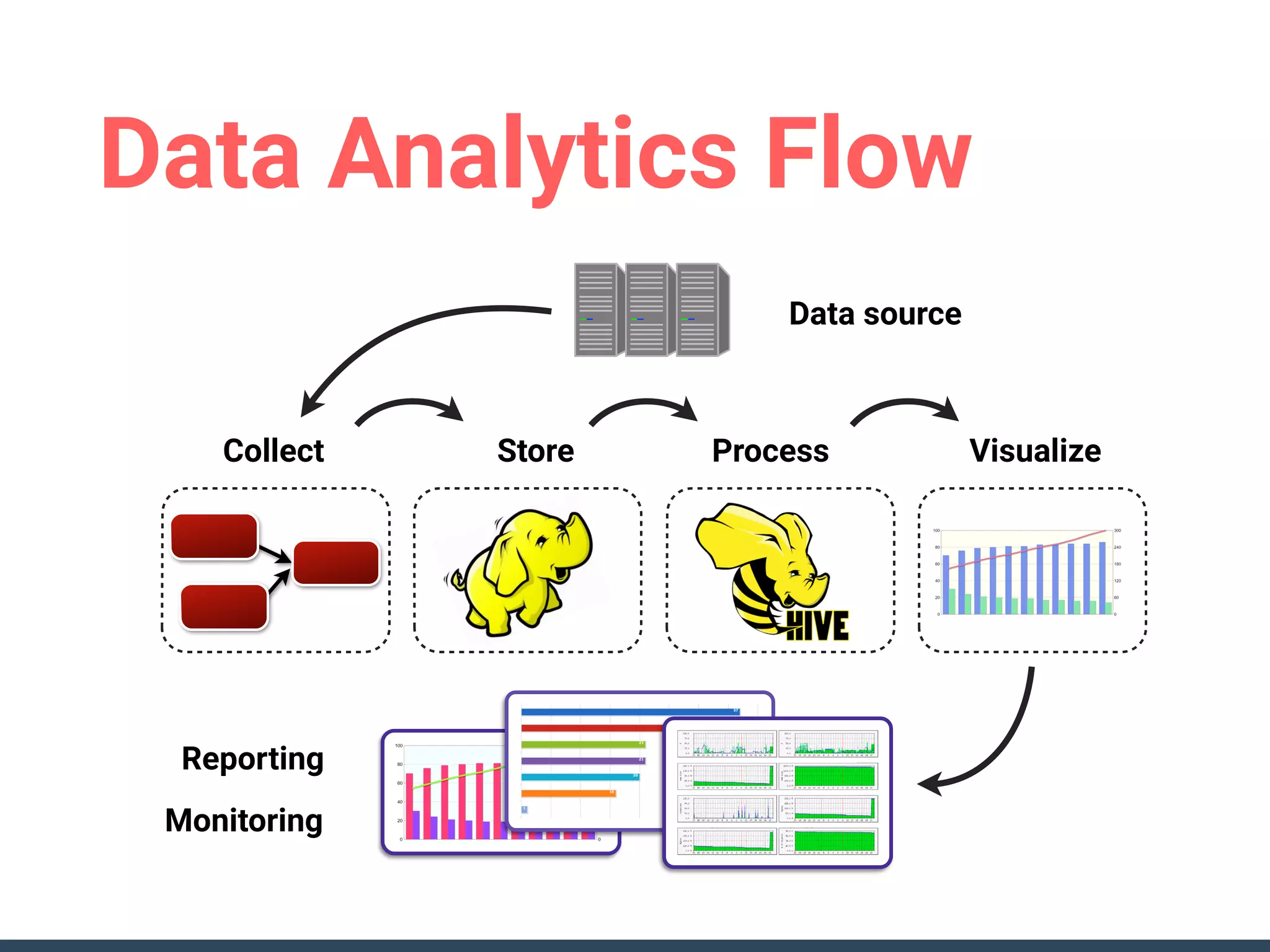
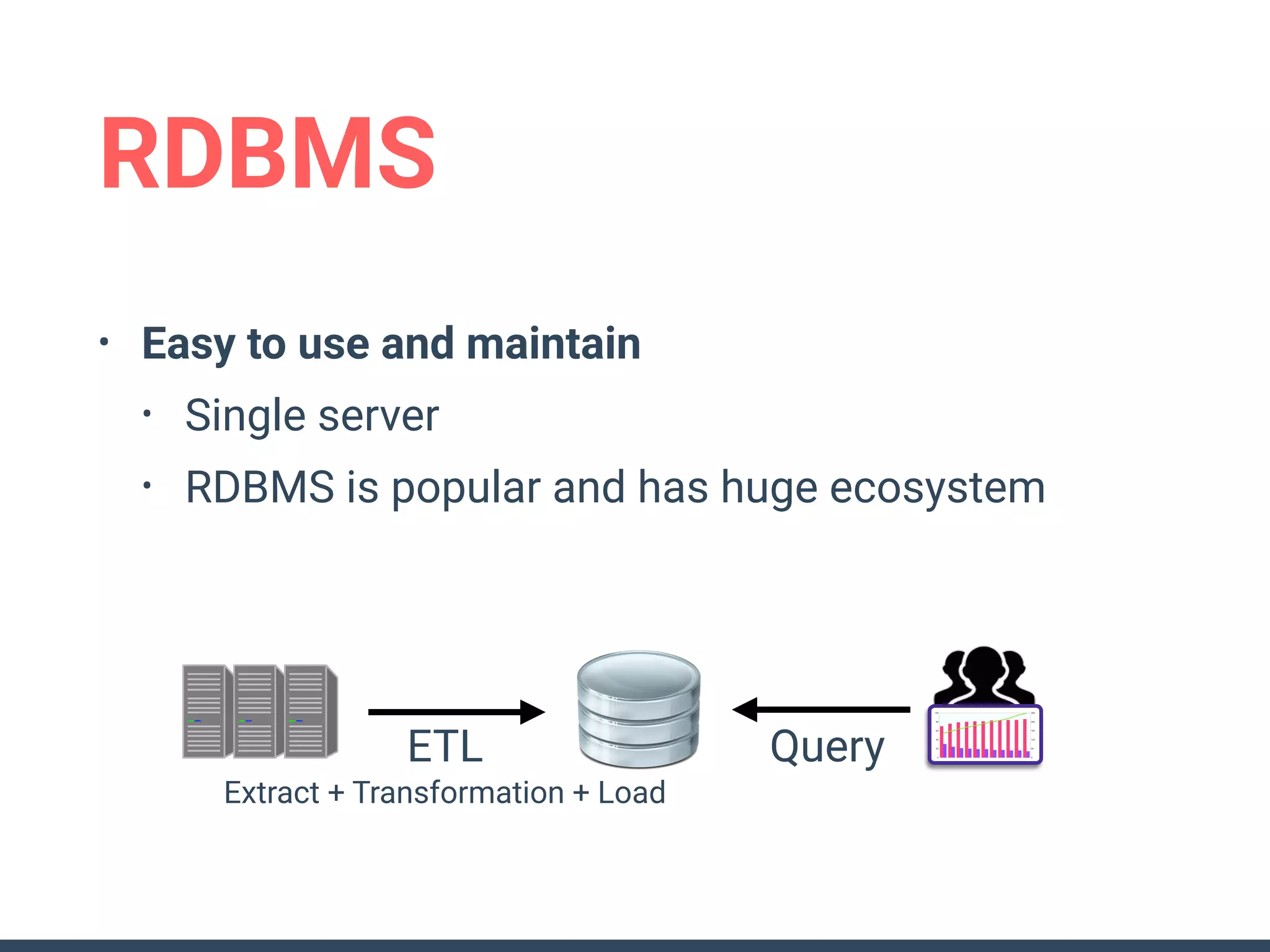
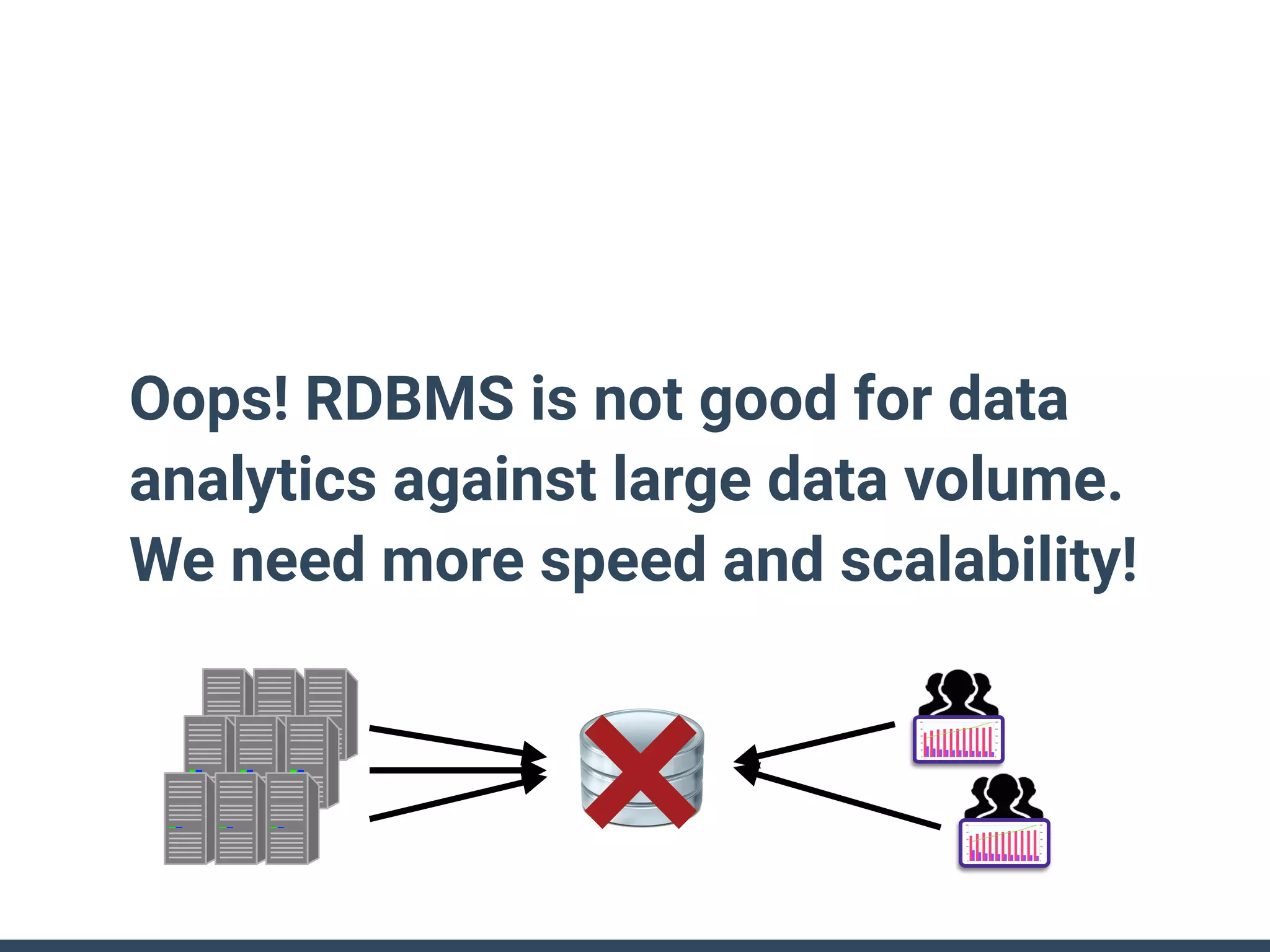
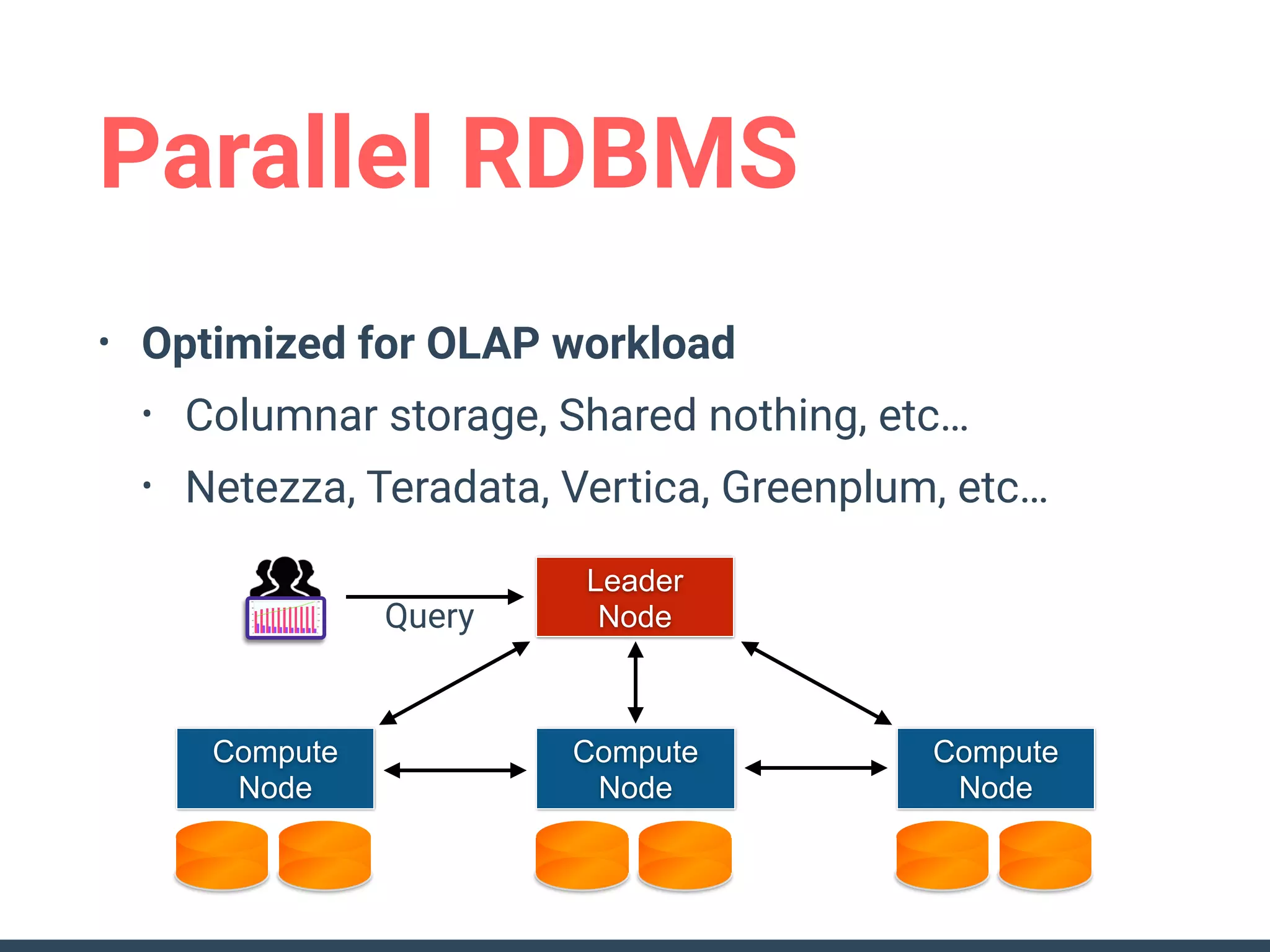
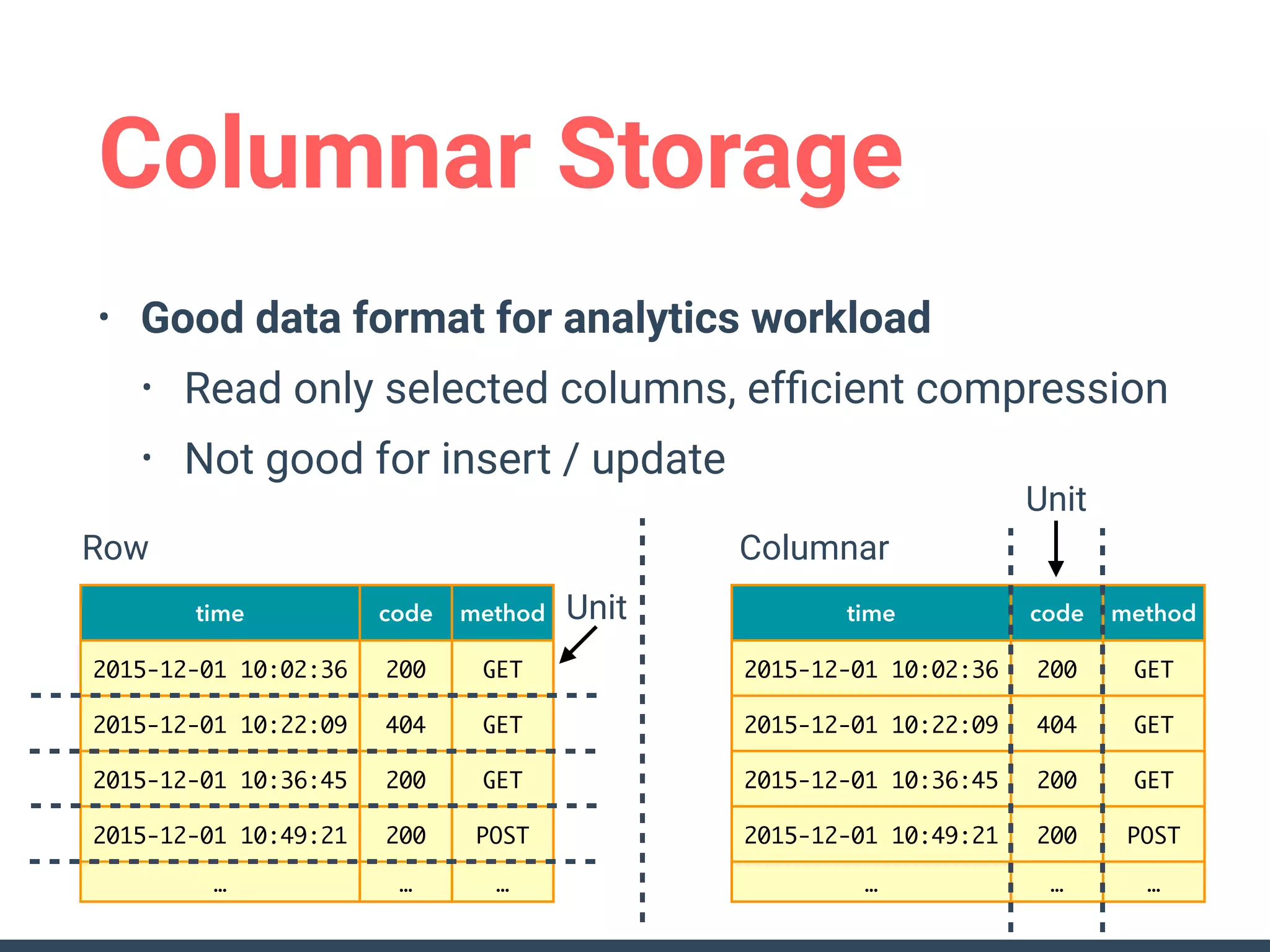
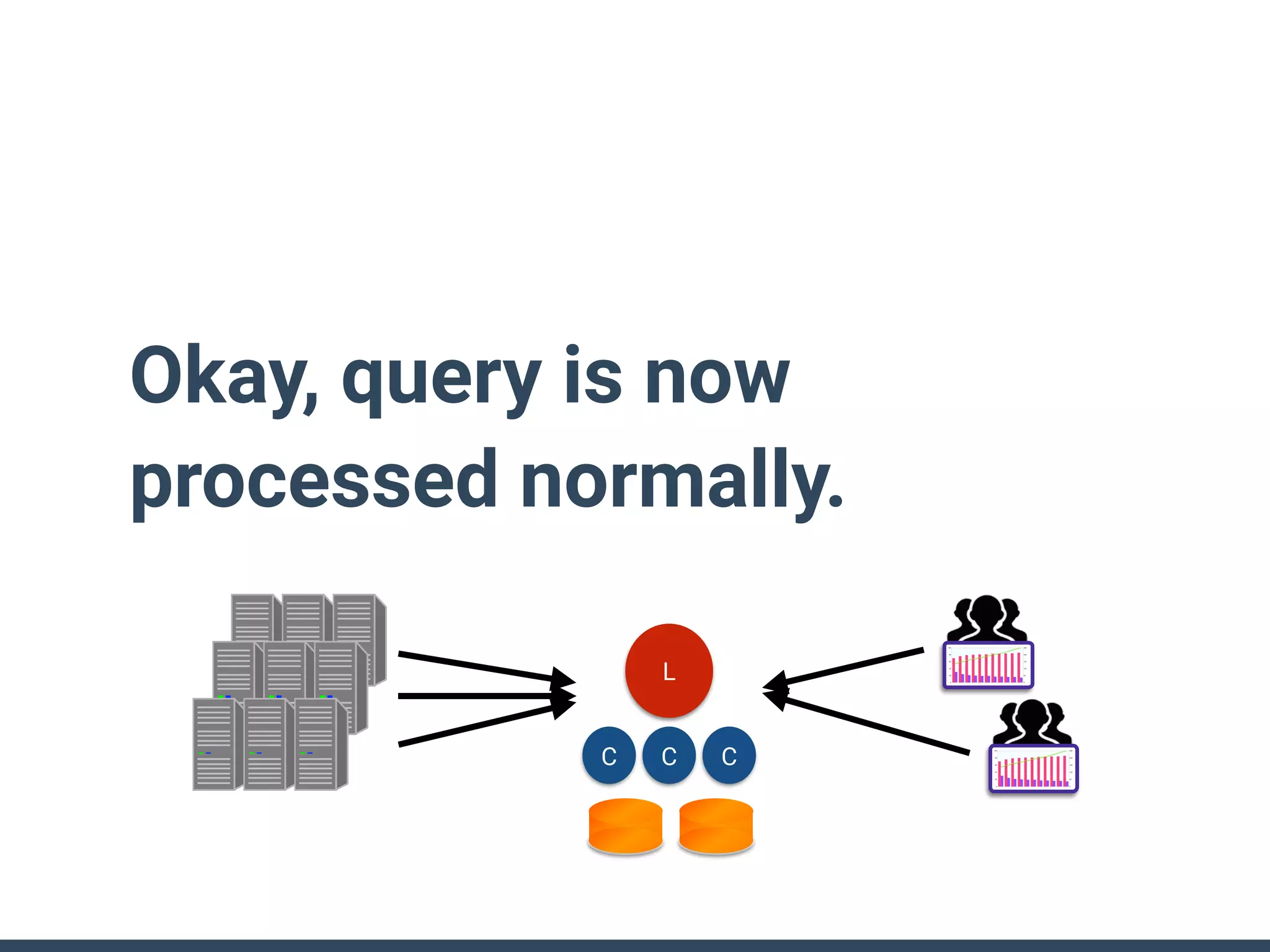
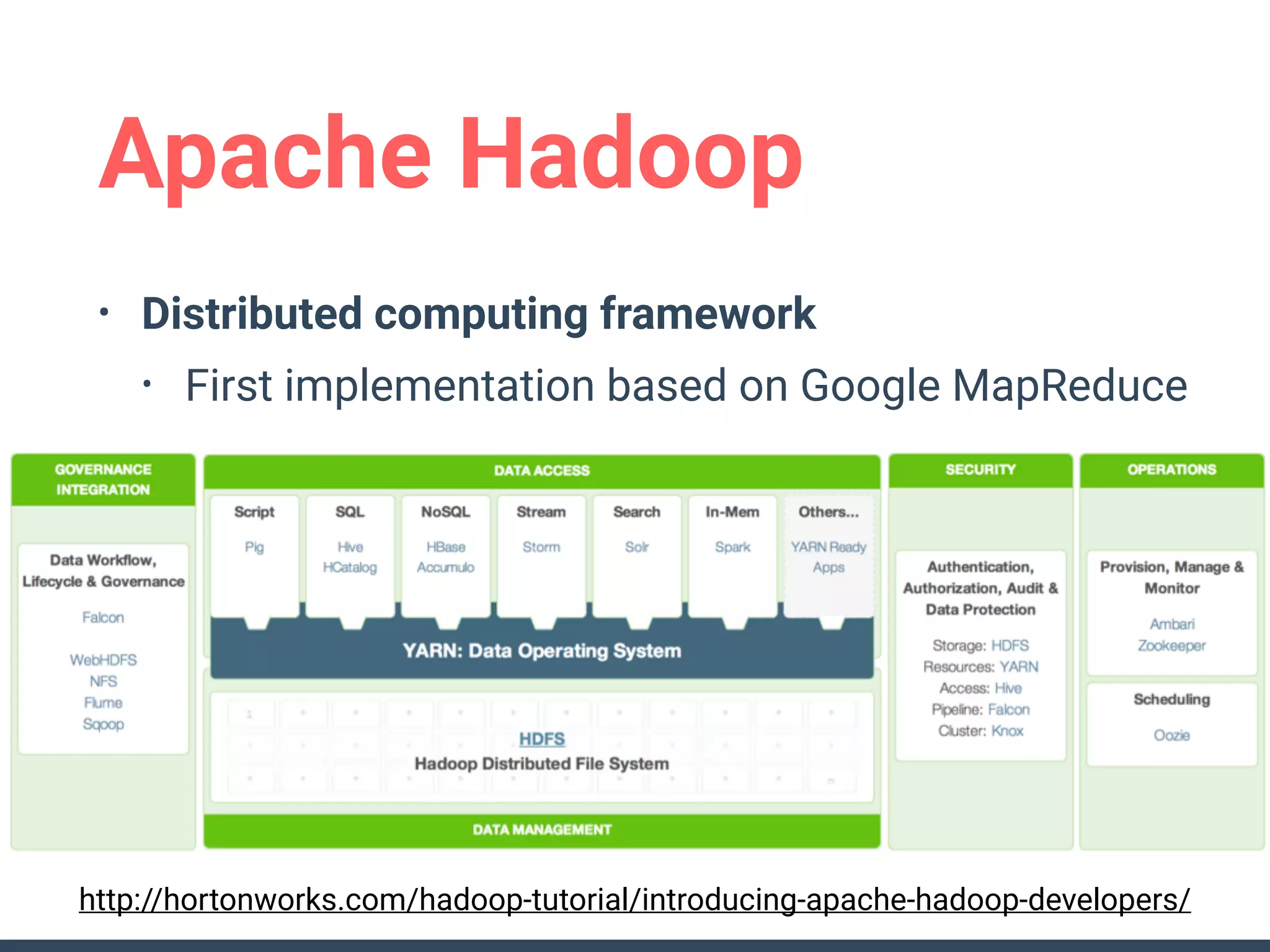
