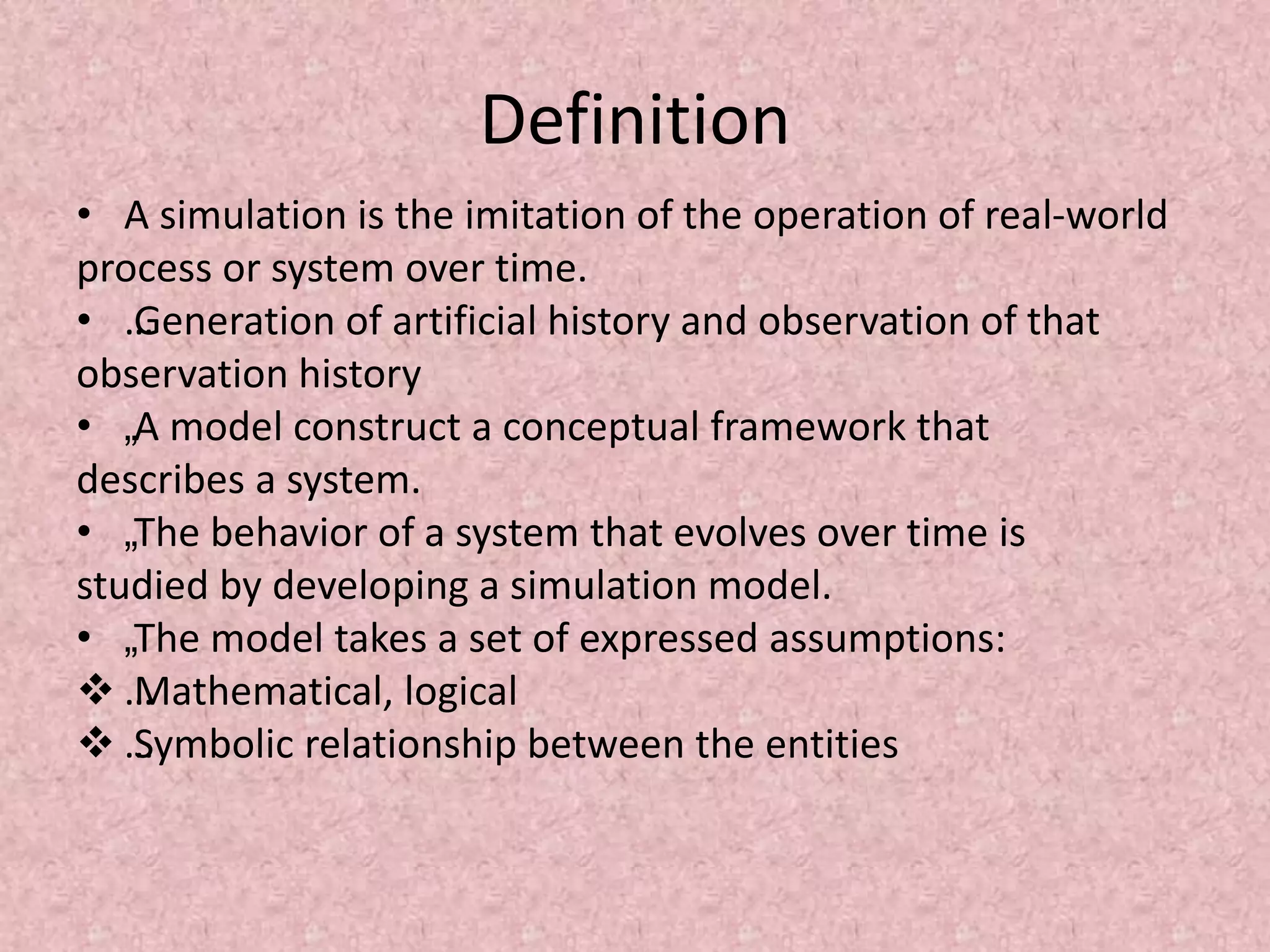
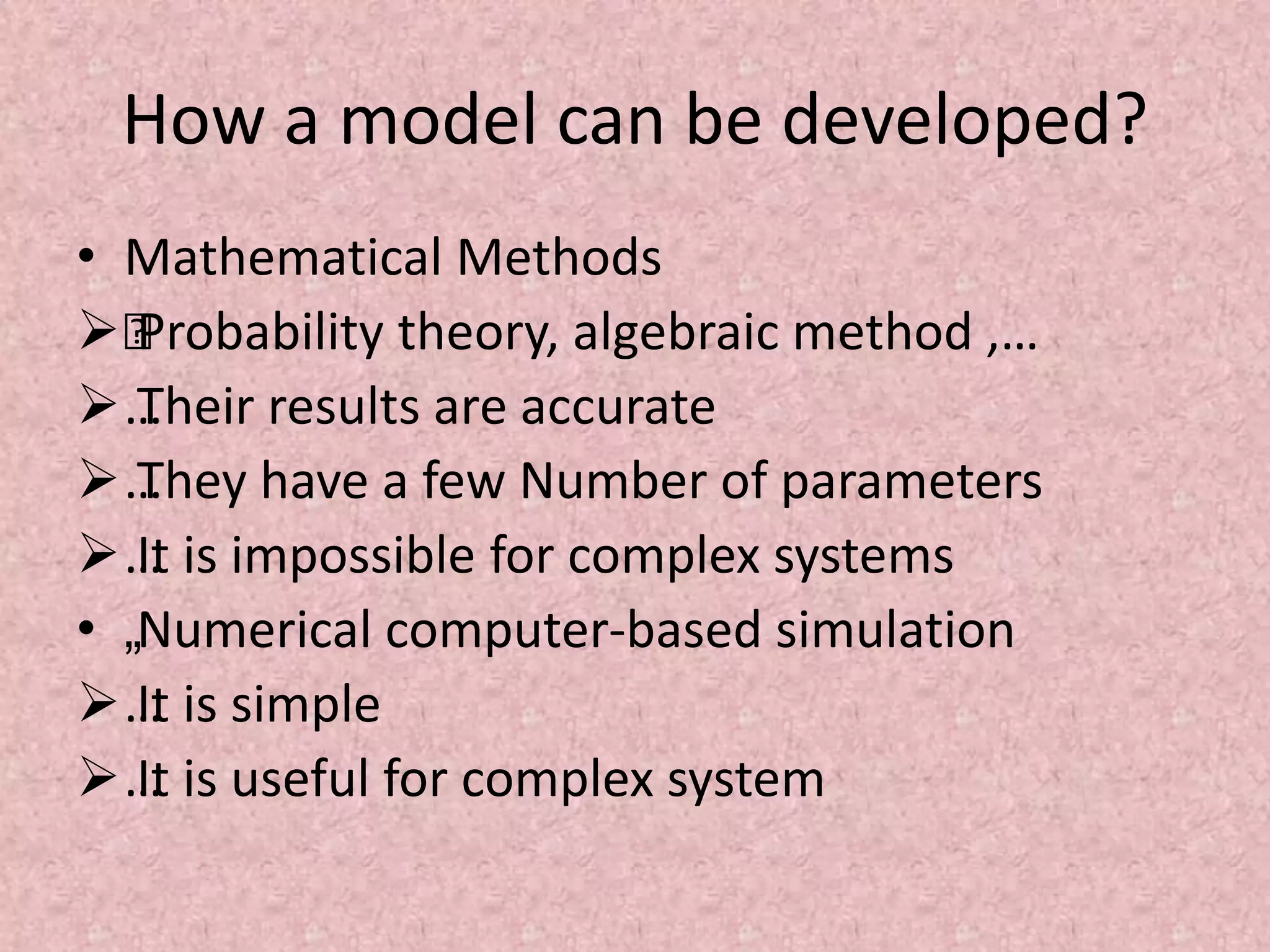
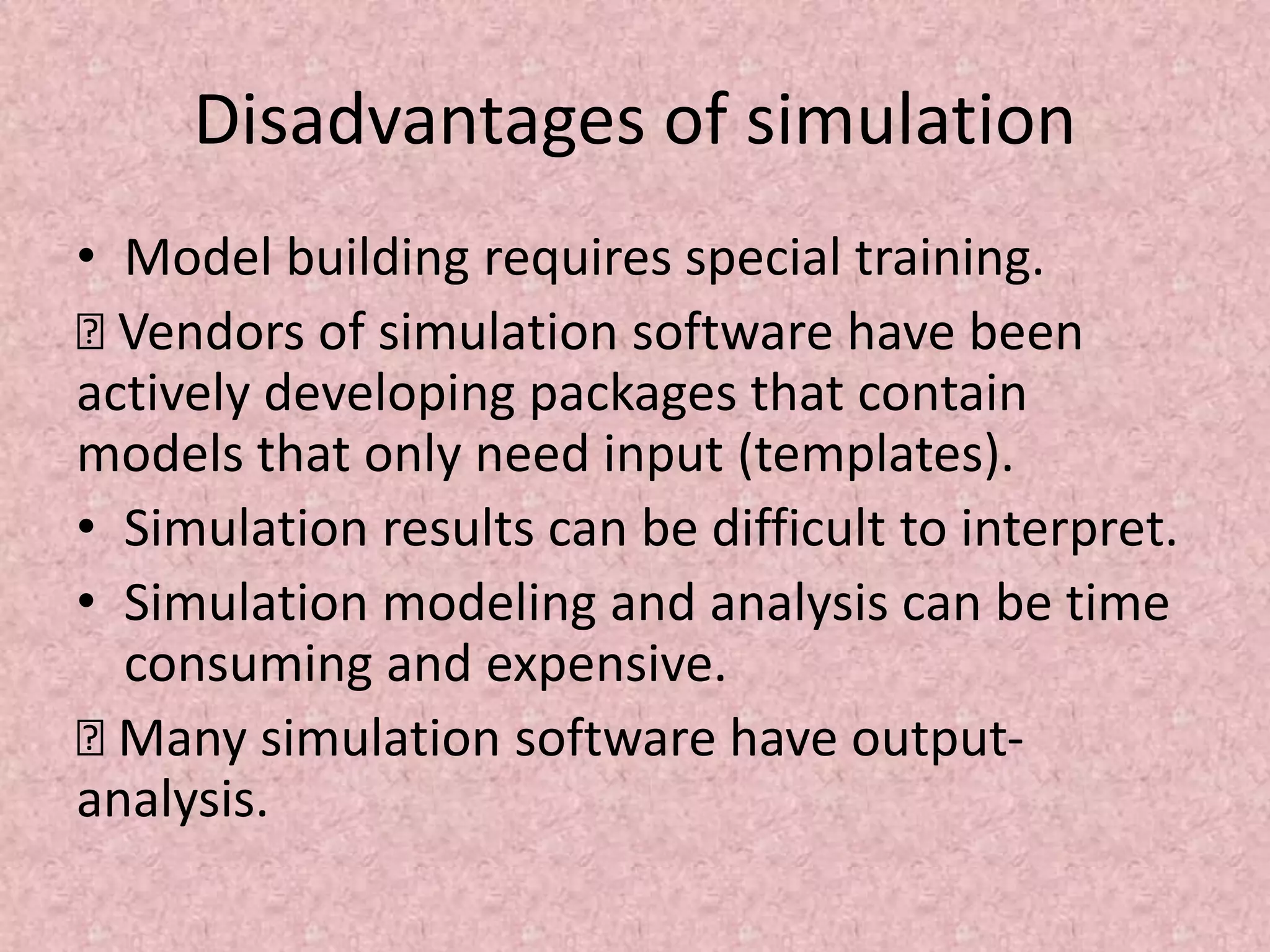
