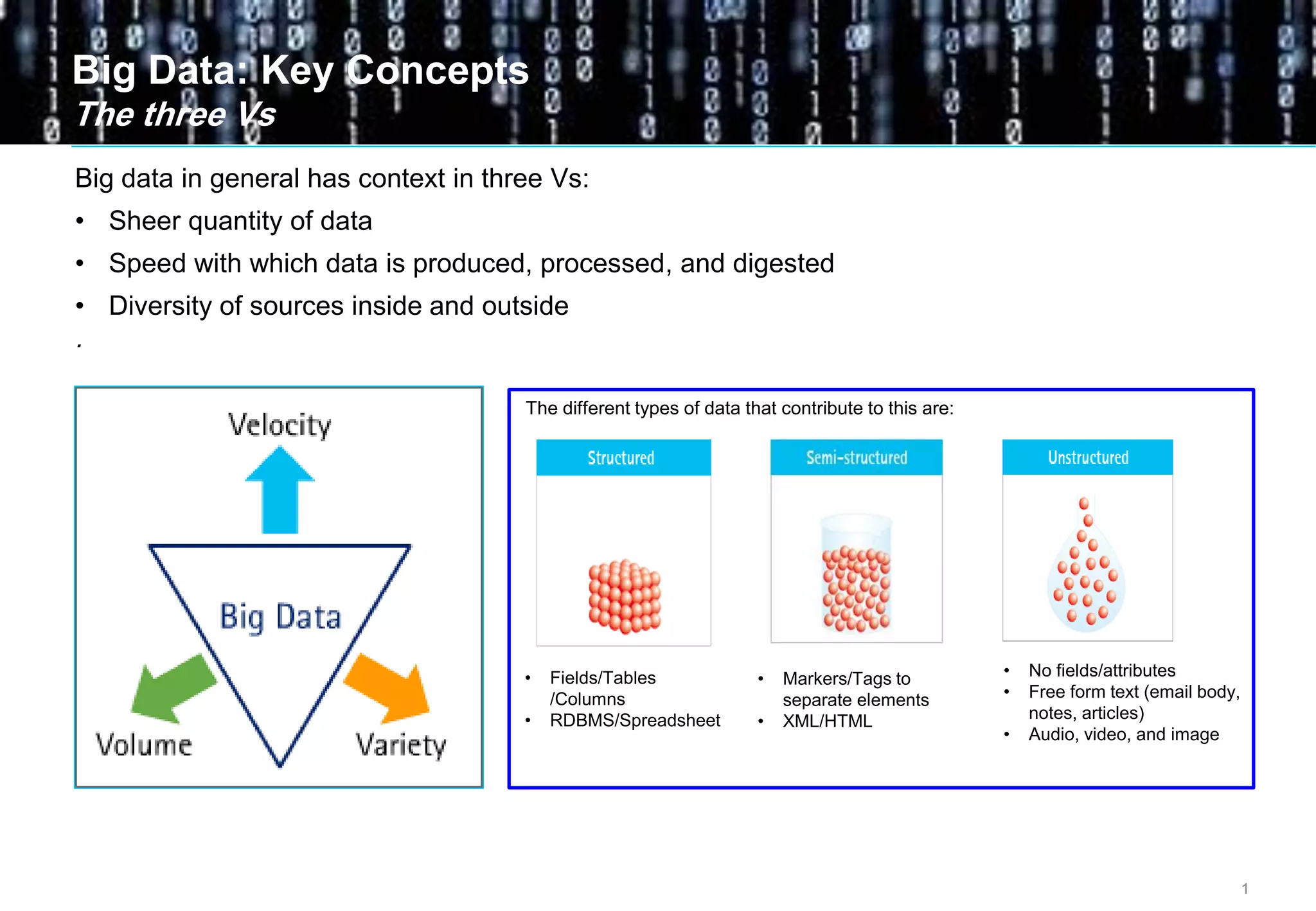
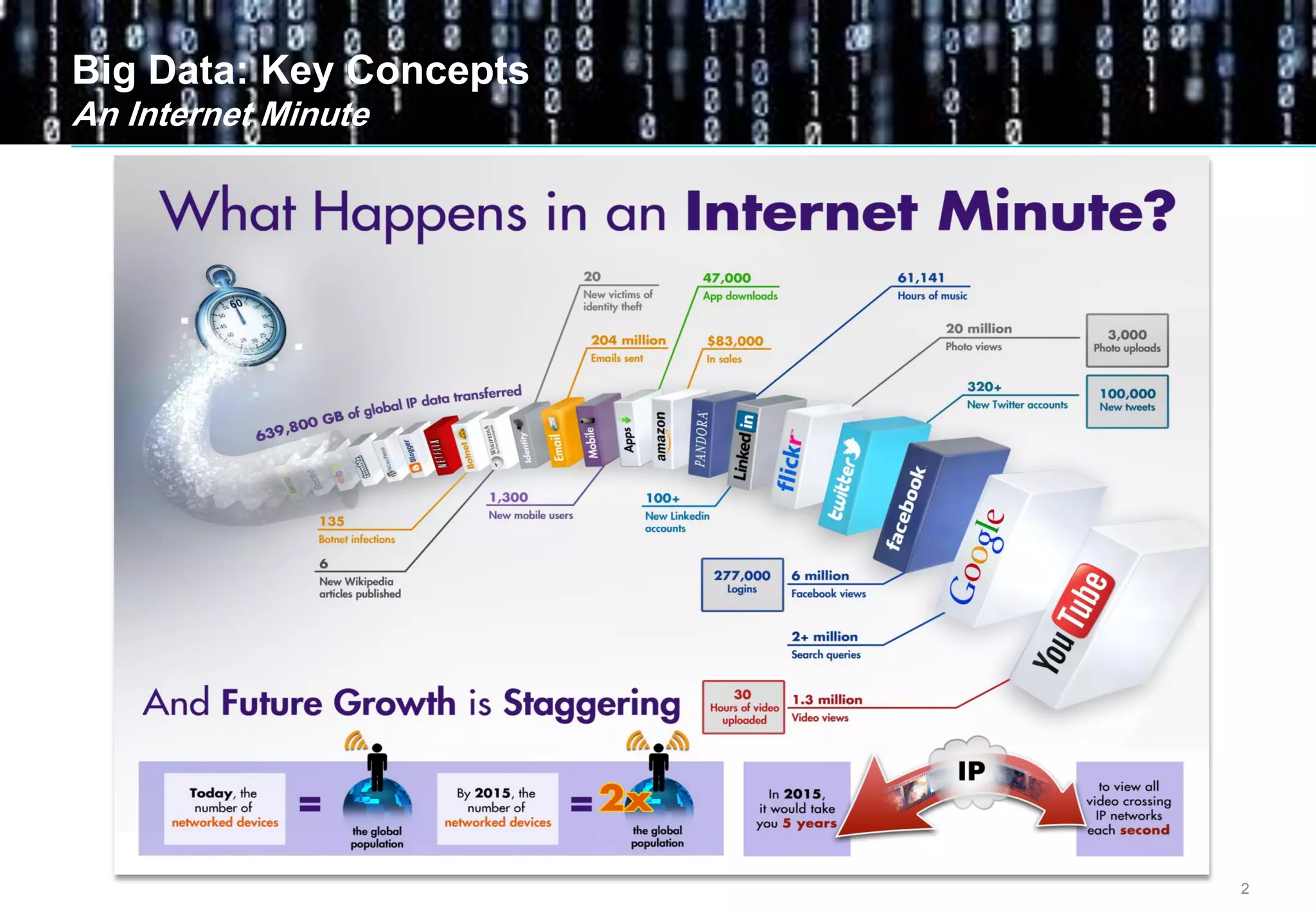
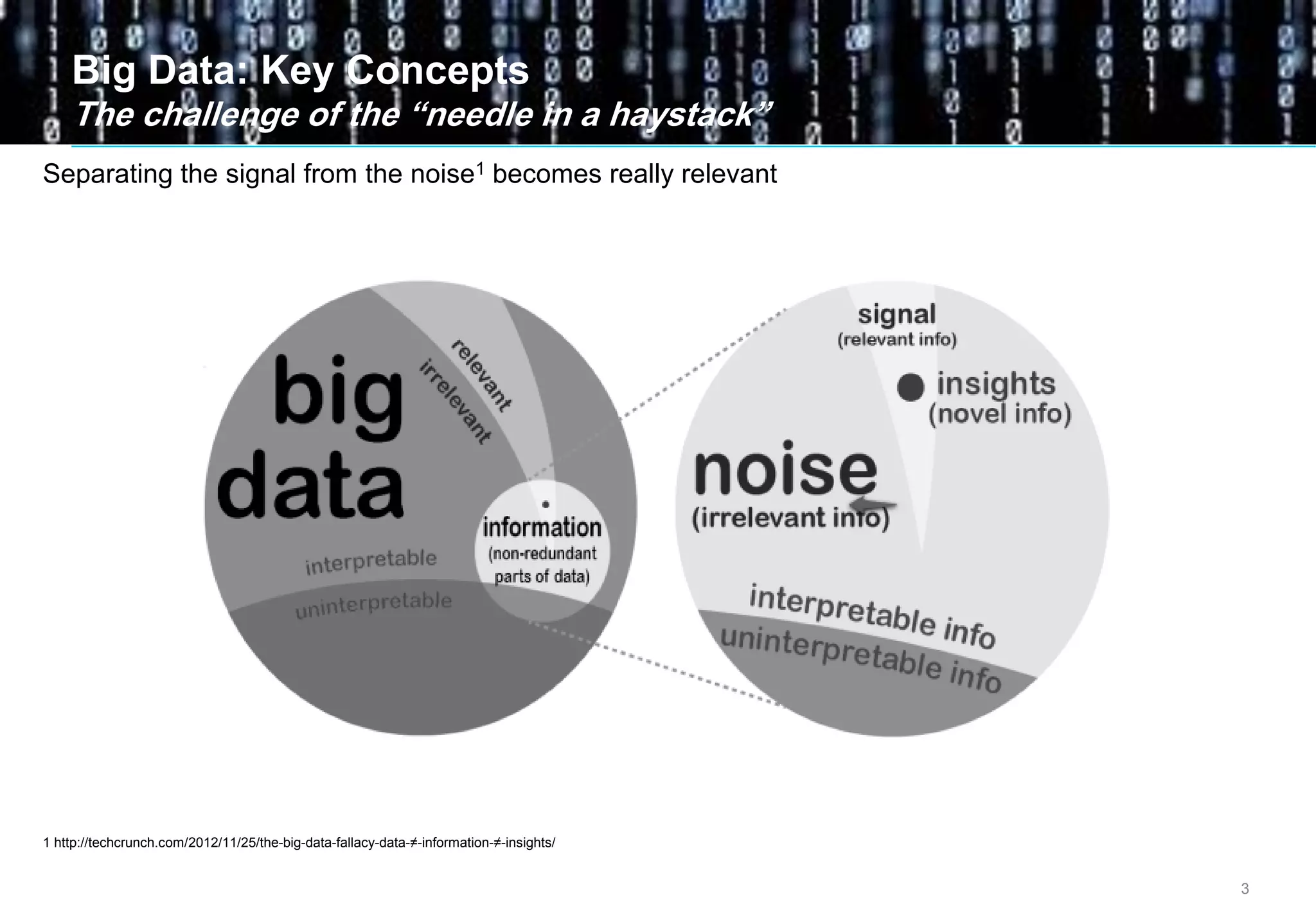
