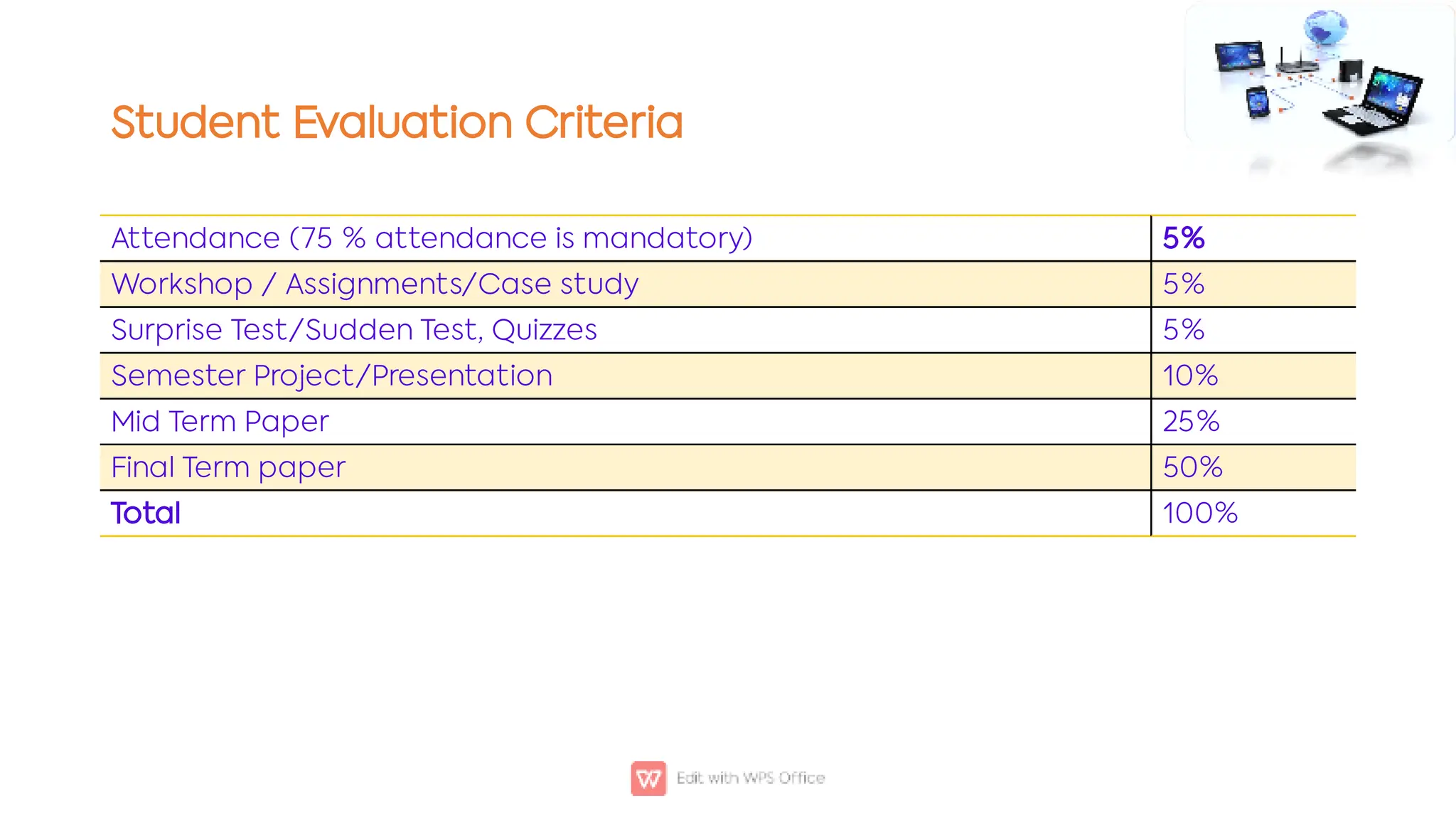
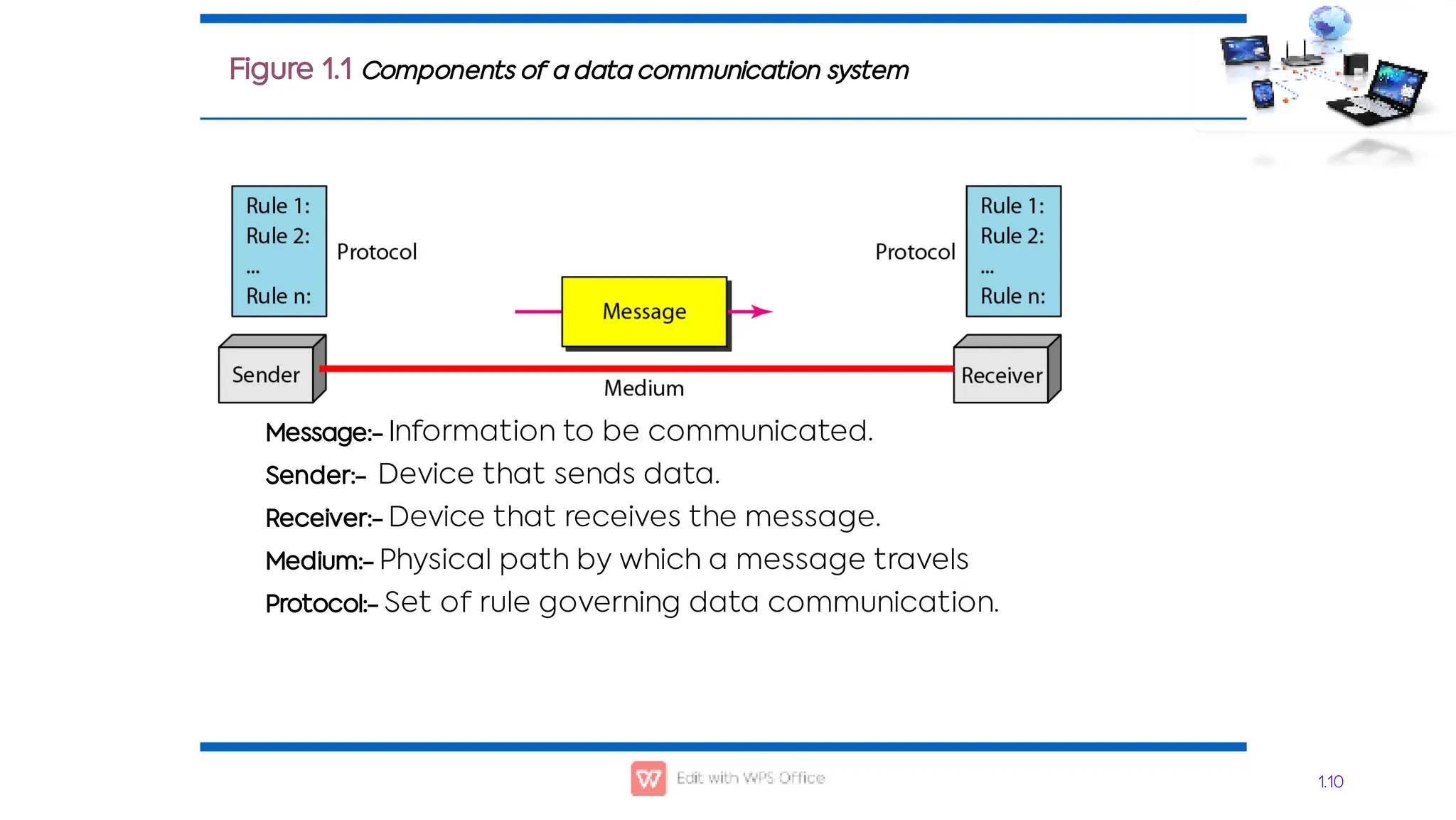
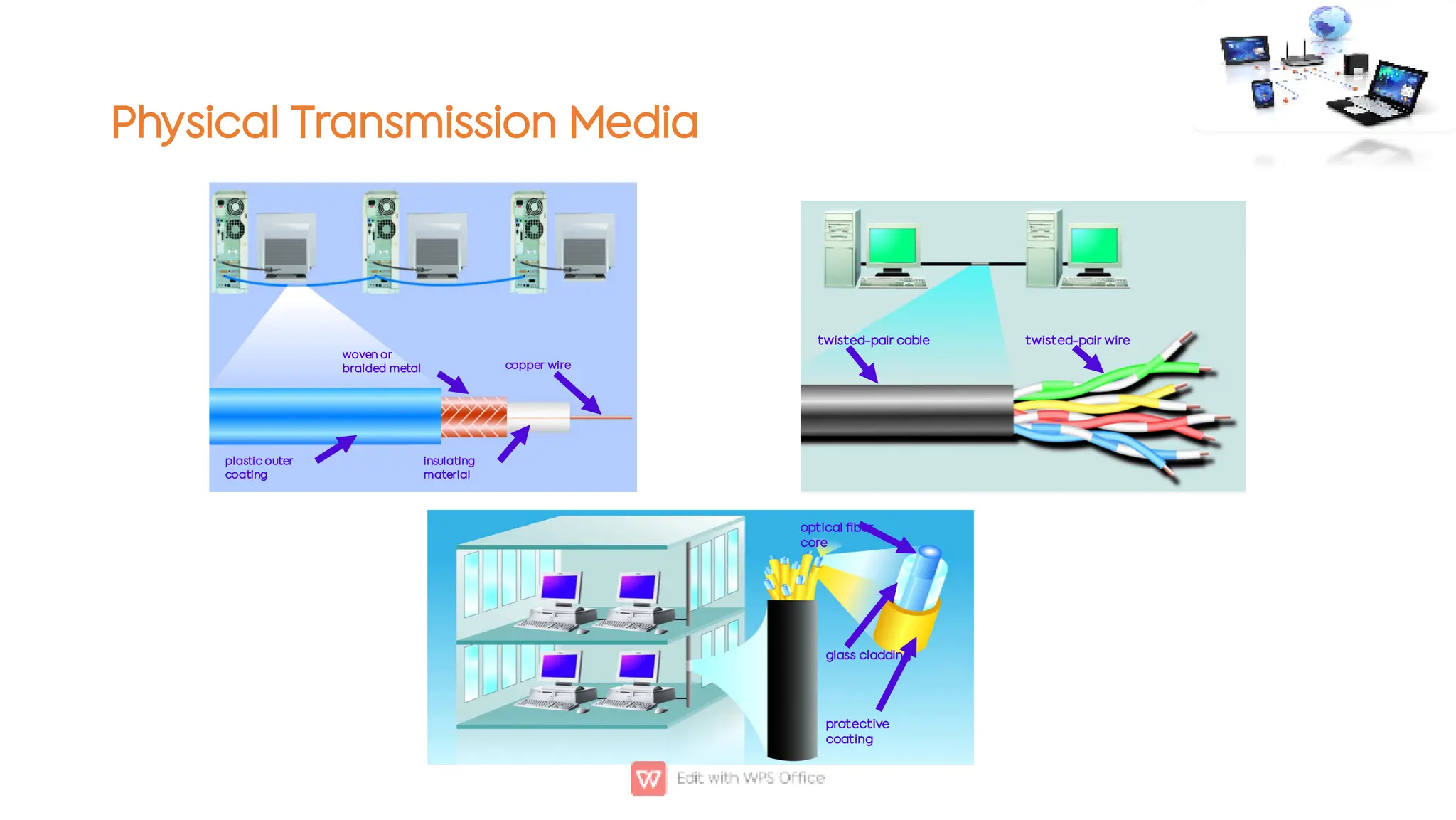
