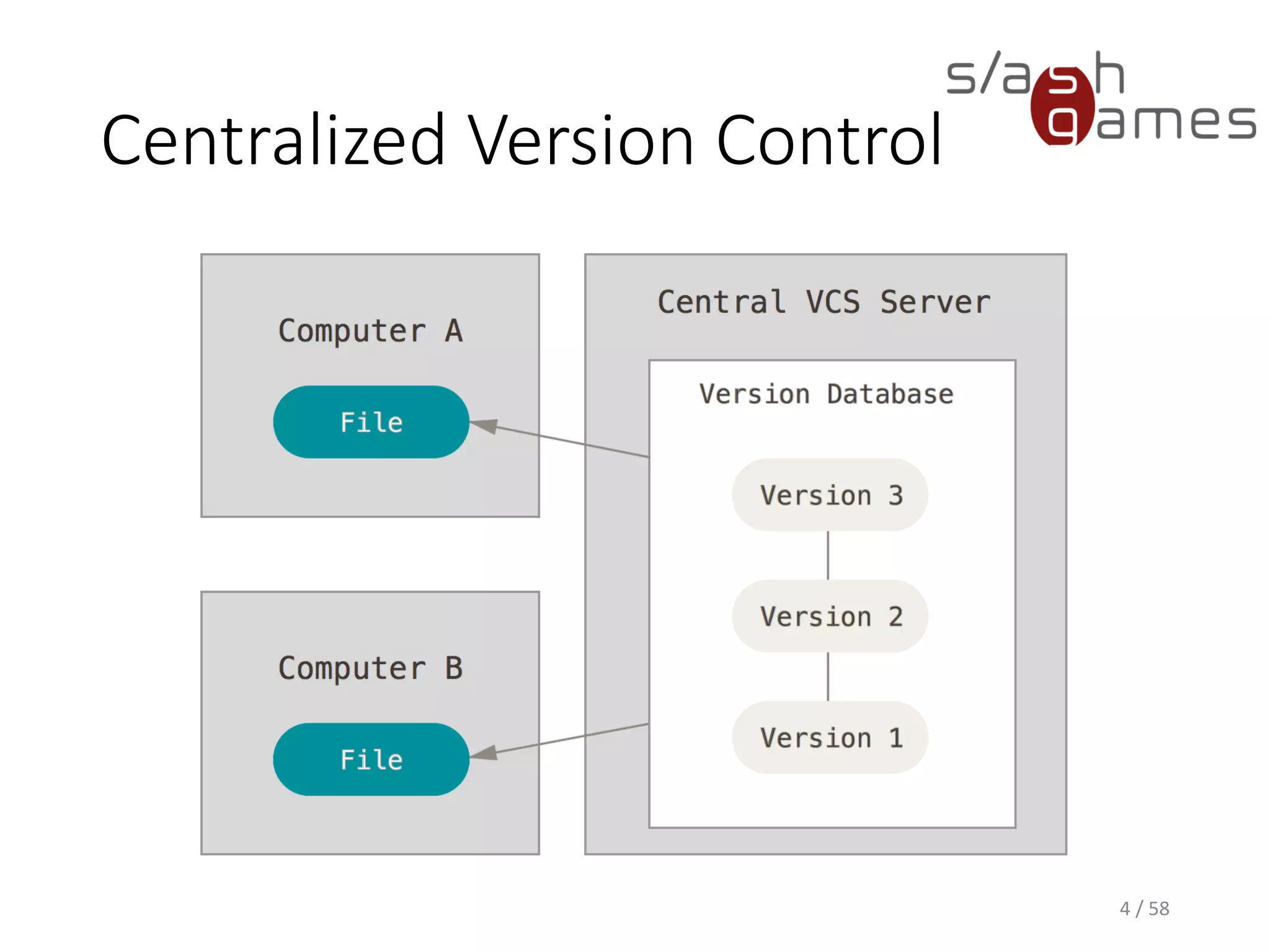
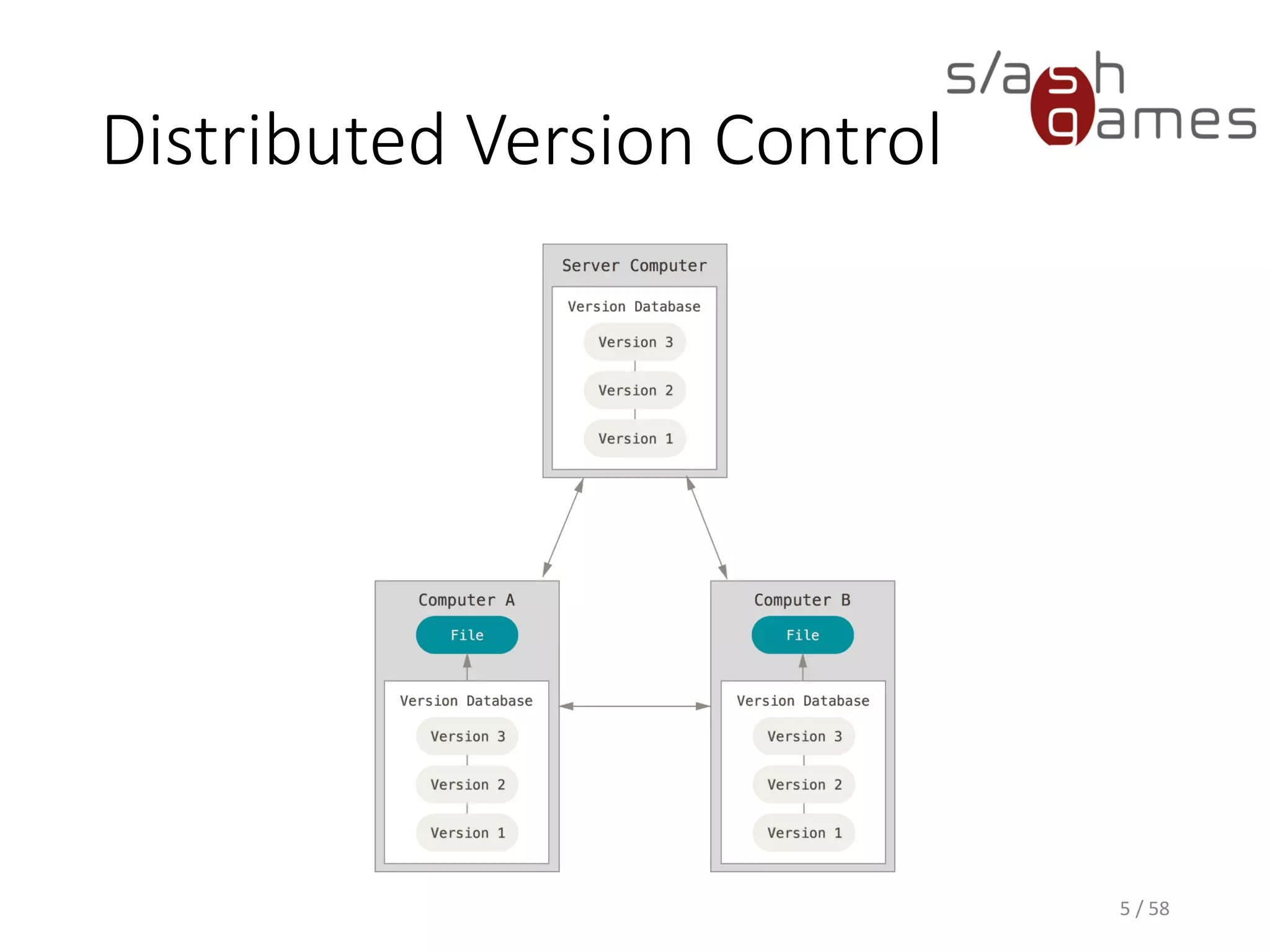
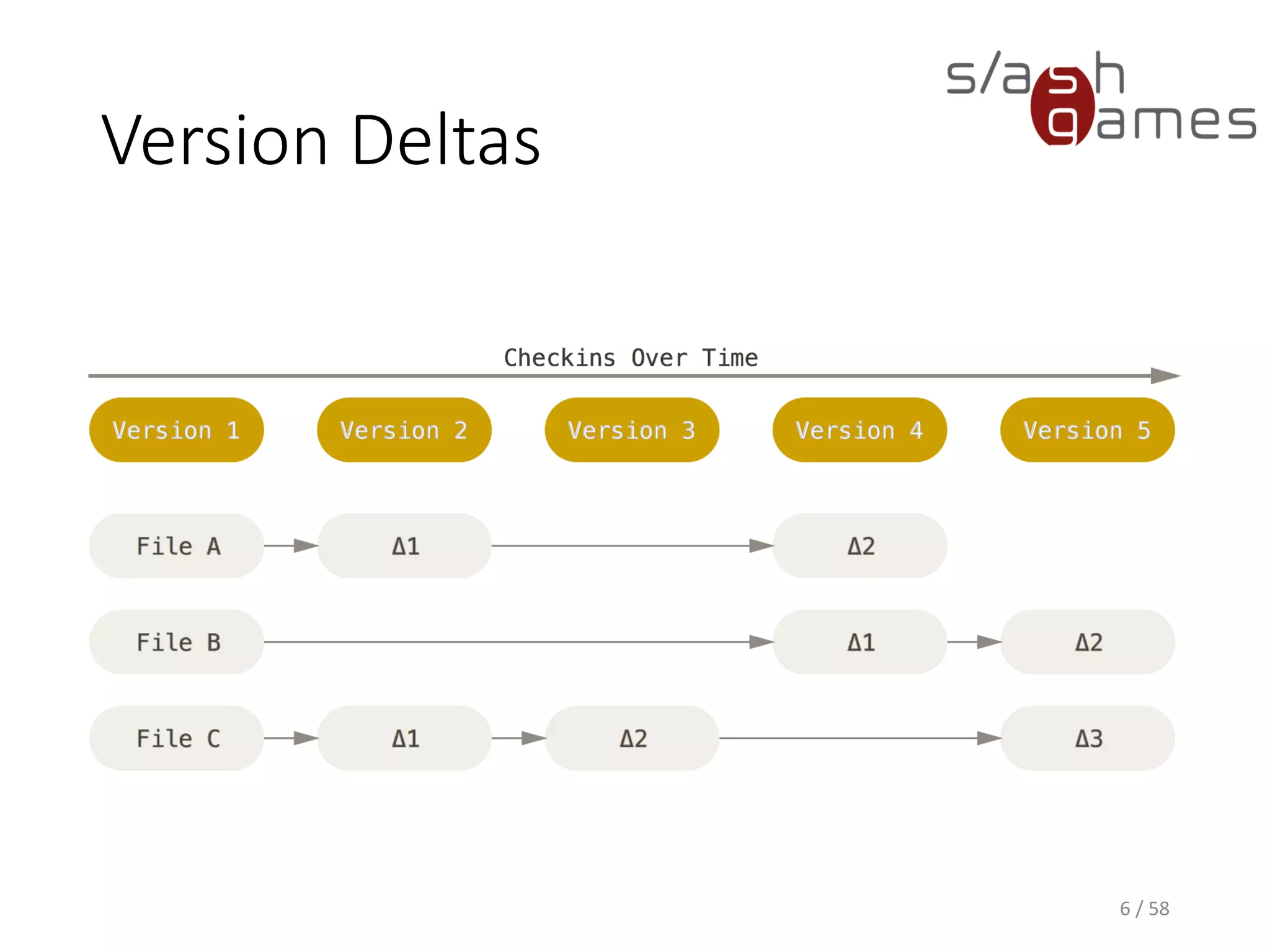
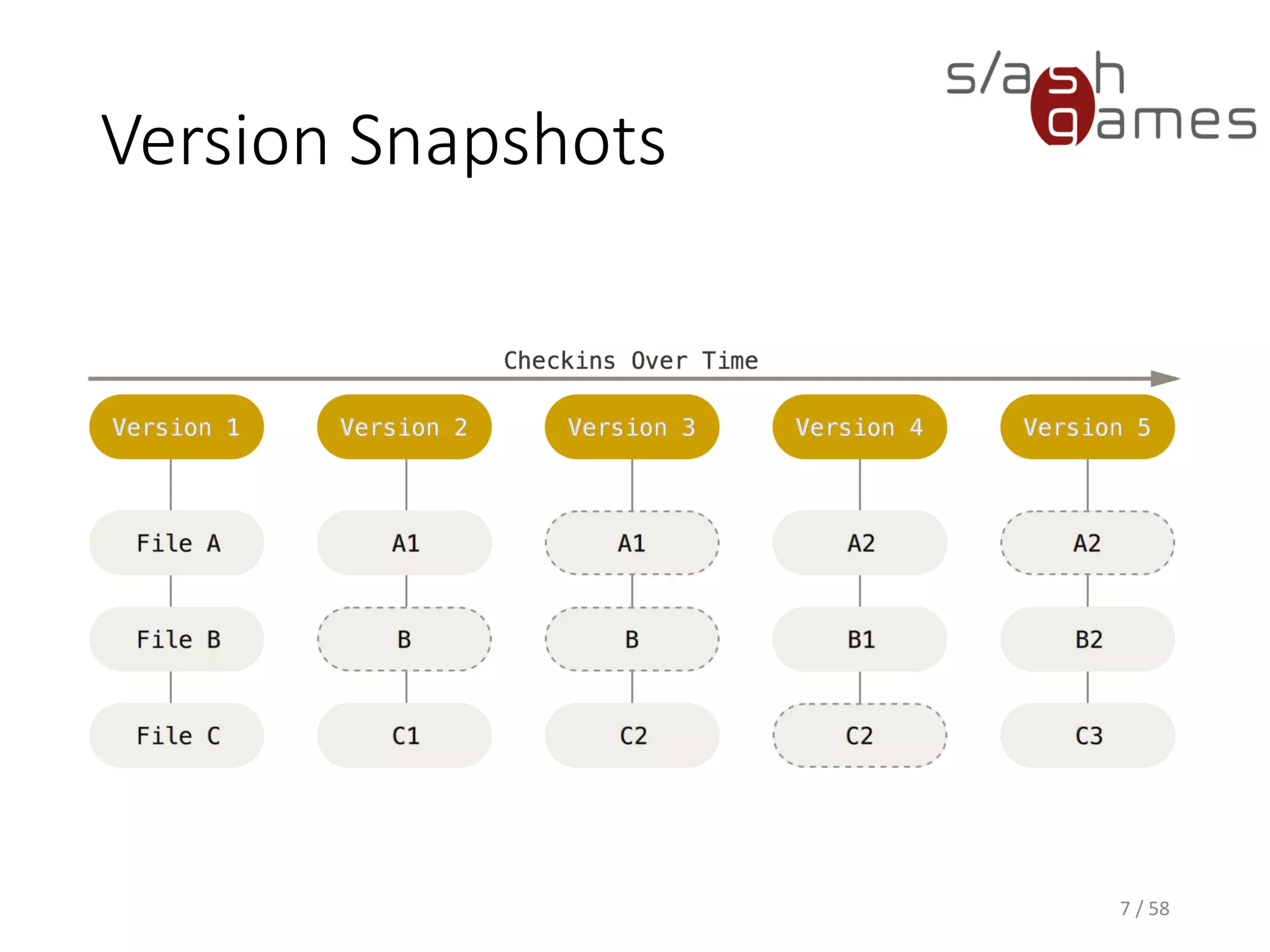
