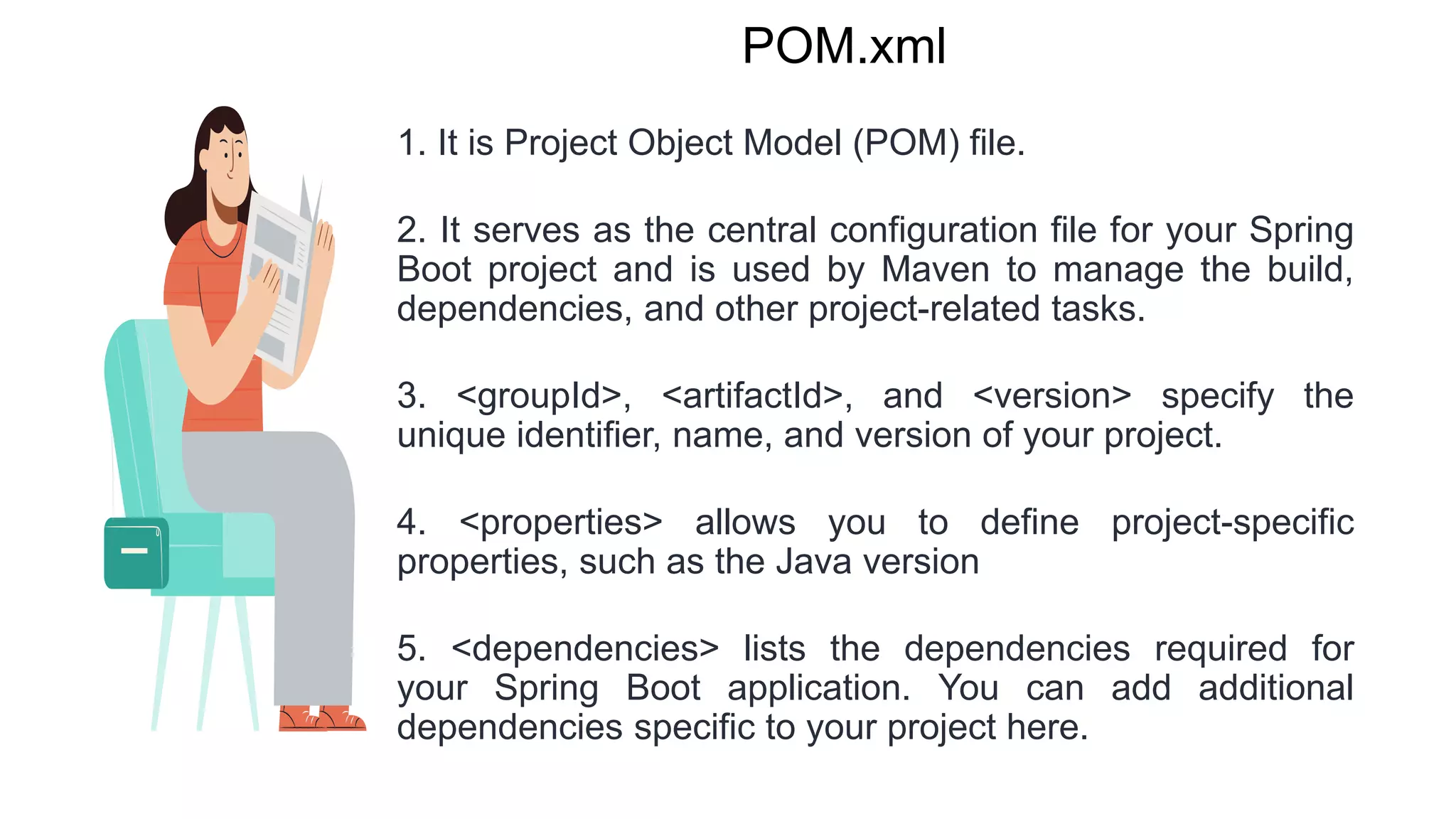
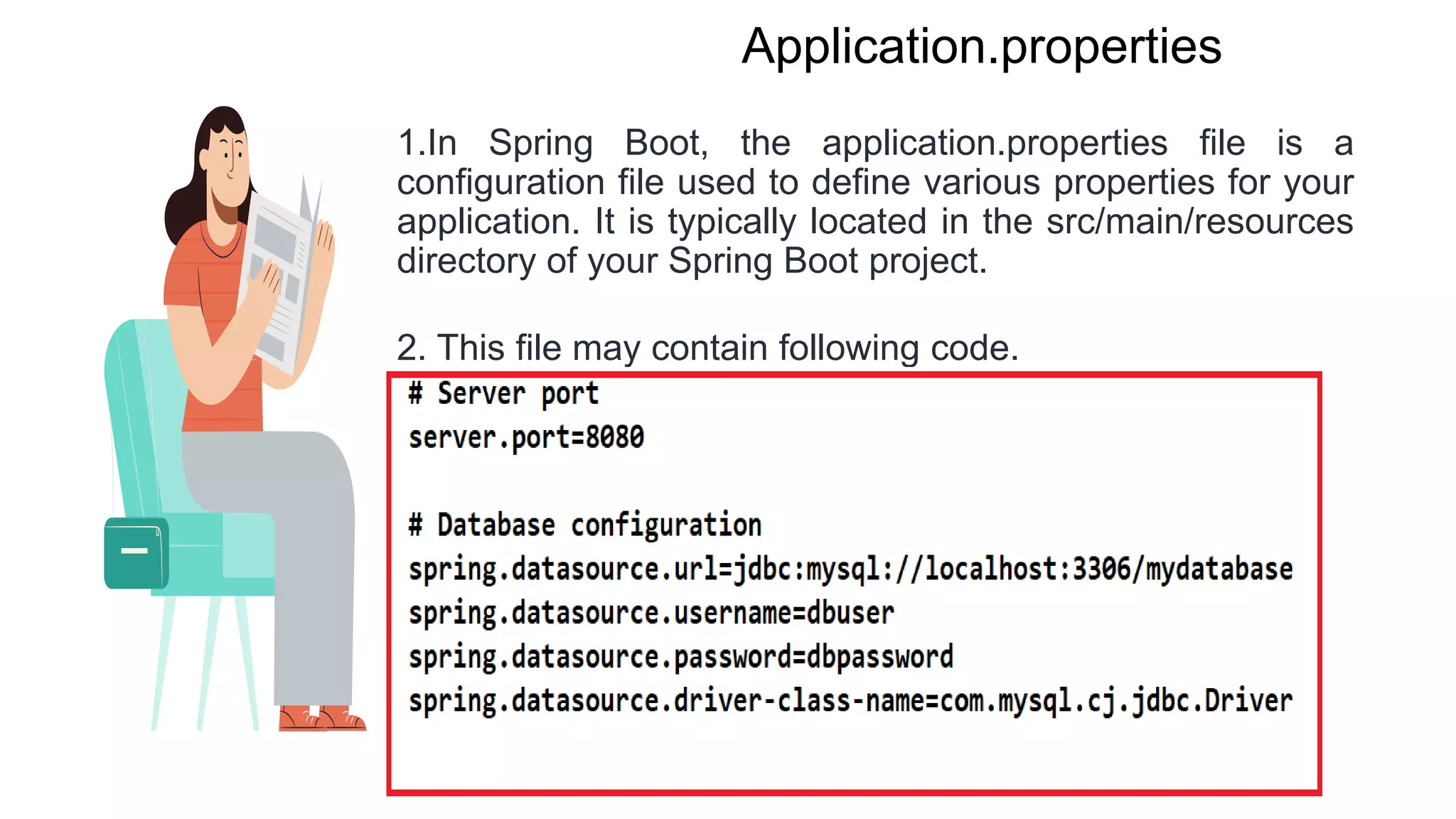
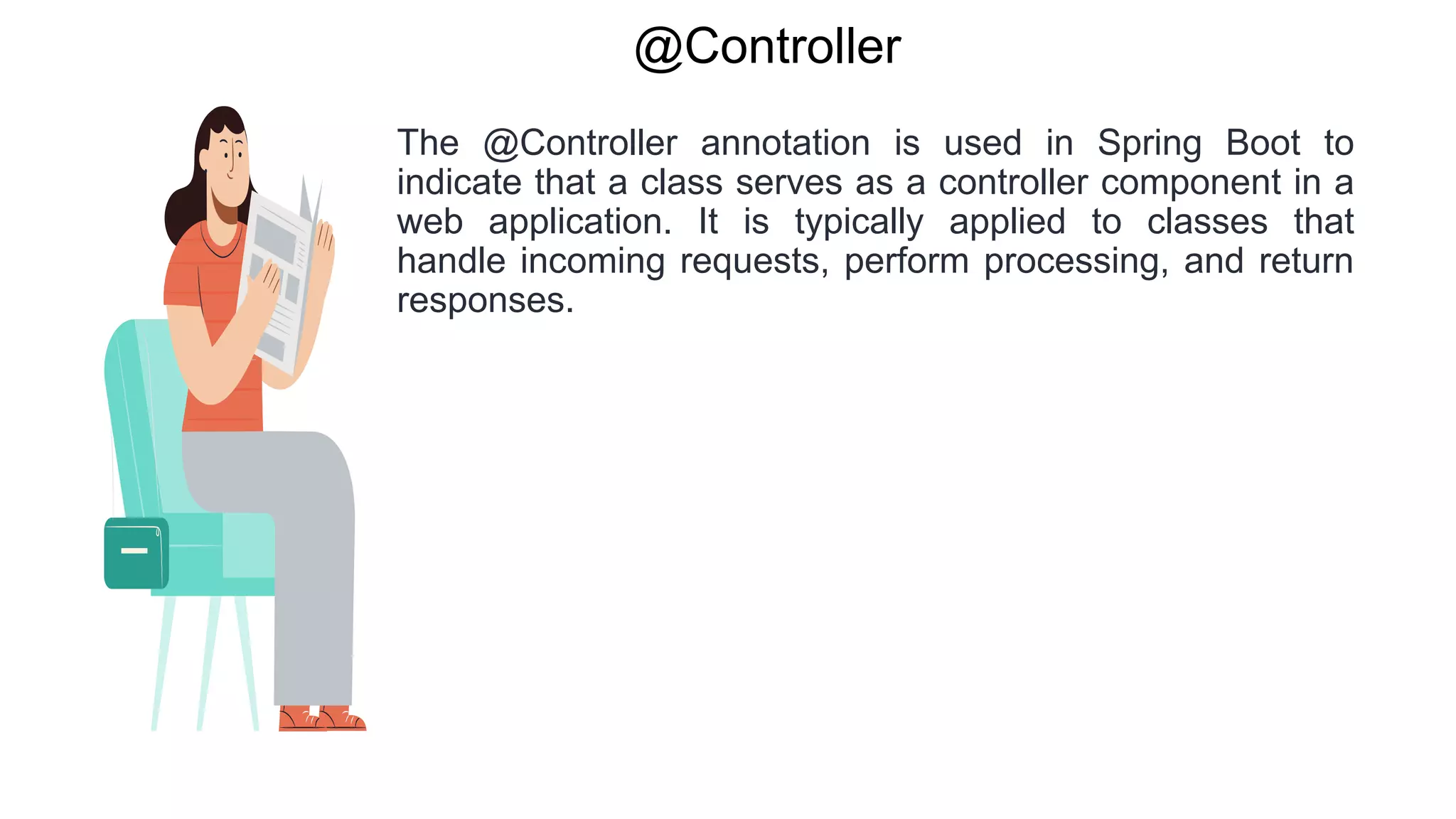
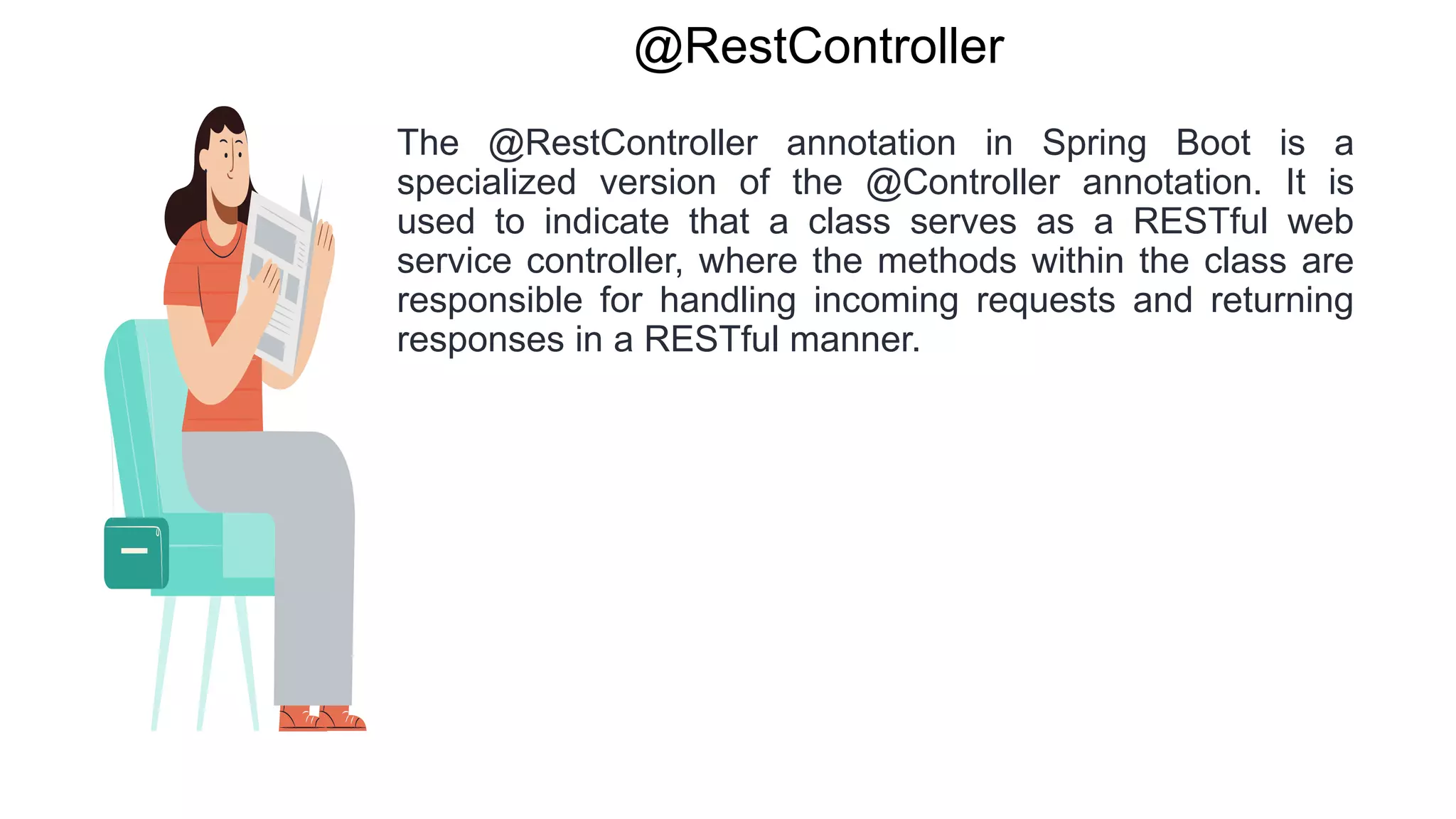
