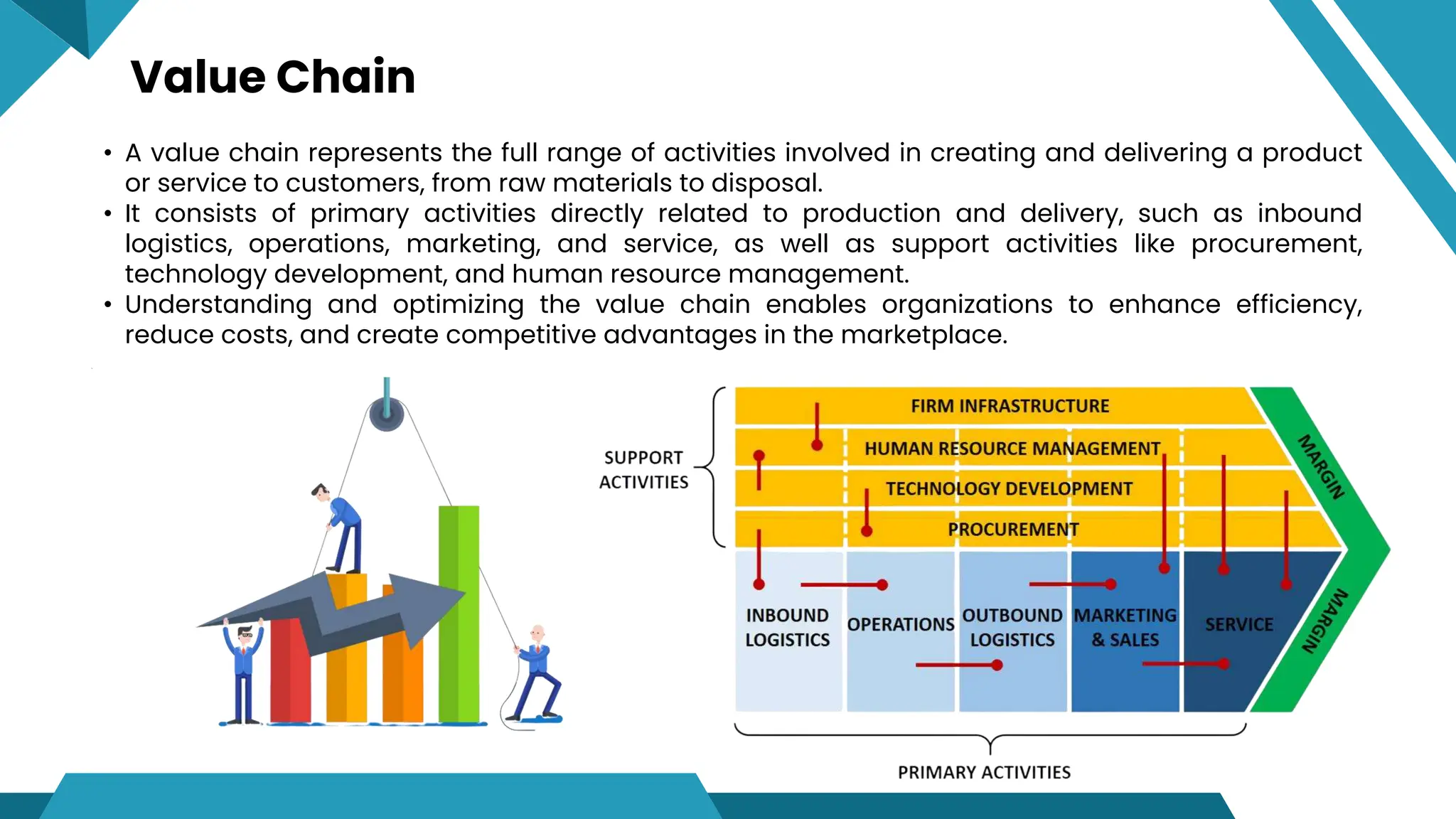
- A value chain represents the full range of activities involved in creating and delivering a product or service, from raw materials to disposal. It includes primary activities like production and marketing as well as support activities.
