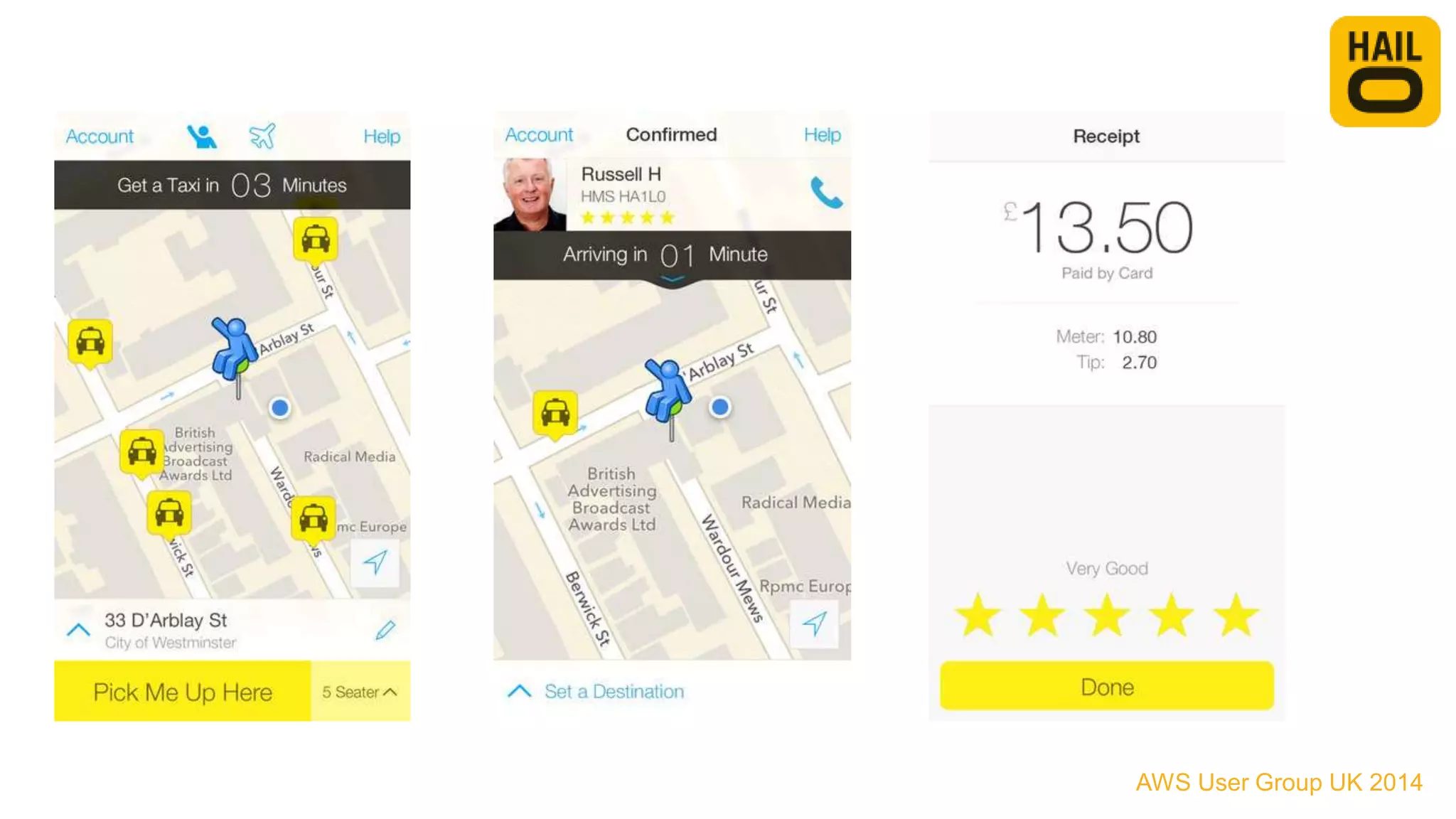