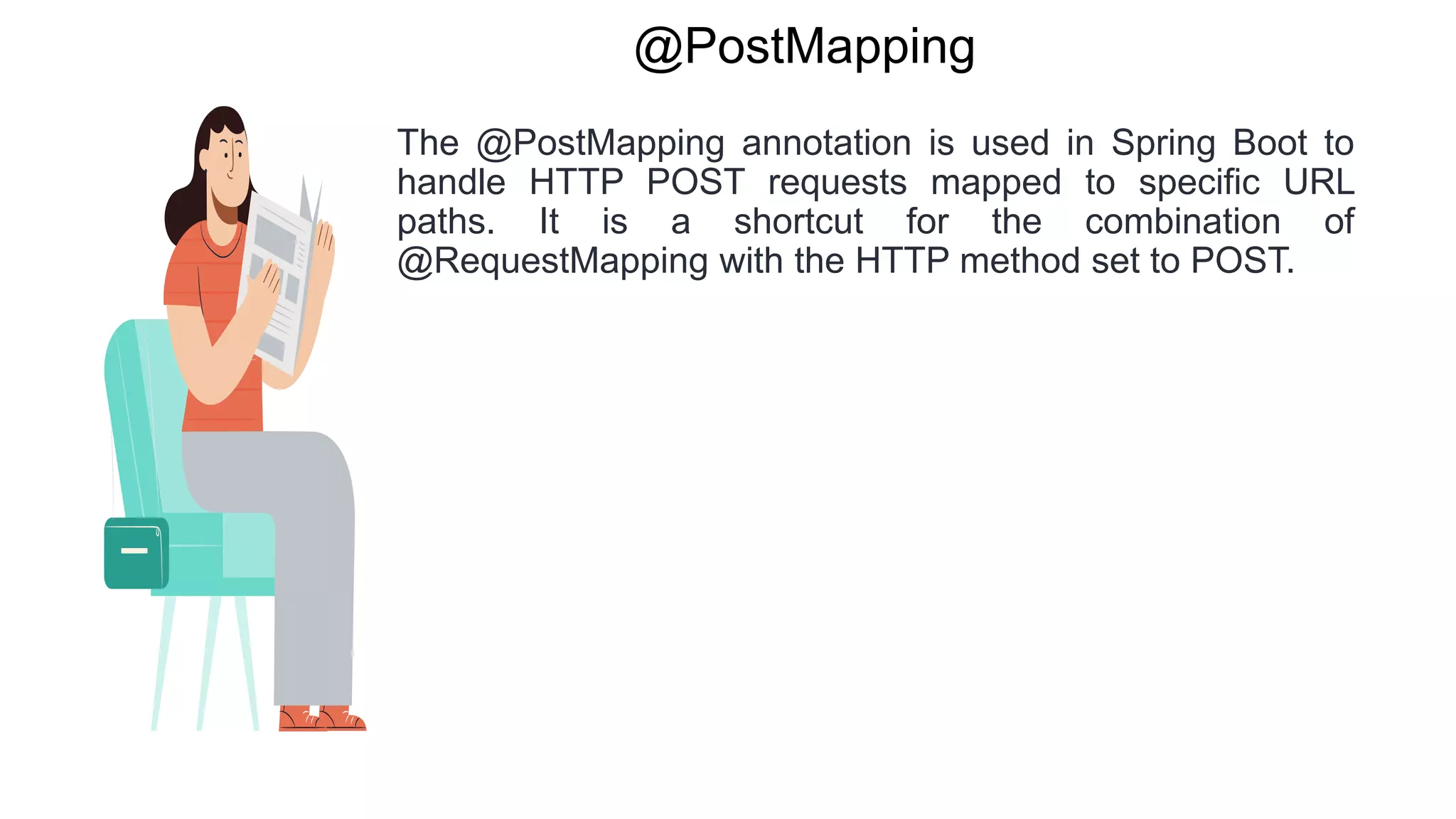
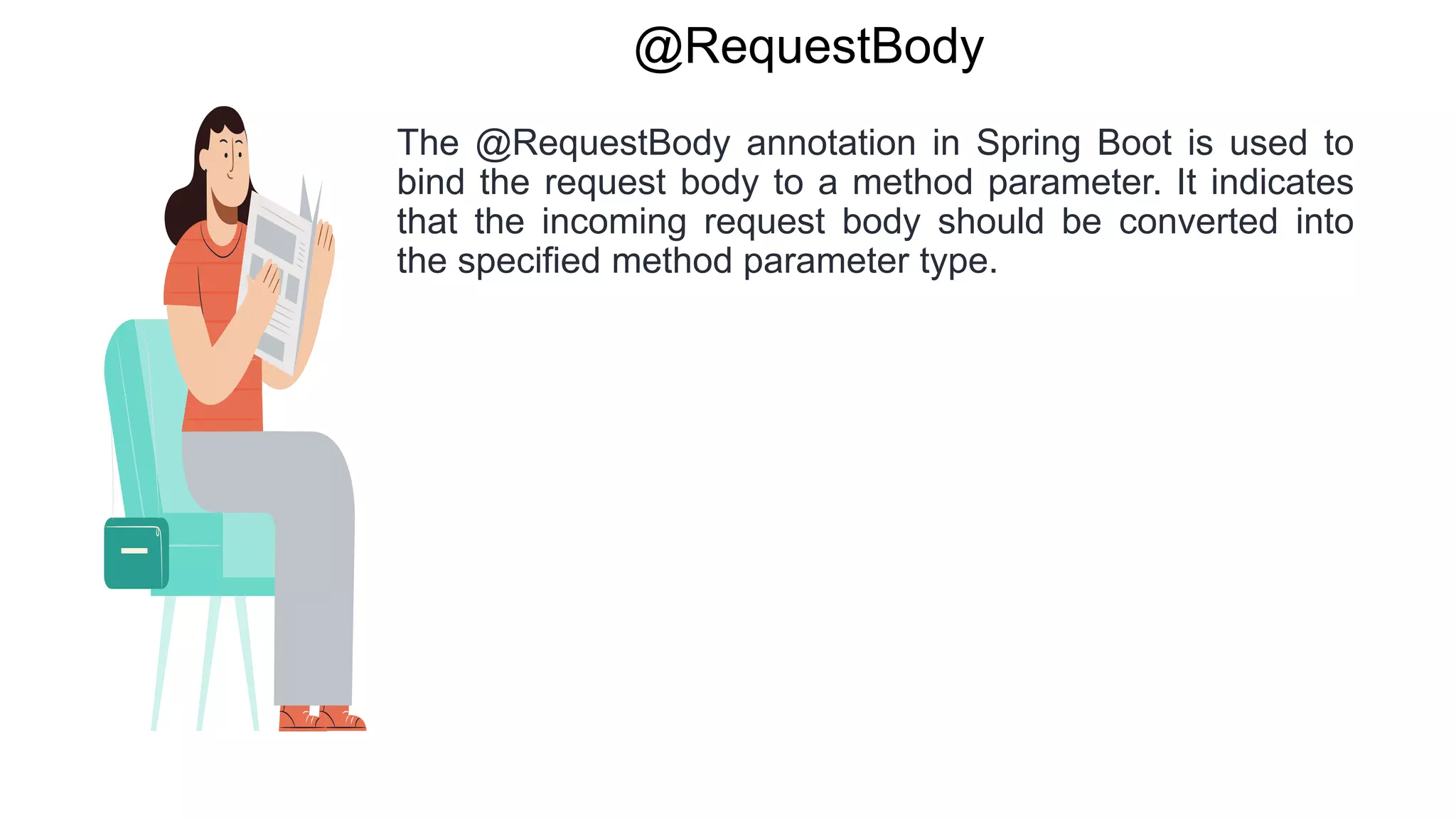
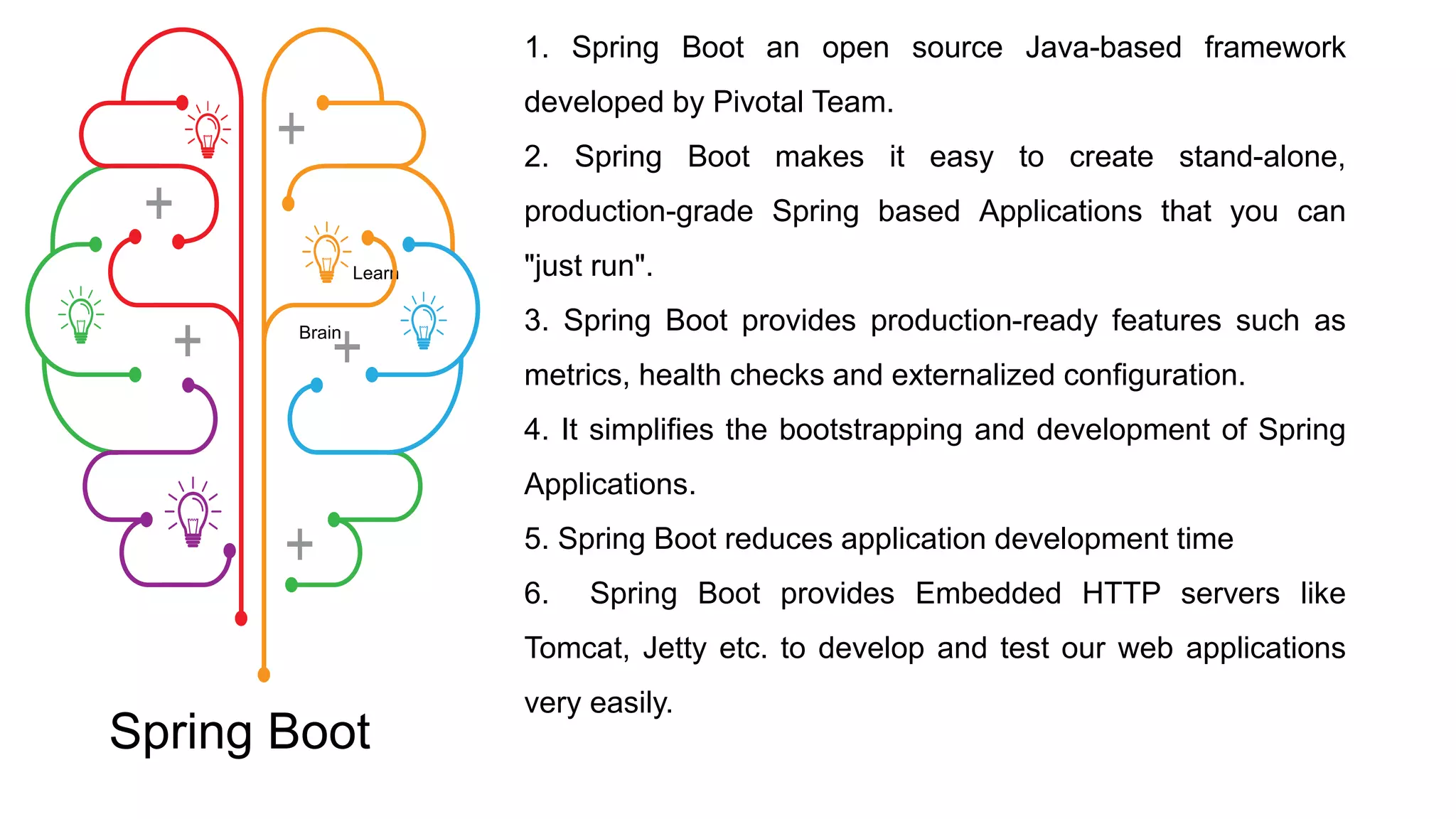
Spring Boot is an open source Java-based framework that makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring based Applications. It provides features such as embedded HTTP servers, externalized configuration, and metrics. Spring Boot uses auto-configuration and starters to minimize configuration work. The main intention of Spring Boot starters is to combine common dependencies into single dependencies to simplify dependency management. Spring Boot also provides auto-configuration to avoid explicit configuration of components like views and ViewResolvers.





![Ways to create Spring Boot Project
1. Using Simple MAVEN project in Eclipse IDE.
2. STS IDE
3. Spring Boot Initializer
4. Spring Boot CLI[Command Line Interface]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spring1-230613010452-898b6203/75/Spring-Boot-8-2048.jpg)