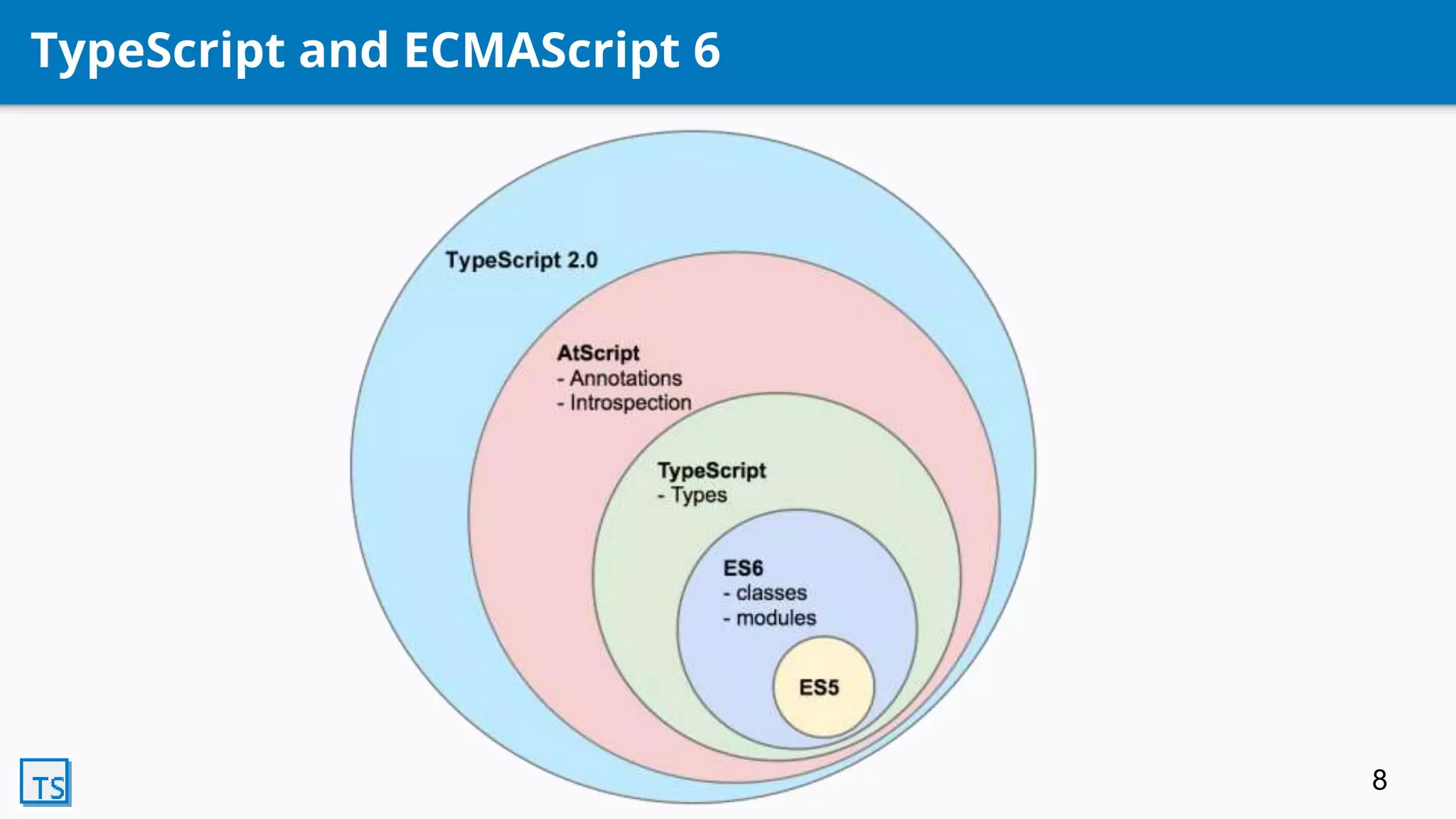
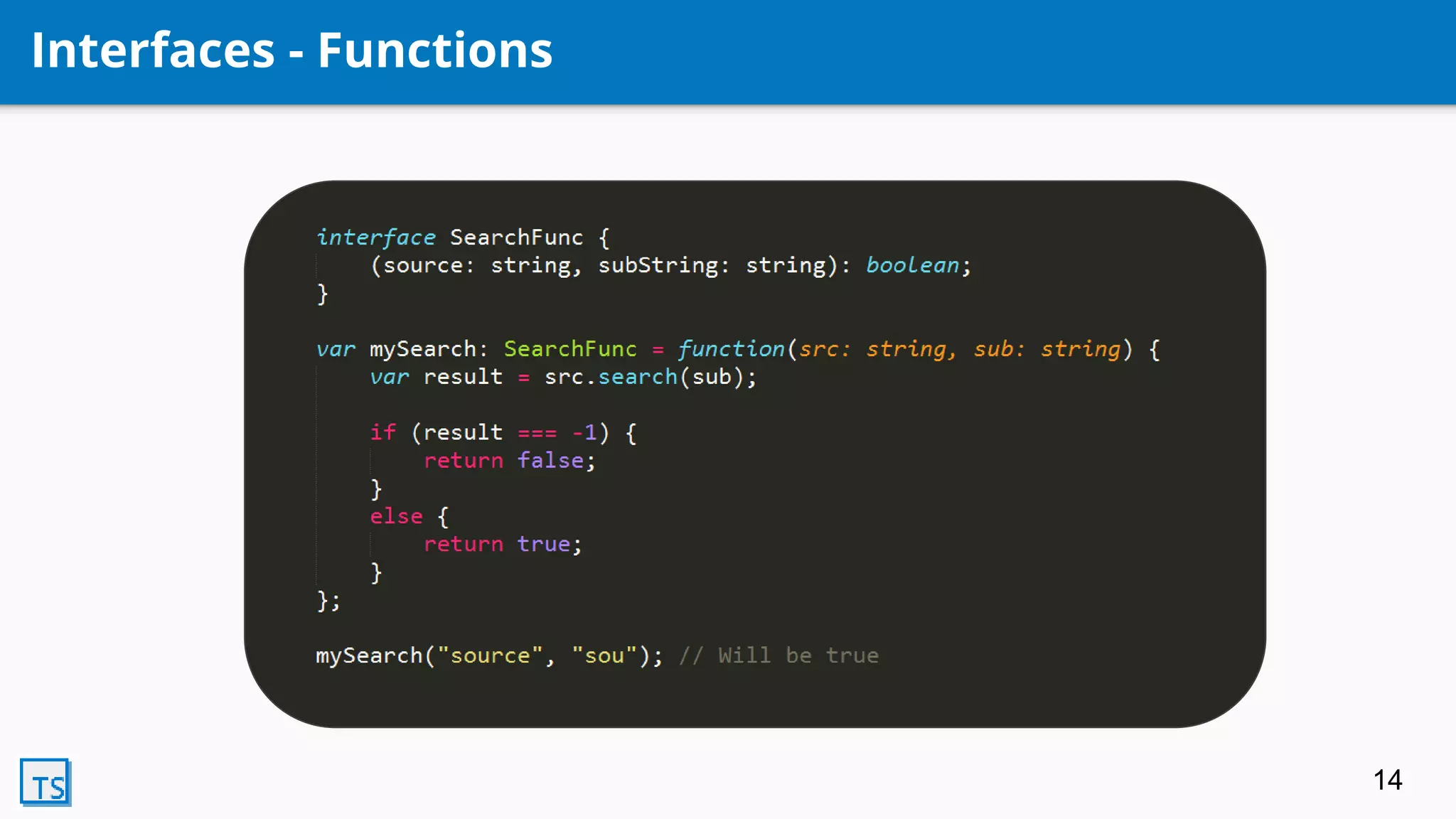
