This document discusses interoperability between Swift and Objective-C. It covers topics like initializing and interacting with Objective-C APIs from Swift, bridging optionals, nullability, lightweight generics, extensions, closures and blocks, object comparison, hashing, selectors, key paths, and more. It also discusses adopting Cocoa design patterns like delegation, lazy initialization, error handling, and key-value observing when using Swift with Cocoa.



![Interacting with Objective-C APIs
- (instancetype)init;
- (instancetype)initWithFrame:(CGRect)frame
style:(UITableViewStyle)style;
init() { /* ... */ }
init(frame: CGRect, style: UITableViewStyle) { /* ... */ }
UITableView *myTableView = [[UITableView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectZero
style:UITableViewStyleGrouped];
let myTableView: UITableView = UITableView(frame: .zero, style: .grouped)
let myTextField = UITextField(frame: CGRect(x: 0.0, y: 0.0,
width: 200.0, height: 40.0))
Initialization
• Objective-C
• Swift](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/useswiftobjc-170421031658/75/Swift-Objective-C-4-2048.jpg)
![Interacting with Objective-C APIs
UIColor *color = [UIColor colorWithRed:0.5 green:0.0 blue:0.5 alpha:1.0];
let color = UIColor(red: 0.5, green: 0.0, blue: 0.5, alpha: 1.0)
Convenience Initializers
• Objective-C
• Swift
To be used with the same syntax as initializers.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/useswiftobjc-170421031658/75/Swift-Objective-C-5-2048.jpg)



![Interacting with Objective-C APIs
myTableView.insertSubview(mySubview, at: 2)
Working with Methods
• Objective-C
• Swift
[myTableView insertSubview:mySubview atIndex:2];
myTableView.layoutIfNeeded()
Can call Objective-C methods from Swift using dot syntax.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/useswiftobjc-170421031658/75/Swift-Objective-C-9-2048.jpg)



![Interacting with Objective-C APIs
Bridging Optionals to Nonnullable Objects
@implementation OptionalBridging
+ (void)logSomeValue:(nonnull id)valueFromSwift {
if ([valueFromSwift isKindOfClass: [NSNull class]]) {
os_log(OS_LOG_DEFAULT, "Received an NSNull value.");
} else {
os_log(OS_LOG_DEFAULT, "%s", [valueFromSwift UTF8String]);
}
}
@end
let someValue: String? = "Bridge me, please."
let nilValue: String? = nil
OptionalBridging.logSomeValue(someValue as Any) // String
OptionalBridging.logSomeValue(nilValue as Any) // an NSNull value.
Optional nil NSNull ,
Optional unwrapped value [T?] => NSArray<T>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/useswiftobjc-170421031658/75/Swift-Objective-C-13-2048.jpg)
![Interacting with Objective-C APIs
Lightweight Generics
@property NSArray<NSDate *> *dates;
@property NSCache<NSObject *, id<NSDiscardableContent>> *cachedData;
@property NSDictionary <NSString *, NSArray<NSLocale *>> *supportedLocales;
var dates: [Date]
var cachedData: NSCache<AnyObject, NSDiscardableContent>
var supportedLocales: [String: [Locale]]
• Objective-C
• Swift](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/useswiftobjc-170421031658/75/Swift-Objective-C-14-2048.jpg)


![Interacting with Objective-C APIs
Closures & Blocks
void (^completionBlock)(NSData *) = ^(NSData *data) {
// ...
}
• Swift
• Objective-C
let completionBlock: (Data) -> Void = { data in
// ...
}
__weak typeof(self) weakSelf = self;
self.block = ^{
__strong typeof(self) strongSelf = weakSelf;
[strongSelf doSomething];
};
self.closure = { [unowned self] in
self.doSomething()
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/useswiftobjc-170421031658/75/Swift-Objective-C-17-2048.jpg)

![Interacting with Objective-C APIs
Hashing
• Swift
• Objective-C
@property NSDictionary *unqualifiedDictionary;
@property NSDictionary<NSString *, NSDate *> *qualifiedDictionary;
@property NSSet *unqualifiedSet;
@property NSSet<NSString *> *qualifiedSet;
var unqualifiedDictionary: [AnyHashable: Any]
var qualifiedDictionary: [String: Date]
var unqualifiedSet: Set<AnyHashable>
var qualifiedSet: Set<String>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/useswiftobjc-170421031658/75/Swift-Objective-C-19-2048.jpg)

![Interacting with Objective-C APIs
Swift Type Compatibility
class Jukebox: NSObject {
var library: Set<String>
var nowPlaying: String?
var isCurrentlyPlaying: Bool {
return nowPlaying != nil
}
class var favoritesPlaylist: [String] {
// return an array of song names
}
init(songs: String...) {
self.library = Set<String>(songs)
}
func playSong(named name: String) throws {
// play song or throw an error if unavailable
}
}
@interface Jukebox : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, strong, nonnull) NSSet<NSString *> *library;
@property (nonatomic, copy, nullable) NSString *nowPlaying;
@property (nonatomic, readonly, getter=isCurrentlyPlaying) BOOL currentlyPlaying;
@property (nonatomic, class, readonly, nonnull) NSArray<NSString *> * favoritesPlaylist;
- (nonnull instancetype)initWithSongs:(NSArray<NSString *> * __nonnull)songs
OBJC_DESIGNATED_INITIALIZER;
- (BOOL)playSong:(NSString * __nonnull)name
error:(NSError * __nullable * __null_unspecified)error;
@end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/useswiftobjc-170421031658/75/Swift-Objective-C-21-2048.jpg)


