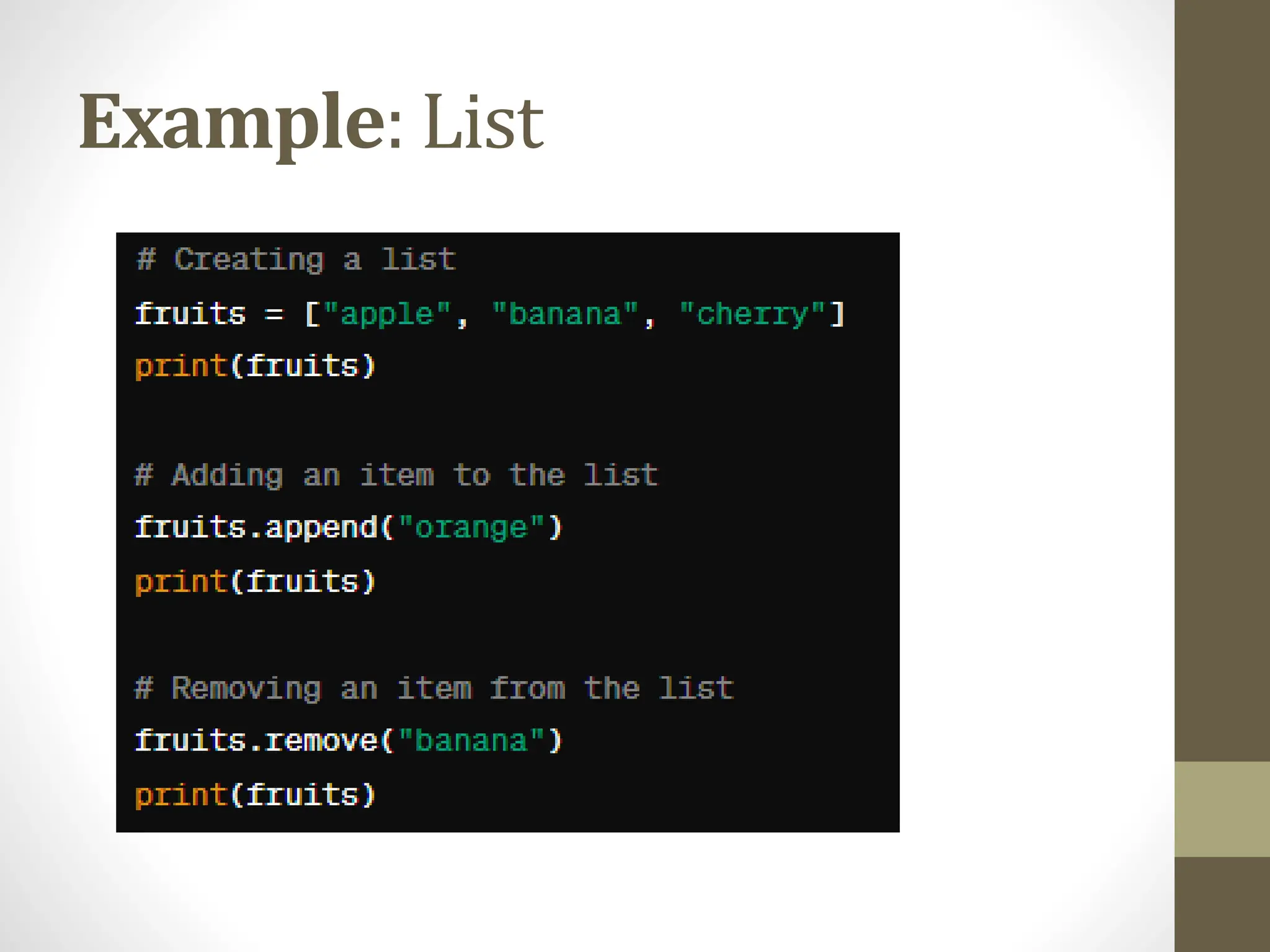
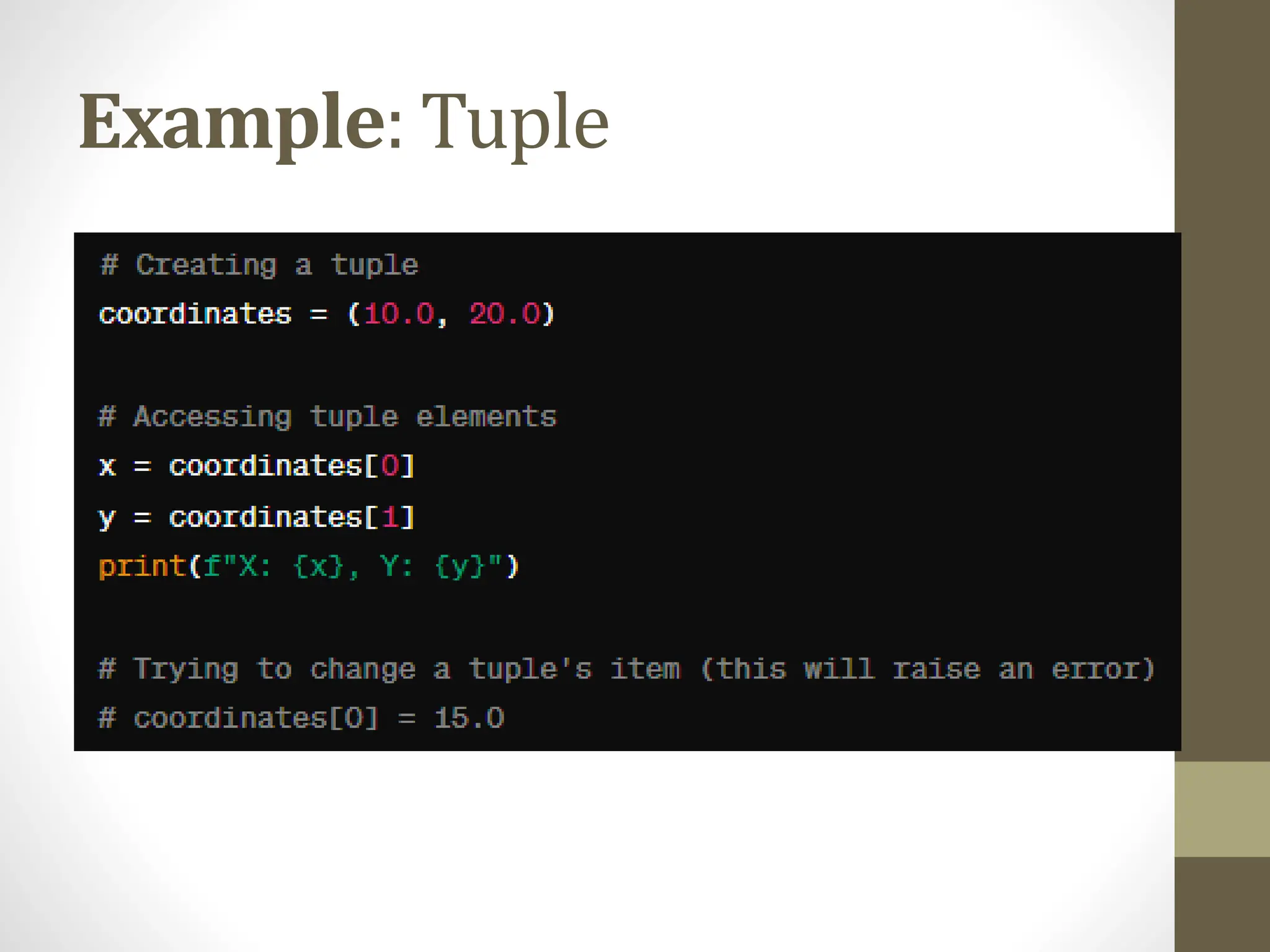
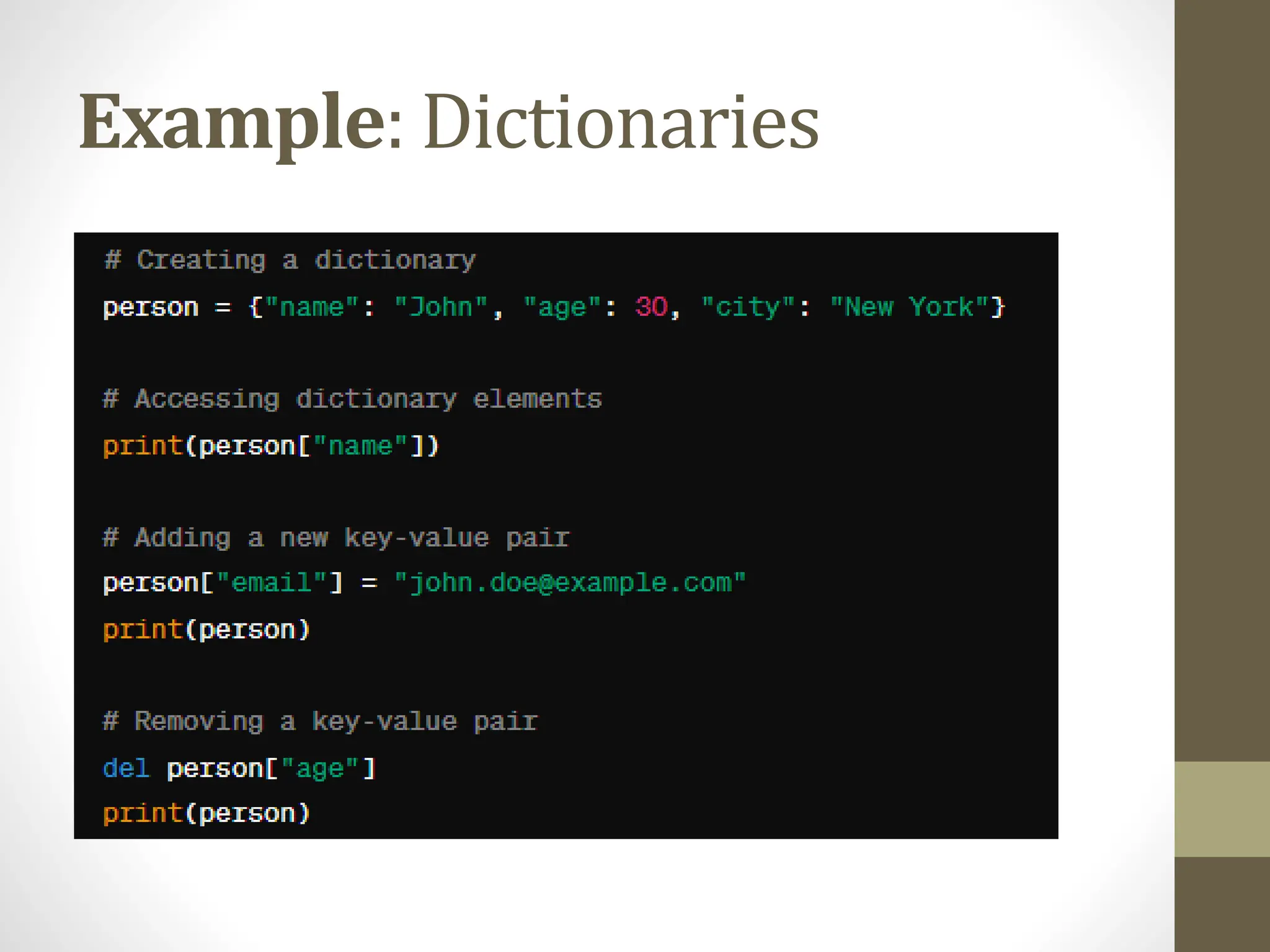
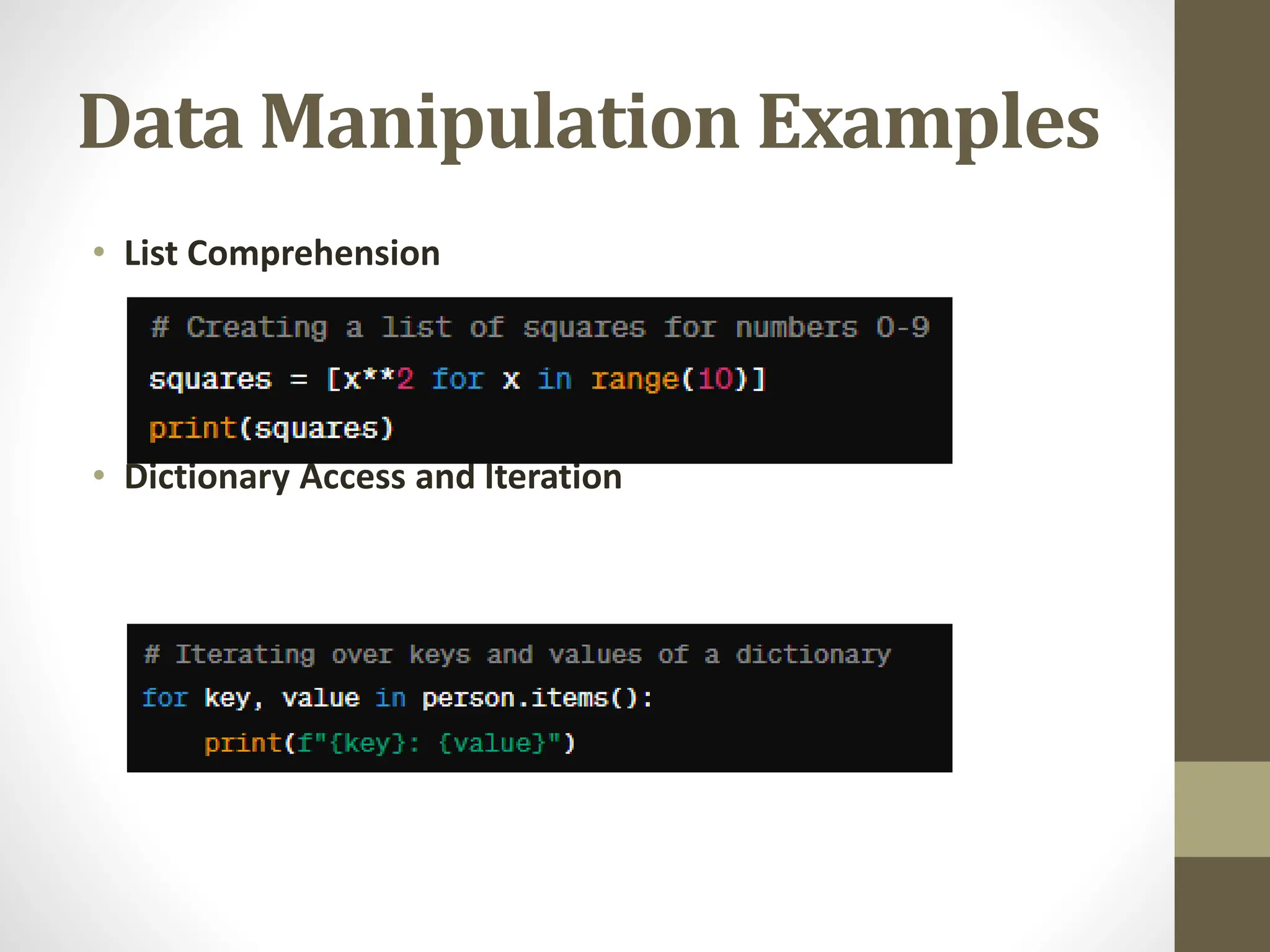
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Python for software development, covering its introduction, data structures, libraries, object-oriented programming, error handling, and best practices. It highlights Python's ease of use, versatility across various domains, and the importance of testing and documentation. The conclusion encourages further exploration of Python's applications in web development, data science, and machine learning.