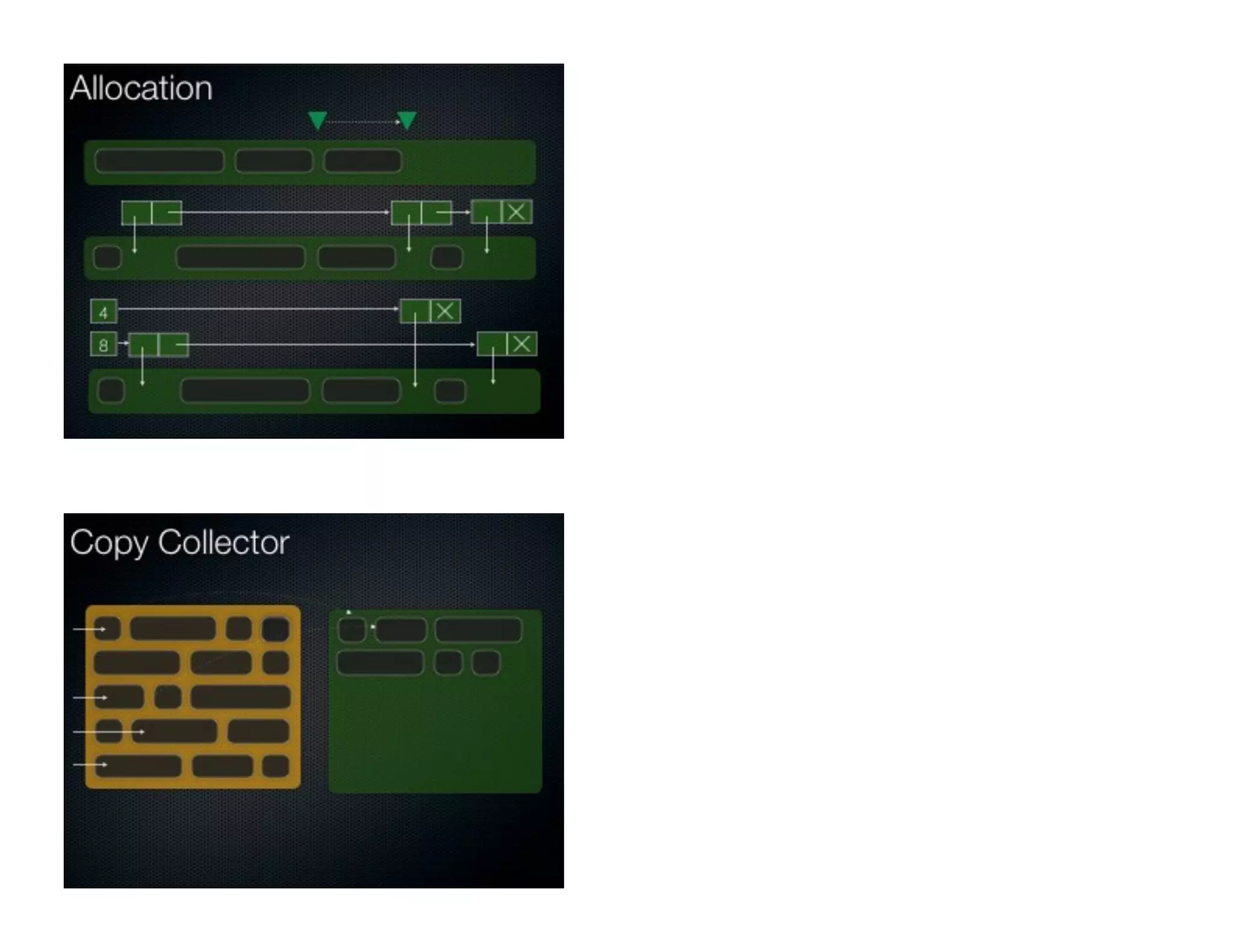
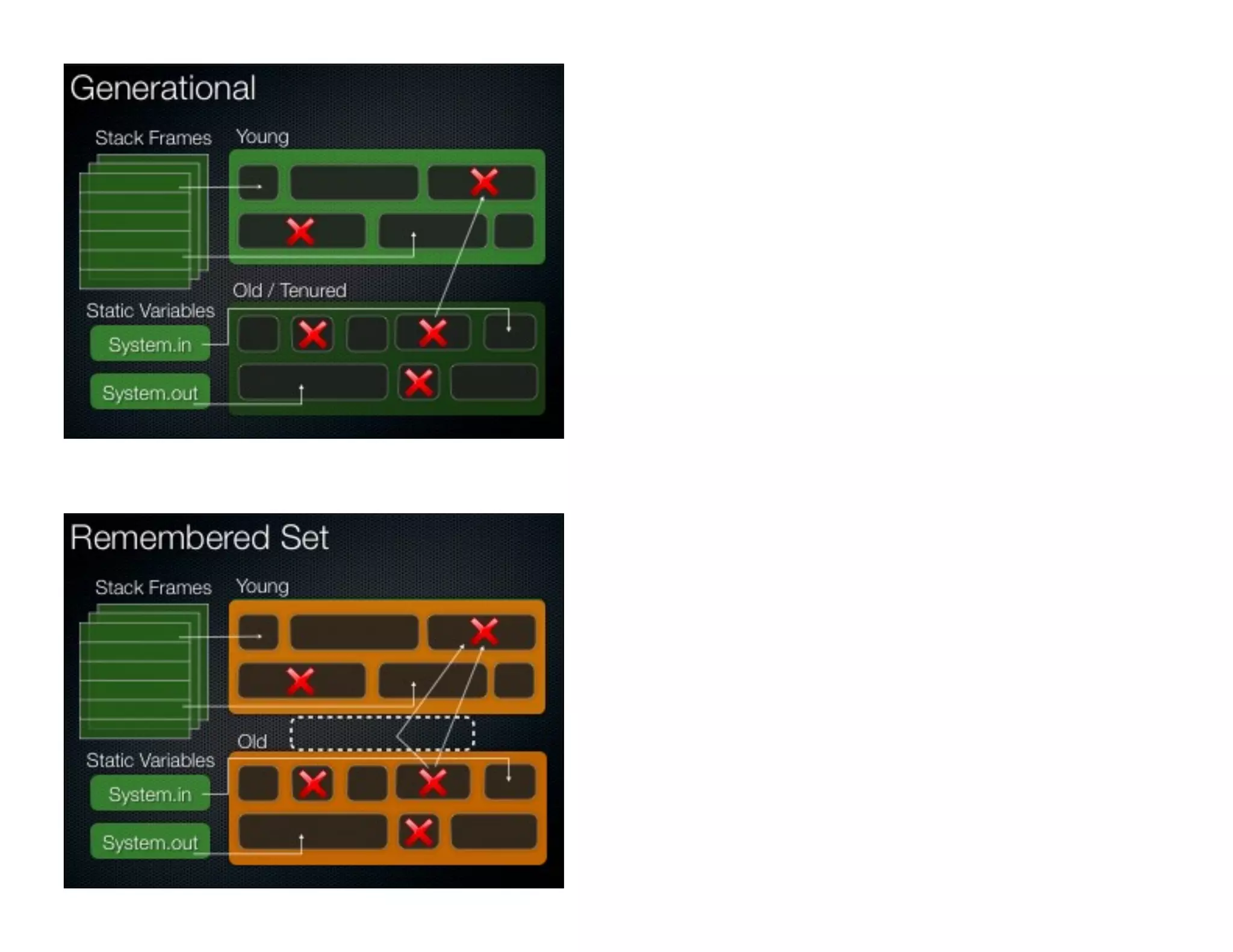
