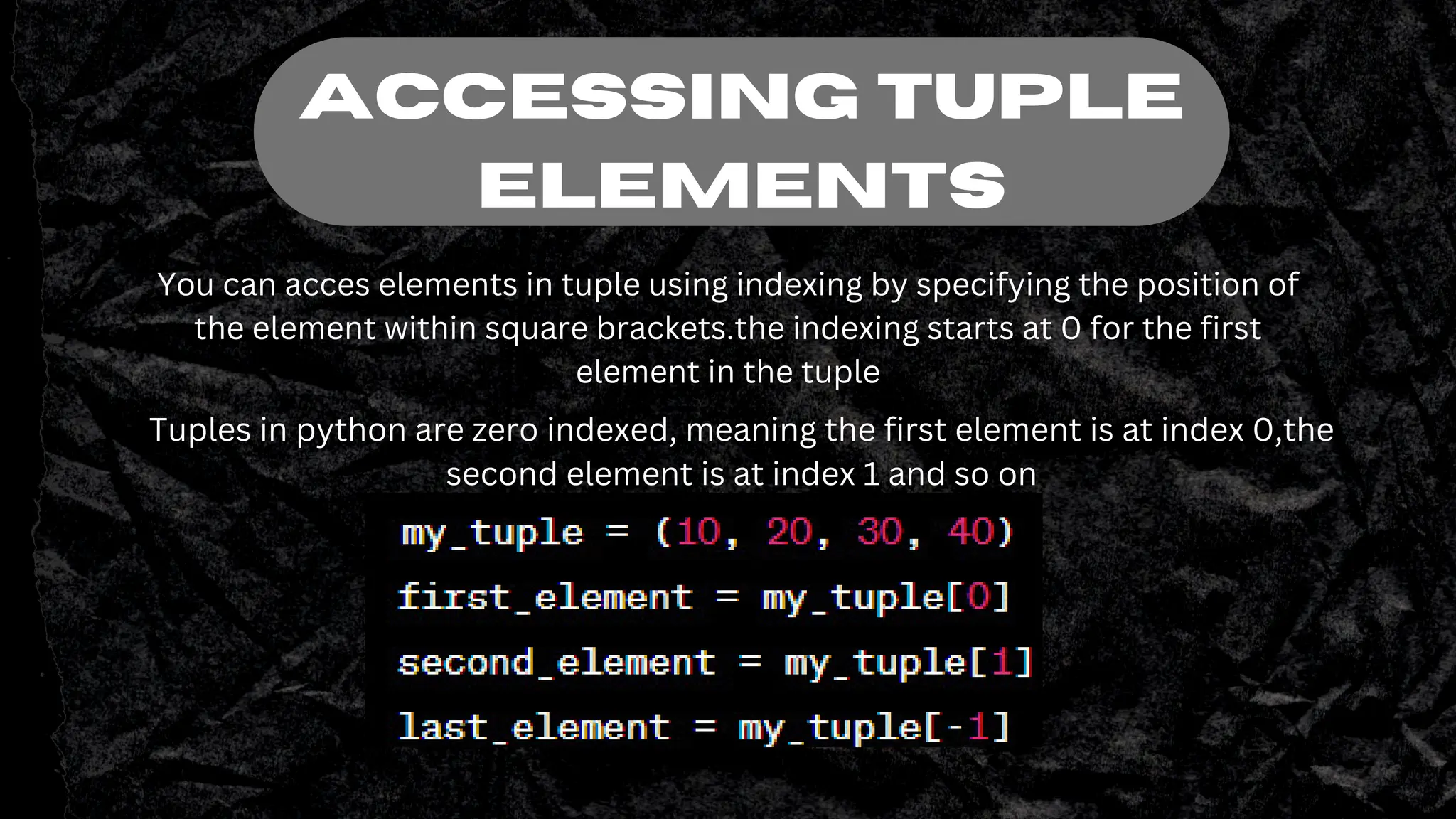
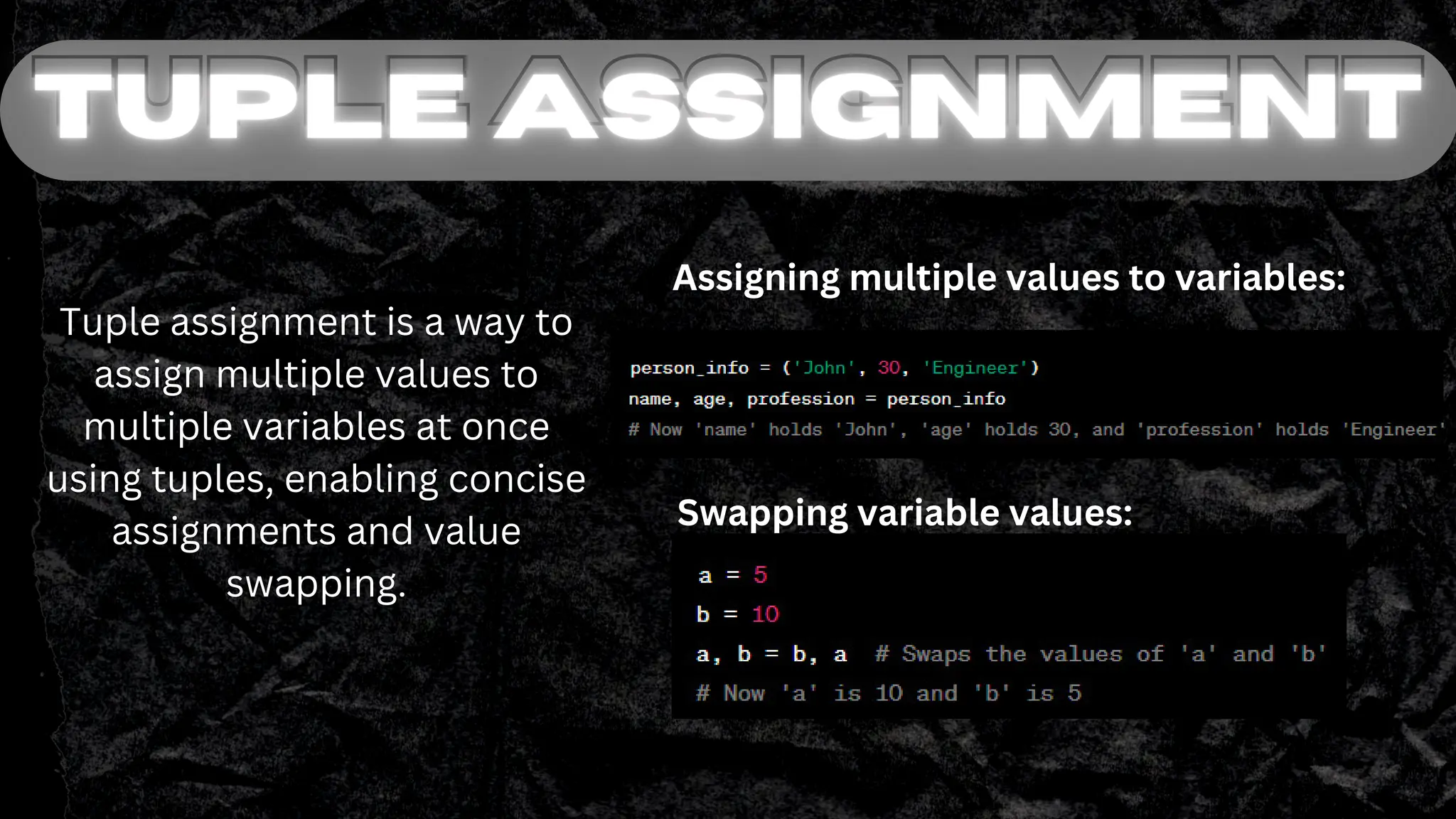
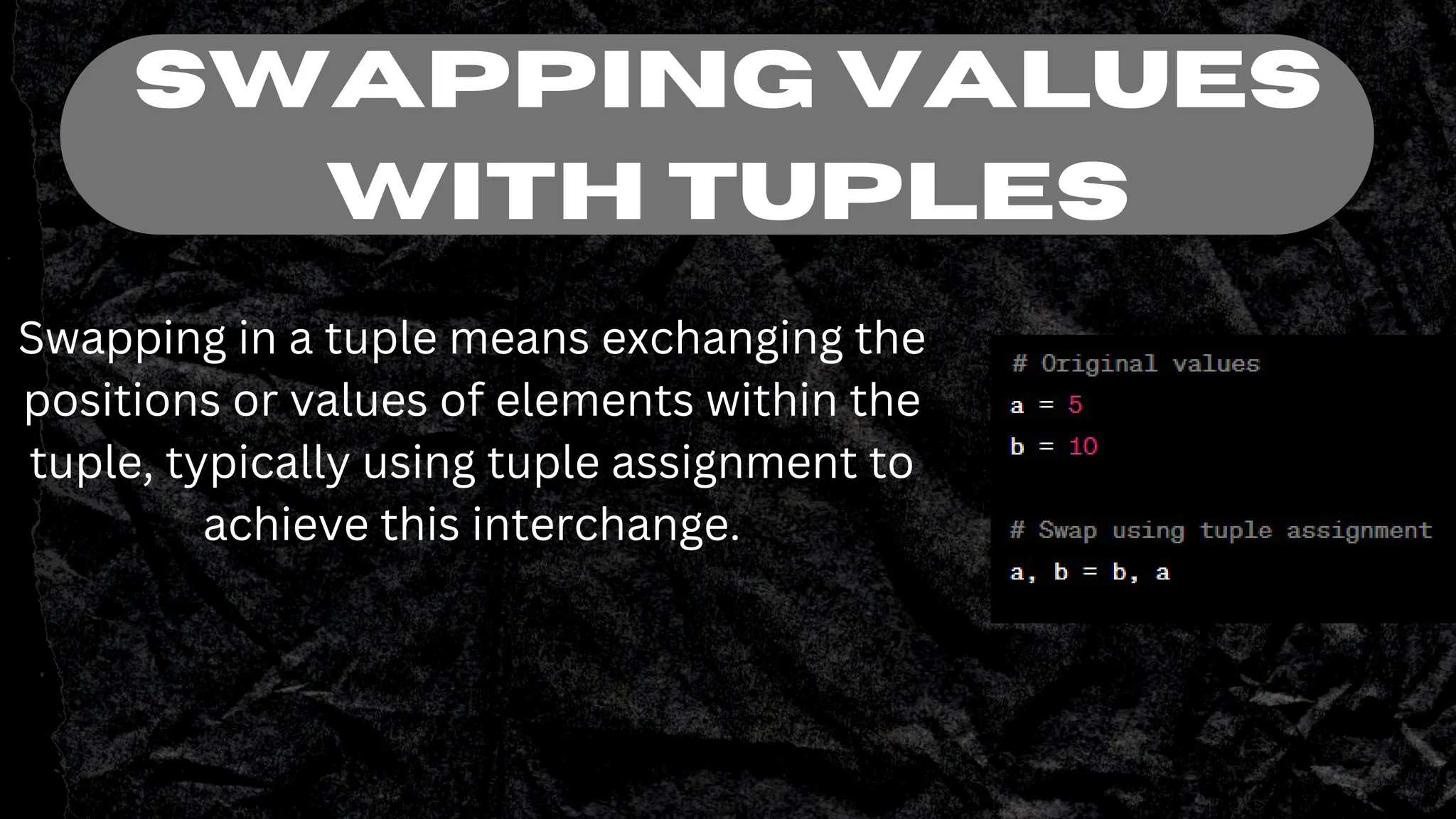
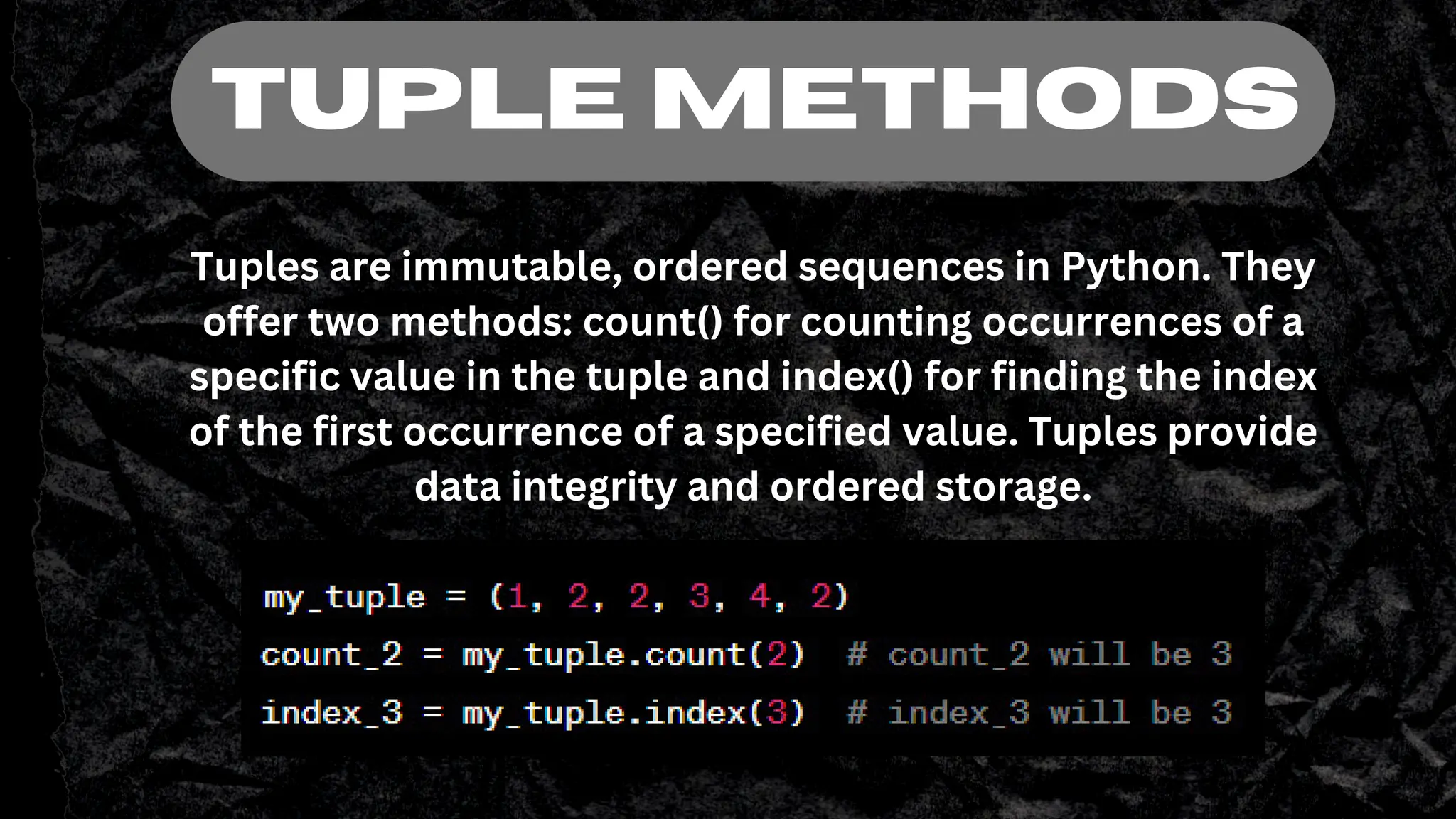
Tuples in Python are immutable ordered sequences that can contain heterogeneous data types. They are defined using parentheses and elements within tuples can be accessed using indexing with square brackets. Tuples support operations like concatenation using +, repetition using *, and slicing elements using a colon notation. Tuple assignment allows assigning multiple values to multiple variables at once, and swapping variable values. Tuples provide a useful way to organize related data in Python.