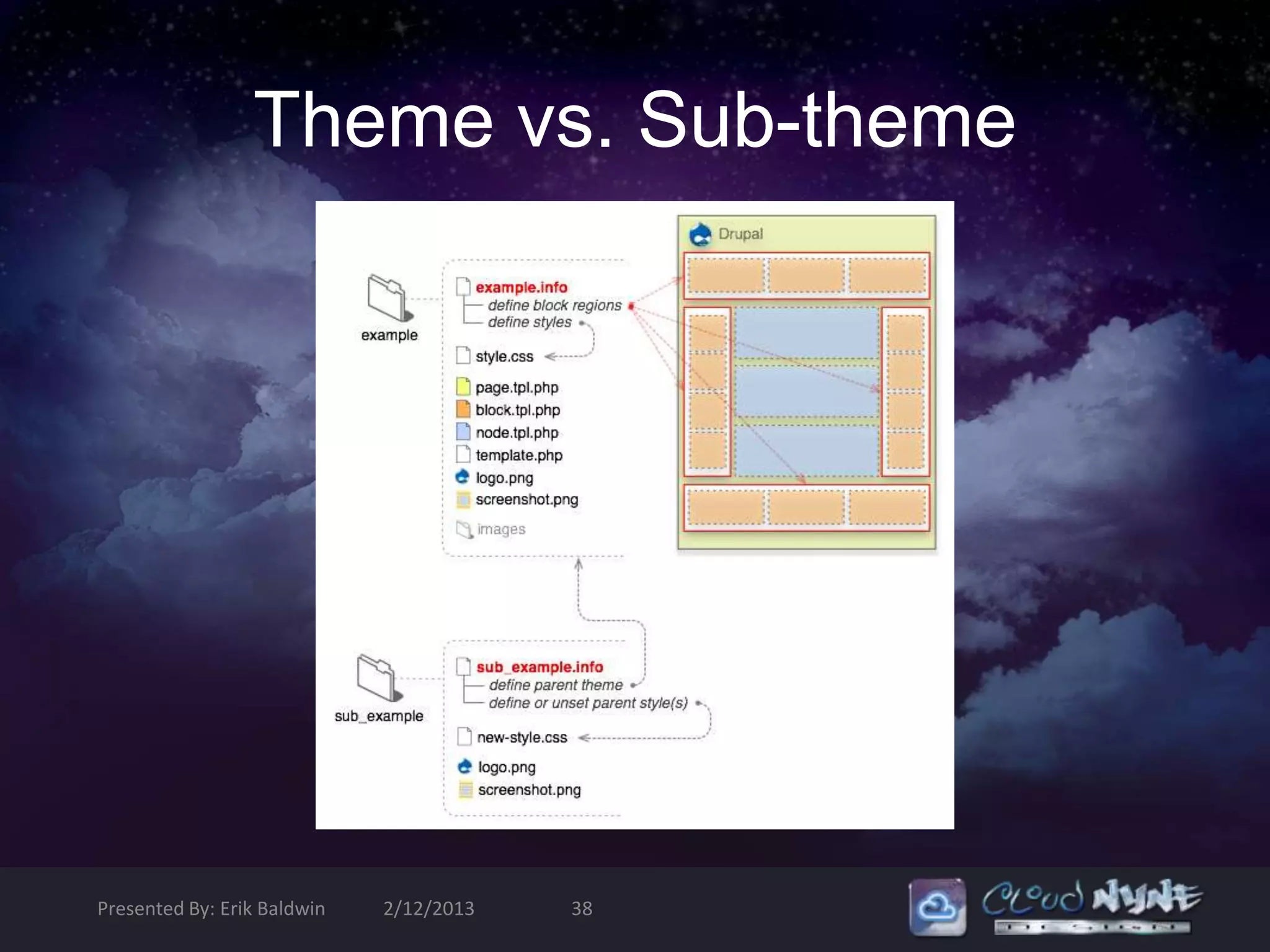
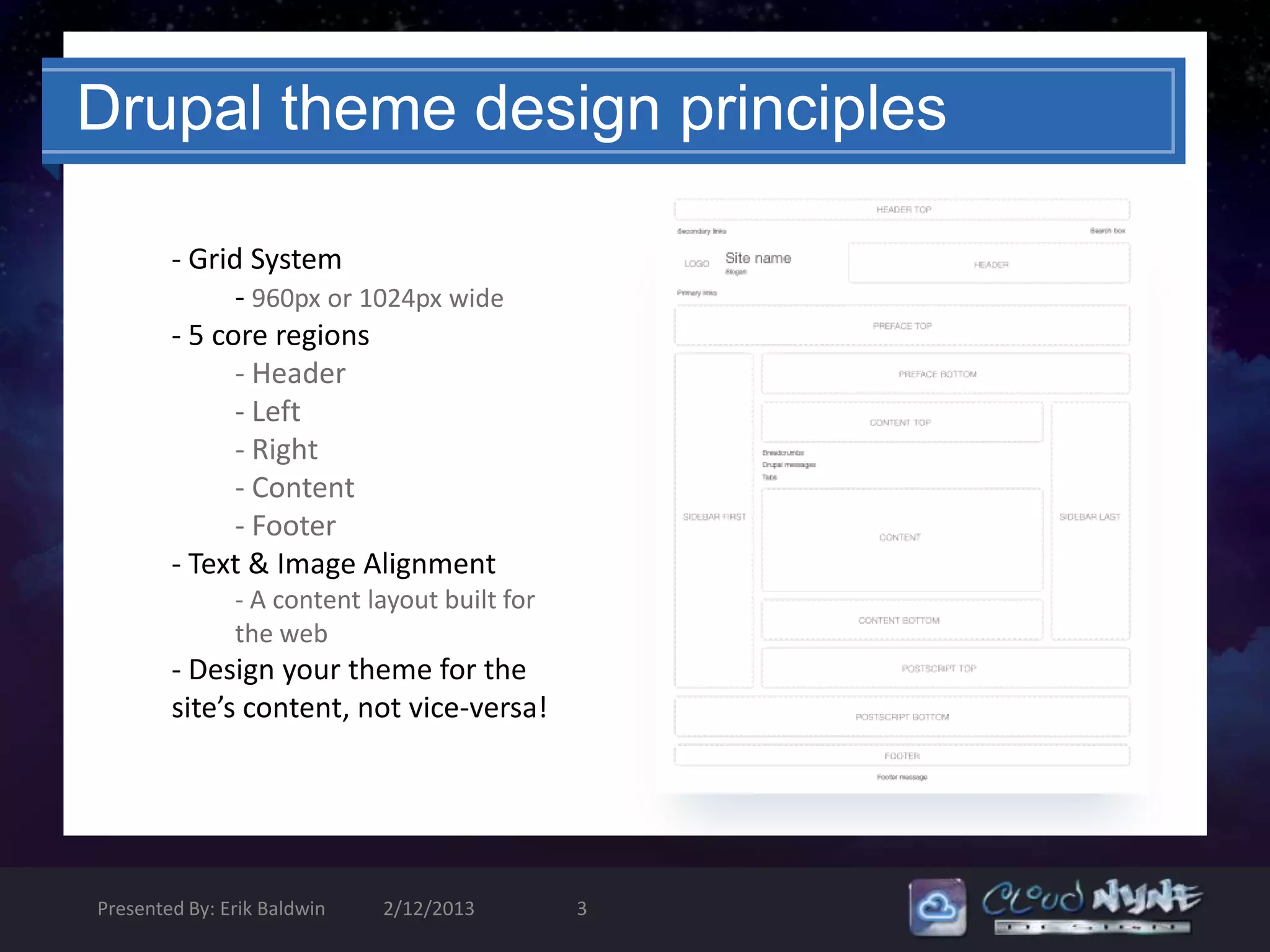
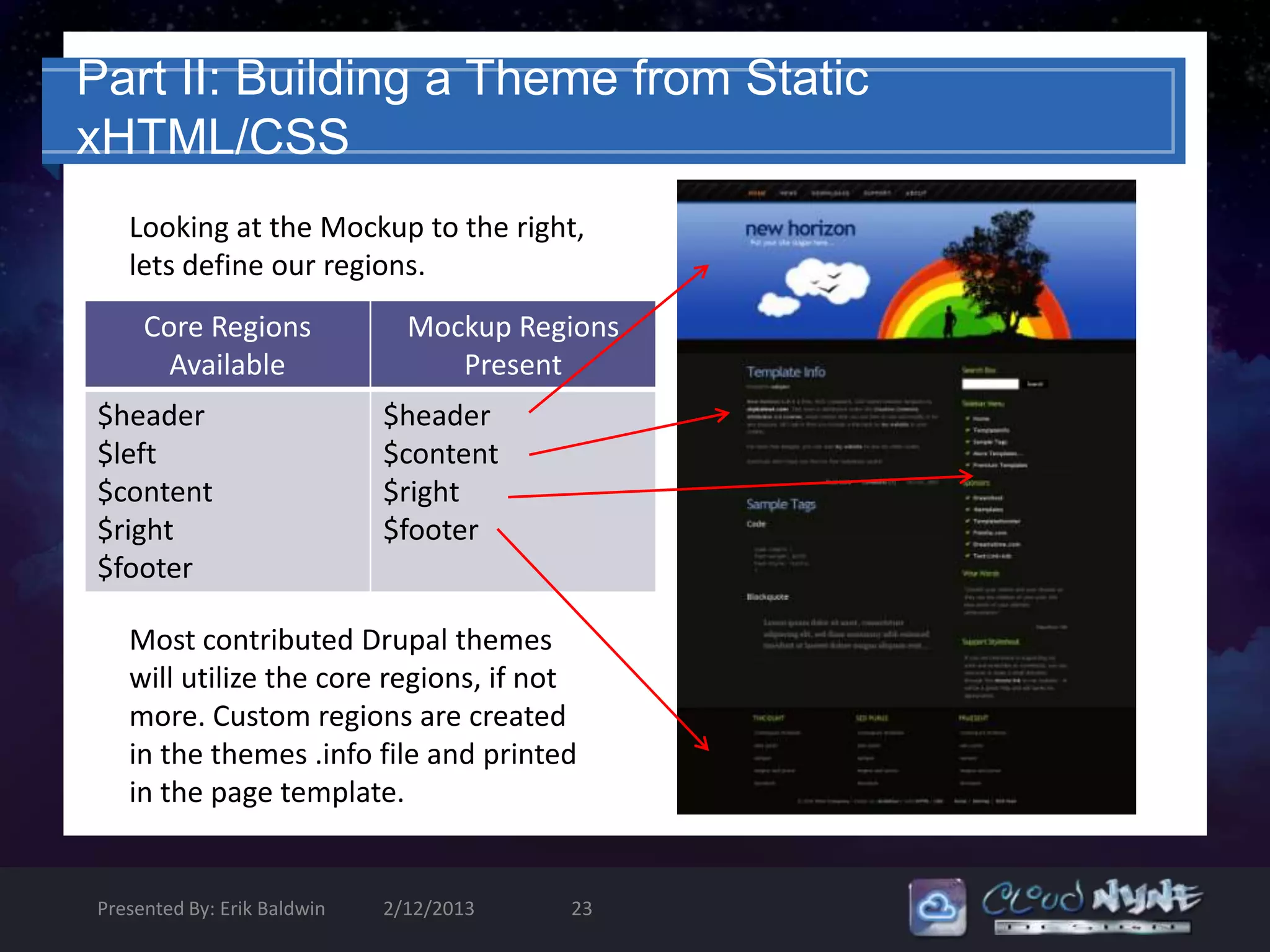
The document provides an introduction to theming in Drupal 6, covering