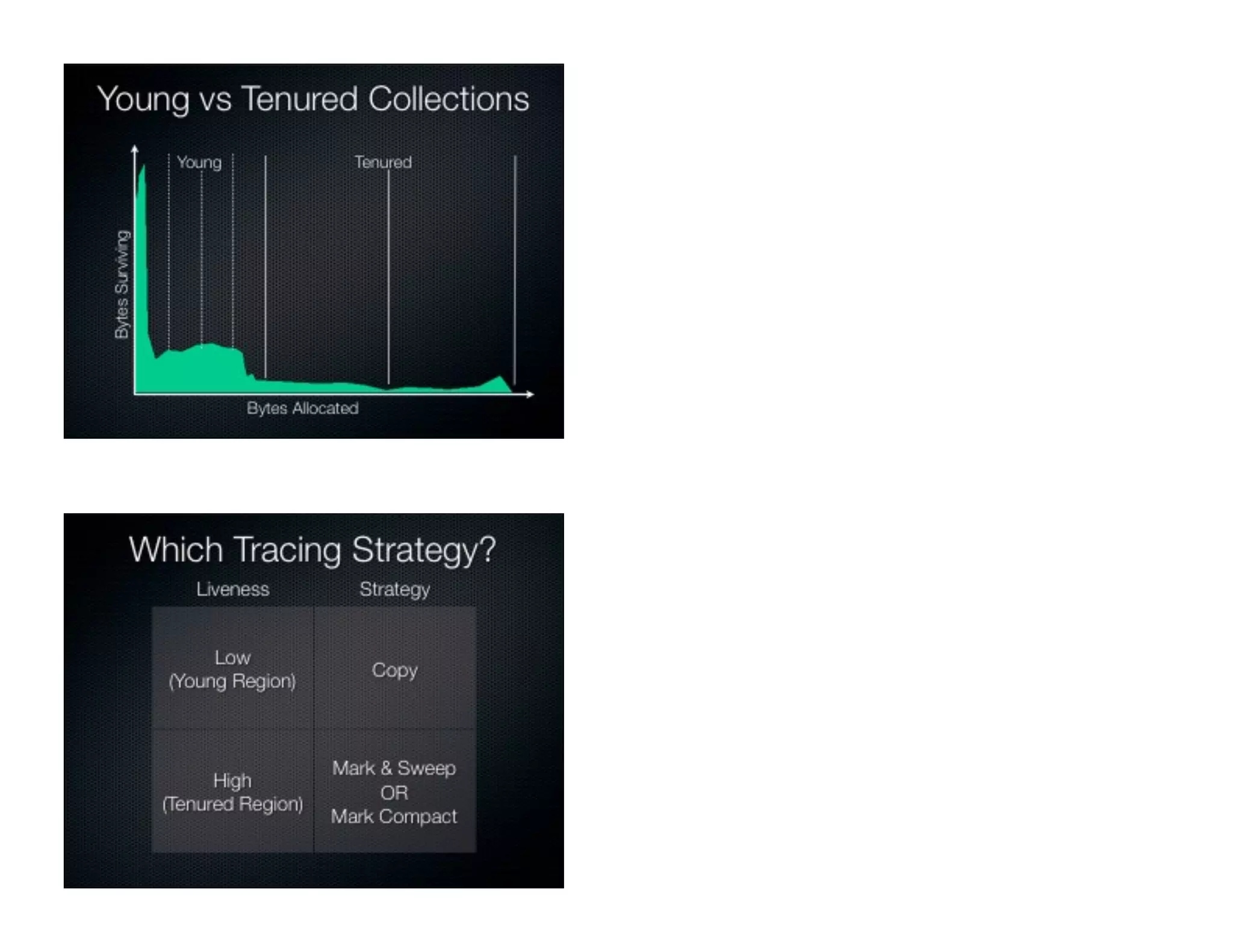
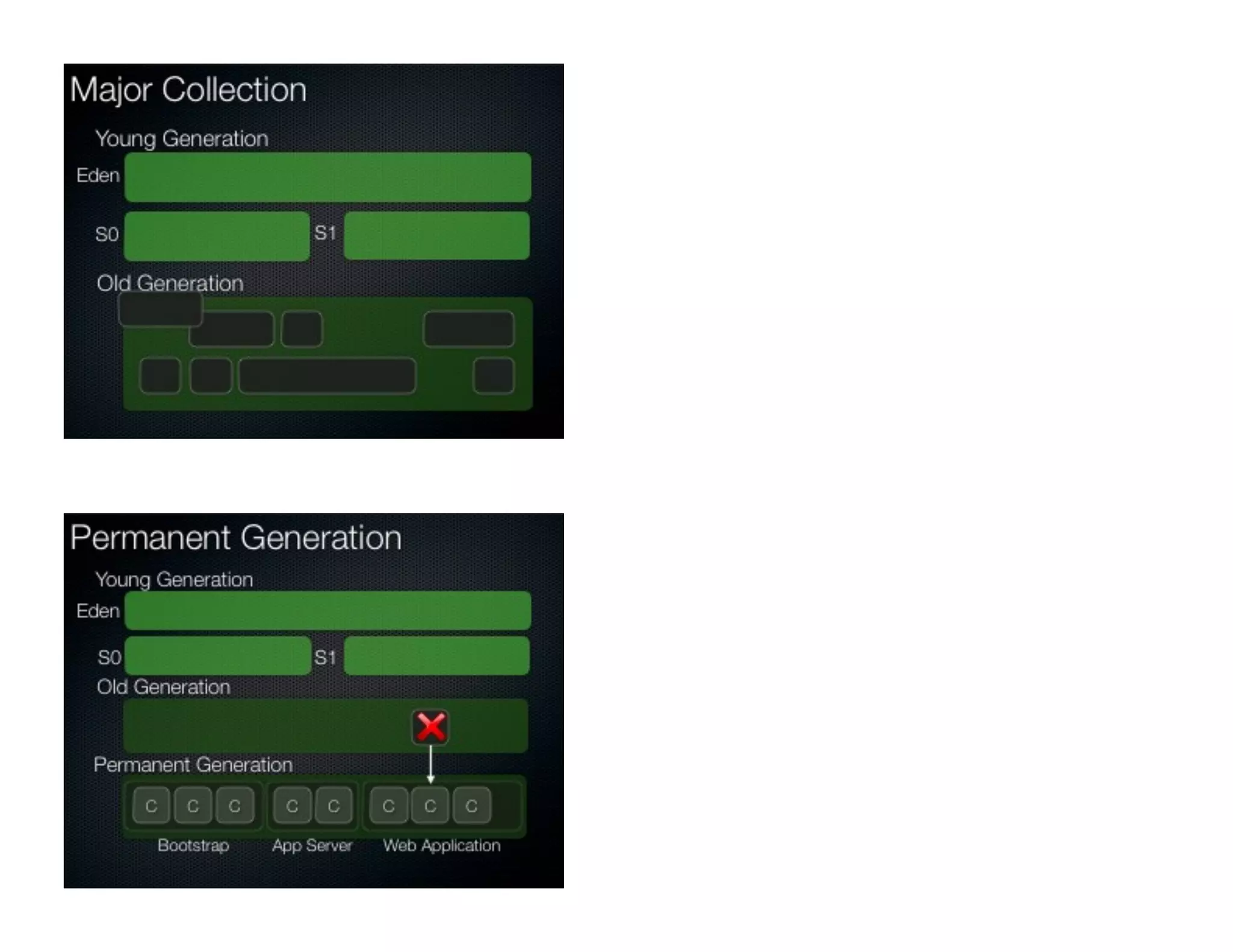
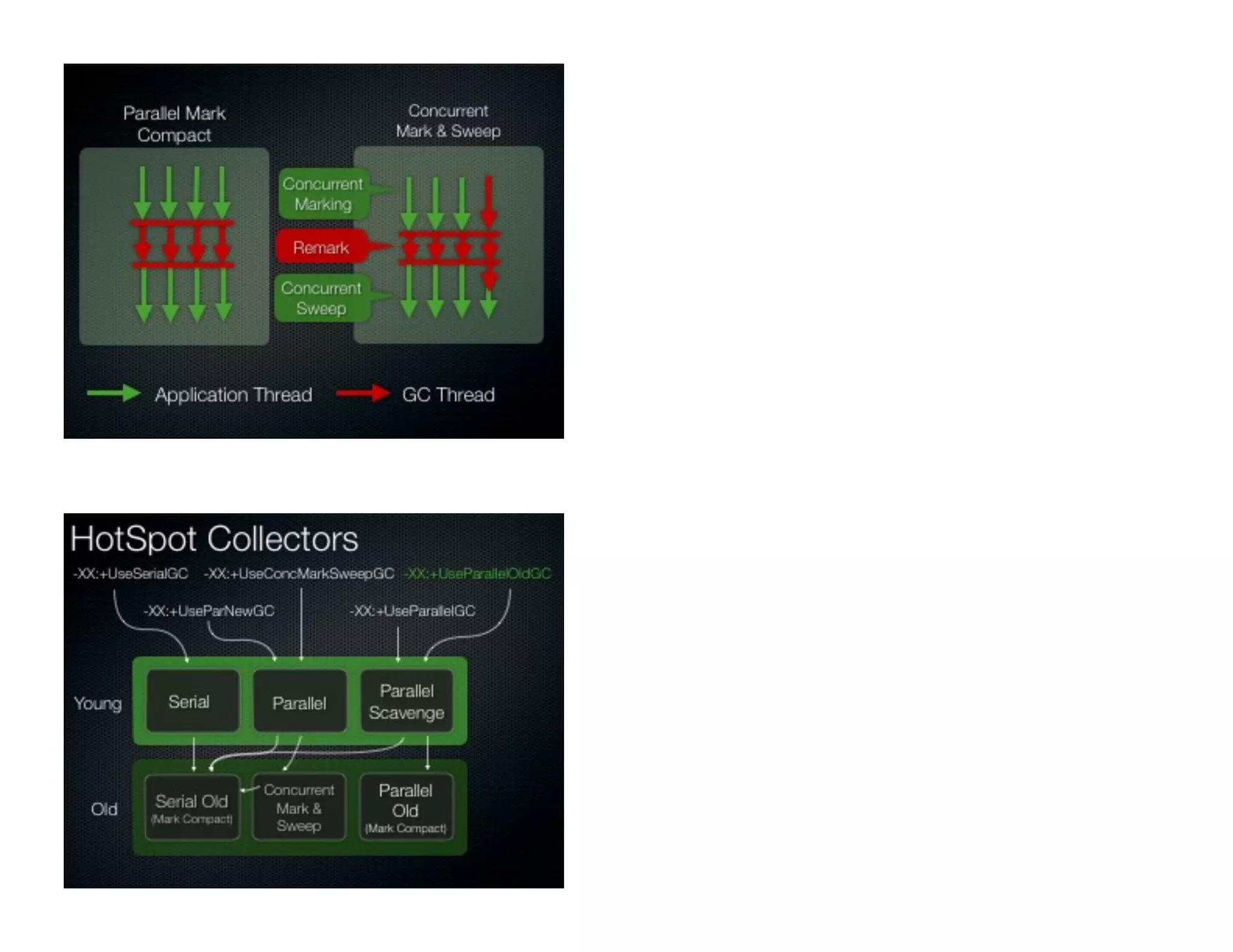
