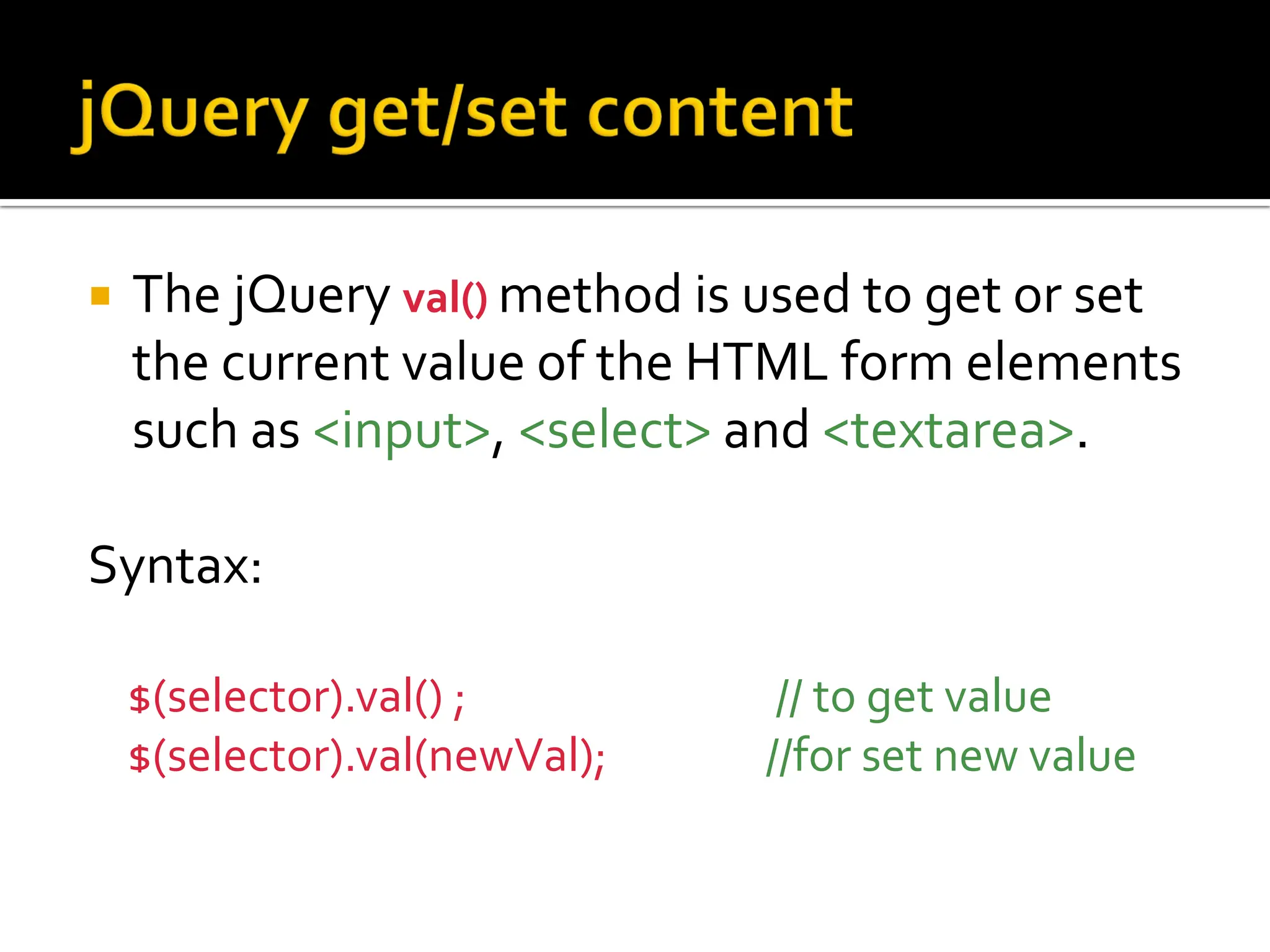
jQuery is a fast and feature-rich JavaScript library used for HTML document traversal and manipulation, event handling, animation, and Ajax interactions. It simplifies tasks like selecting elements, adding/removing classes, handling events, and performing animations. jQuery selects elements using CSS-style selectors and provides methods for manipulating, traversing, and modifying pages on the fly.