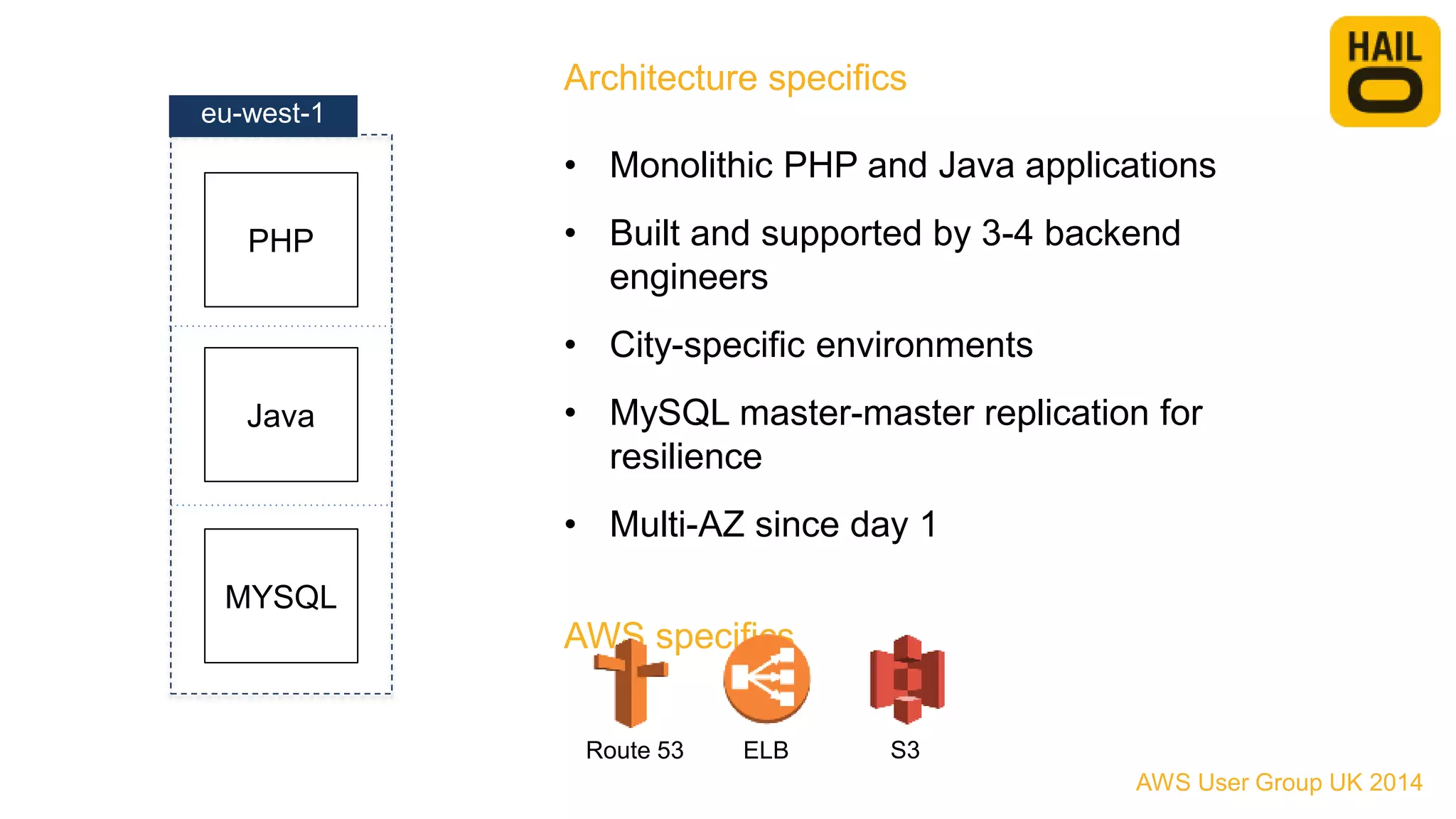