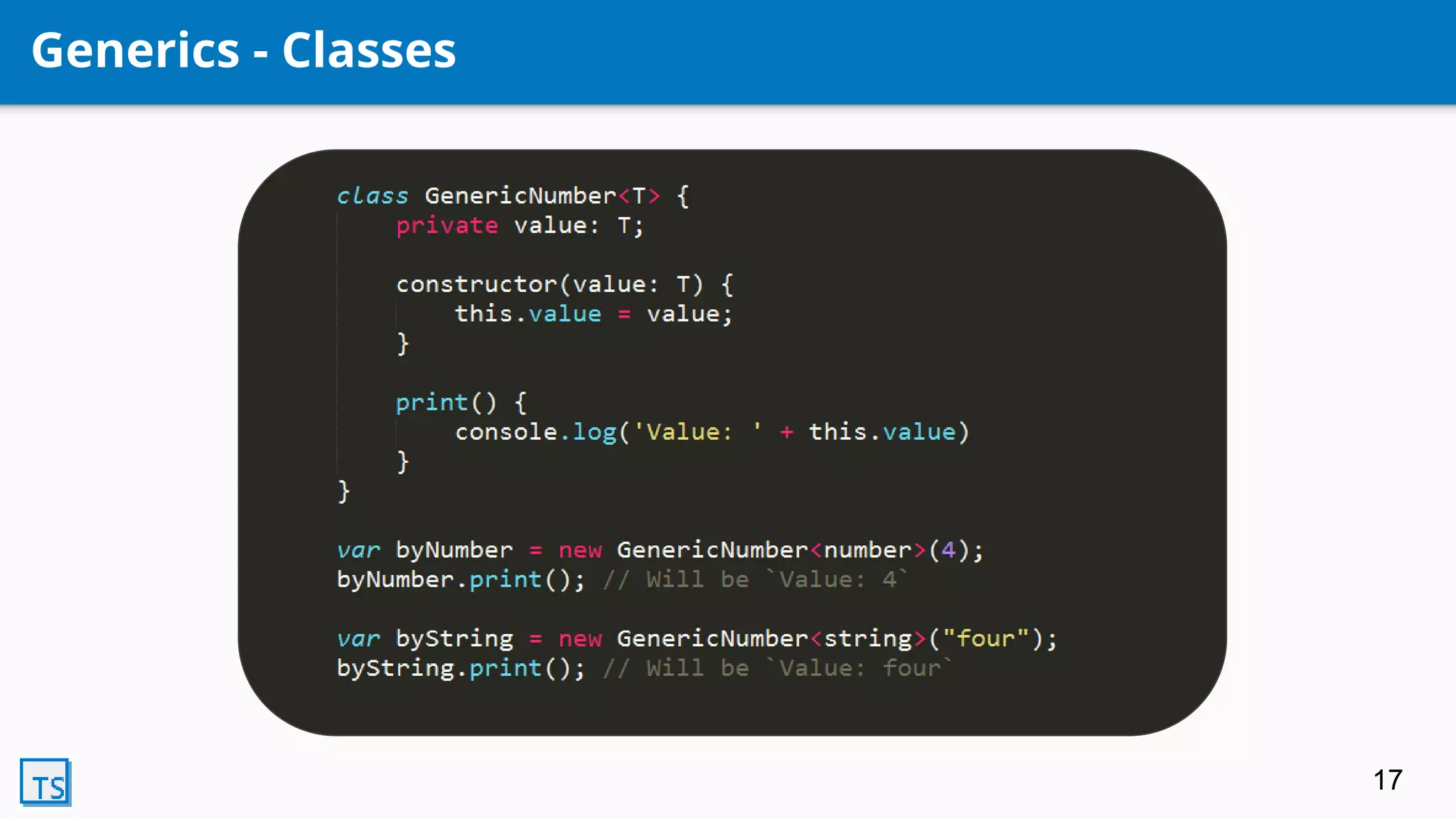
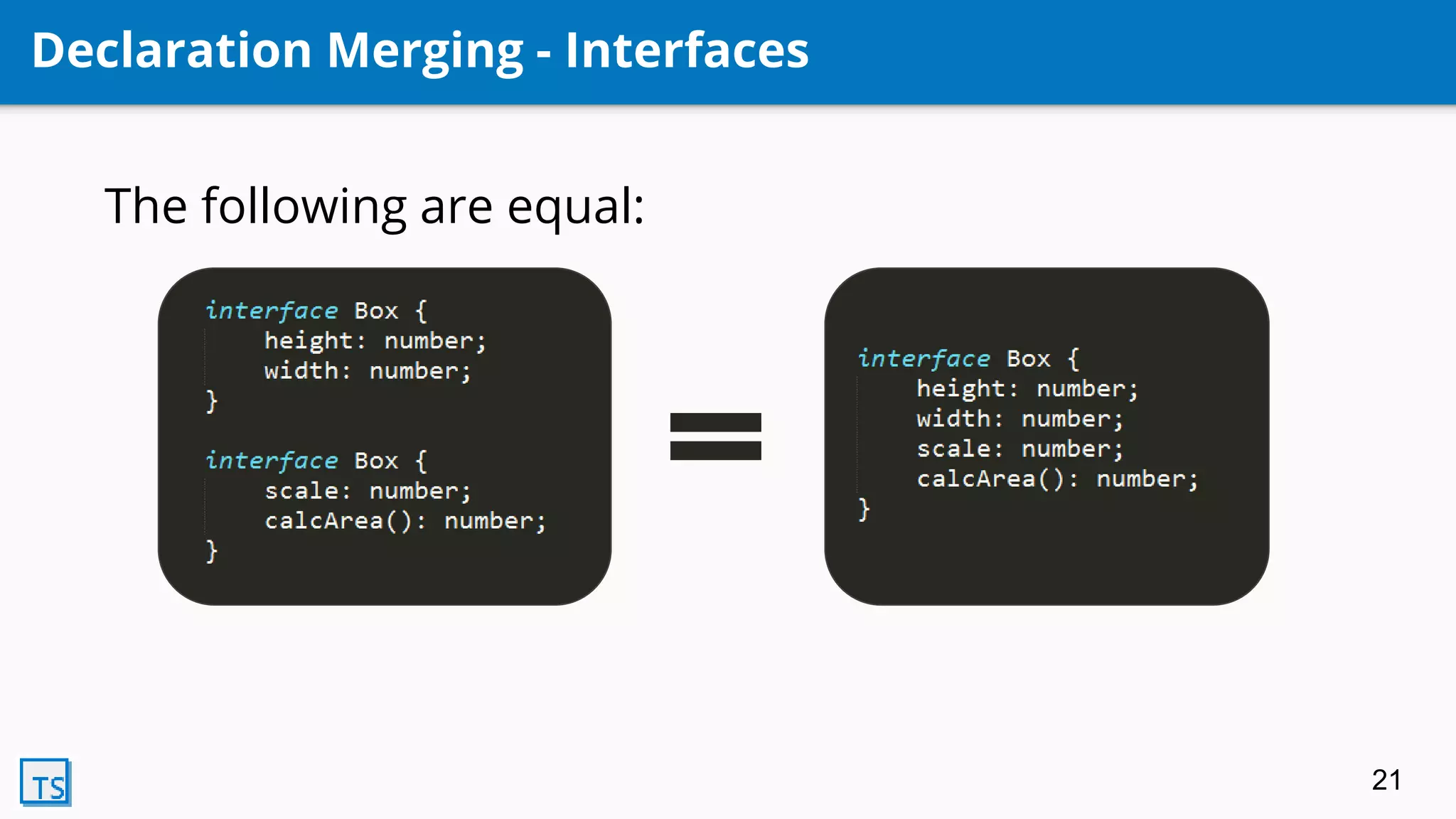
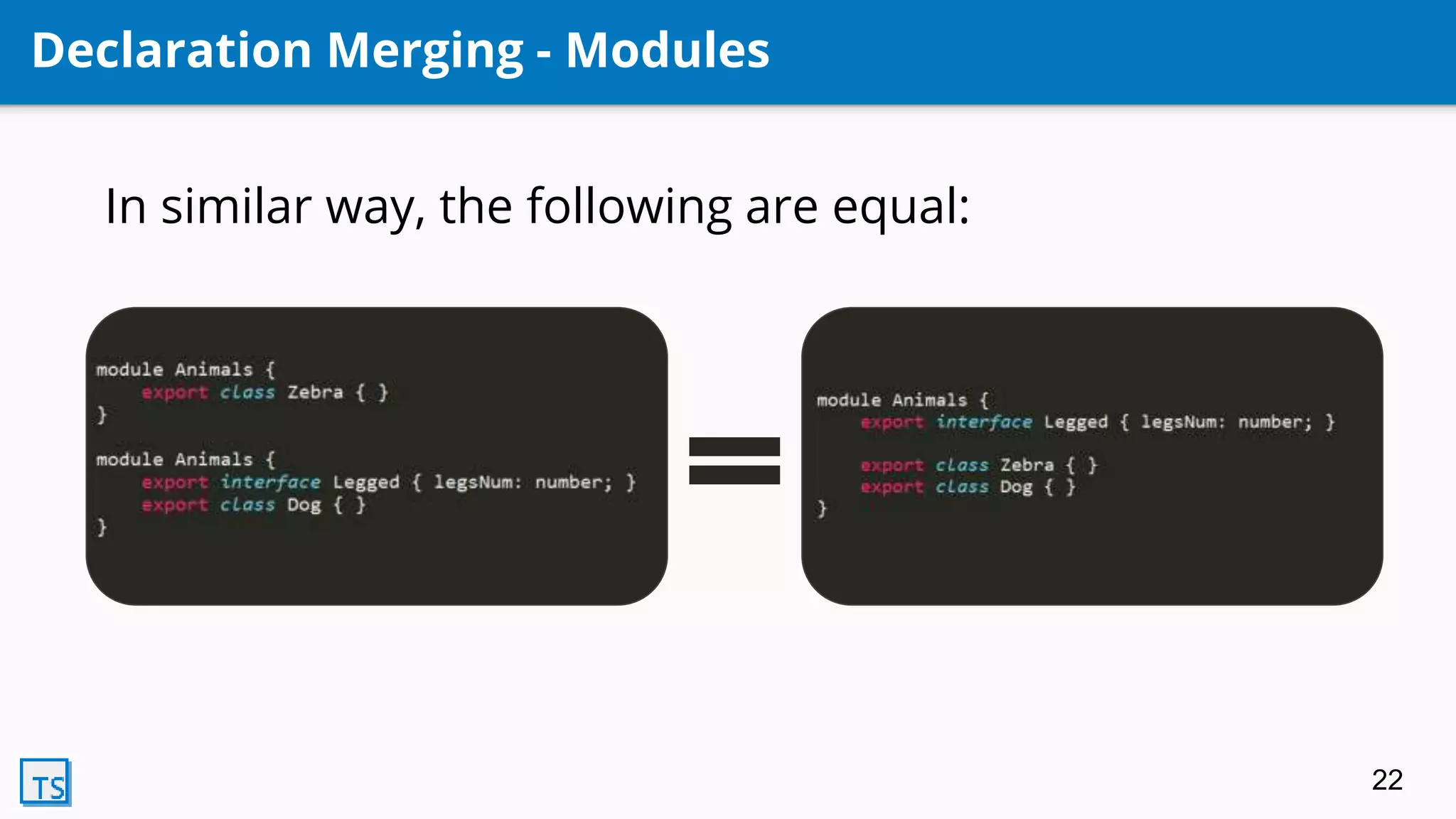
