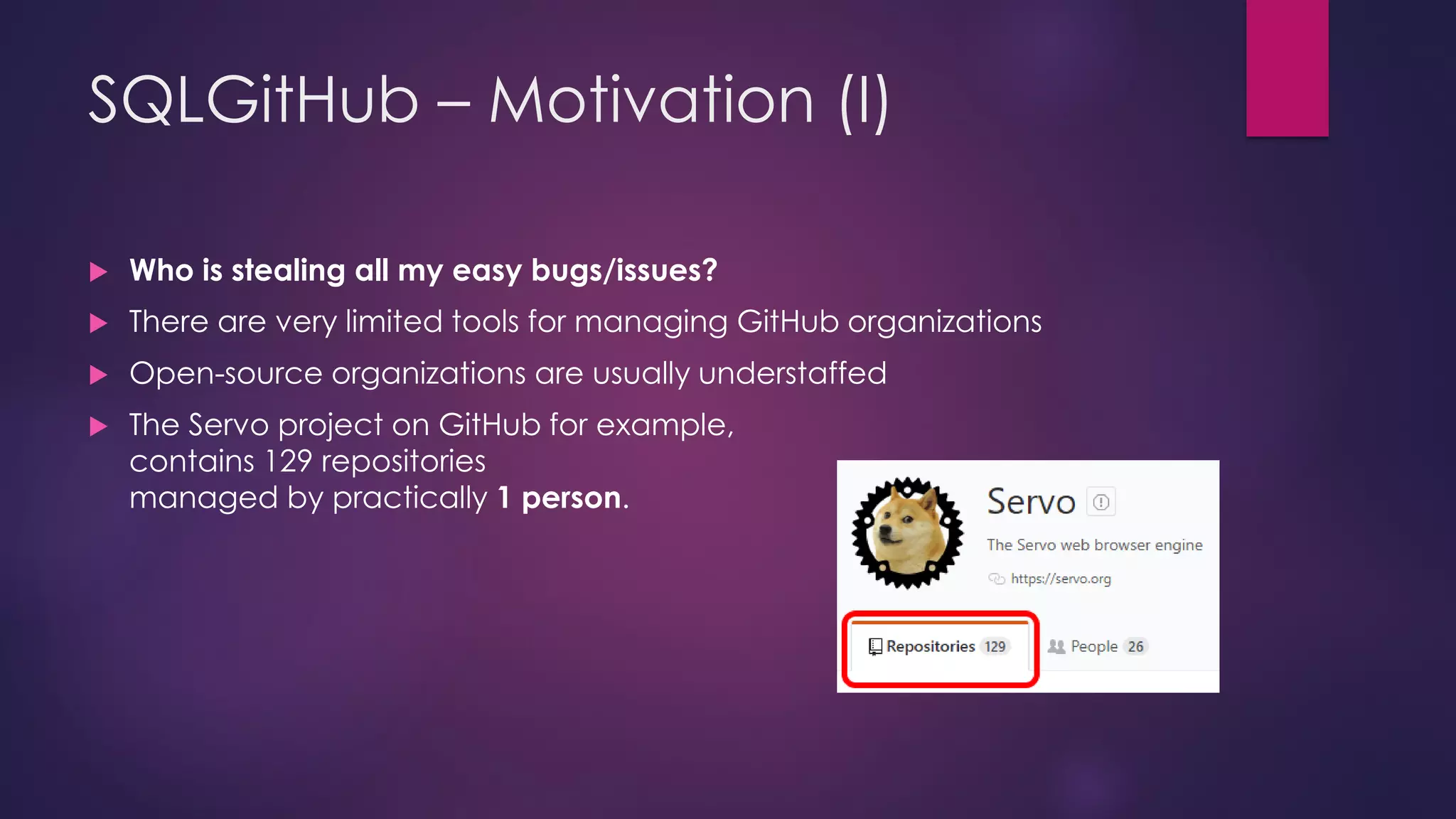
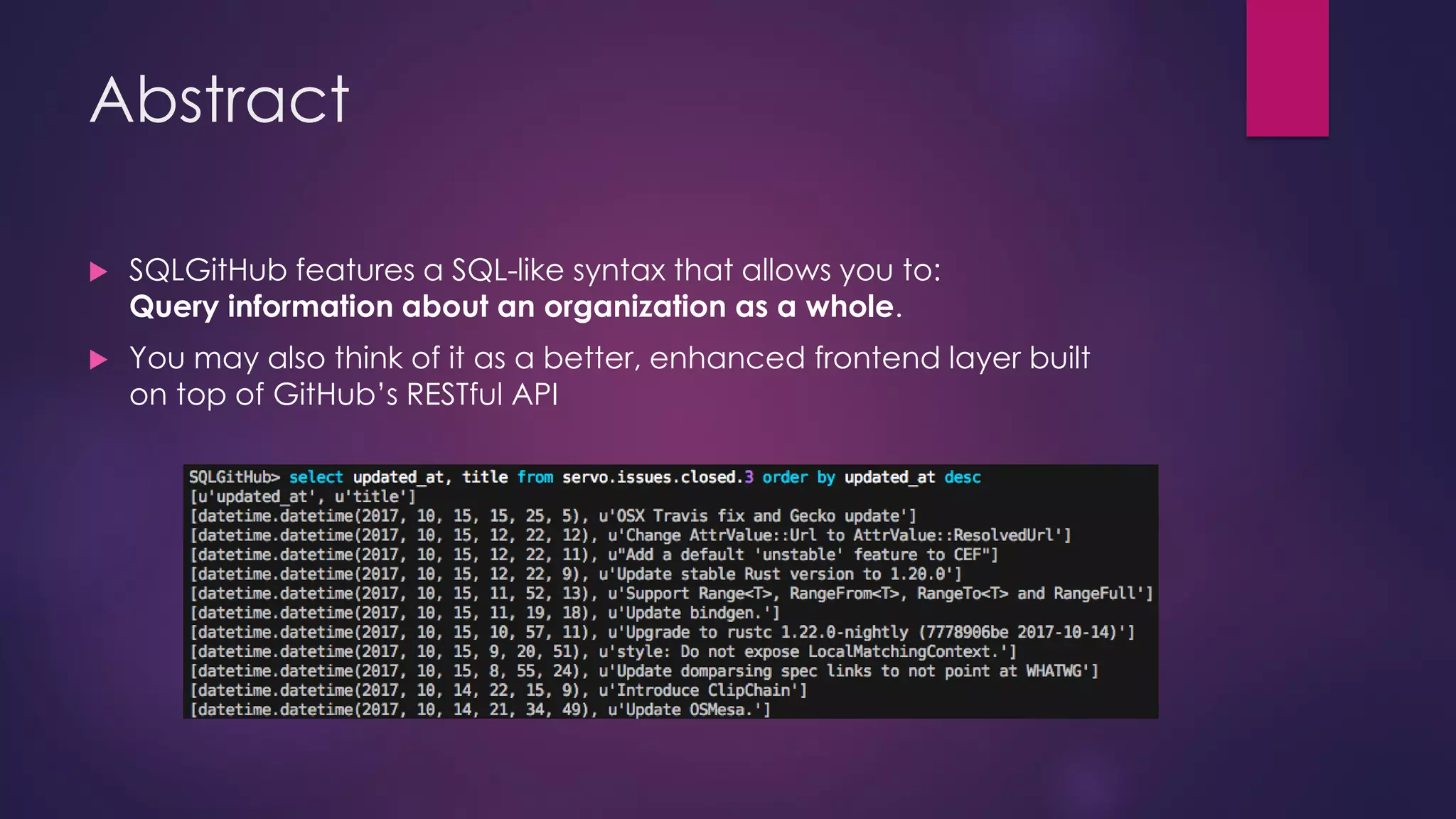
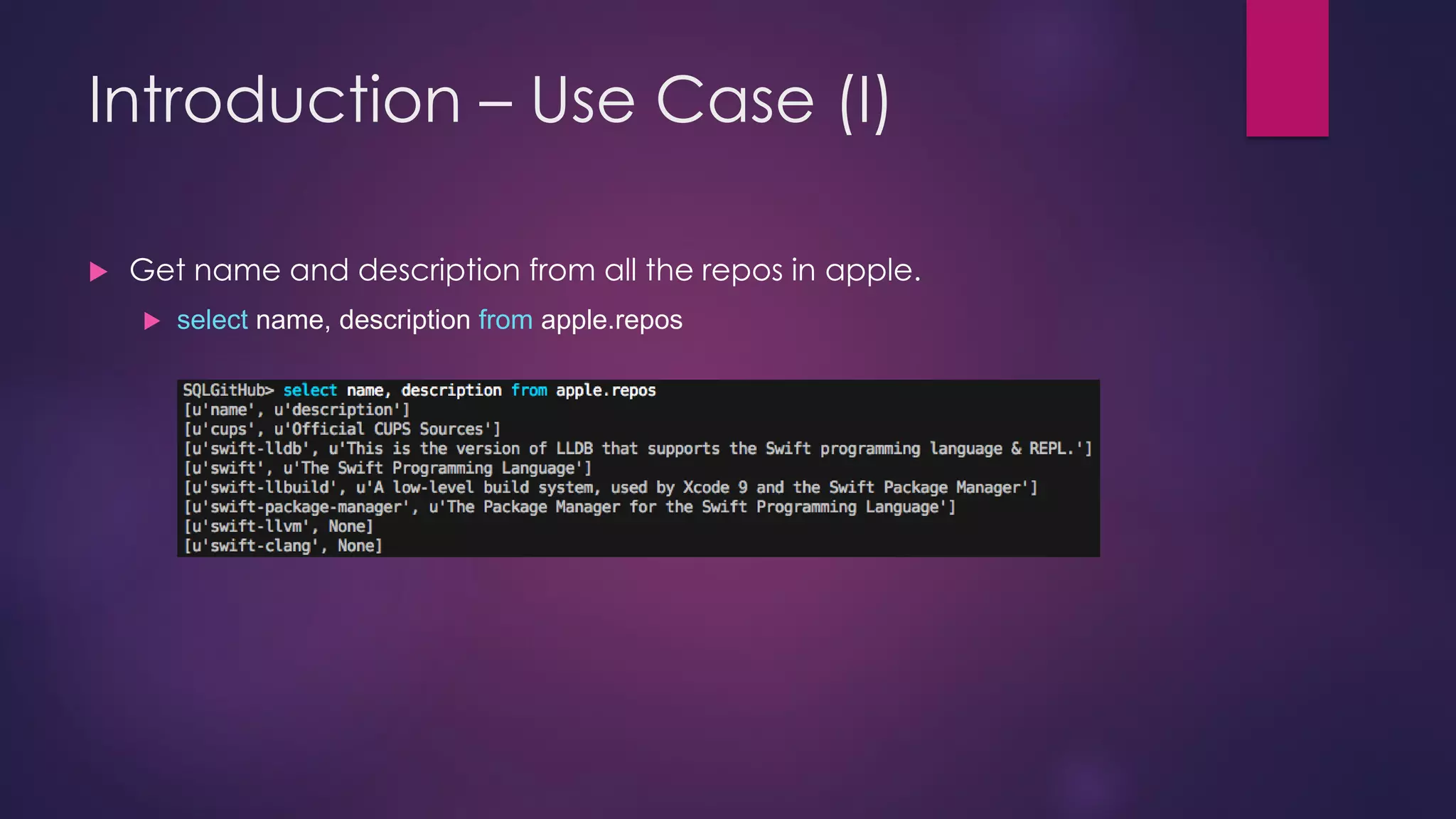
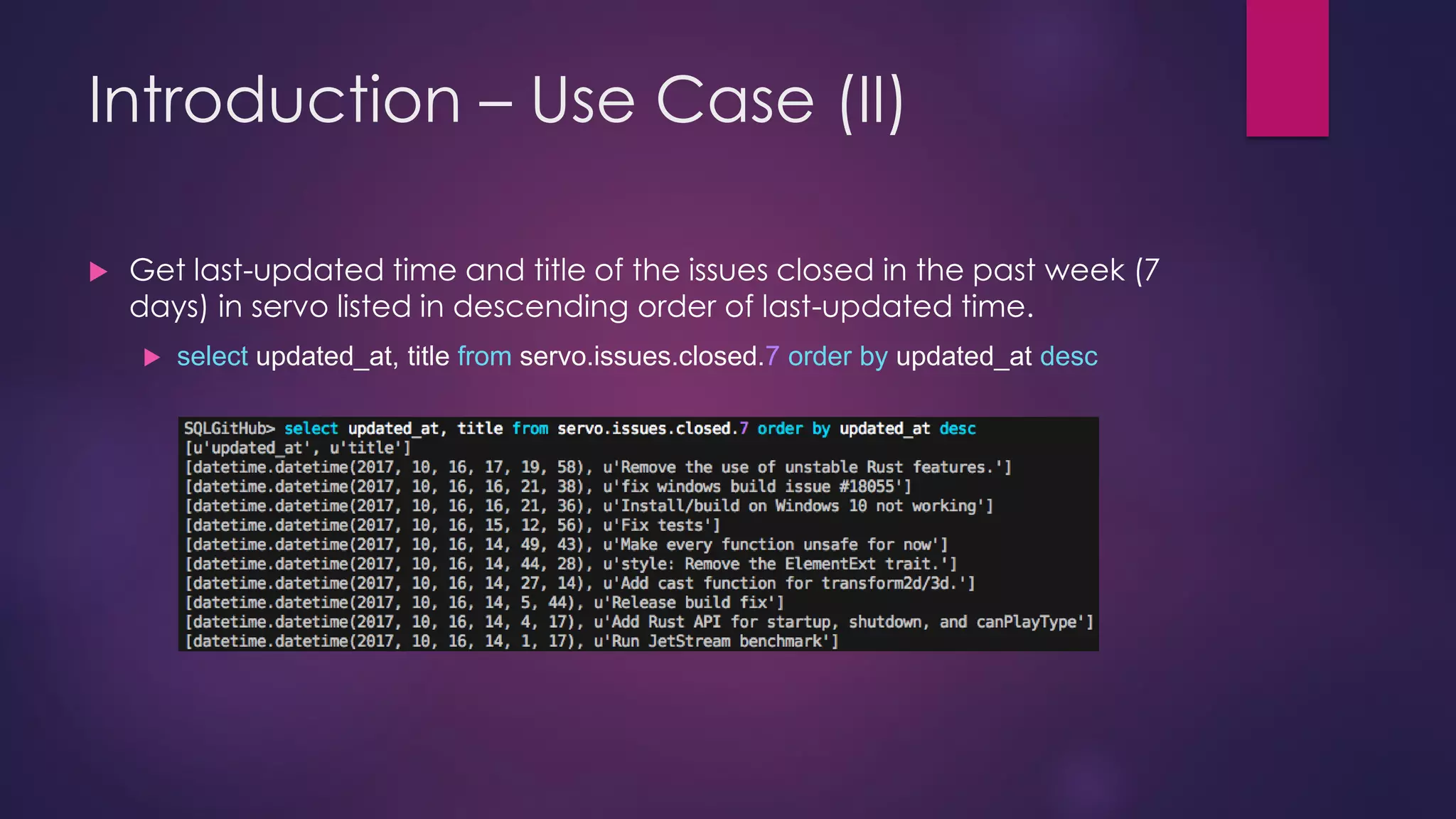
The document discusses the development of sqlgithub, a tool for querying GitHub organizations, spurred by challenges faced with the Servo project. It highlights the motivations behind its creation, including the lack of management tools for GitHub organizations, and outlines the features, supported schemas, use cases, technology stack, and various challenges encountered during its development. The document concludes with proposed future directions for enhancing sqlgithub's compatibility and efficiency.