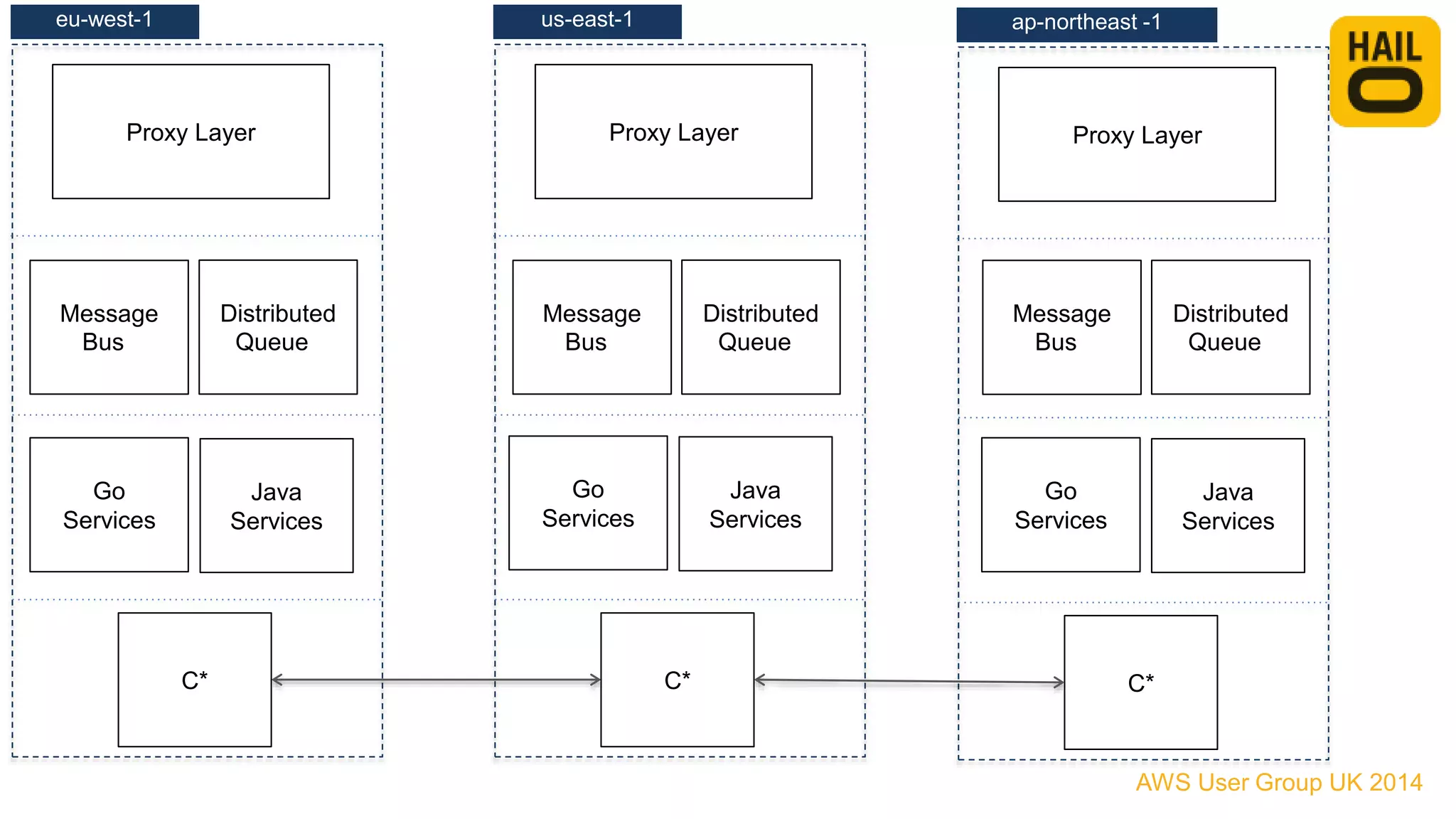
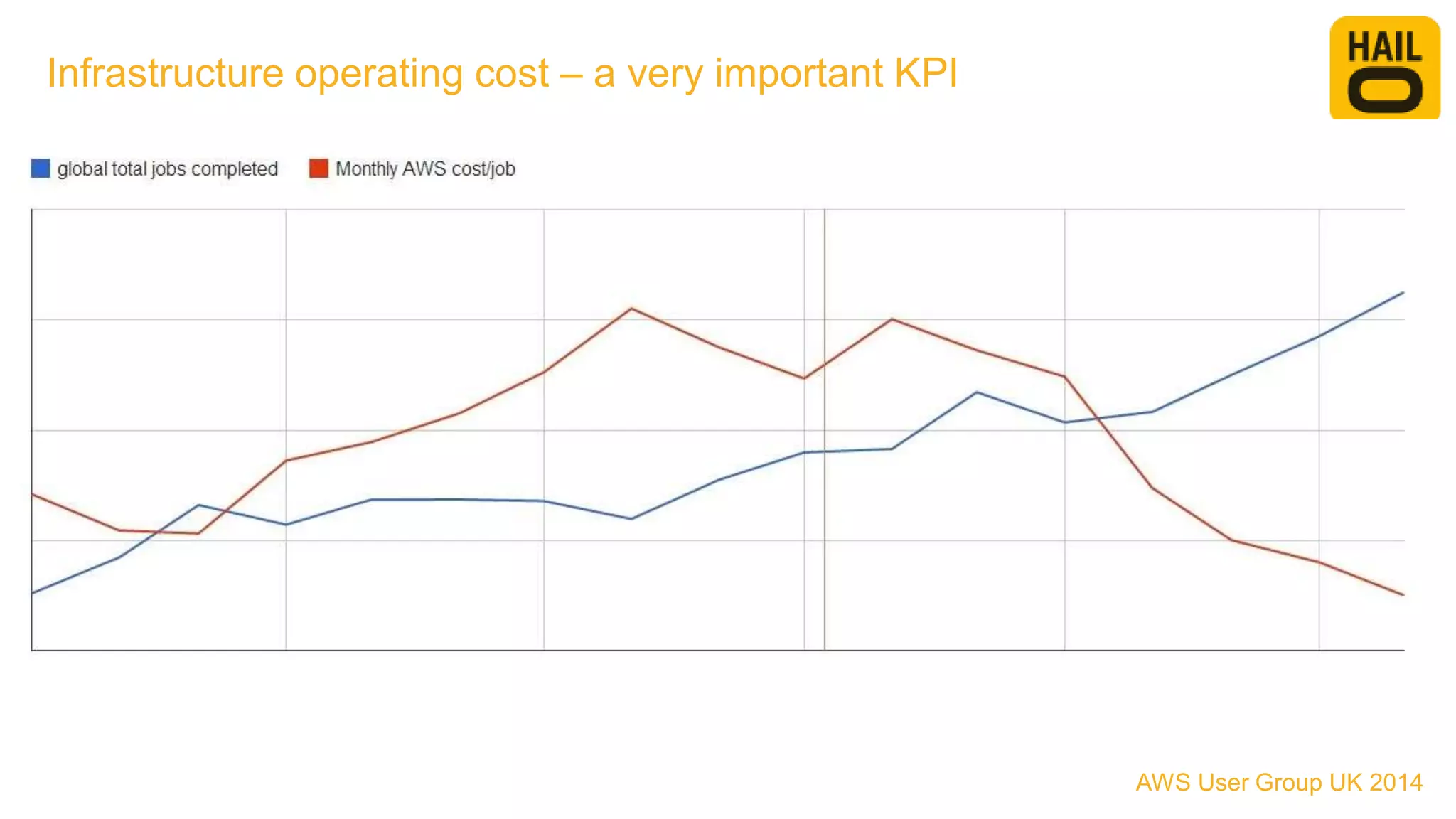