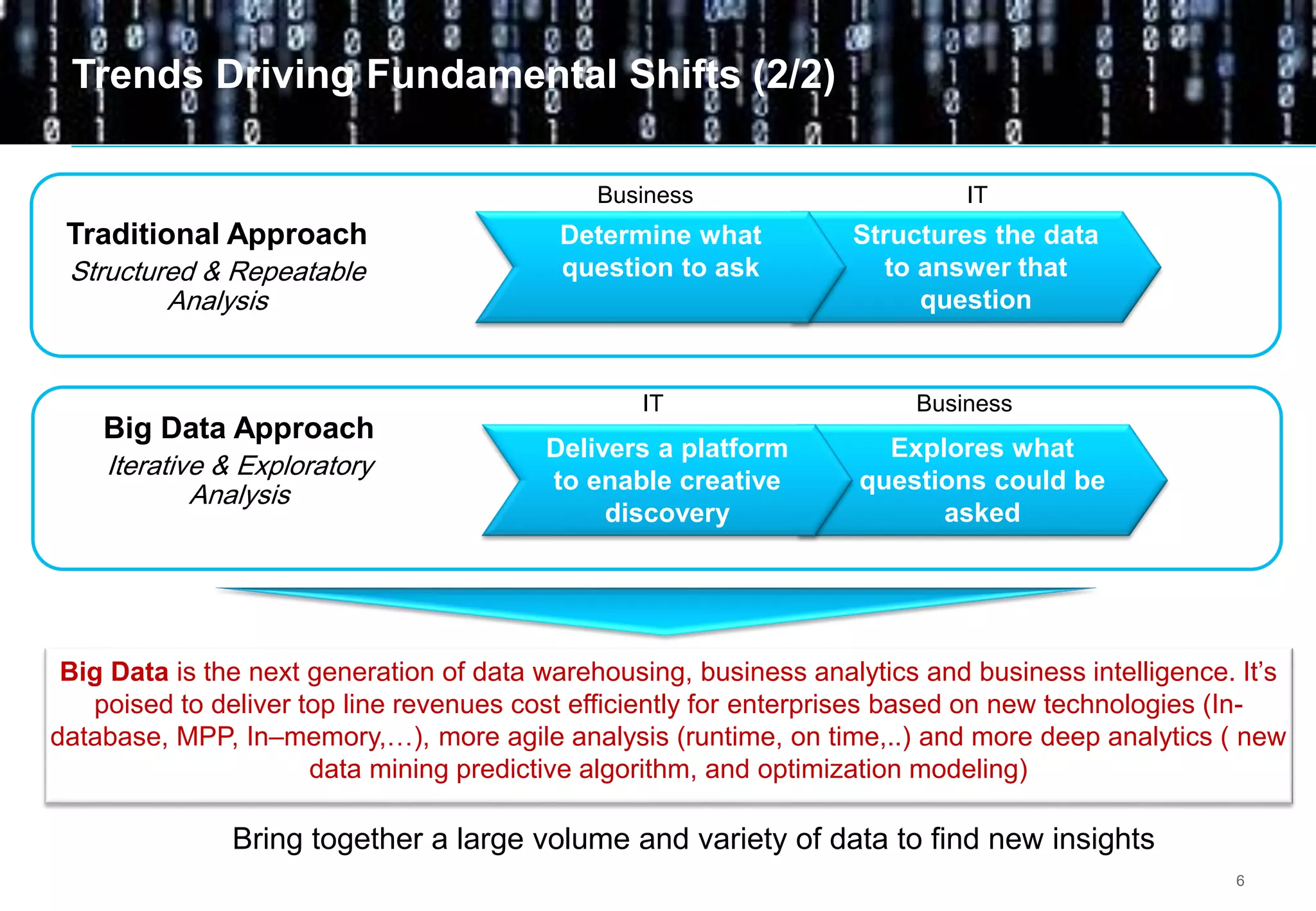
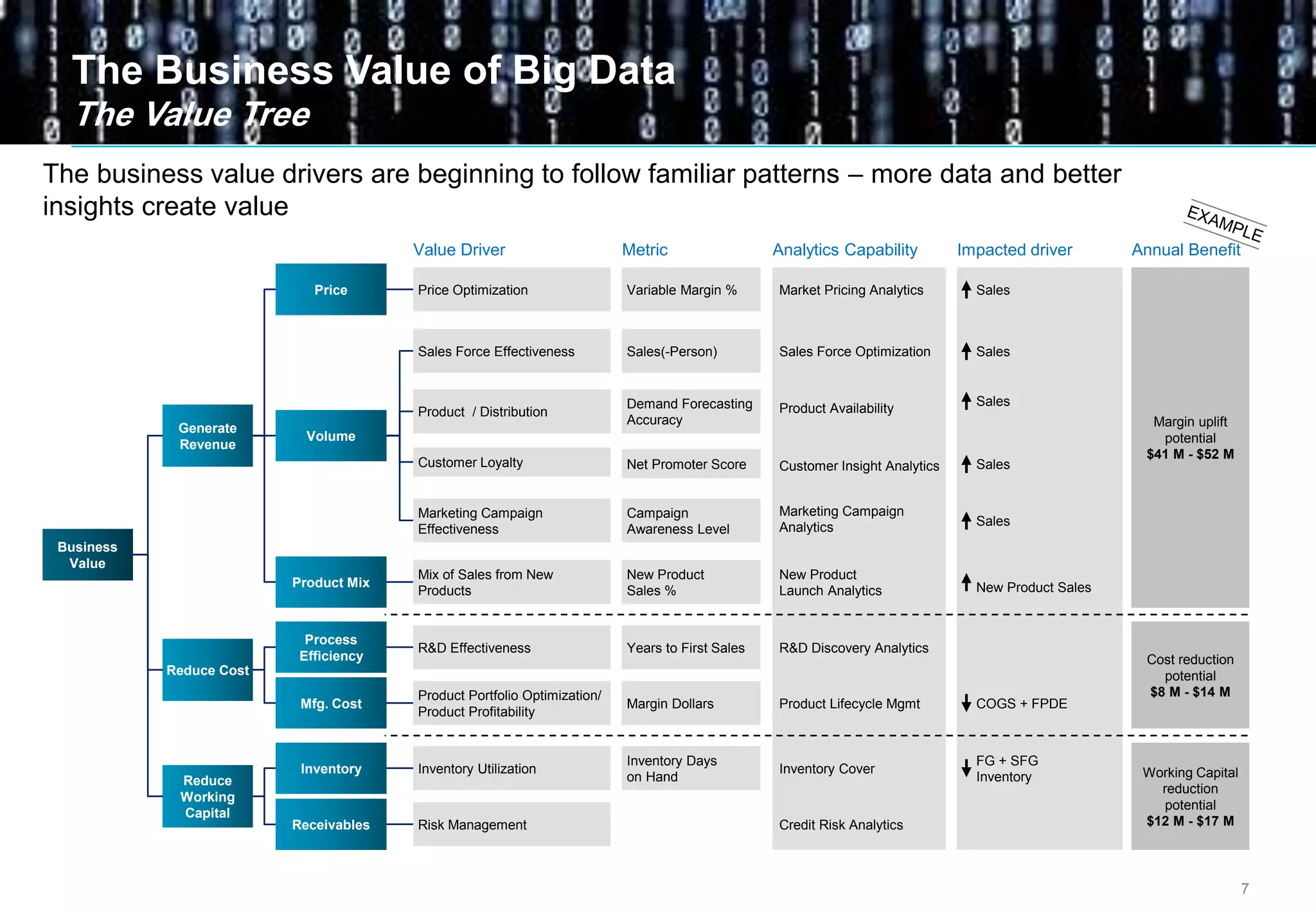
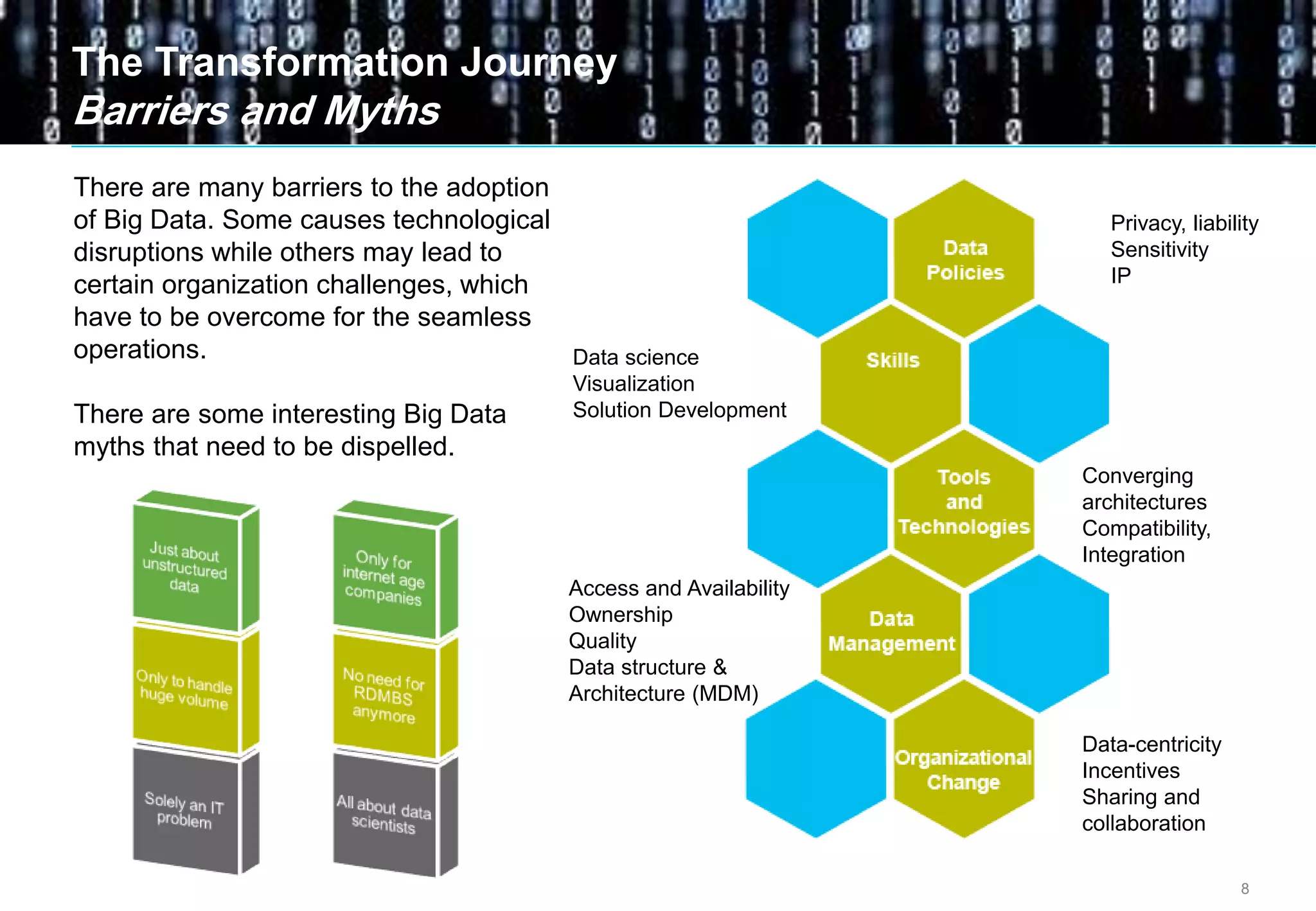