the basics and some advanced concepts. It discusses the anatomy of a Drupal theme including files like the .info file, templates, styles, and scripts. It explains Drupal's theme engine and template language, emphasizing separation of design and logic. It also covers common template files, preprocessing functions, and the template hierarchy. The goal is to explain the fundamental components and best practices for building Drupal themes.


![Theming Caveats
… ‘cause it can’t always be
easy.
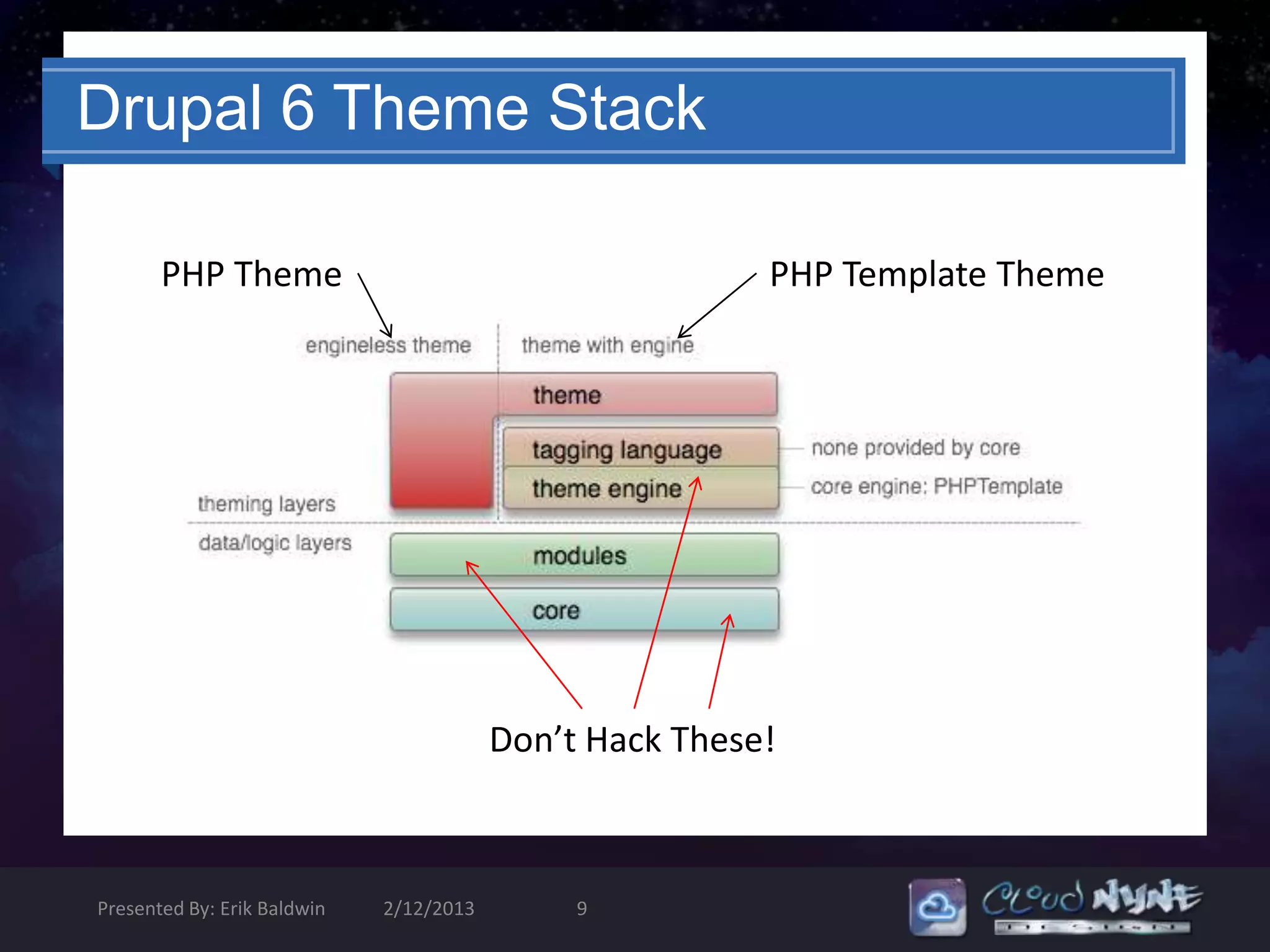
Don’t hack core!
Don’t hack modules!
