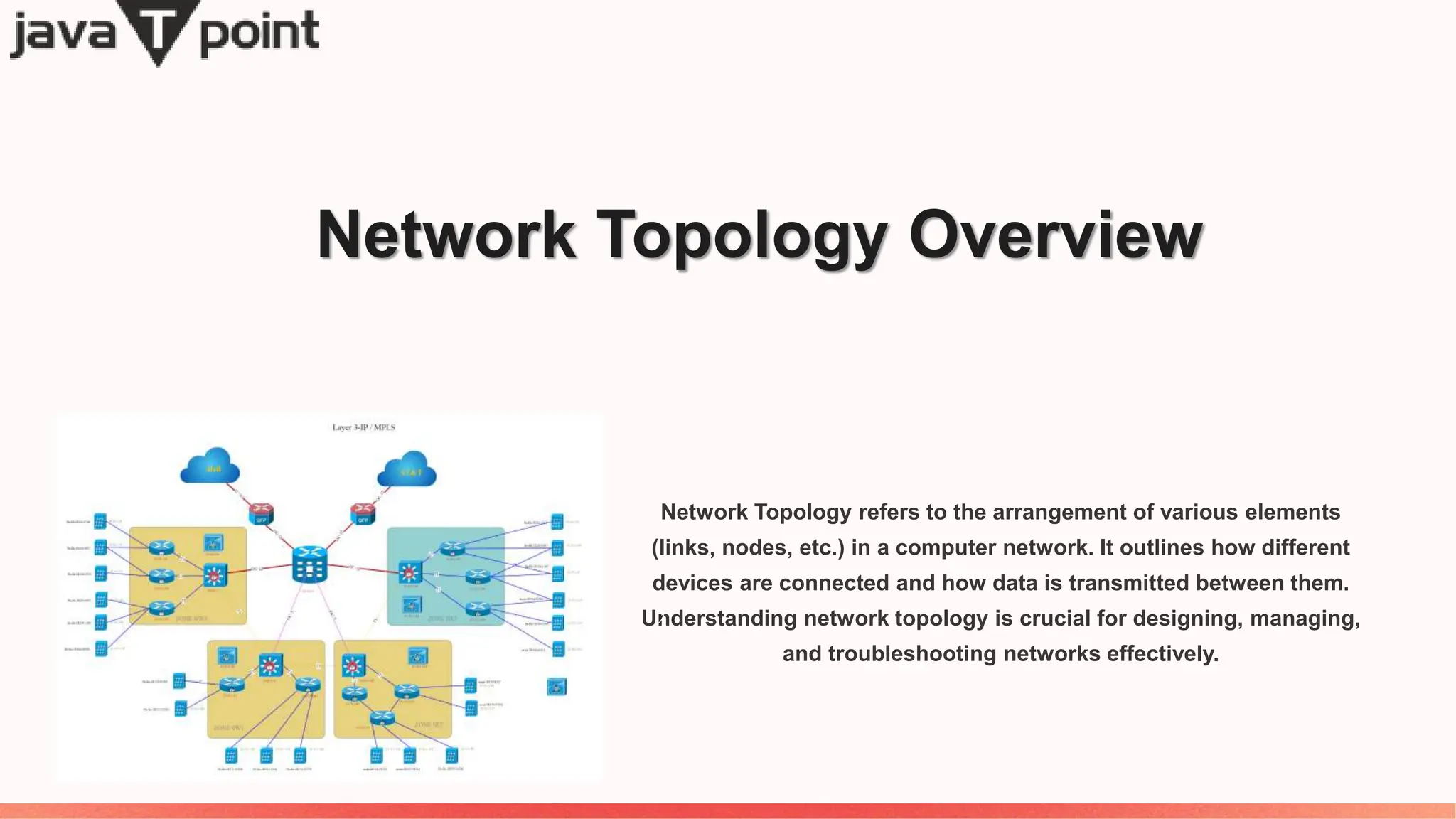
Network topology refers to the arrangement of devices in a computer network, affecting how data is transmitted and resources utilized. Different types of topology, such as bus, star, ring, and mesh, are explored for their efficiencies, performance, and scalability, as well as their implications for security and fault tolerance. Hybrid topologies combine elements of various types to meet specific organizational needs effectively.