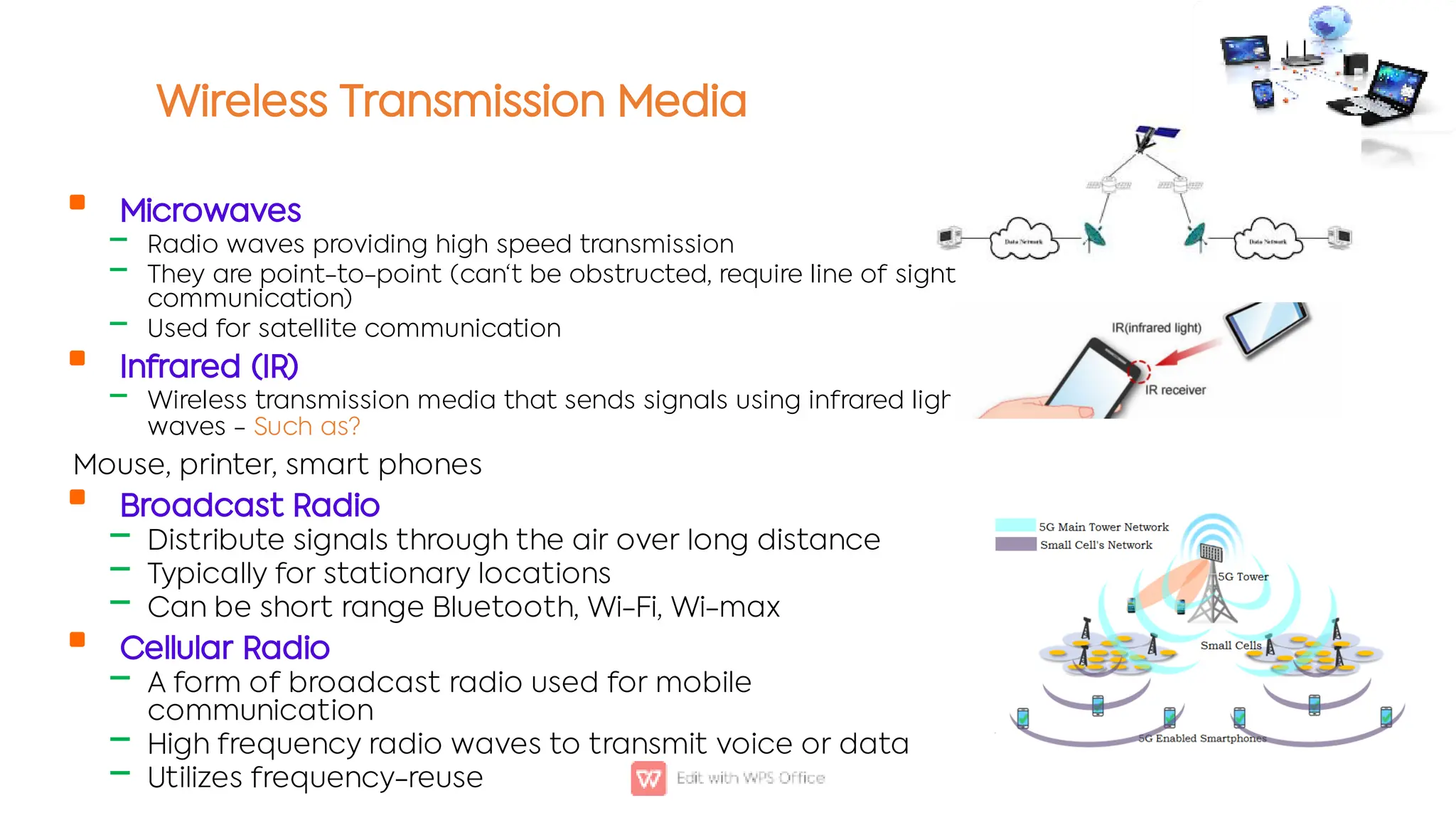
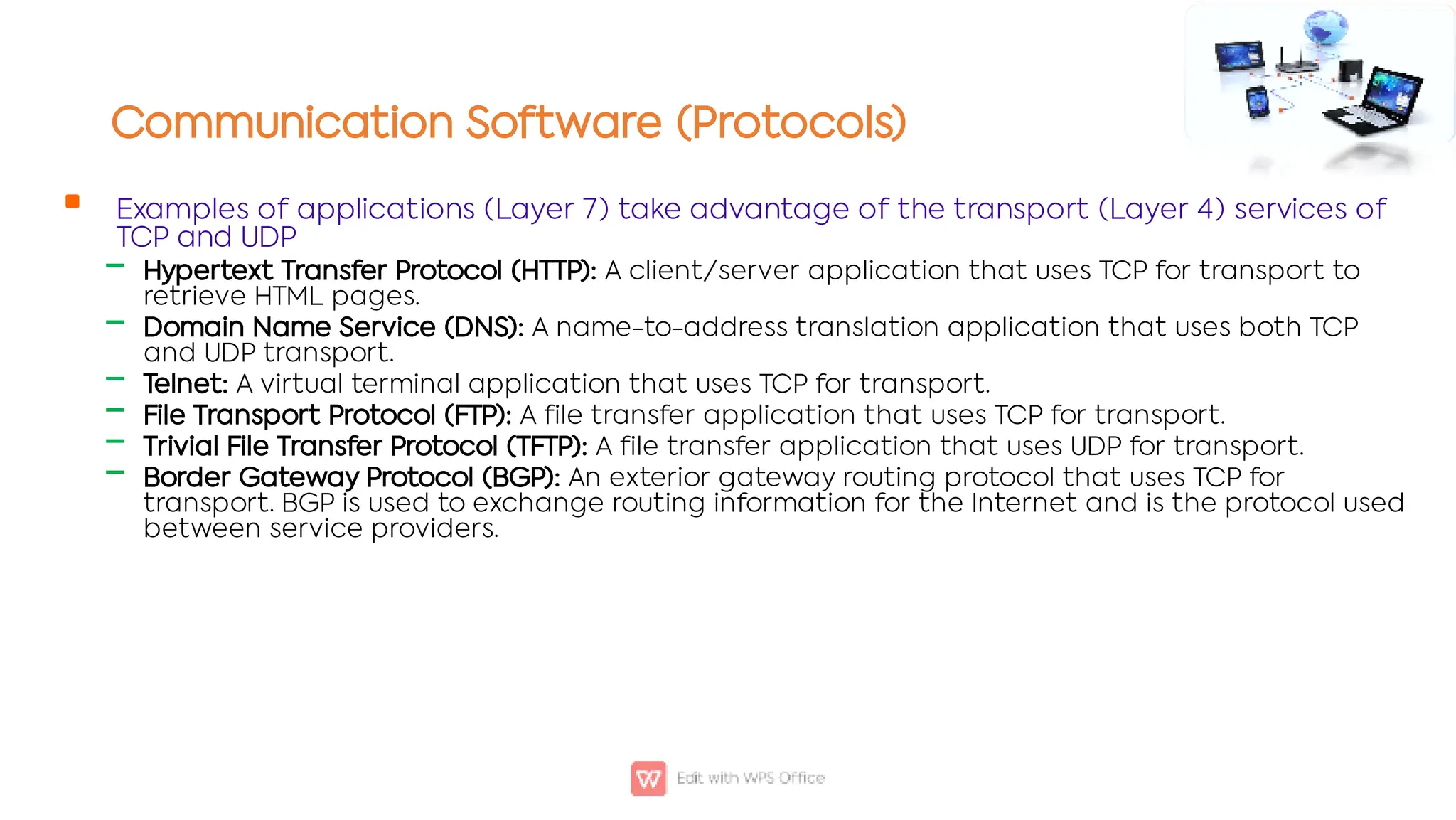