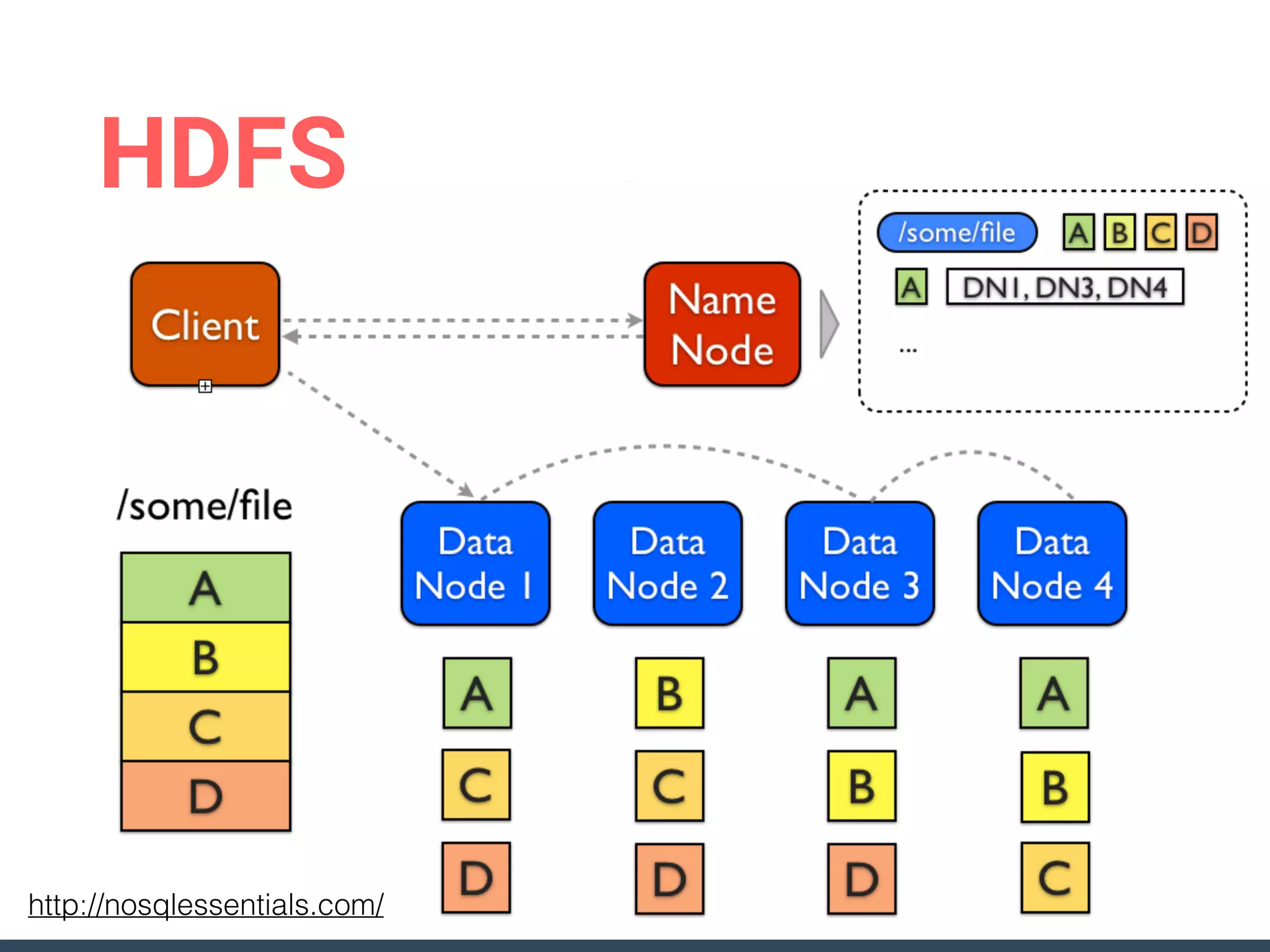
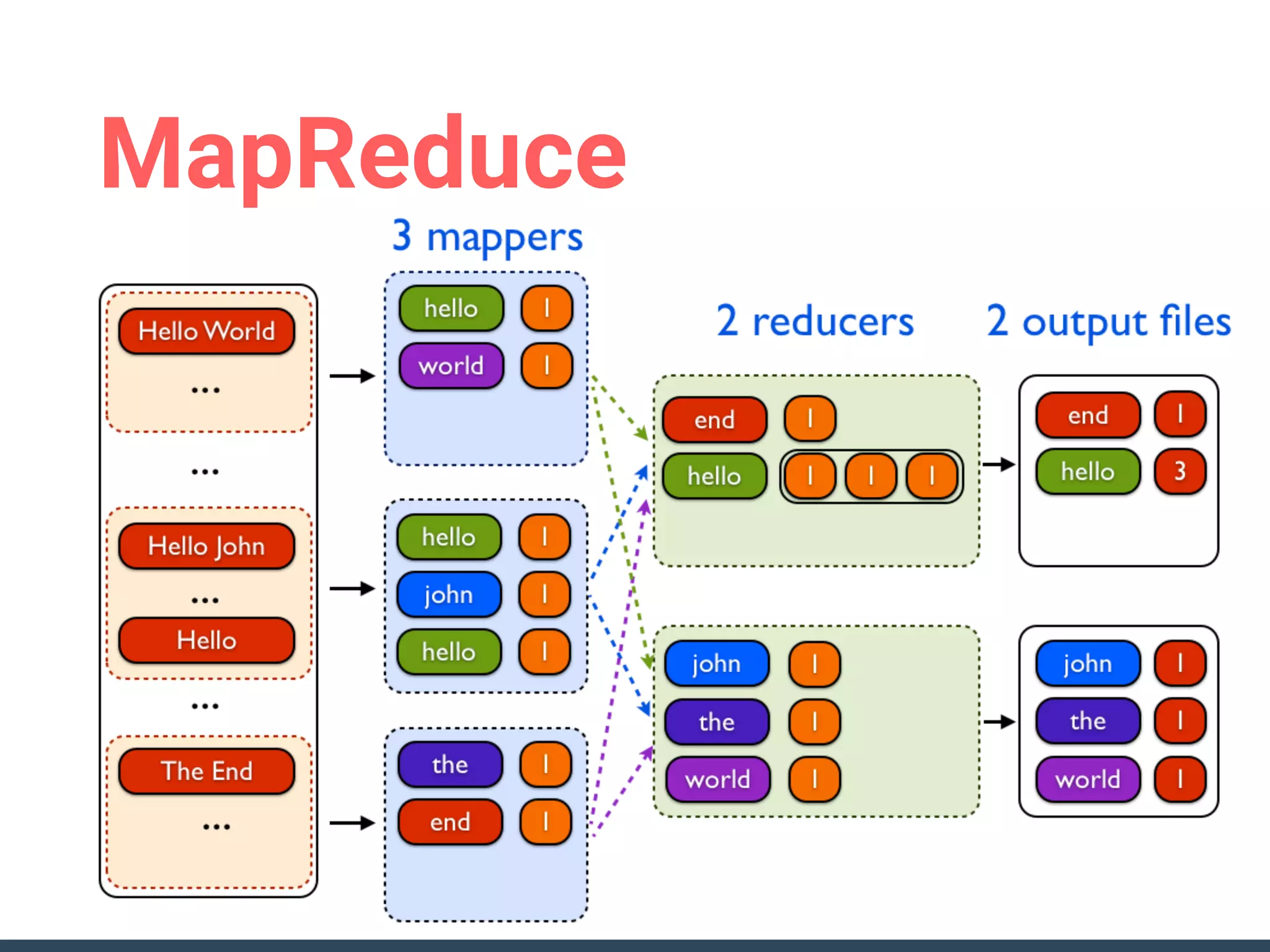
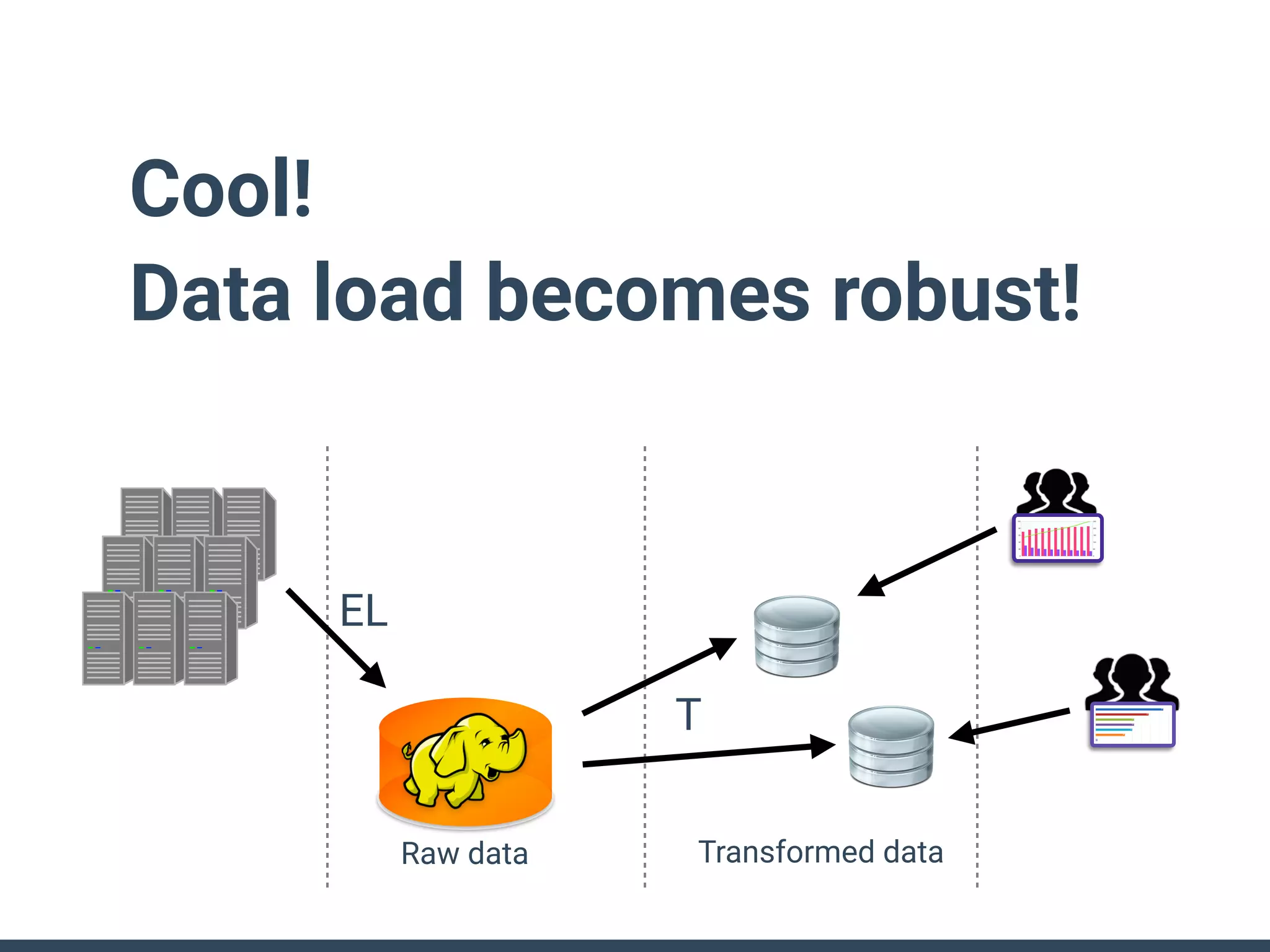
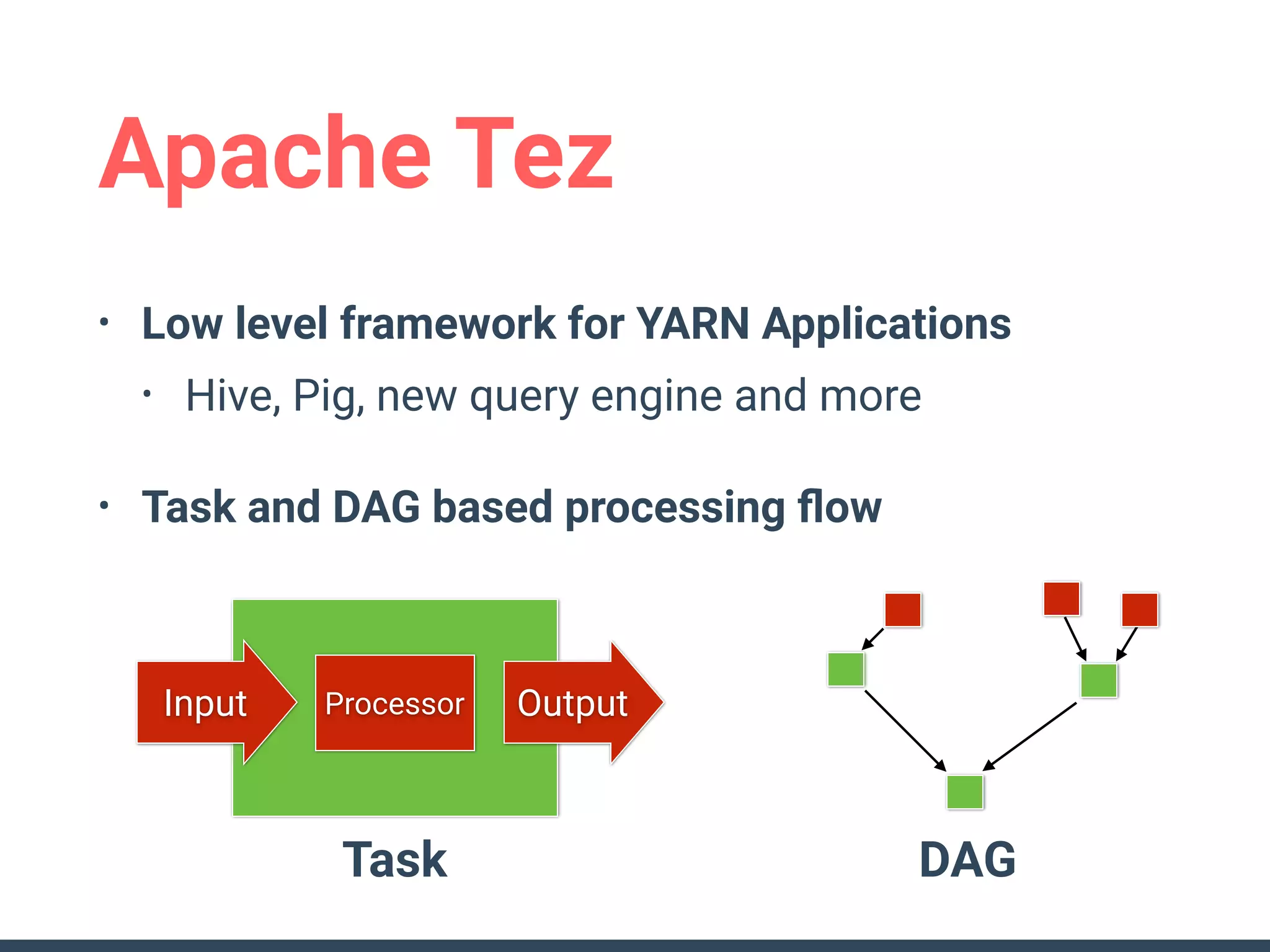
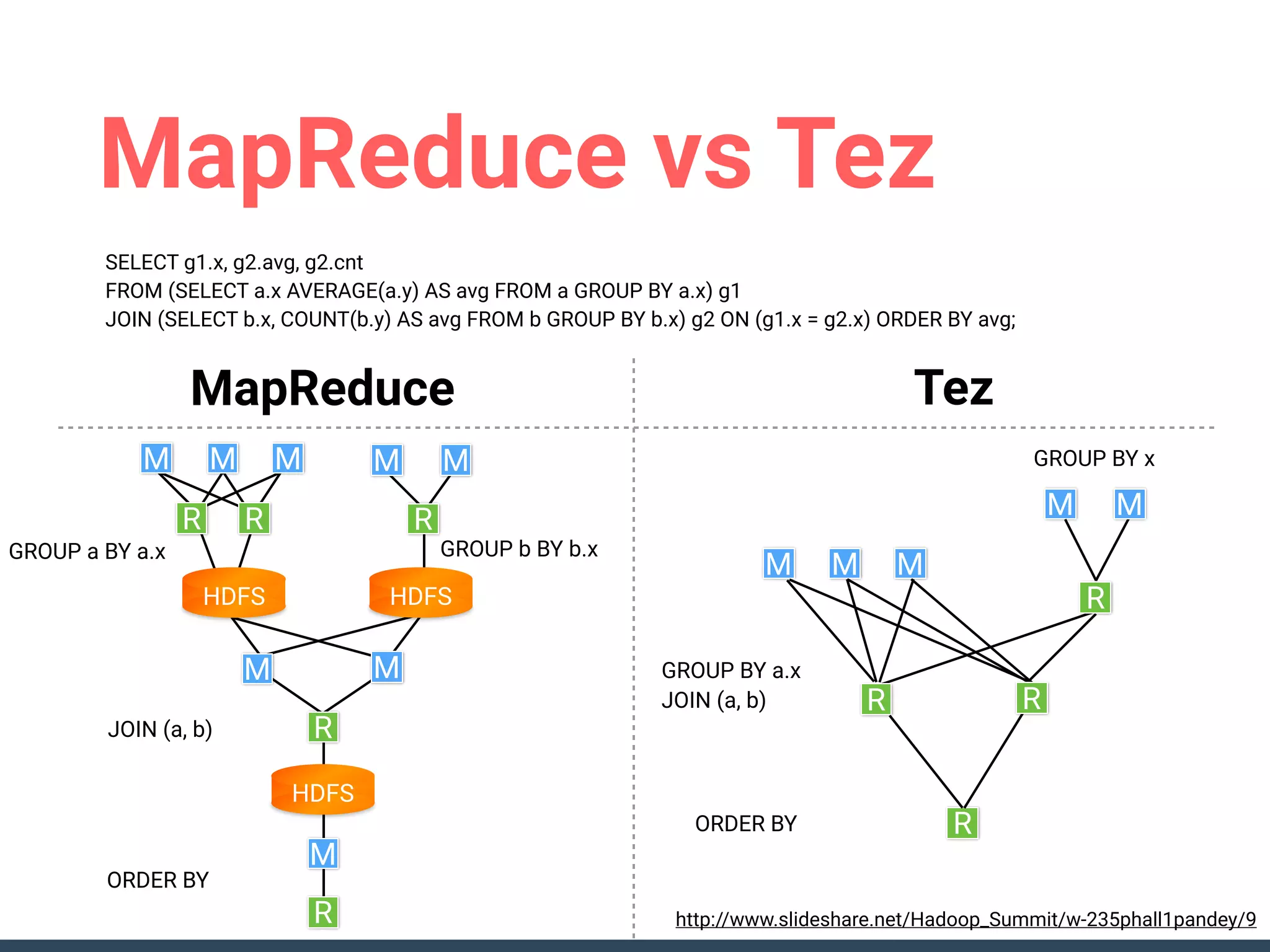
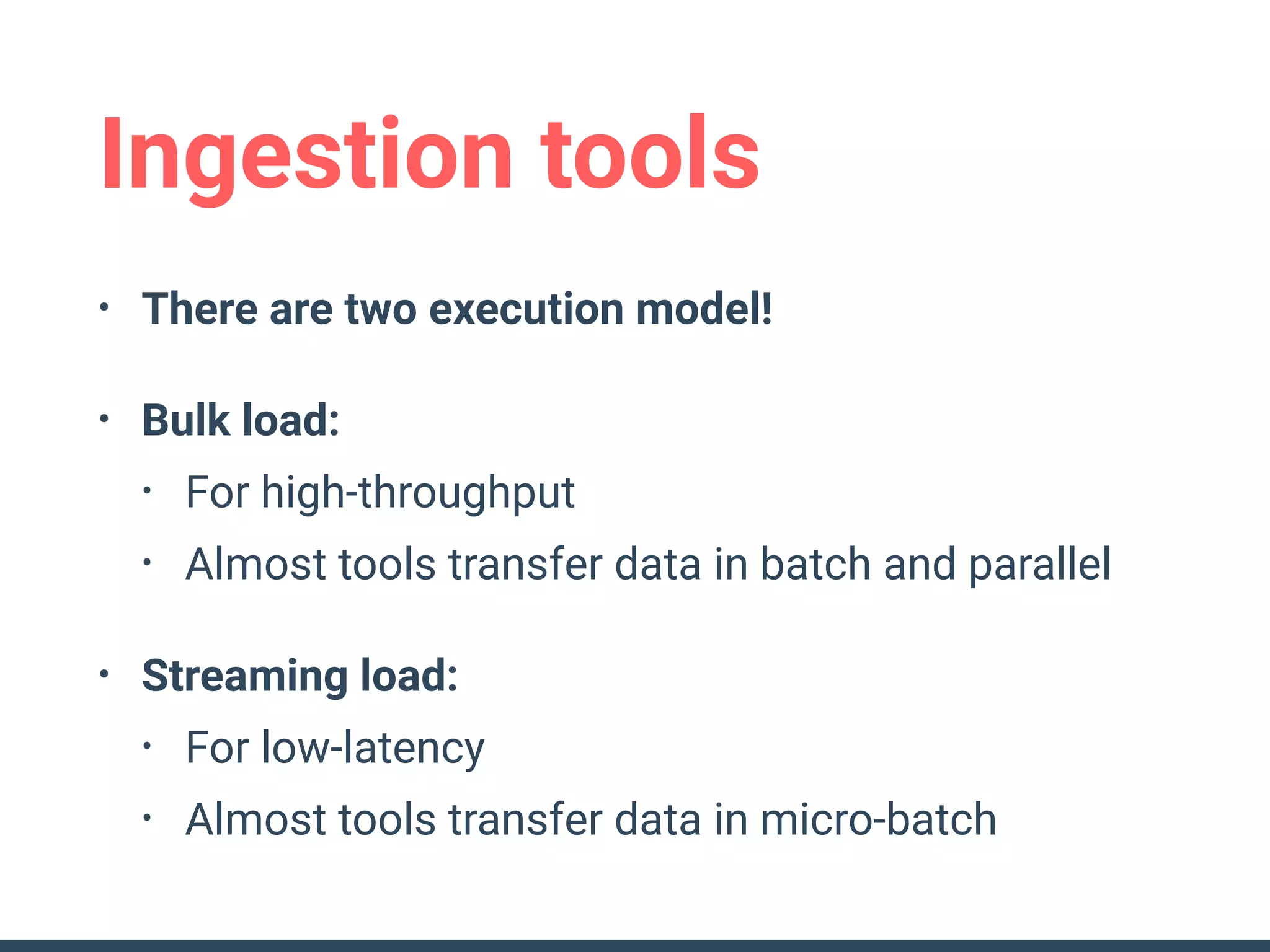
