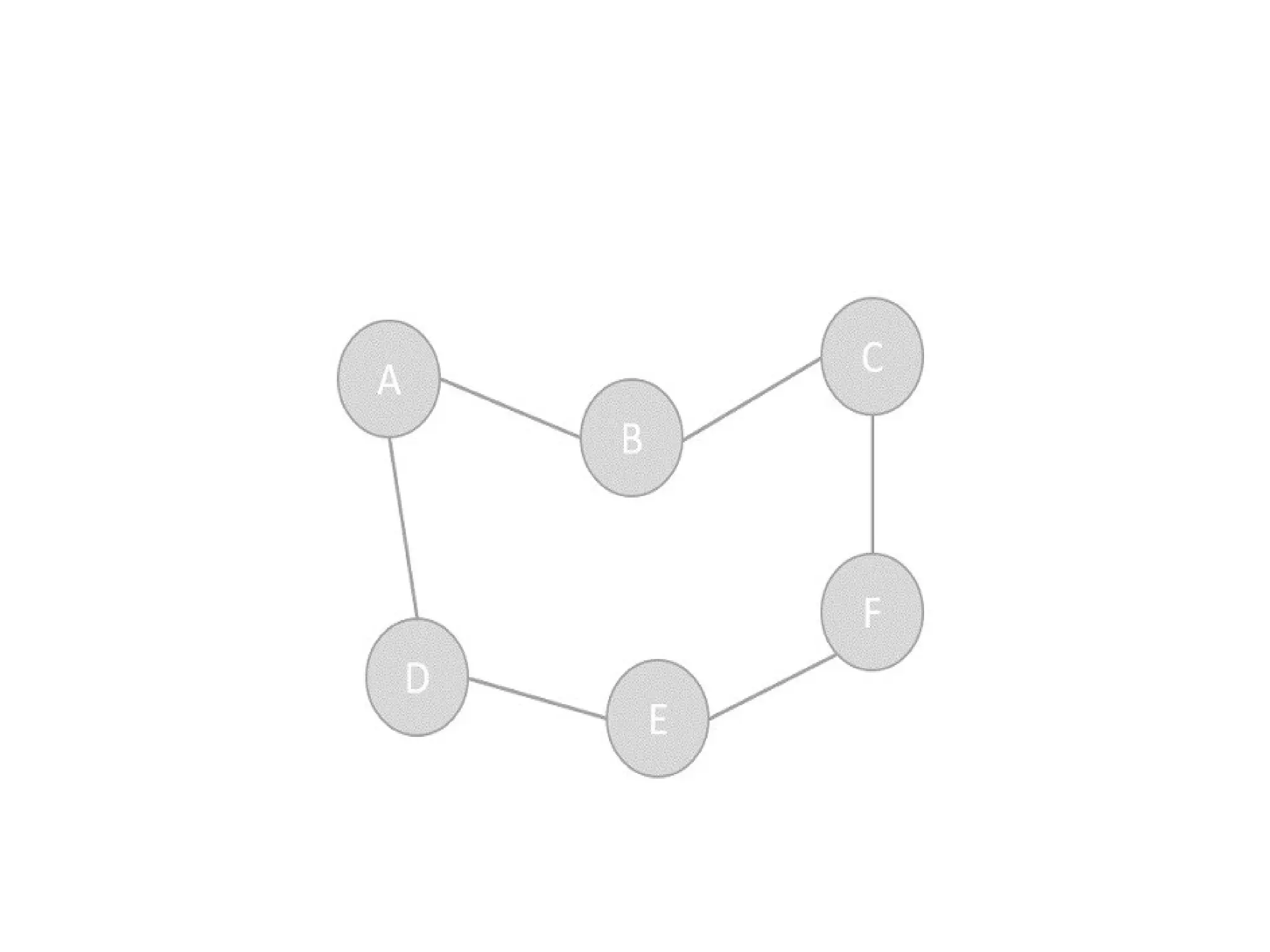
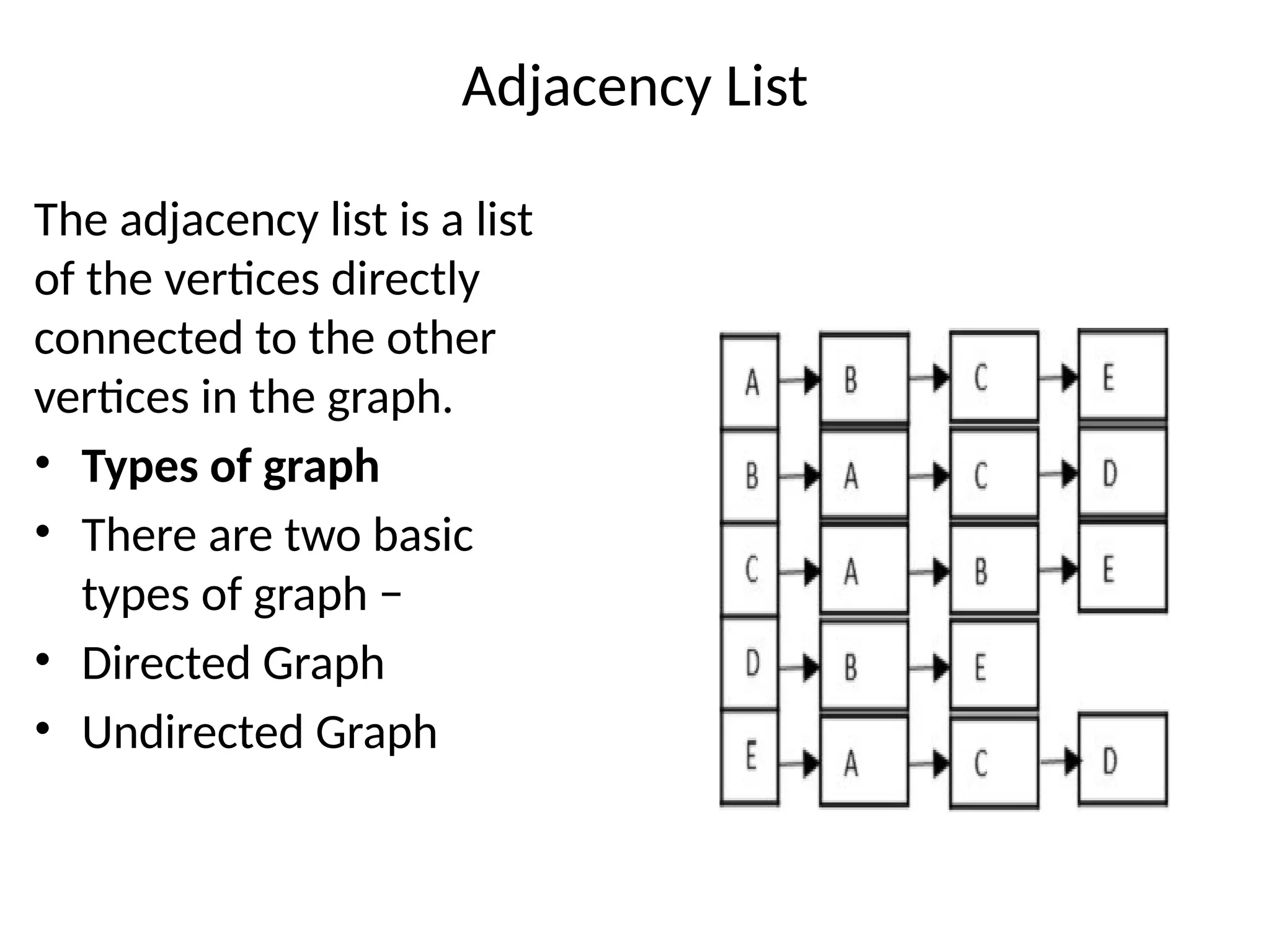
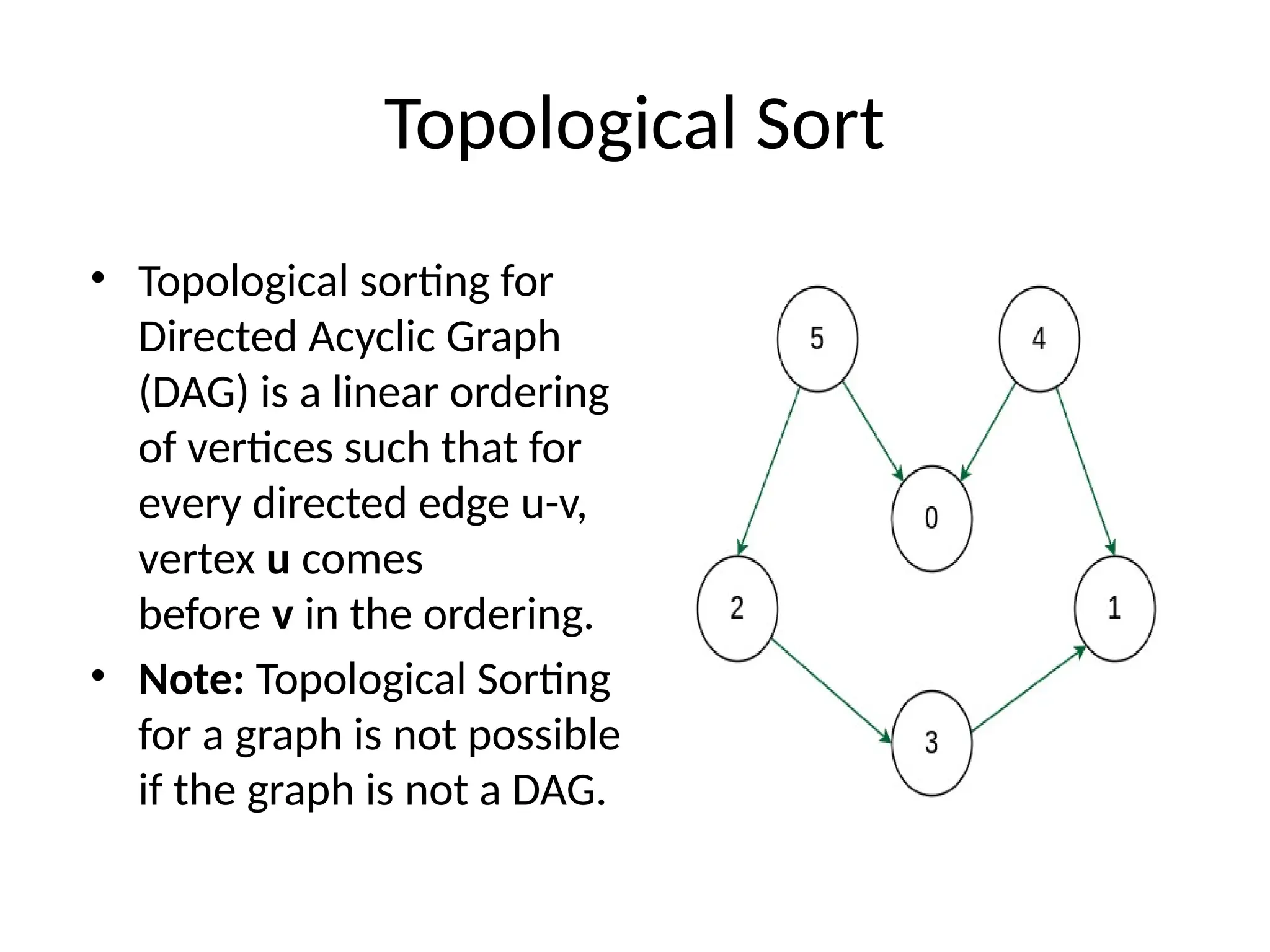