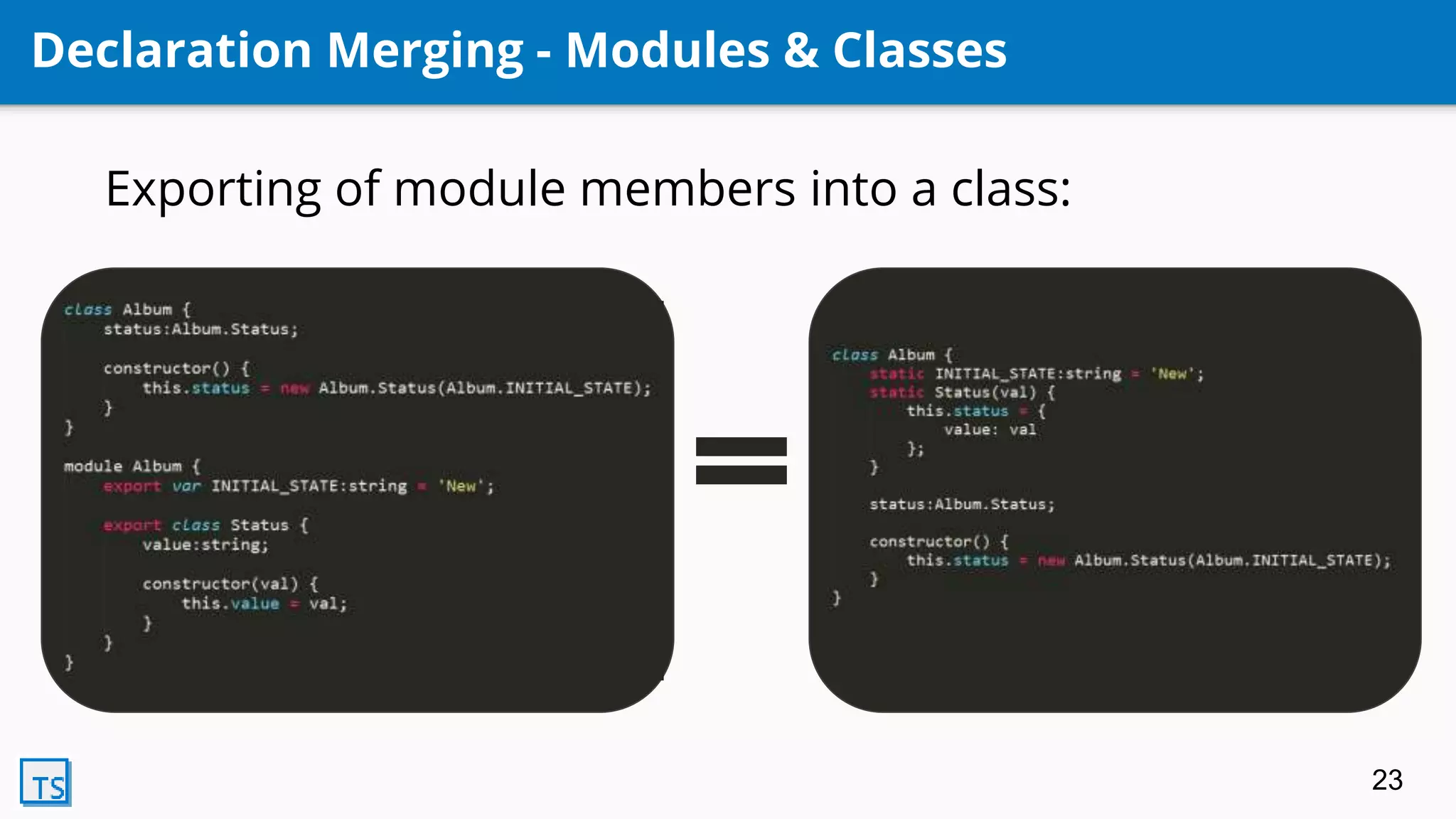
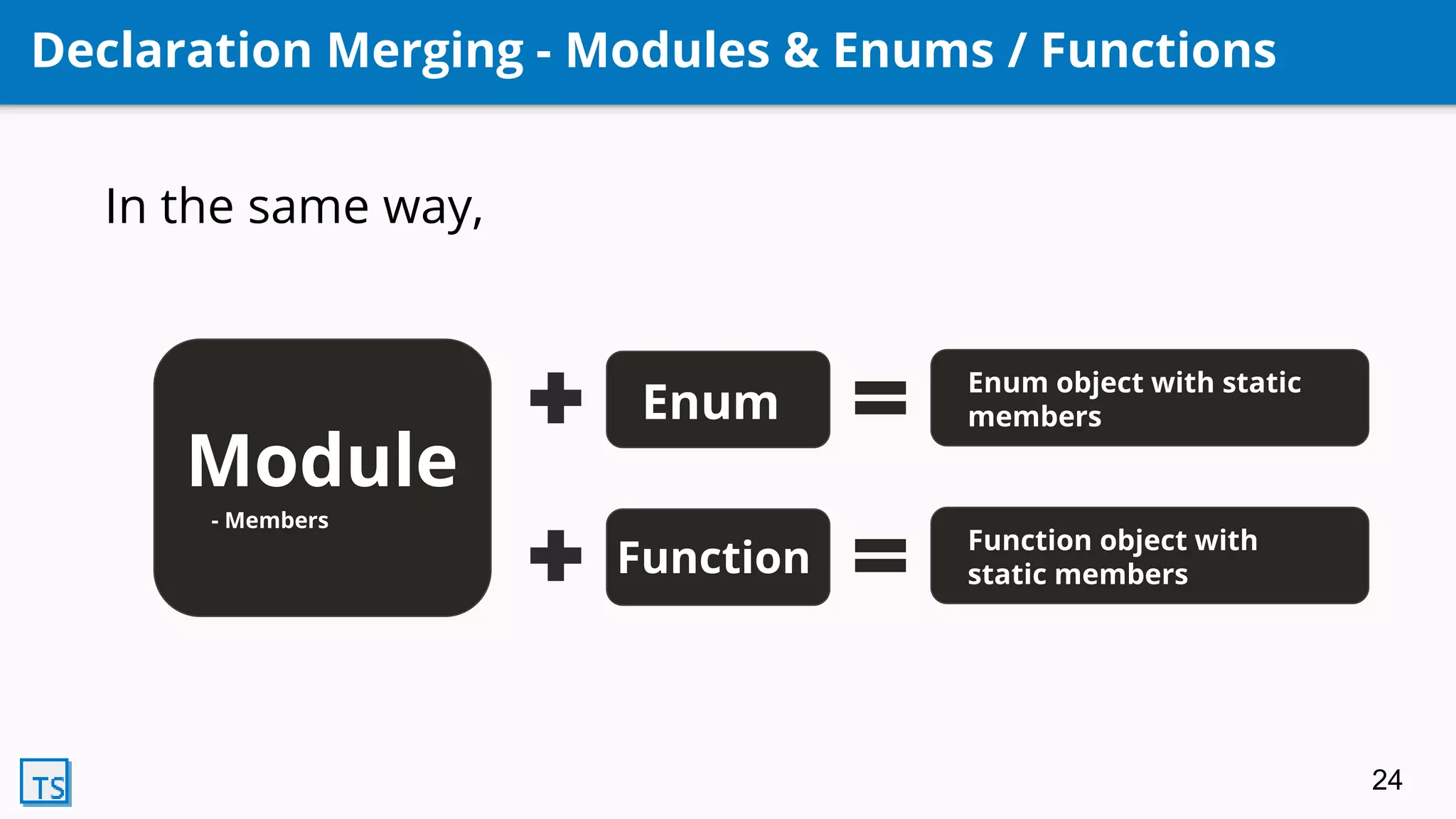
TypeScript is a superset of JavaScript that adds optional static typing and class-based object-oriented programming. It allows for code completion, type annotations, and helps support AngularJS 2.0. Developed by Microsoft in 2010, it transpiles code into pure JavaScript. Its features include classes, modules, interfaces, generics, mixins, and declaration merging, providing syntax checking and preparing code for ES6 support.