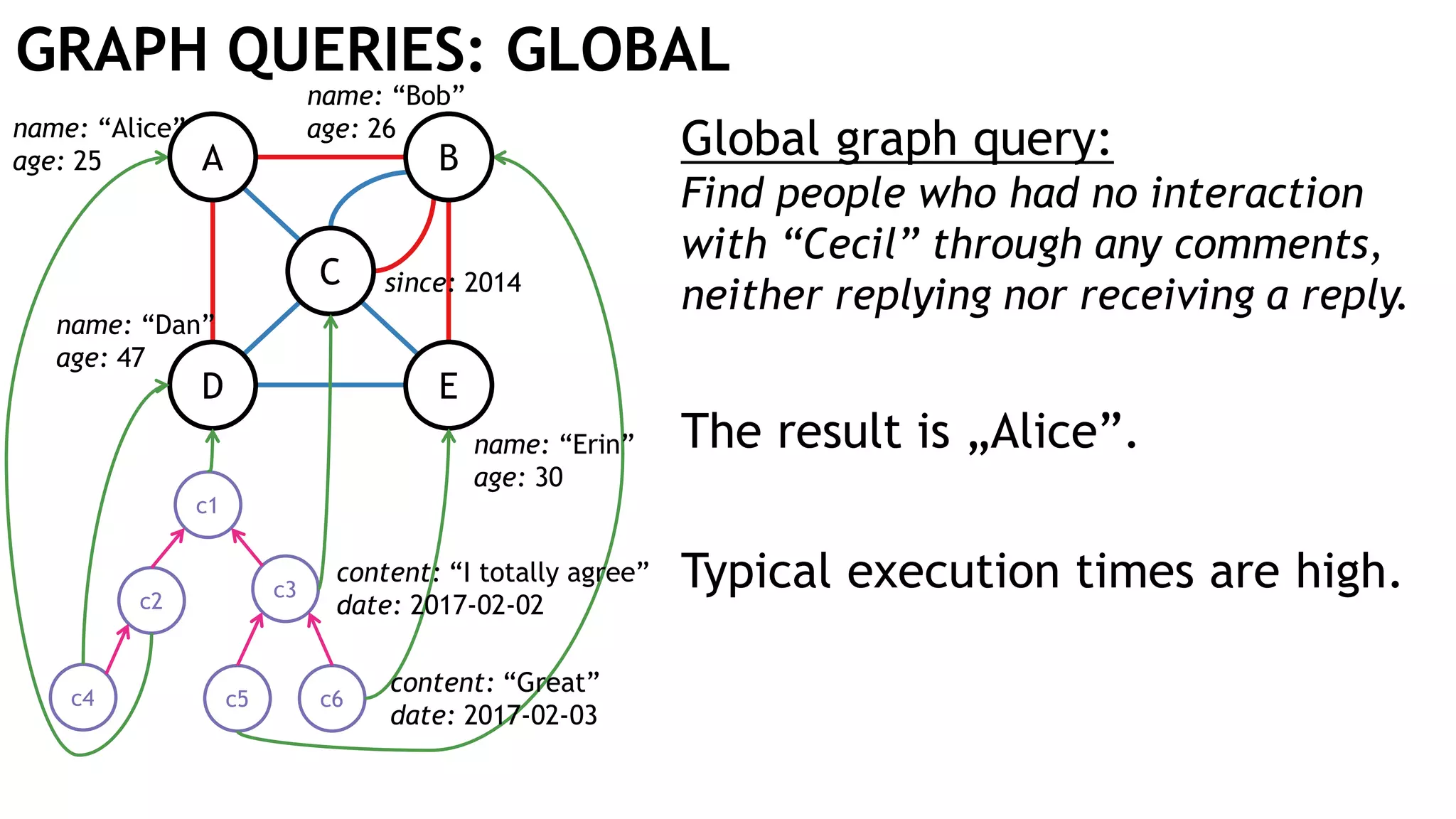
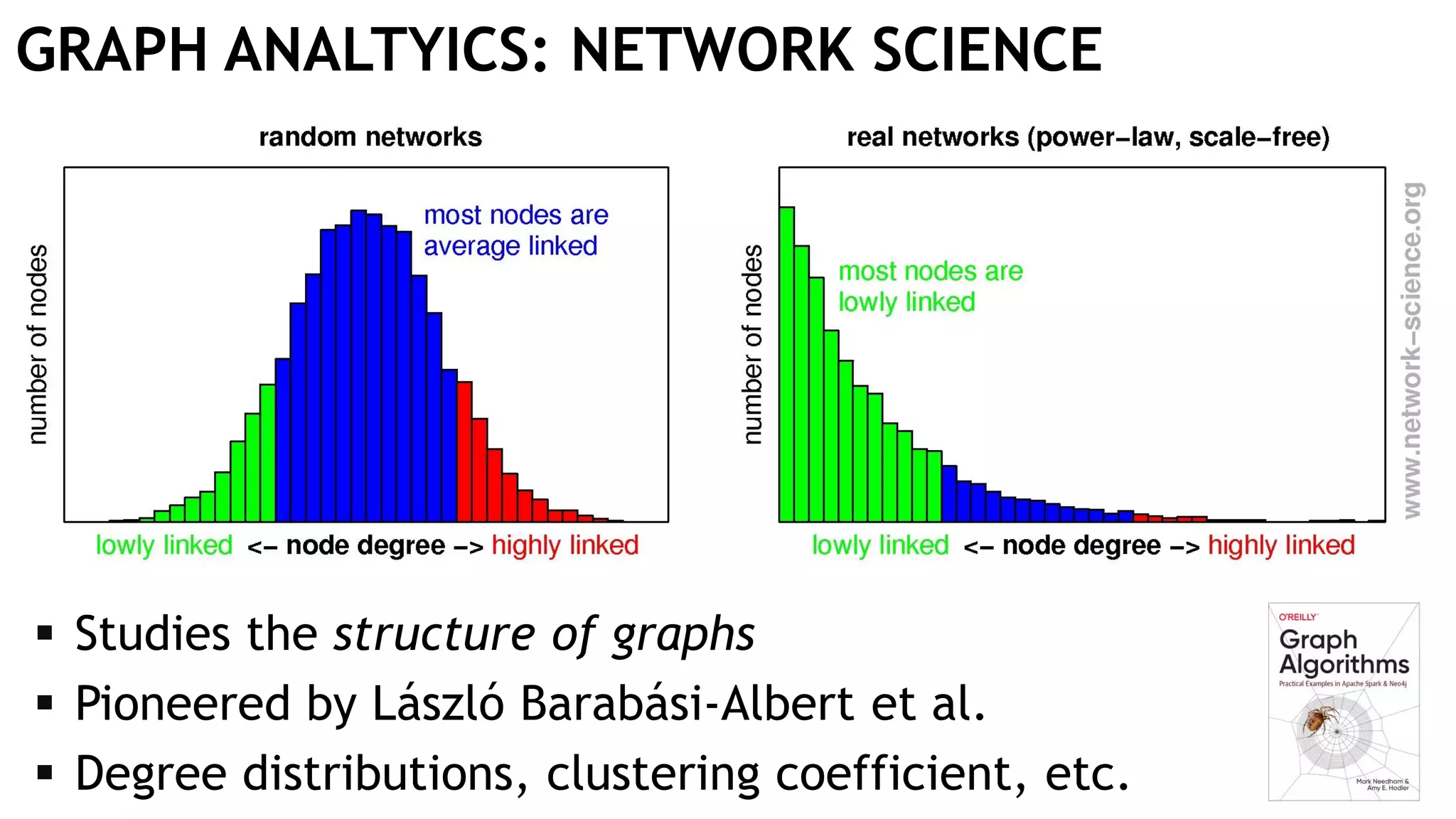
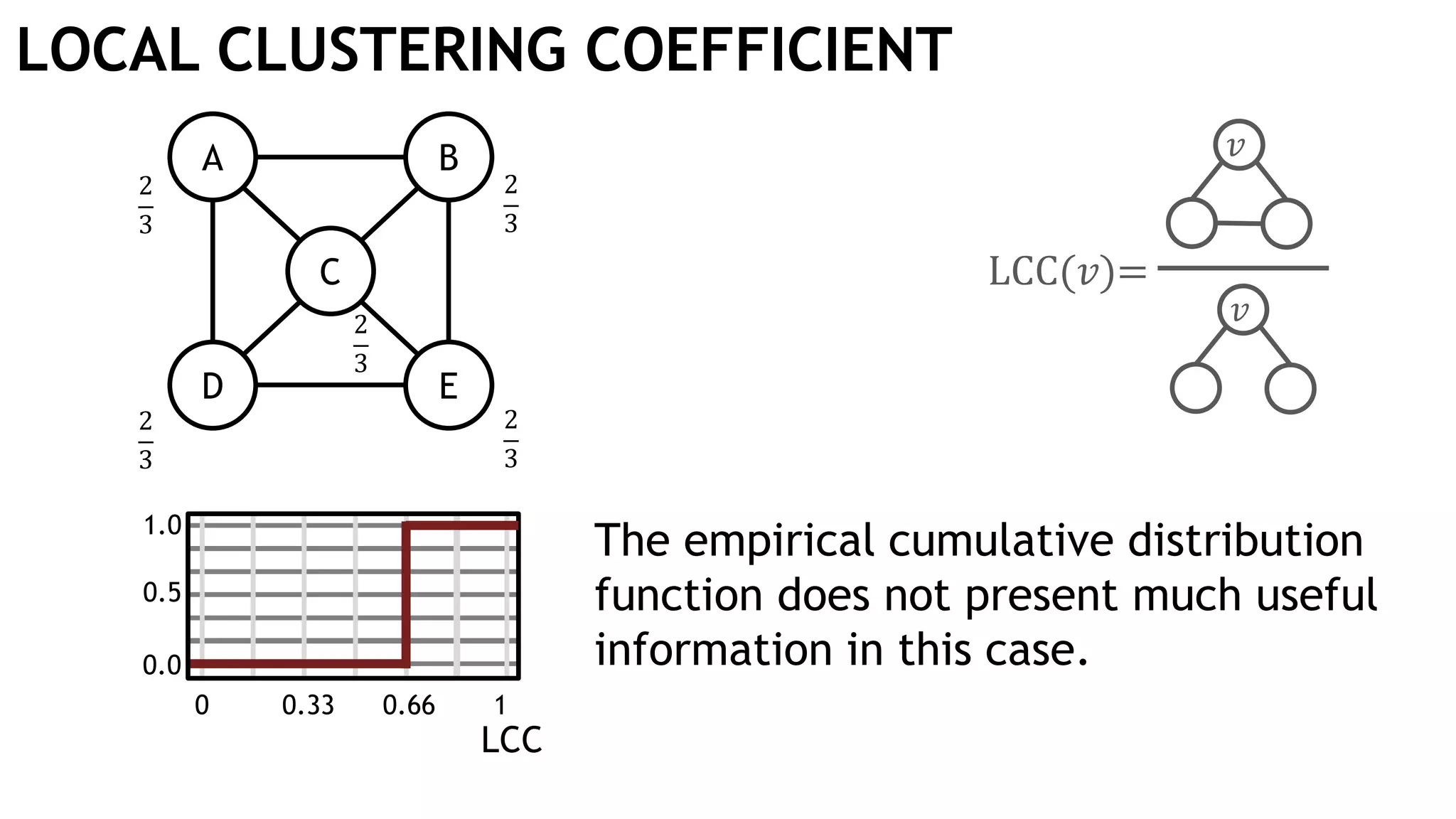
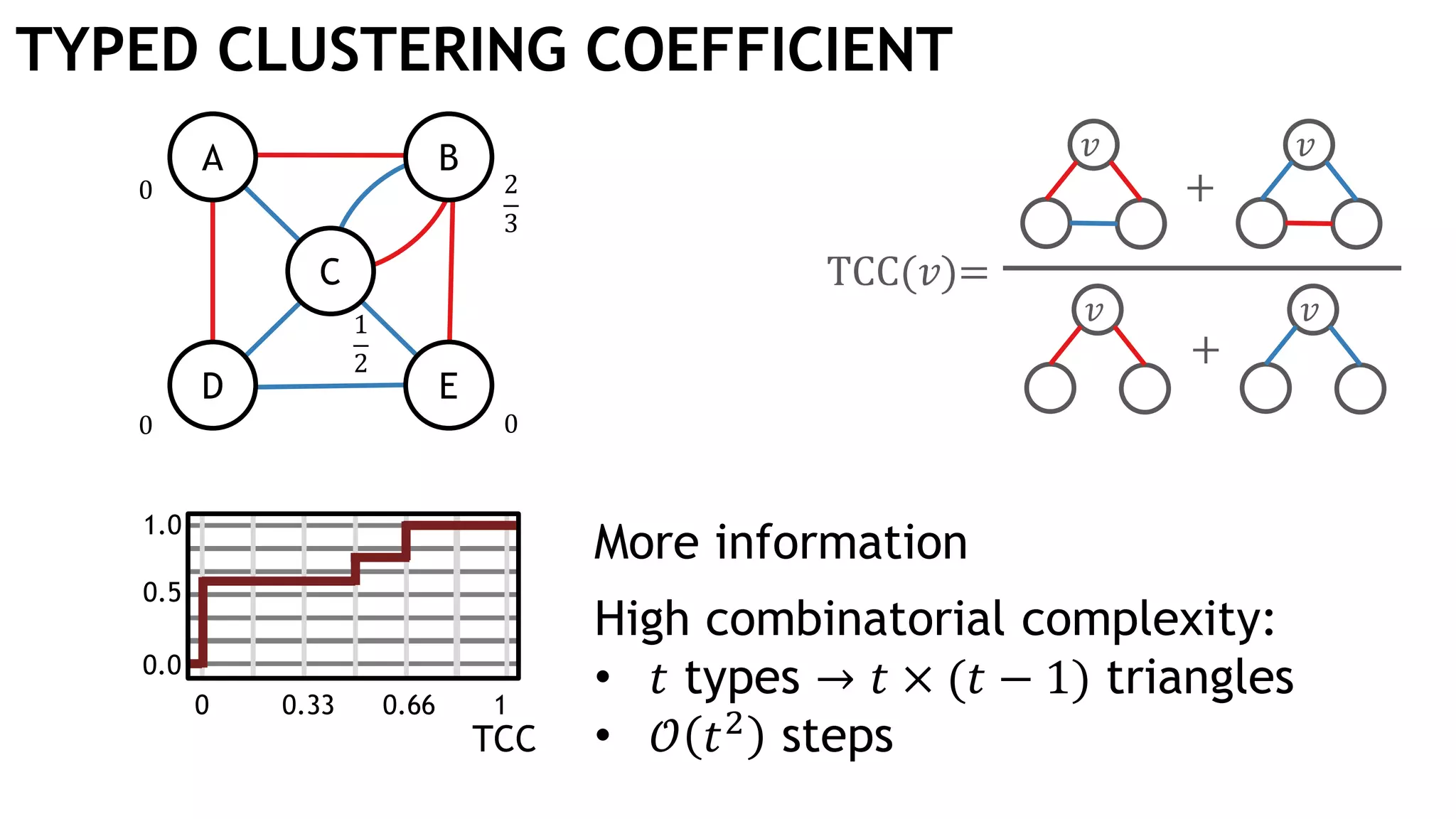
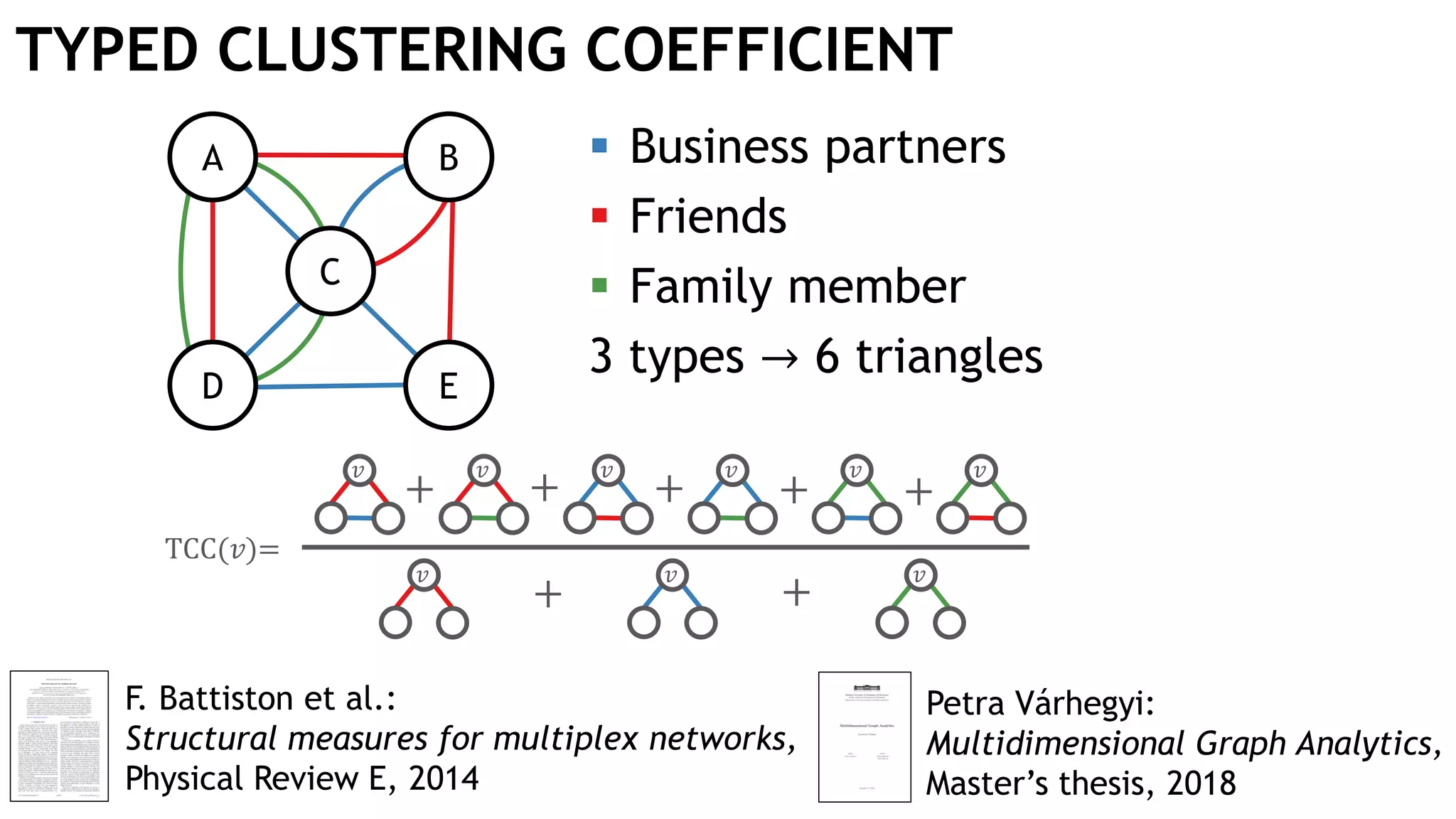
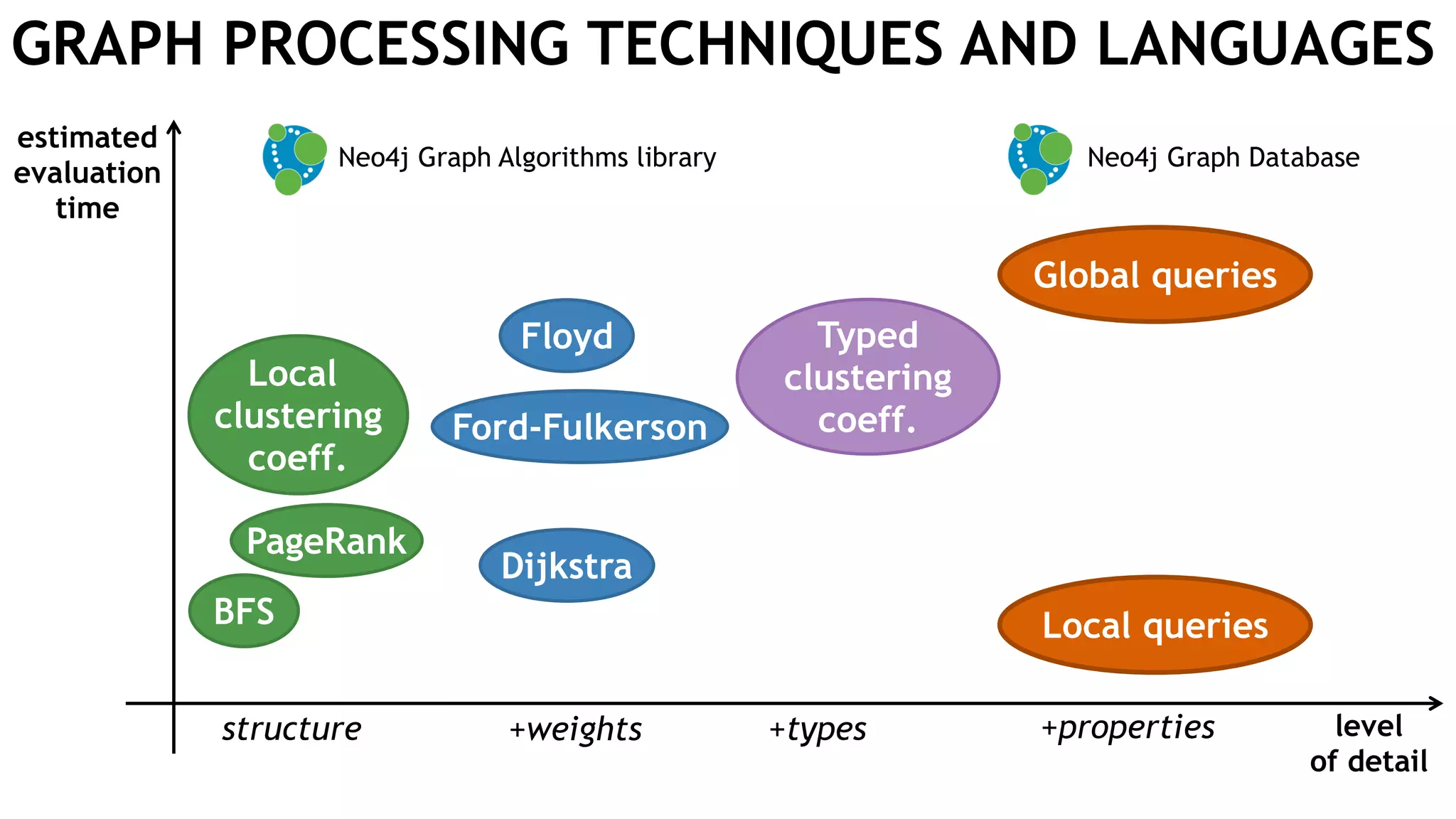
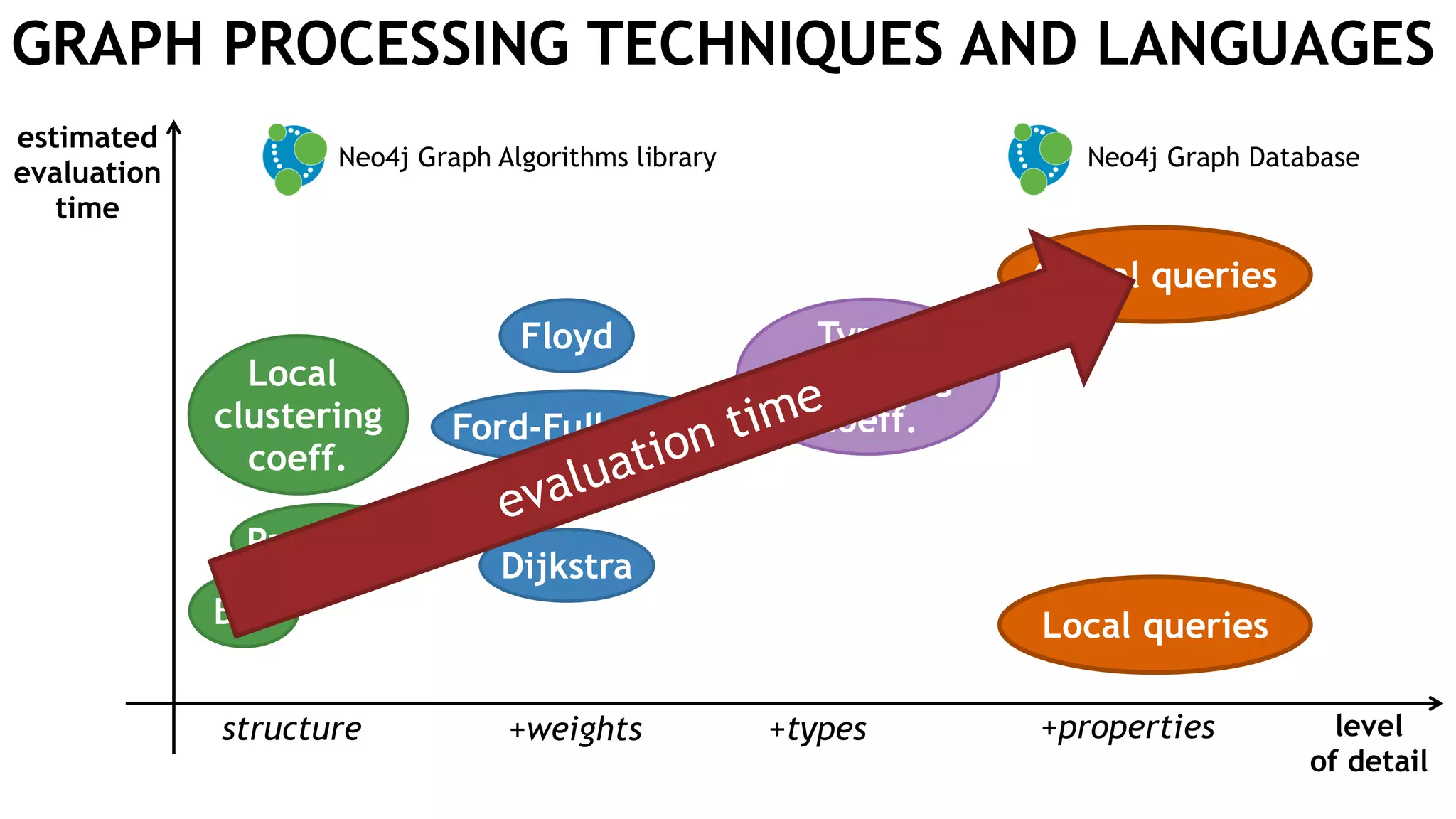
Graph queries and analytics pose several challenges. Graphs have an