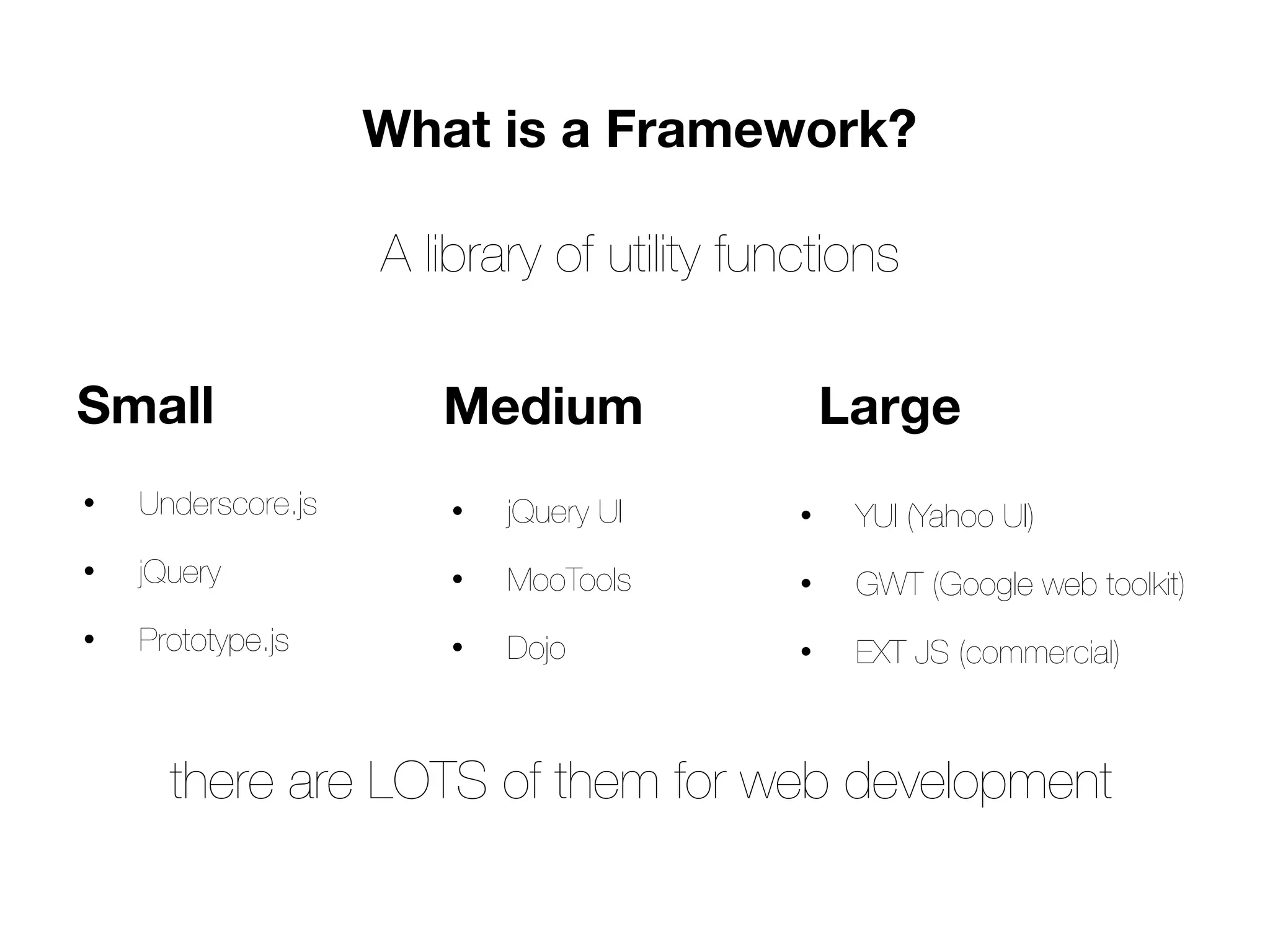
This document provides an introduction to jQuery, including what jQuery is, why it's useful, how to include it, and some common jQuery syntax and methods. Key points:
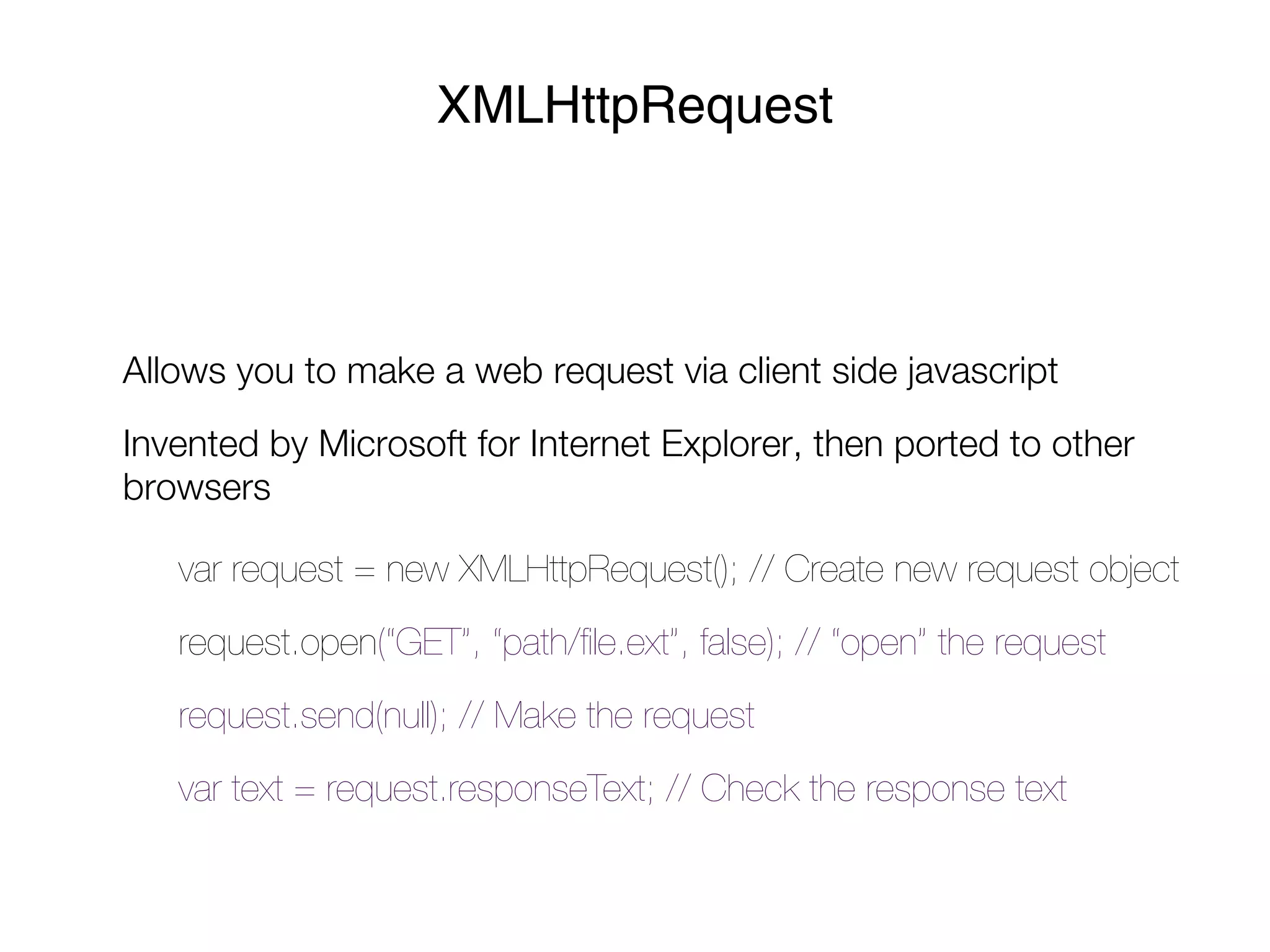
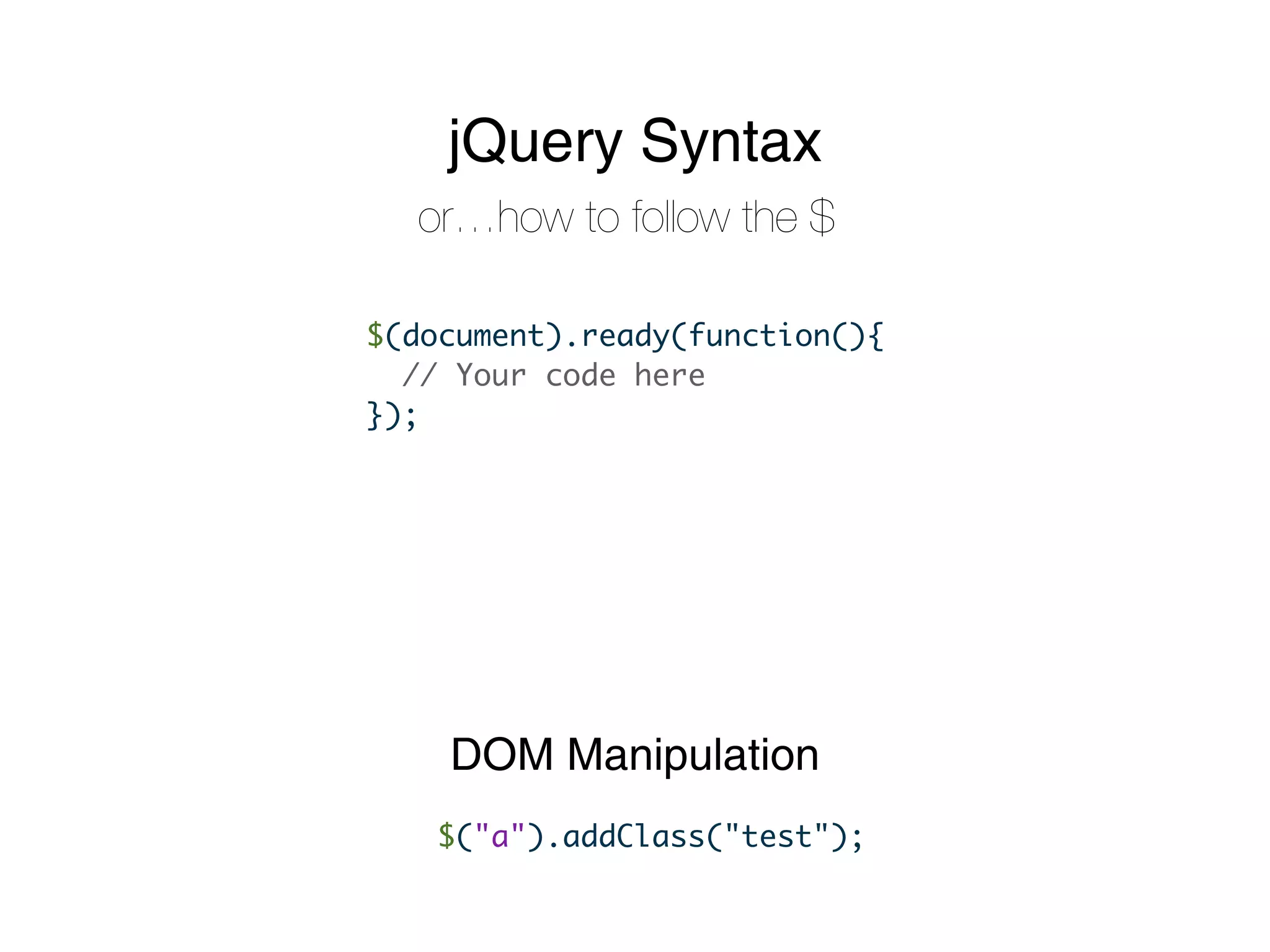
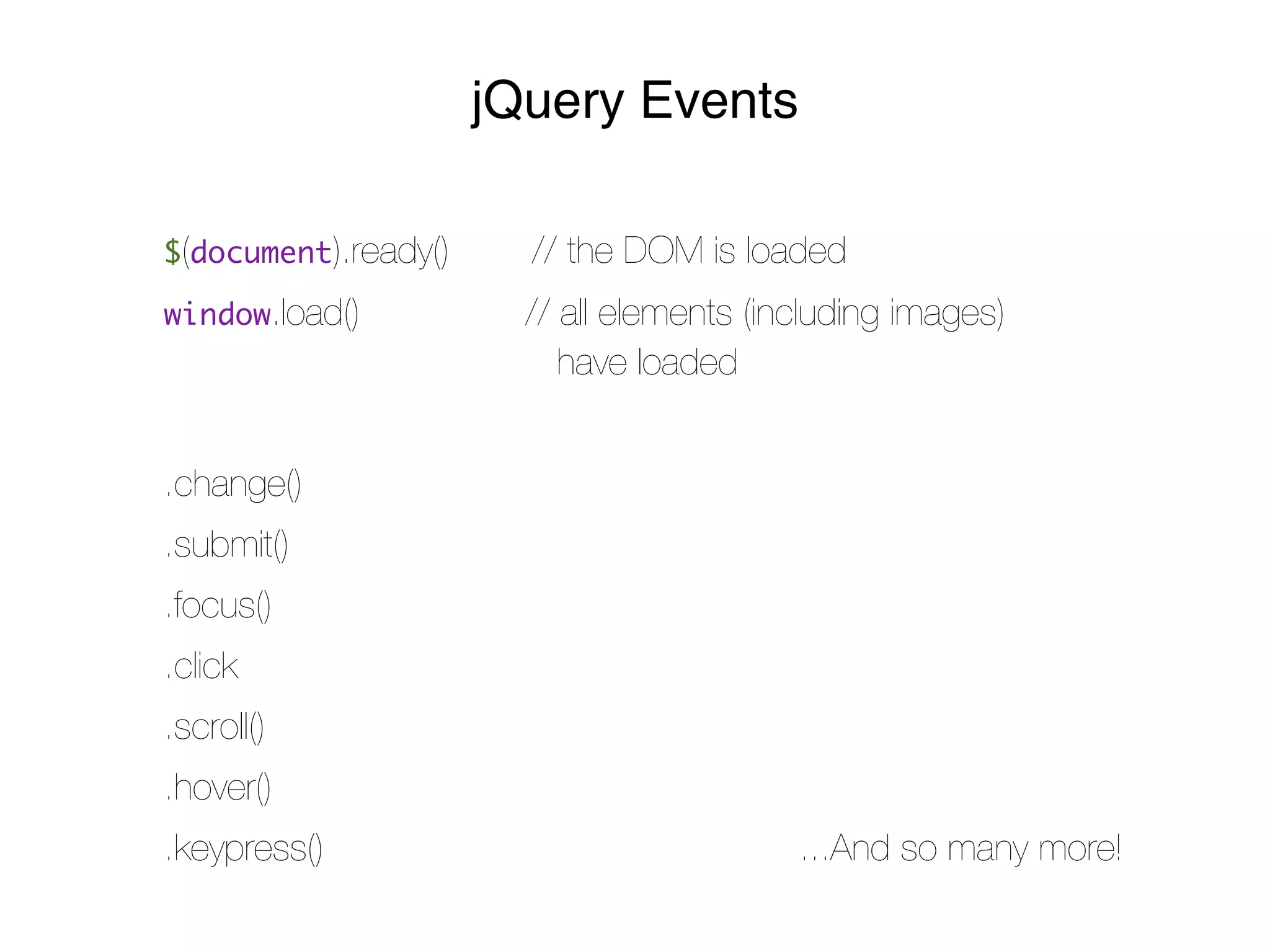
- jQuery is a JavaScript framework that makes interacting with HTML, CSS, and browser functionality simpler. It provides methods for DOM manipulation, AJAX requests, and event handling.
- jQuery uses CSS selector syntax to select elements and chainable methods to manipulate them. Common methods include show(), hide(), addClass(), removeClass(), and more.
- Events like click and change can have callback functions attached via jQuery. AJAX requests allow asynchronous data retrieval without page reloads.
- jQuery handles cross-browser compatibility and provides a consistent




![Arrays
data structure for ordered values
var team = [‘ben’,‘jeff’,‘kam’];
team[0] // => ‘ben’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-111028195640-phpapp01/75/Week-4-jQuery-Ajax-6-2048.jpg)






![Selecting Elements
Using CSS!
$("#foo") // the [element] at id “foo”
$(".bloop") // the [elements] with class “bloop”
$("a.buzz") // the [links] with class ‘buzz’
$(".bloop:first") // specialty! The first bloop!