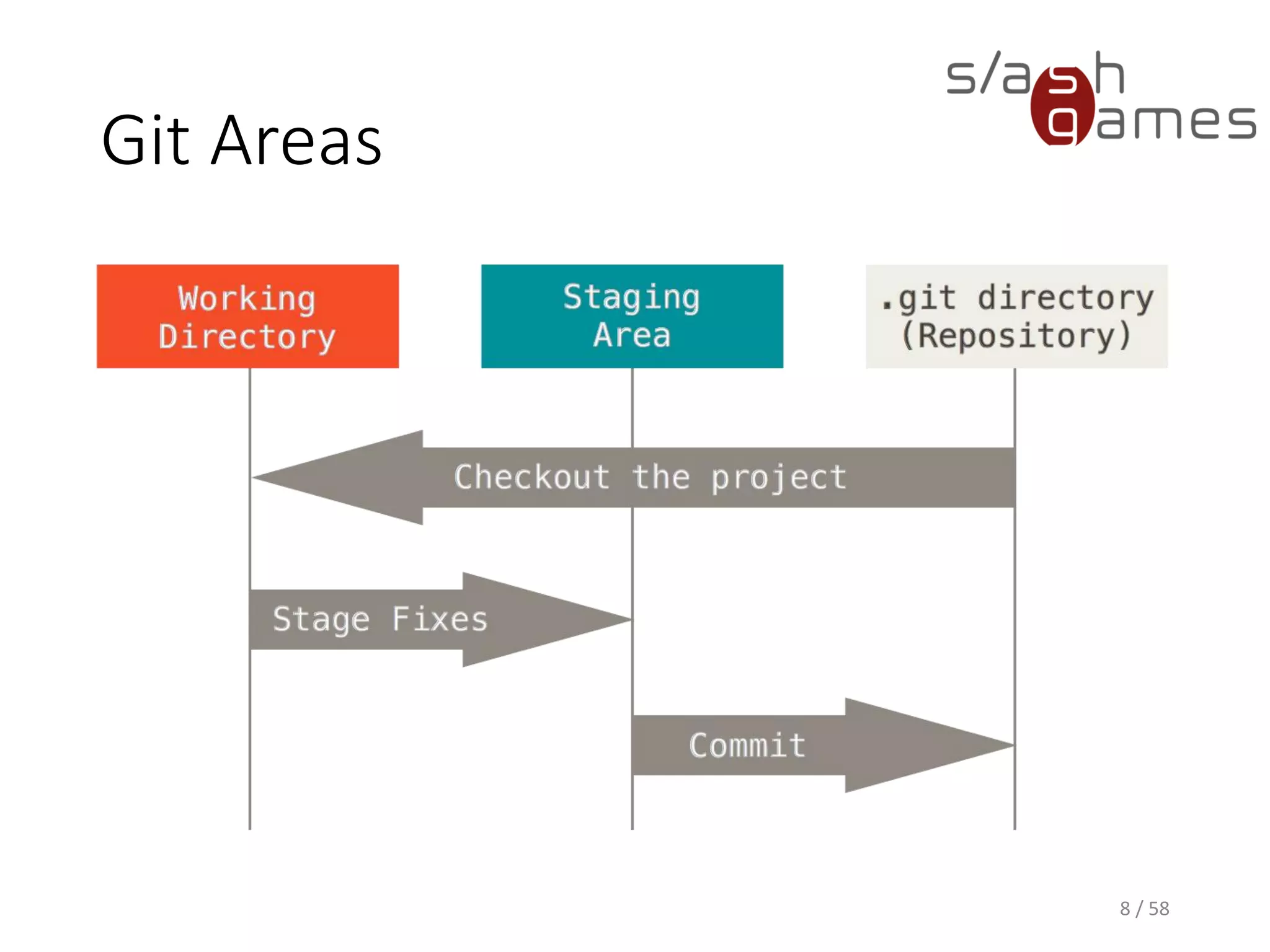
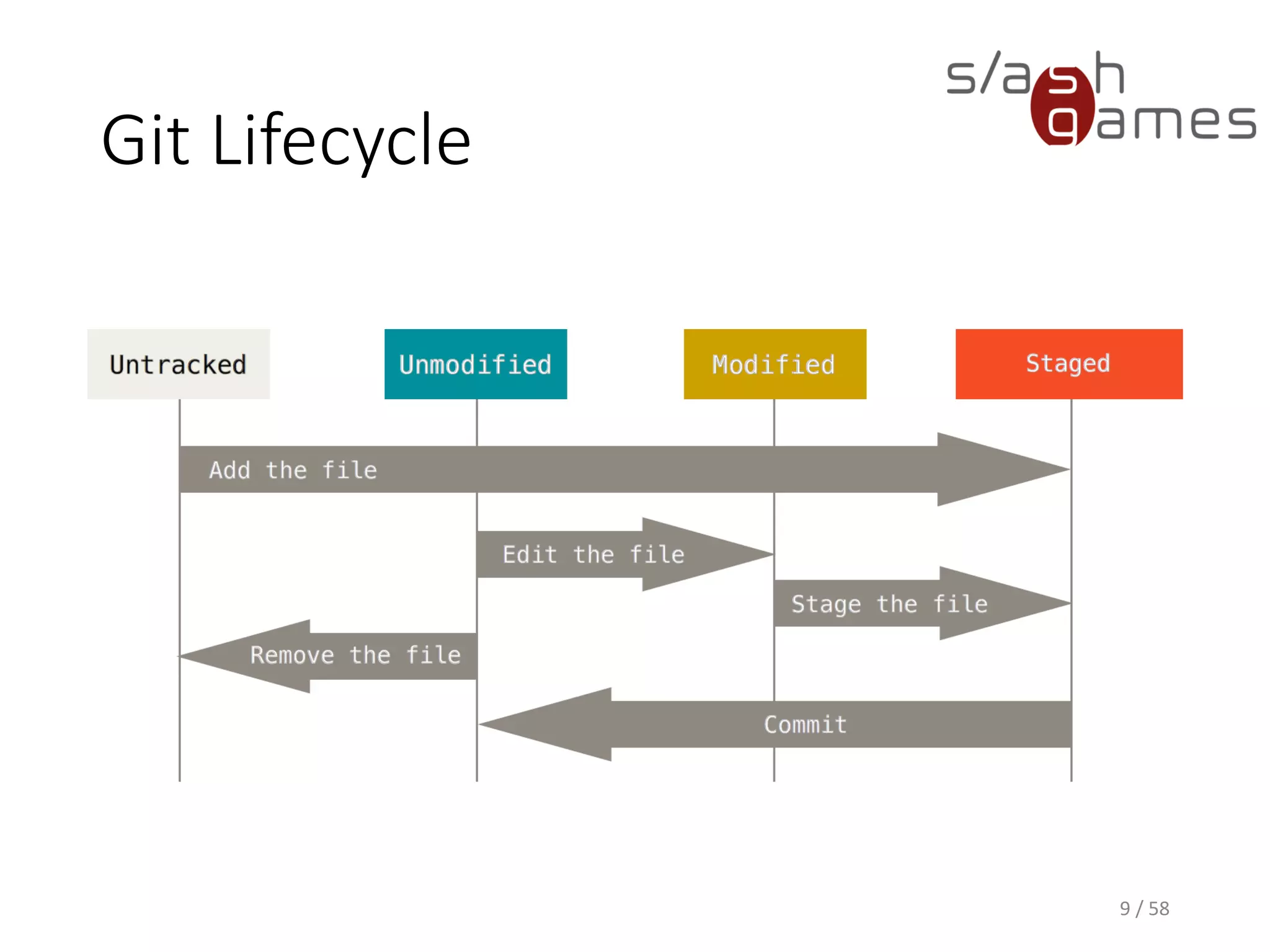
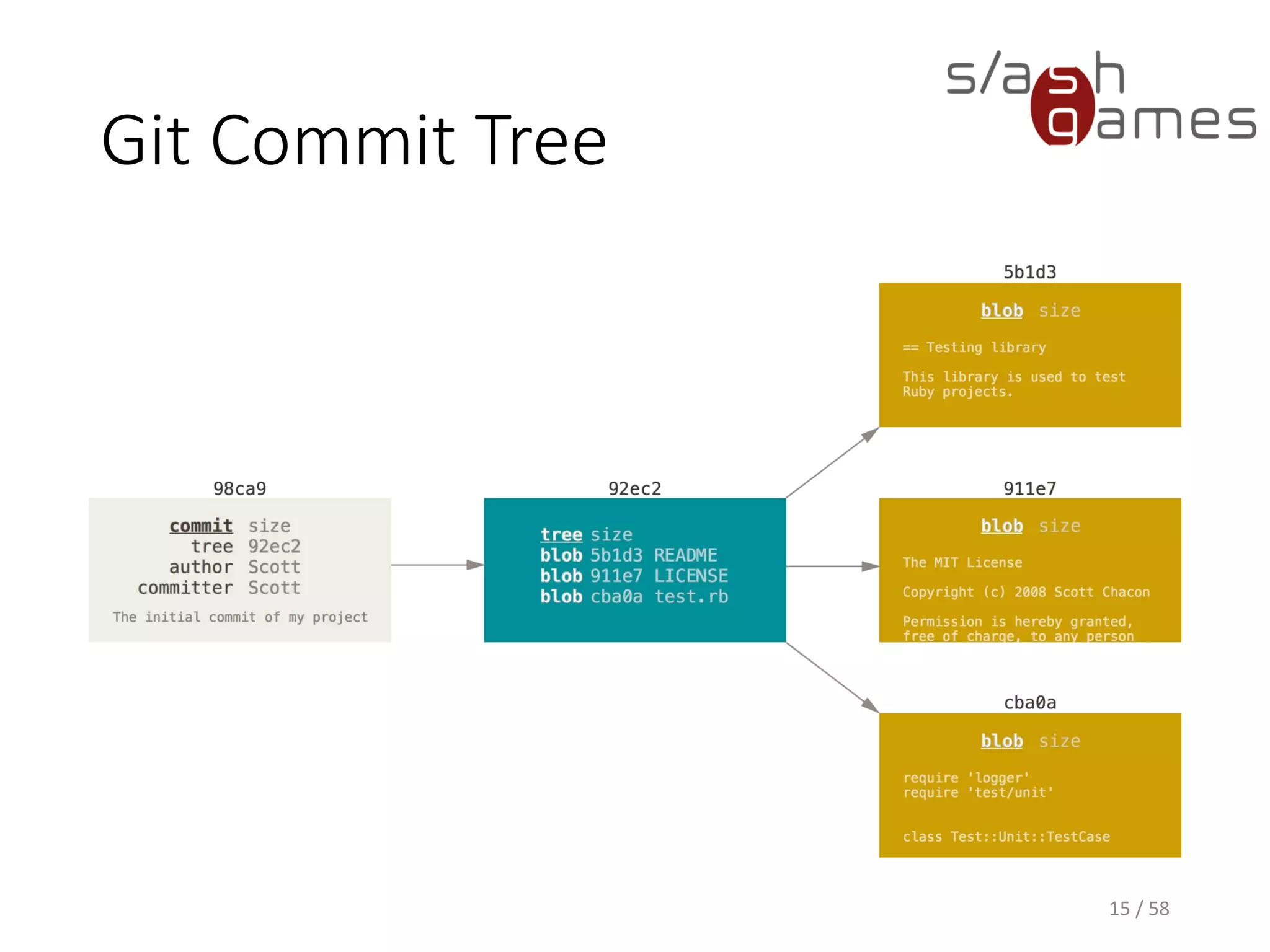
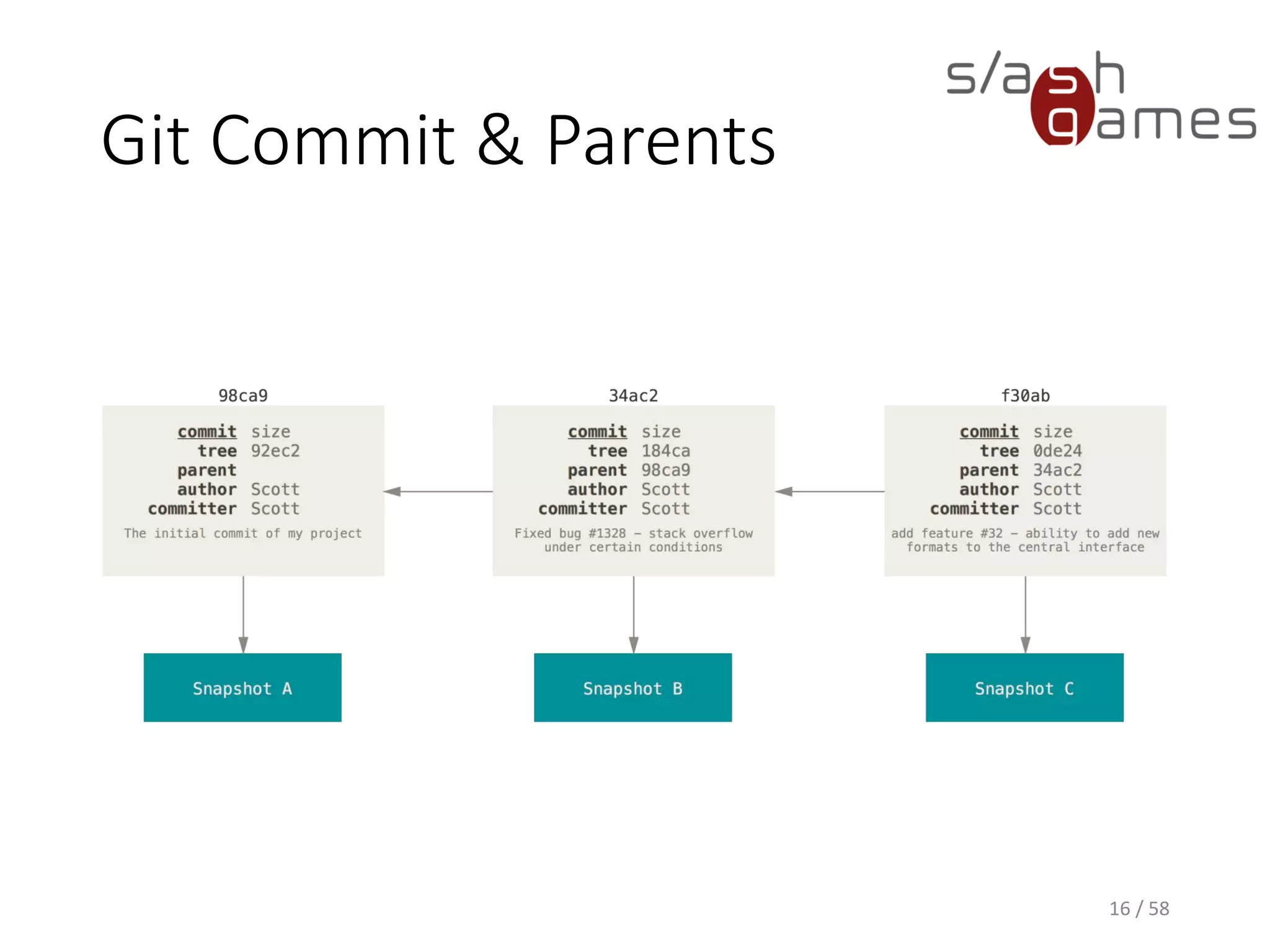