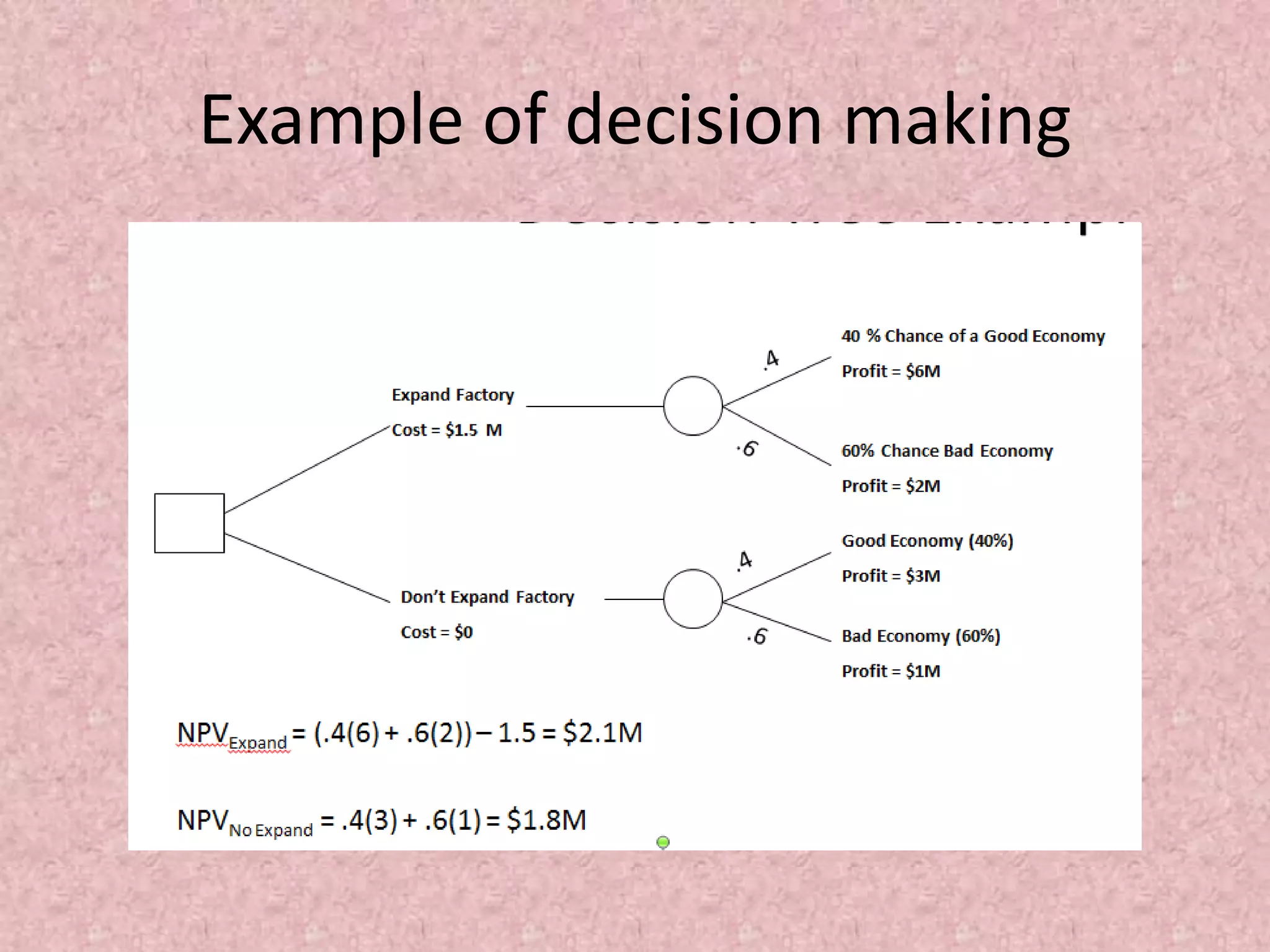
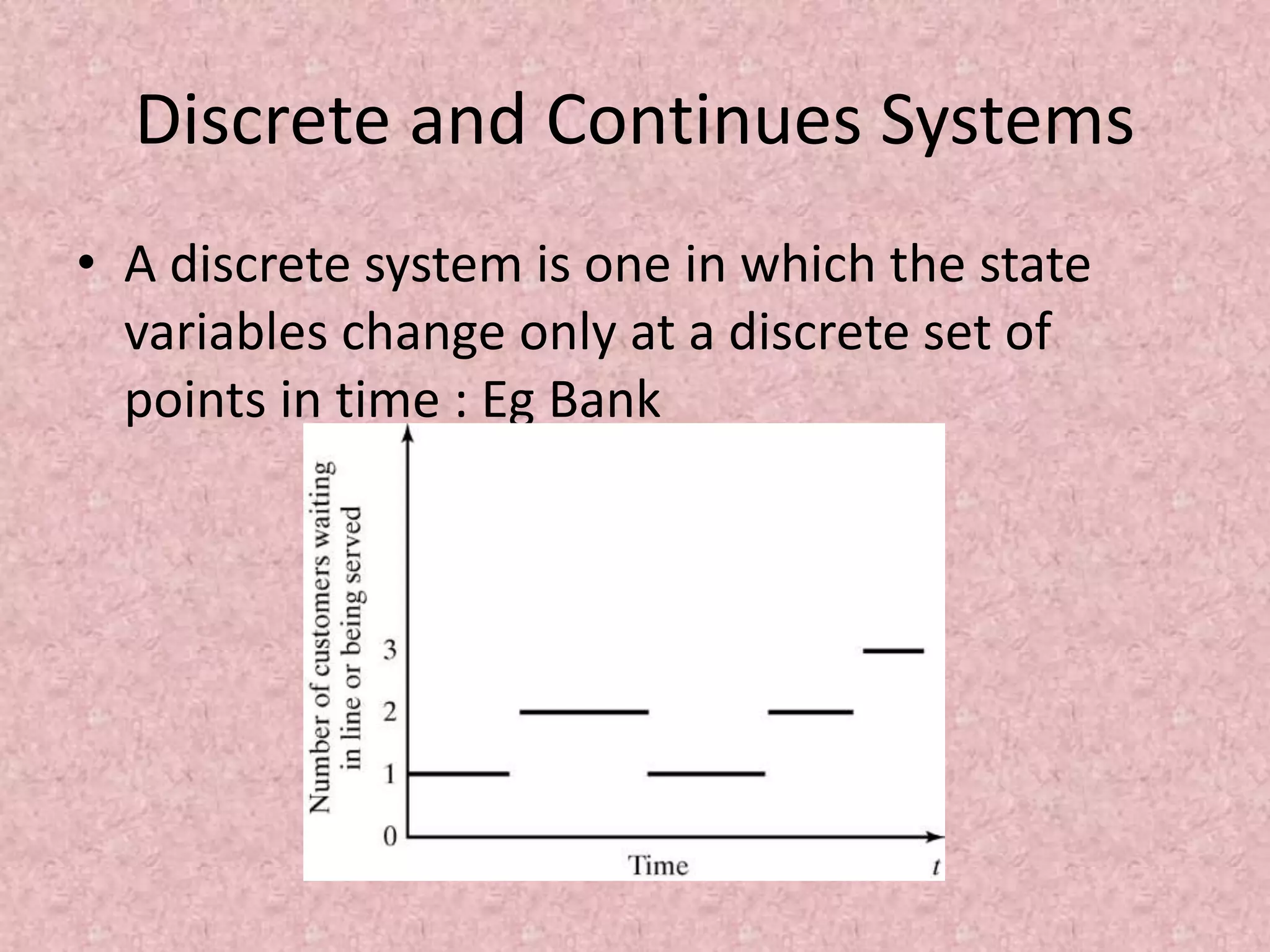
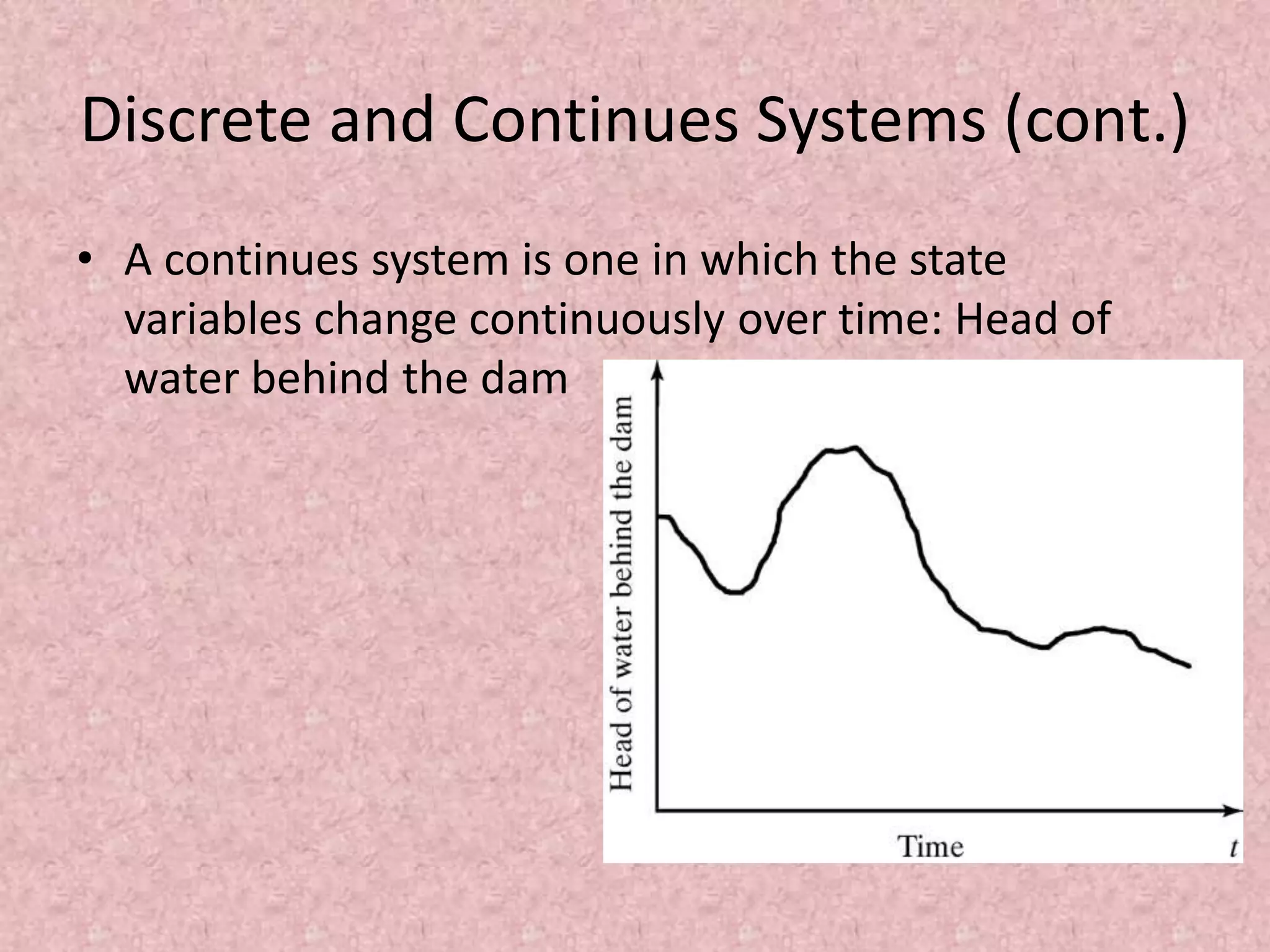