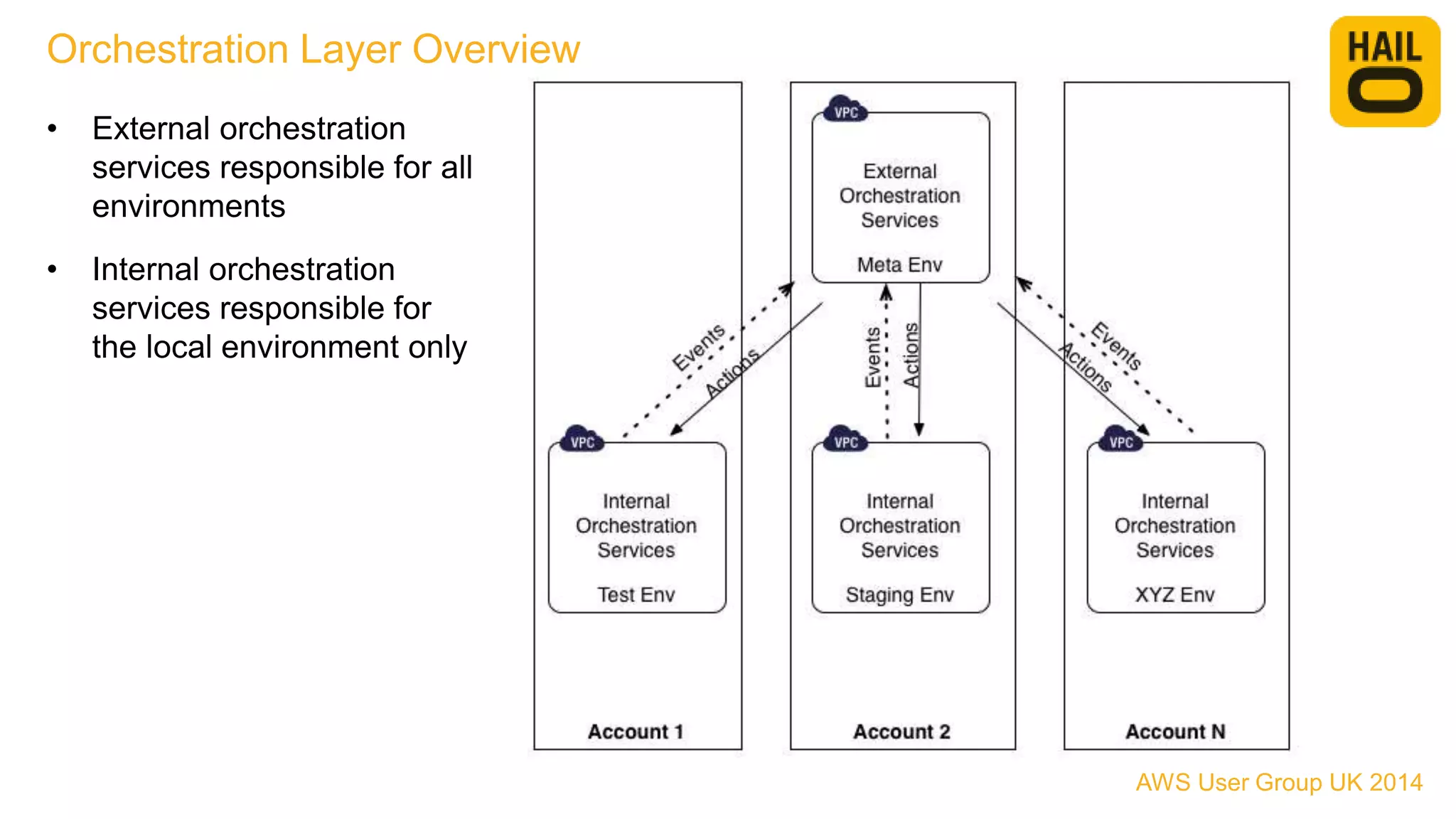