![Interacting with Objective-C APIs
Unsafe Invocation of Objective-C Methods
let string: NSString = "Hello, Cocoa!"
let selector = #selector(NSString.lowercased(with:))
let locale = Locale.current
if let result = string.perform(selector, with: locale) {
print(result.takeUnretainedValue())
}
// Prints "hello, cocoa!"
let array: NSArray = ["delta", "alpha", "zulu"]
// Not a compile-time error because NSDictionary has this selector.
let selector = #selector(NSDictionary.allKeysForObject)
// Raises an exception because NSArray does not respond to this selector.
array.perform(selector)
Perform Selector
Unsafe invocation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/useswiftobjc-170421031658/75/Swift-Objective-C-24-2048.jpg)
![Interacting with Objective-C APIs
Keys & Key Paths
class Person: NSObject {
var name: String
var friends: [Person] = []
var bestFriend: Person? = nil
init(name: String) {
self.name = name
}
}
let gabrielle = Person(name: "Gabrielle")
let jim = Person(name: "Jim")
let yuanyuan = Person(name: "Yuanyuan")
gabrielle.friends = [jim, yuanyuan]
gabrielle.bestFriend = yuanyuan
#keyPath(Person.name)
// "name"
gabrielle.value(forKey: #keyPath(Person.name))
// "Gabrielle"
#keyPath(Person.bestFriend.name)
// "bestFriend.name"
gabrielle.value(forKeyPath: #keyPath(Person.bestFriend.name))
// "Yuanyuan"
#keyPath(Person.friends.name)
// "friends.name"
gabrielle.value(forKeyPath: #keyPath(Person.friends.name))
// ["Yuanyuan", "Jim"]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/useswiftobjc-170421031658/75/Swift-Objective-C-25-2048.jpg)






![Adopting Cocoa Design Patterns
Lazy Initialization
@property NSXMLDocument *XML;
- (NSXMLDocument *)XML {
if (_XML == nil) {
_XML = [[NSXMLDocument alloc] initWithContentsOfURL:[[Bundle mainBundle]
URLForResource:@"/path/to/resource" withExtension:@"xml"] options:0 error:nil];
}
return _XML;
}
lazy var XML: XMLDocument = try! XMLDocument(contentsOf:
Bundle.main.url(forResource: "document", withExtension: "xml")!, options: 0)
• Objective-C
• Swift](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/useswiftobjc-170421031658/75/Swift-Objective-C-32-2048.jpg)
![Adopting Cocoa Design Patterns
Lazy property
var pattern: String
lazy var regex: NSRegularExpression = try! NSRegularExpression(pattern: self.pattern,
options: [])
lazy var currencyFormatter: NumberFormatter = {
let formatter = NumberFormatter()
formatter.numberStyle = .currency
formatter.currencySymbol = "¤"
return formatter
}()
• Swift
use self-evaluating closure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/useswiftobjc-170421031658/75/Swift-Objective-C-33-2048.jpg)
![Adopting Cocoa Design Patterns
Error Handling
NSFileManager *fileManager = [NSFileManager defaultManager];
NSURL *fromURL = [NSURL fileURLWithPath:@"/path/to/old"];
NSURL *toURL = [NSURL fileURLWithPath:@"/path/to/new"];
NSError *error = nil;
BOOL success = [fileManager moveItemAtURL:fromURL toURL:toURL error:&error];
if (!success) {
NSLog(@"Error: %@", error.domain);
}
• Swift
• Objective-C
let fileManager = FileManager.default
let fromURL = URL(fileURLWithPath: "/path/to/old")
let toURL = URL(fileURLWithPath: "/path/to/new")
do {
try fileManager.moveItem(at: fromURL, to: toURL)
} catch let error as NSError {
print("Error: (error.domain)")
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/useswiftobjc-170421031658/75/Swift-Objective-C-34-2048.jpg)
![Adopting Cocoa Design Patterns
Converting errors to Optional values
• Swift
• Objective-C
NSFileManager *fileManager = [NSFileManager defaultManager];
NSURL *tmpURL = [fileManager URLForDirectory:NSCachesDirectory
inDomain:NSUserDomainMask
appropriateForURL:nil
create:YES
error:nil];
if (tmpURL != nil) {
// ...
}
let fileManager = FileManager.default
if let tmpURL = try? fileManager.url(for: .cachesDirectory, in: .userDomainMask,
appropriateFor: nil, create: true) {
// ...
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/useswiftobjc-170421031658/75/Swift-Objective-C-35-2048.jpg)
![Adopting Cocoa Design Patterns
Throwing error
• Swift
• Objective-C
// an error occurred
if (errorPtr) {
*errorPtr = [NSError errorWithDomain:NSURLErrorDomain
code:NSURLErrorCannotOpenFile
userInfo:nil];
}
// an error occurred
throw NSError(domain: NSURLErrorDomain, code: NSURLErrorCannotOpenFile, userInfo: nil)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/useswiftobjc-170421031658/75/Swift-Objective-C-36-2048.jpg)
![Adopting Cocoa Design Patterns
Key-value Observing
KVO with a Swift class inherits from NSObject class
1) Add dynamic modifier to any property
2) Create a global context variable
3) Add an observer for the key-path, override the observeValue() method
and remove the observer in deinit.
class MyObjectToObserve: NSObject {
dynamic var myDate = NSDate()
func updateDate() {
myDate = NSDate()
}
}
private var myContext = 0
class MyObserver: NSObject {
var objectToObserve = MyObjectToObserve()
override init() {
super.init()
objectToObserve.addObserver(self, forKeyPath: #keyPath(MyObjectToObserve.myDate),
options: .new, context: &myContext)
}
override func observeValue(forKeyPath keyPath: String?, of object: Any?, change:
[NSKeyValueChangeKey : Any]?, context: UnsafeMutableRawPointer?) {
if context == &myContext {
if let newValue = change?[.newKey] { print("Date changed: (newValue)”) }
} else {
super.observeValue(forKeyPath: keyPath, of: object, change: change, context: context)
}
}
deinit {
objectToObserve.removeObserver(self, forKeyPath: #keyPath(MyObjectToObserve.myDate),
context: &myContext)
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/useswiftobjc-170421031658/75/Swift-Objective-C-37-2048.jpg)