unstructured, connected nature that makes them difficult for computers to process efficiently. This is due to poor cache locality and difficulties in parallelization. Adding properties, types, weights, or global queries further increases complexity. There is also no consensus on a unified theory for graph processing, between relational algebra and linear algebra approaches. The speaker's PhD dissertation aims to address these challenges through contributions across different domains including databases, high-performance computing, network science, and software engineering.




![GRAPH PROCESSING CHALLENGES / STRUCTURE
the “curse of connectedness”
data structures contemporary computer architectures are
good at processing are linear and simple hierarchical
structures, such as Lists, Stacks, or Trees
a massive amount of random data access is required […]
poor performance since the CPU cache is not in effect for
most of the time. […] parallelism is difficult to extract
because of the unstructured nature of graphs.
B. Shao, Y. Li, H. Wang, H. Xia (Microsoft Research):
Trinity Graph Engine and its Applications,
IEEE Data Engineering Bulleting 2017
connectedness
computer
architectures
caching and
parallelization](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20190625szarnyasgabor-whatmakesgraphqueriesdifficult-200217120021/75/What-Makes-Graph-Queries-Difficult-19-2048.jpg)
![GRAPH PROCESSING CHALLENGES / PROPERTIES
existing graph query methods […] focus on the topological
structure of graphs and few have considered attributed graphs.
applications of large graph databases would involve querying the
graph data (attributes) in addition to the graph topology.
answering queries that involve predicates on the attributes of
the graphs in addition to the topological structure […] makes
evaluation and optimization more complex.
S. Sakr, S. Elnikety, Y. He (Microsoft Research):
G-SPARQL: A Hybrid Engine for Querying Large Attributed Graphs,
CIKM 2012
topology
properties
complex
optimization](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20190625szarnyasgabor-whatmakesgraphqueriesdifficult-200217120021/75/What-Makes-Graph-Queries-Difficult-20-2048.jpg)