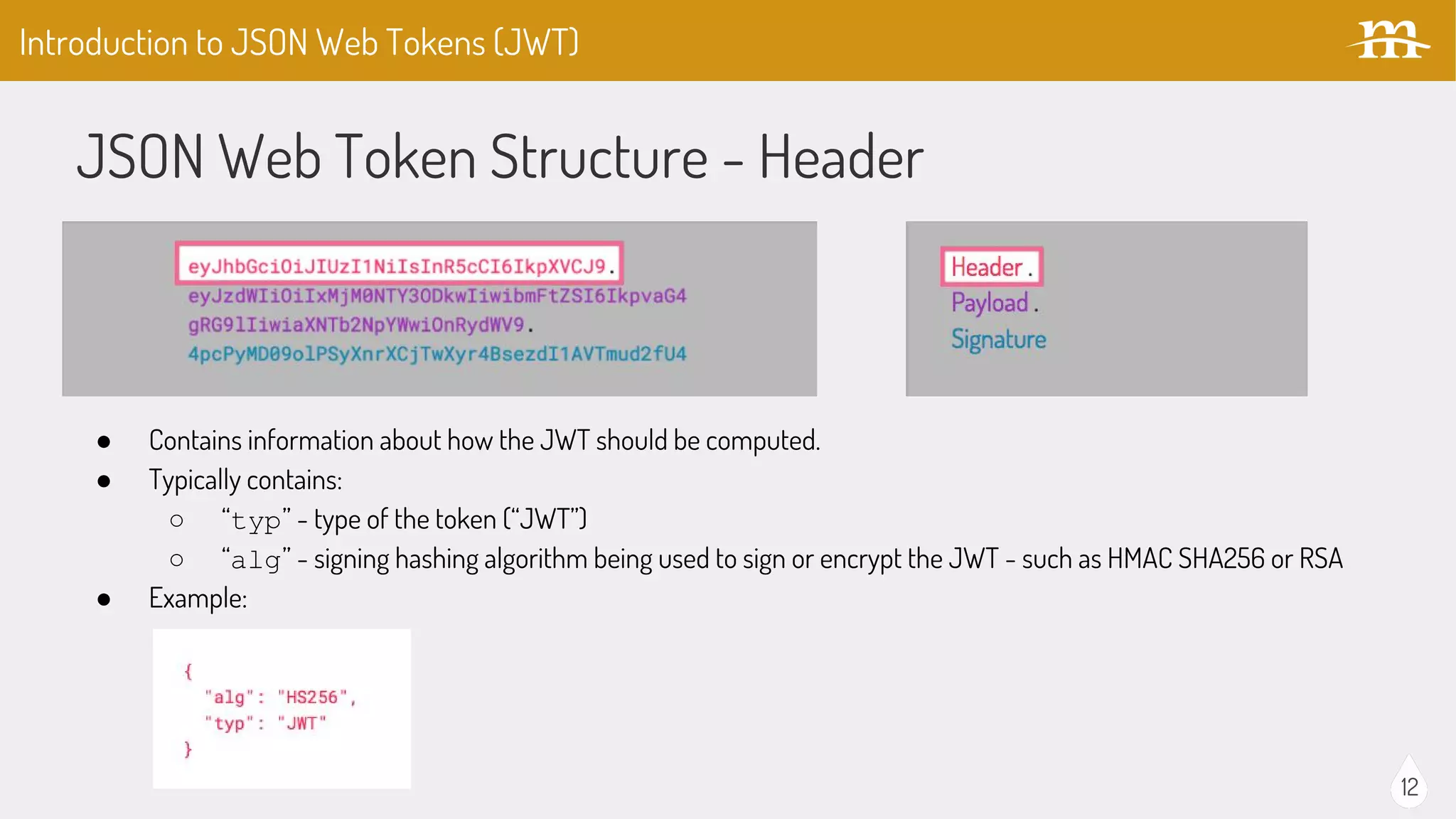
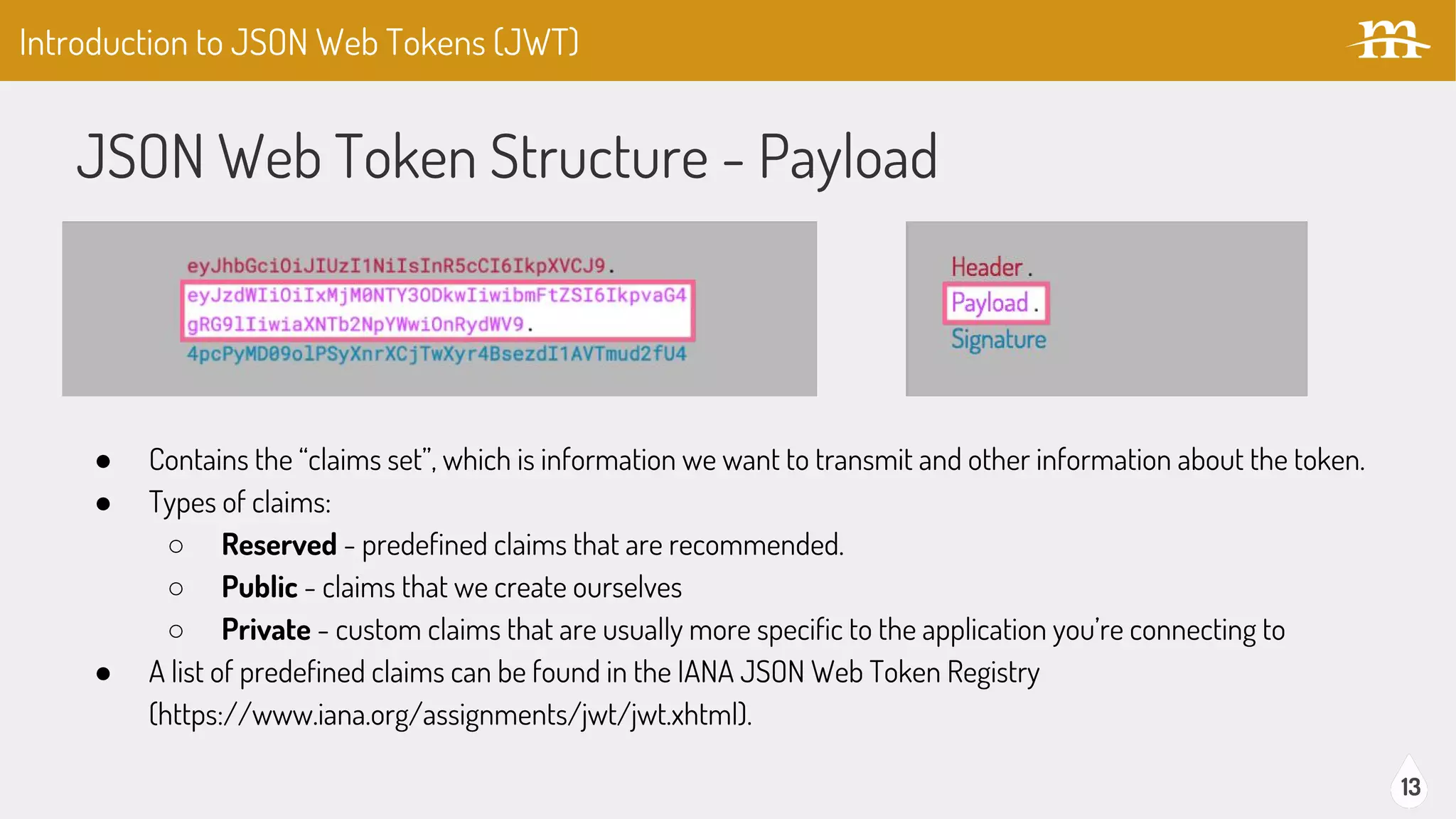
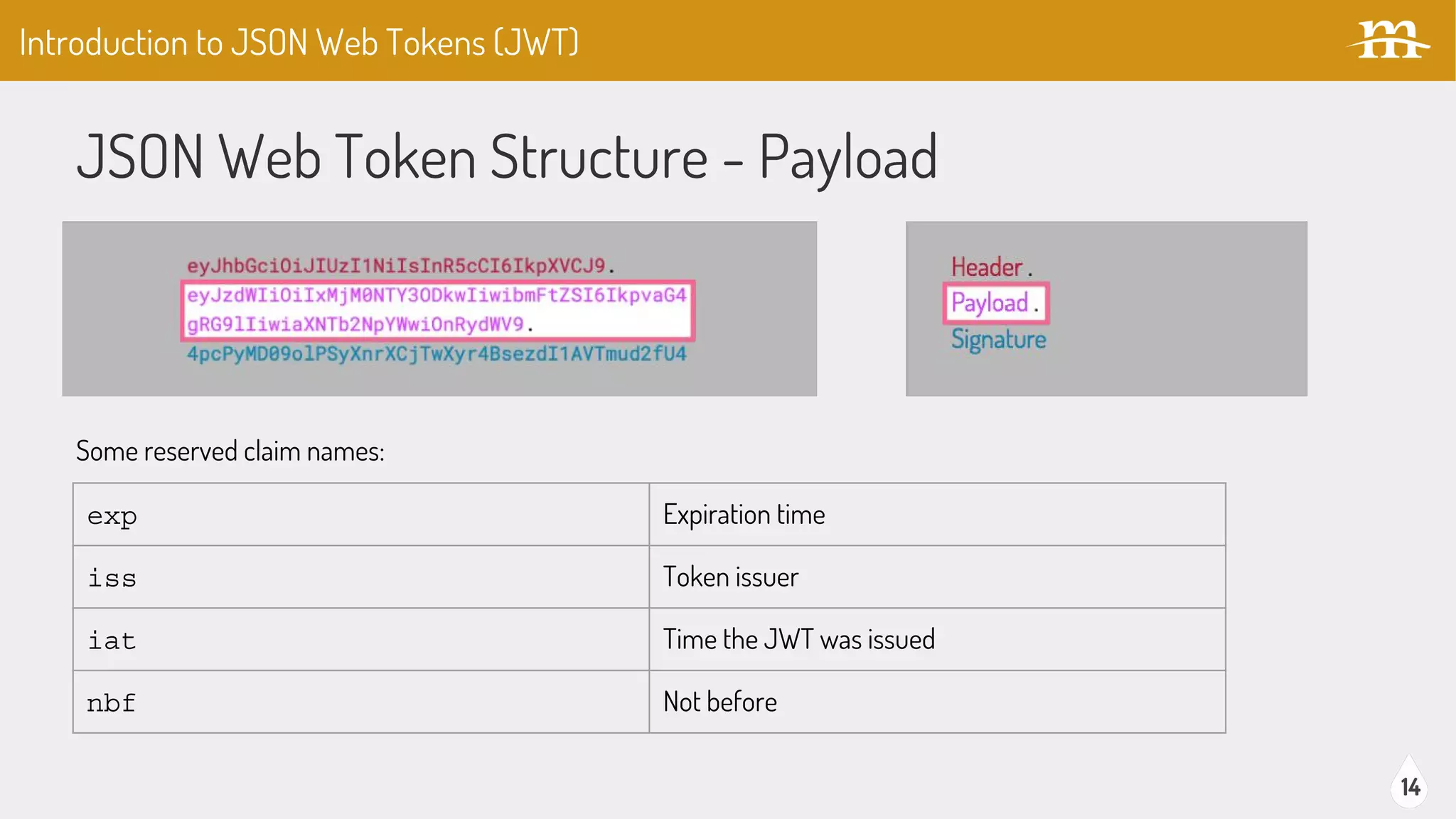
