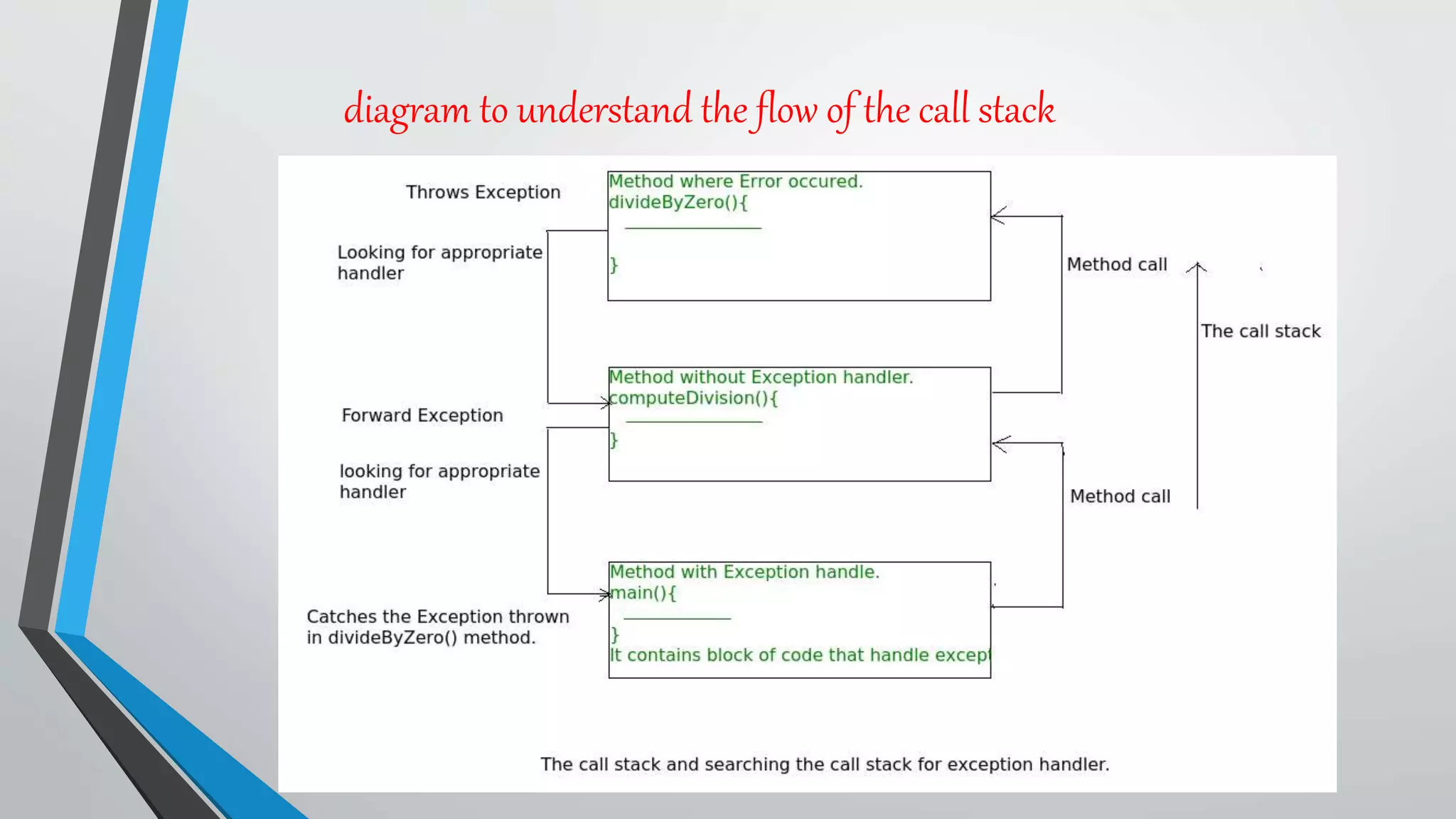
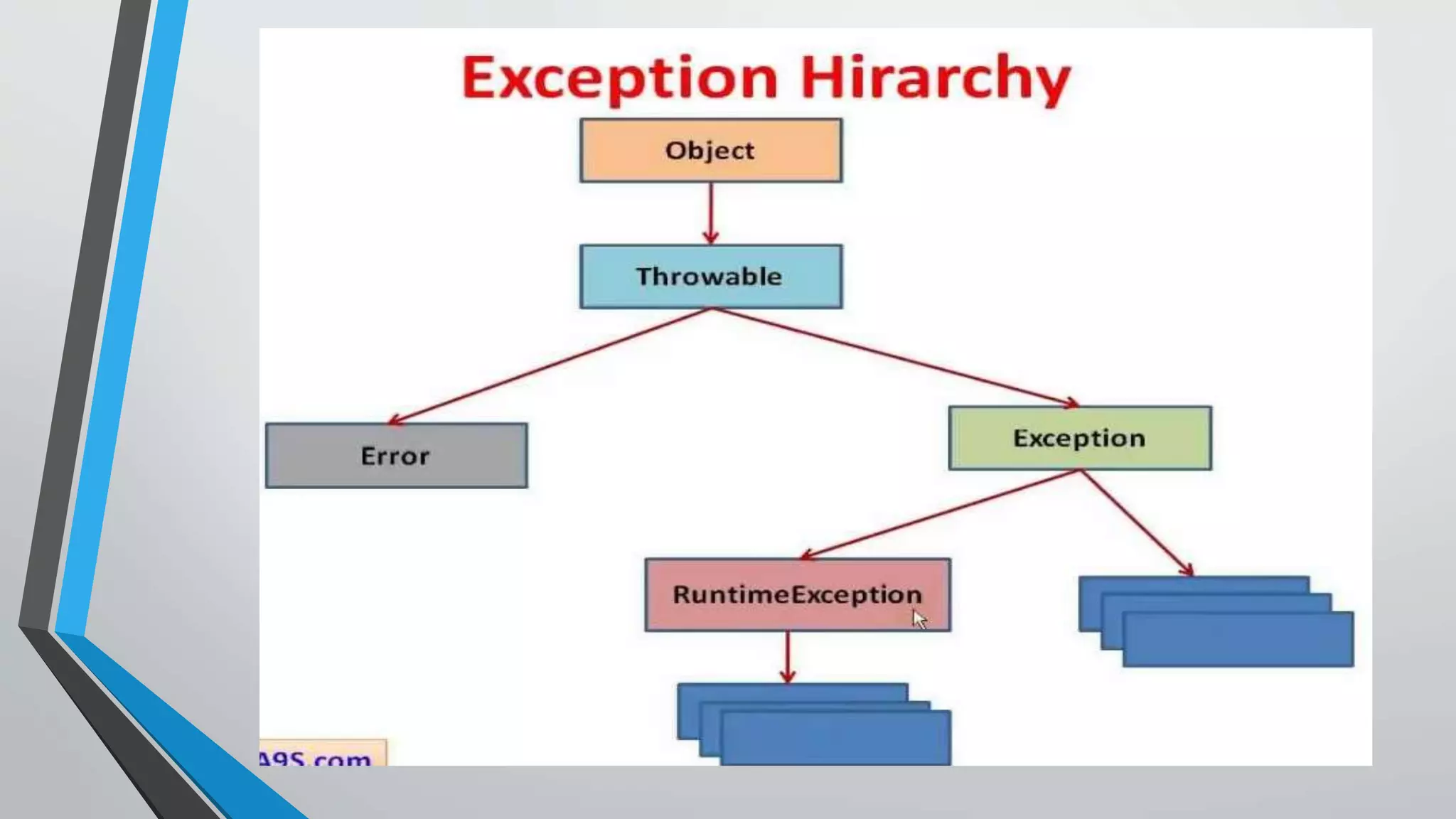
The document explains Java exceptions, which are problems that occur during program execution, disrupting the normal flow and potentially causing abnormal termination. It details different types of exceptions, such as checked, unchecked, compile-time, and runtime errors, along with the importance of exception handling in Java through try-catch blocks to maintain application flow. Additionally, it outlines how the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) handles exceptions via an exception object and the call stack to find appropriate handlers.



![What is Exceptional handling in java ?