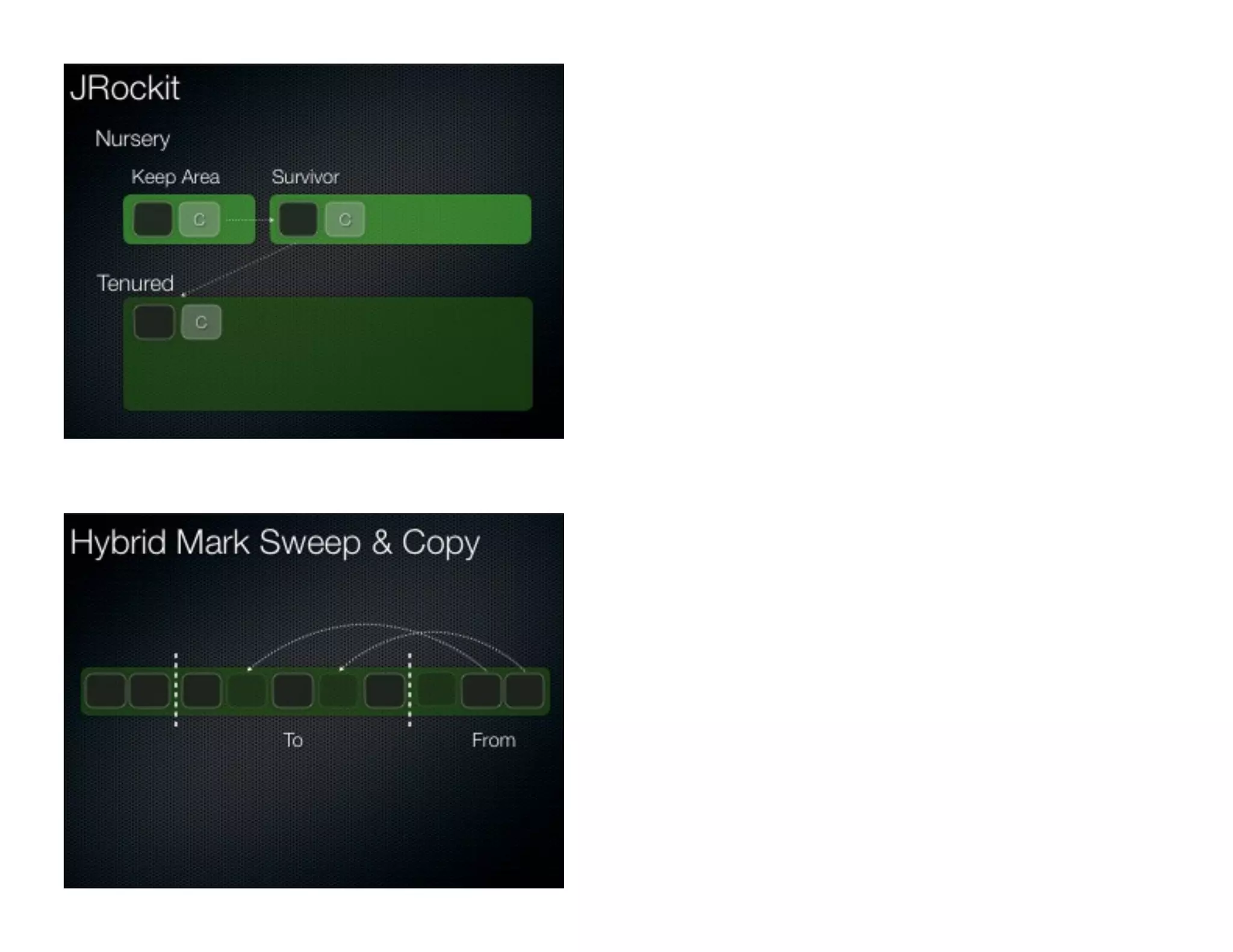
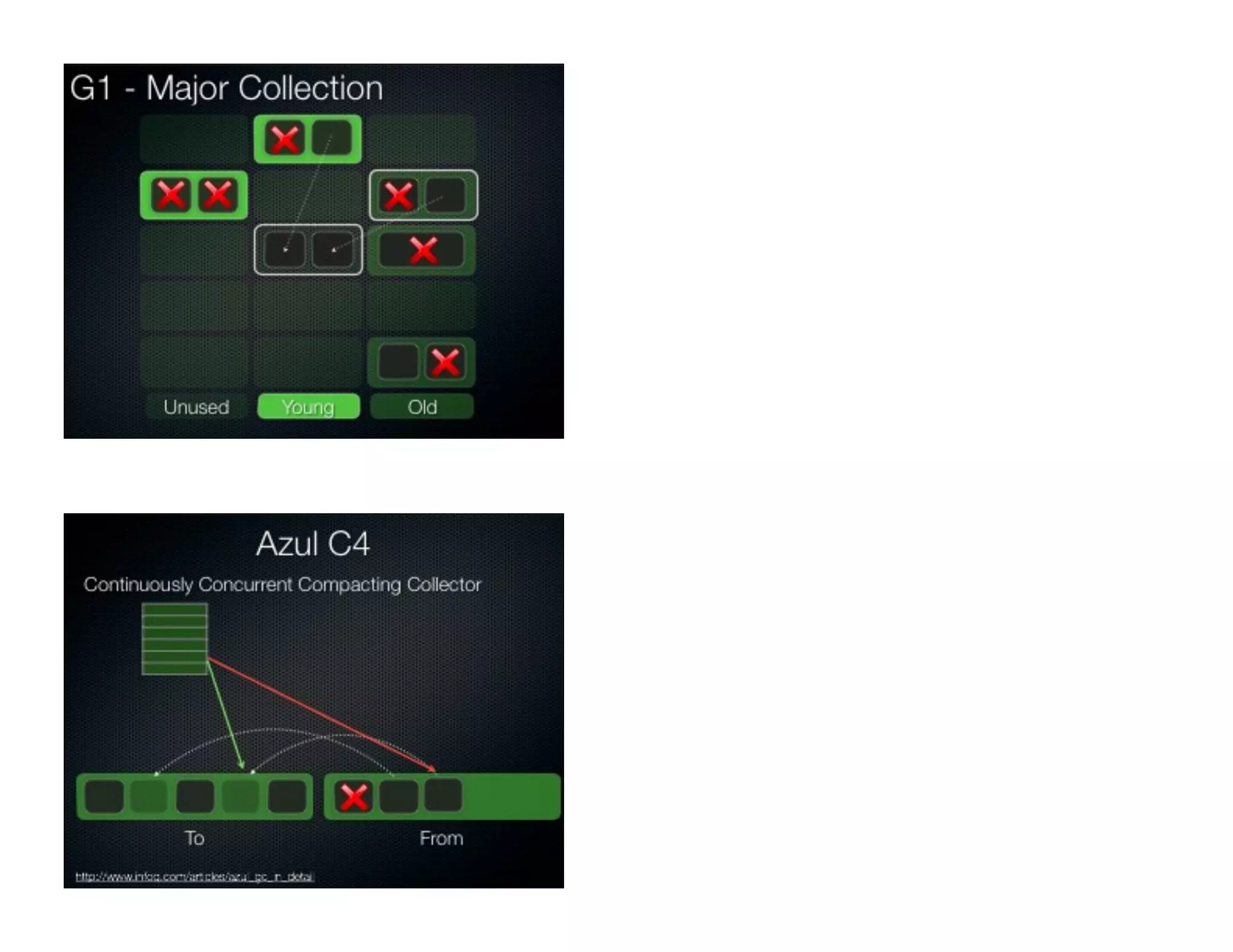