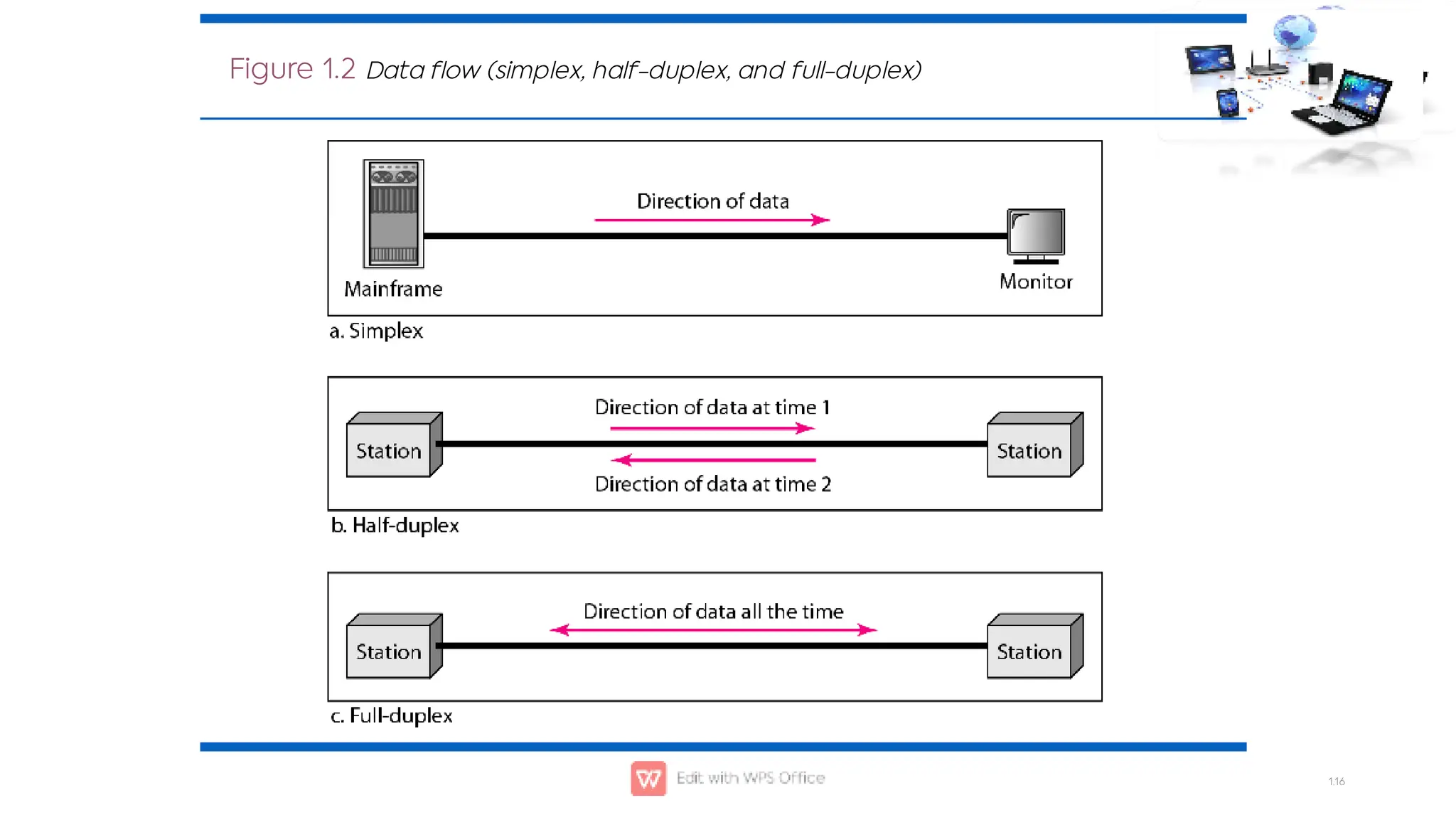
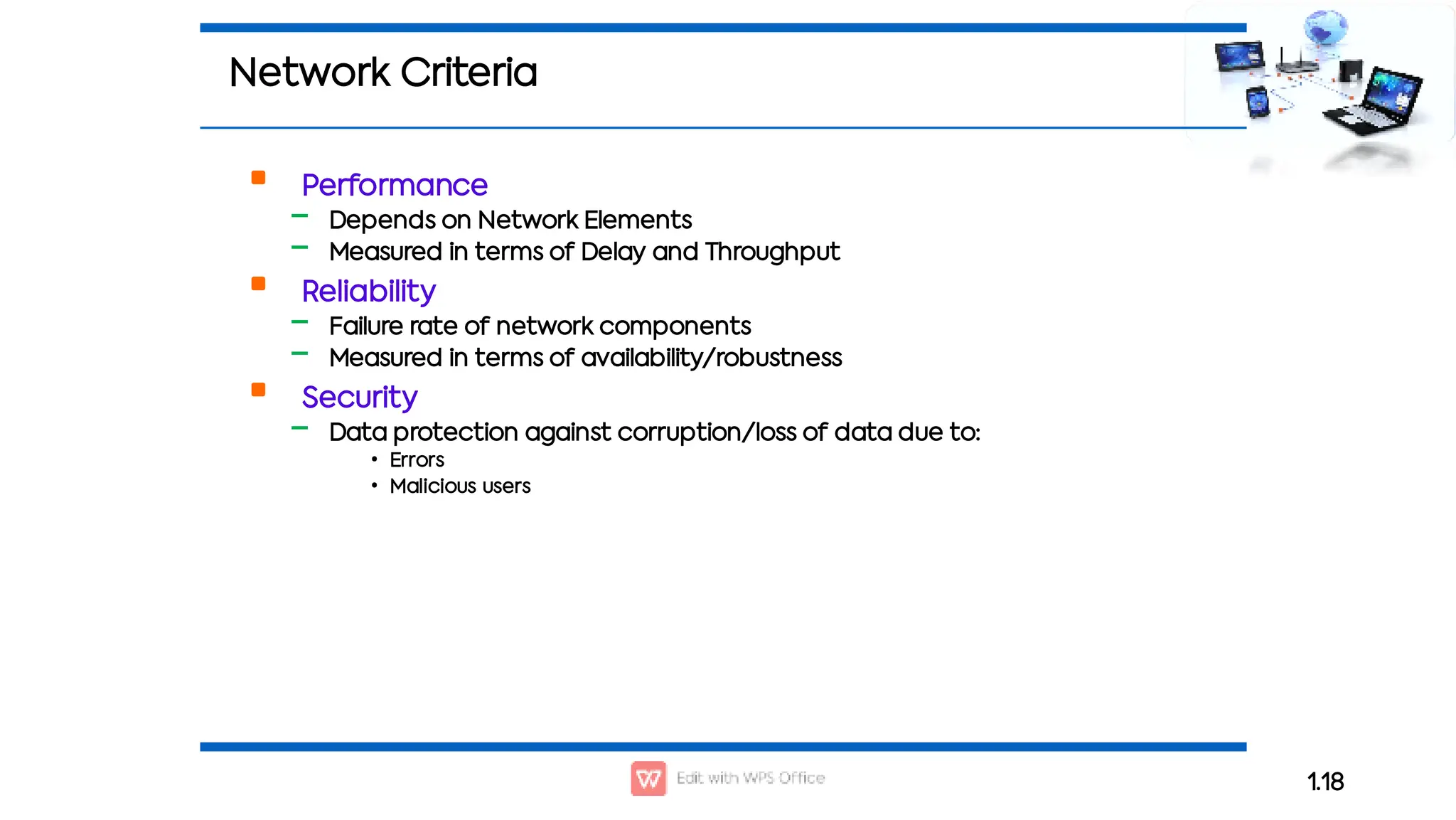
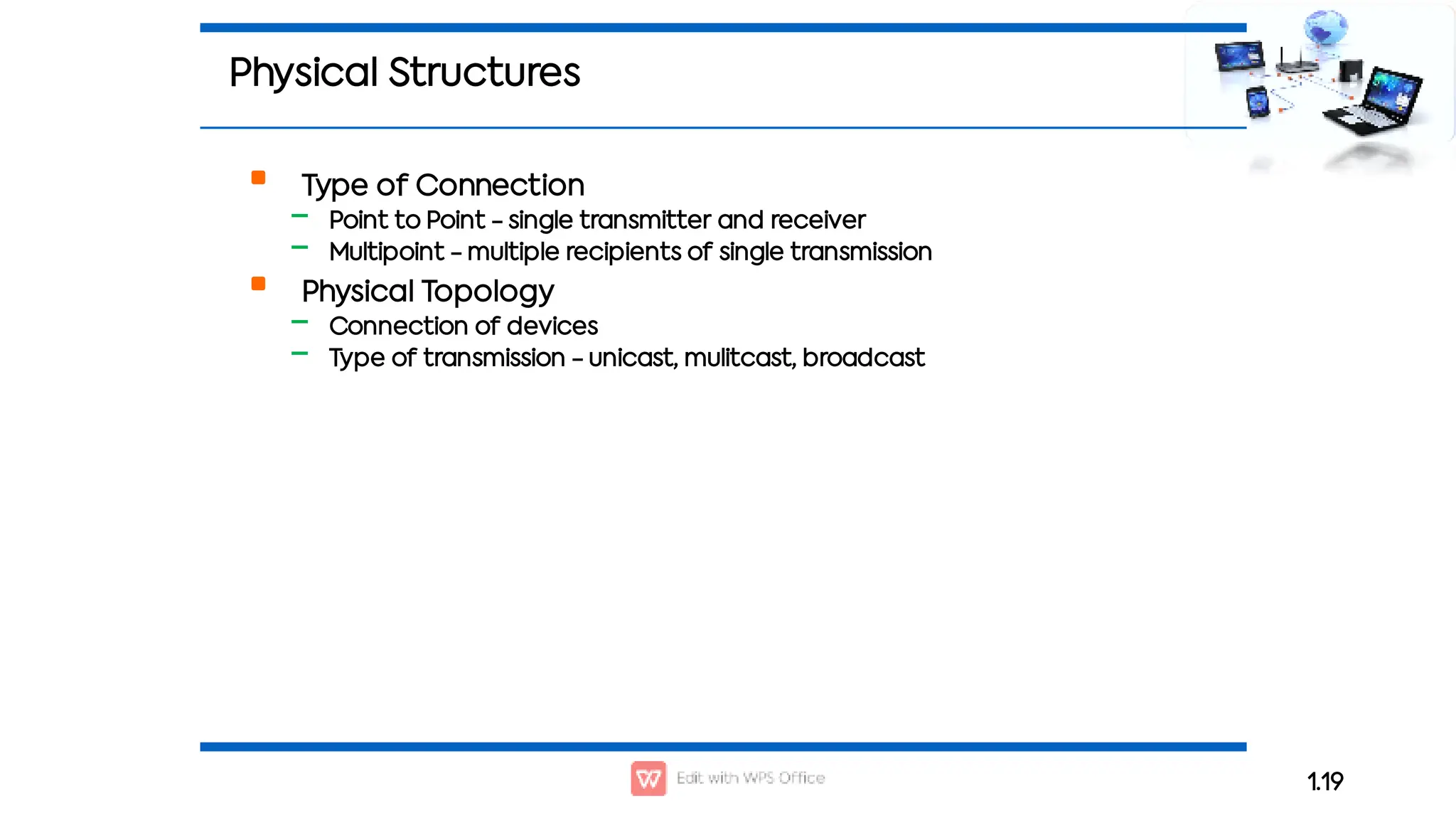
