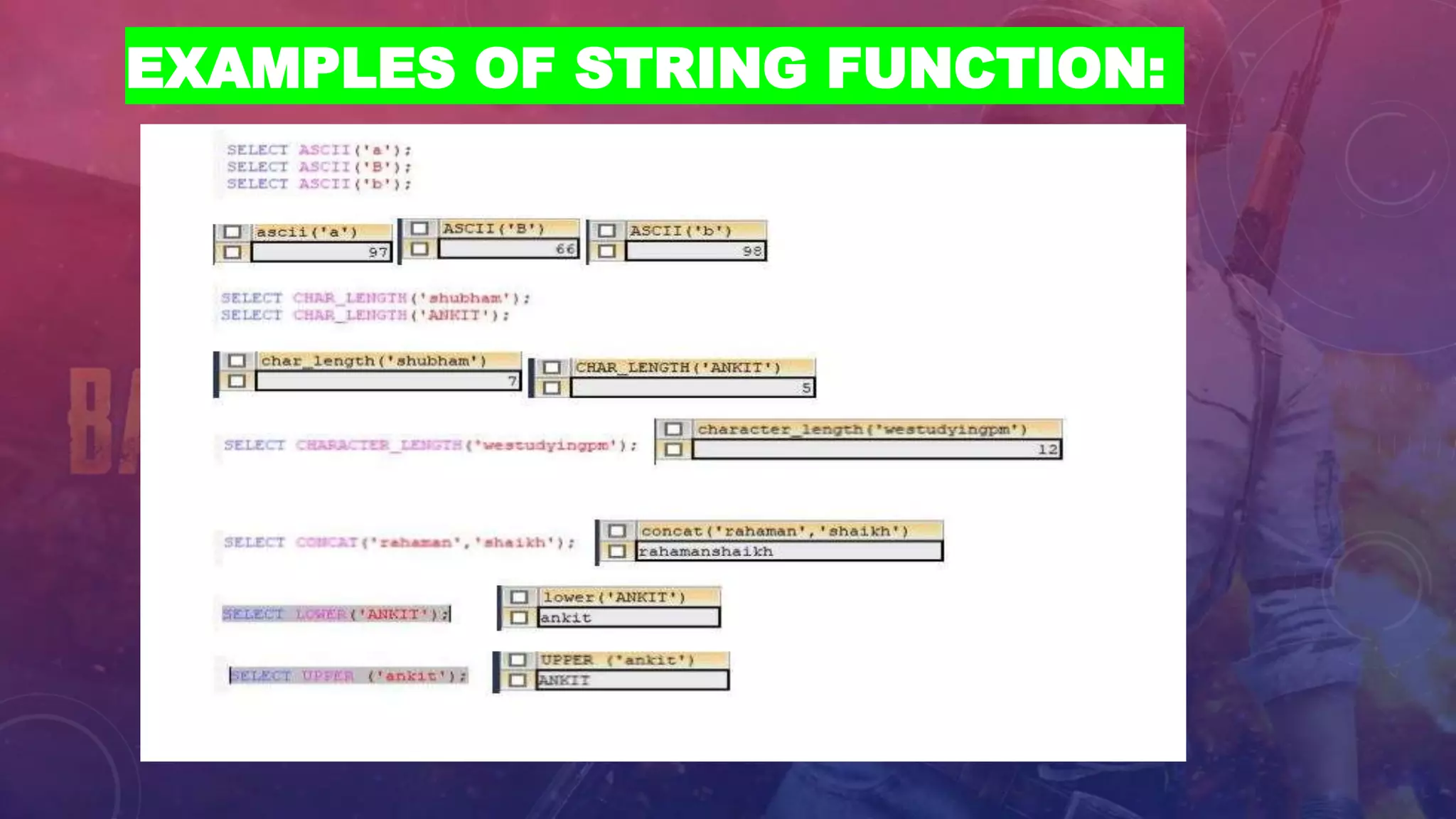
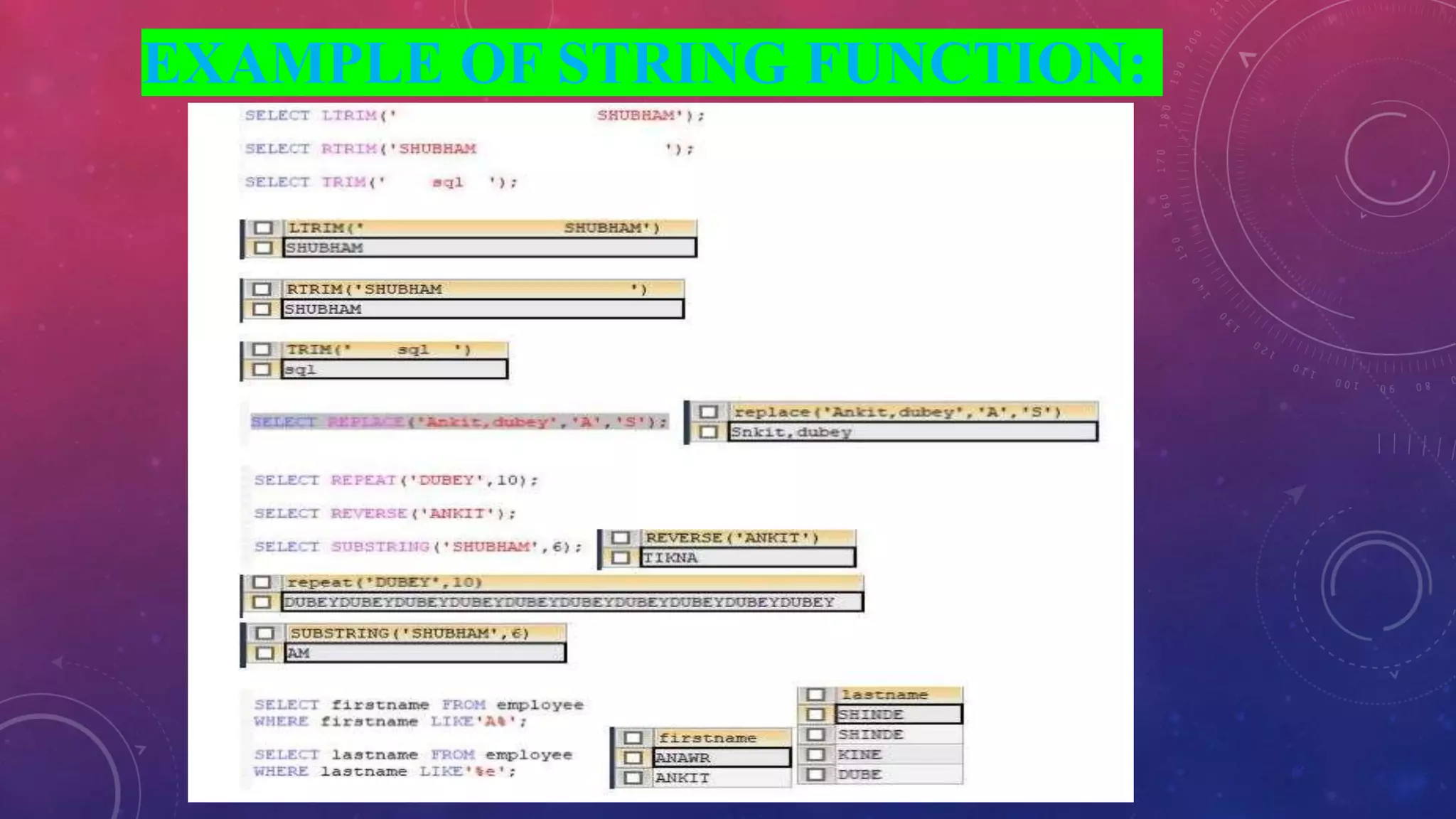
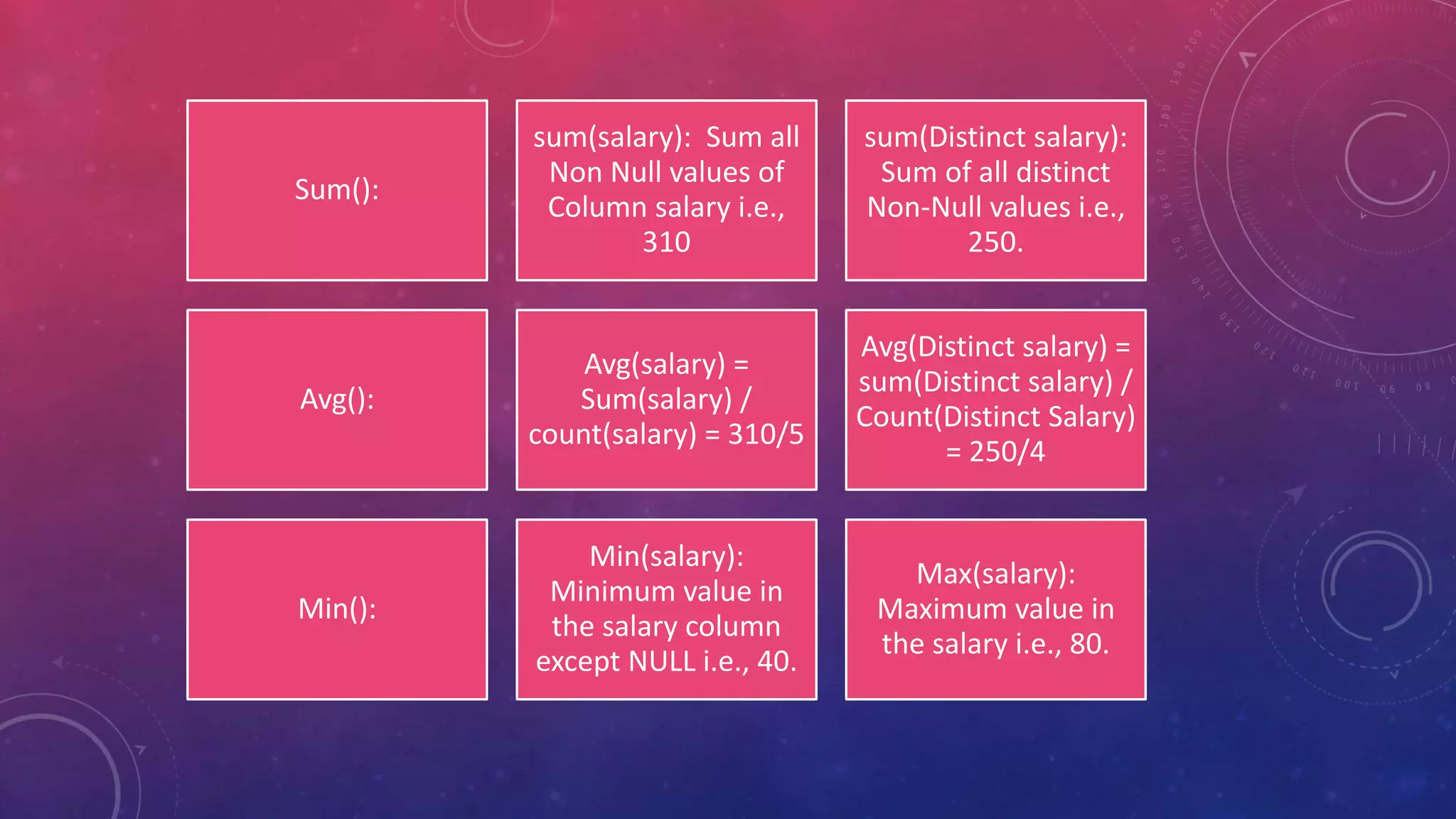