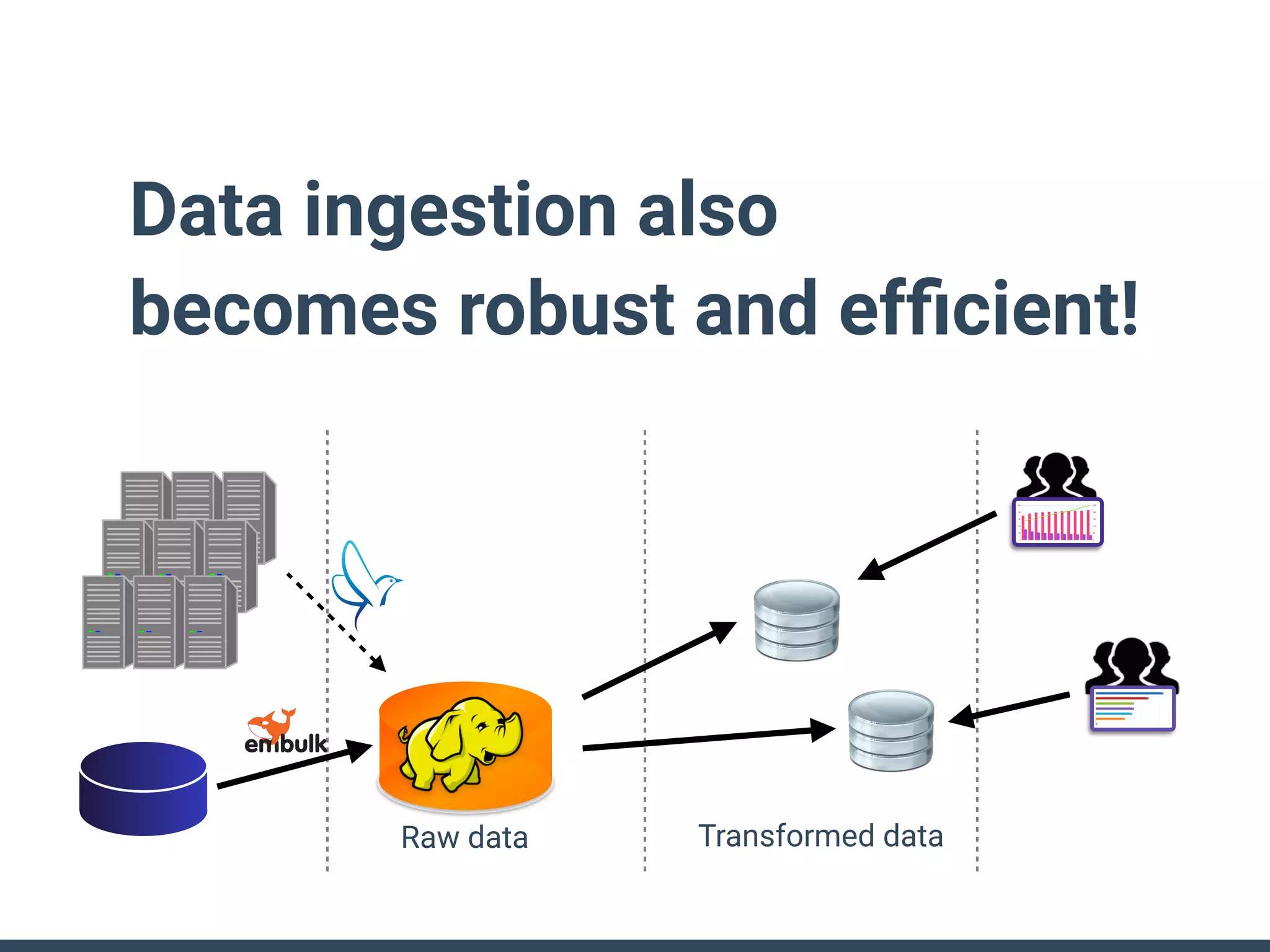
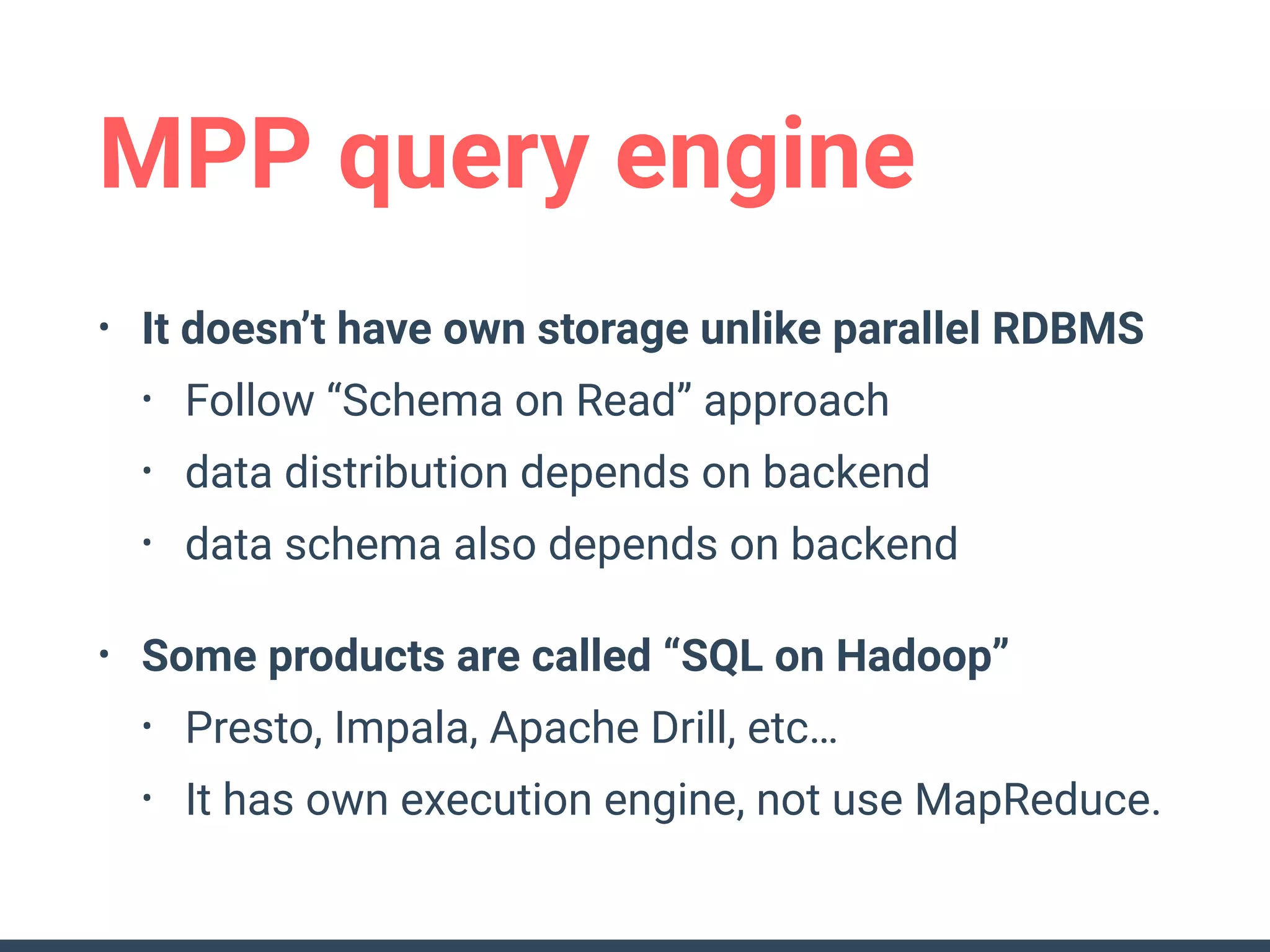
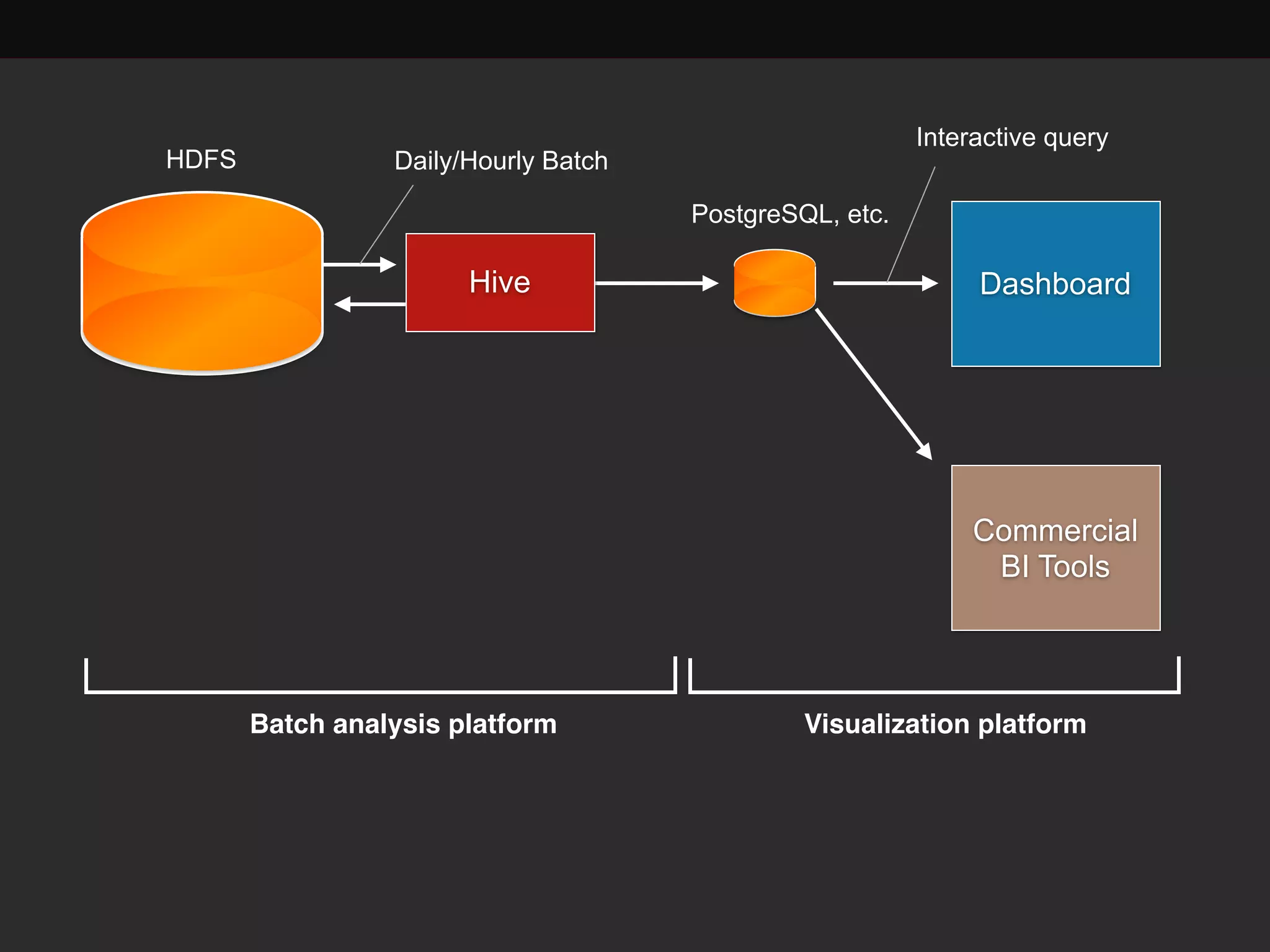
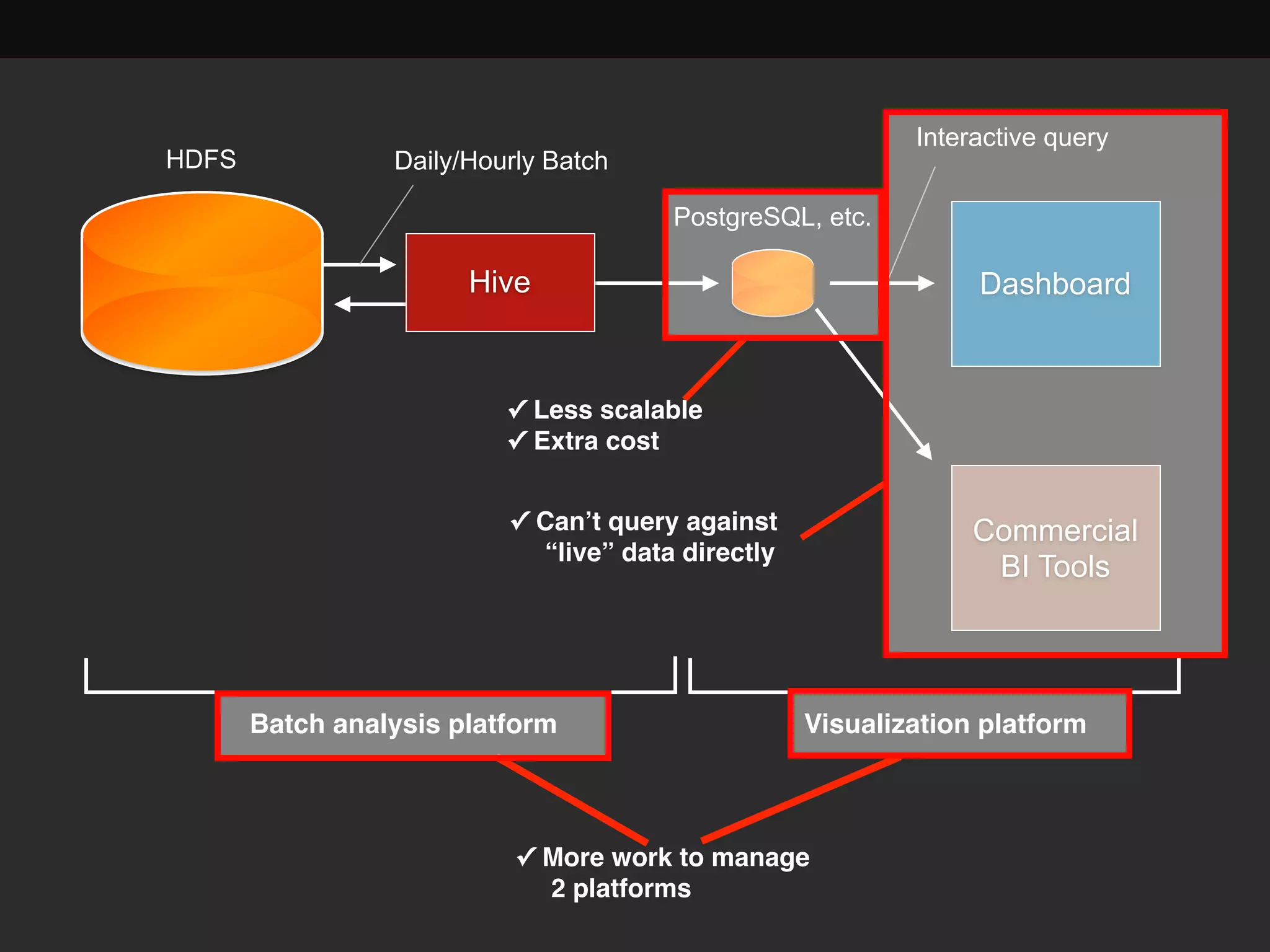
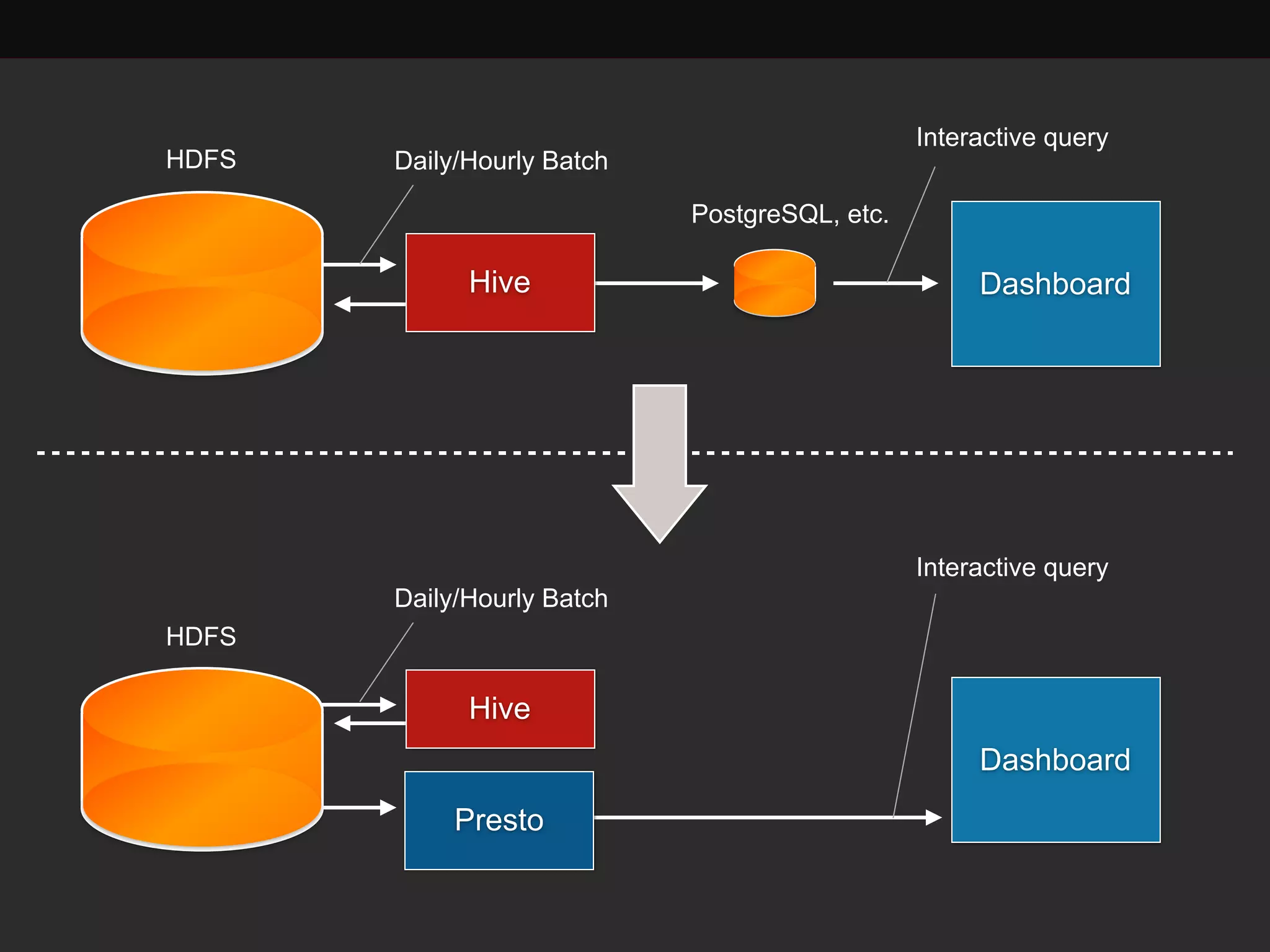
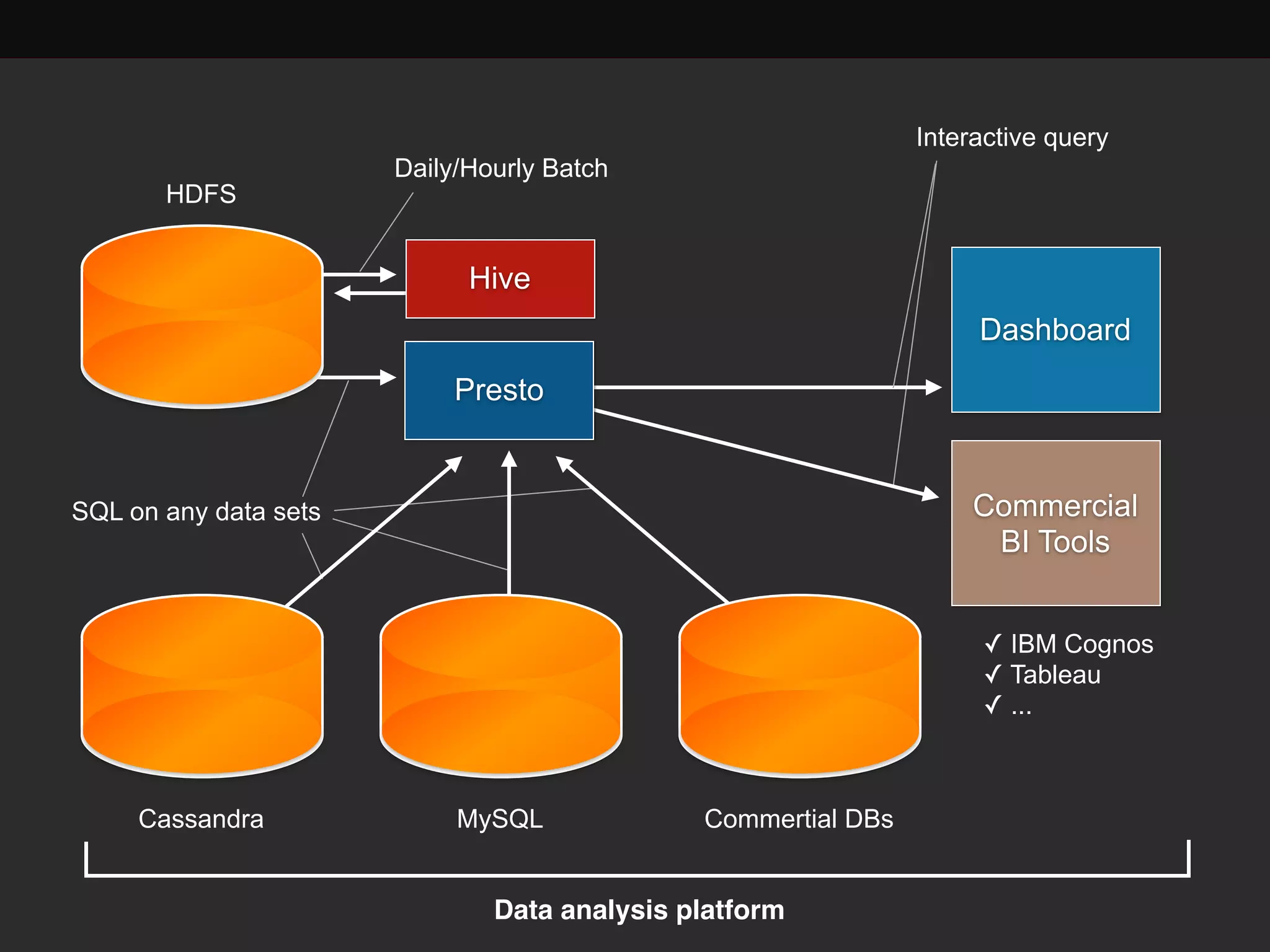
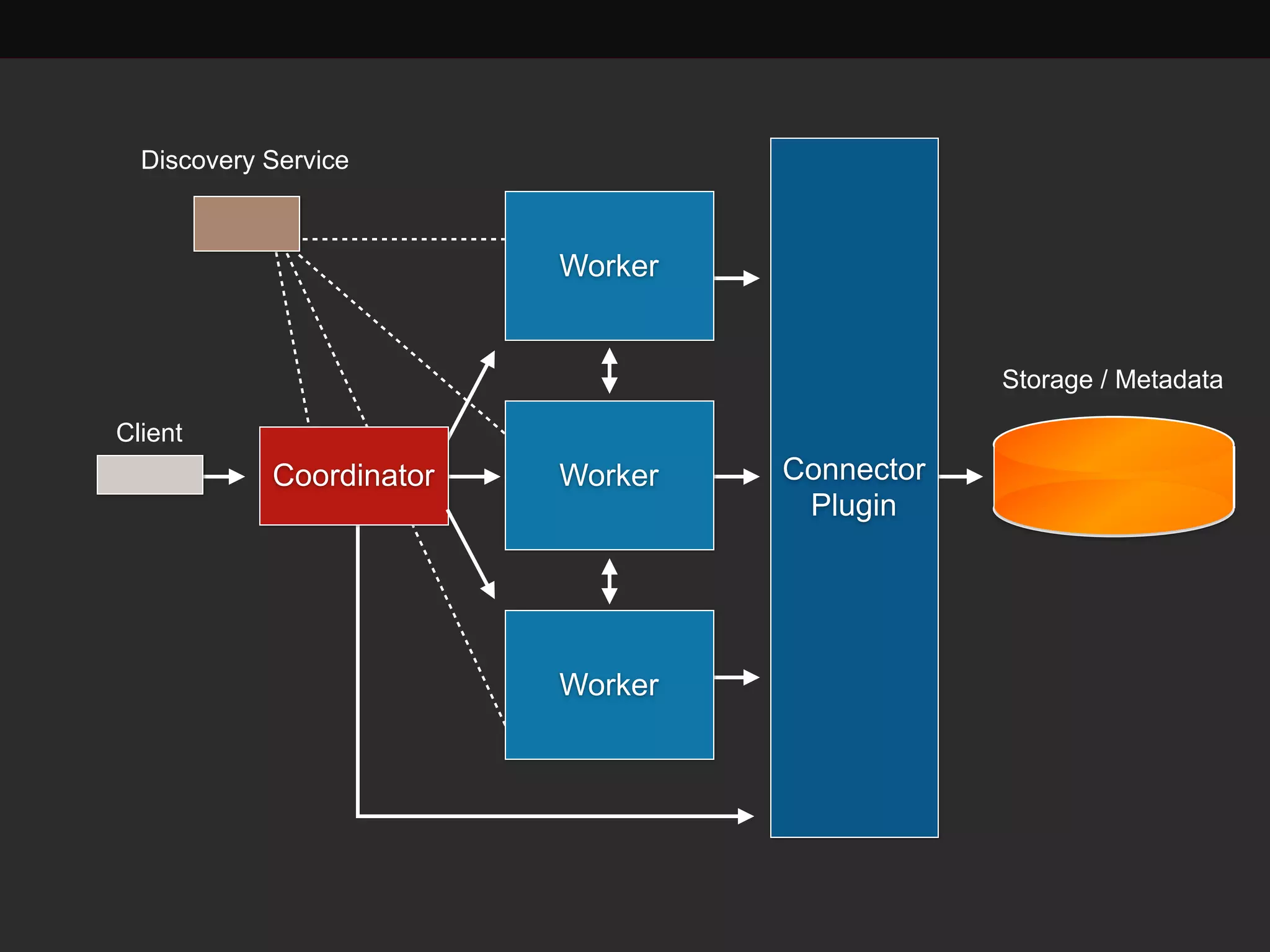