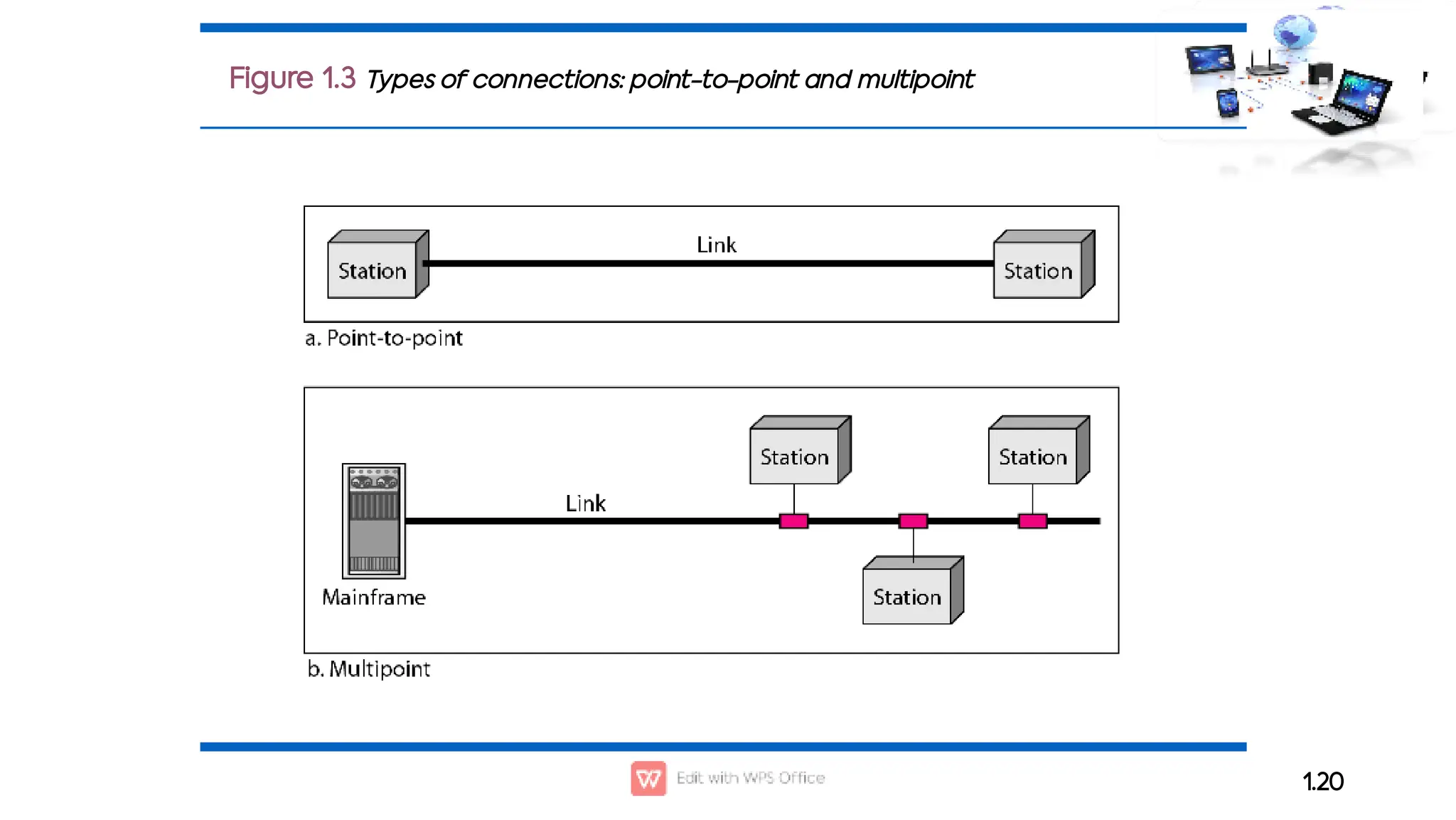
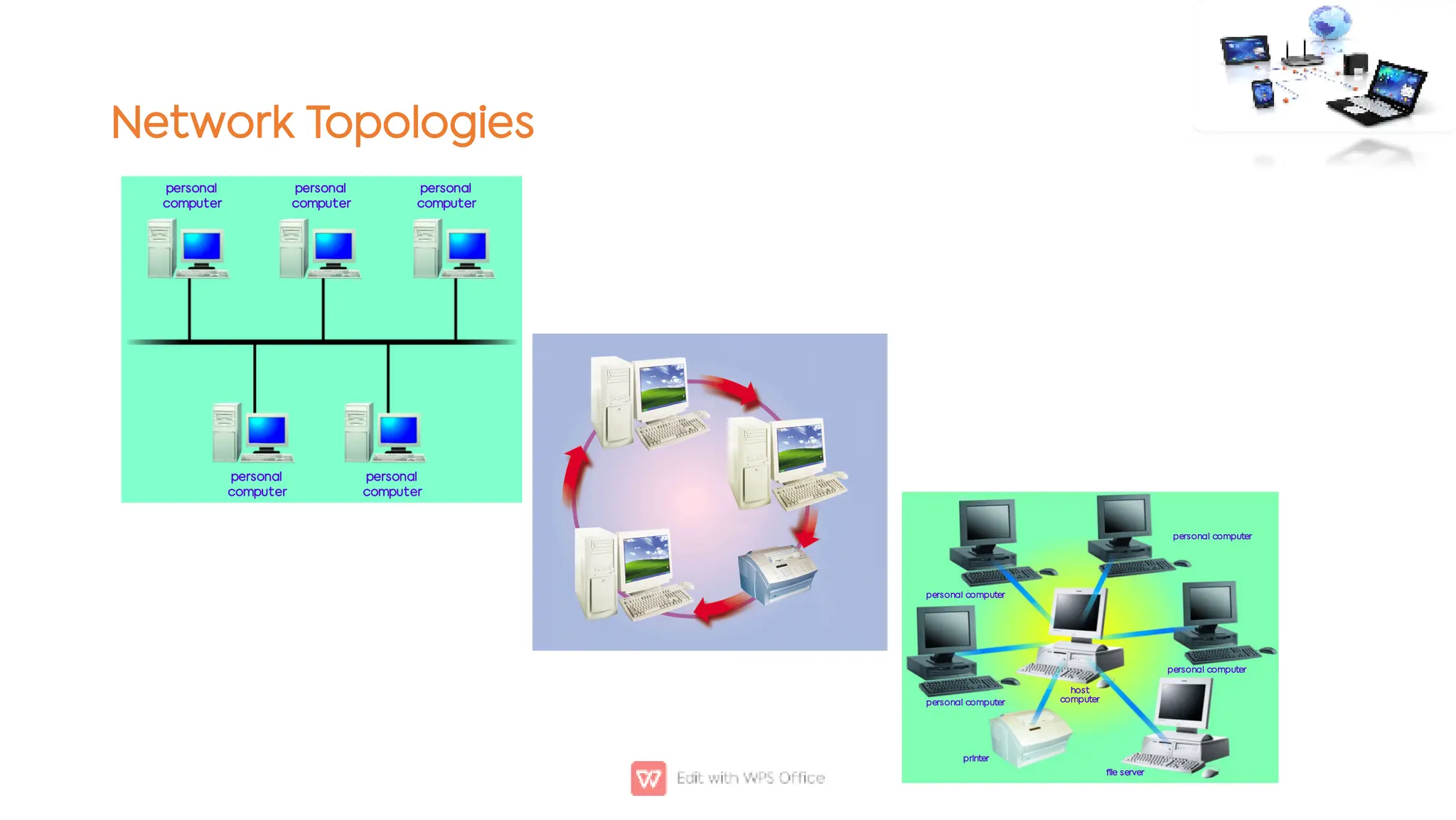