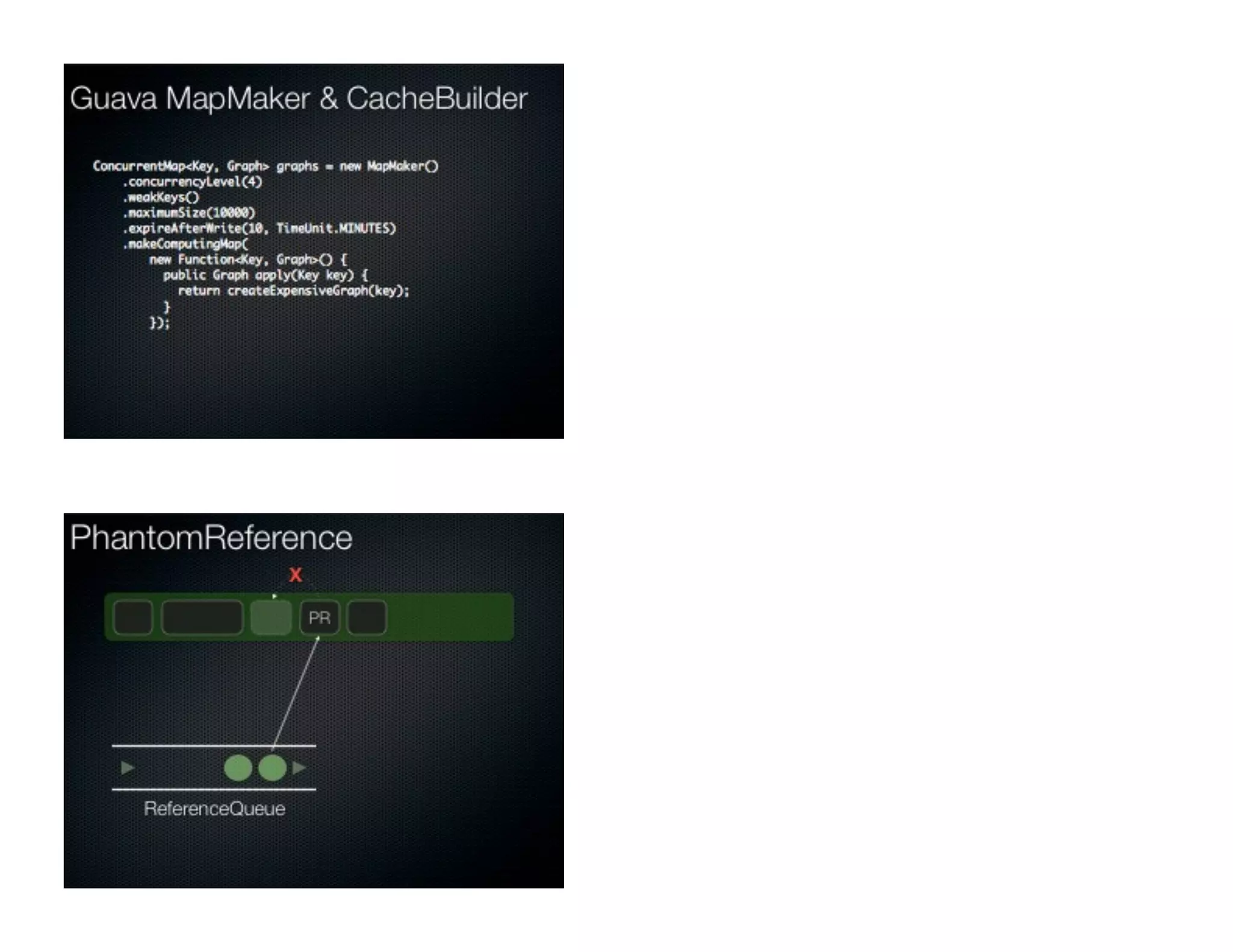
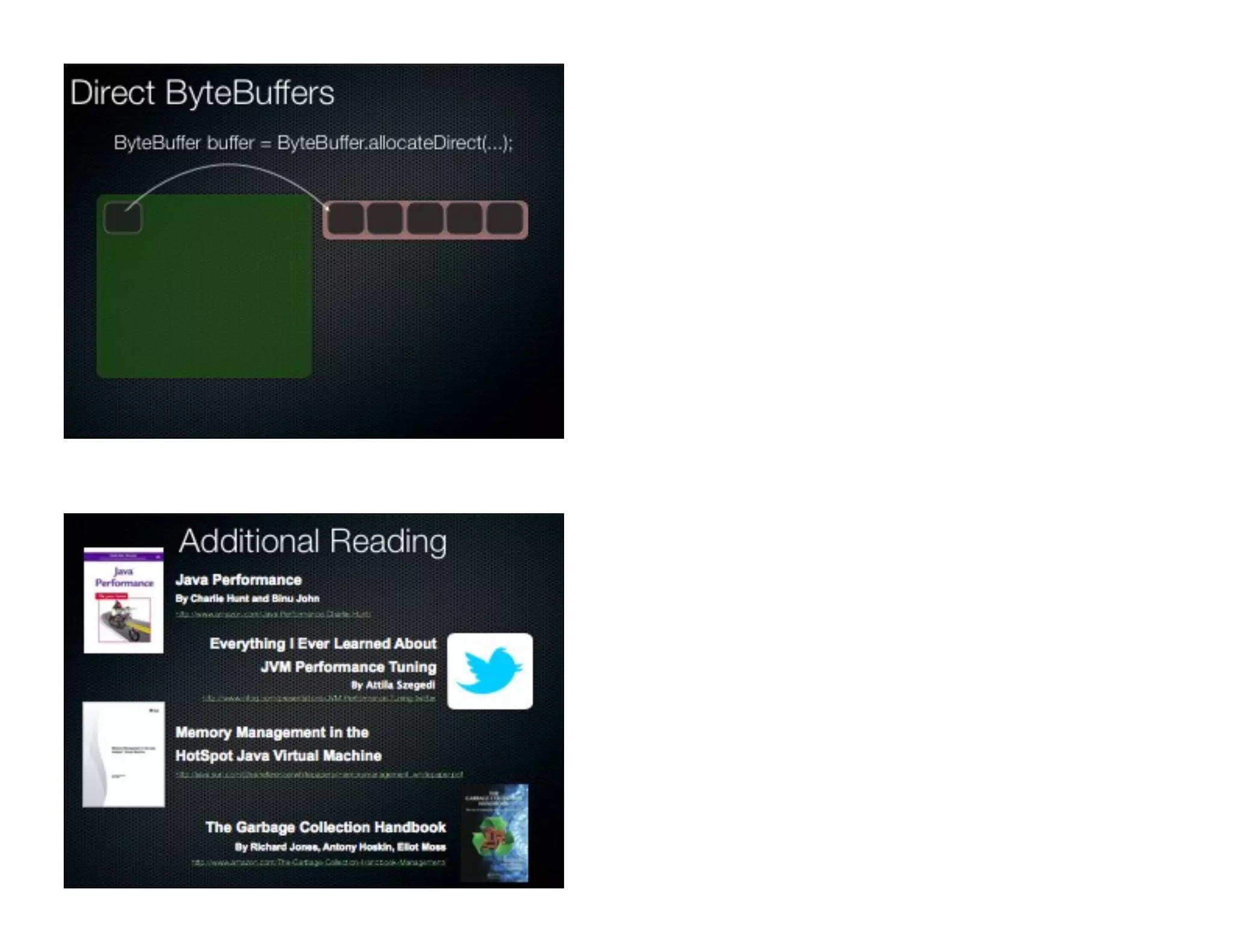
This document discusses garbage collection and automatic memory management in Java. It covers the basic strategies used in garbage collection like mark and sweep. It also discusses the different garbage collectors used in HotSpot like SerialGC, ParallelGC, ConcMarkSweepGC and G1. It provides an overview of garbage collection in J9 and JRockit as well. The document also touches on alternatives to garbage collection like weak and soft references.