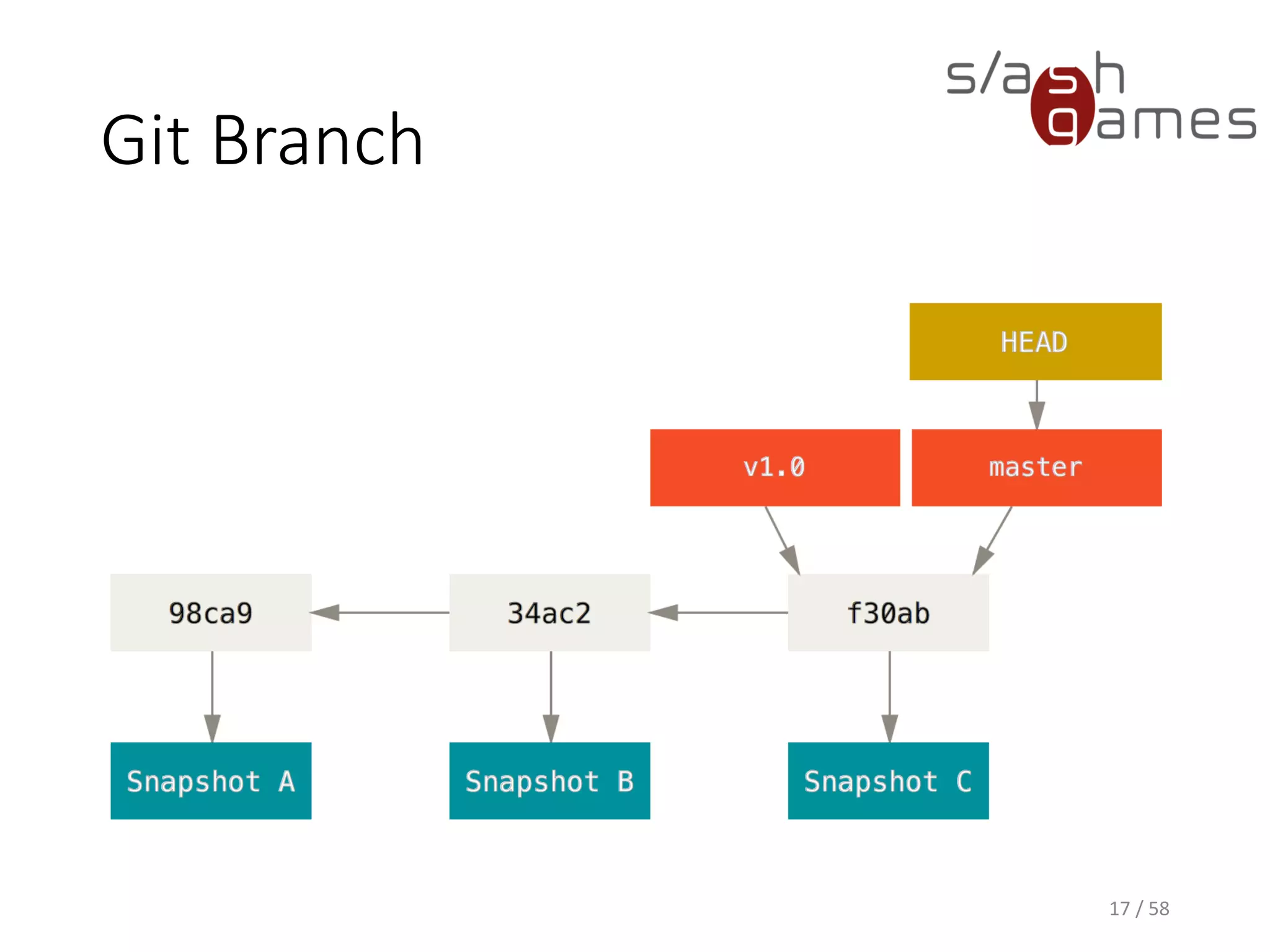
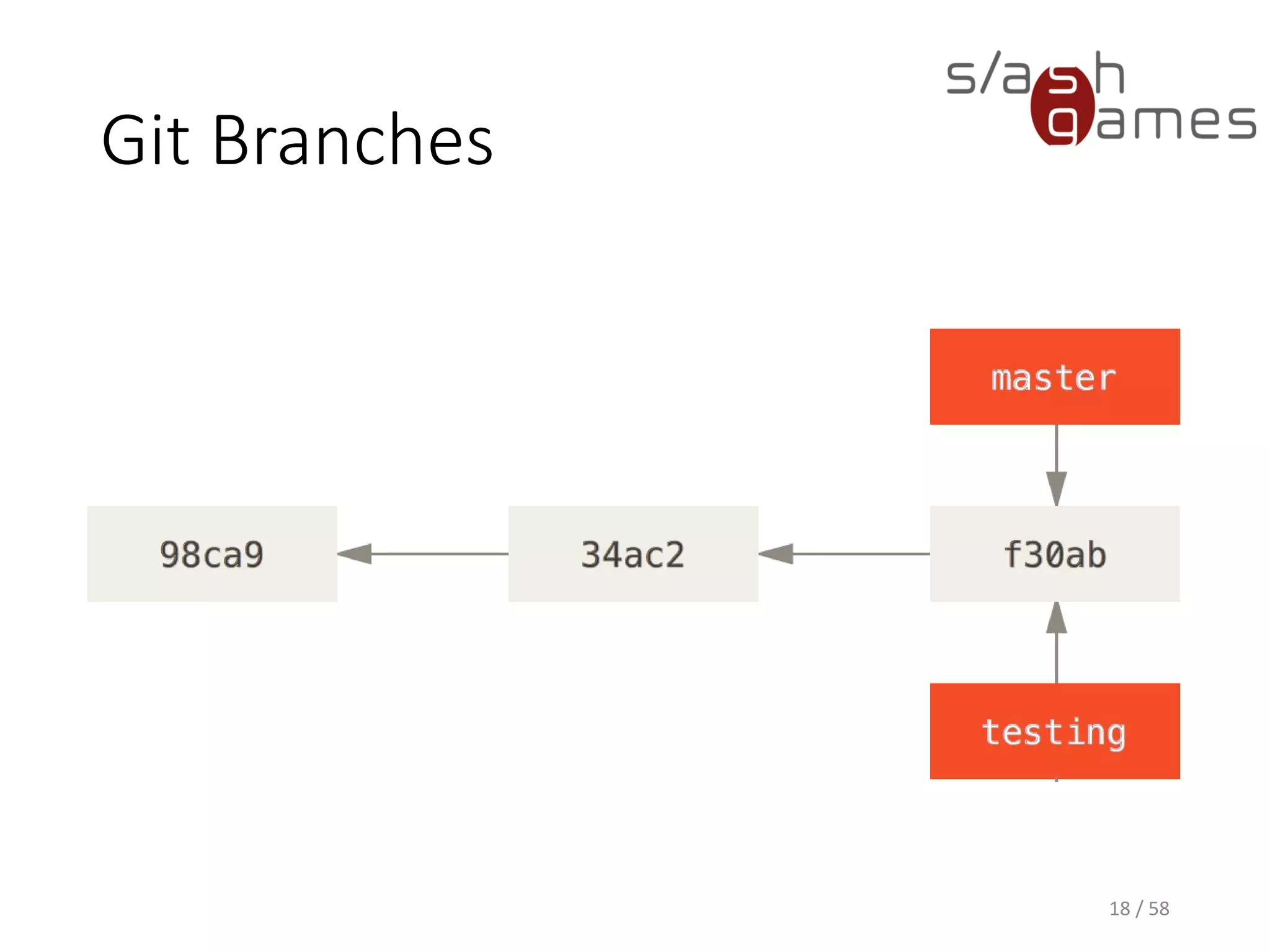
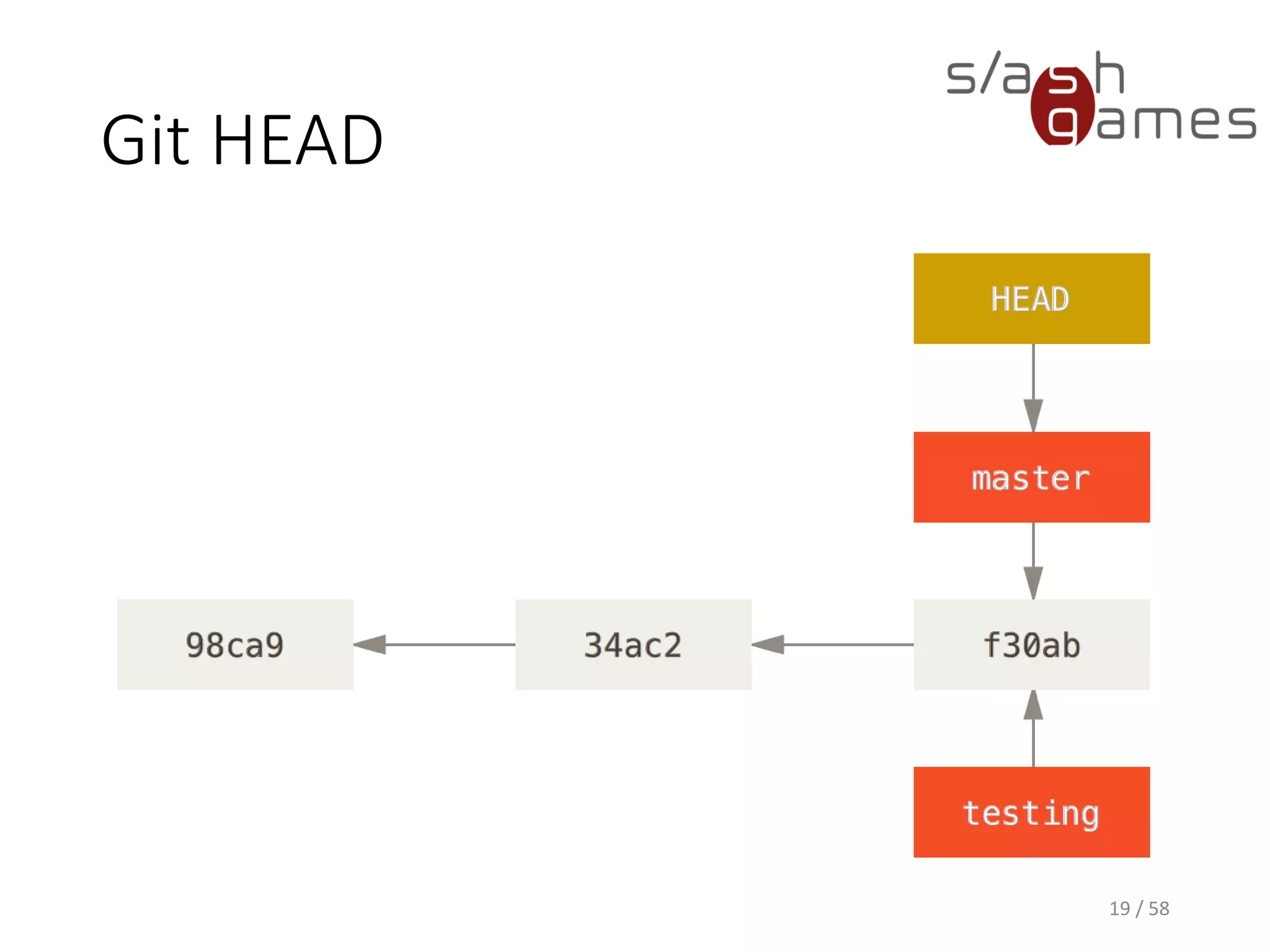
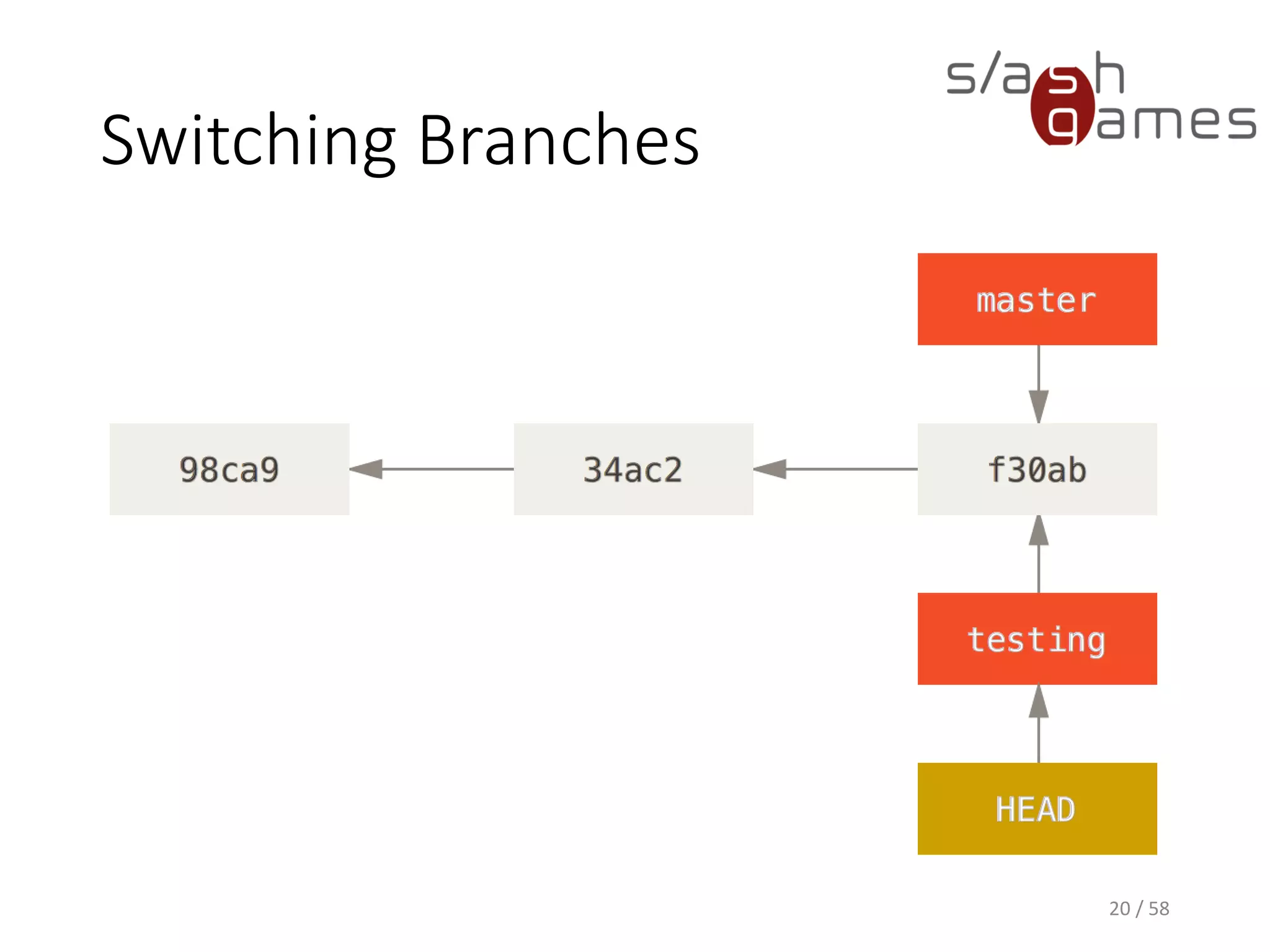
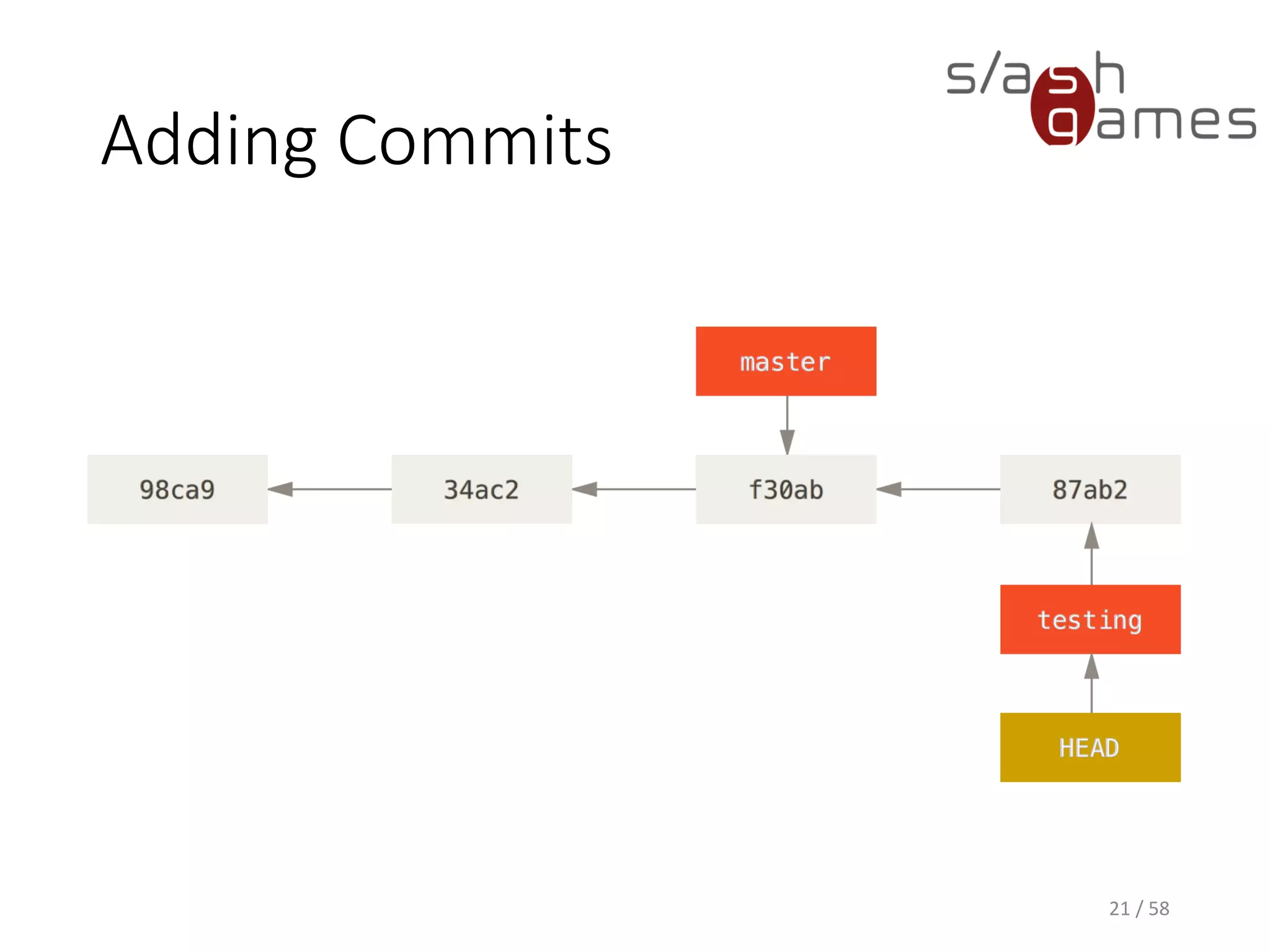