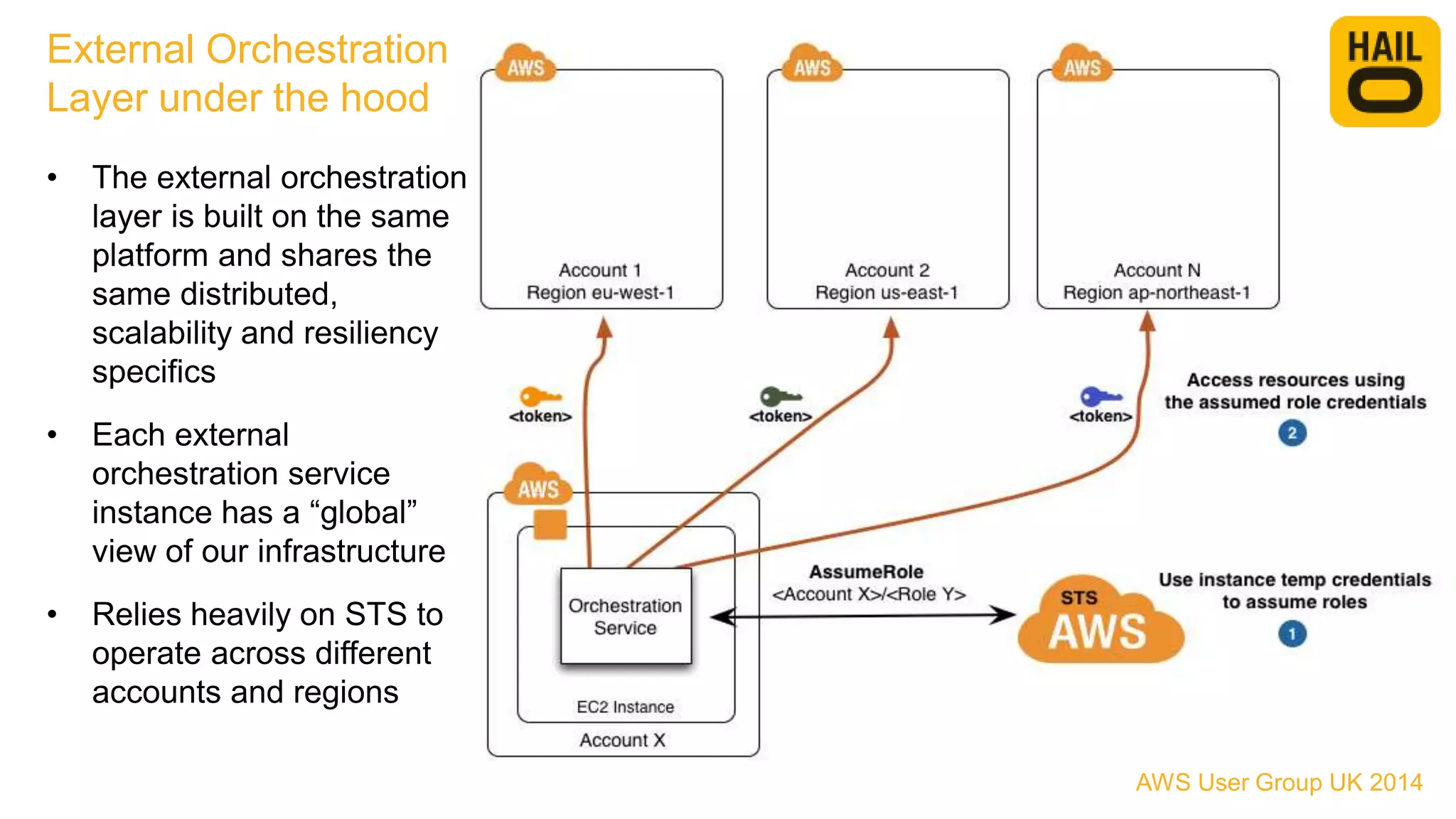