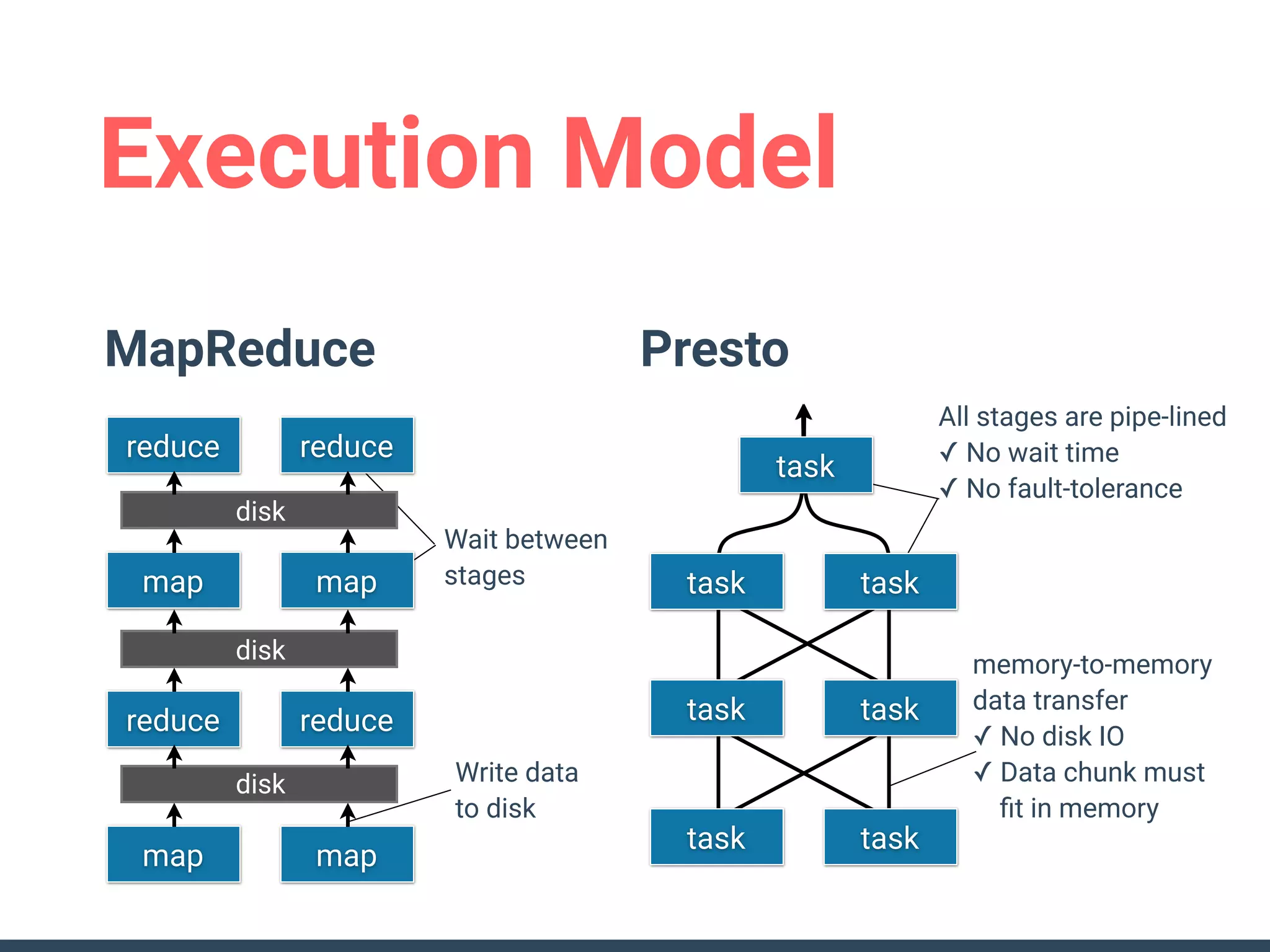
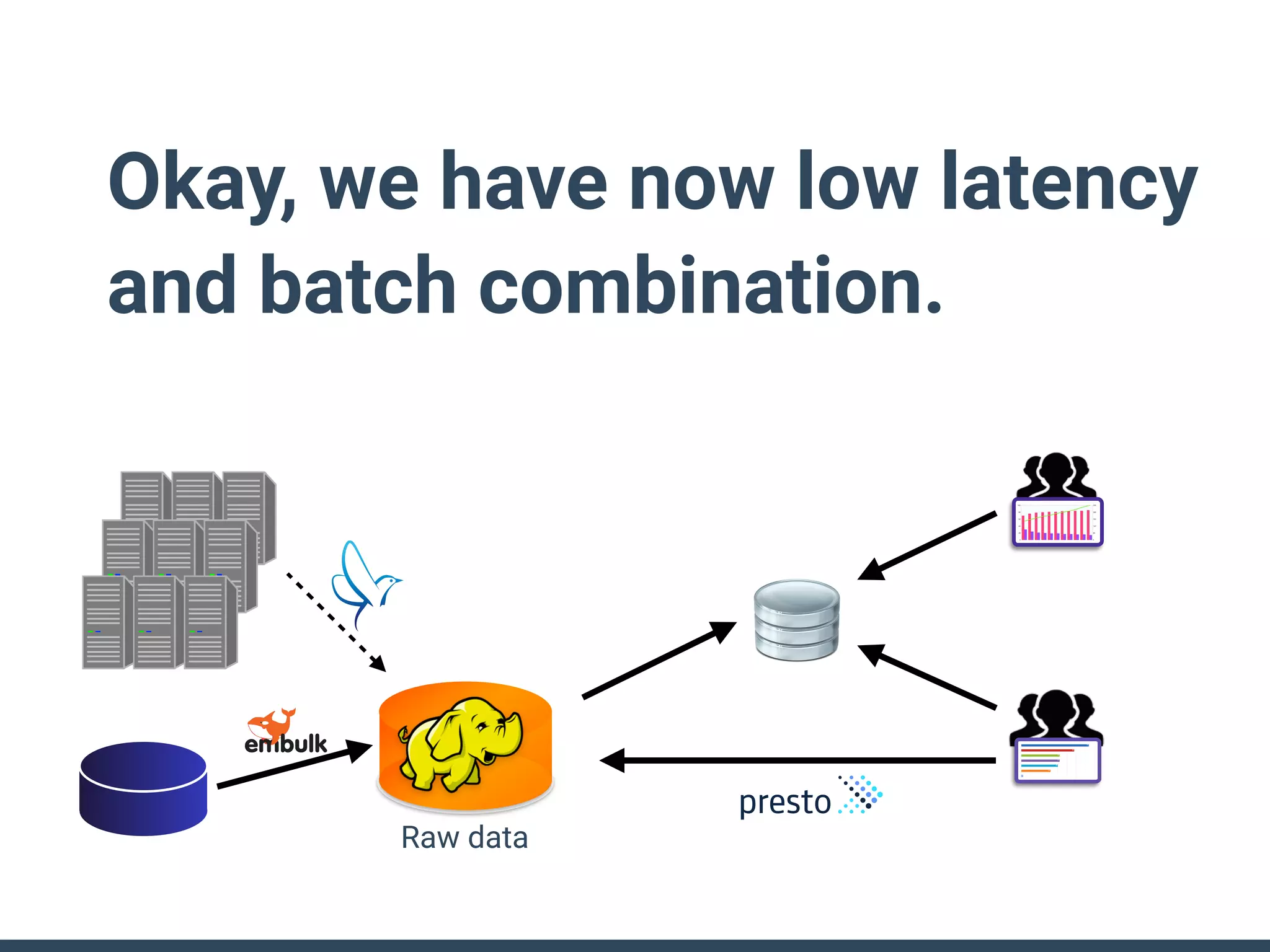
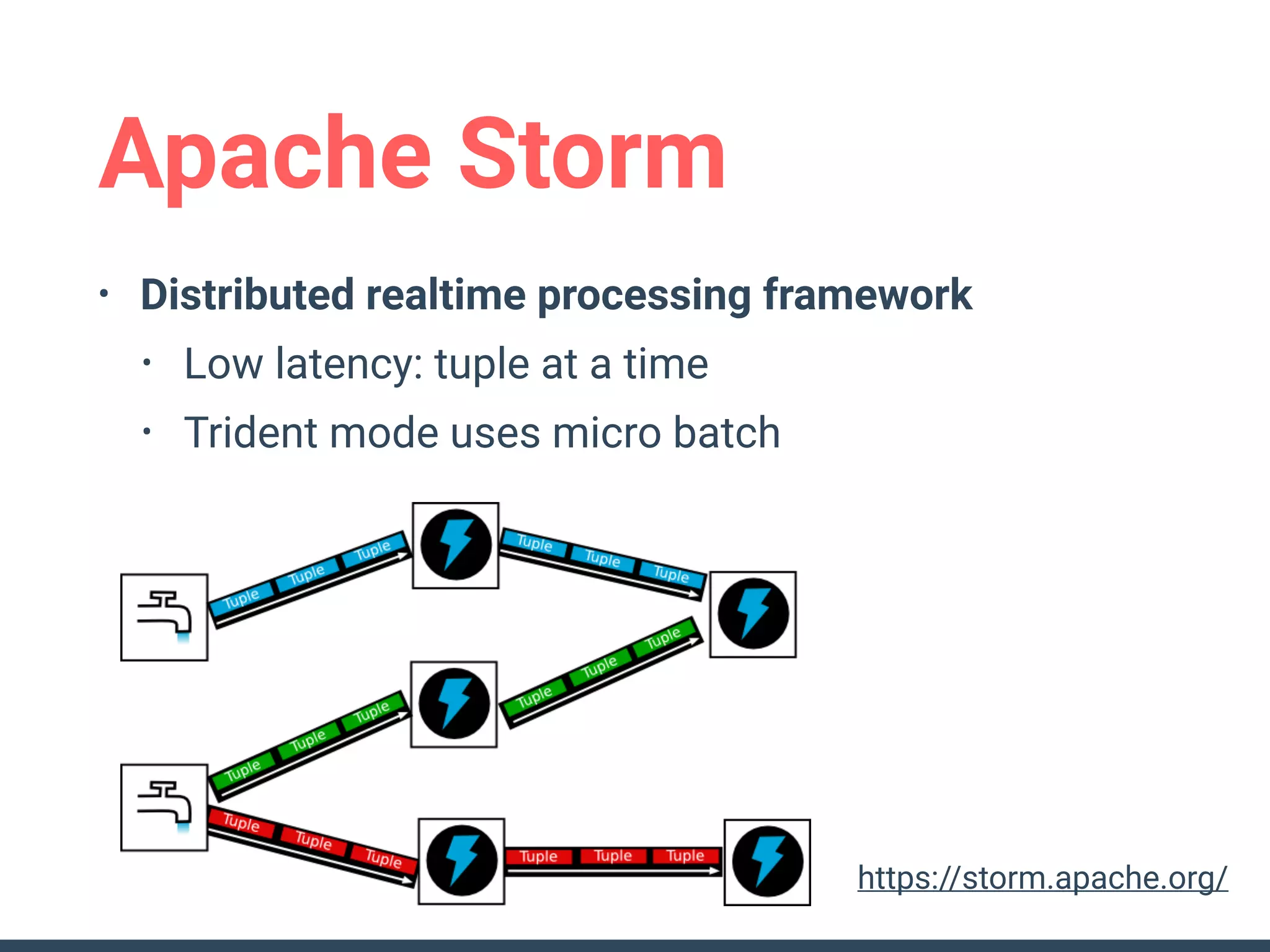
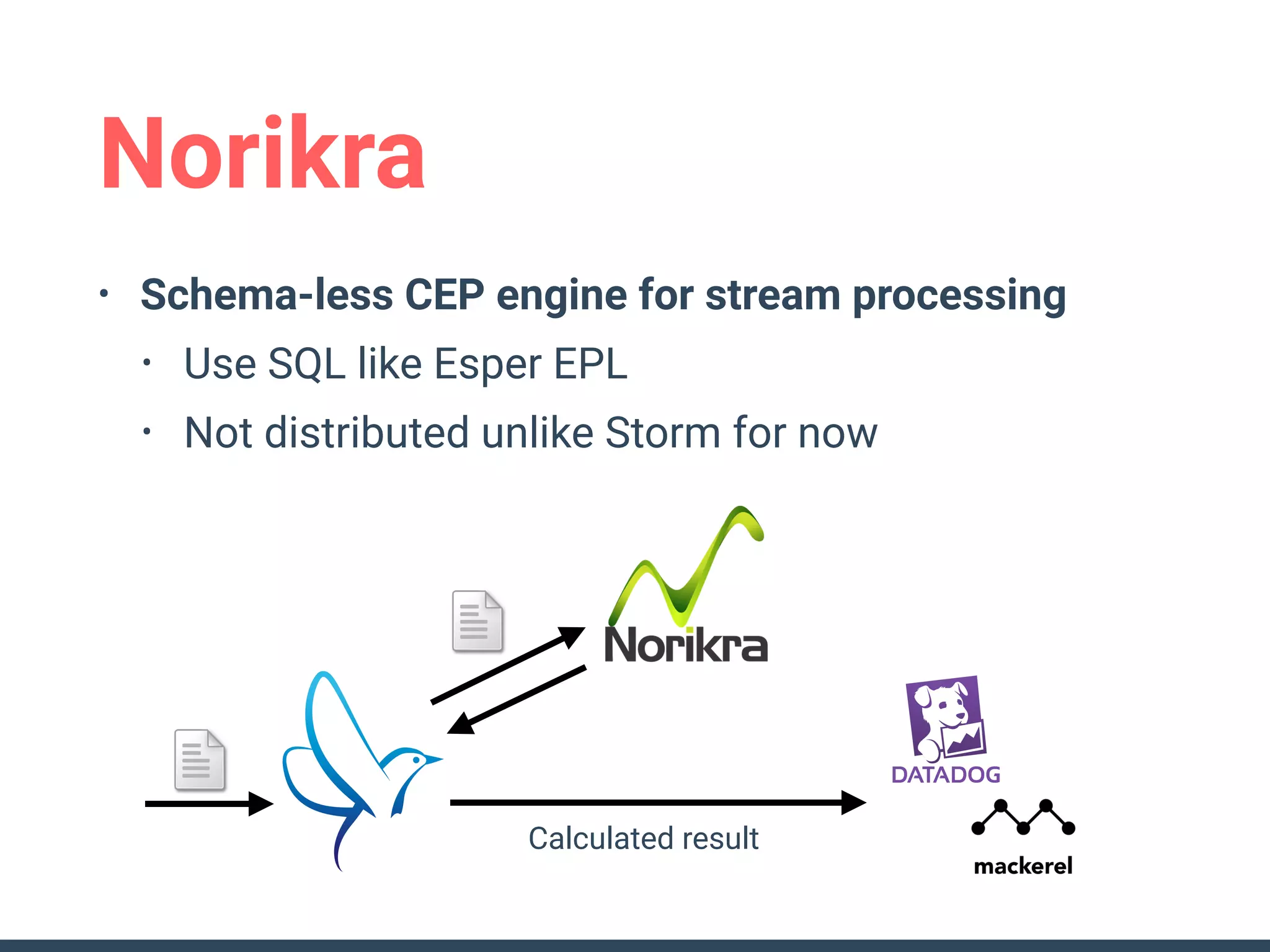
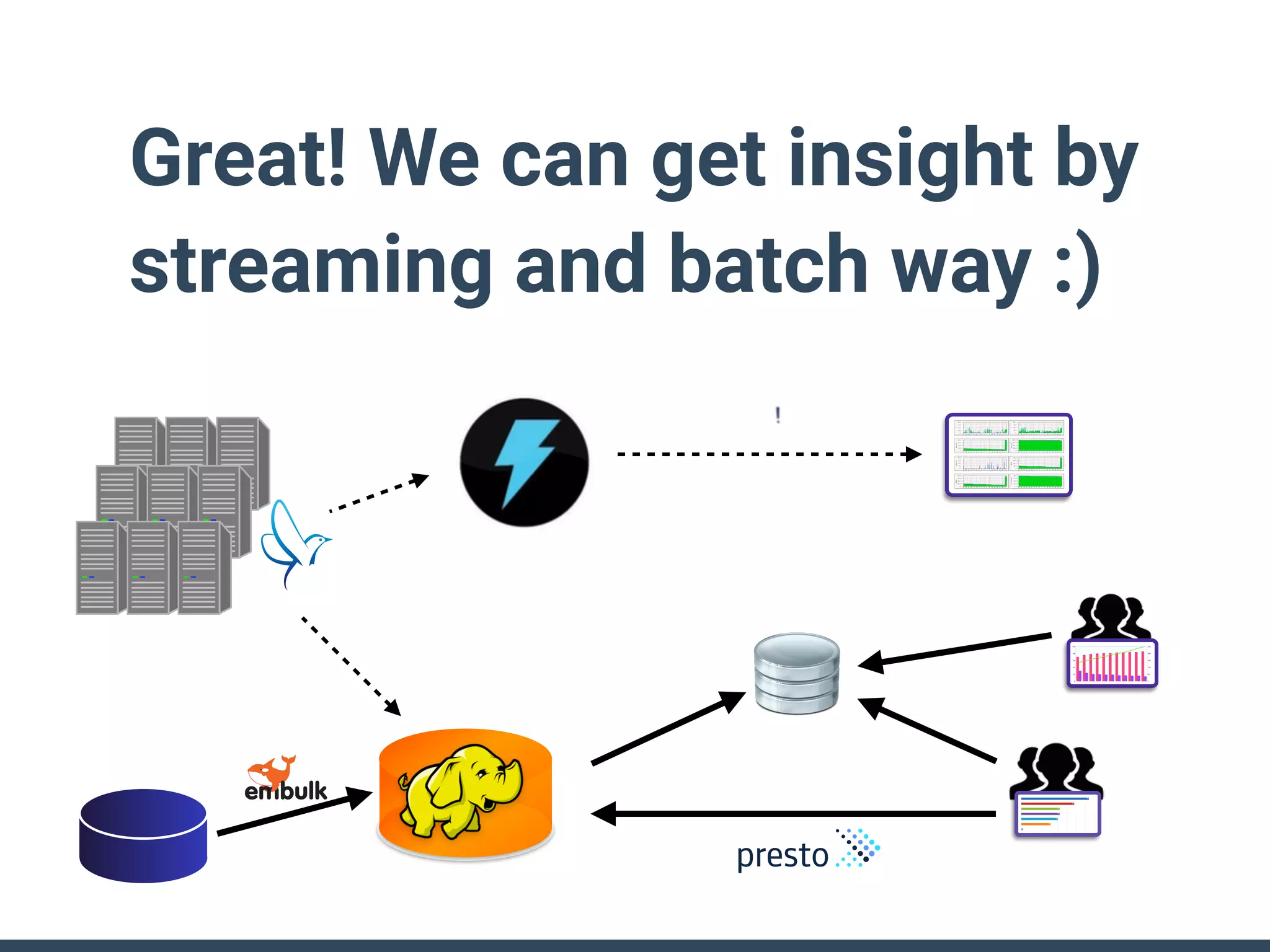
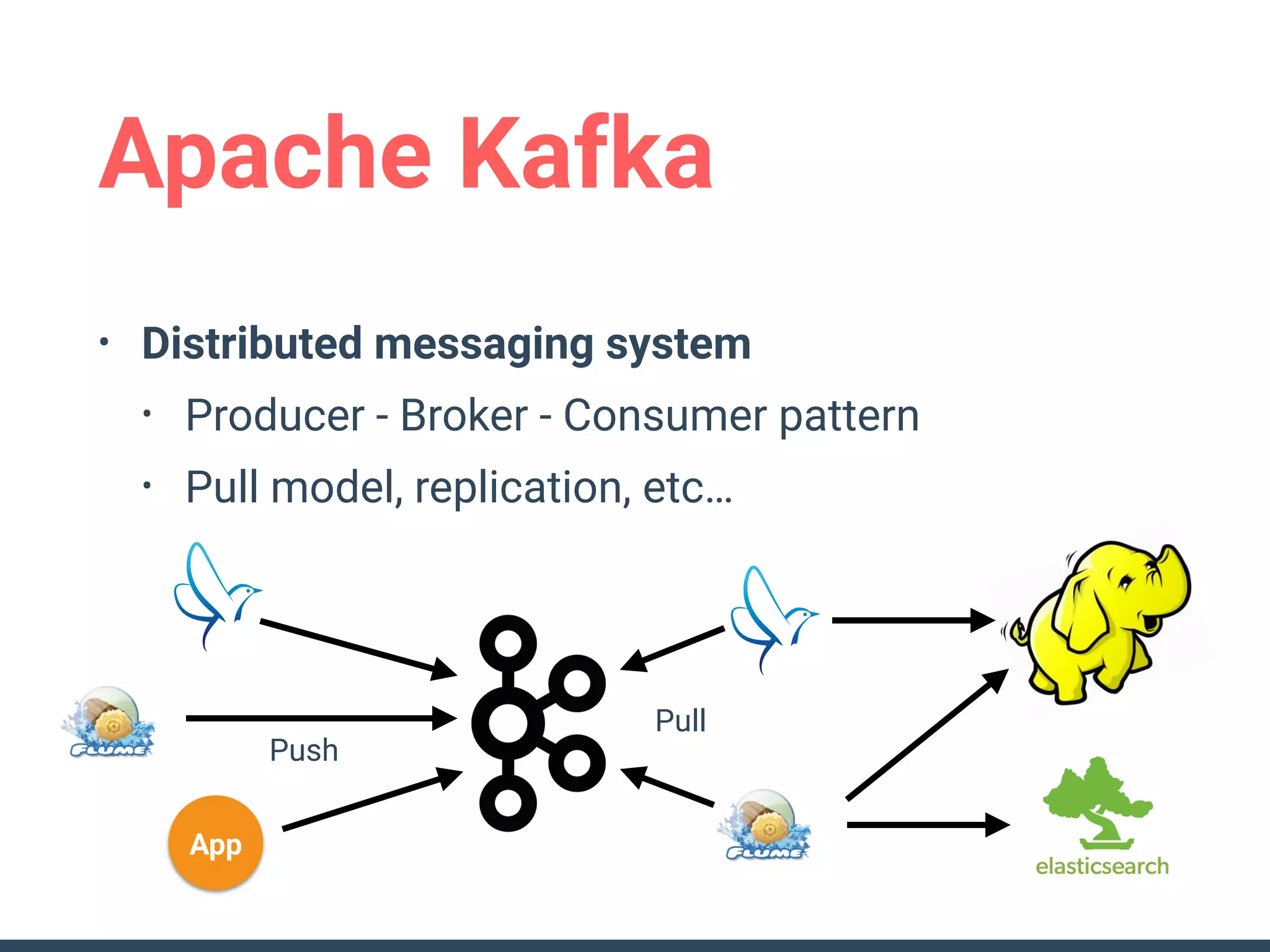
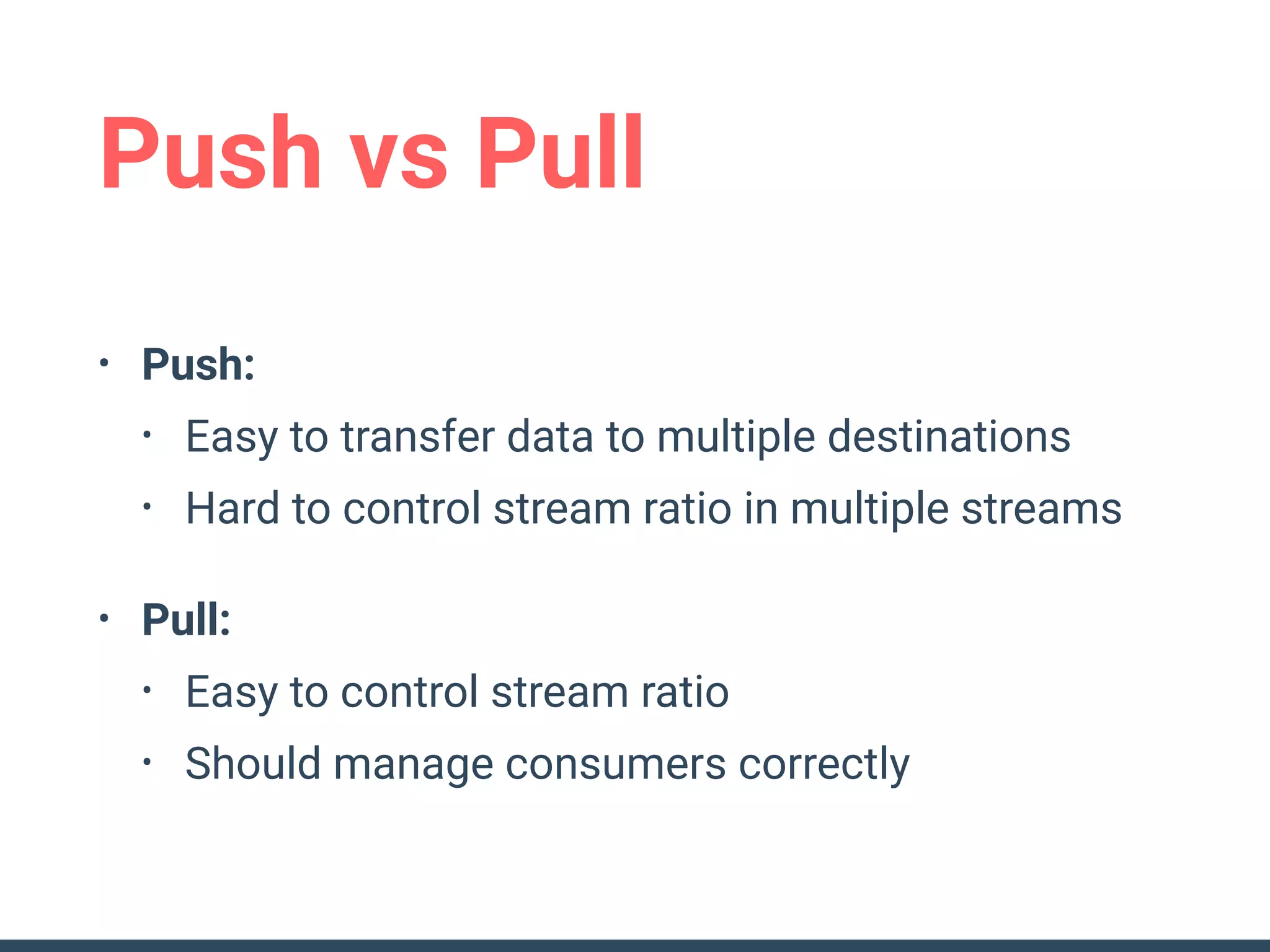