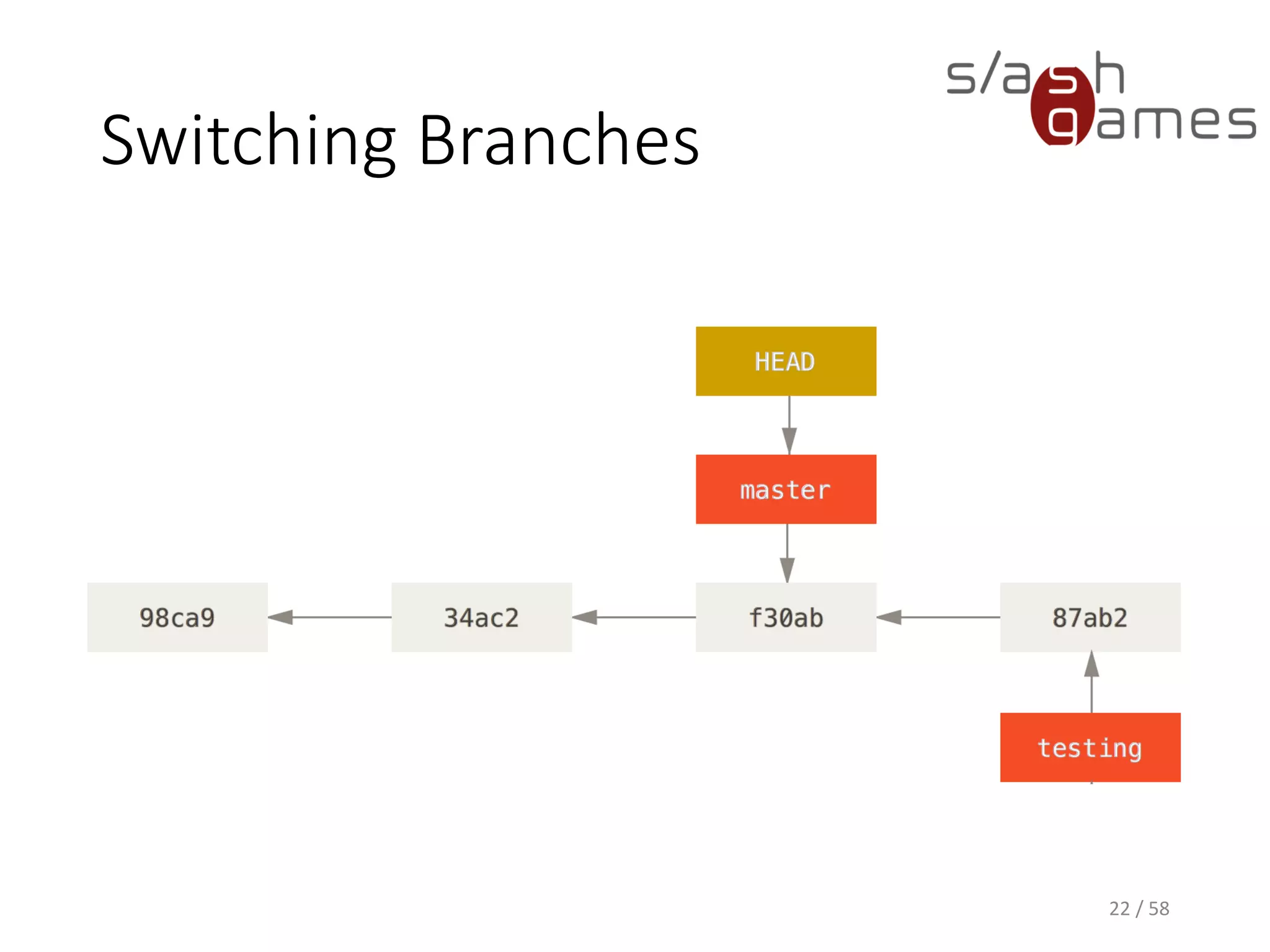
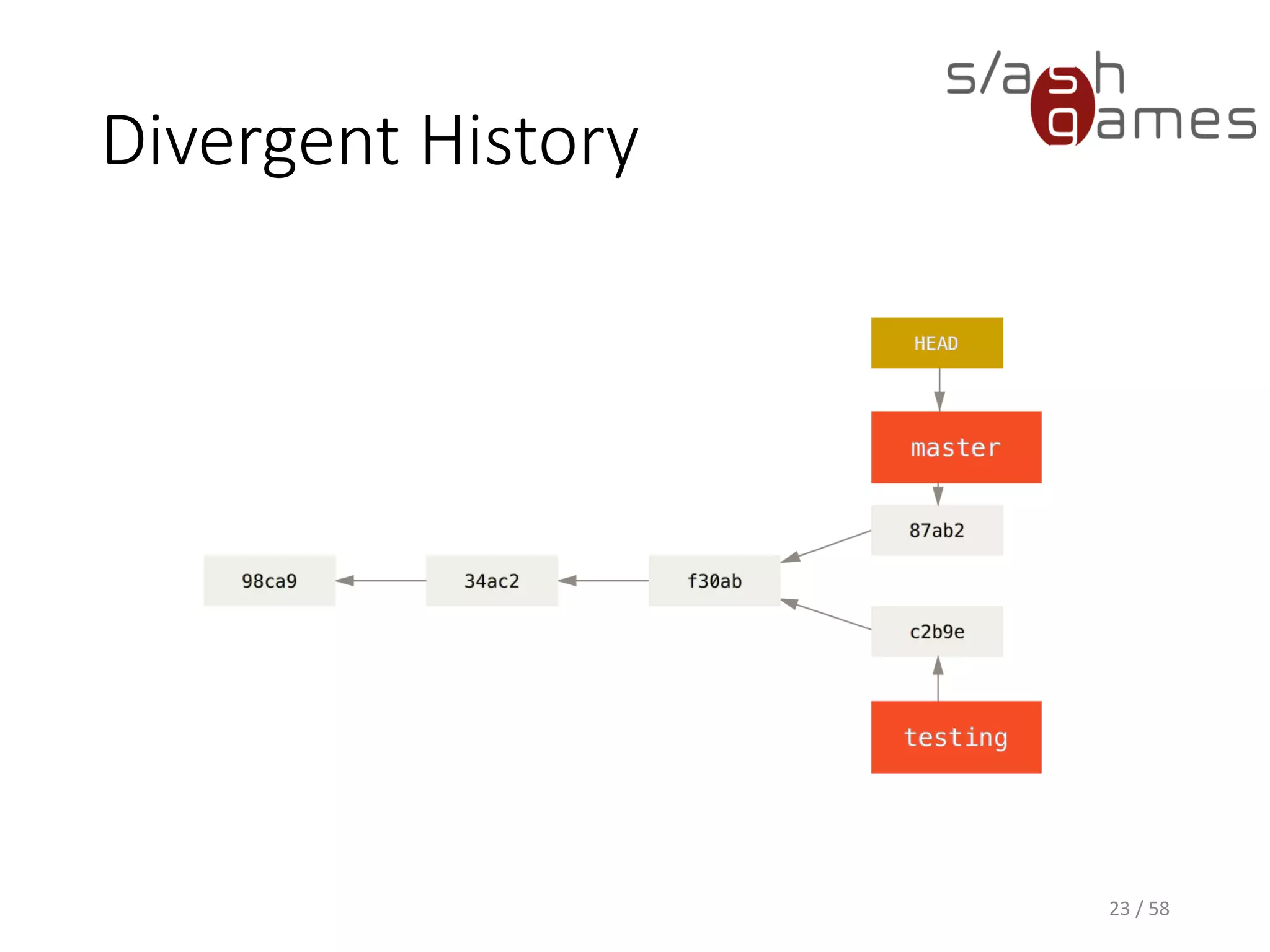
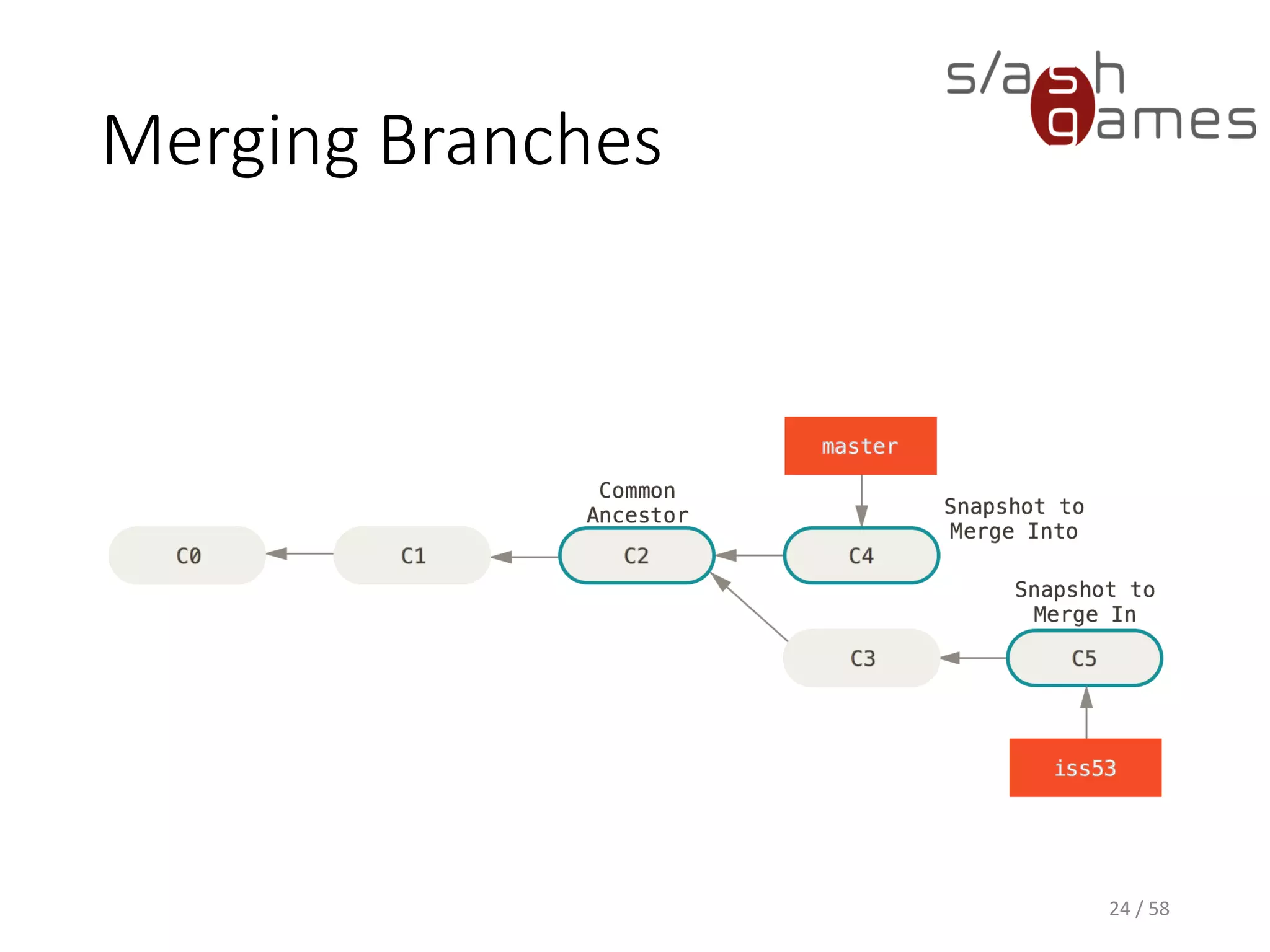
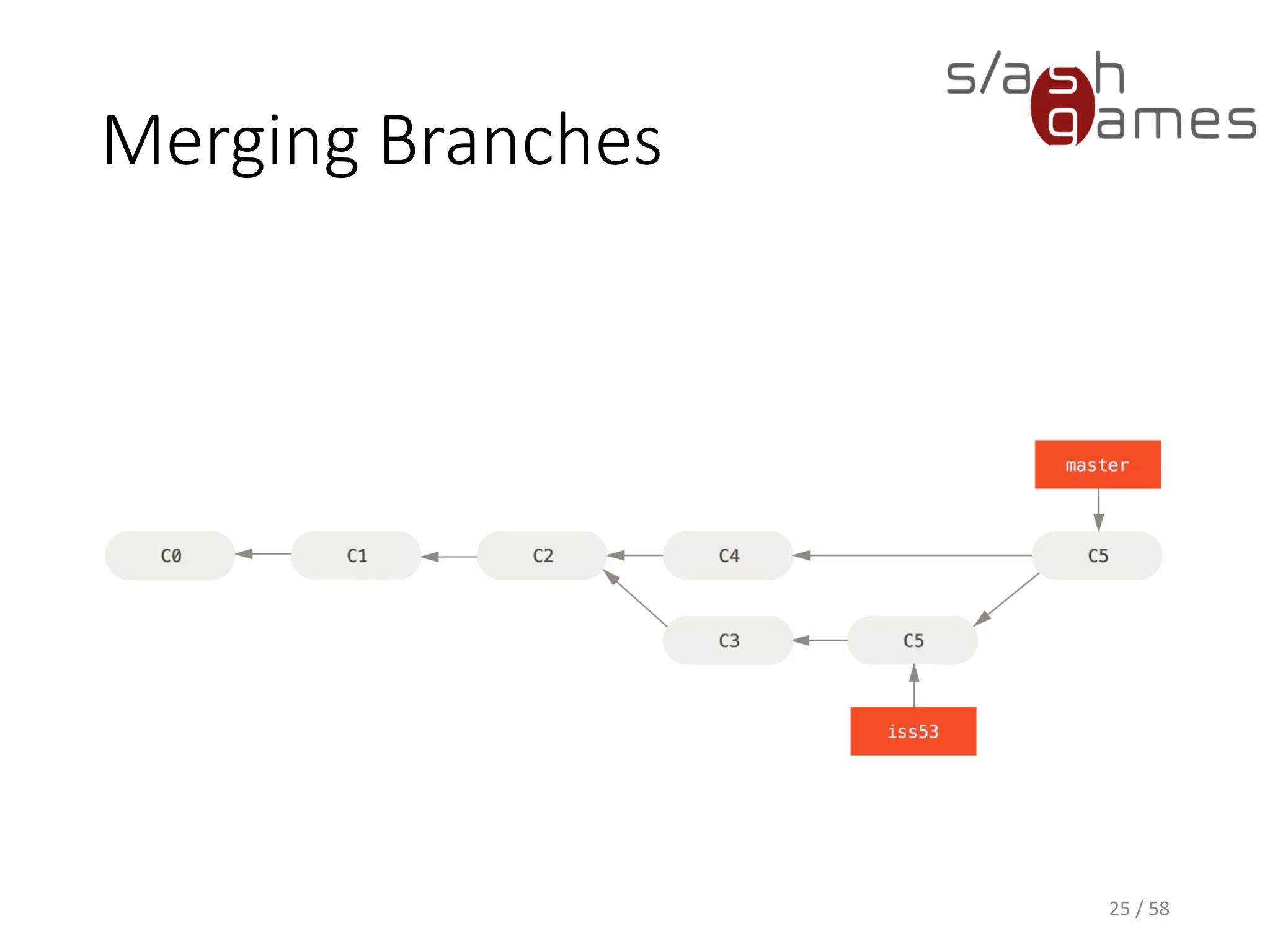