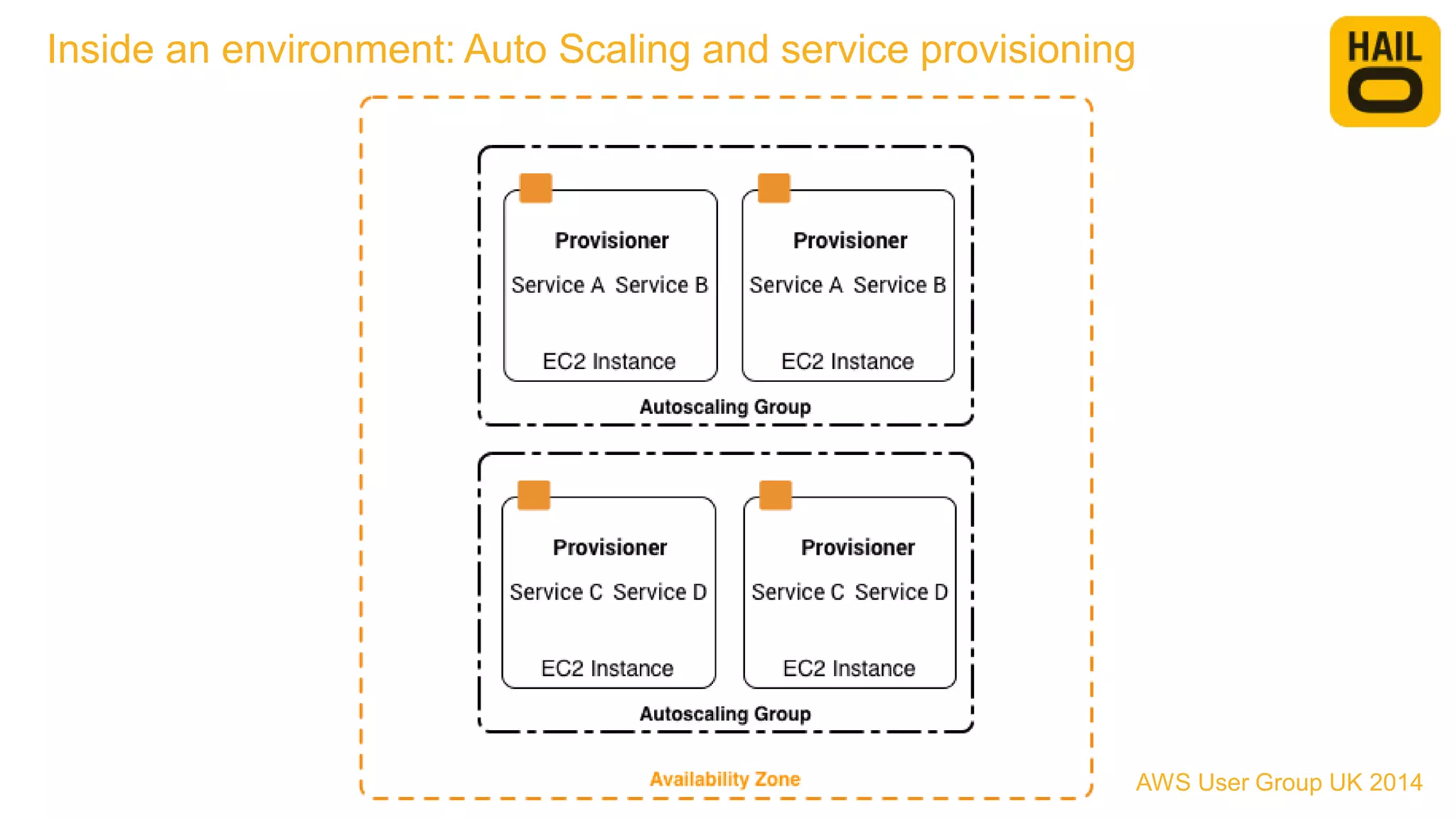
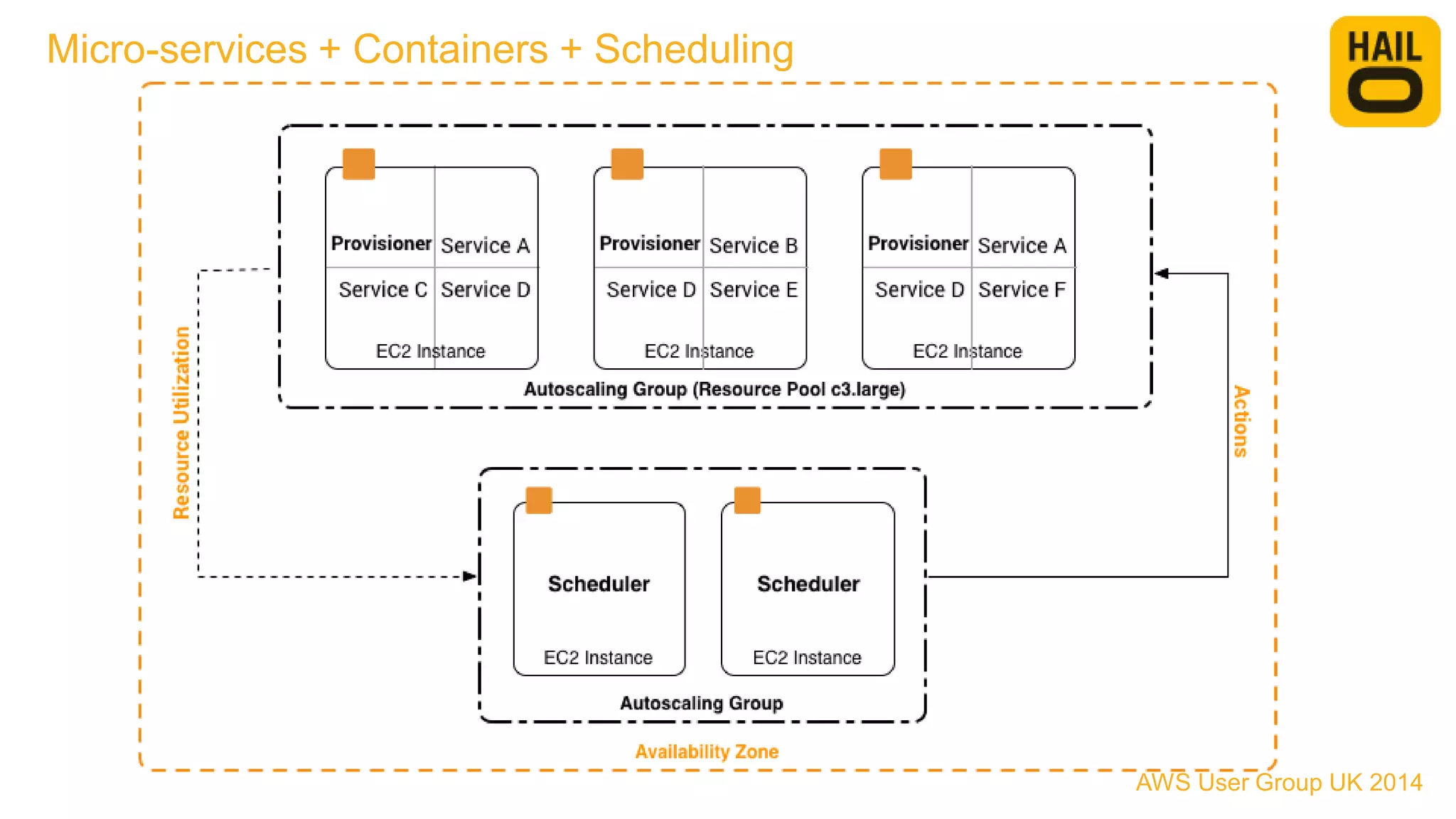