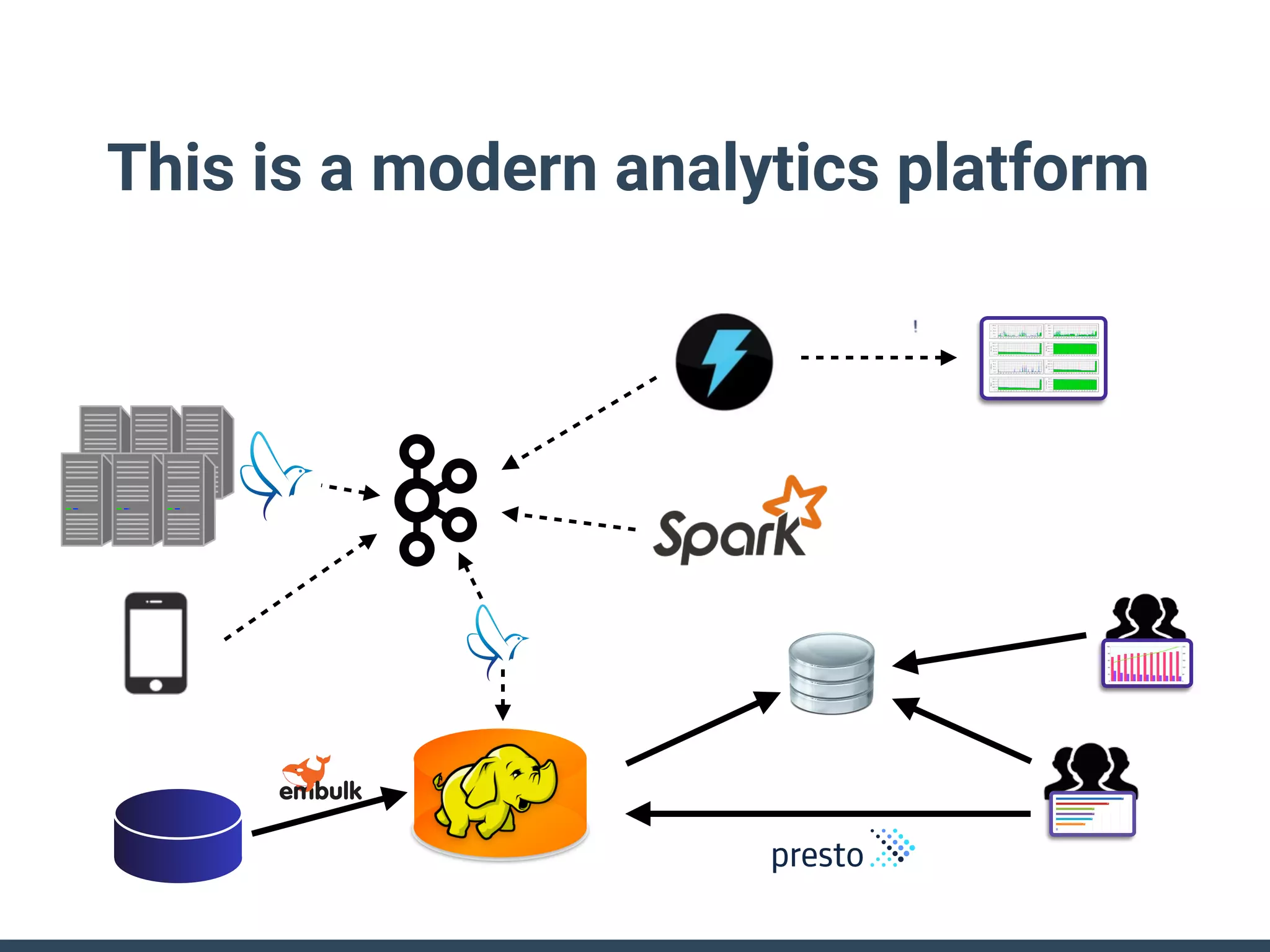
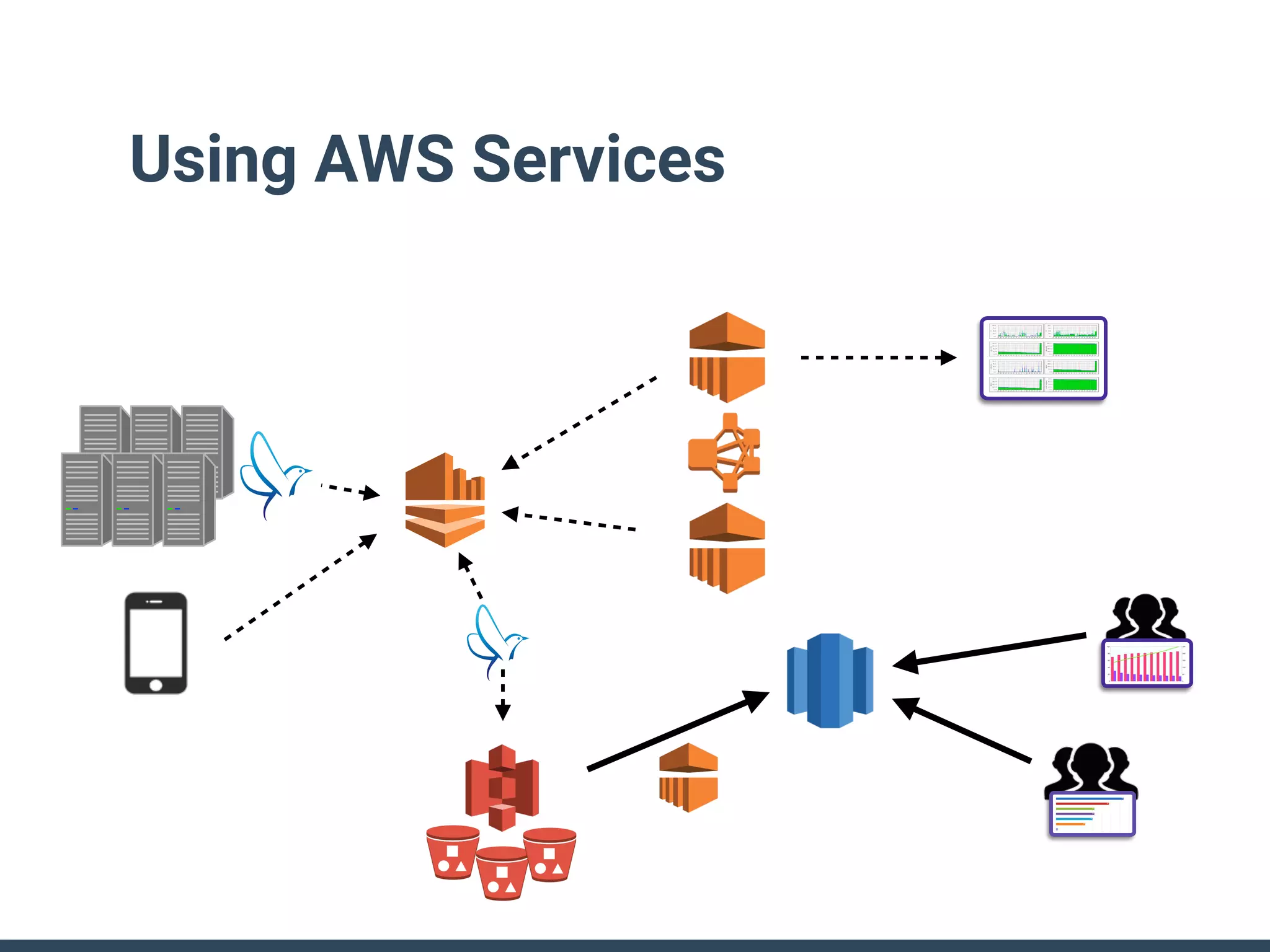
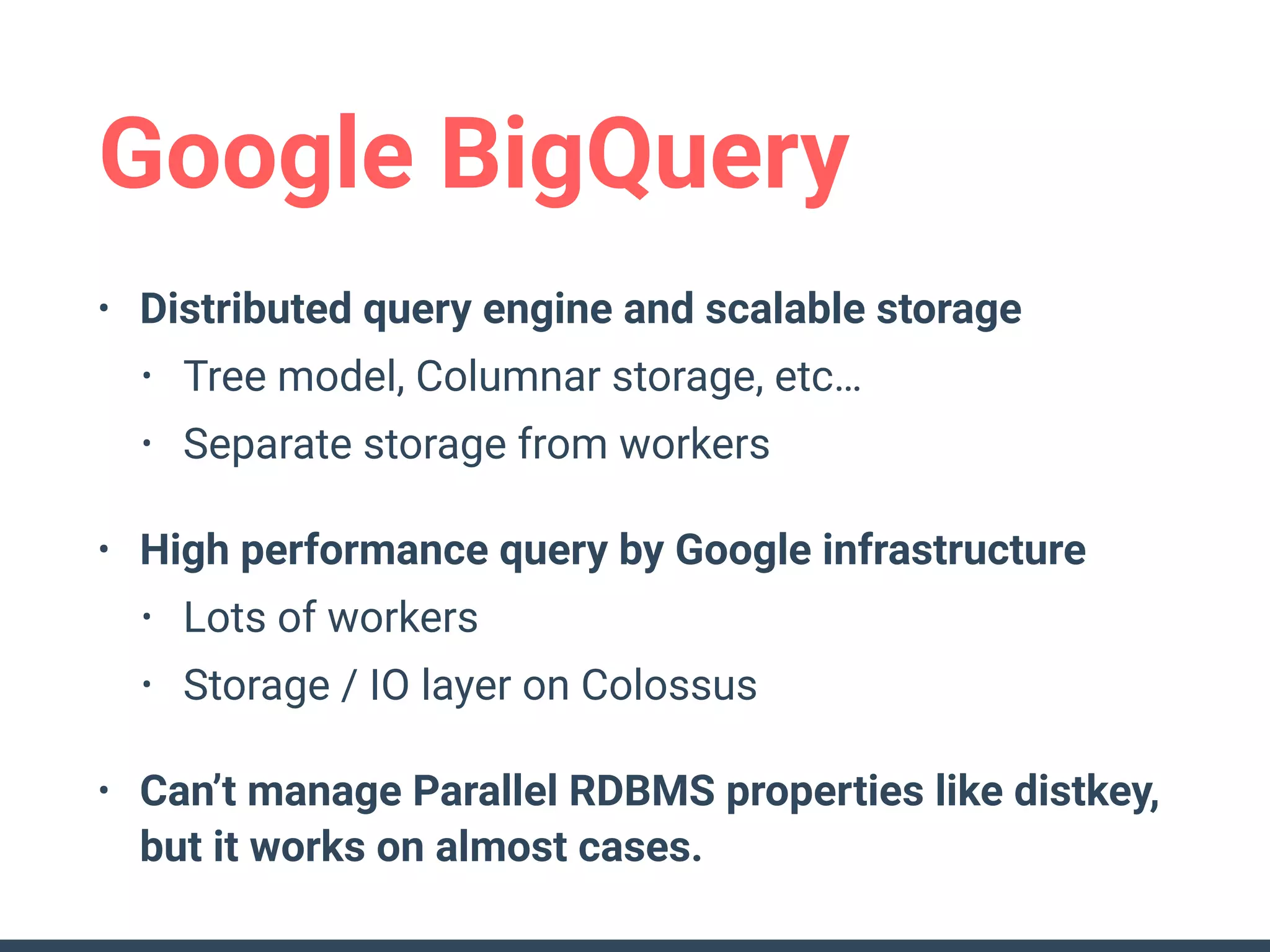
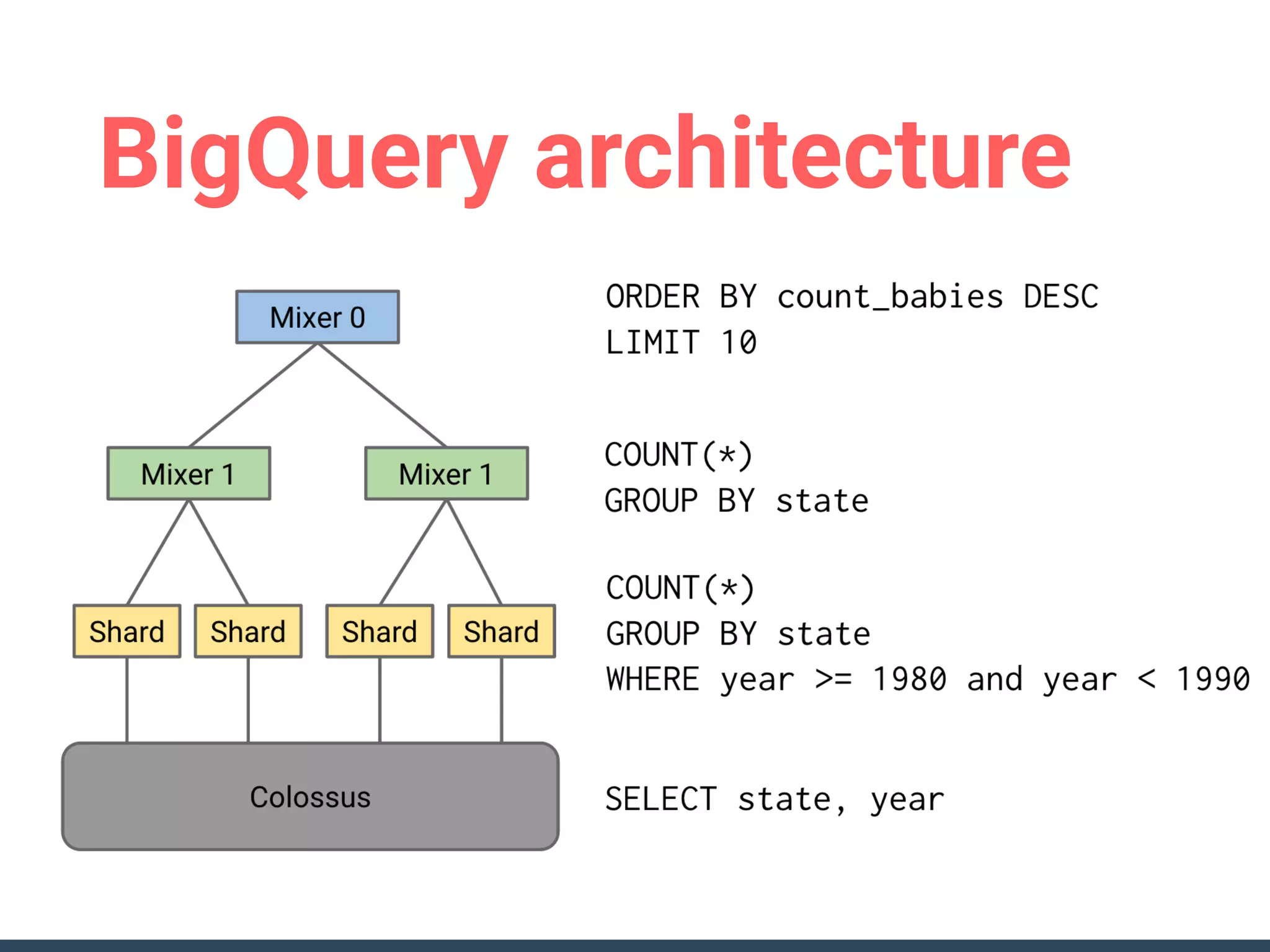
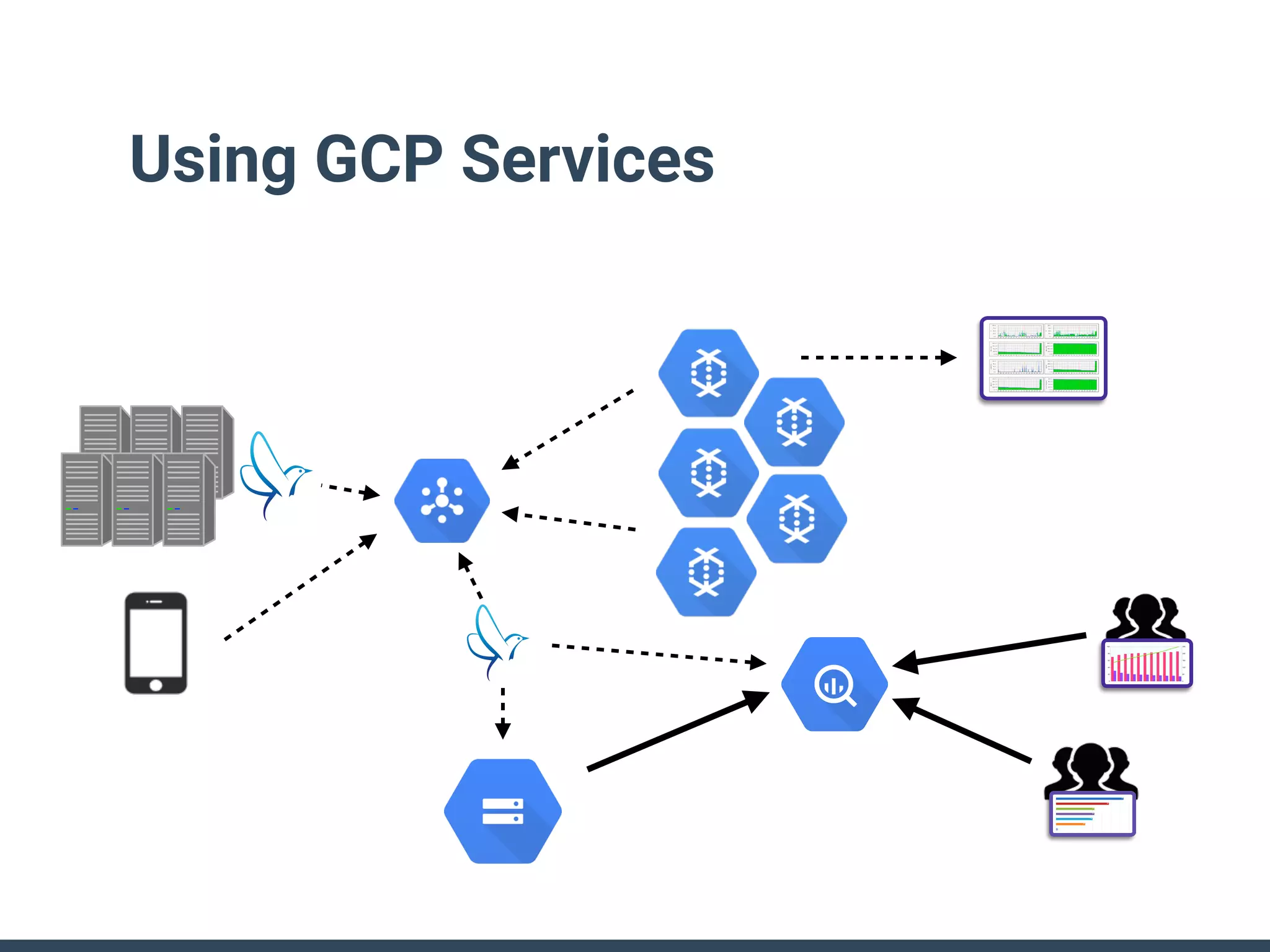
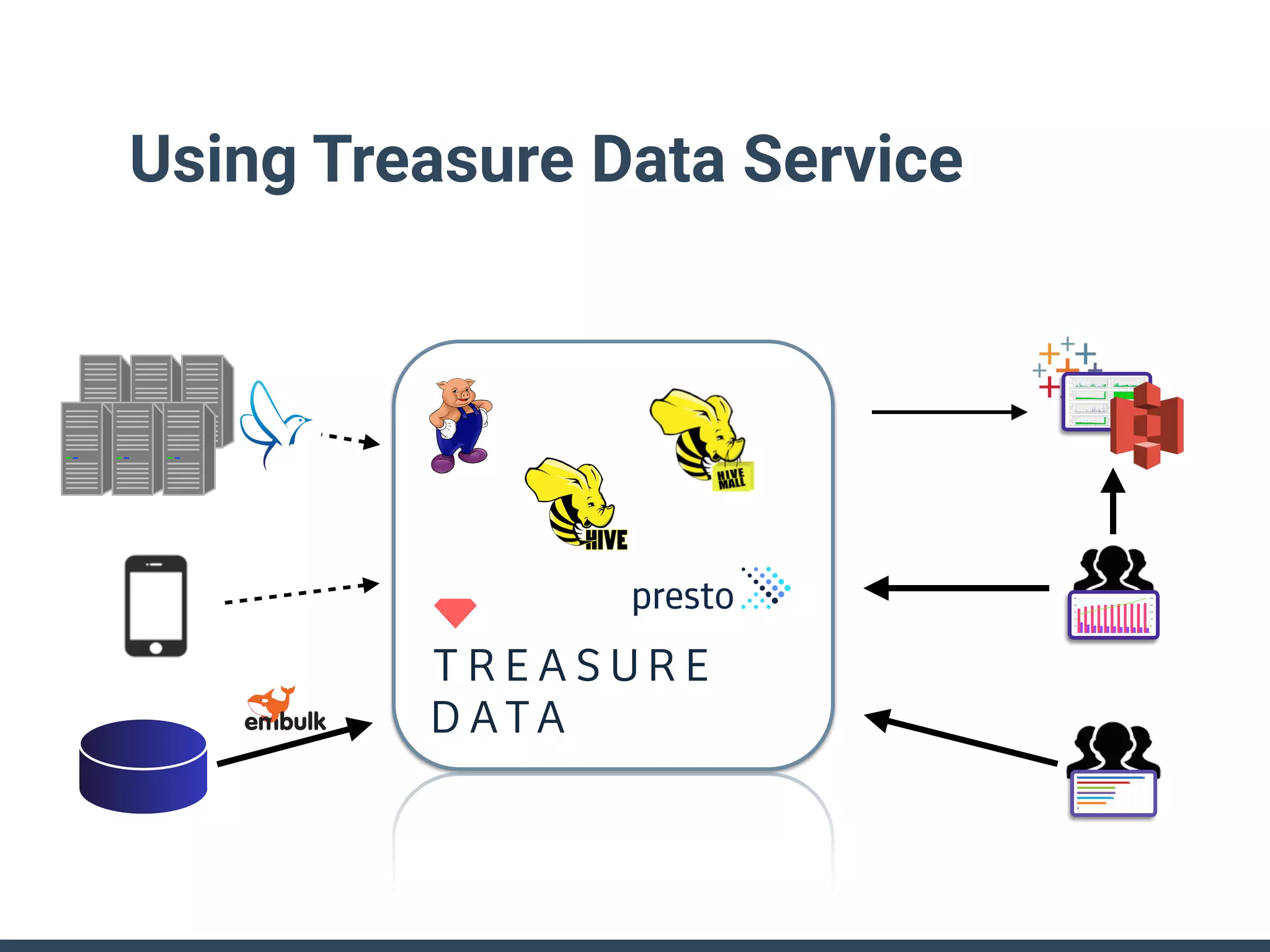
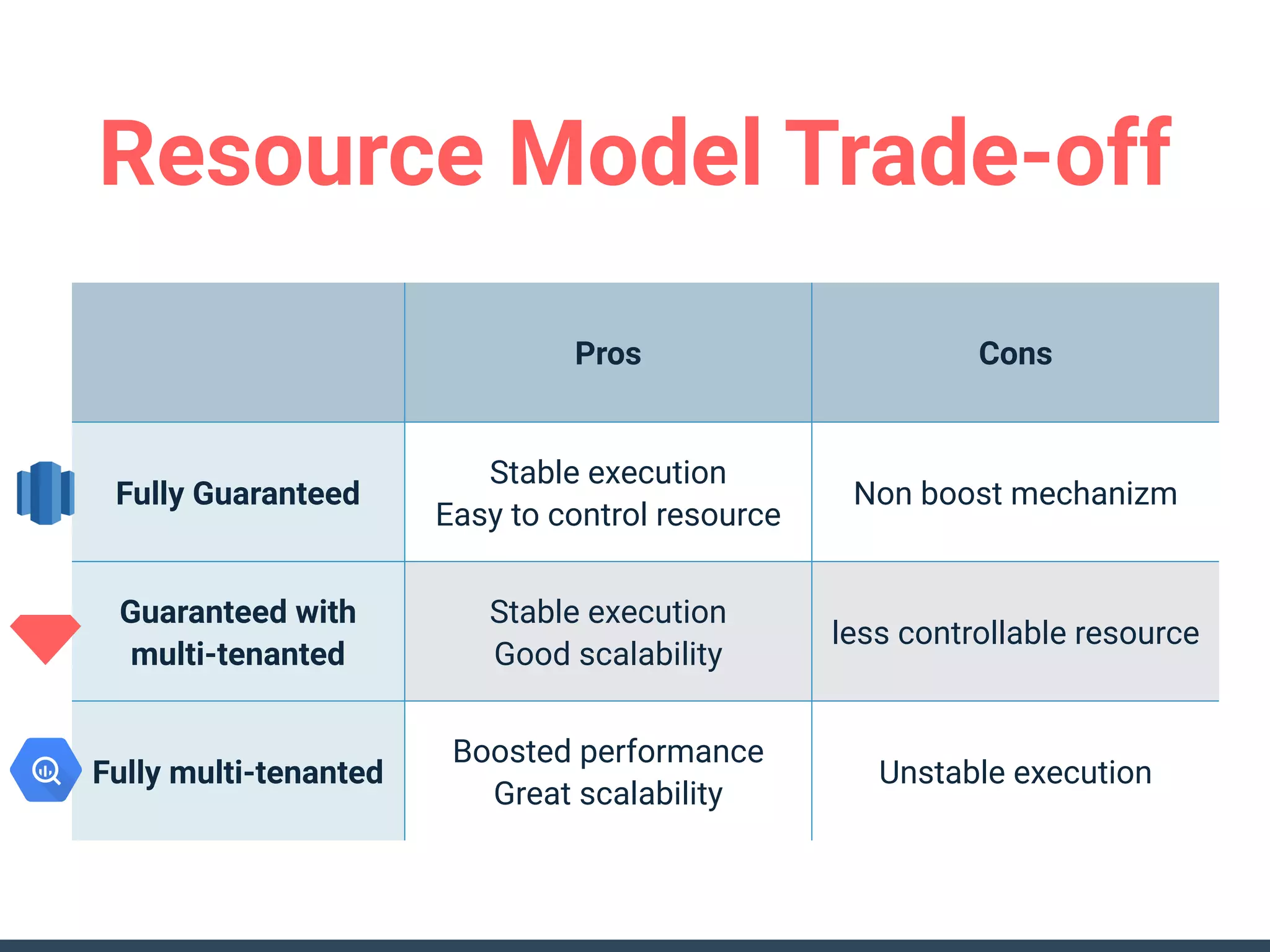
