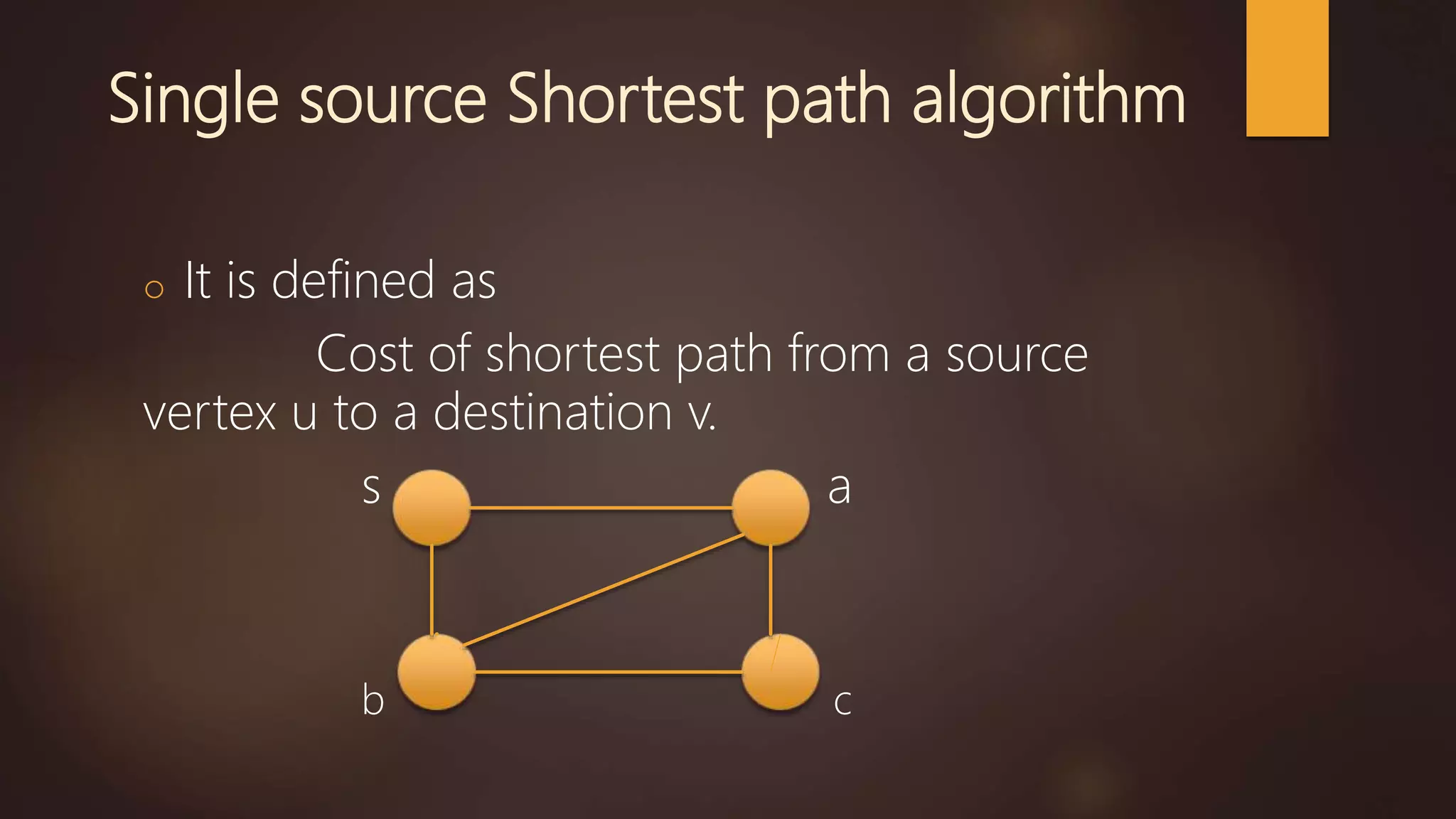
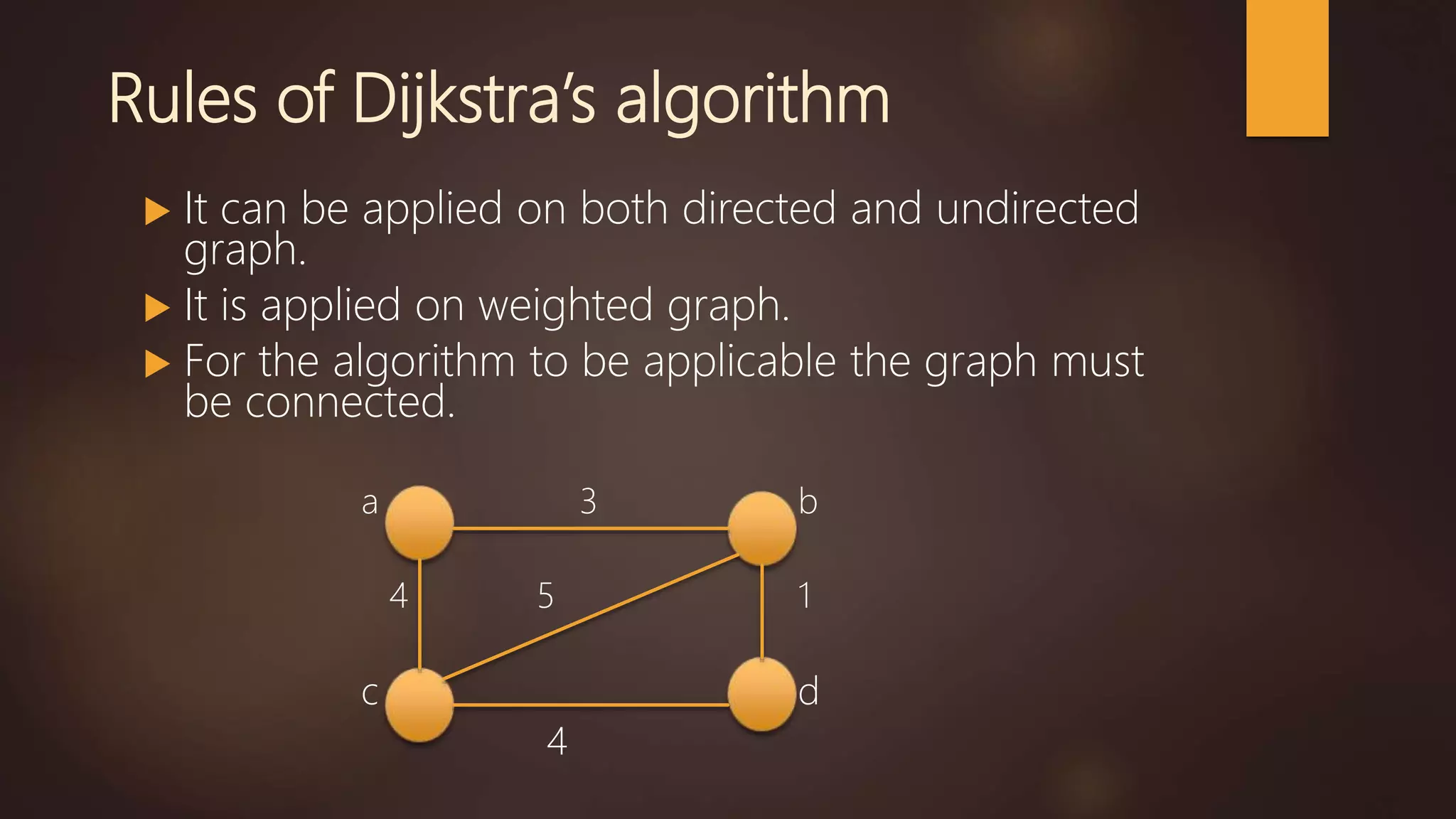
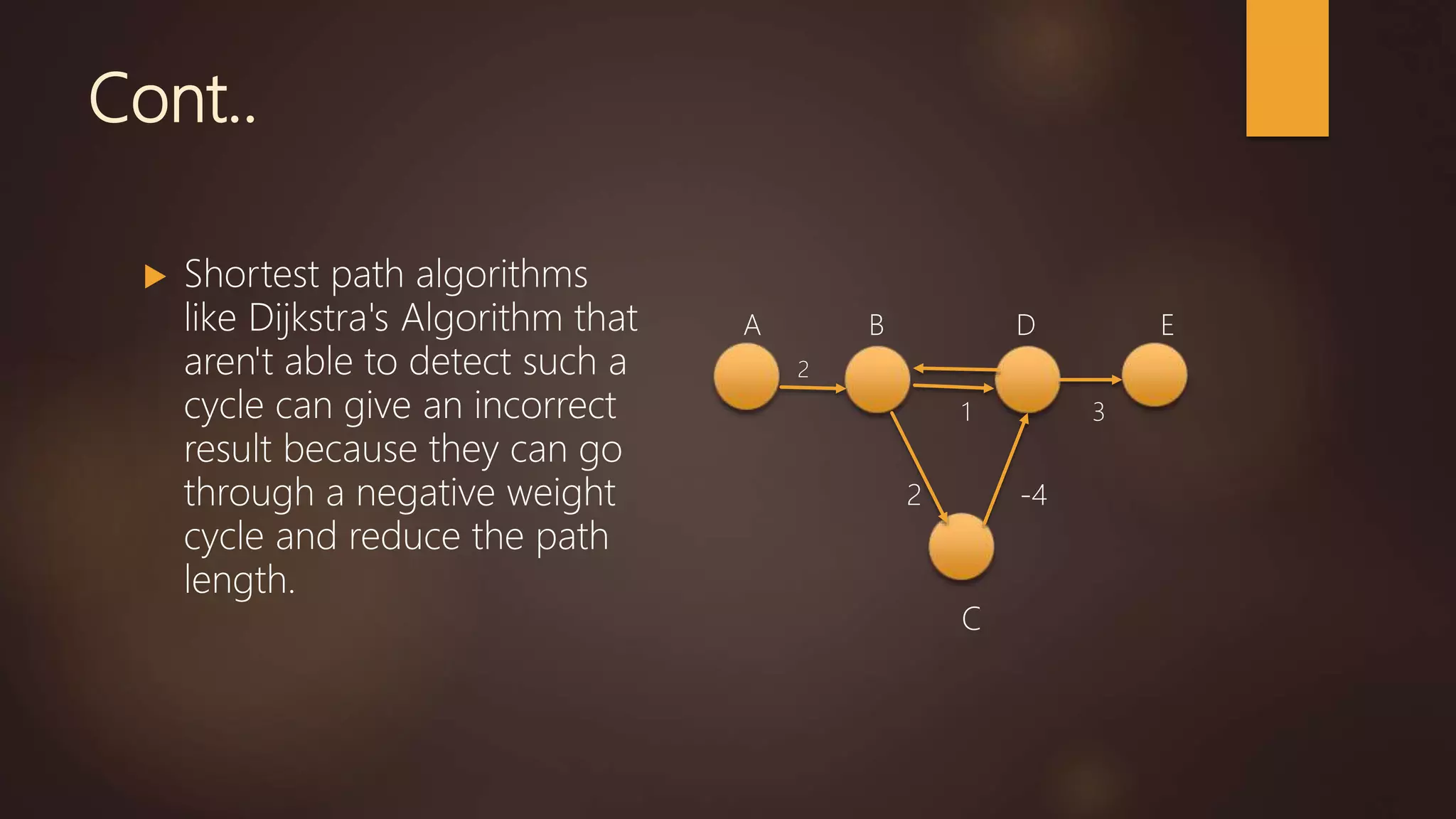