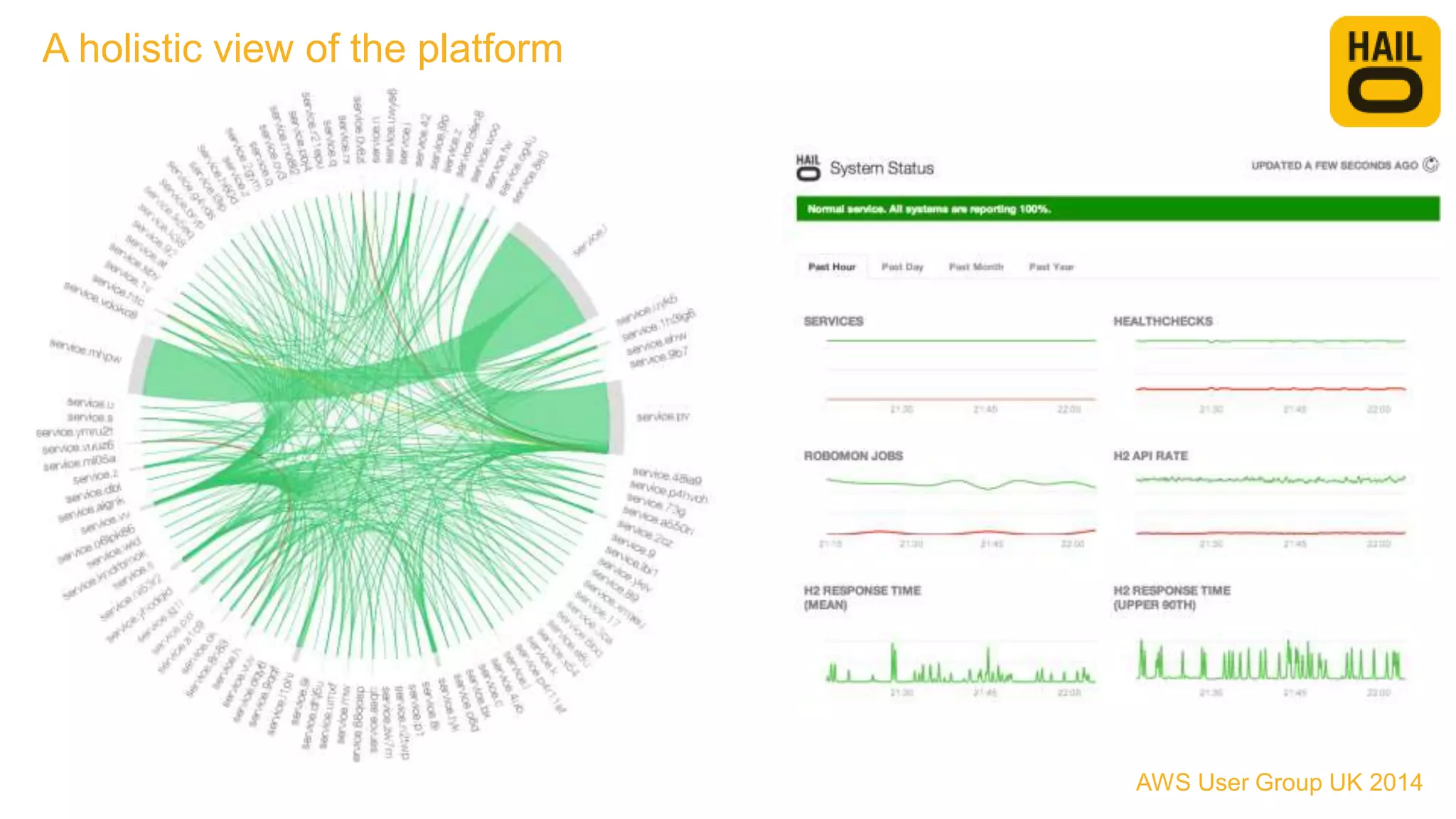