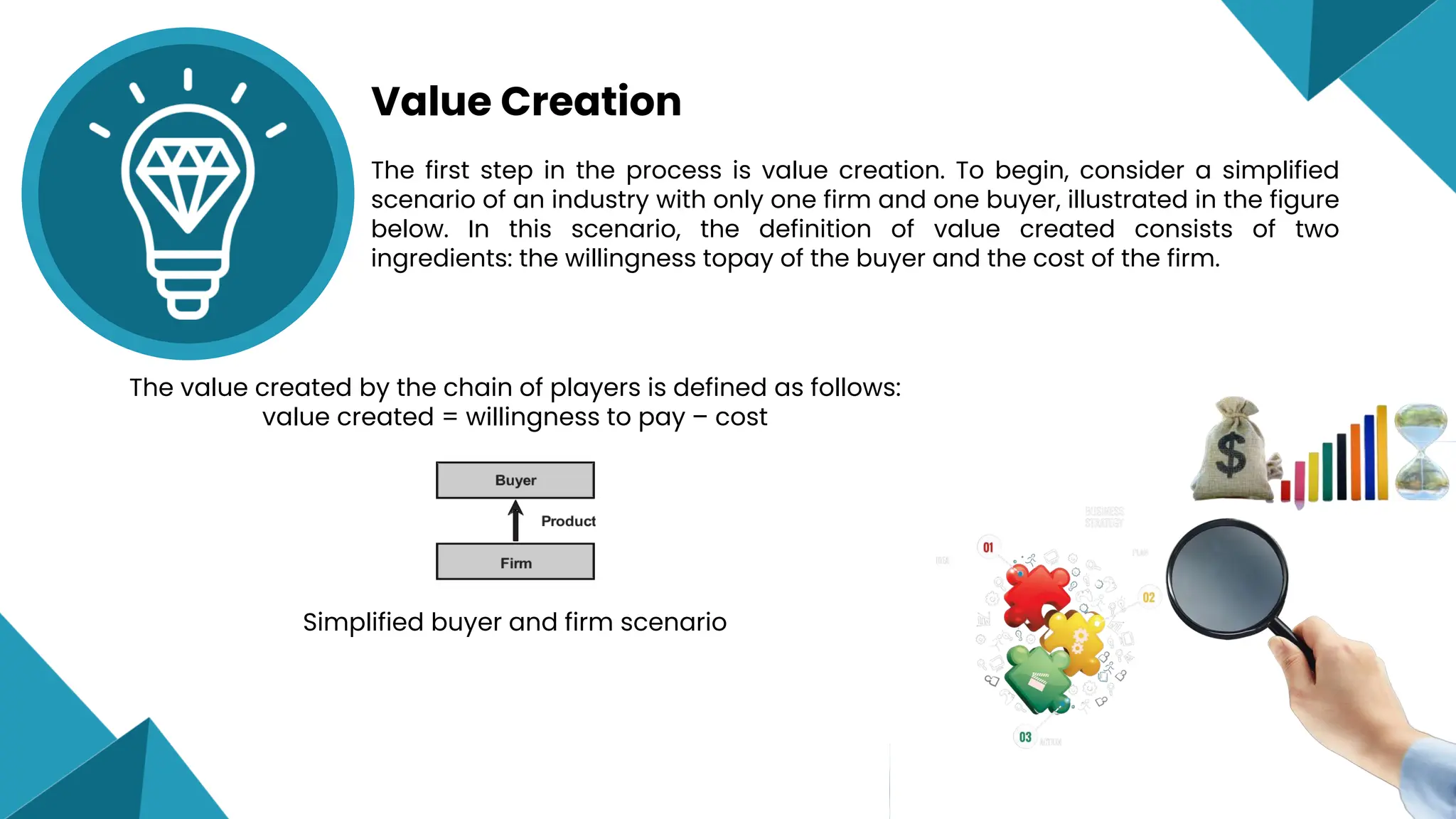
- Understanding and optimizing the value chain enables organizations to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and gain competitive advantages. Value is defined as willingness to pay minus costs.