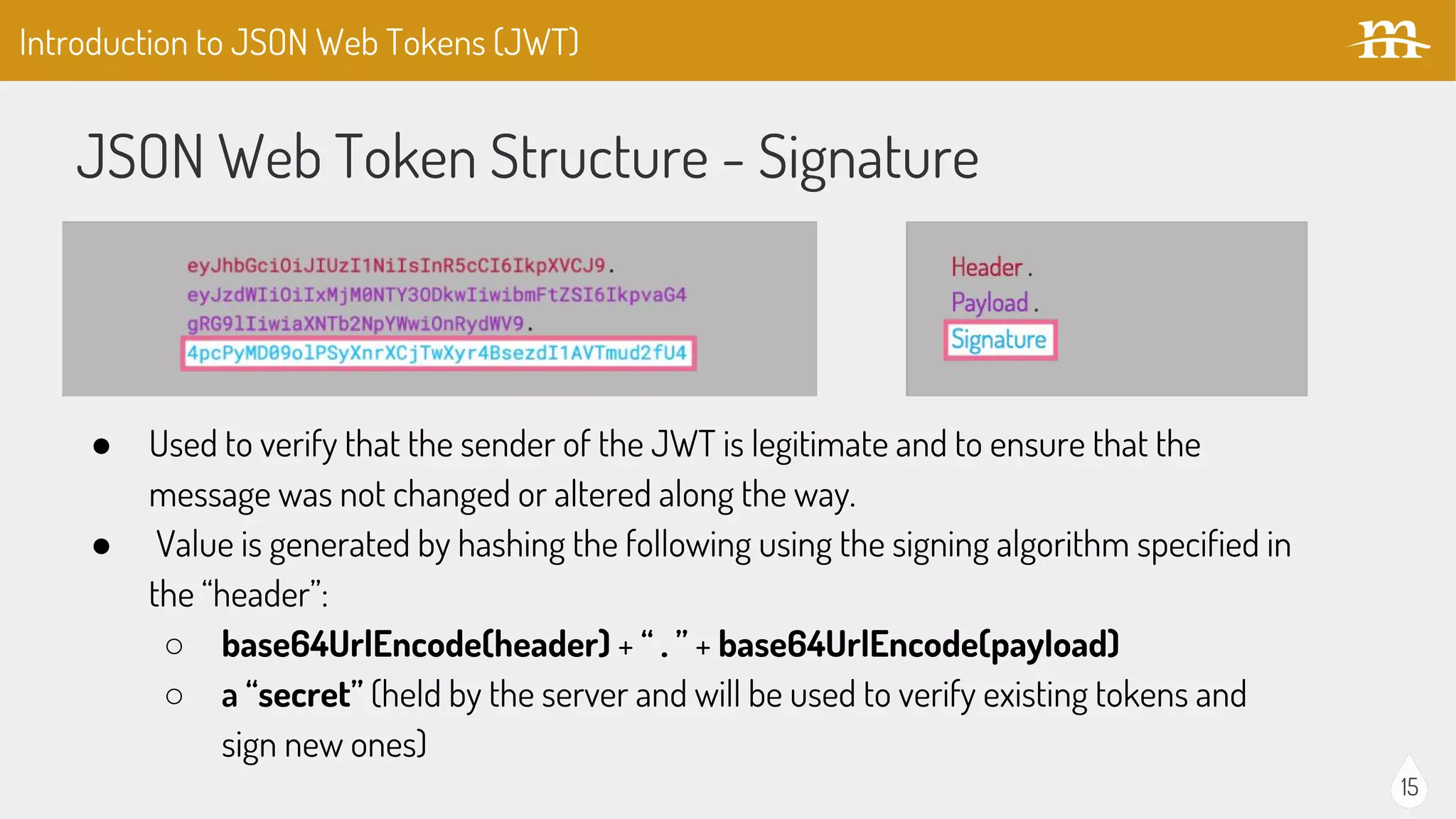
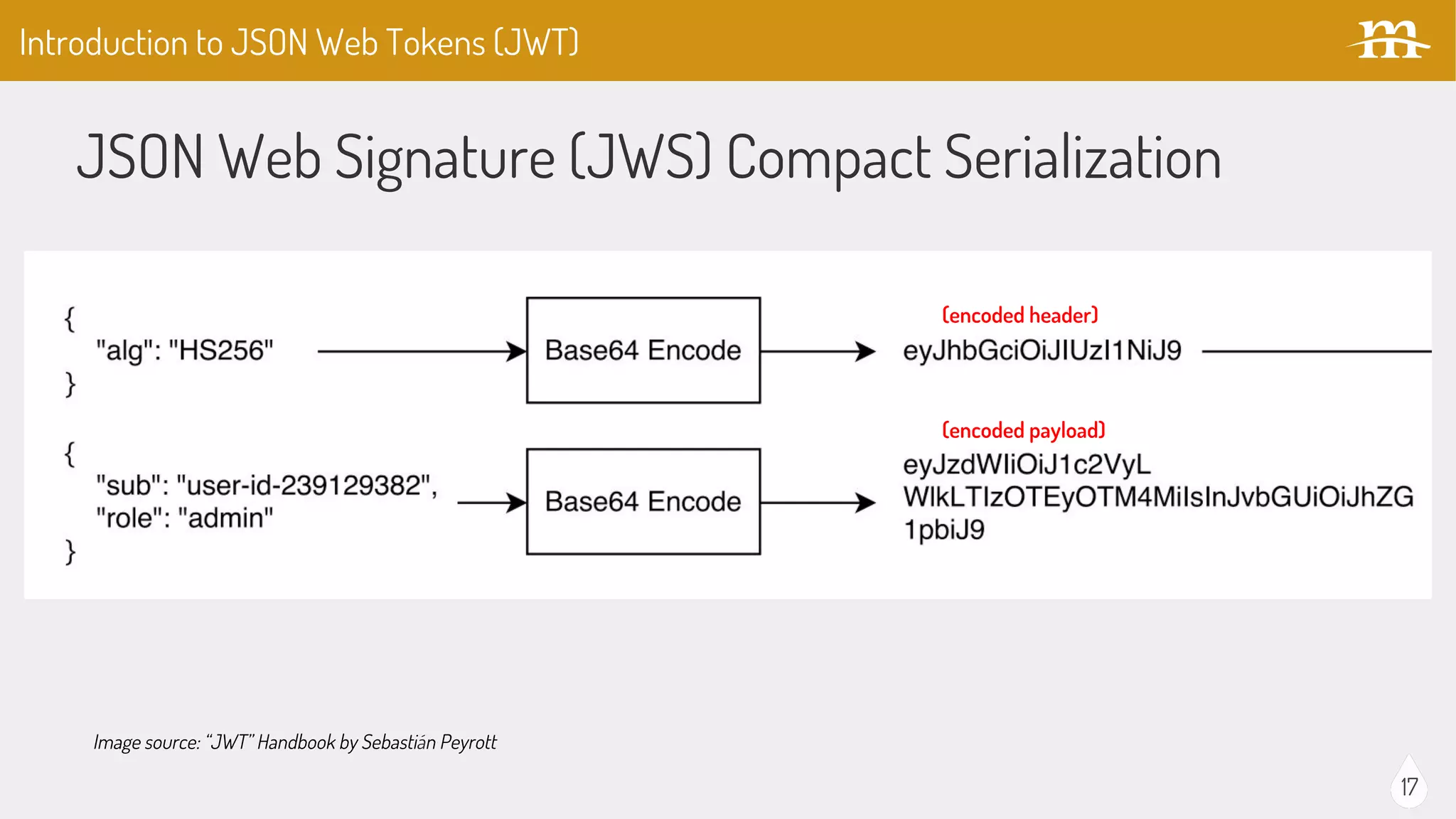
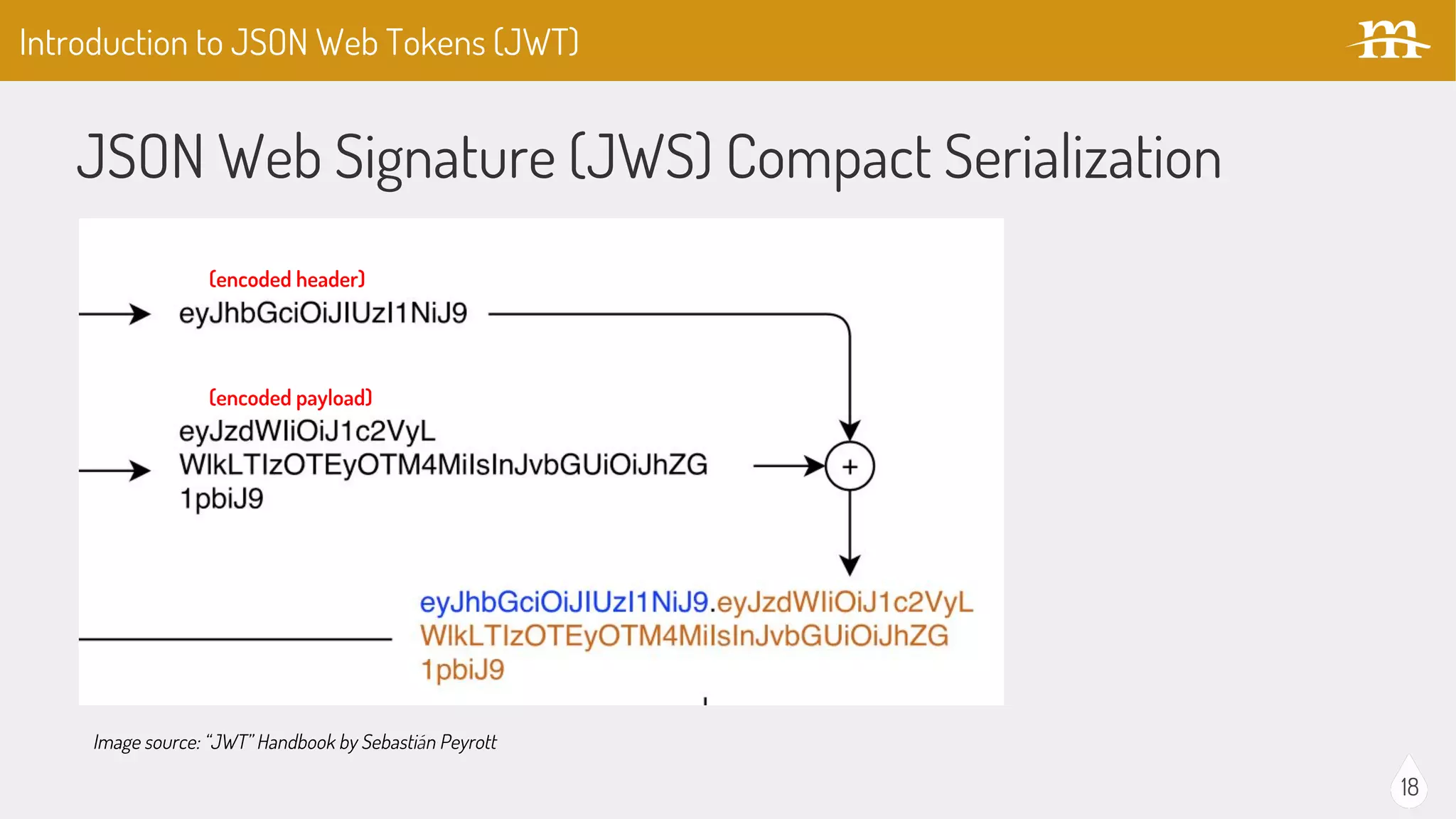