Don’t hack contrib themes!
The output from all of these is
THEMABLE!
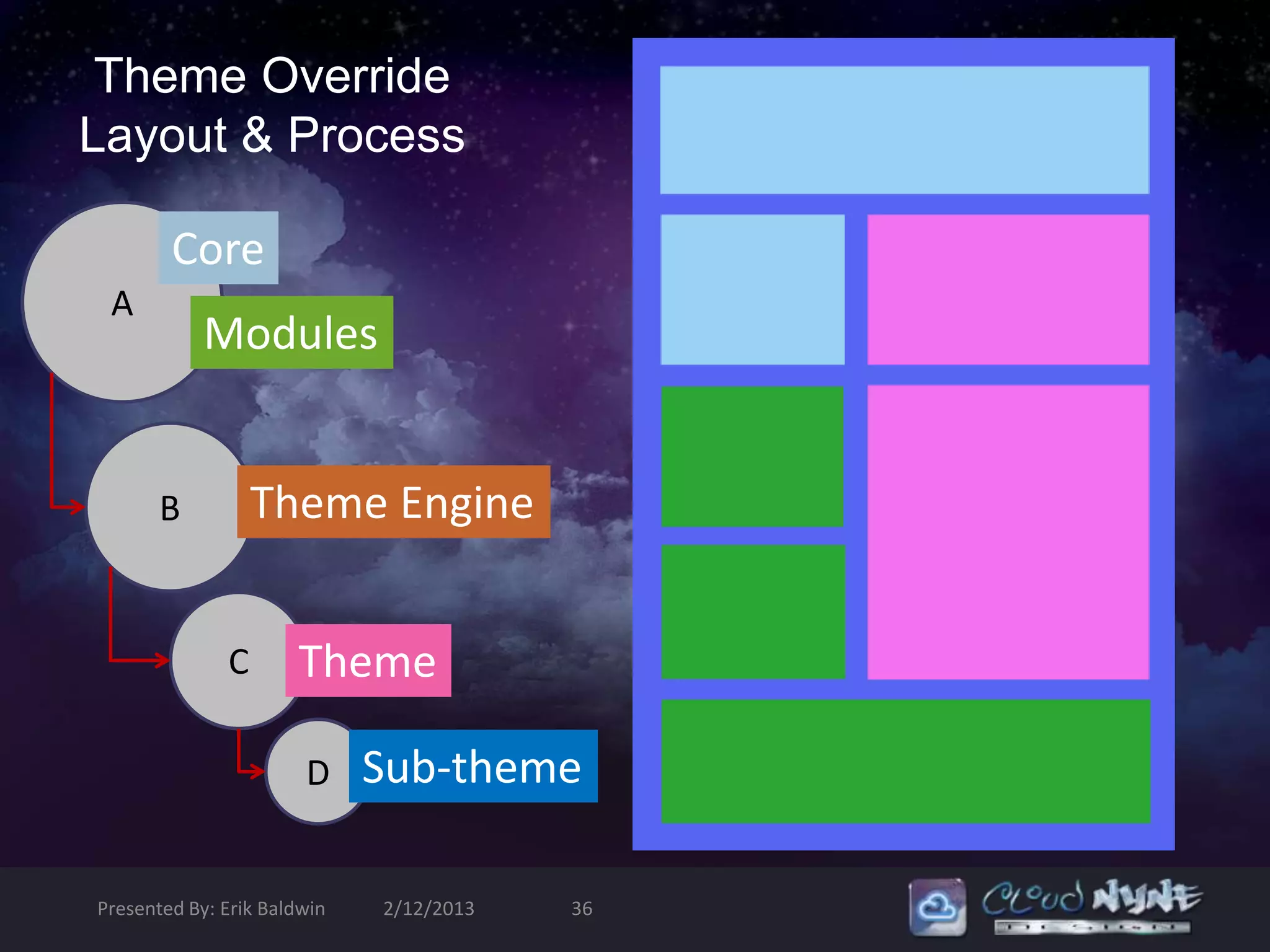
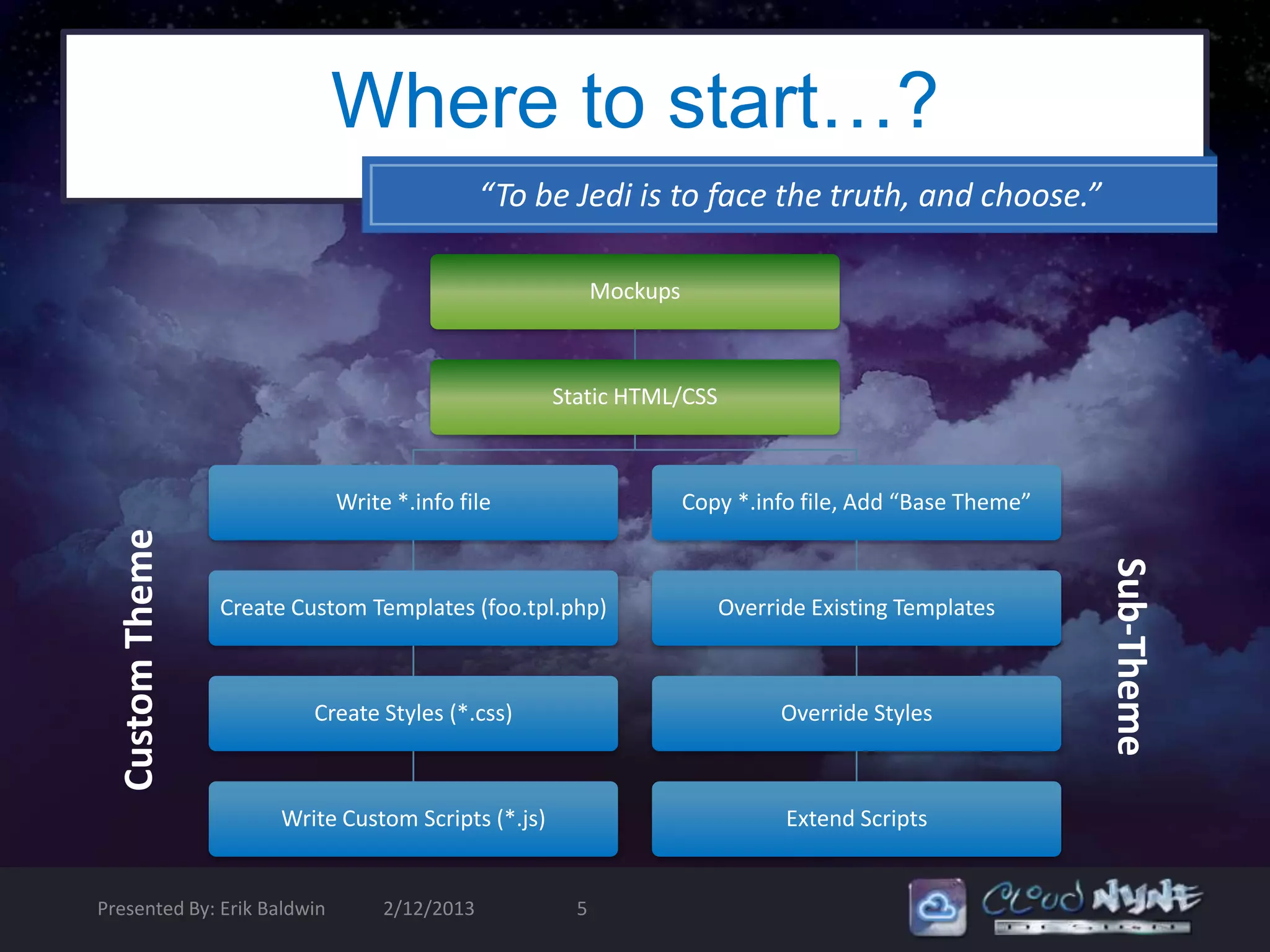
Intercept , Override [template.php] & Sub-Theme [foo.tpl.php]