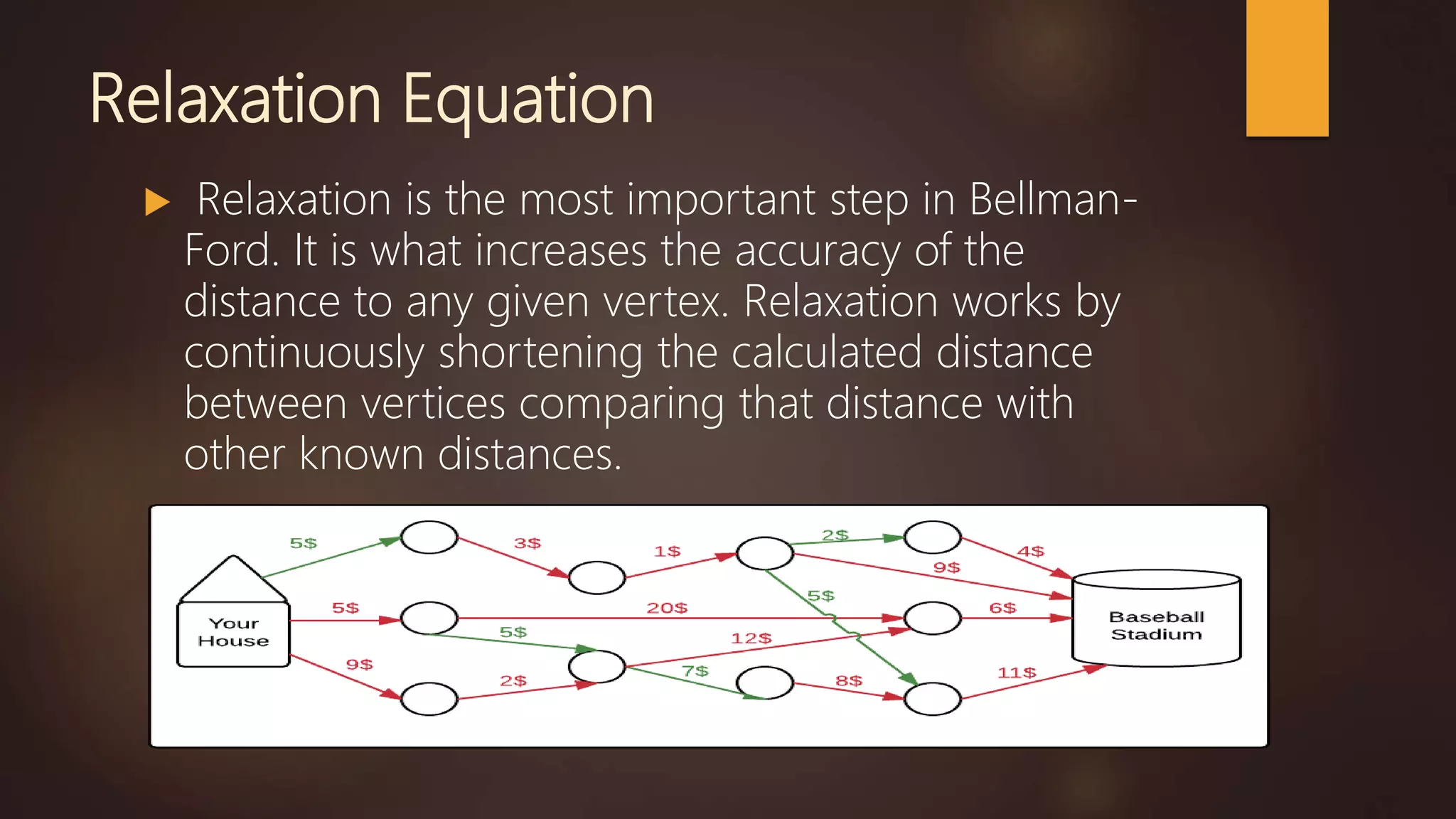
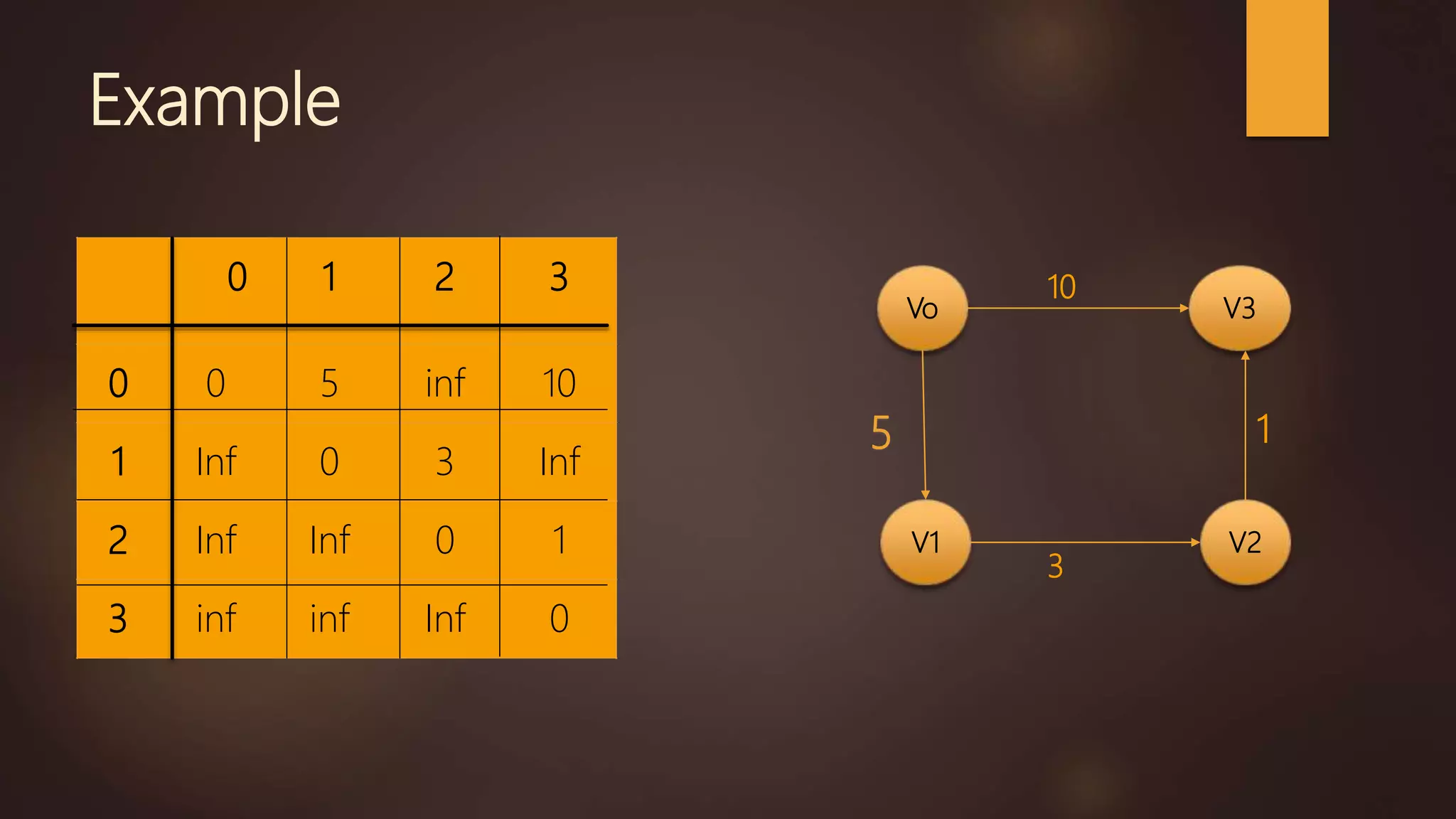
The document discusses several shortest path algorithms for graphs, including Dijkstra's algorithm, Bellman-Ford algorithm, and Floyd-Warshall algorithm. Dijkstra's algorithm finds the shortest path from a single source node to all other nodes in a graph with non-negative edge weights. Bellman-Ford can handle graphs with negative edge weights but is slower. Floyd-Warshall can find shortest paths in a graph between all pairs of nodes.