![Adopting Cocoa Design Patterns
Singleton
initialization in a call the dispatch_once function
+ (instancetype)sharedInstance {
static id _sharedInstance = nil;
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
_sharedInstance = [[self alloc] init];
});
return _sharedInstance;
}
class Singleton {
static let sharedInstance = Singleton()
}
class Singleton {
static let sharedInstance: Singleton = {
let instance = Singleton()
// setup code
return instance
}()
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/useswiftobjc-170421031658/75/Swift-Objective-C-39-2048.jpg)

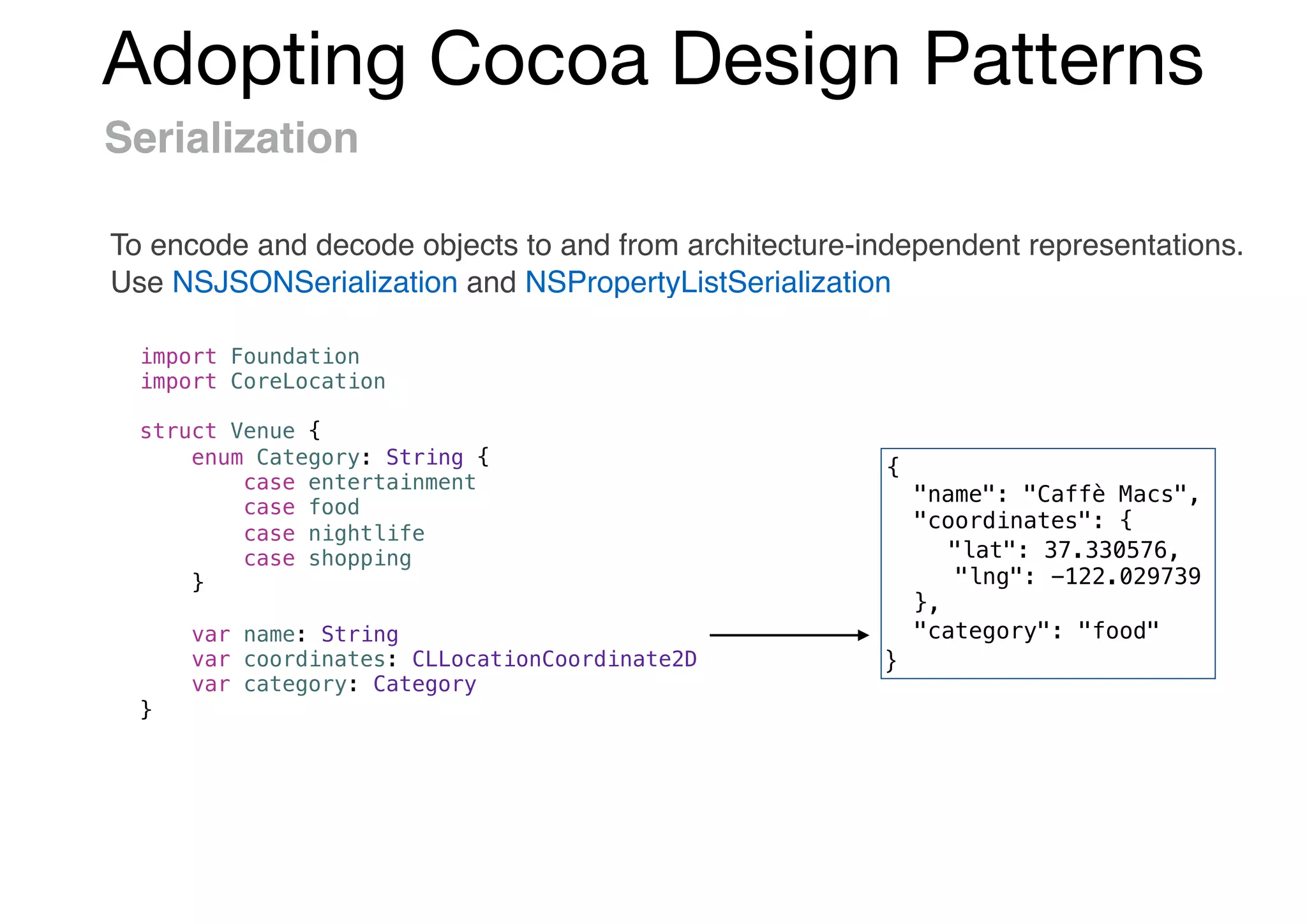
![Adopting Cocoa Design Patterns
Serialization : Initializer
init?(attributes: [String: Any]) {
guard let name = attributes["name"] as? String,
let coordinates = attributes["coordinates"] as? [String: Double],
let latitude = coordinates["lat"],
let longitude = coordinates["lng"],
let category = Category(rawValue: attributes["category"] as? String ?? "Invalid")
else {
return nil
}
self.name = name
self.coordinates = CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: latitude, longitude: longitude)
self.category = category
}
let JSON = "{"name": "Caffè Macs","coordinates": {"lat": 37.330576,"lng": -122.029739},
"category": "food"}"
let data = JSON.data(using: String.Encoding.utf8)!
let attributes = try! JSONSerialization.jsonObject(with: data, options: []) as! [String: Any]
let venue = Venue(attributes: attributes)!
print(venue.name)
// Prints "Caffè Macs"
Initialize with Dictionary<String, Any>
Create a Venue from a JSON representation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/useswiftobjc-170421031658/75/Swift-Objective-C-42-2048.jpg)
![Adopting Cocoa Design Patterns
Serialization : Validating
enum ValidationError: Error {
case missing(String)
case invalid(String)
}
init(attributes: [String: Any]) throws {
guard let name = attributes["name"] as? String else {
throw ValidationError.missing("name")
}
guard let coordinates = attributes["coordinates"] as? [String: Double] else {
throw ValidationError.missing("coordinates")
}
guard let latitude = coordinates["lat"],
let longitude = coordinates["lng"]
else {
throw ValidationError.invalid("coordinates")
}
guard let categoryName = attributes["category"] as? String else {
throw ValidationError.missing("category")
}
guard let category = Category(rawValue: categoryName) else {
throw ValidationError.invalid("category")
}
self.name = name
self.coordinates = CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: latitude, longitude: longitude)
self.category = category
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/useswiftobjc-170421031658/75/Swift-Objective-C-43-2048.jpg)
![Adopting Cocoa Design Patterns
Localization
use NSLocalizedString, NSLocalizedStringFromTable,
NSLocalizedStringFromTableInBundle, NSLocalizedStringWithDefaultValue
• Objective-C
• Swift
A single function: NSLocalizedString(_:tableName:bundle:value:comment:)
let format = NSLocalizedString("Hello, %@!", comment: "Hello, {given name}!")
let name = "Mei"
let greeting = String(format: format, arguments: [name as CVarArg])
print(greeting)
// Prints "Hello, Mei!"
if let path = Bundle.main.path(forResource: "Localization", ofType: "strings",
inDirectory: nil, forLocalization: "ja"),
let bundle = Bundle(path: path) {
let translation = NSLocalizedString("Hello", bundle: bundle, comment: "")
print(translation)
}
// Prints " "](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/useswiftobjc-170421031658/75/Swift-Objective-C-44-2048.jpg)
![Adopting Cocoa Design Patterns
API Availability
use respondsToSelector: and instancesRespondToSelector: methods
• Objective-C
• Swift
let locationManager = CLLocationManager()
if #available(iOS 8.0, macOS 10.10, *) {
locationManager.requestWhenInUseAuthorization()
}
if ([CLLocationManager instancesRespondToSelector:@selector(requestWhenInUseAuthorization)]) {
// Method is available for use.
} else {
// Method is not available.
}
let locationManager = CLLocationManager()
guard #available(iOS 8.0, macOS 10.10, *) else { return }
locationManager.requestWhenInUseAuthorization()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/useswiftobjc-170421031658/75/Swift-Objective-C-45-2048.jpg)