Presented By: Erik Baldwin 2/12/2013 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/themingdrupal6-anintroductiontothebasics-130212134348-phpapp02/75/Theming-Drupal-6-An-Introduction-to-the-Basics-4-2048.jpg)

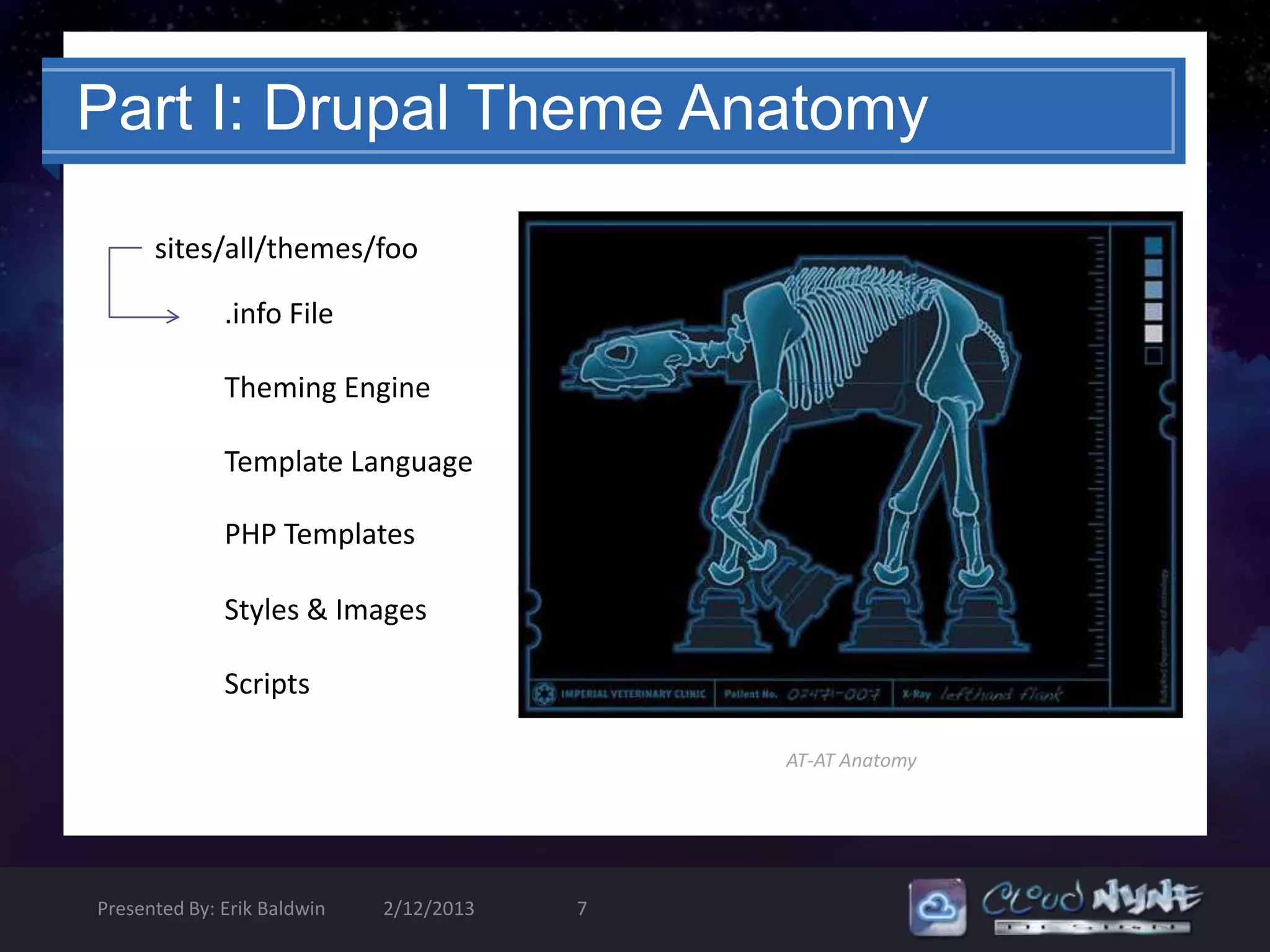



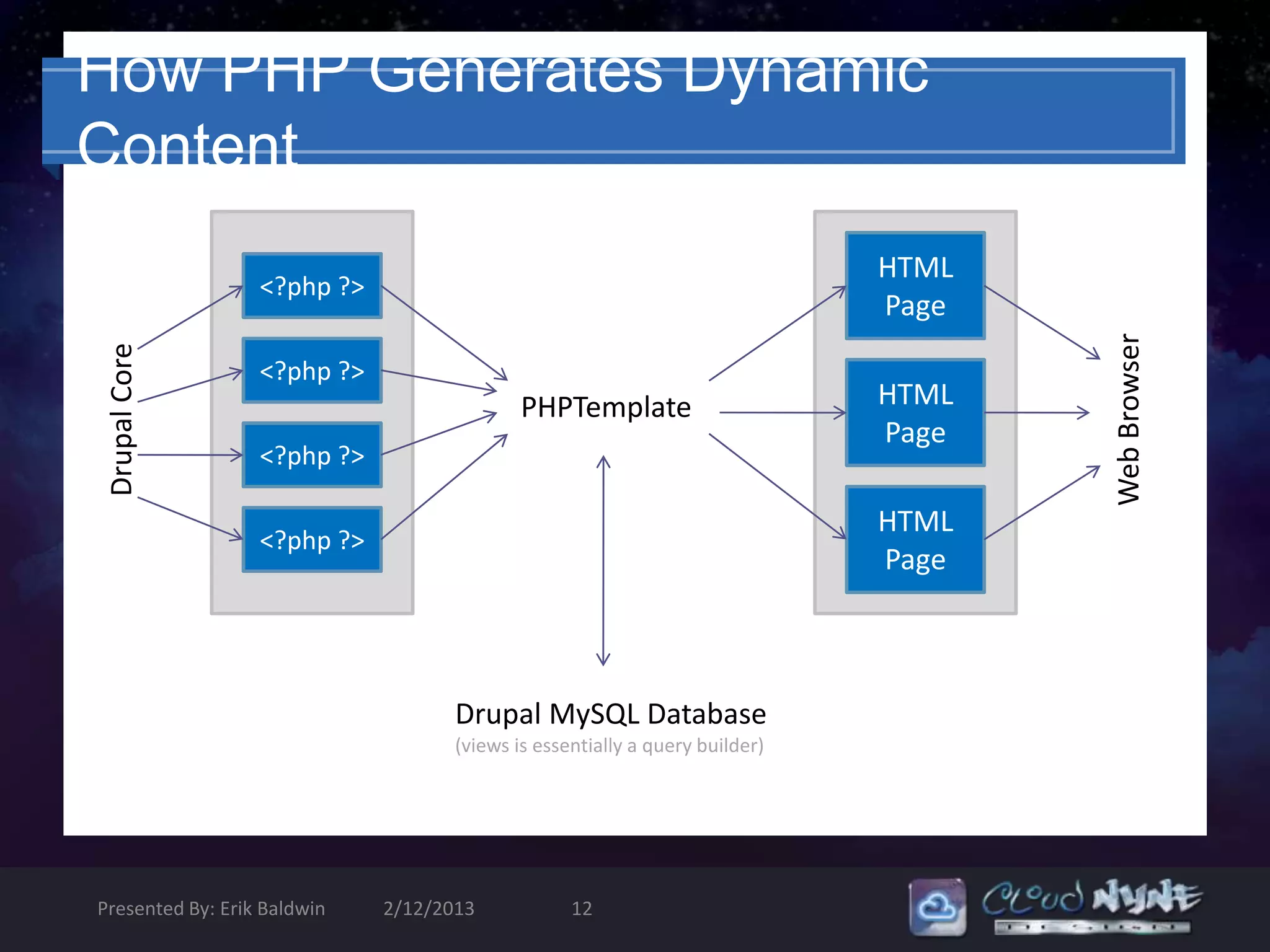
![Template.php
What am I supposed to do with this?!