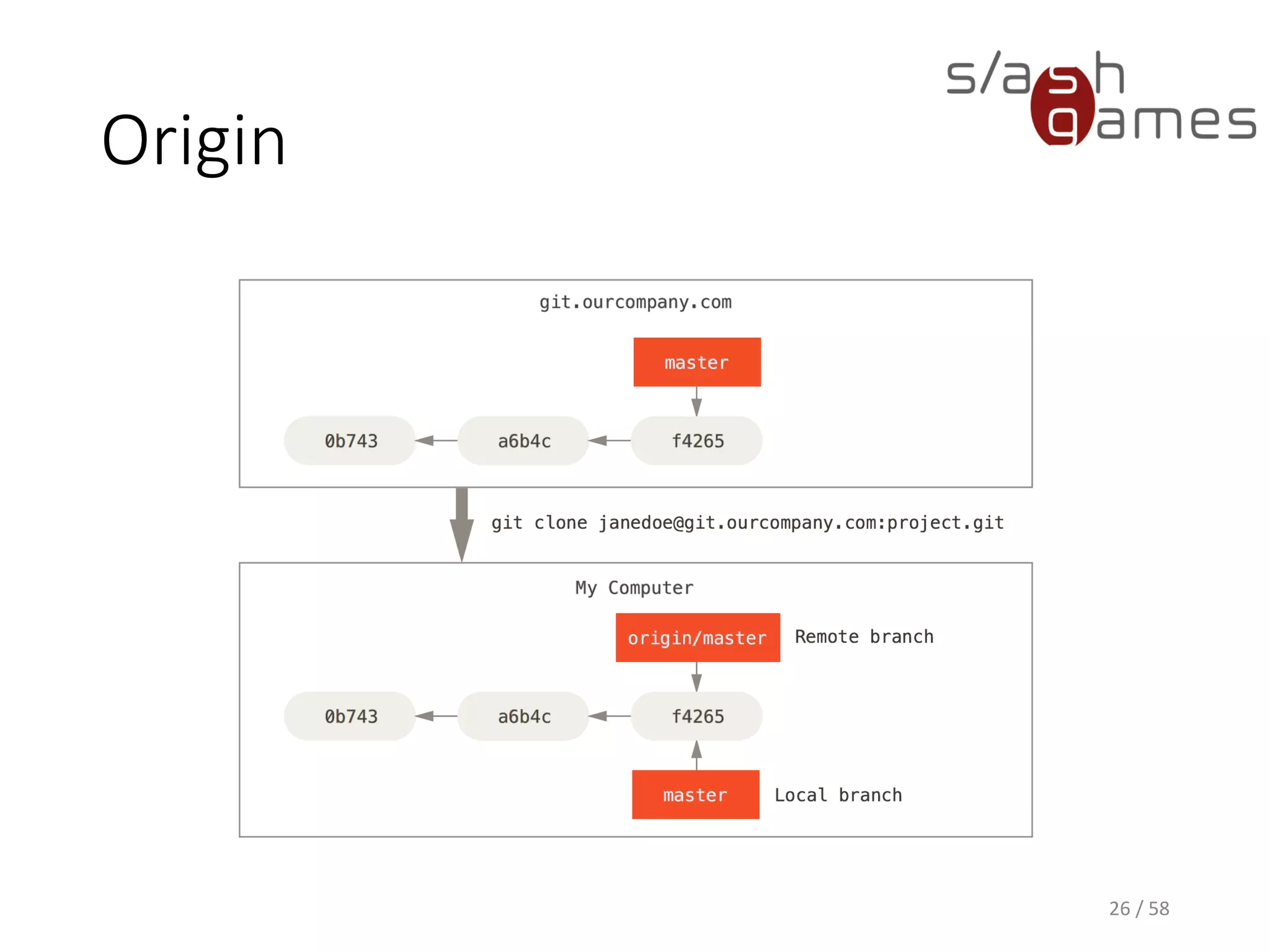
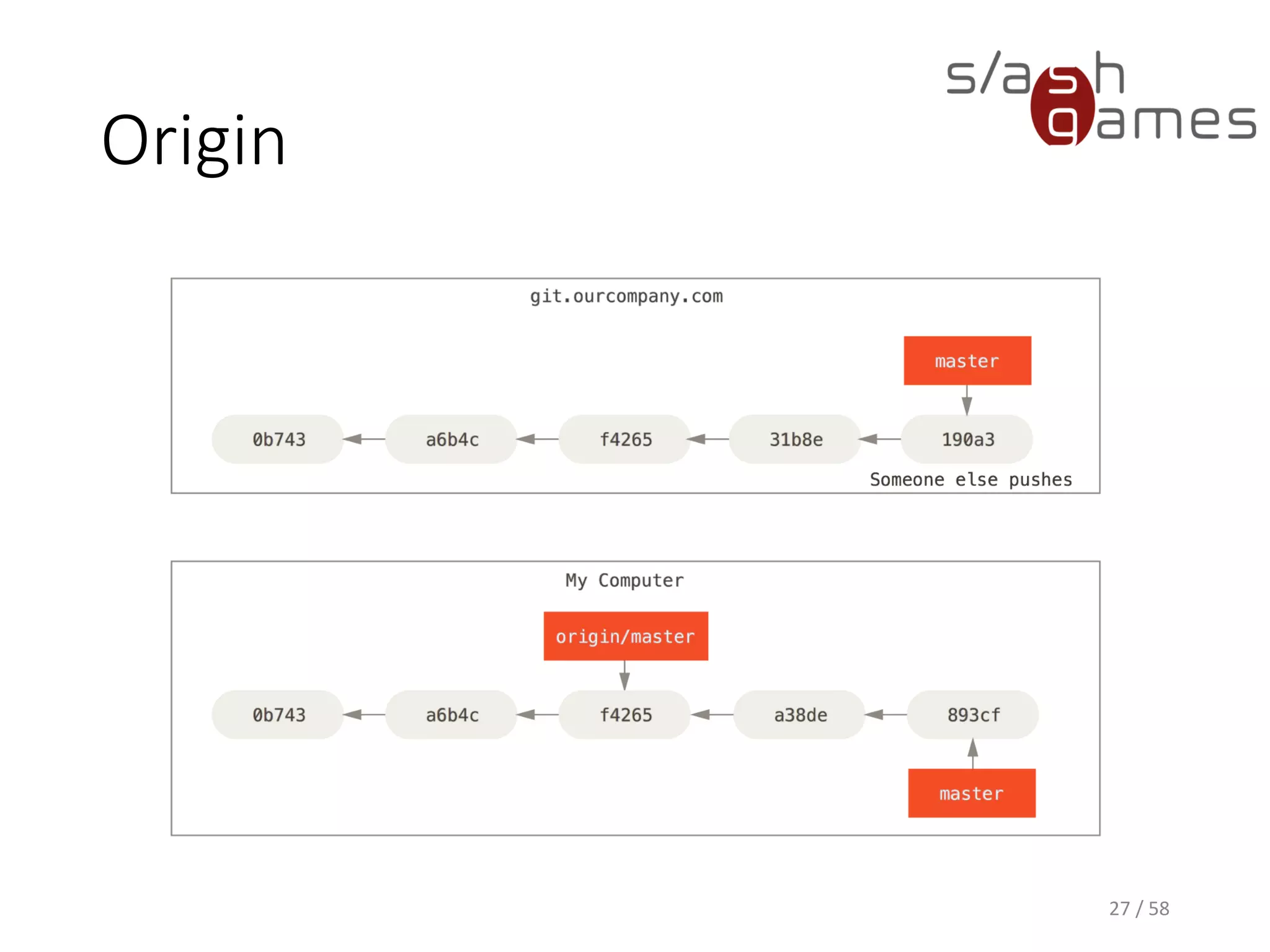
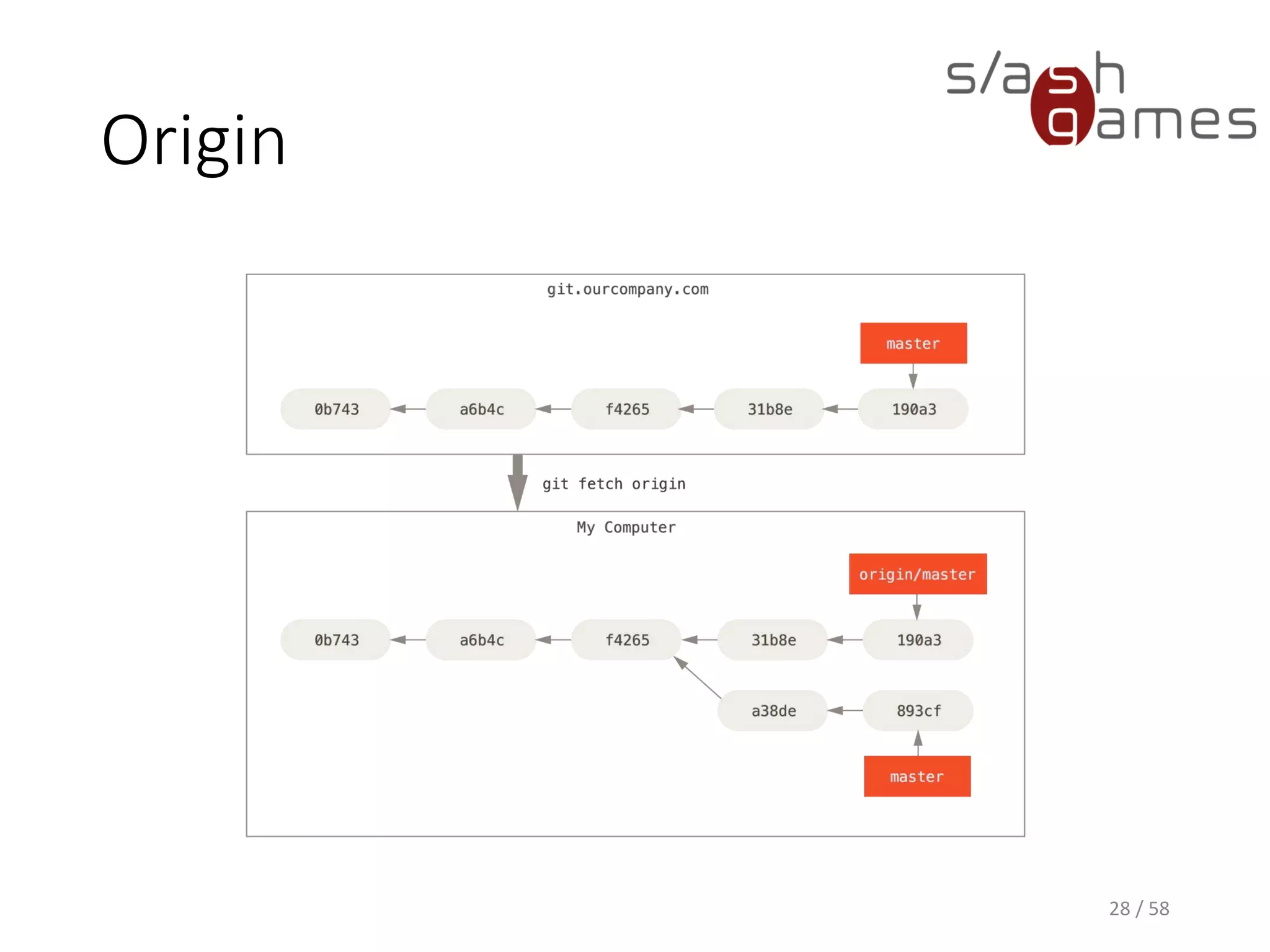
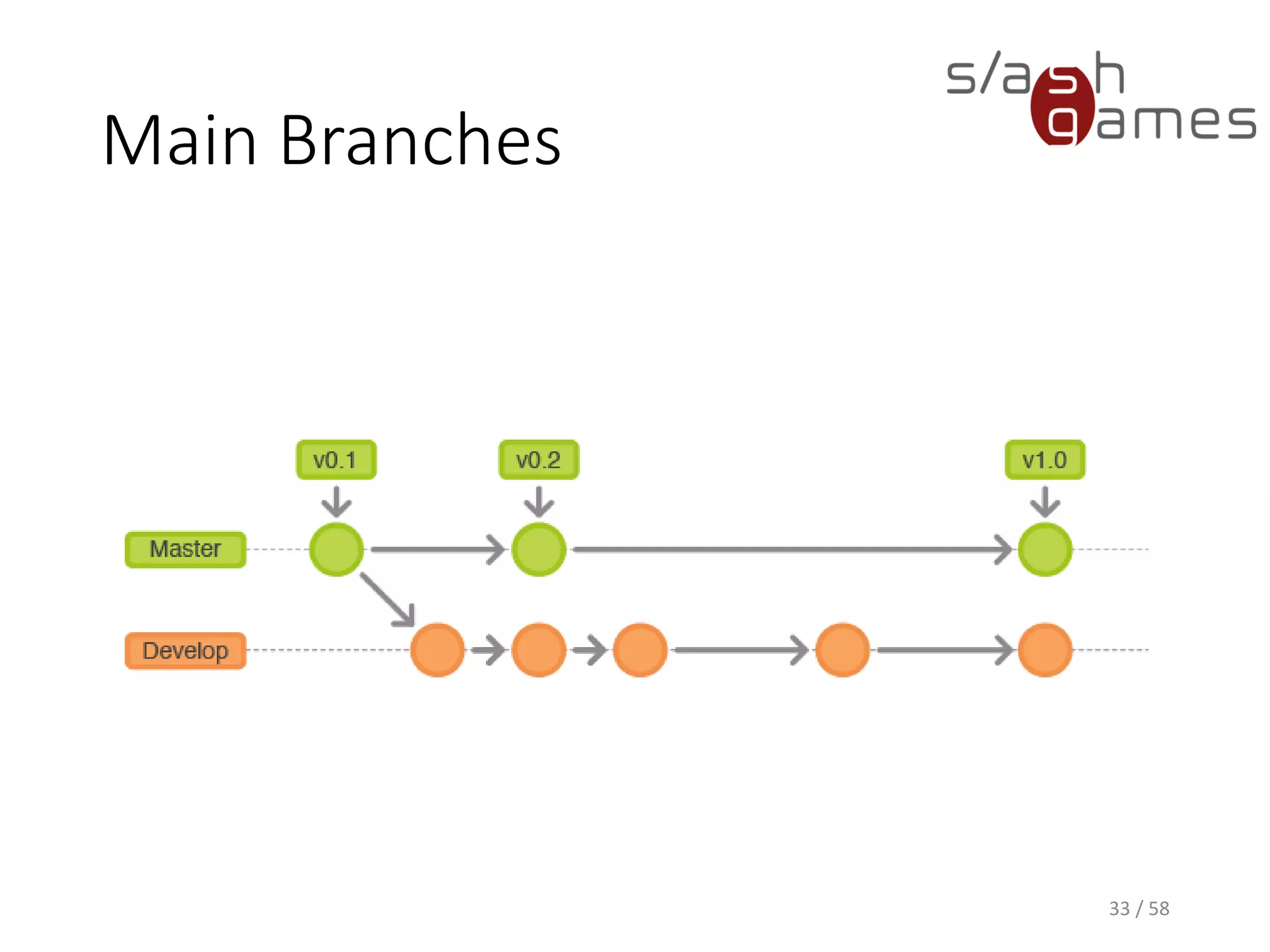
