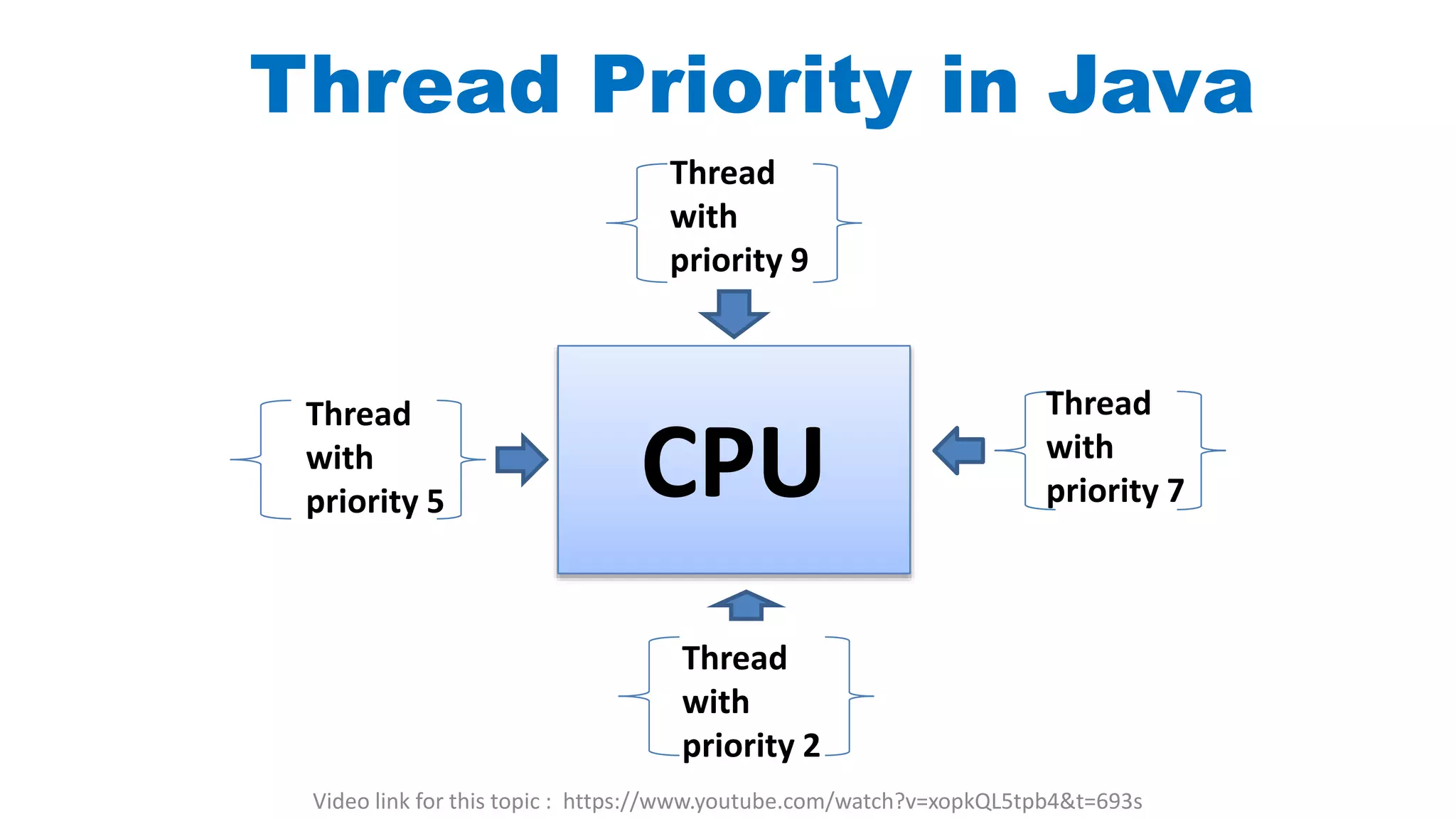
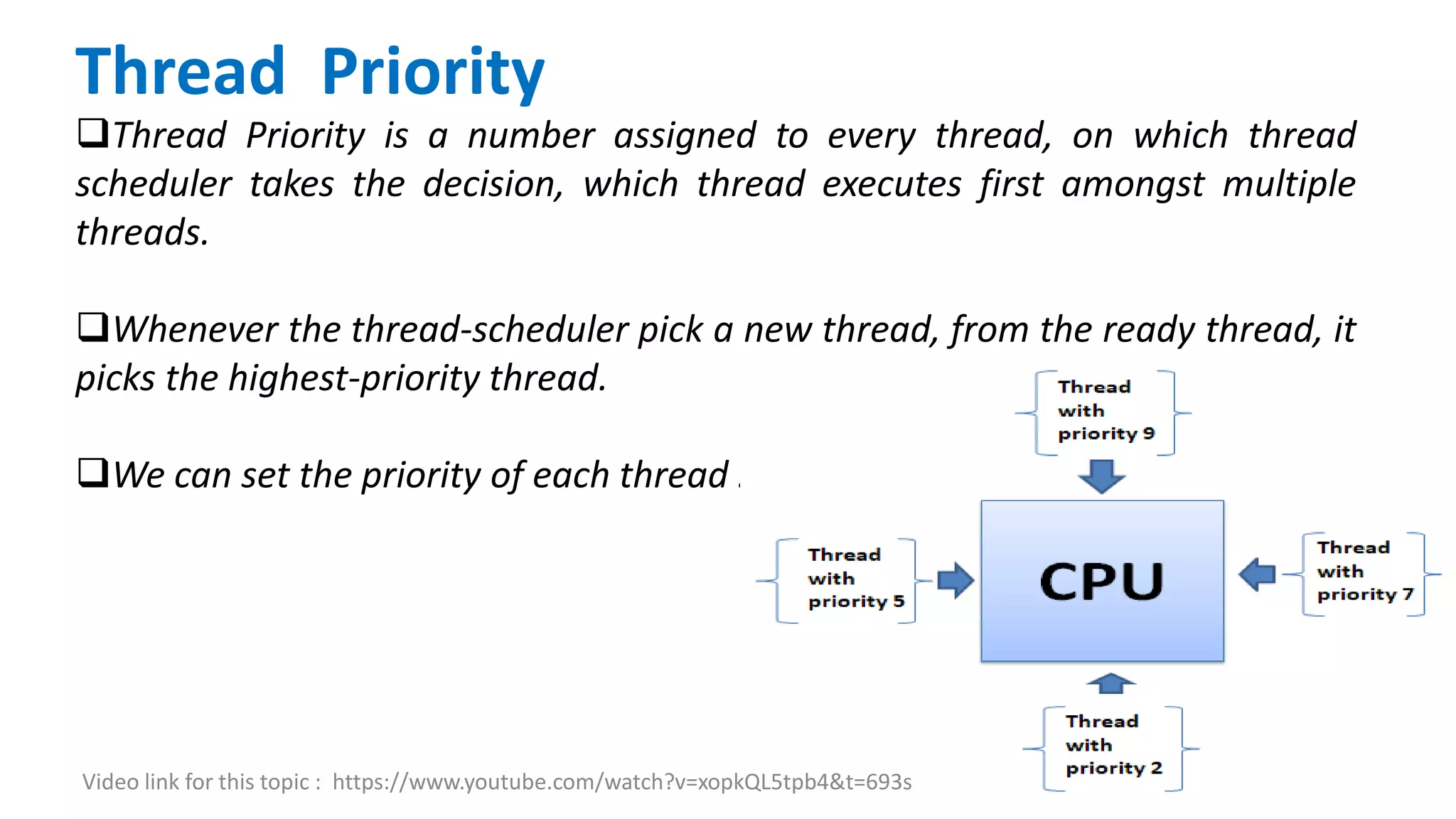
In Java, each thread has a priority that is used by the thread scheduler to determine execution order. The priority can be set from 1 to 10, where 10 is the highest priority. When multiple threads have the same priority, the scheduler will select one to execute based on its algorithm. Methods like getPriority() and setPriority() allow retrieving and setting a thread's priority at runtime. Common priority levels defined as constants include MAX_PRIORITY, MIN_PRIORITY, and NORM_PRIORITY. However, the actual effect of priority depends on the underlying operating system.





![public class CheckRunnable {
public static void main(String args[])
{
AThread1 obj1 = new AThread1();
BThread1 obj2 = new BThread1();
CThread1 obj3 = new CThread1();
Thread.currentThread().setPriority(8);
Thread Athread = new Thread(obj1);
Thread Bthread = new Thread(obj2);
Thread Cthread = new Thread(obj3);
System.out.println(Athread.getPriority());
System.out.println(Bthread.getPriority());
System.out.println(Cthread.getPriority());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
Bthread.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
System.out.println(Bthread.getPriority());
Athread.start();
Bthread.start();
Cthread.start();
}
}
class AThread1 implements Runnable
{
public void run()
{
for(int i = 1;i<=5;i++)
{
System.out.println("Athread" + " " + i);
try {Thread.sleep(500);
}catch(Exception e)
{}}}}
class BThread1 implements Runnable
{
public void run()
{
System.out.println("BThread");
}}
class CThread1 implements Runnable
{
public void run()
{
System.out.println("CThread");
}
}
Program to set priority of current thread/parent thread and use of constant
Video link for this topic : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xopkQL5tpb4&t=693s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/threadpriorityinjava-200602074819/75/Thread-priority-in-java-8-2048.jpg)