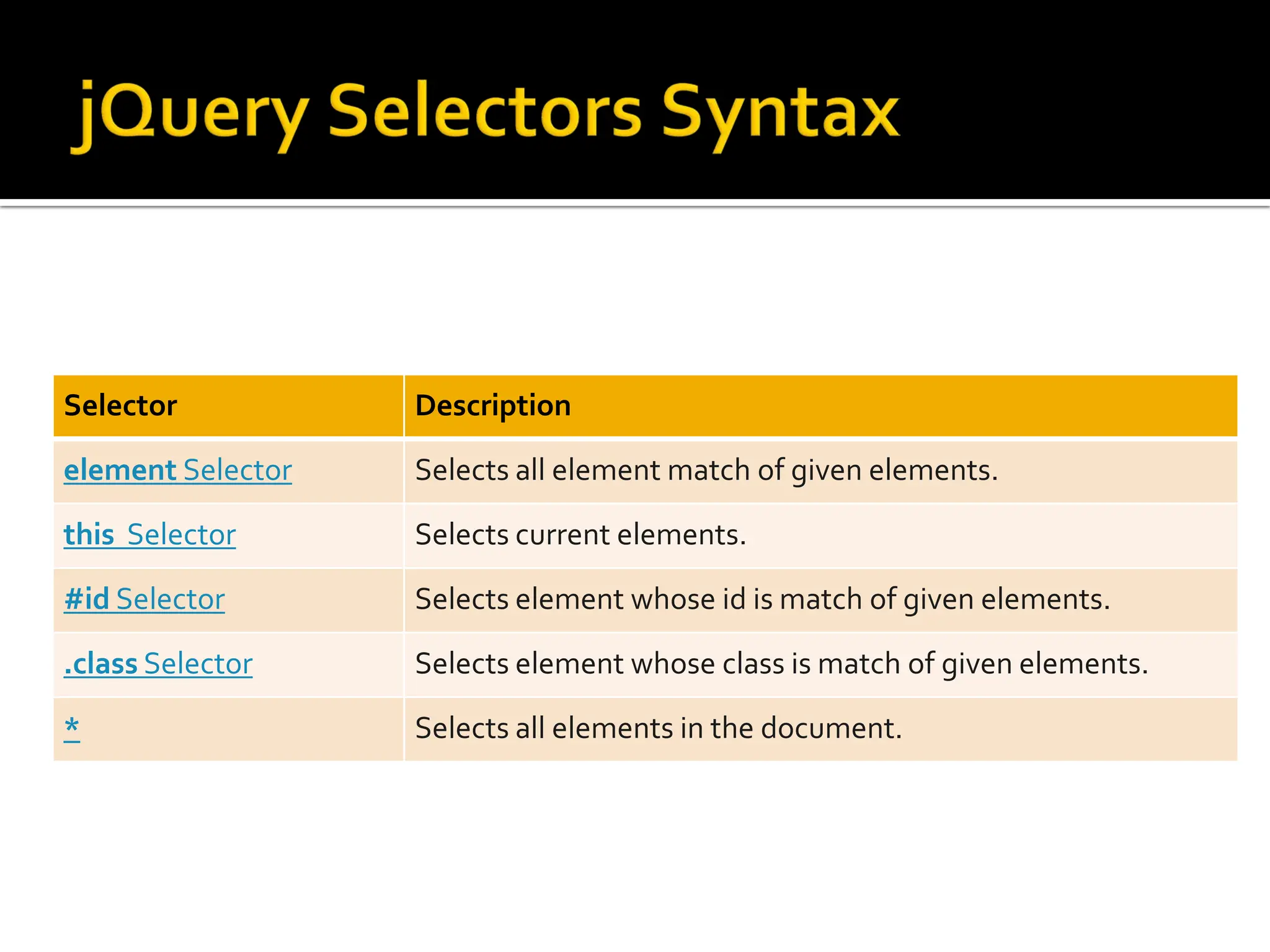







![ To select the element by their attribute or attribute with
specific value attribute selector is used
Syntax $( ‘[attribute]’ )
$( ‘[attribute=“value”]’ )
$(‘[title]’) : Selects all elements having
title attribute
$(‘div [title]’) : Select all elements having
title attribute
$(‘[title]=“tt1’) : Select all elements that
have title attribute value - tt1
$(‘div [title]=“tt1’) : Select all div elements
that have title attribute value - tt1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1-whatisjquerywhyjquerysyntaxselectors-240227112420-f0fa5585/75/Unit-1-What-is-jQuery_Why-jQuery_Syntax_Selectors-pdf-18-2048.jpg)







![ The jQuery animate() allows us to animate CSS
properties
$(selector).animate(properties,[duration],[easing],[compl
ete])
Properties: CSS Properties
Duration: Duration of animation in milliseconds.
Default is 400.
Easing: Used for transition. Default is swing.
Complete: A function to call once animation is
complete.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1-whatisjquerywhyjquerysyntaxselectors-240227112420-f0fa5585/75/Unit-1-What-is-jQuery_Why-jQuery_Syntax_Selectors-pdf-27-2048.jpg)