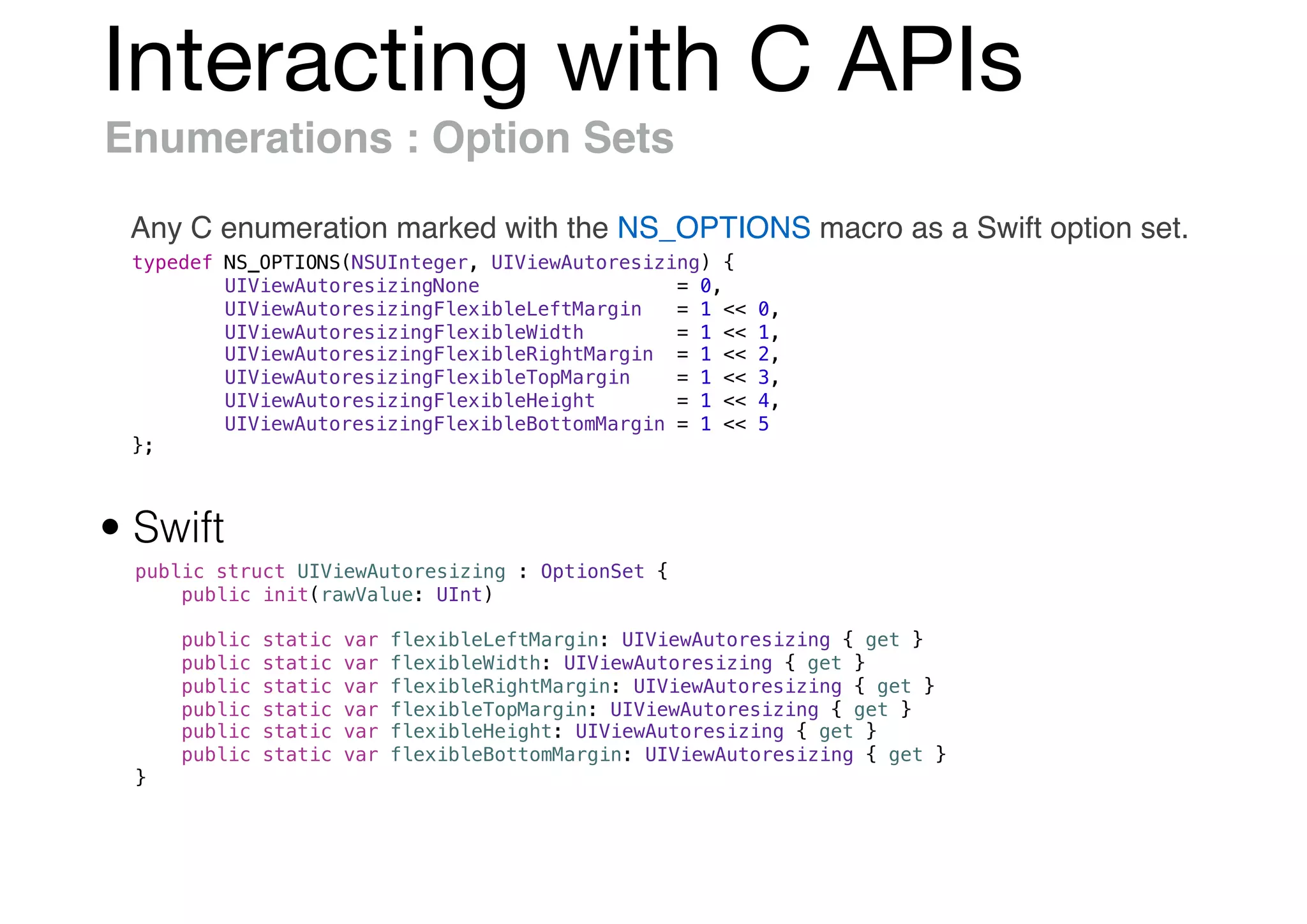

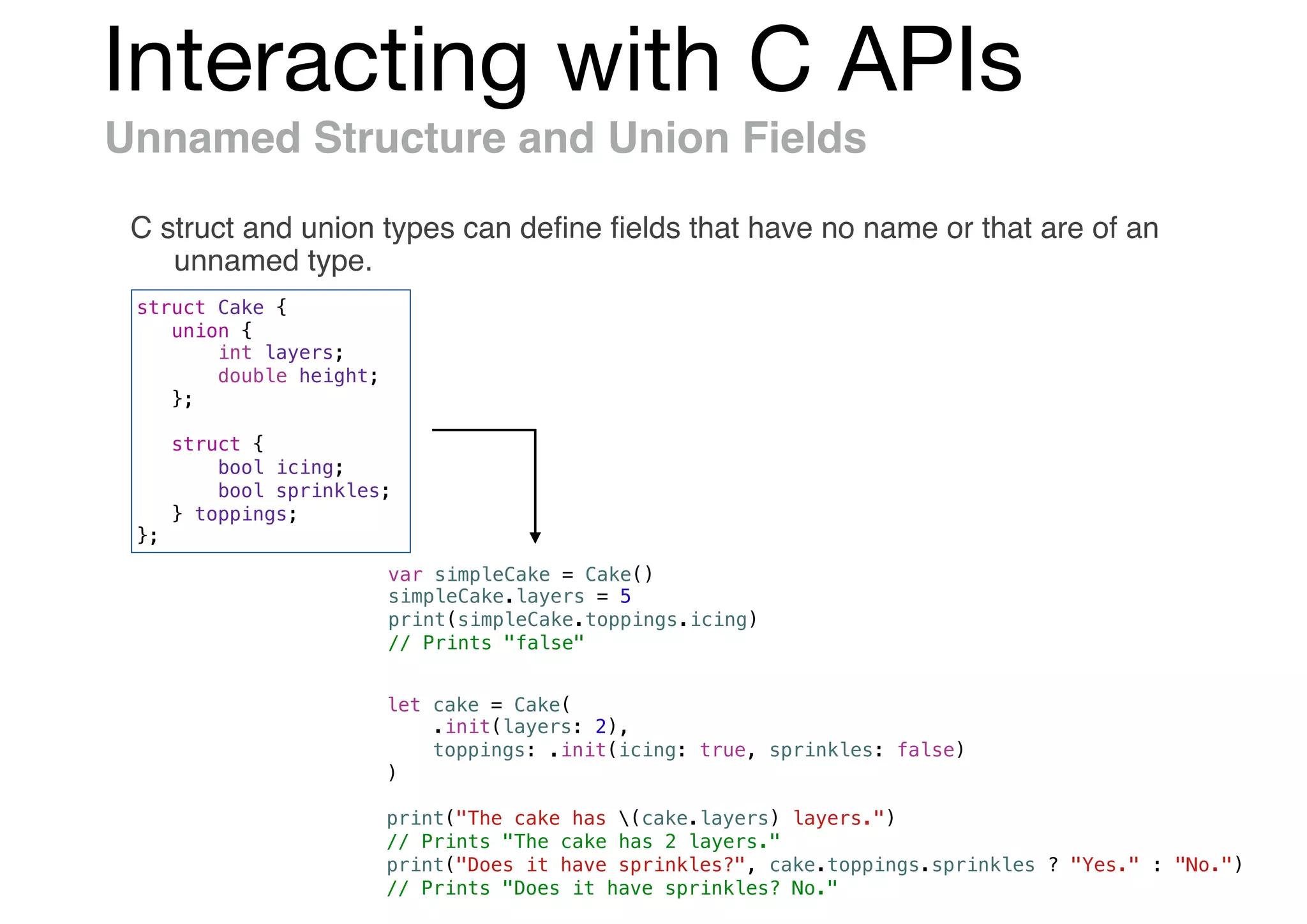
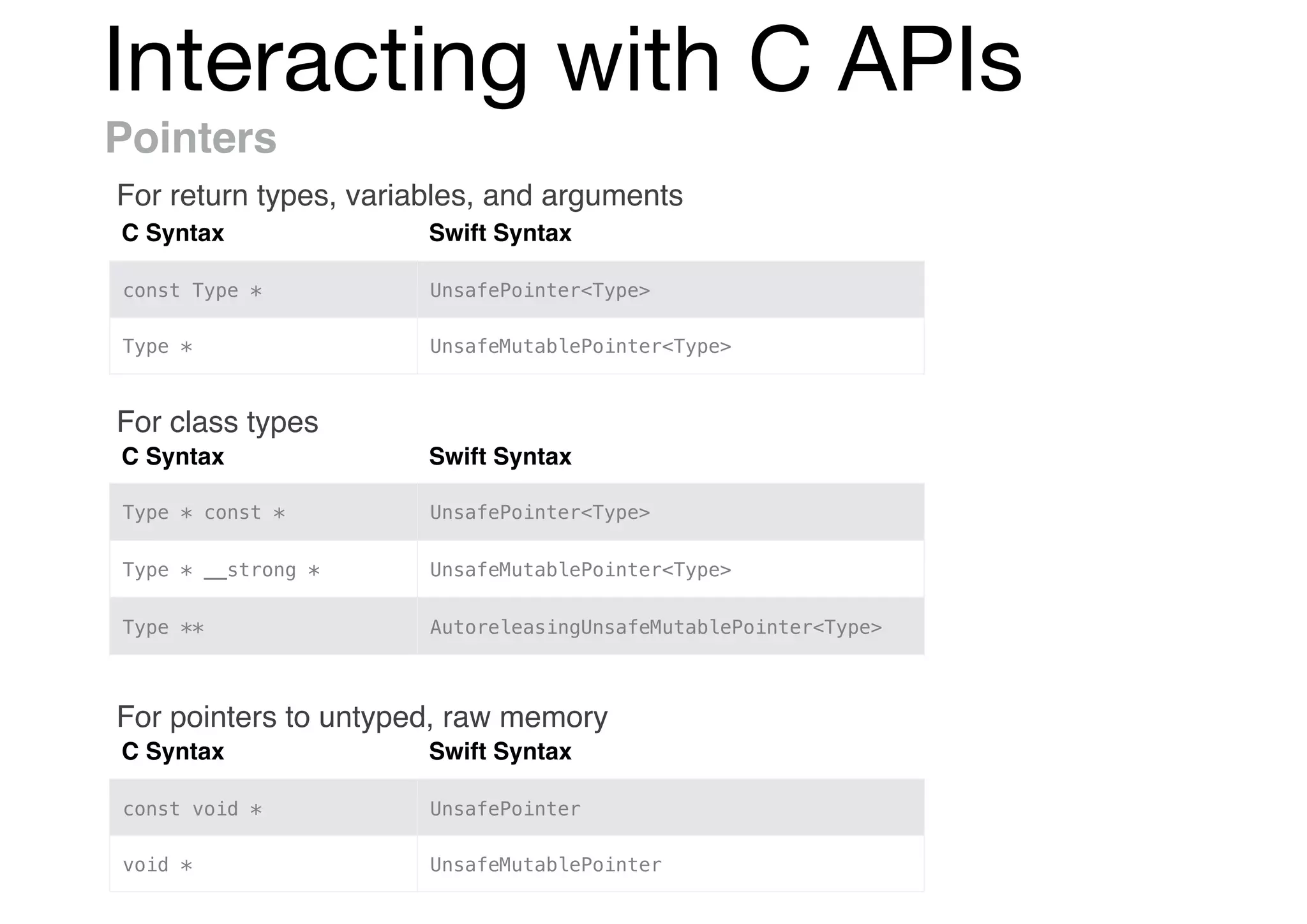
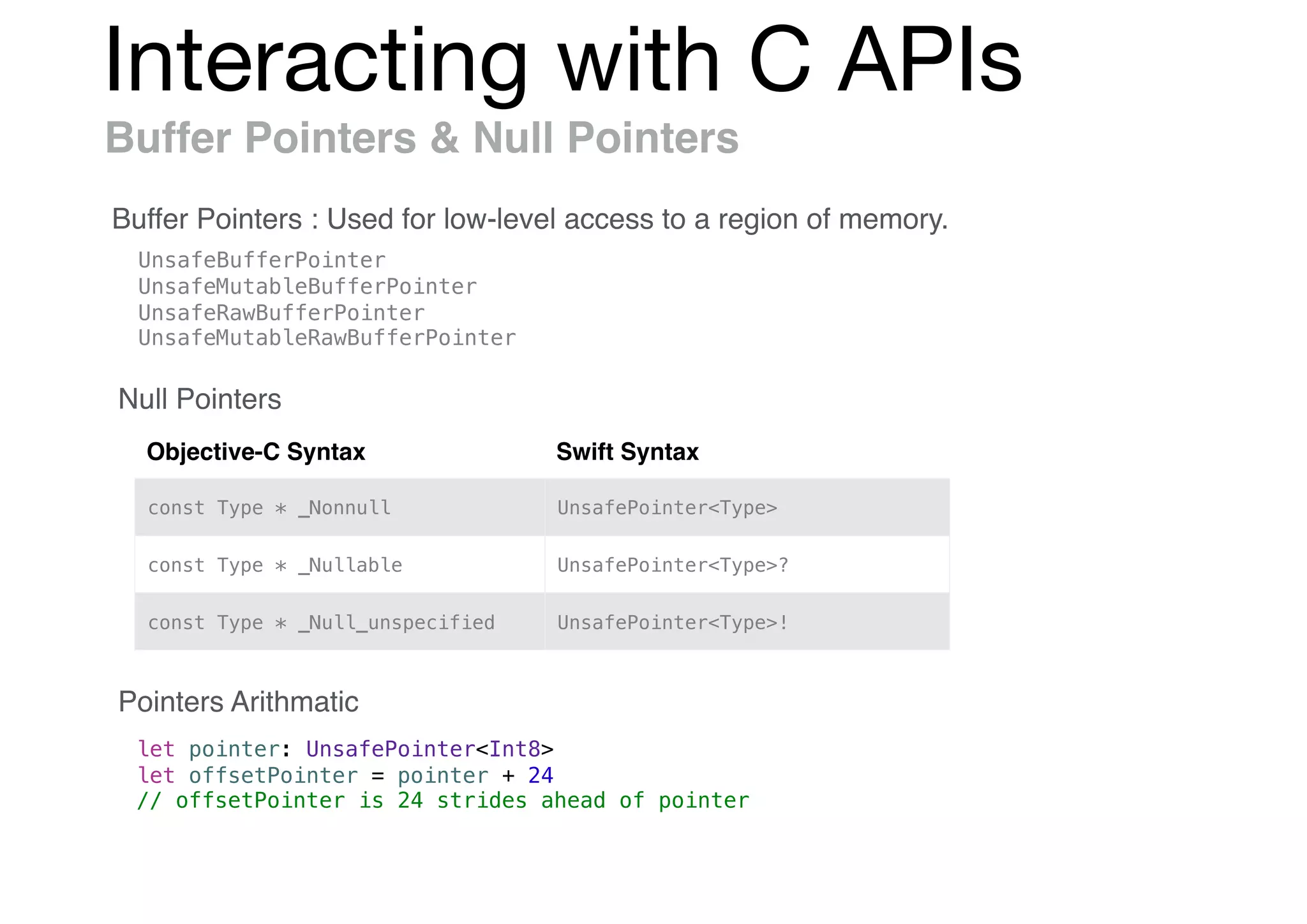
![Interacting with C APIs
Constant Pointers
func takesAPointer(_ p: UnsafePointer<Float>) {
// ...
}
var x: Float = 0.0
takesAPointer(&x)
takesAPointer([1.0, 2.0, 3.0])
var x: Float = 0.0, y: Int = 0
takesARawPointer(&x)
takesARawPointer(&y)
takesARawPointer([1.0, 2.0, 3.0] as [Float])
let intArray = [1, 2, 3]
takesARawPointer(intArray)
func takesARawPointer(_ p: UnsafeRawPointer?) {
// ...
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/useswiftobjc-170421031658/75/Swift-Objective-C-58-2048.jpg)
![Interacting with C APIs
Mutable Pointers
func takesAMutablePointer(_ p: UnsafeMutablePointer<Float>) {
// ...
}
var x: Float = 0.0
var a: [Float] = [1.0, 2.0, 3.0]
takesAMutablePointer(&x)
takesAMutablePointer(&a)
var x: Float = 0.0, y: Int = 0
var a: [Float] = [1.0, 2.0, 3.0], b: [Int] = [1, 2, 3]
takesAMutableRawPointer(&x)
takesAMutableRawPointer(&y)
takesAMutableRawPointer(&a)
takesAMutableRawPointer(&b)
func takesAMutableRawPointer(_ p: UnsafeMutableRawPointer?) {
// ...
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/useswiftobjc-170421031658/75/Swift-Objective-C-59-2048.jpg)