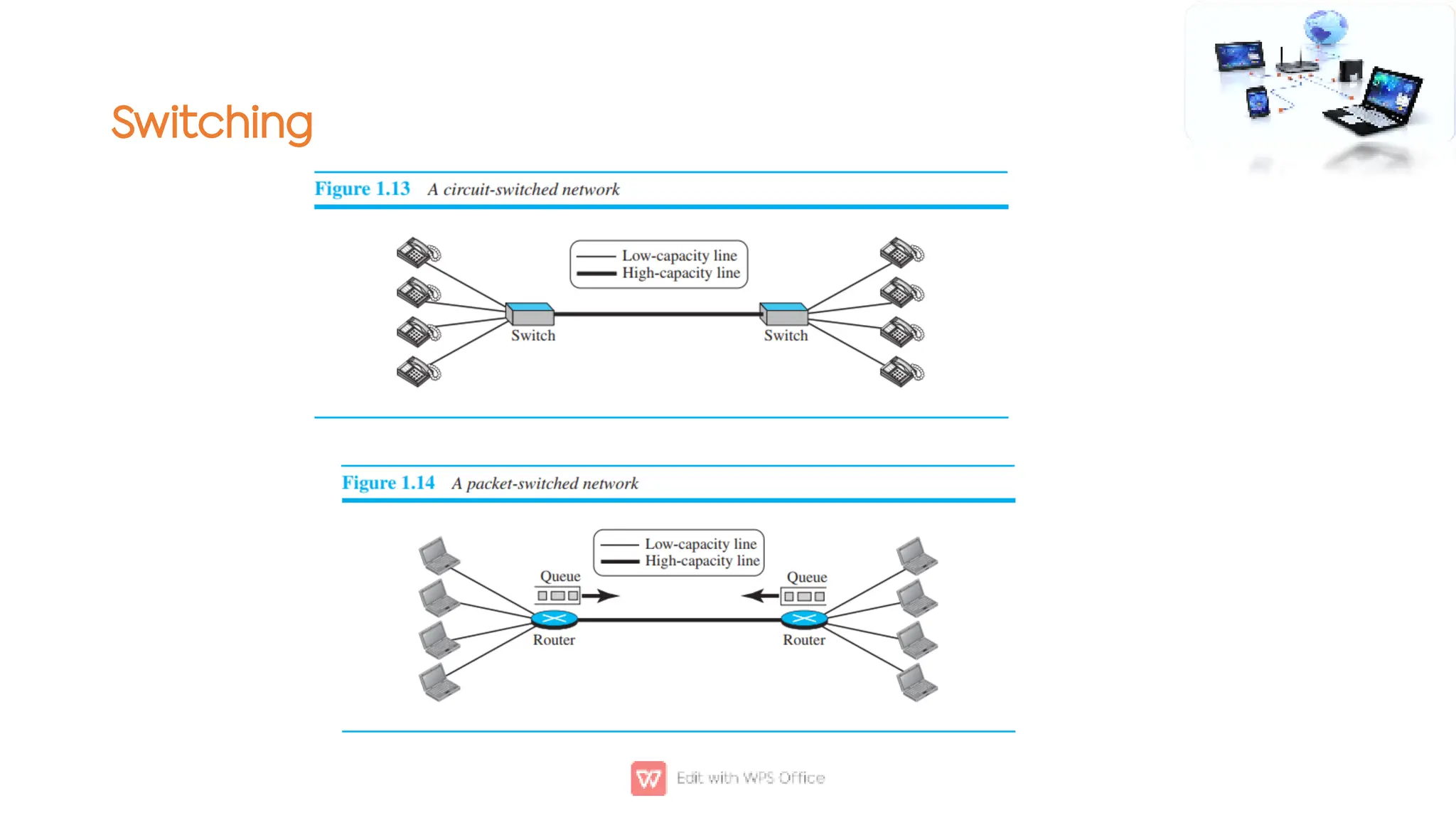
This document outlines the COSC-2104 Computer Networks course taught by Dr. Madiha Amjad at KFUEIT, detailing course objectives, pedagogy, and evaluation criteria. It introduces key concepts in data communication and networking, including protocols, network topologies, and emerging technologies. Additionally, it sets expectations for student responsibilities and assignments.