• Template.php holds the conditional logic and data processing
required for output
• It is where you create your preprocessors for generating variables
before they merge with *.tpl.php file – each individual template
file (.tpl.php) gets assigned to regions
• This is also where you override existing theme functions and
create other raw output customization (example below)
function theme_name_preprocess_page(&$vars) {
//override for mission statement to appear on every page, not just <front>
$vars['mission'] = filter_xss_admin (theme_get_setting('mission'));
//creates raw output for $foo that can be printed in any *.tpl.php
$vars[‘foo’] = t(‘FooBar’);}
Presented By: Erik Baldwin 2/12/2013 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/themingdrupal6-anintroductiontothebasics-130212134348-phpapp02/75/Theming-Drupal-6-An-Introduction-to-the-Basics-13-2048.jpg)







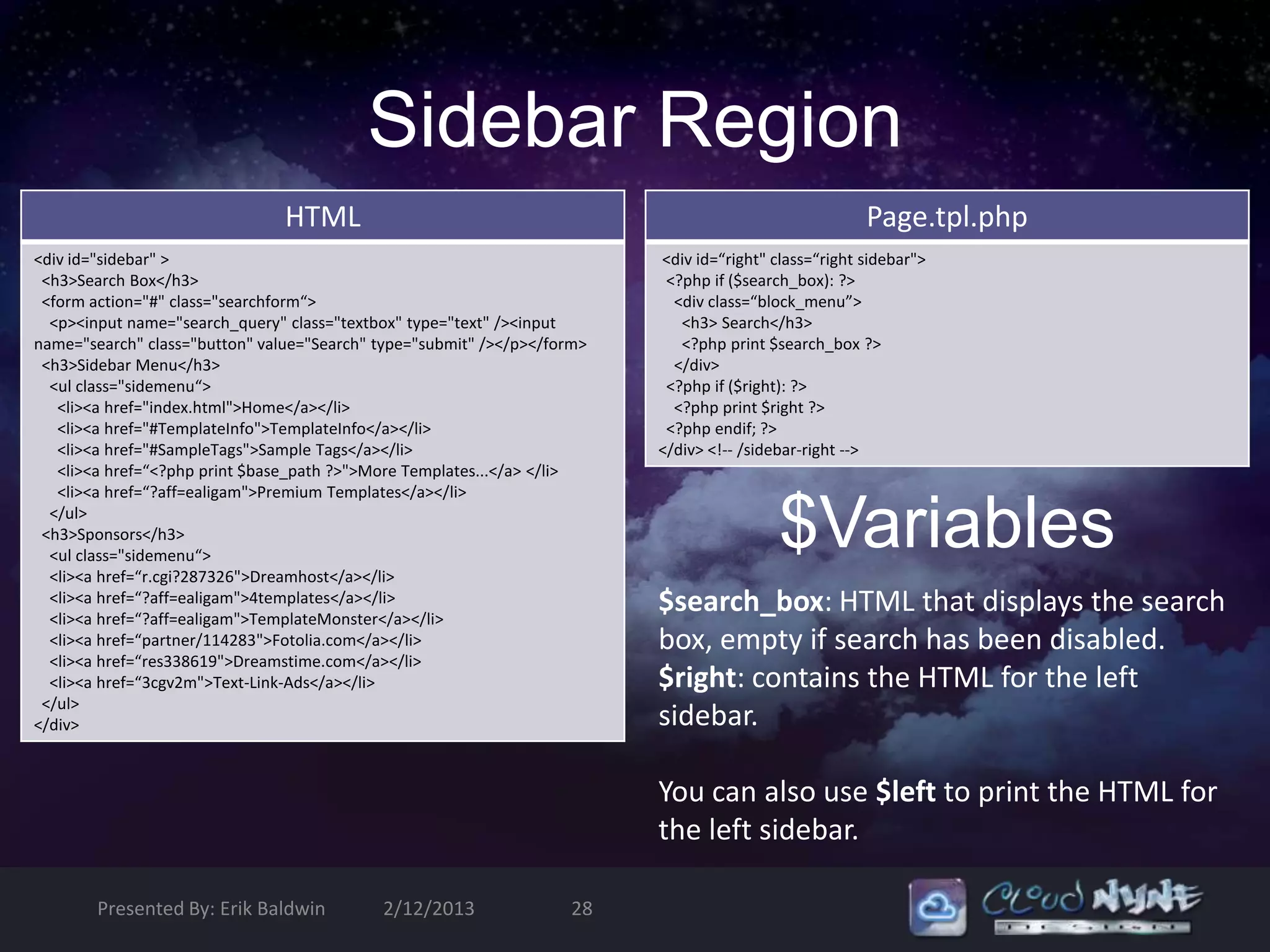
![Header $Variables
$logo: The path to the linked logo image that is defined in the
theme’s configuration.
$site_name: The name of the site. This value will be empty
when display has been disabled in theme settings
(features[] = name).
$front_page: The URL of the front page. Use this instead of
$base_path to link to the front page. This variable includes the
language domain or prefix.
$primary_links (array): An Array containing the primary
navigation links for the site, if they have been configured.
$secondary_links (array): An array containing secondary
navigation links for the site, if they have been configured.
Presented By: Erik Baldwin 2/12/2013 27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/themingdrupal6-anintroductiontothebasics-130212134348-phpapp02/75/Theming-Drupal-6-An-Introduction-to-the-Basics-27-2048.jpg)