![Introduction – Supported Schema
SELECT
select_expr [, select_expr ...]
FROM {org_name | org_name.{repos | issues | pulls | commits}}
[WHERE where_condition]
[GROUP BY {col_name | expr}
[ASC | DESC], ...]
[HAVING where_condition]
[ORDER BY {col_name | expr}
[ASC | DESC], ...]
[LIMIT row_count]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlgithub-171023085625/75/SQLGitHub-Access-GitHub-API-with-SQL-like-syntaxes-7-2048.jpg)



![Introduction – Challenges (II)
Extracting all relevant fields from expressions to fetch at once
select concat("[)"-> avg(stargazers_count)"(: ", stargazers_count -
avg(stargazers_count), "] ", name) from apple.repos where description
like "%library%" order by id
Algorithm: for each expression,
Remove all literal strings. Use r""(?:[^"]|.)*"" to match.
Find all possible tokens with r"([a-zA-Z_]+)(?:[^(a-zA-Z_]|$)".
For each token, check if it’s a predefined token (ie. part of SQL).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlgithub-171023085625/75/SQLGitHub-Access-GitHub-API-with-SQL-like-syntaxes-16-2048.jpg)
![Introduction – Challenges (III)
Expression Evaluation is really complicated
Regular (eg. concat, floor) and Aggregate functions (eg. max, min)
Have to evaluate an entire table at once
Nested functions (eg. sum(avg(field_a) + avg(field_b)))
Use recursive regex patterns to extract tokens – r”((?:(?>[^()]+|(?R))*))”
Assign special precedence and insert extra logic in place
Operator Precedence
Modified 2-stack evaluation approach +
Finite State Machine + One-token Lookahead](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlgithub-171023085625/75/SQLGitHub-Access-GitHub-API-with-SQL-like-syntaxes-17-2048.jpg)