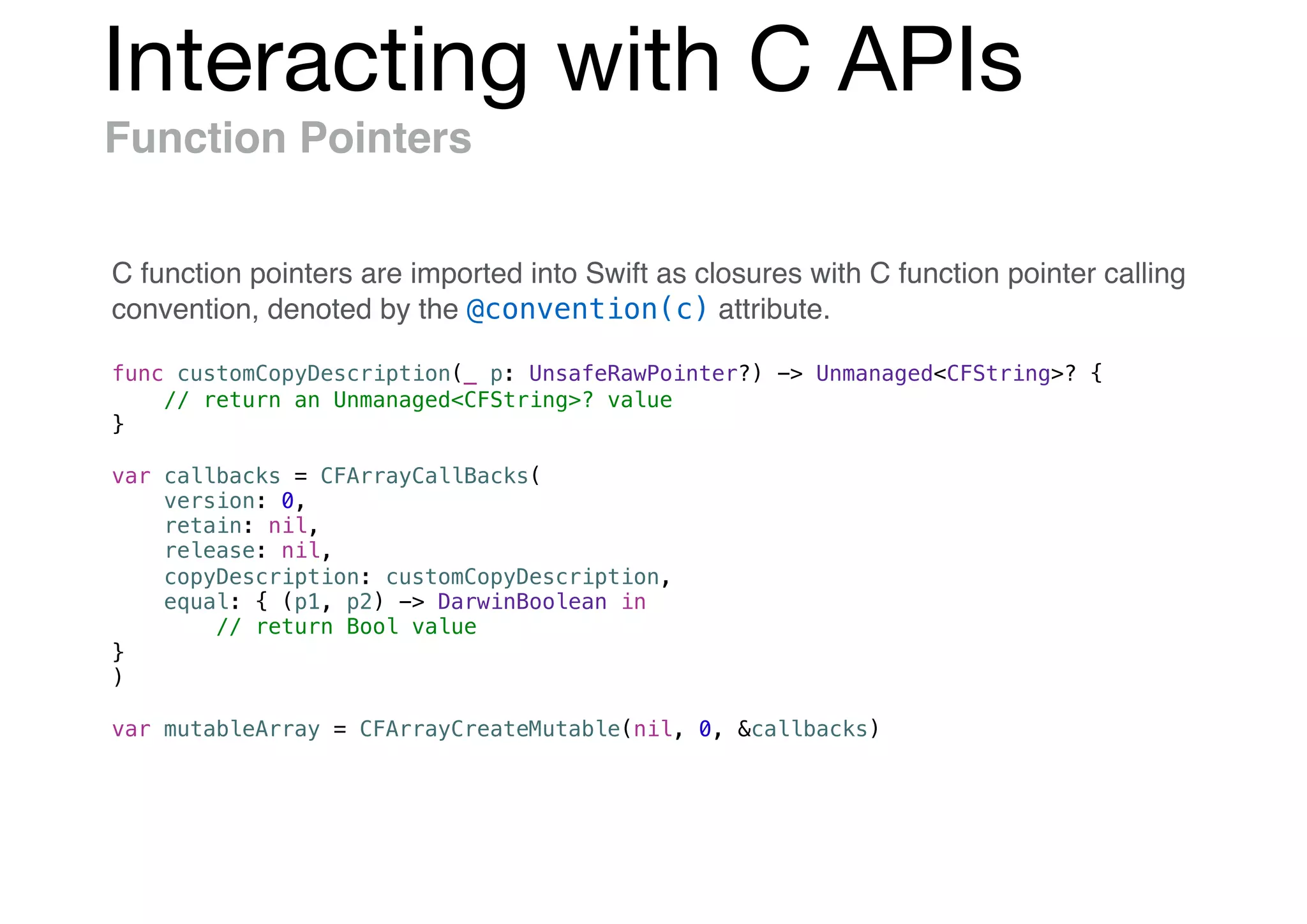

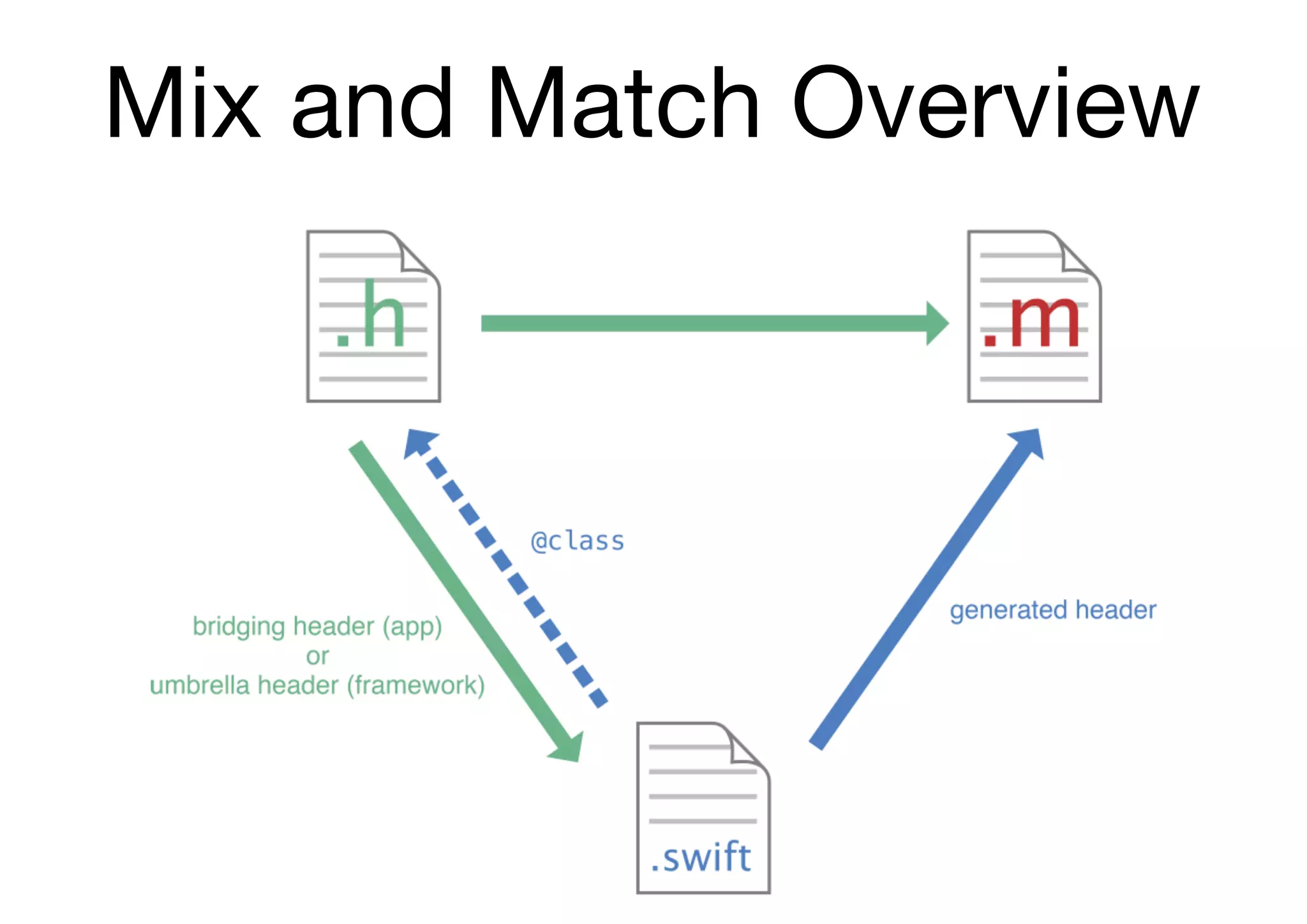



![Swift & Objective-C in the Same Project
Using Swift from Objective-C
Swift class
MySwiftClass *swiftObject = [[MySwiftClass alloc] init];
[swiftObject swiftMethod];
// MyObjcClass.h
@class MySwiftClass;
@protocol MySwiftProtocol;
@interface MyObjcClass : NSObject
- (MySwiftClass *)returnSwiftClassInstance;
- (id <MySwiftProtocol>)returnInstanceAdoptingSwiftProtocol;
// ...
@end
Referencing a Swift Class or Protocol in an Objective-C Header](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/useswiftobjc-170421031658/75/Swift-Objective-C-70-2048.jpg)