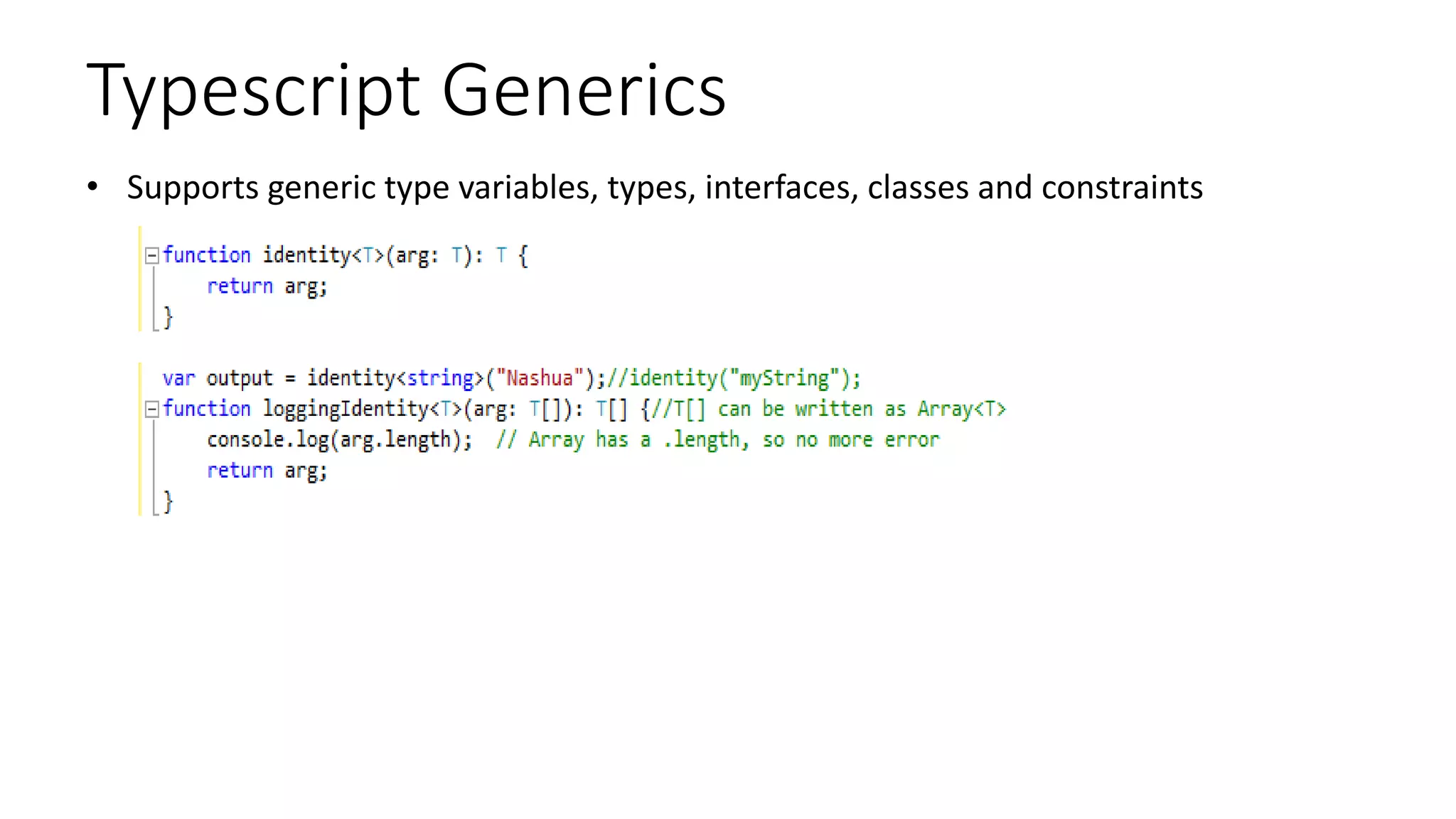
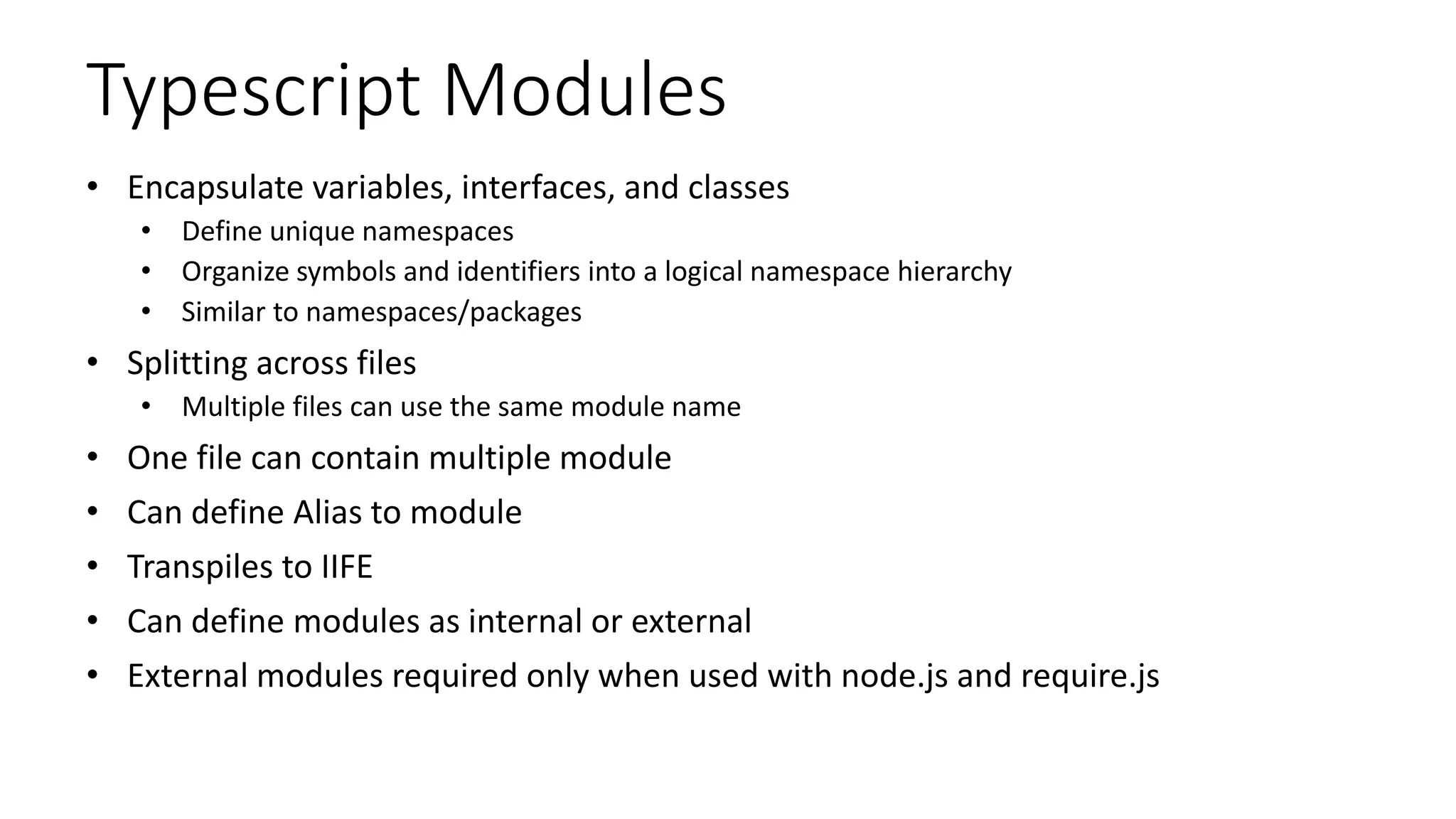
Udaiappa Ramachandran is a CTO at Akumina, Inc., specializing in cloud computing, IoT, and SharePoint Online, and is involved in various technology communities. The document outlines the features, benefits, and usage of TypeScript, emphasizing its static typing, object-oriented design, and compatibility with JavaScript. Key topics discussed include basic types, functions, classes, interfaces, and modules within TypeScript.








![Tyepscript Annotation
• Type Annotation
• var [identifier]:[type annotation]=value
• var [identifier]:[type annotation];
• var [identifier]=value;
• Example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/typescript-160223033201/75/TypeScript-10-2048.jpg)
![Typescript Functions
• Optional Parameters using ?
• function getAverage(a: number, b: number, c?: number): void { }
• Default parameters using =value
• function concatenate(items: string[], separator = ",", beginAt = 0, endAt = items.length) :void{ }
• Rest parameter using …
• Only one allowed, it must appear last in the parameter list and must be an array type
• function getSum(...a: number[]): number {
• var t = 0;a.forEach(p=>t=t+ p);
• return t;
• }
• var result = getSum(1, 2, 3, 4);
• Overloads
• Overloads in typescript cannot have own implementation but decorate a single implementation
• function getSum(a: string, b: string, c: string): number;
• function getSum(a: number, b: number, c: number): number;
• function getSum(a: any, b: any, c: any): number {
• // implementation signature
• return parseInt(a, 10) + parseInt(b, 10) + parseInt(c, 10);
• }
• Arrow function
• var getSum: (a: number, b: number) => number =(x, y) => (x + y);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/typescript-160223033201/75/TypeScript-11-2048.jpg)