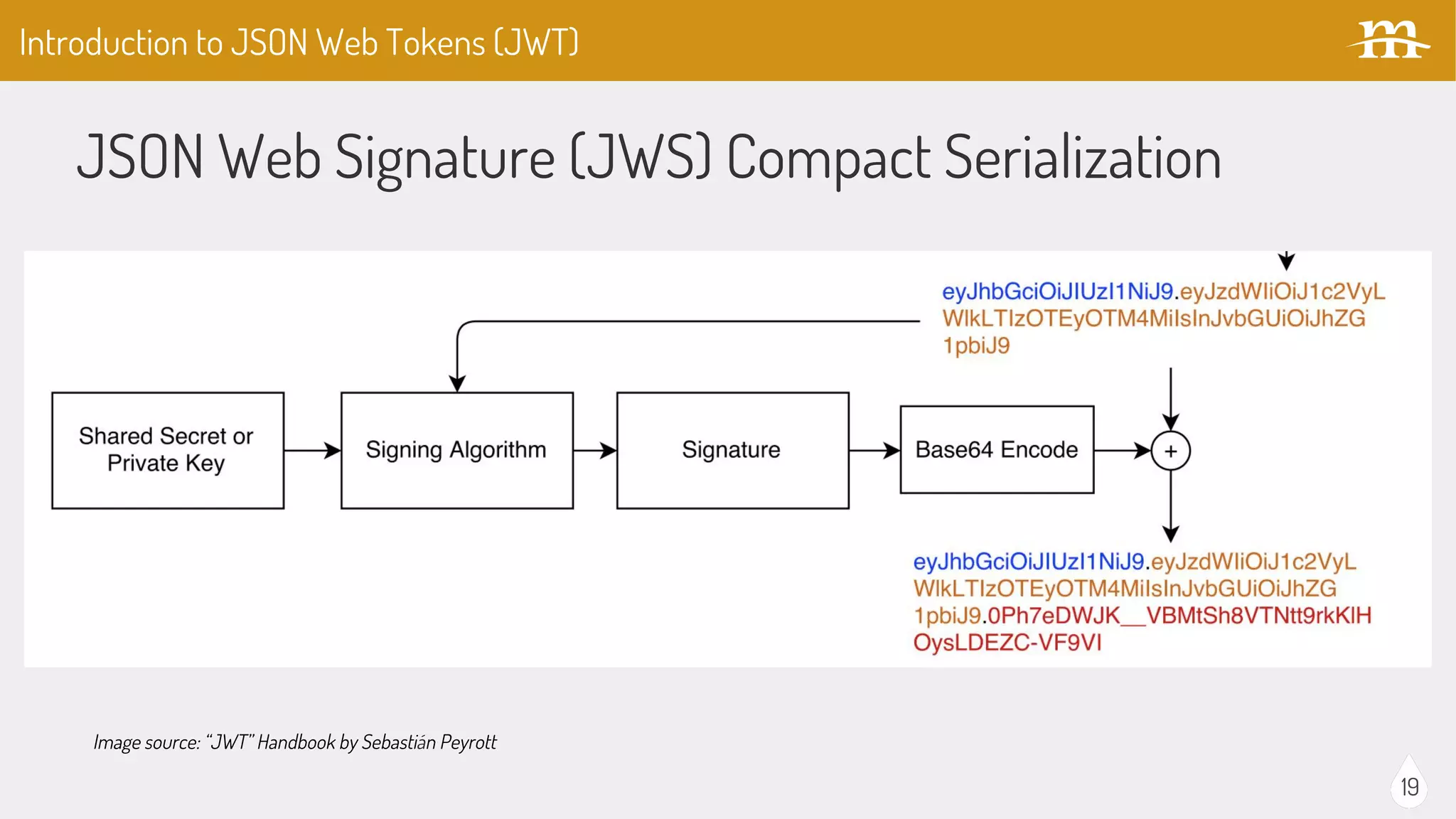
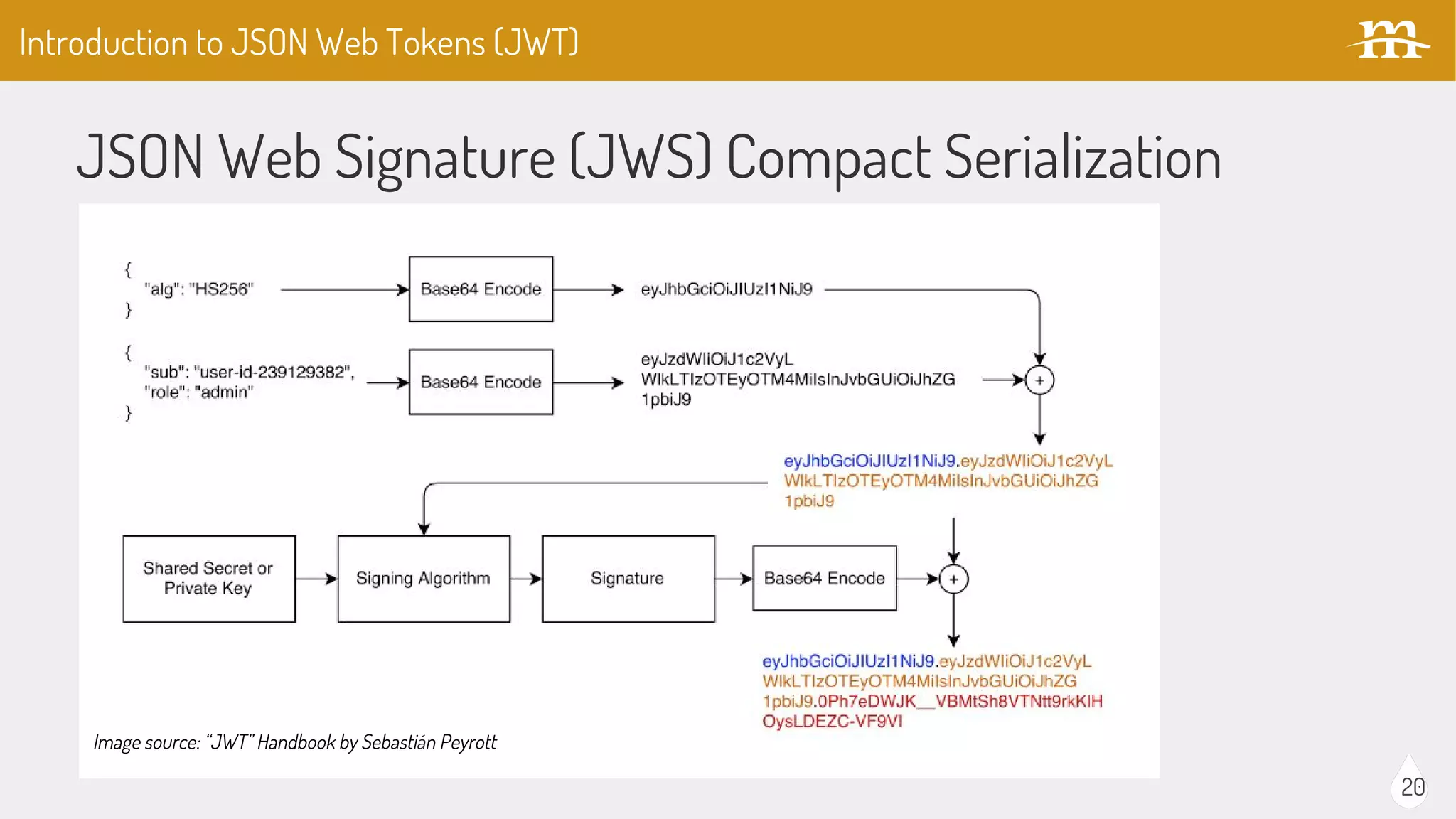
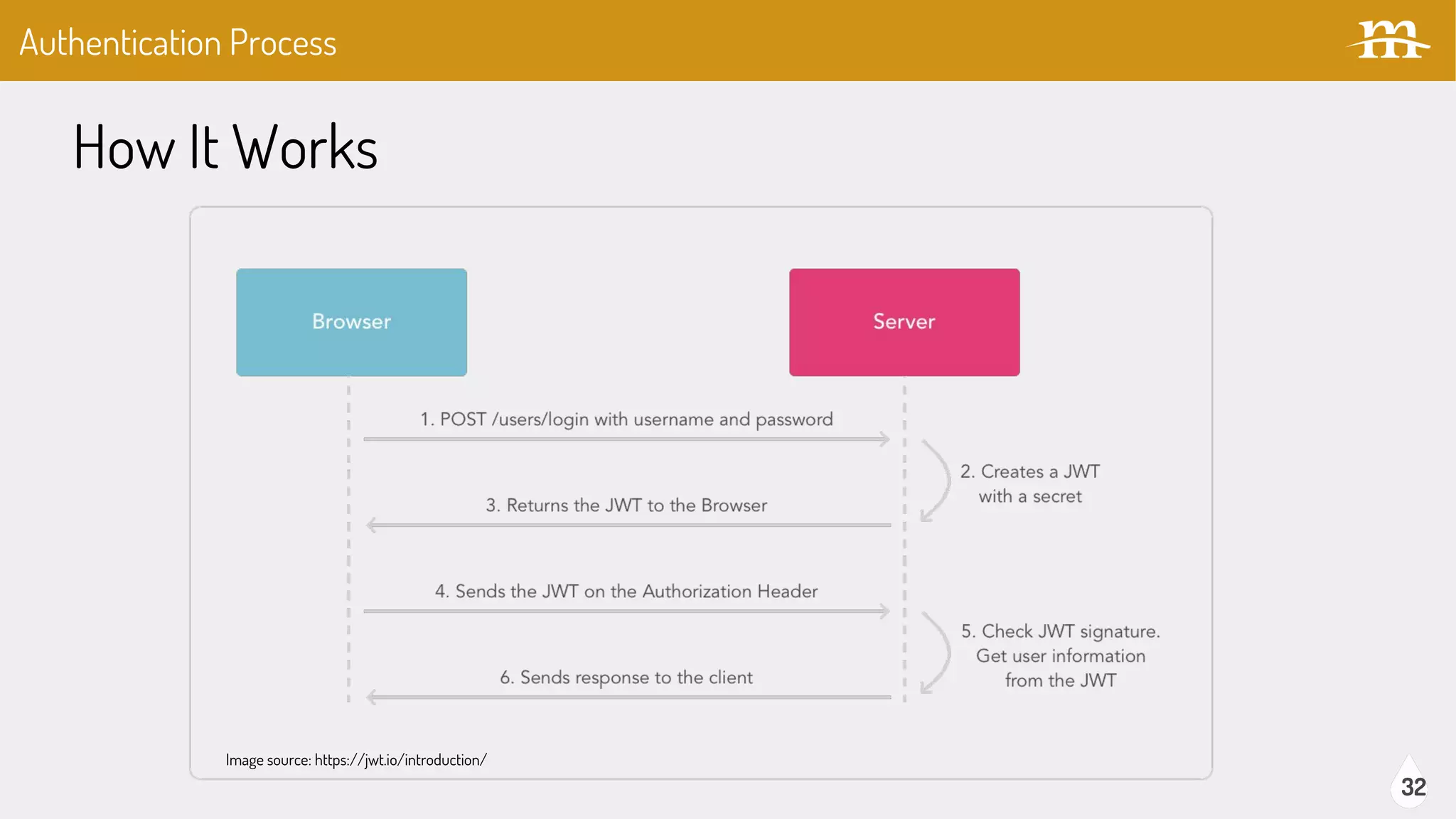