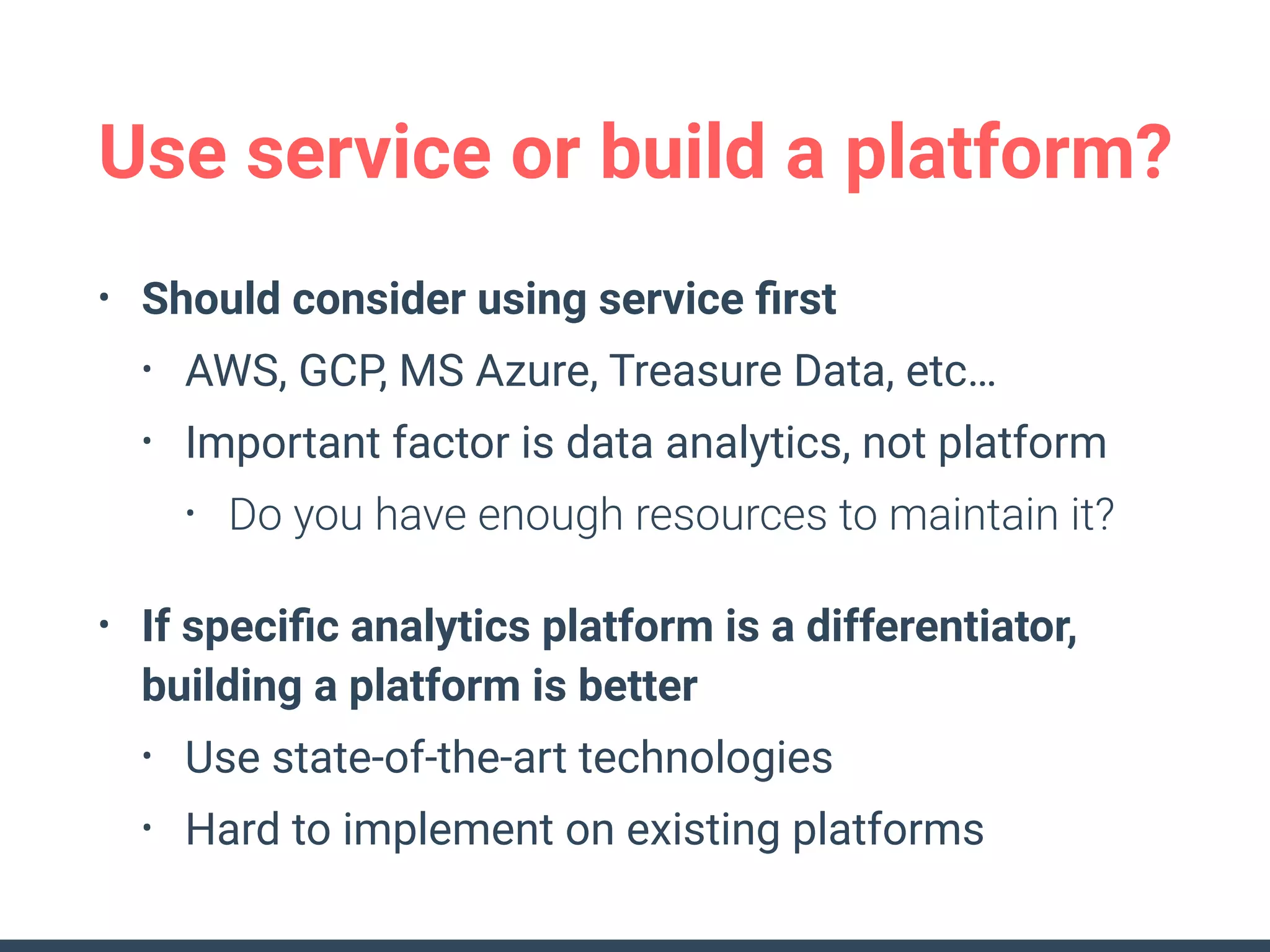
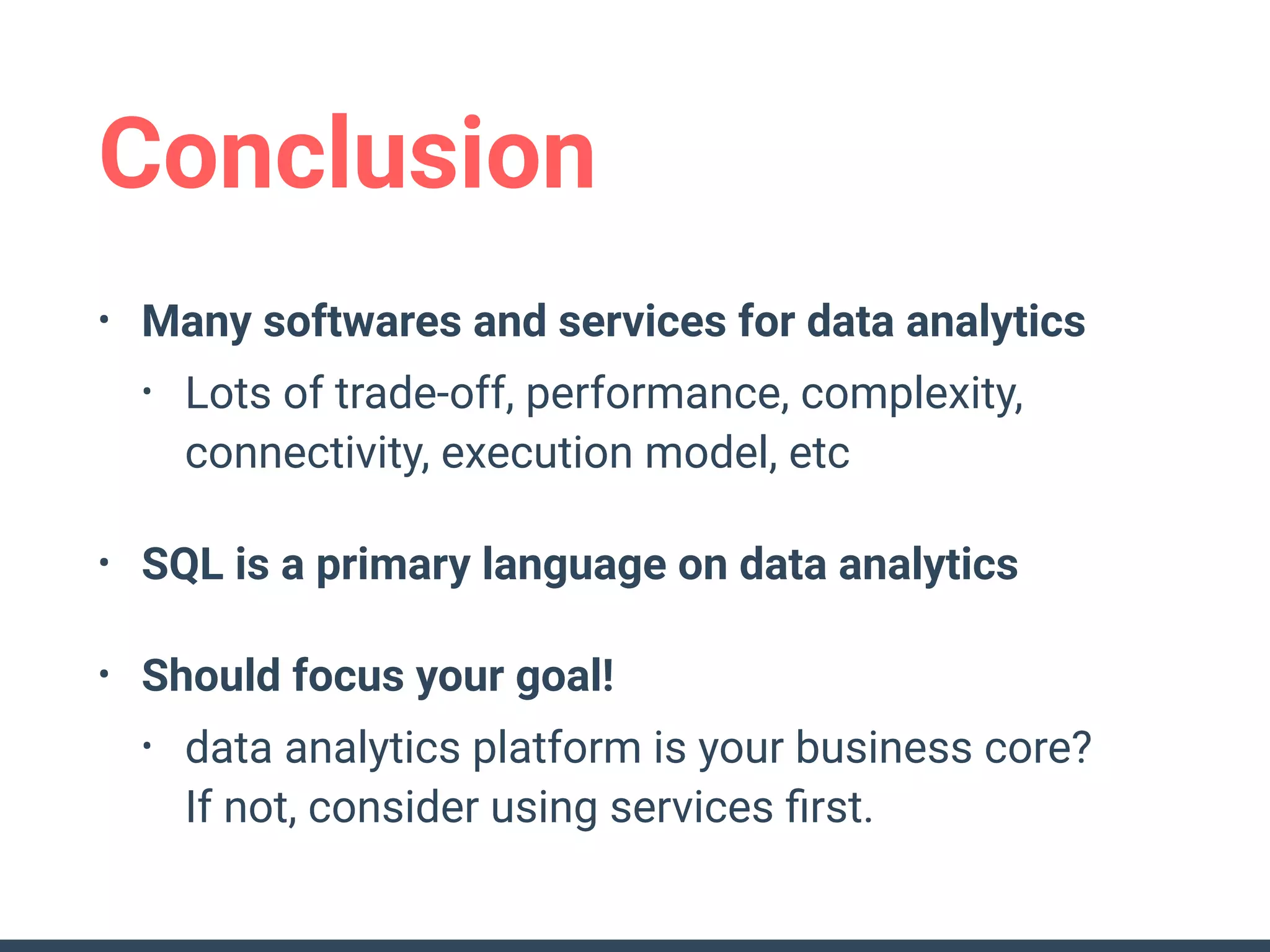
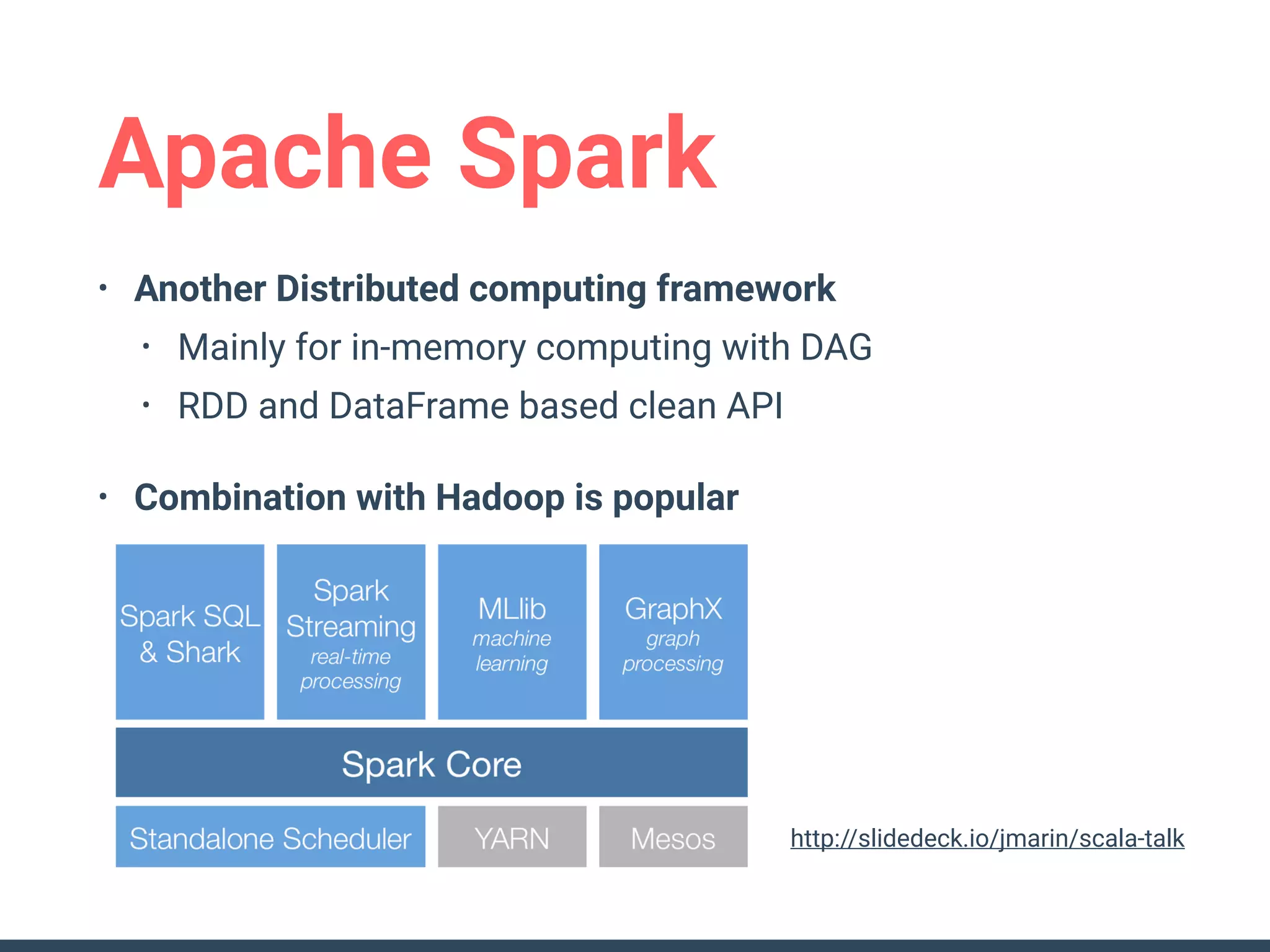
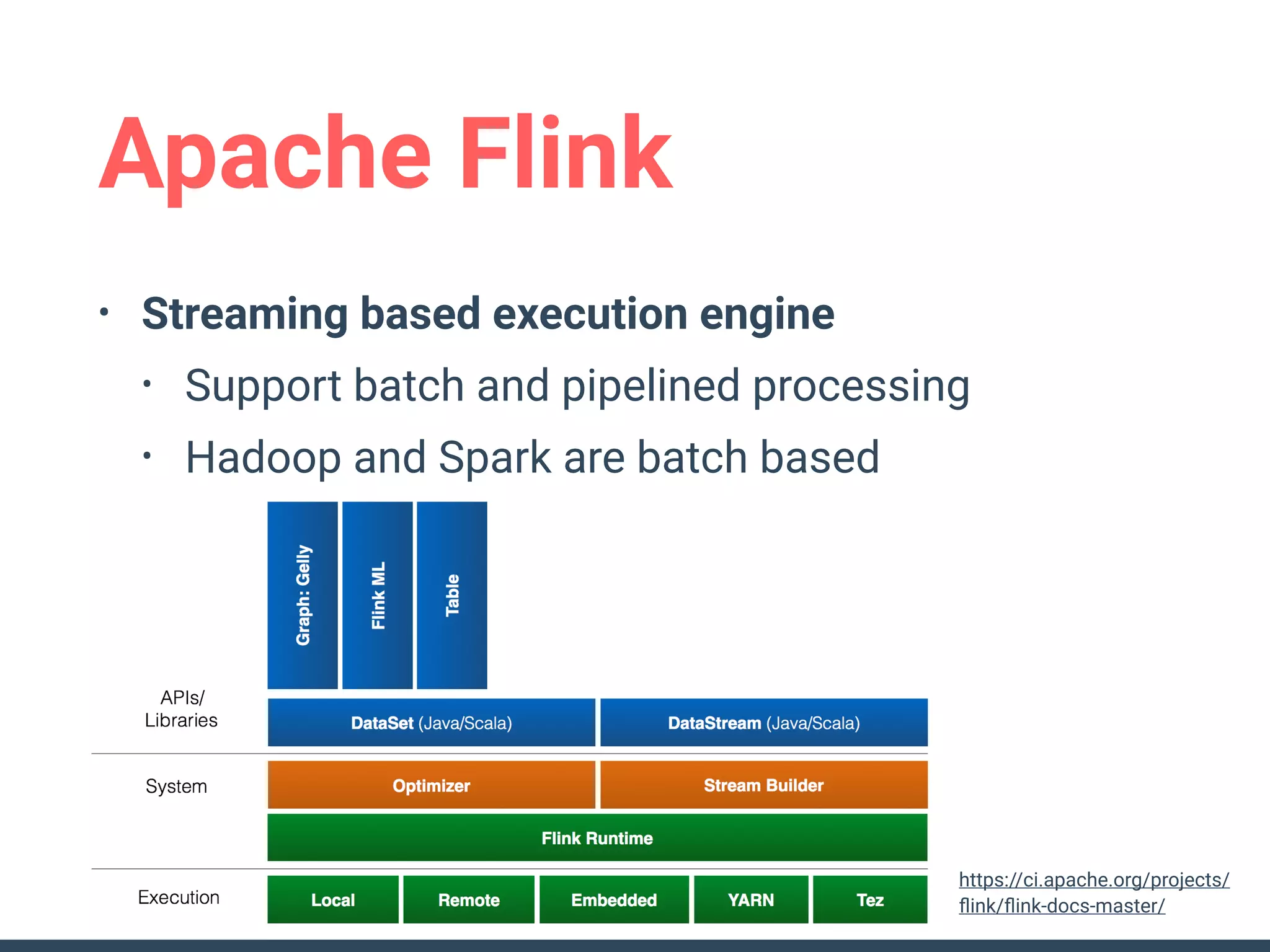
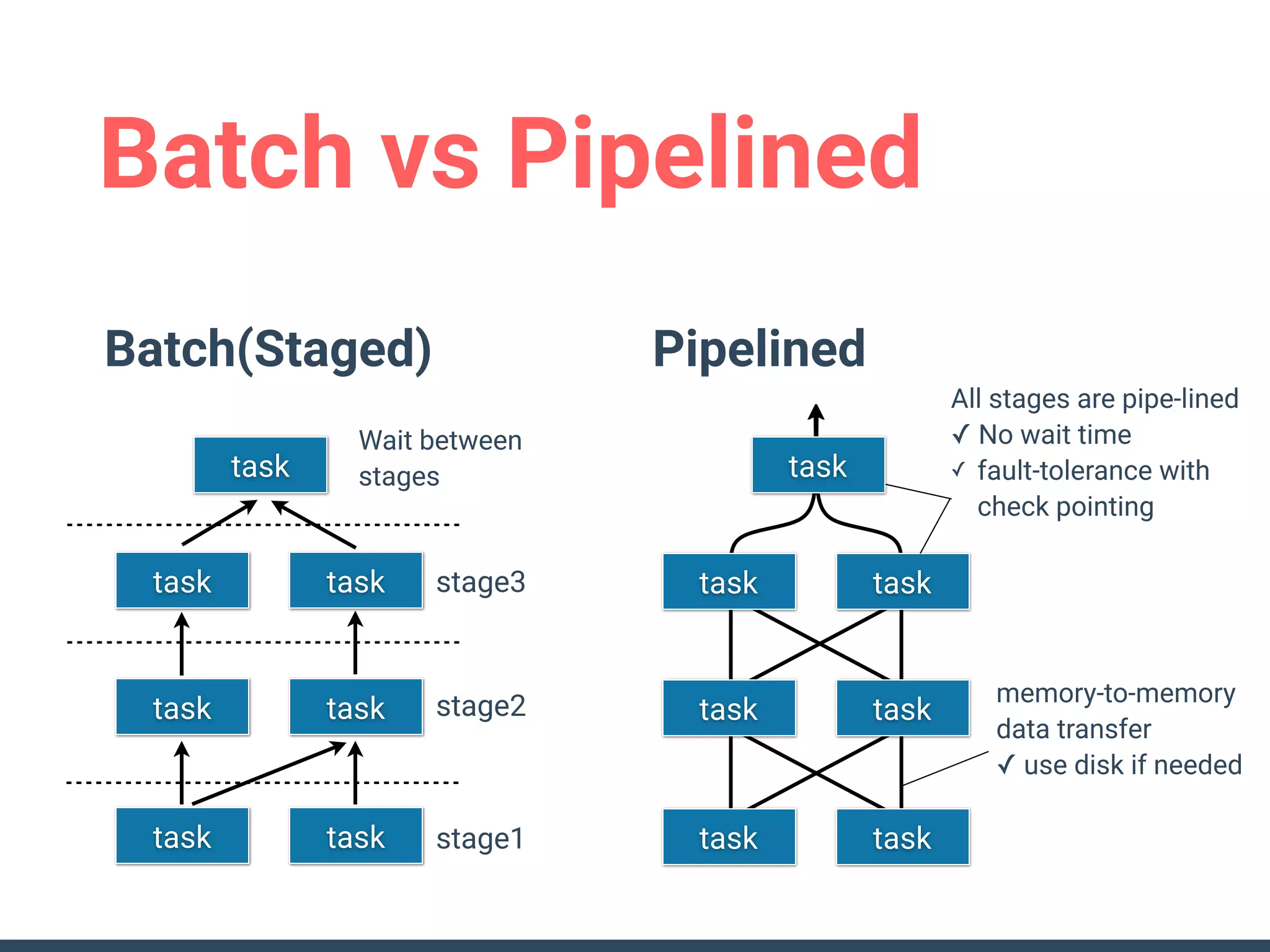
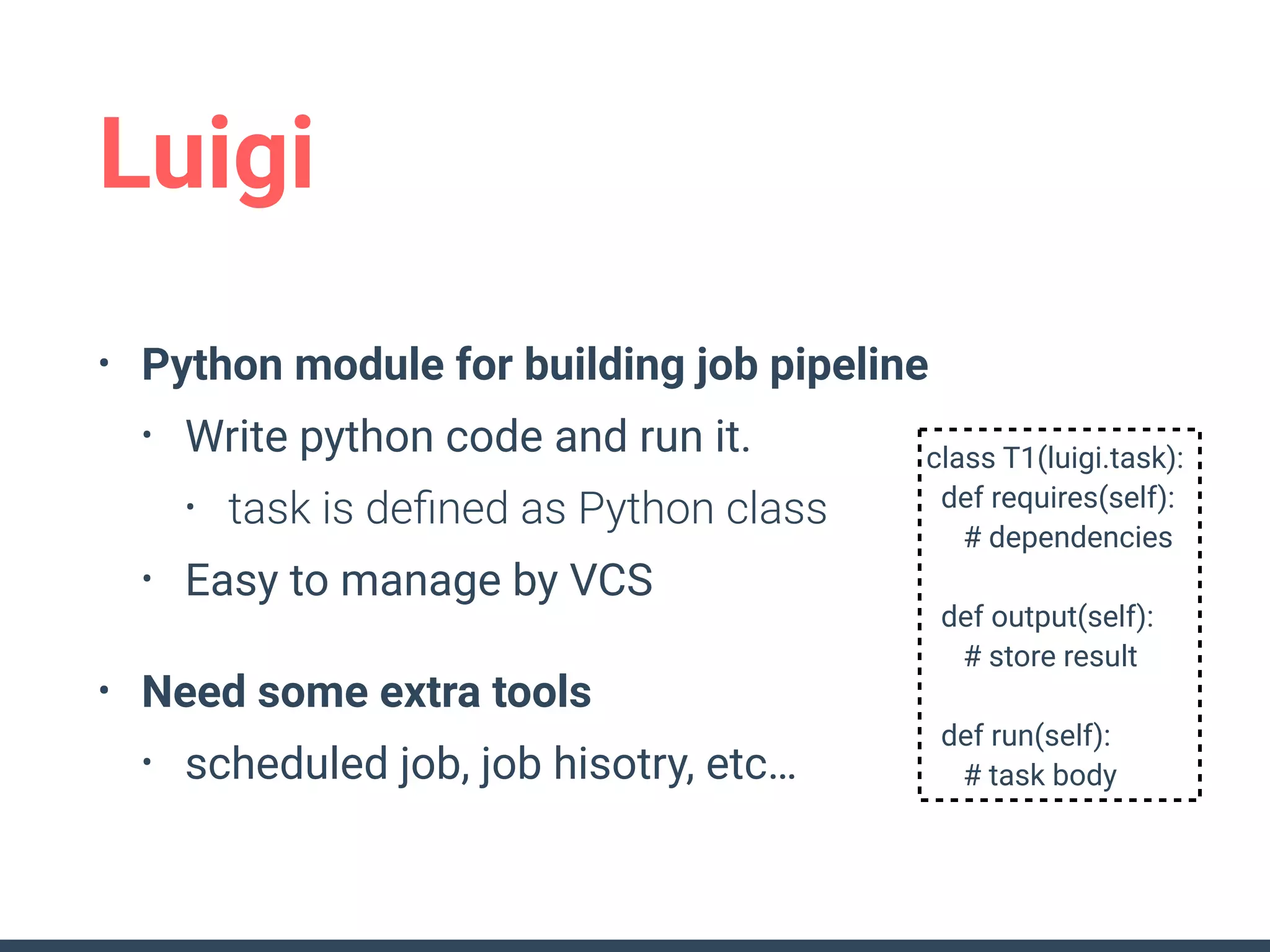