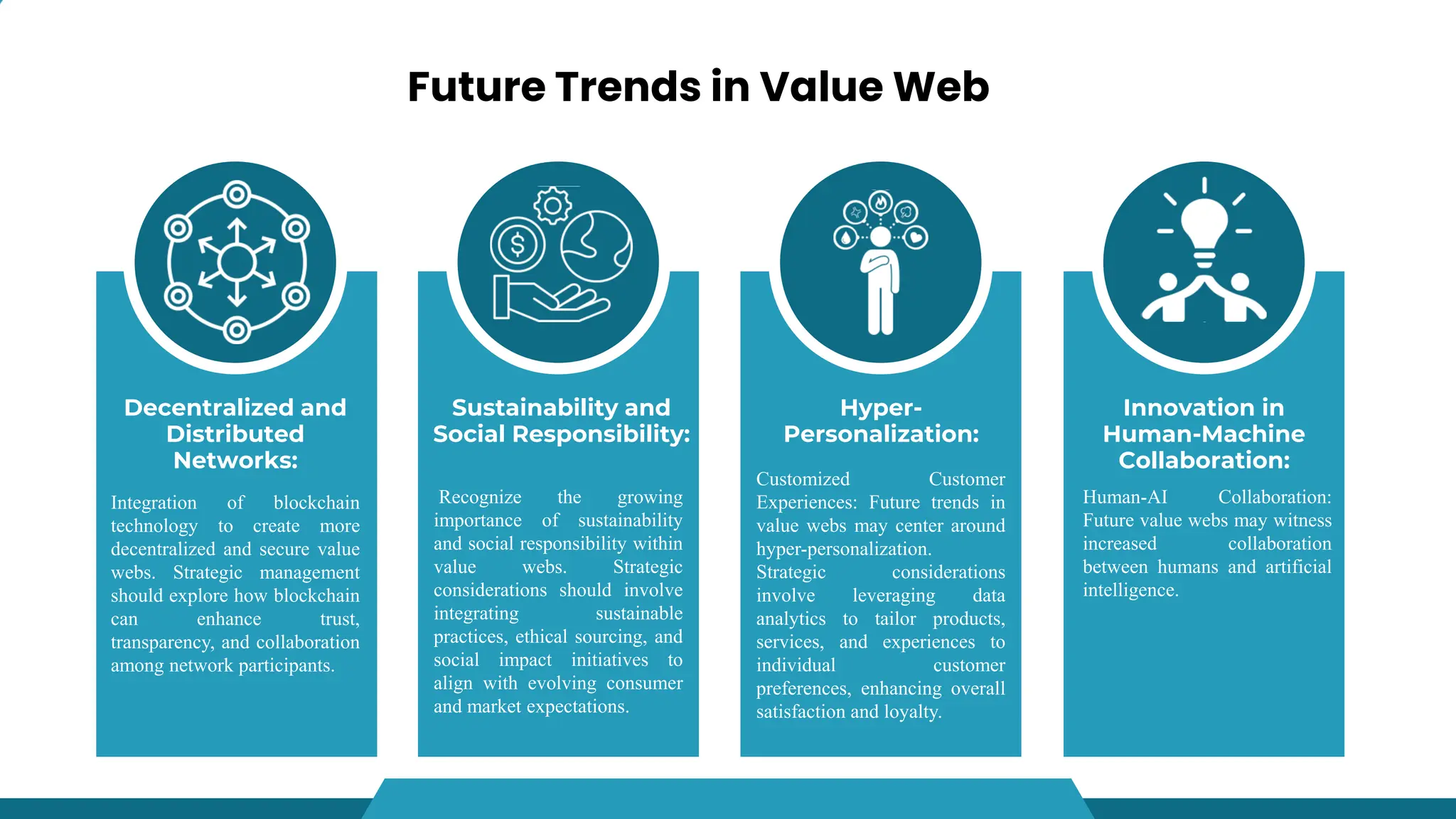
- A value web is a collaborative network of businesses, suppliers, distributors, and customers that emphasizes dynamic relationships. Value flows in multiple directions and participants mutually benefit through shared resources and knowledge exchange. Value webs enhance competitiveness and customer satisfaction.