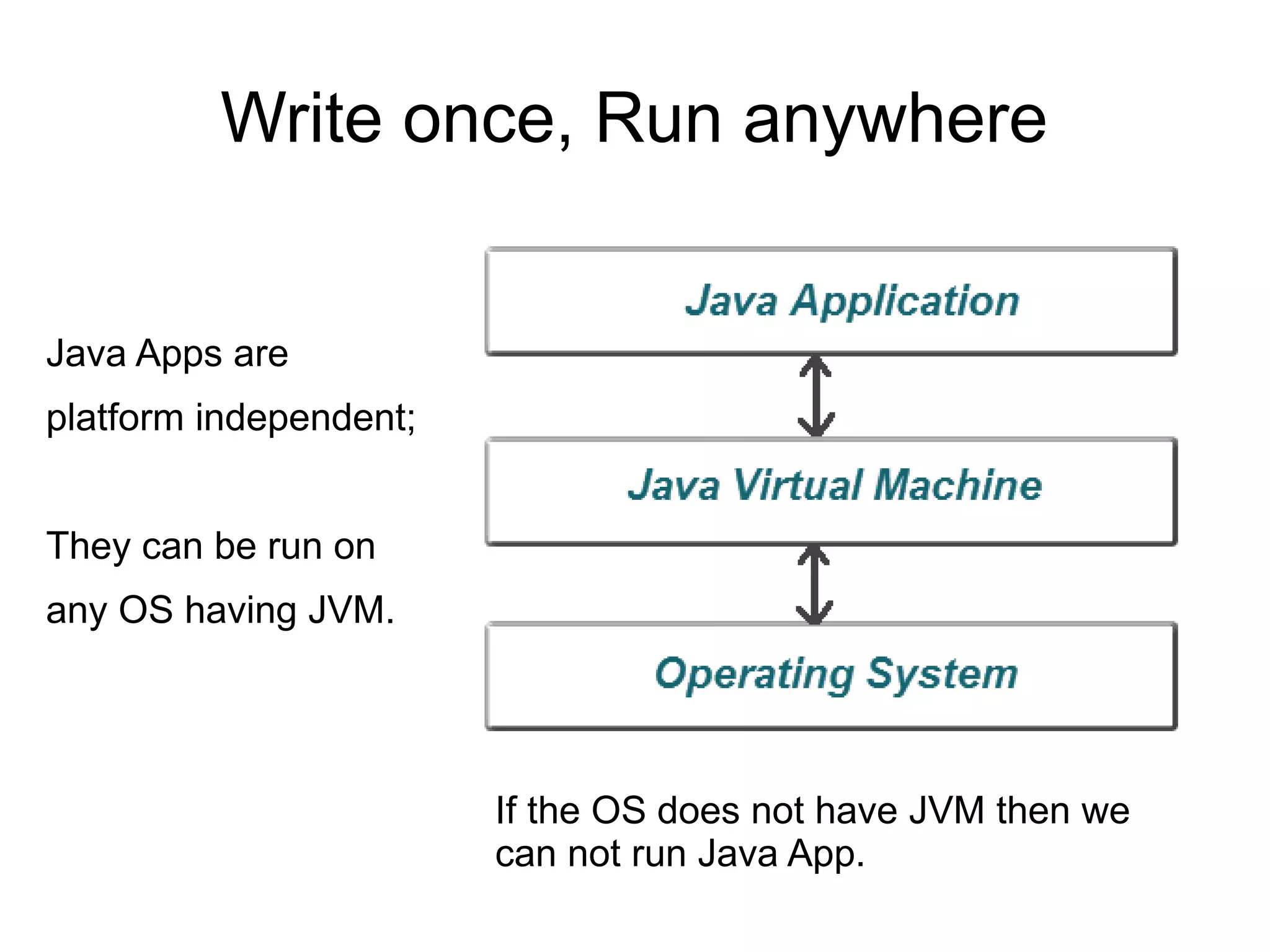
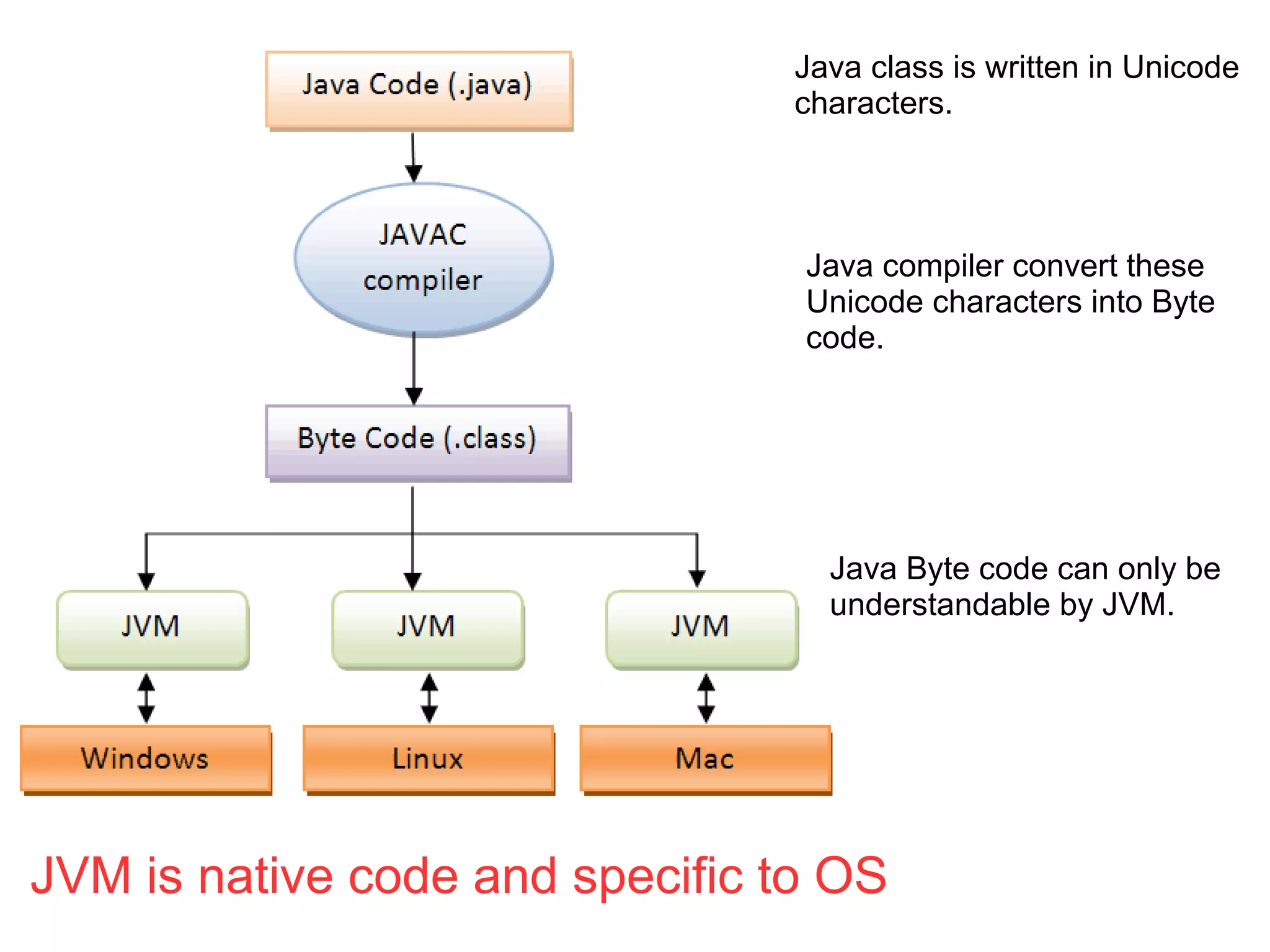
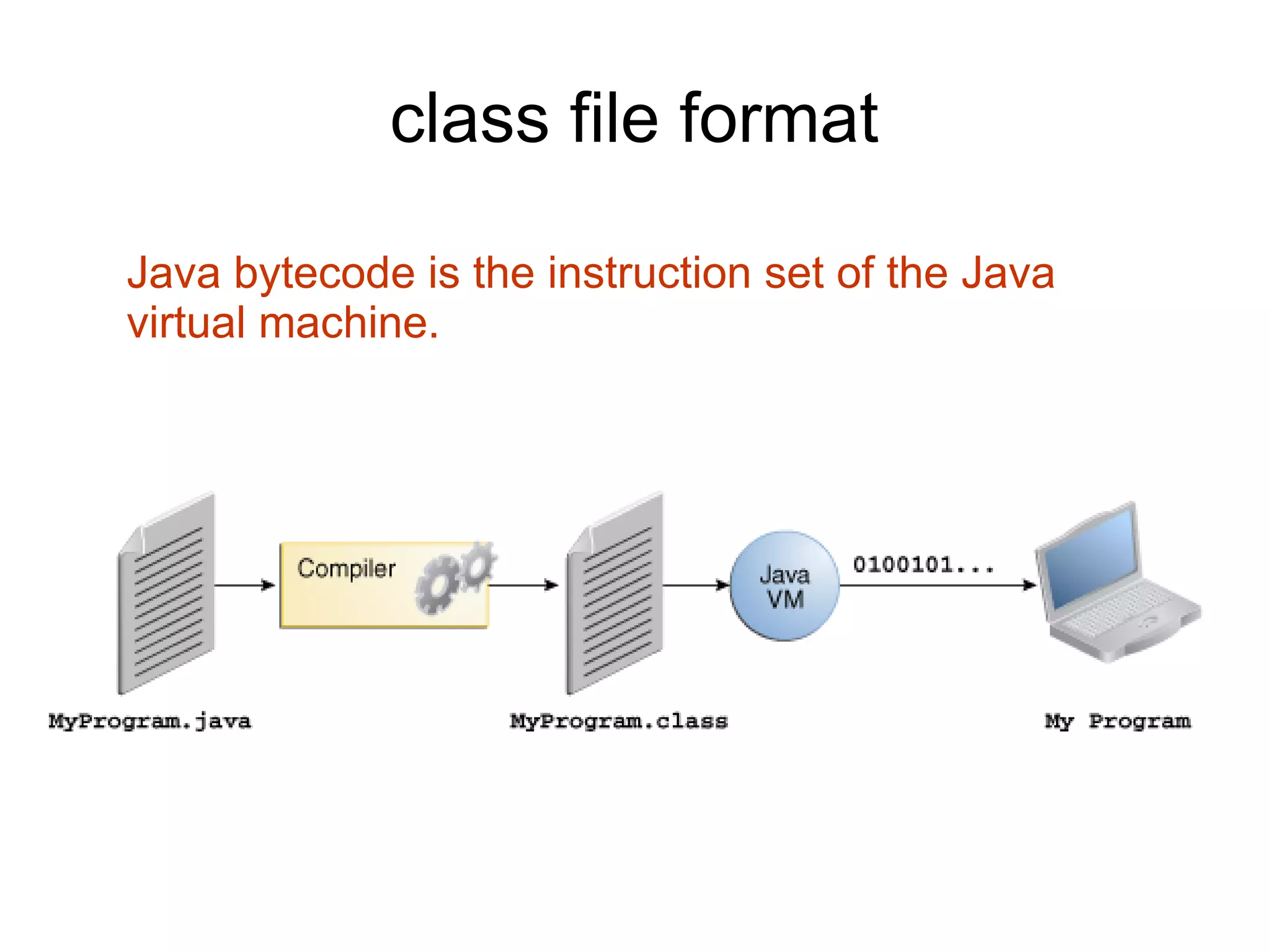
Java applications are platform-independent and require a Java Virtual Machine (JVM) to run on any operating system. The Java programming language is designed to be simple, secure, and high-performance, and it includes a rich Java API that facilitates various functions such as input/output and networking. Java comes in two versions: the Java Runtime Environment (JRE), which runs applications, and the Java Development Kit (JDK), which includes tools for developing applications.