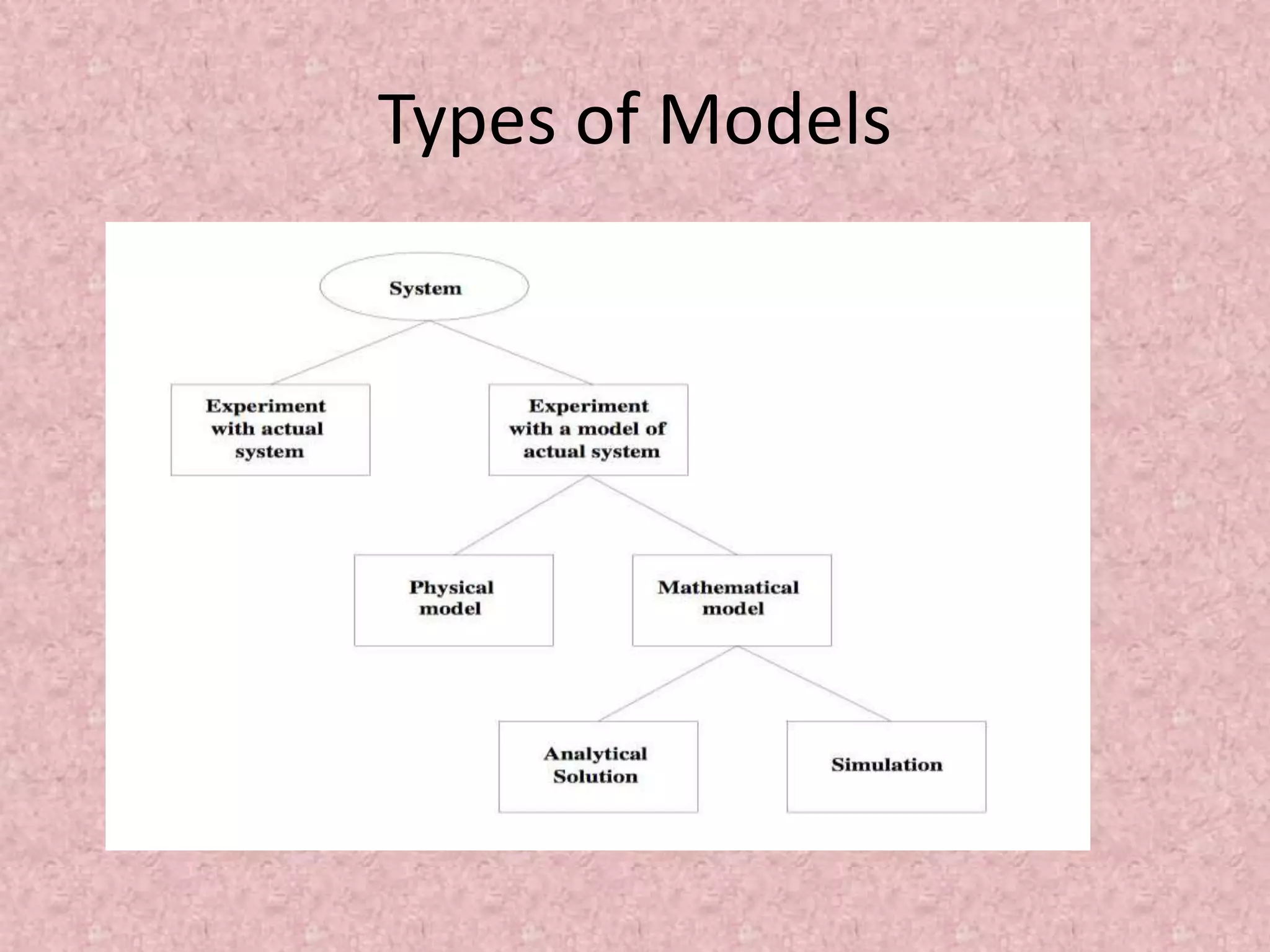
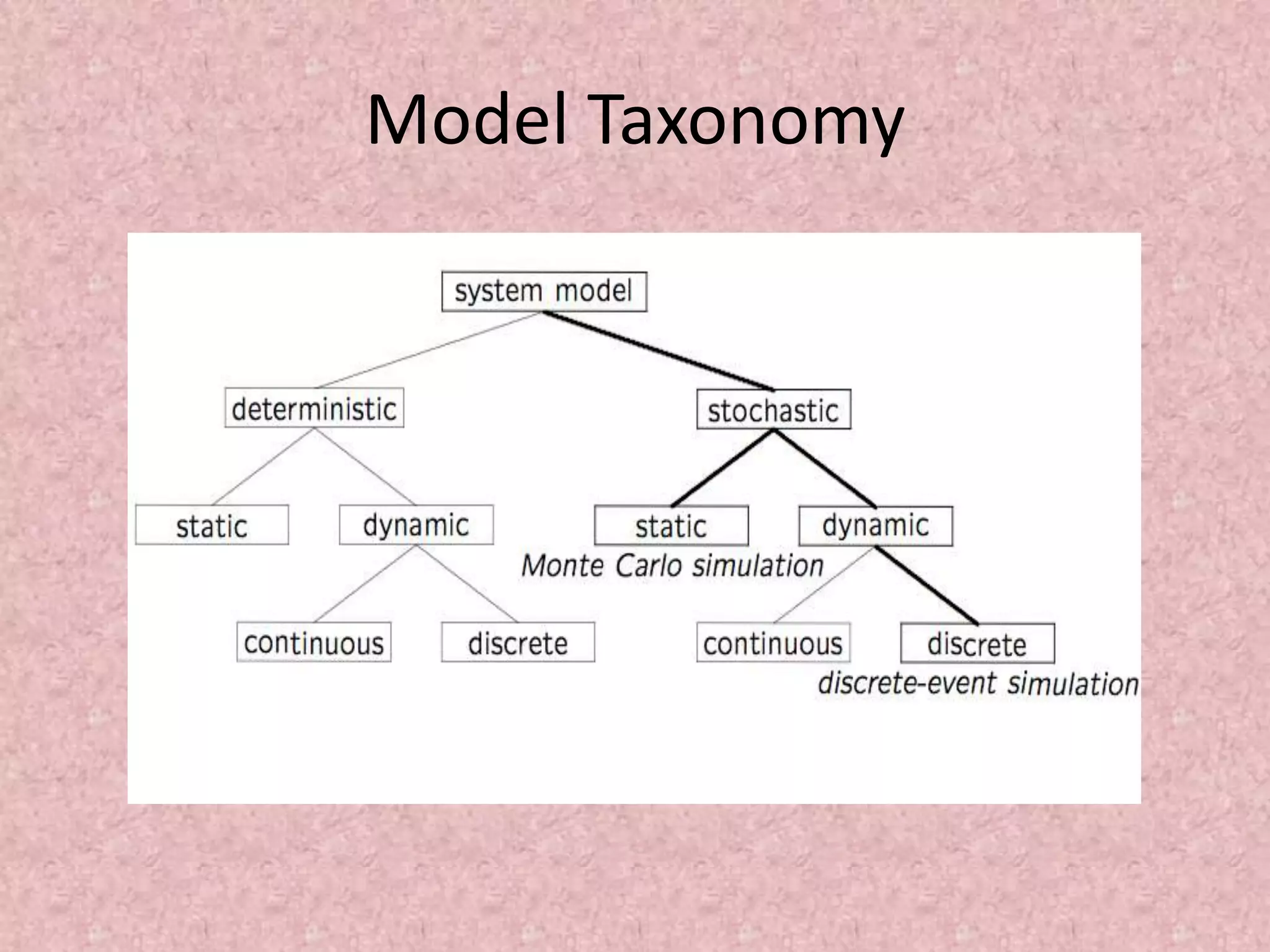
Simulation involves developing a model of a real-world system over time to analyze its behavior and performance. The key aspects covered in this document include defining simulation as modeling the operation of a system over time through artificial history generation and observation. Simulation models can be used as analysis and design tools to predict the effects of changes to a system before actual implementation. Discrete event simulation is discussed as a common technique that models systems with state changes occurring at discrete points in time. The document also outlines the steps in a typical simulation study including problem formulation, model conceptualization, experimentation and analysis.