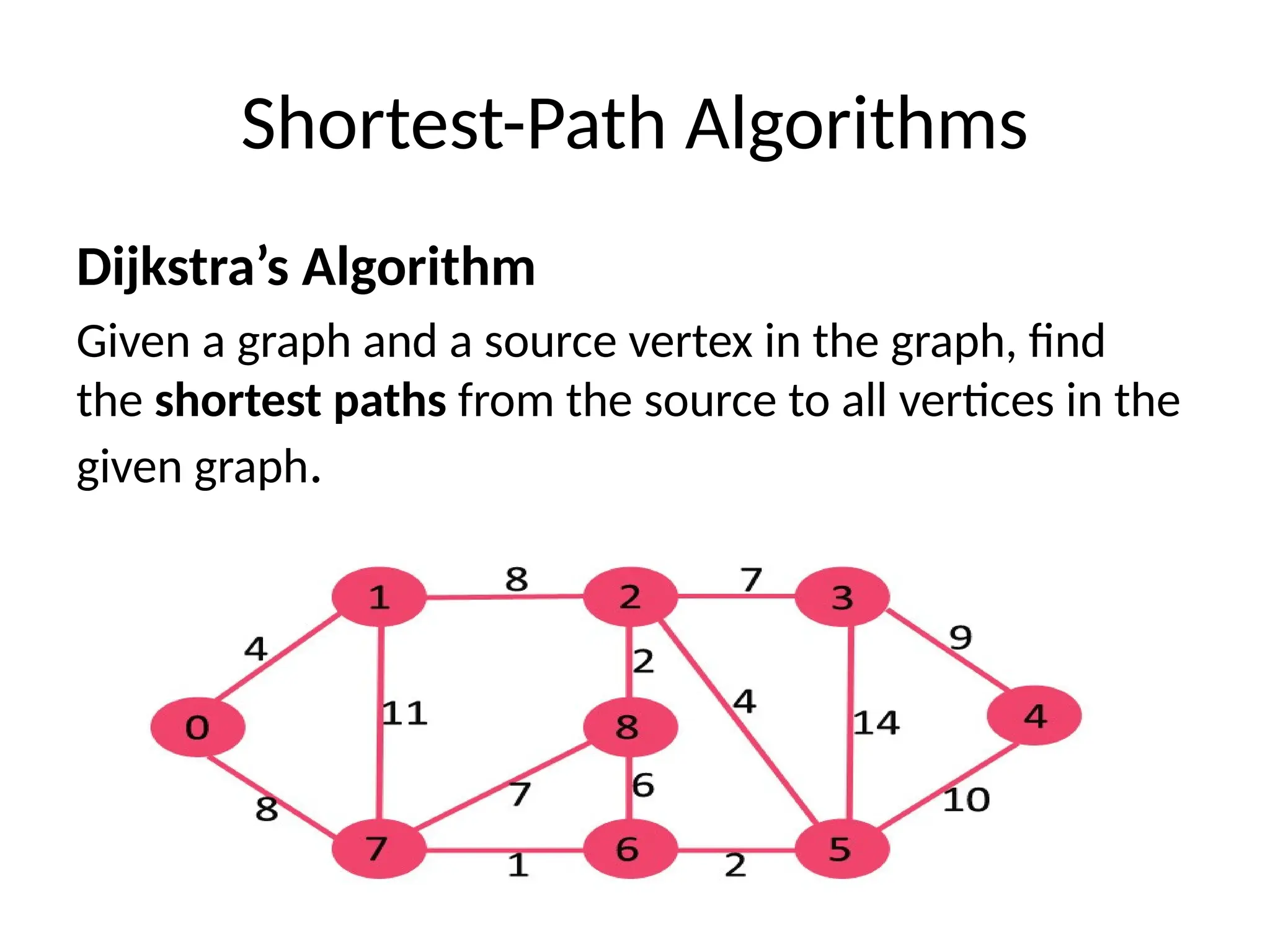
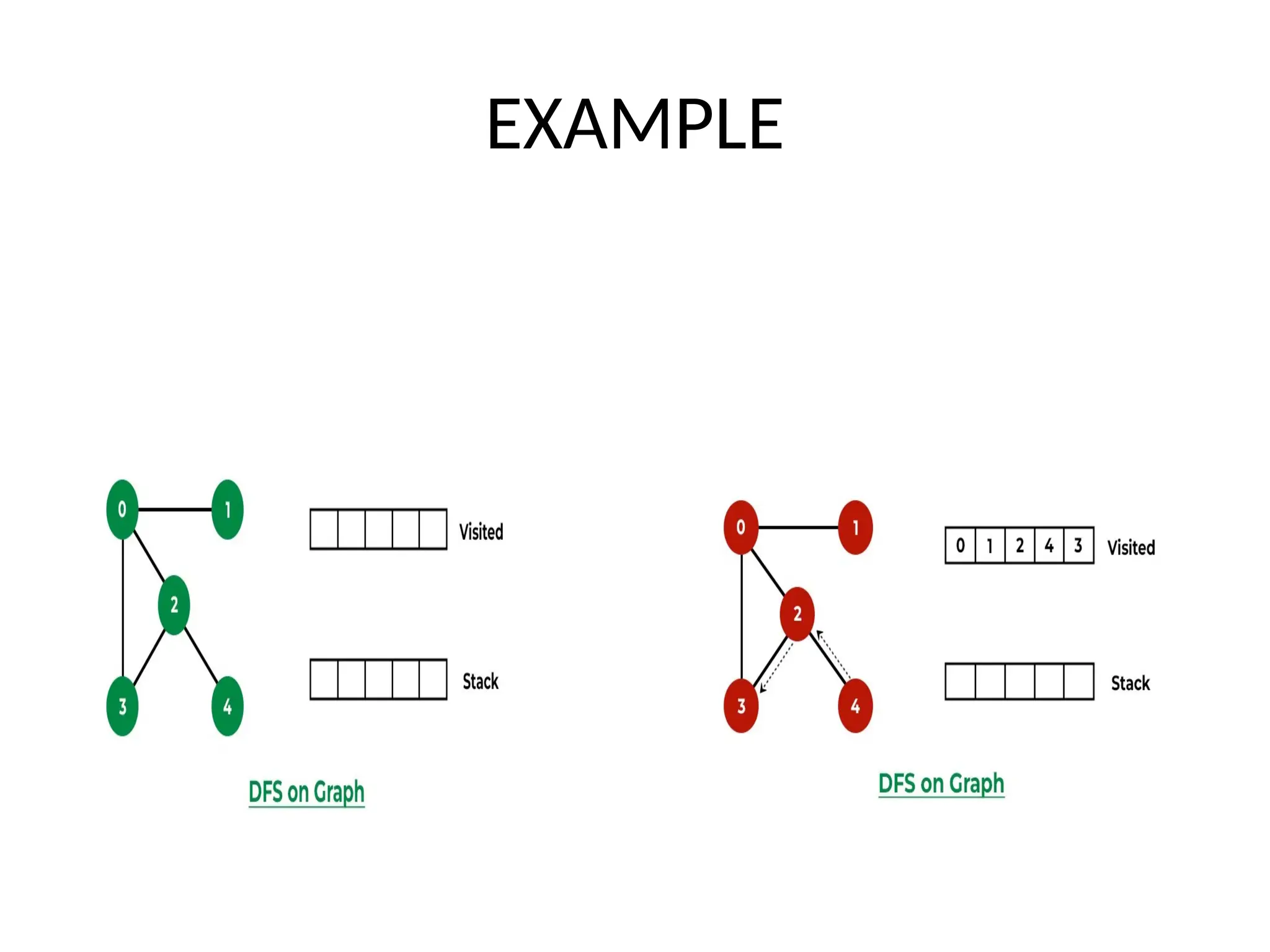