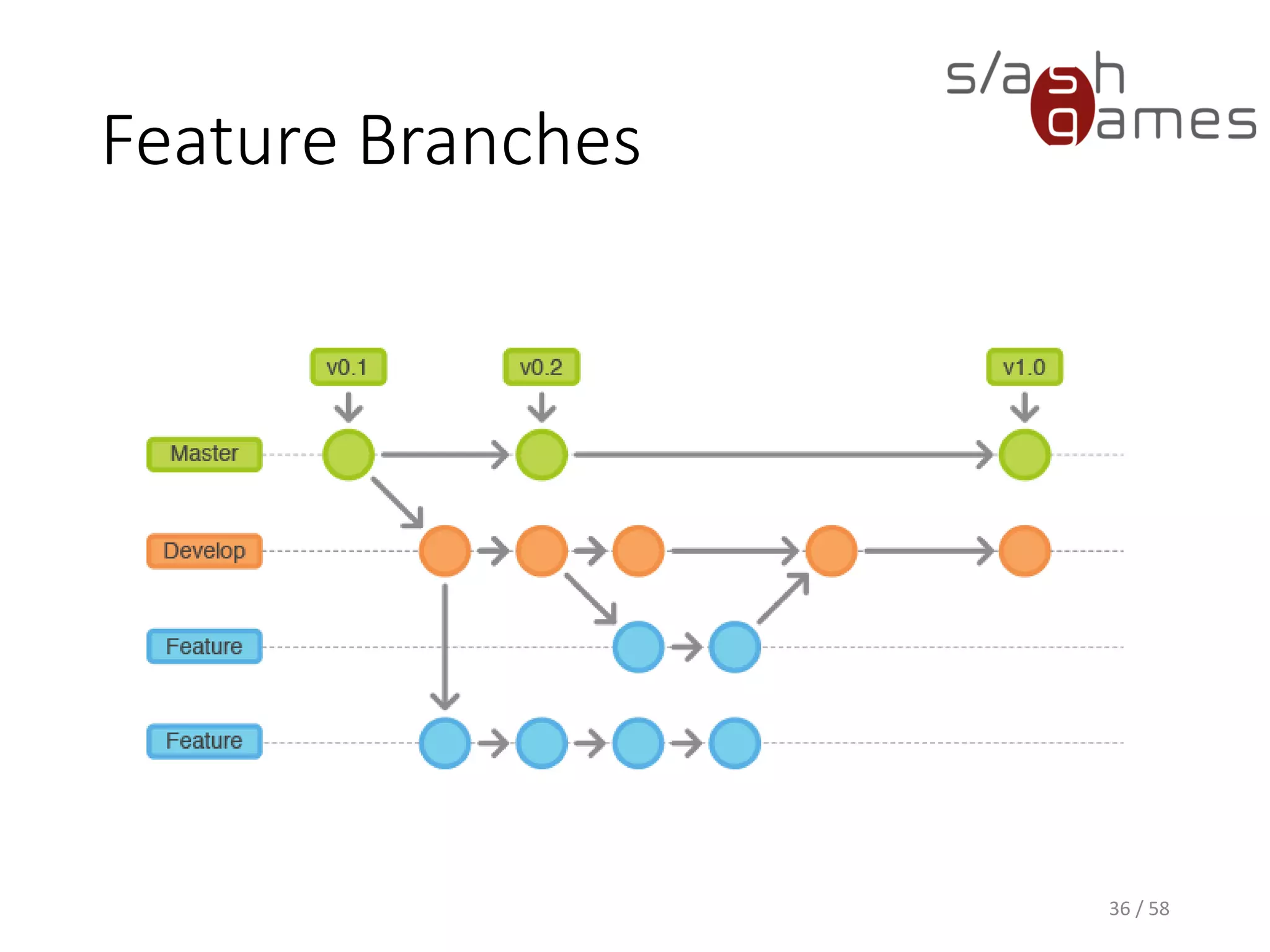
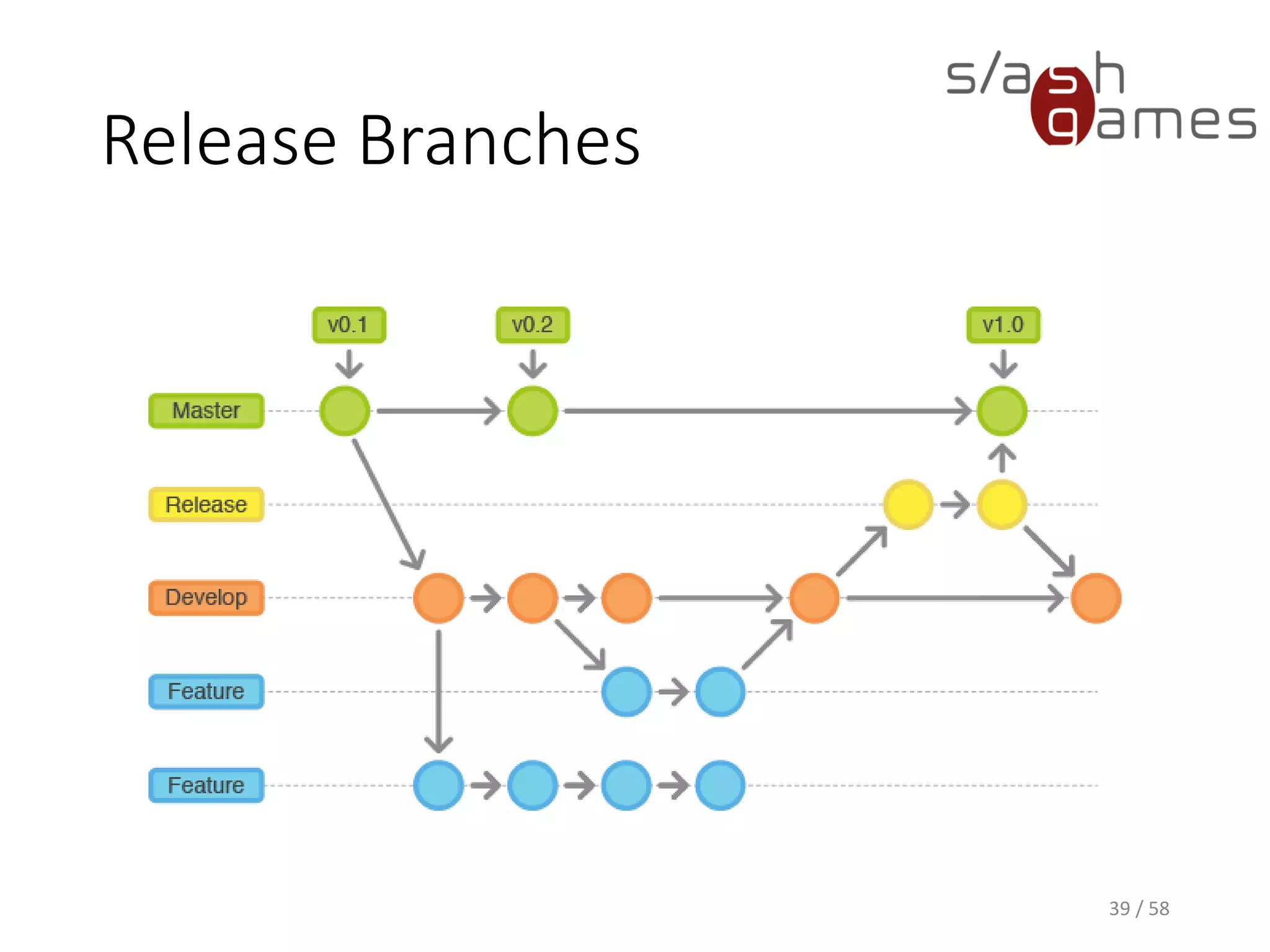
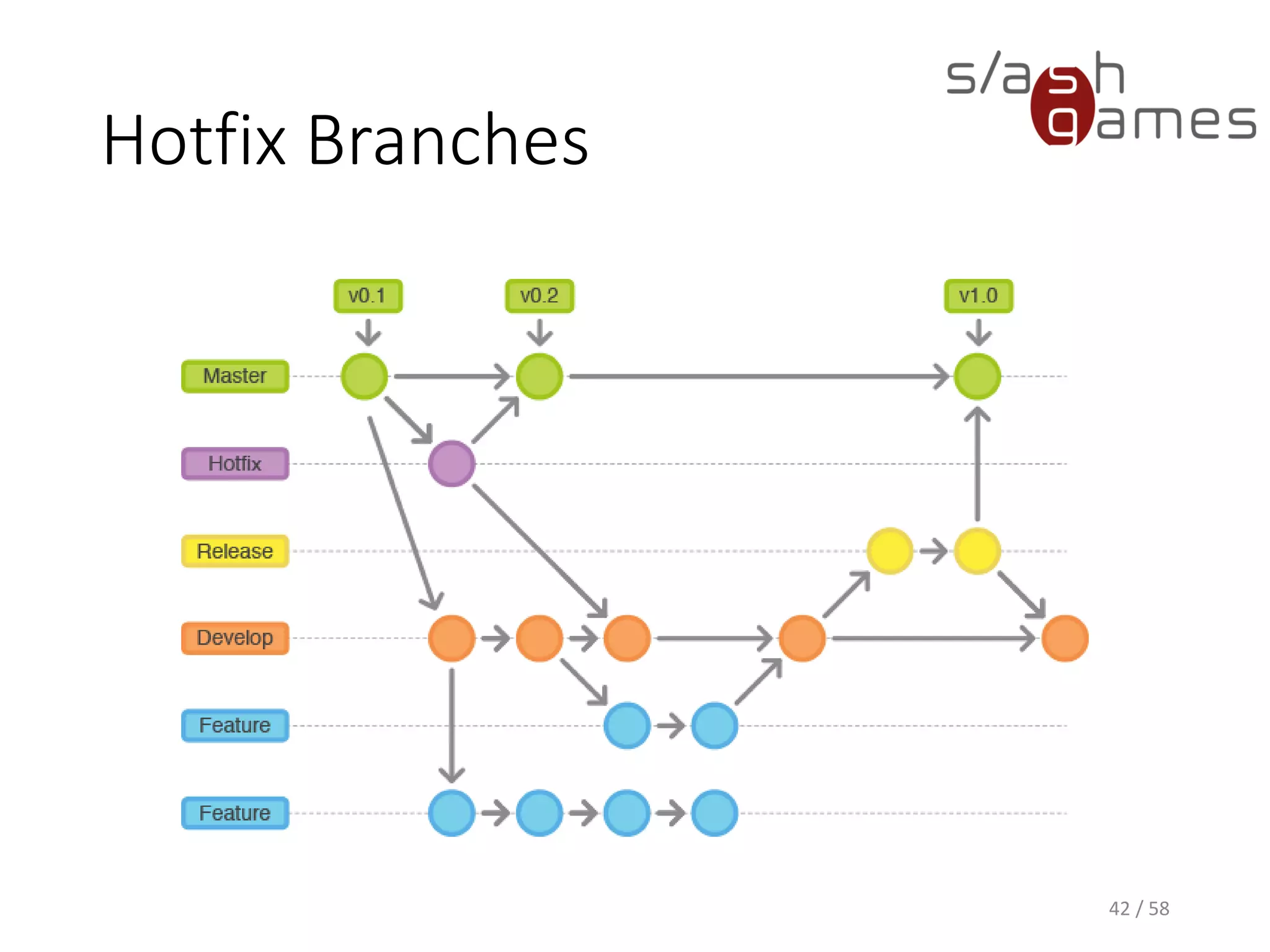
The document outlines the objectives of learning Git, covering version control systems, installation of Git and SourceTree, and basic operations like pulling, committing, and merging. It explains Git branching strategies, including main, feature, release, and hotfix branches, along with best practices for merging. References for further reading and contact information are also provided.