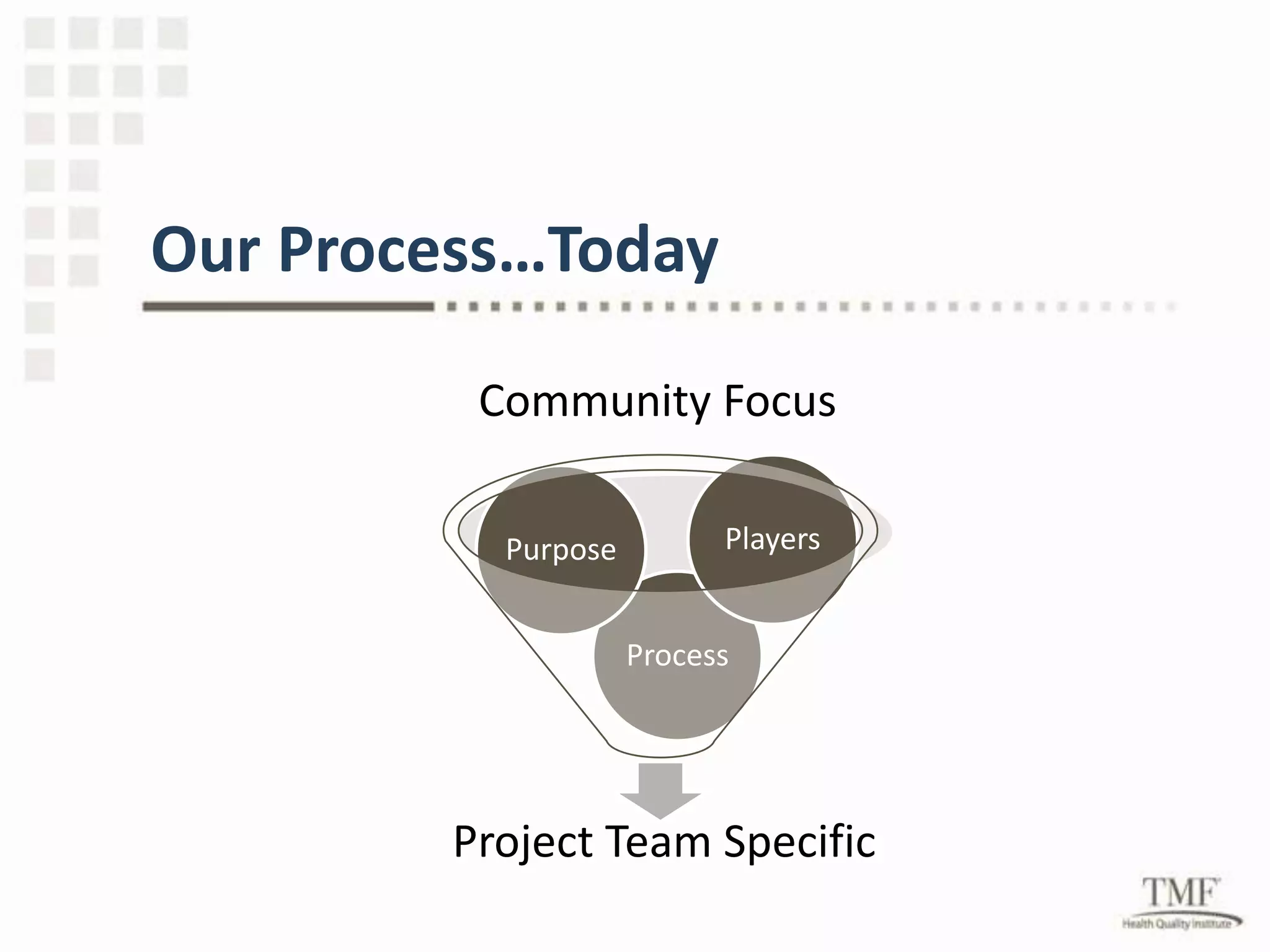
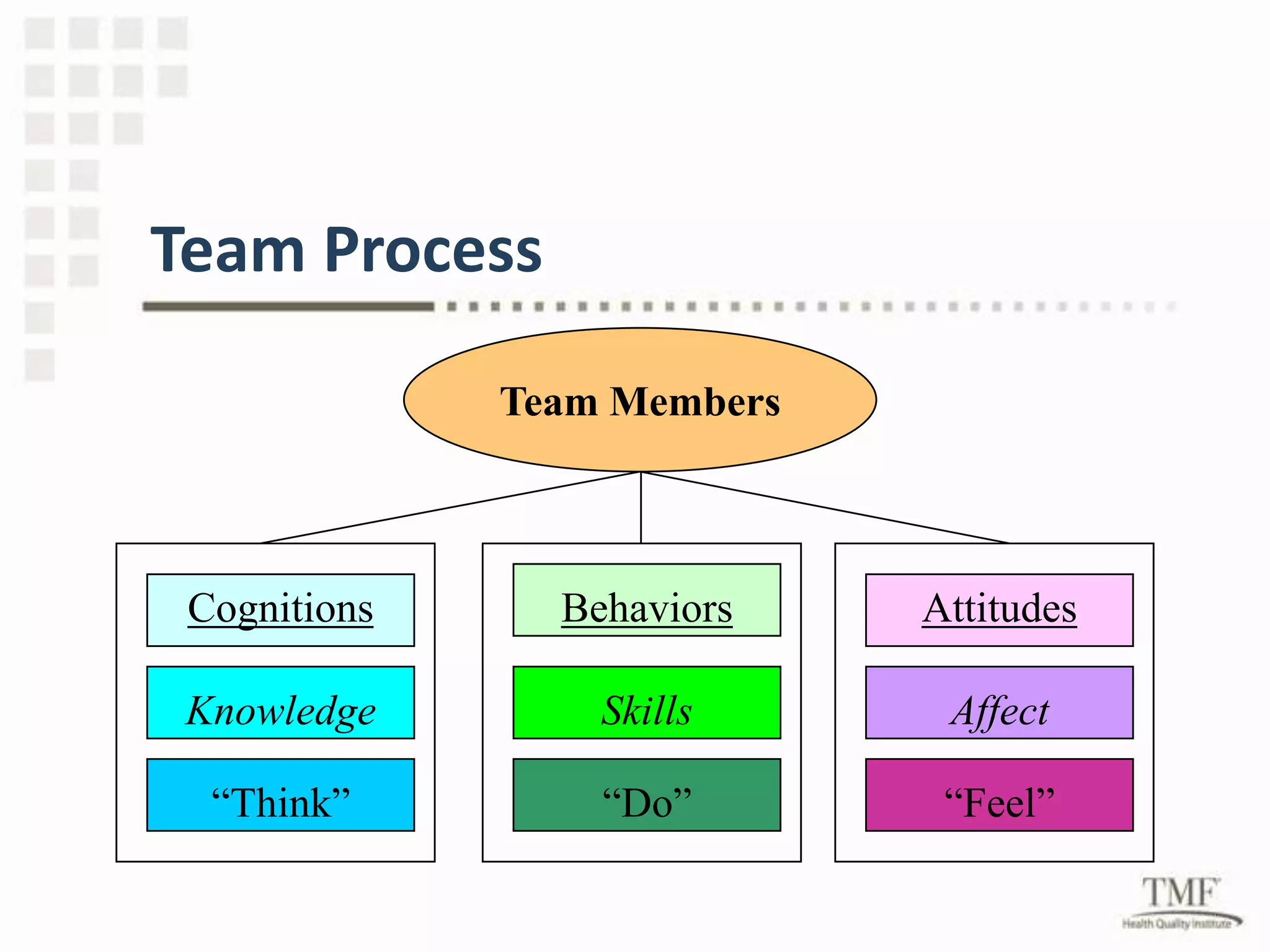
This document outlines the benefits of collaboration and forming coalitions to achieve common goals. It discusses how to form successful project teams focused on specific outcomes, including having a clear purpose, plan, measurable goals, shared ownership, and open communication. The benefits of collaboration include resource sharing, expertise, community presence, cohesion, shared responsibility, and collective leverage. Successful quality improvement project teams require an organizational culture of quality, shared understanding, accountability, and a blame-free environment focused on system issues rather than human error.