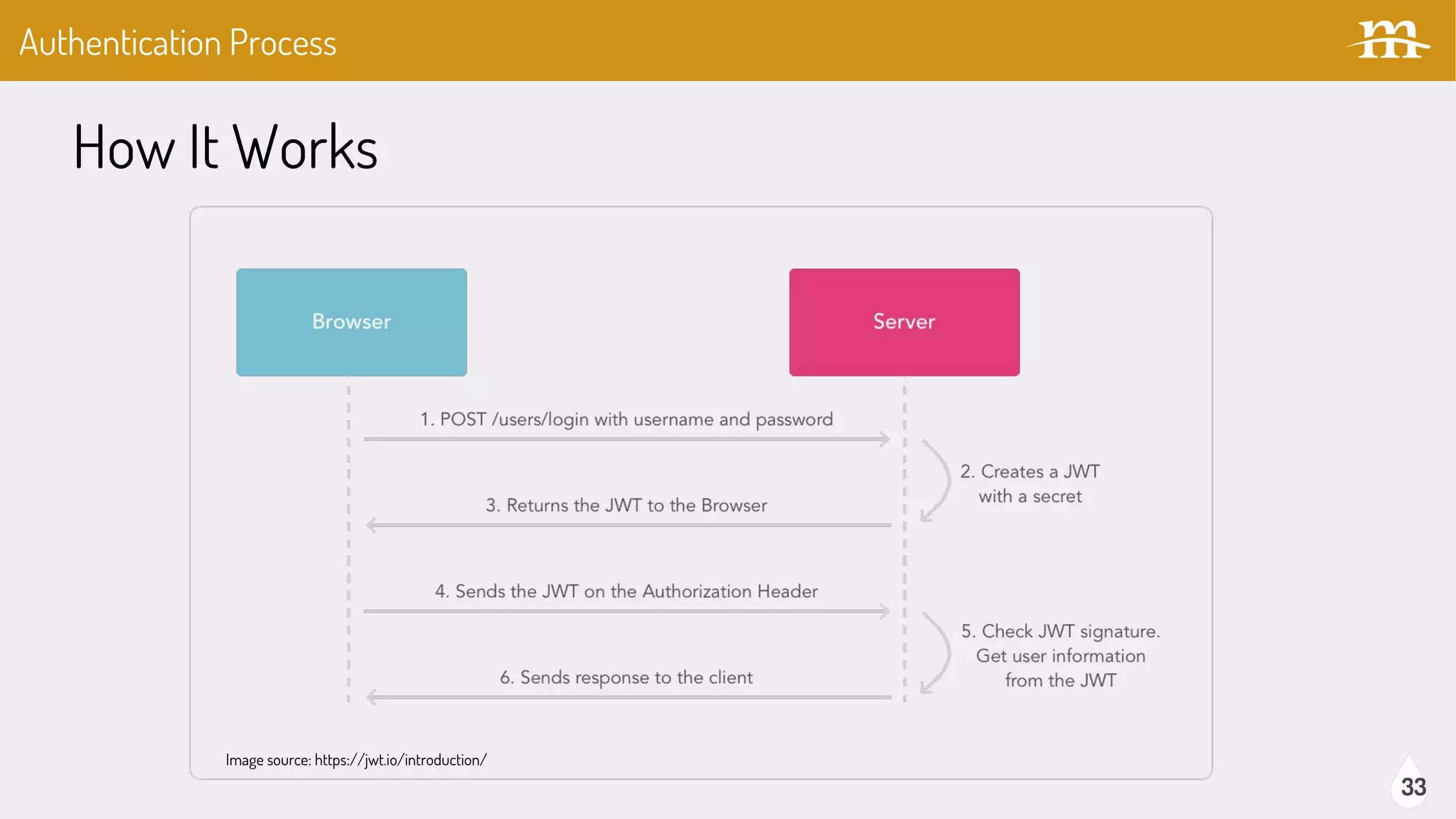
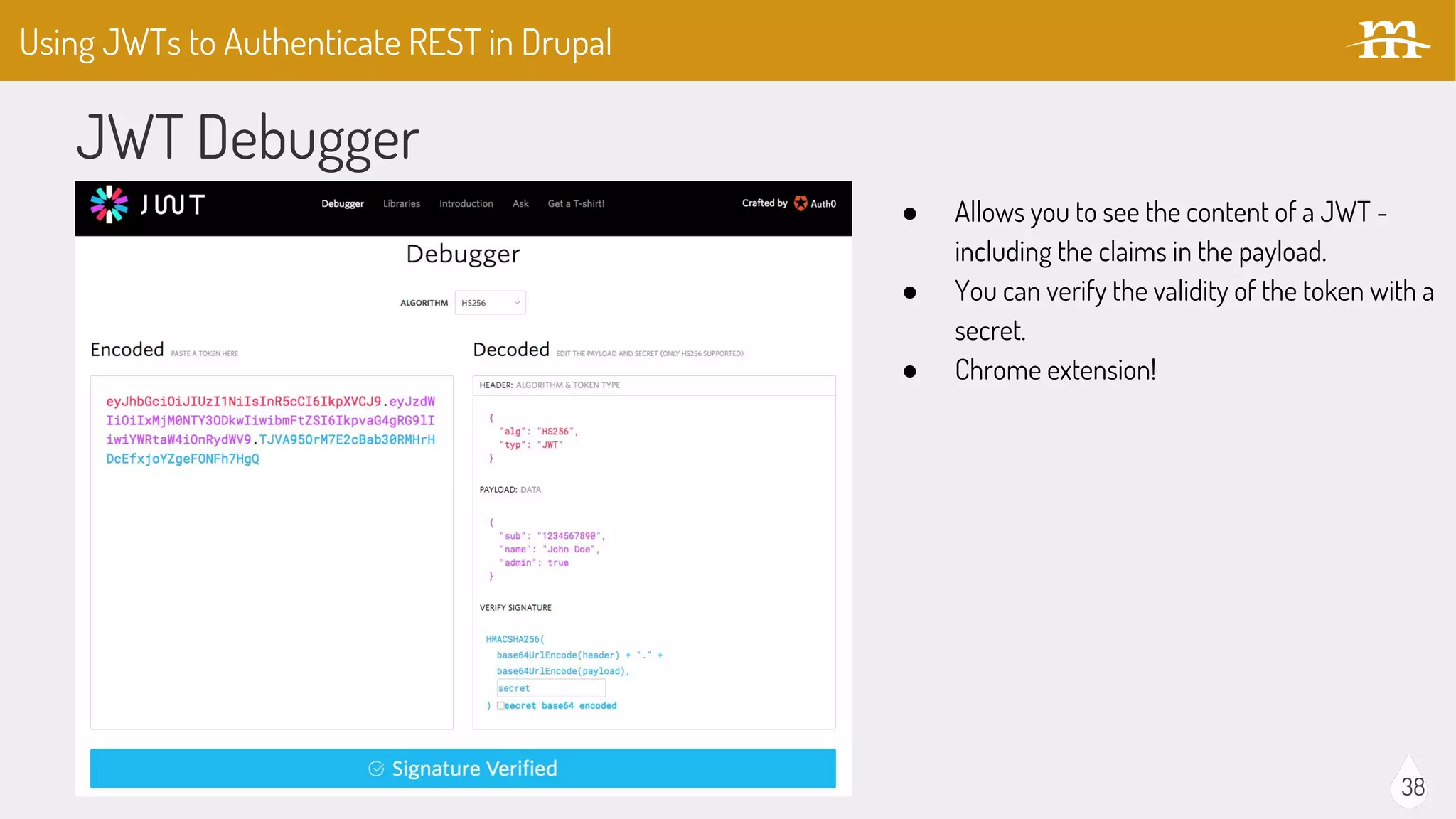
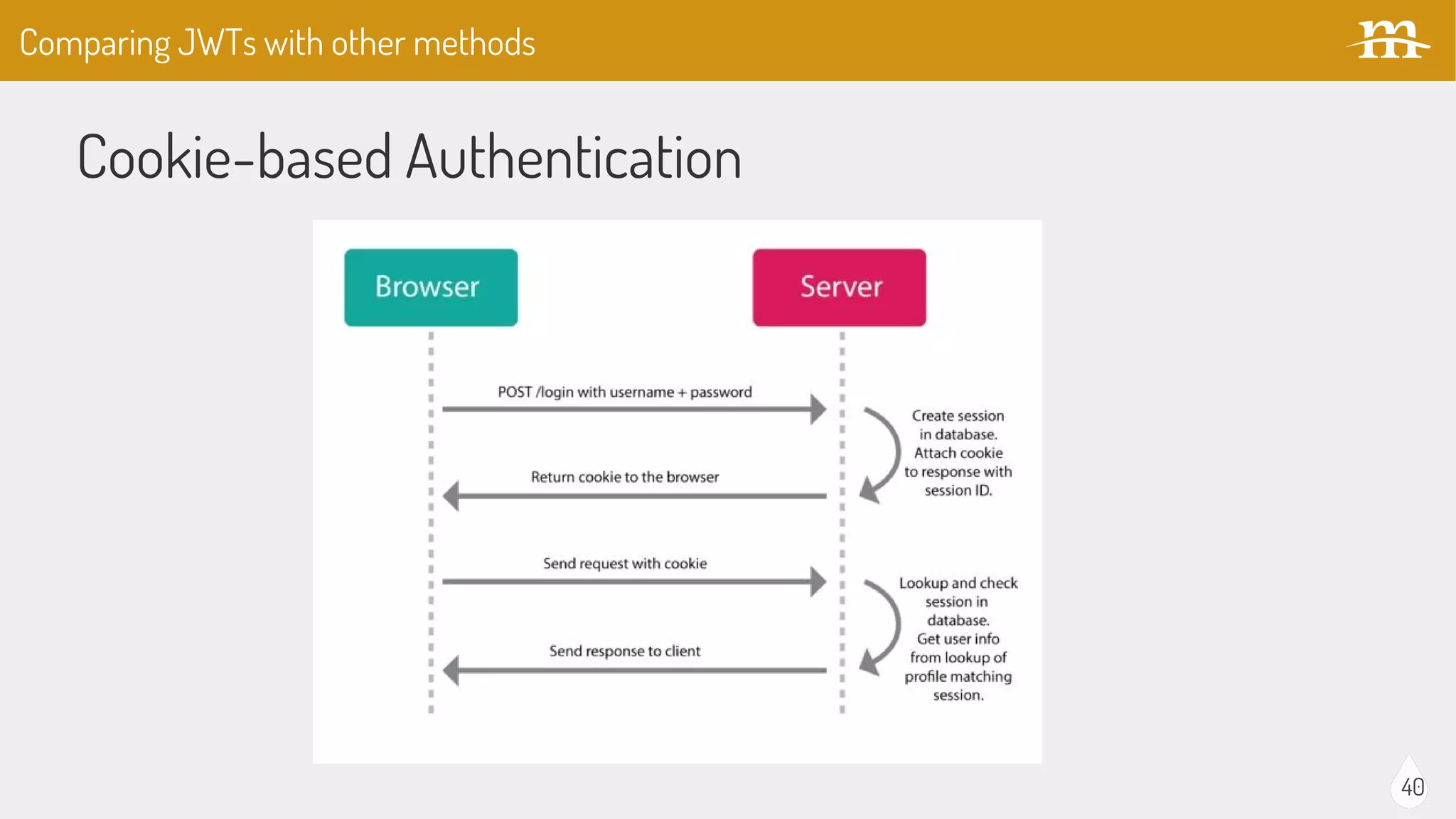
The document provides an overview of JSON Web Tokens (JWTs) for REST authentication, detailing their structure and how they facilitate stateless communication in decoupled architectures. It compares JWTs with other authentication methods, highlighting their advantages such as scalability and being digitally signed, as well as drawbacks like token size and revocation challenges. The content also discusses the implementation of JWTs in Drupal, including relevant modules and their functionality.