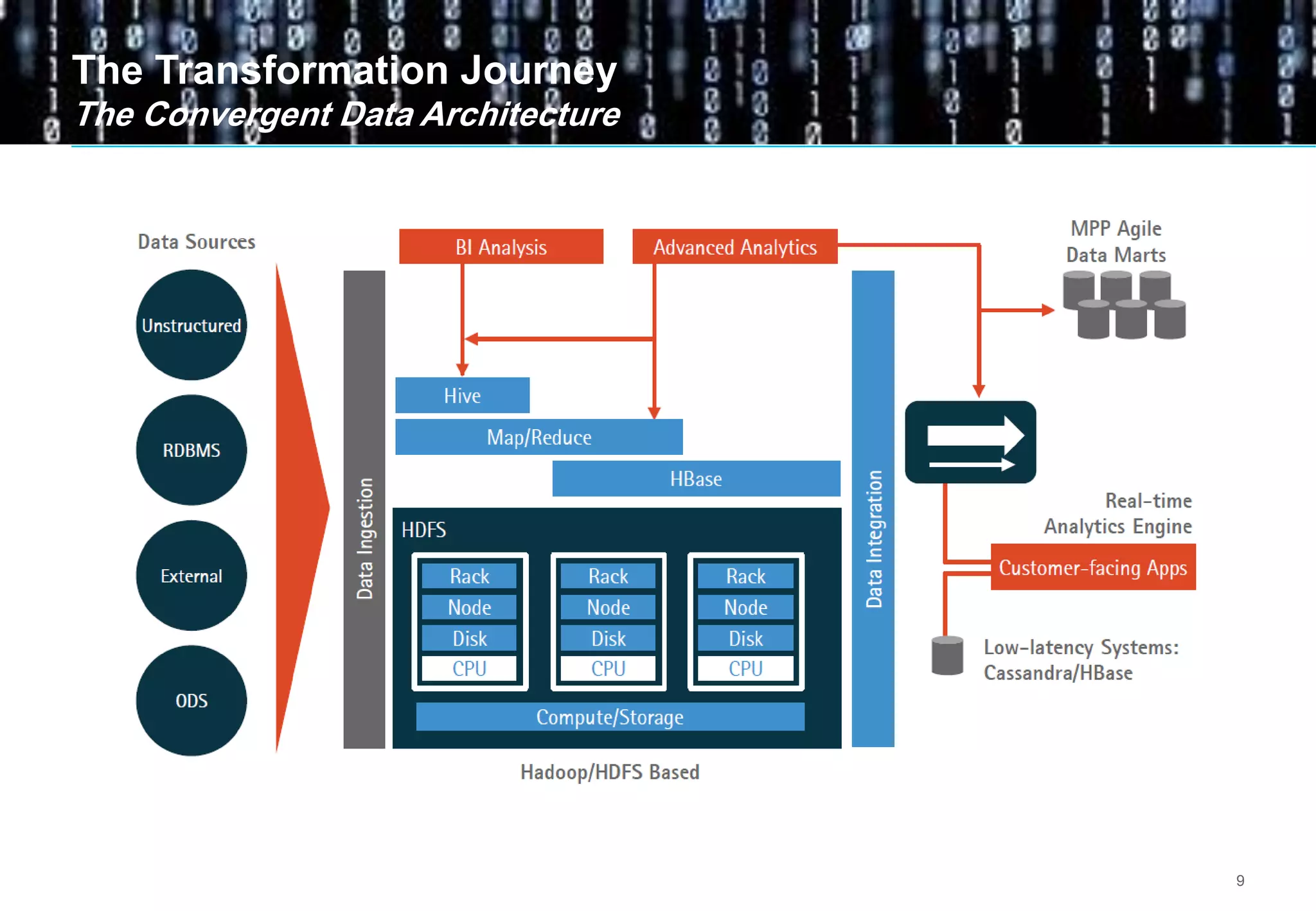
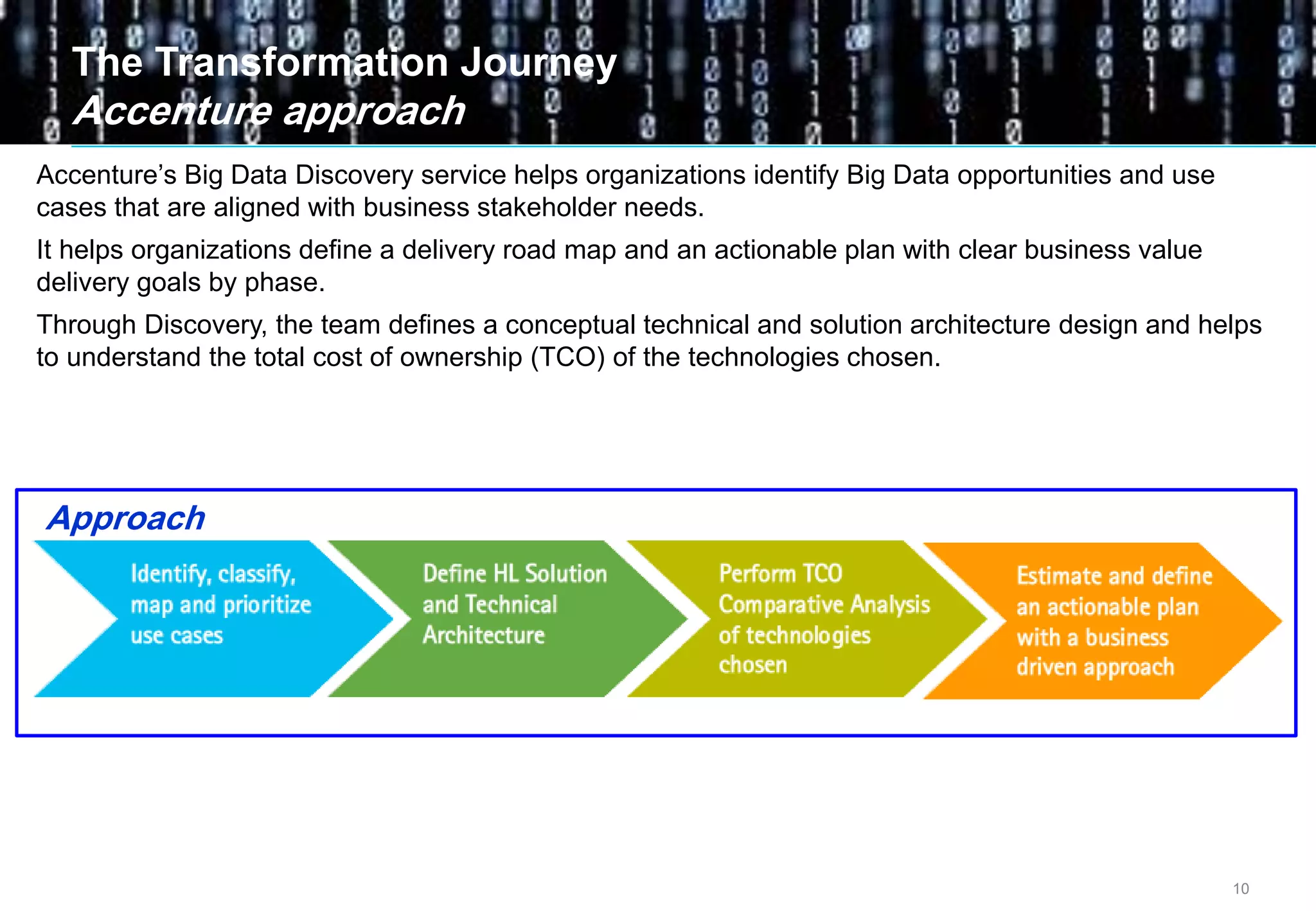
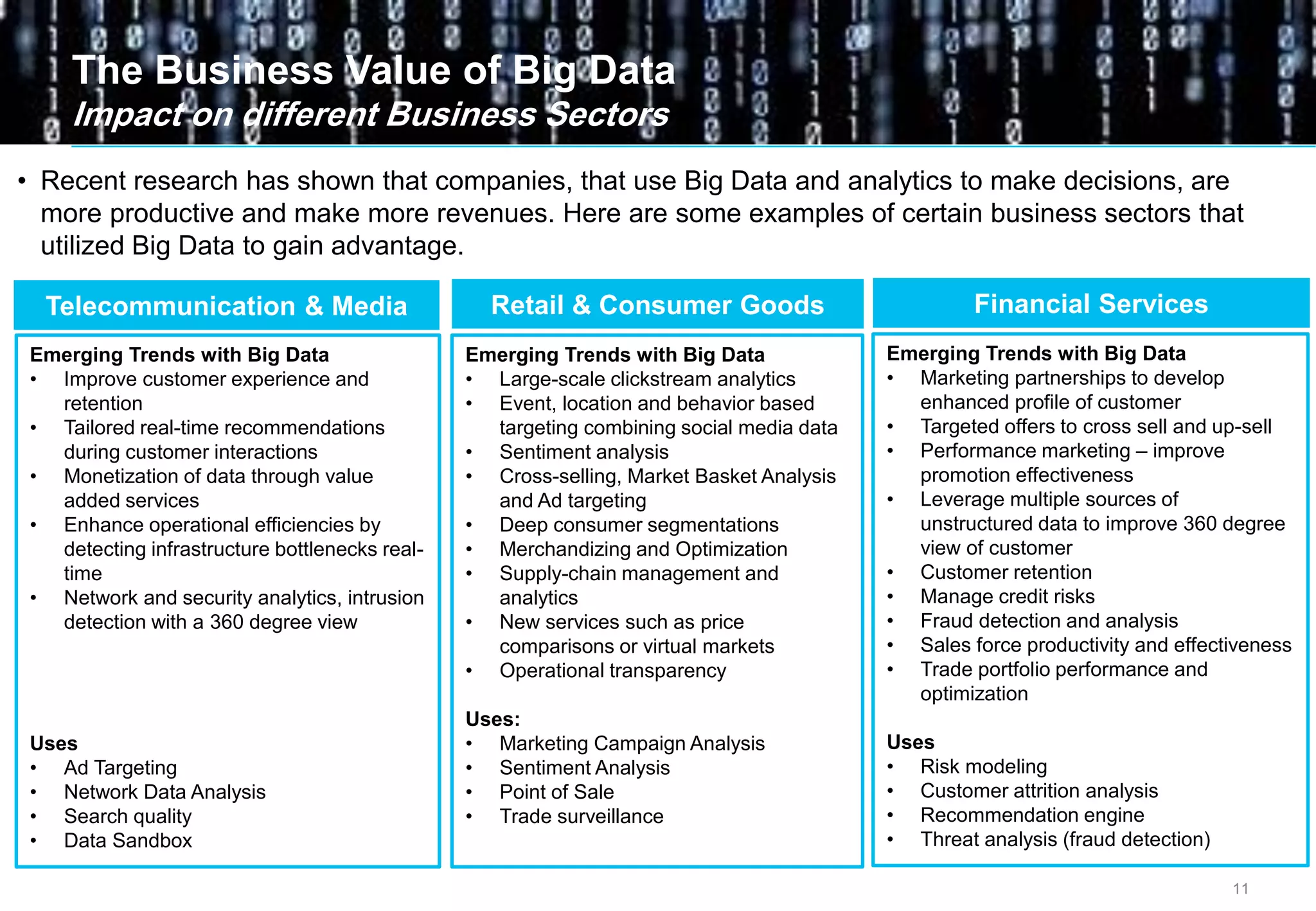