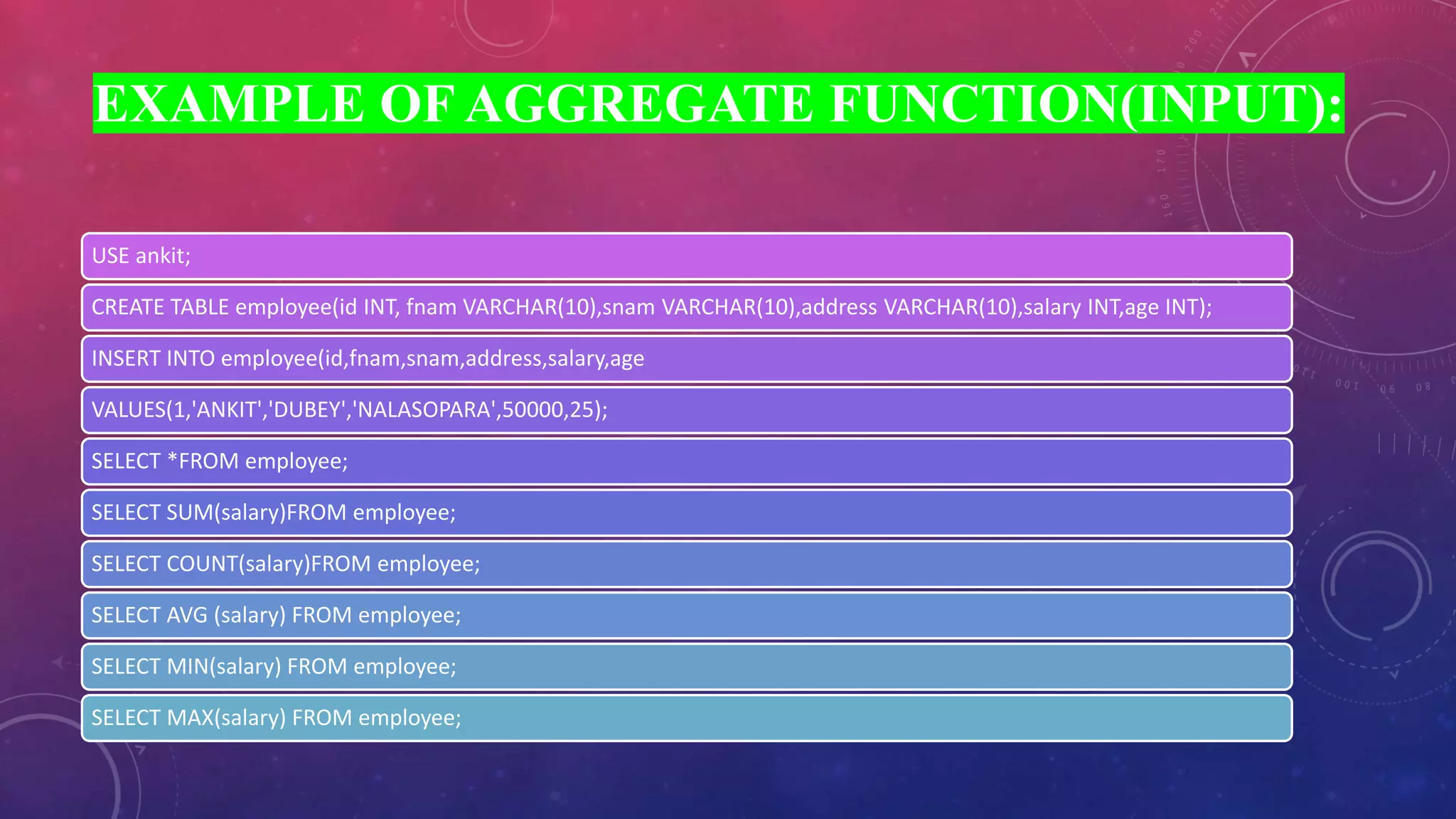
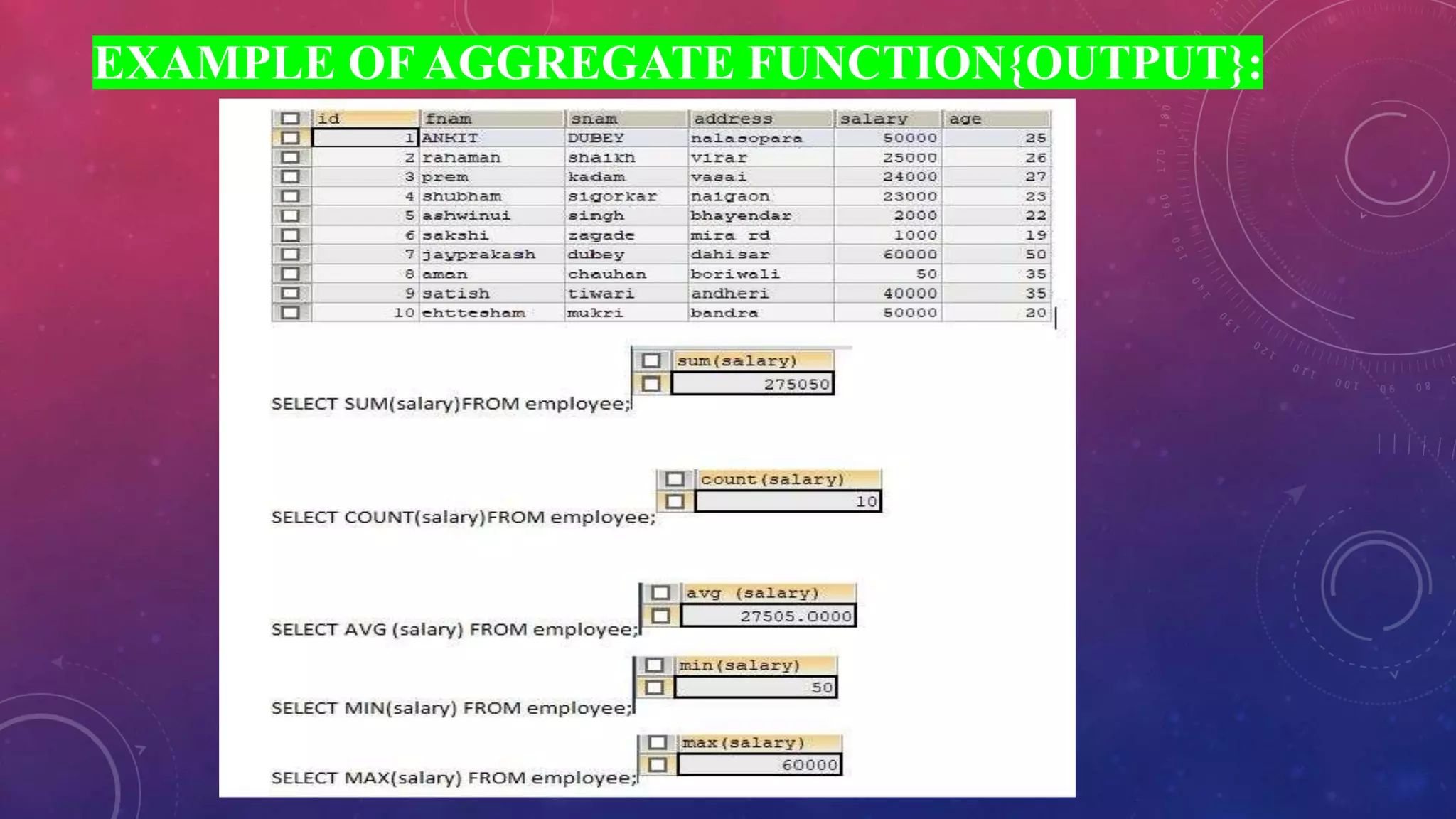
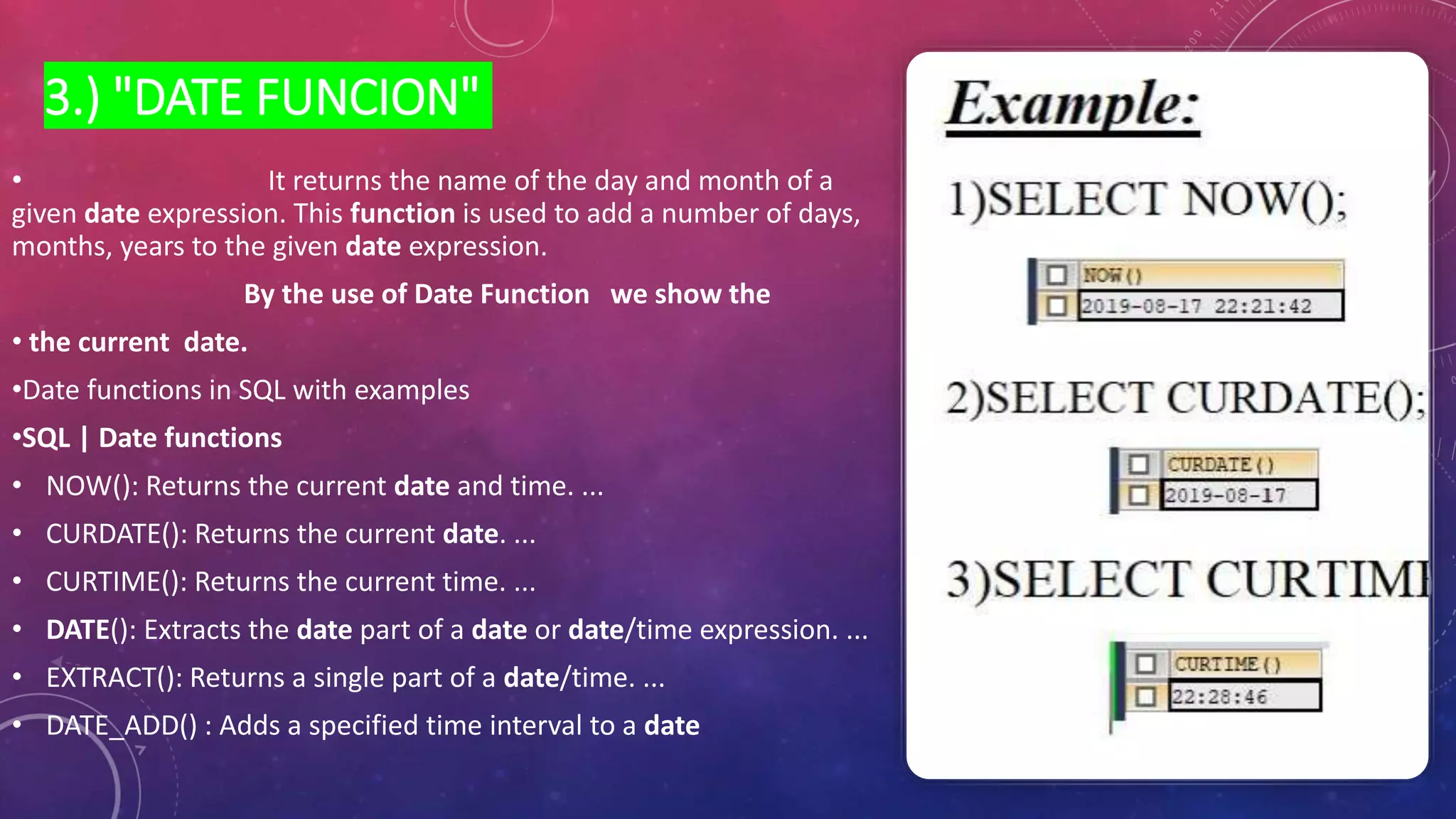
This document discusses different types of functions in SQL including string, aggregate, date, and time functions. String functions perform operations on strings and return output strings. Examples of string functions include ASCII, CHAR_LENGTH, and CONCAT. Aggregate functions operate on multiple rows and return a single value, such as COUNT, SUM, AVG, MIN, and MAX. Date functions return date part values and perform date calculations. Time functions extract and format time values.