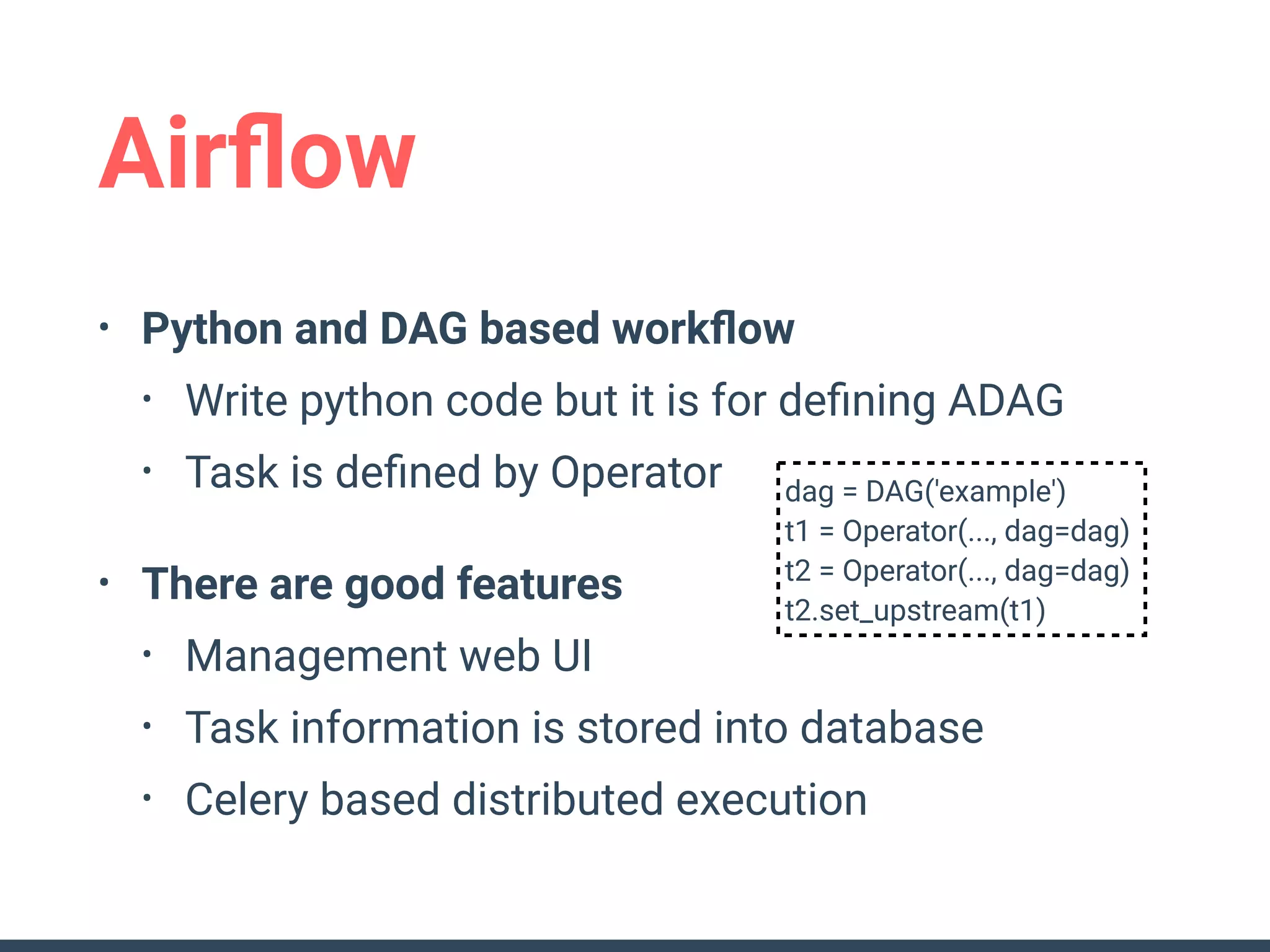
This document discusses building a data analytics platform and summarizes various technologies that can be used. It begins by outlining reasons for analyzing data like reporting, monitoring, and exploratory analysis. It then discusses using relational databases, parallel databases, Hadoop, and columnar storage to store and process large volumes of data. Streaming technologies like Storm, Kafka, and services like Redshift, BigQuery, and Treasure Data are also summarized as options for a complete analytics platform.