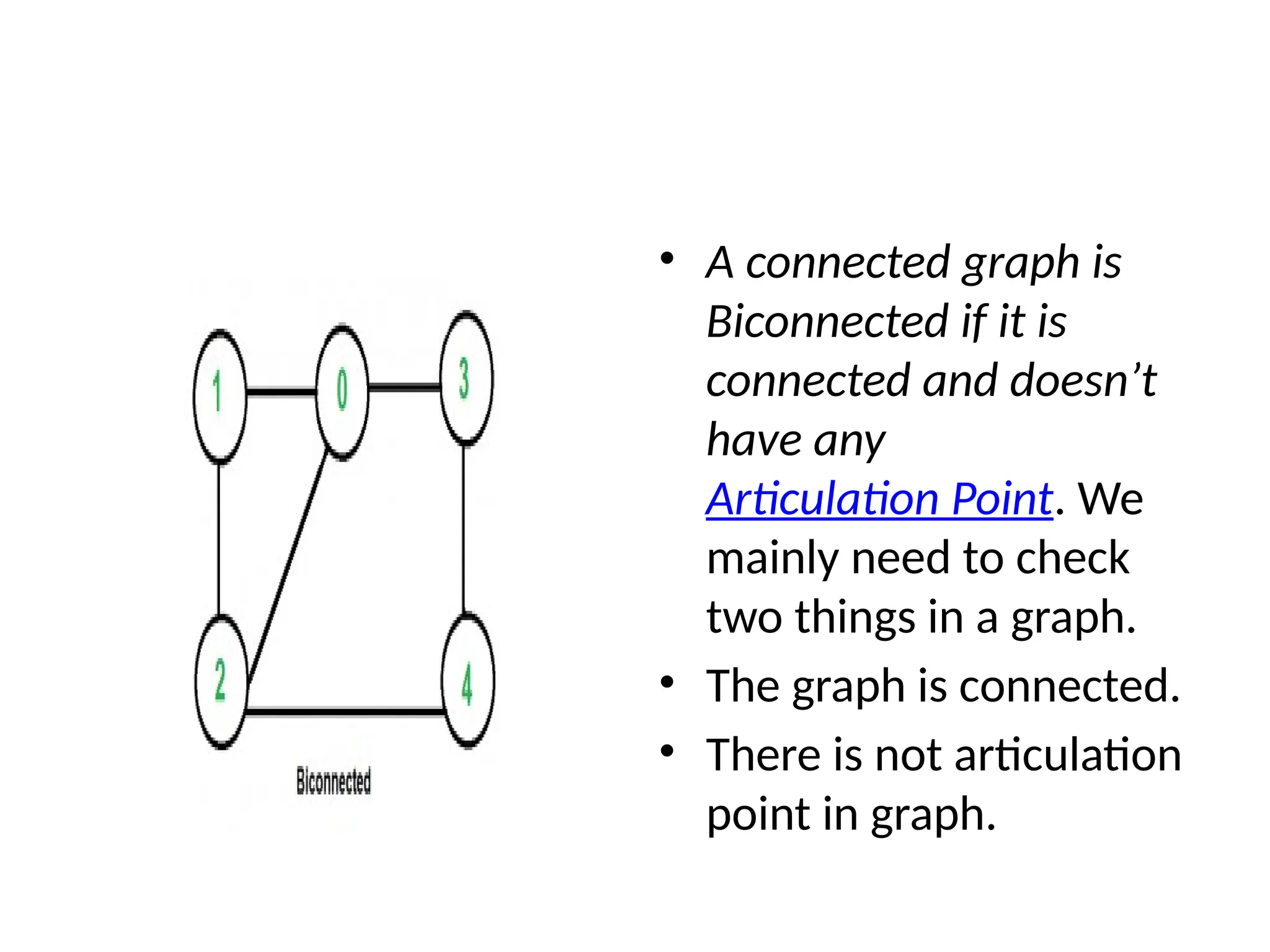
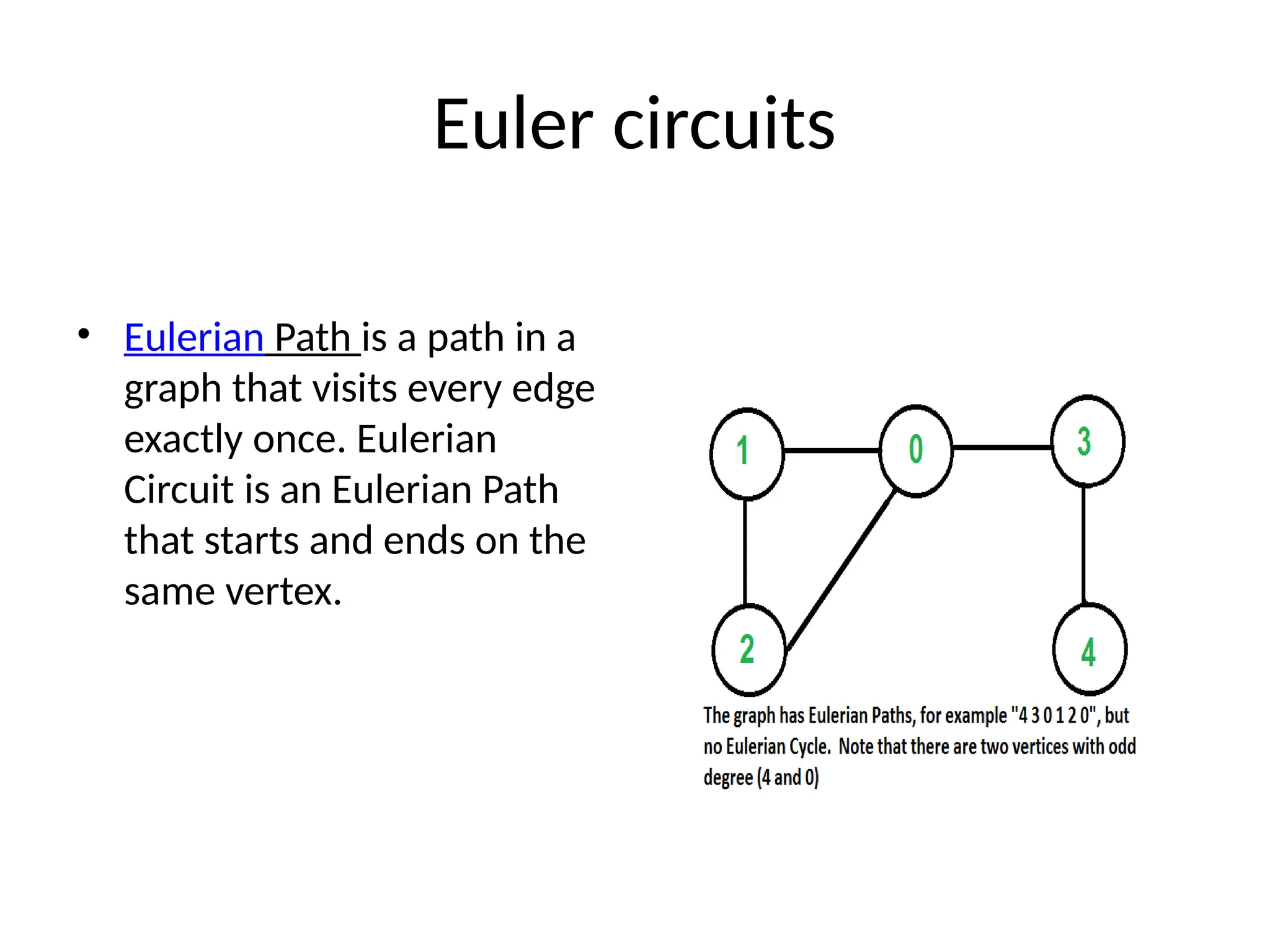
The document provides definitions and properties of graphs, detailing their structure as consisting of vertices and edges. It explains key algorithms such as Dijkstra's for shortest paths, Kruskal's and Prim's for minimum spanning trees, as well as concepts like depth-first traversal, biconnectivity, and Eulerian paths. Additionally, it highlights real-world applications of graphs in systems like Google Maps and Facebook's friend suggestions.