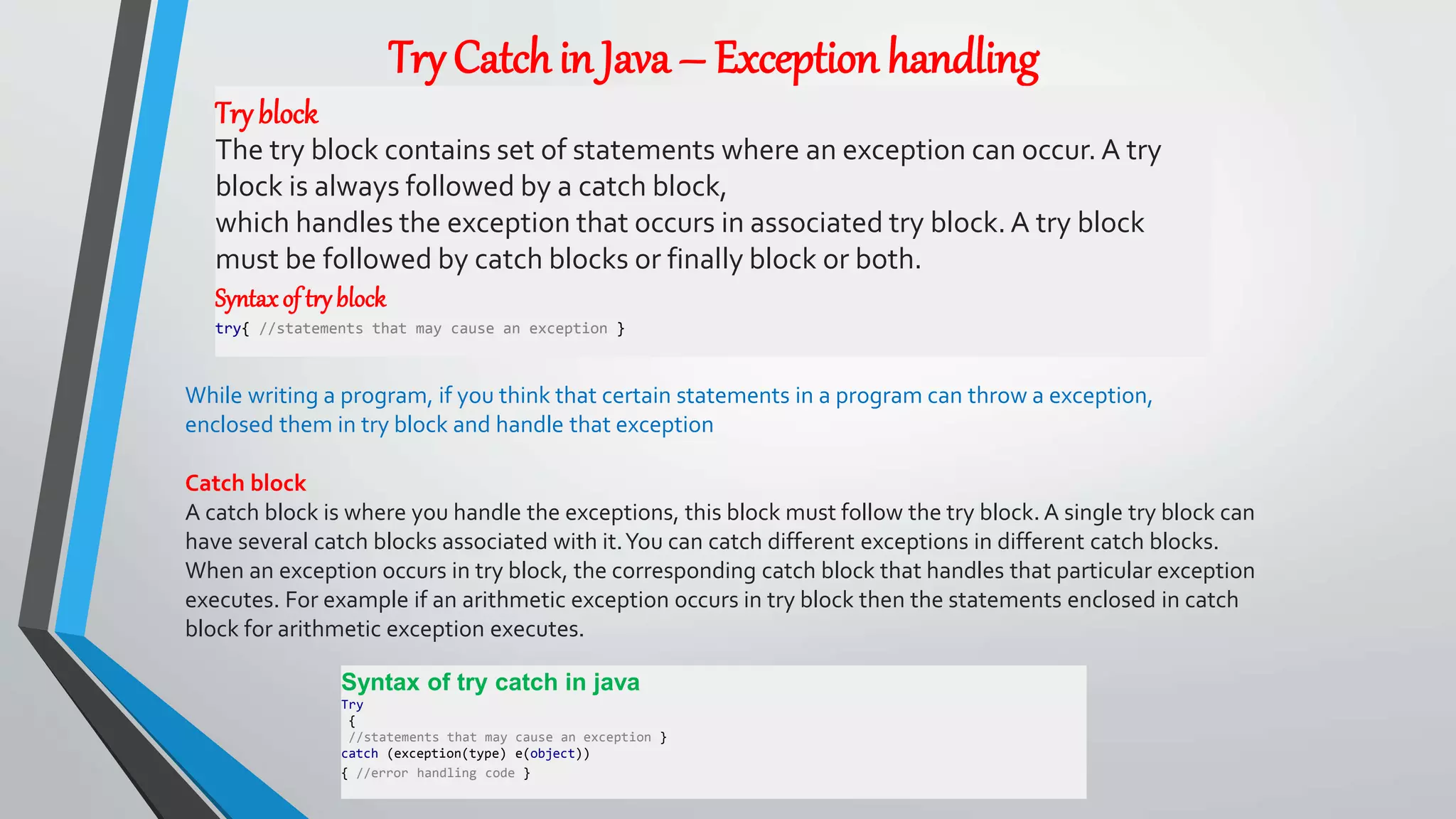
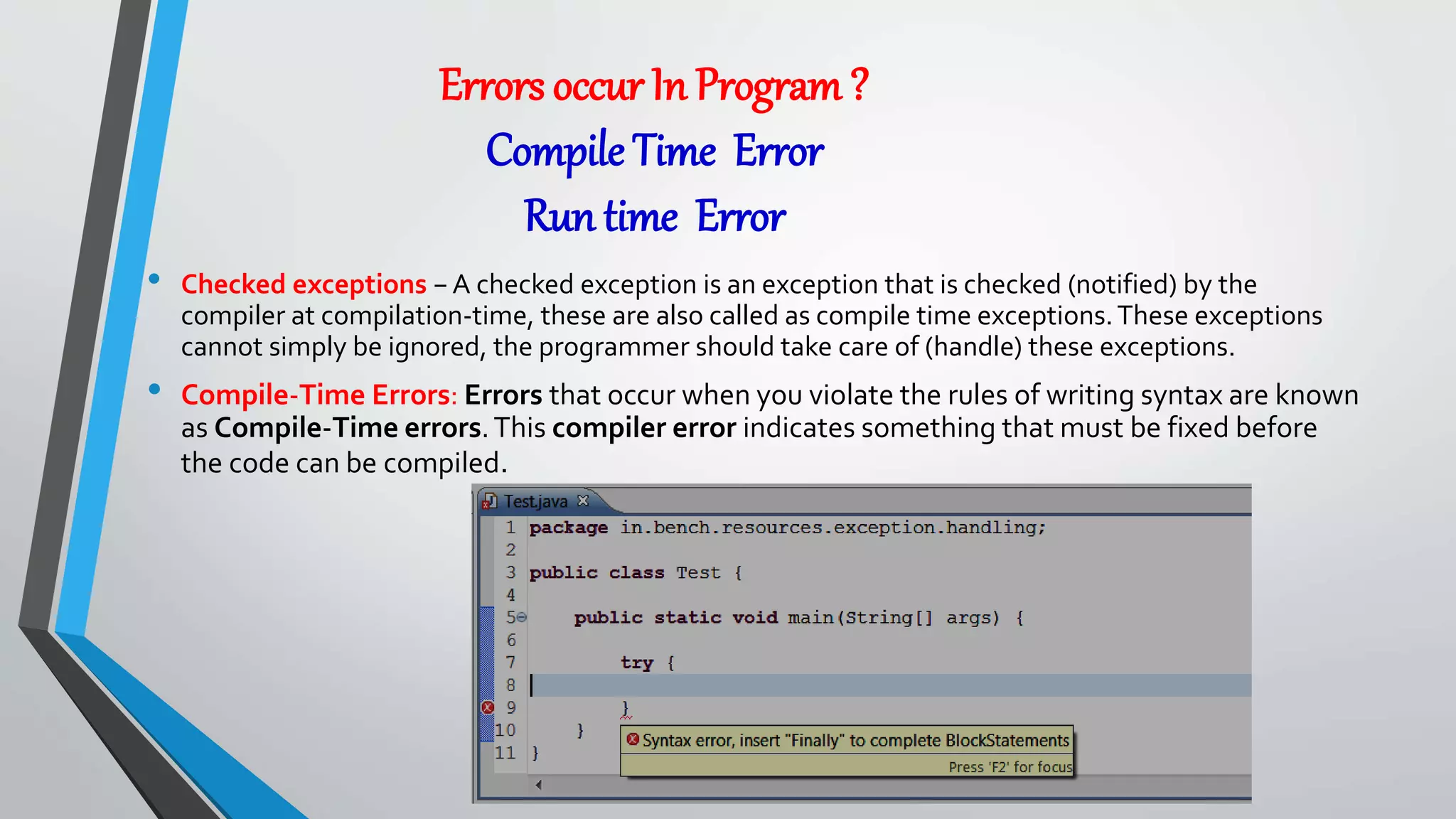
• The Exception Handling in Java is one of the powerful mechanism to handle the runtime errors so that normal flow of the application can be
maintained.