=> :hidden, :visible, :last, :checked, :empty, :odd...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-111028195640-phpapp01/75/Week-4-jQuery-Ajax-17-2048.jpg)






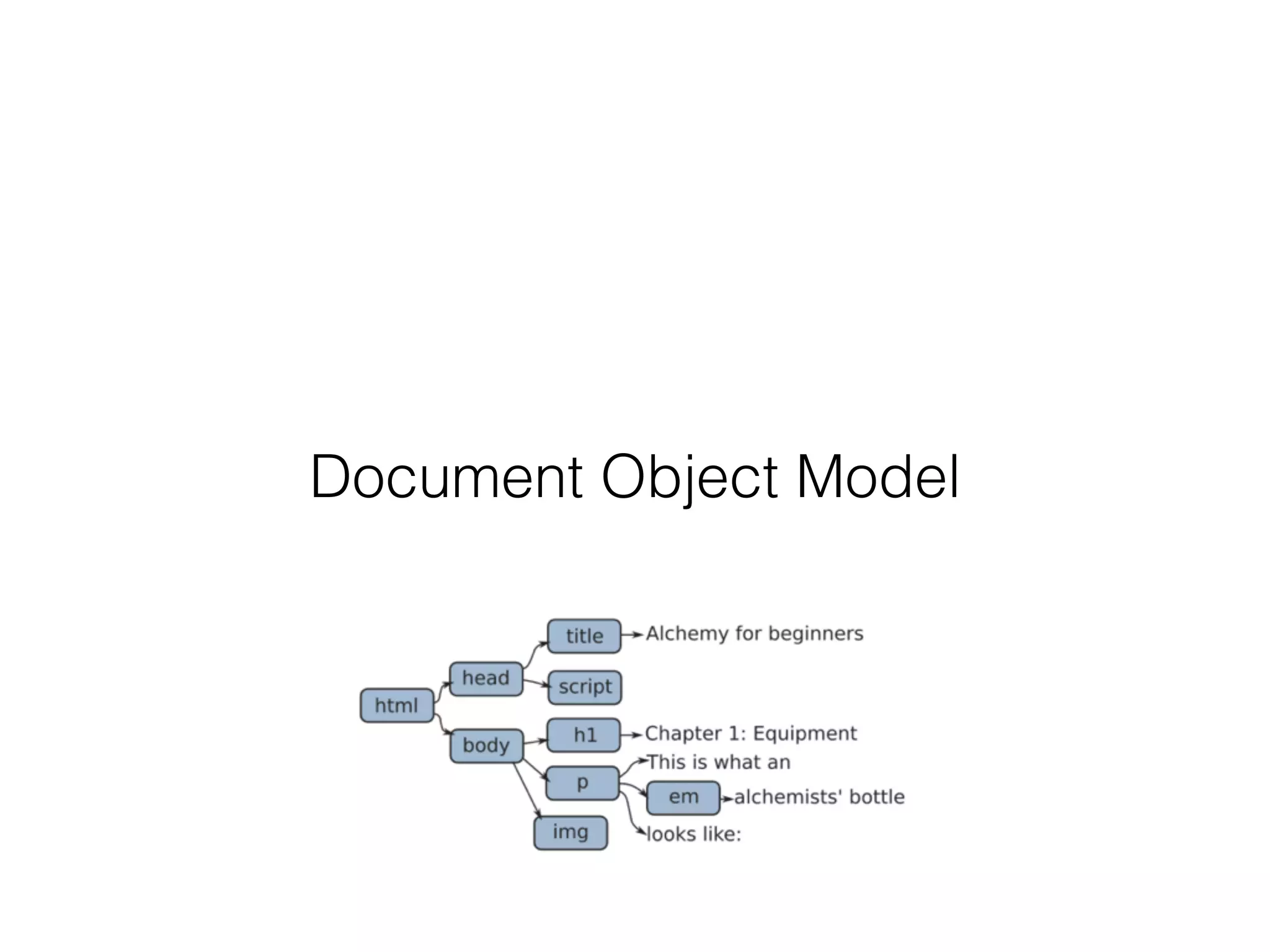
![Client Side
Requests
[XHR and AJAX]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-111028195640-phpapp01/75/Week-4-jQuery-Ajax-25-2048.jpg)