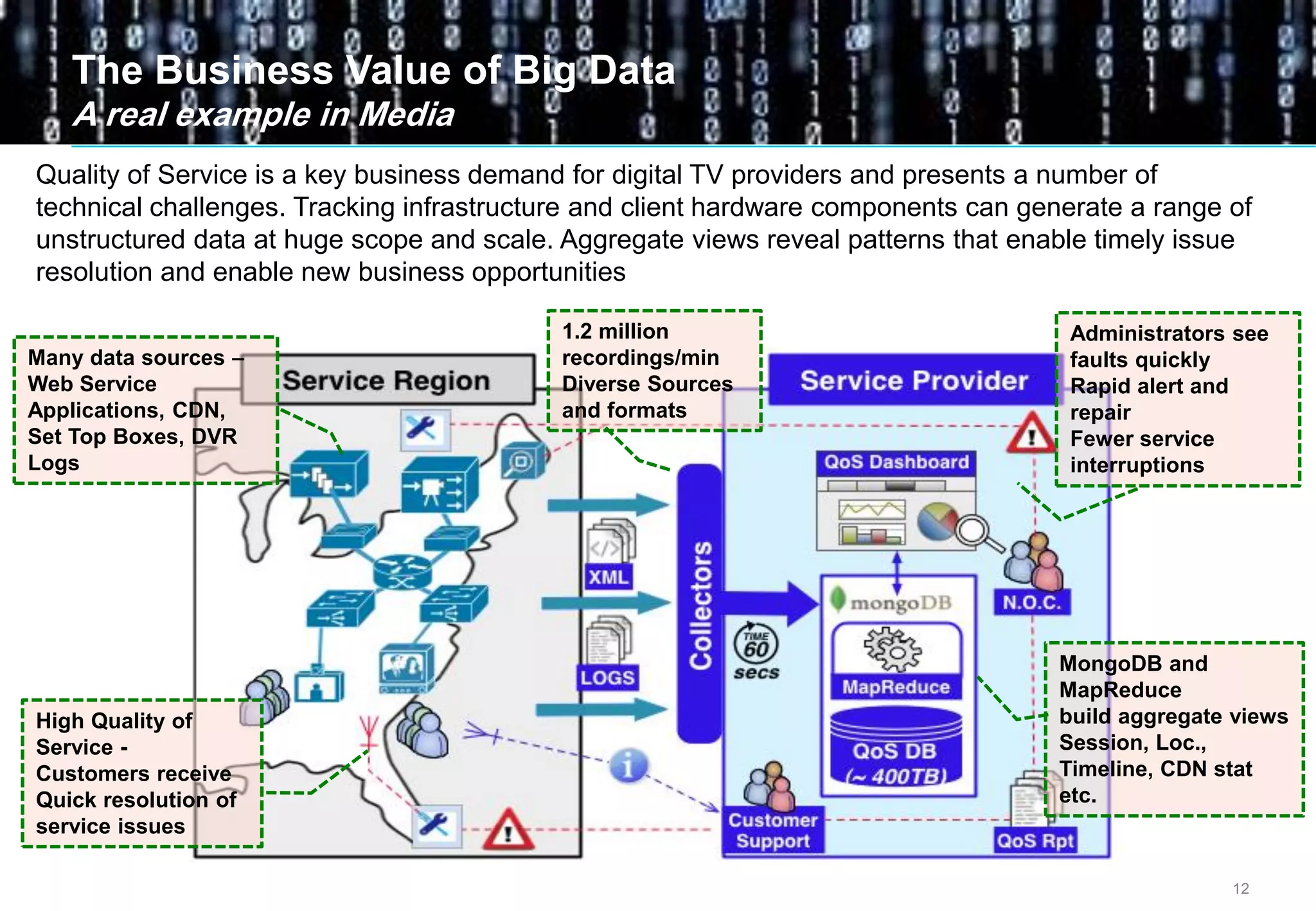
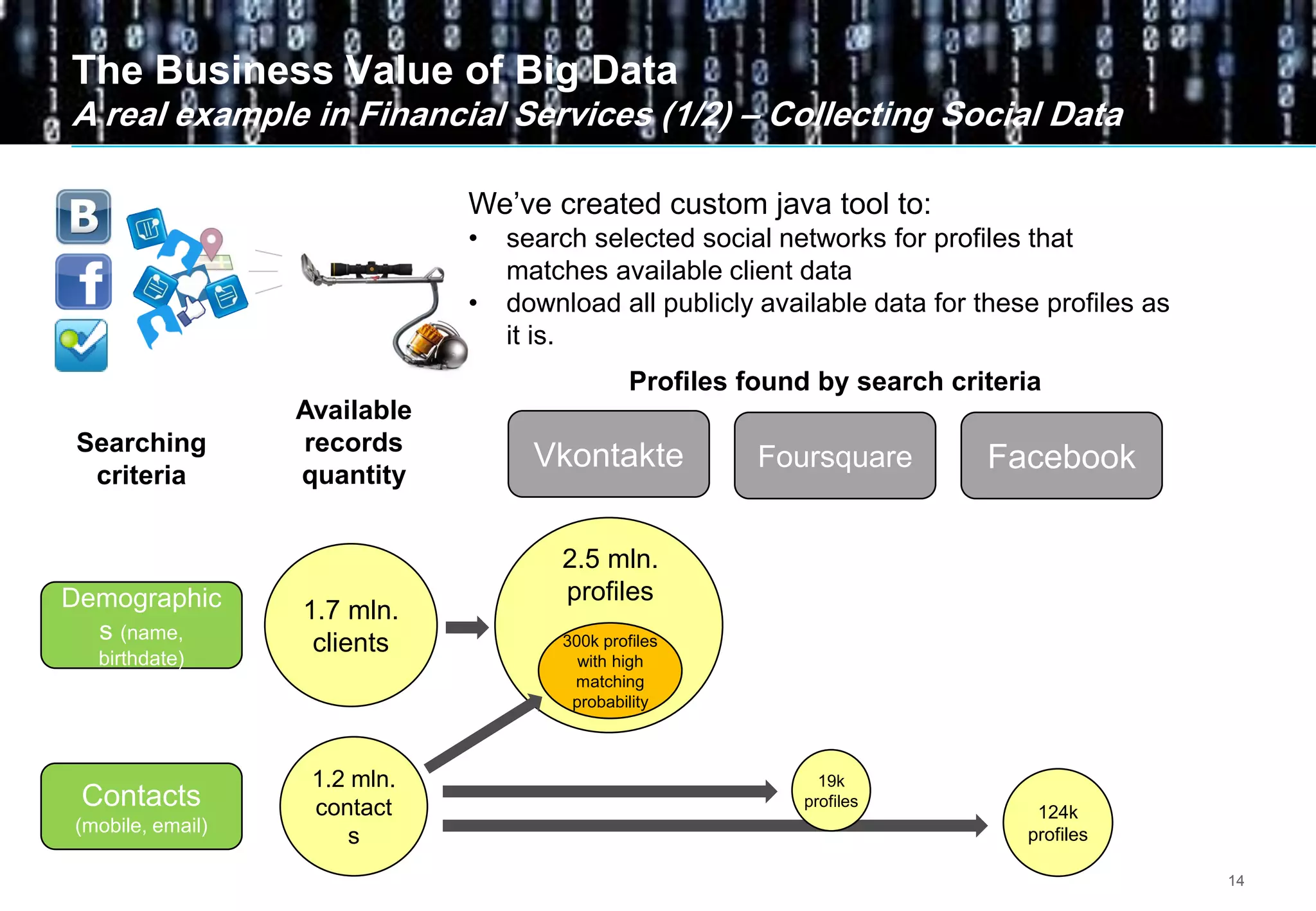
Big data comes from a variety of sources and in different formats. It is characterized by its volume, velocity, and variety. Organizations are using big data to gain business insights through analytics. This allows them to increase revenue, reduce costs, optimize processes, and manage risks. Examples of big data uses include marketing campaign analysis, customer segmentation, and fraud detection. Companies must overcome technological and organizational challenges to successfully leverage big data.