• Exception Handling is a mechanism to handle runtime errors such as ClassNotFoundException, IOException, SQLException,
• public class JavaExceptionExample{
• public static void main(String args[]){
• try{
• //code that may raise exception
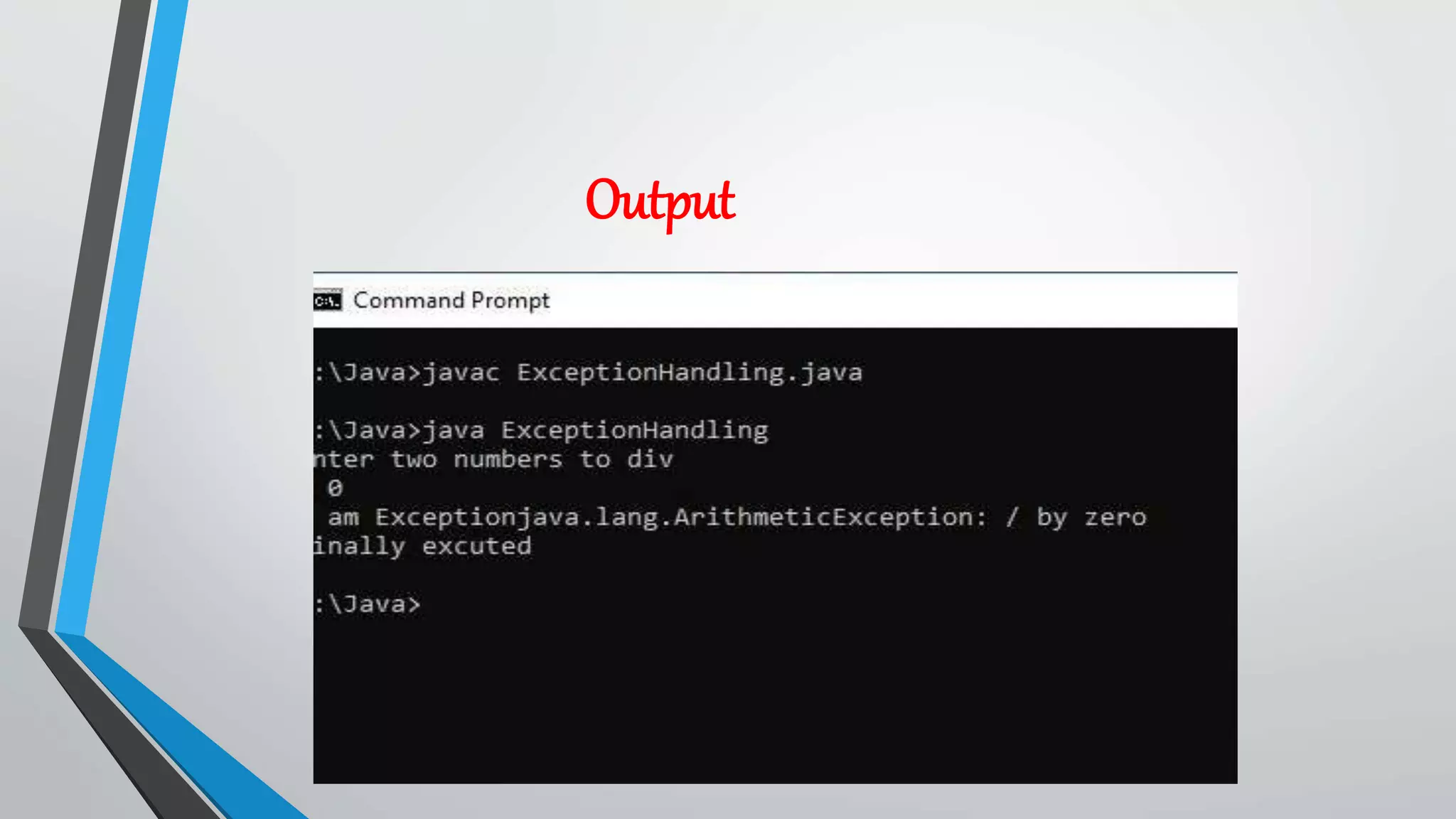
• int data=100/0;
• }
• catch(ArithmeticException e)
• {
• System.out.println(e);
• }
• //rest code of the program
• System.out.println("rest of the code...");
• }
• }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/understandingjavaexceptions-200311090306/75/Java-Exceptions-and-Exception-Handling-5-2048.jpg)
![• class Yasir
• {
• public static void main(String args [ ])
• {
• try {
• int a = 30, b = 0;
• int c = a/b;
• System.out.println ("Result = " + c);
• }
• catch(ArithmeticException e) or (Exception e)
• System.out.println ("Can't divide a number by 0");
• }
• }
• }
Values Defined](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/understandingjavaexceptions-200311090306/75/Java-Exceptions-and-Exception-Handling-6-2048.jpg)