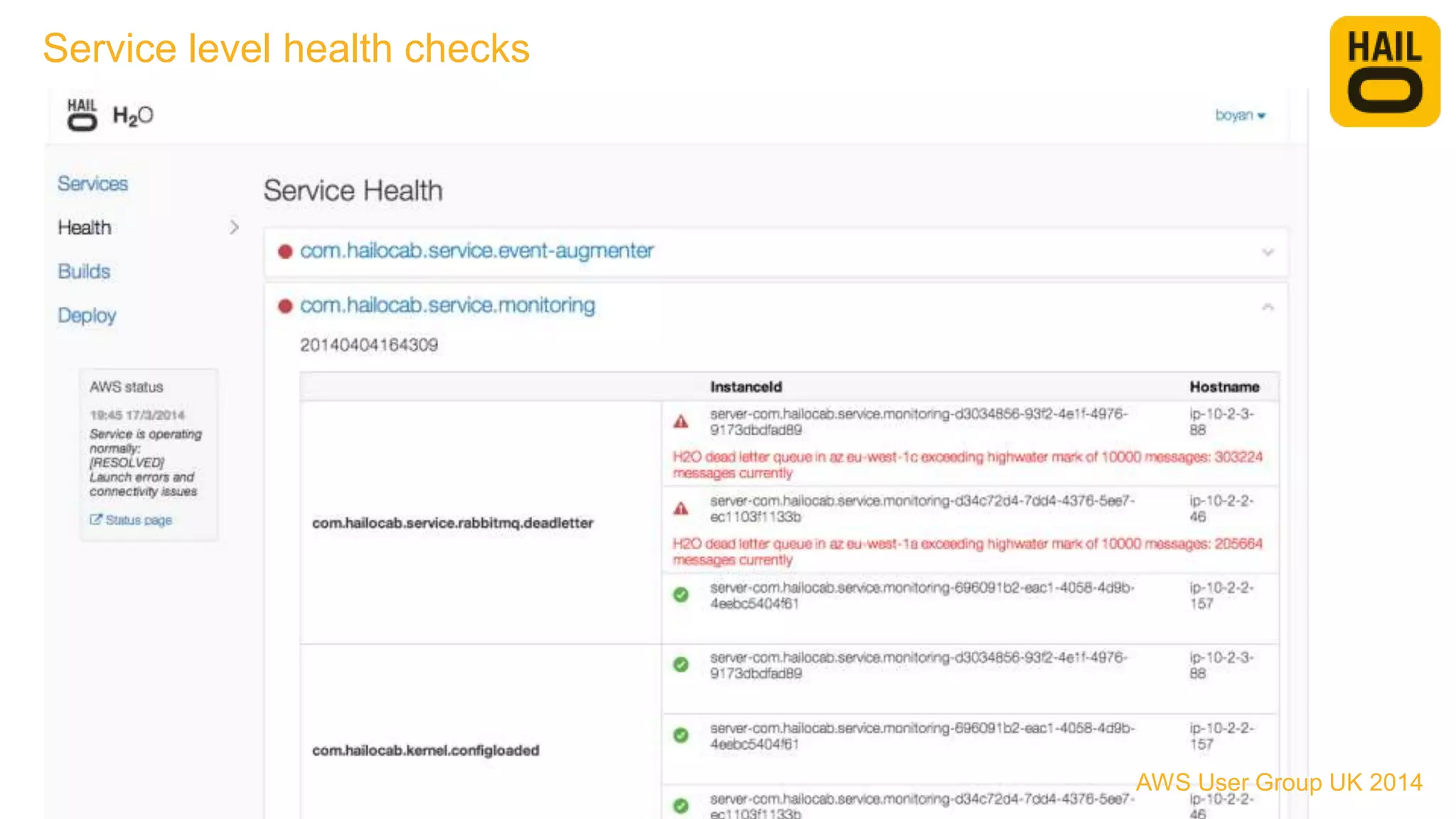
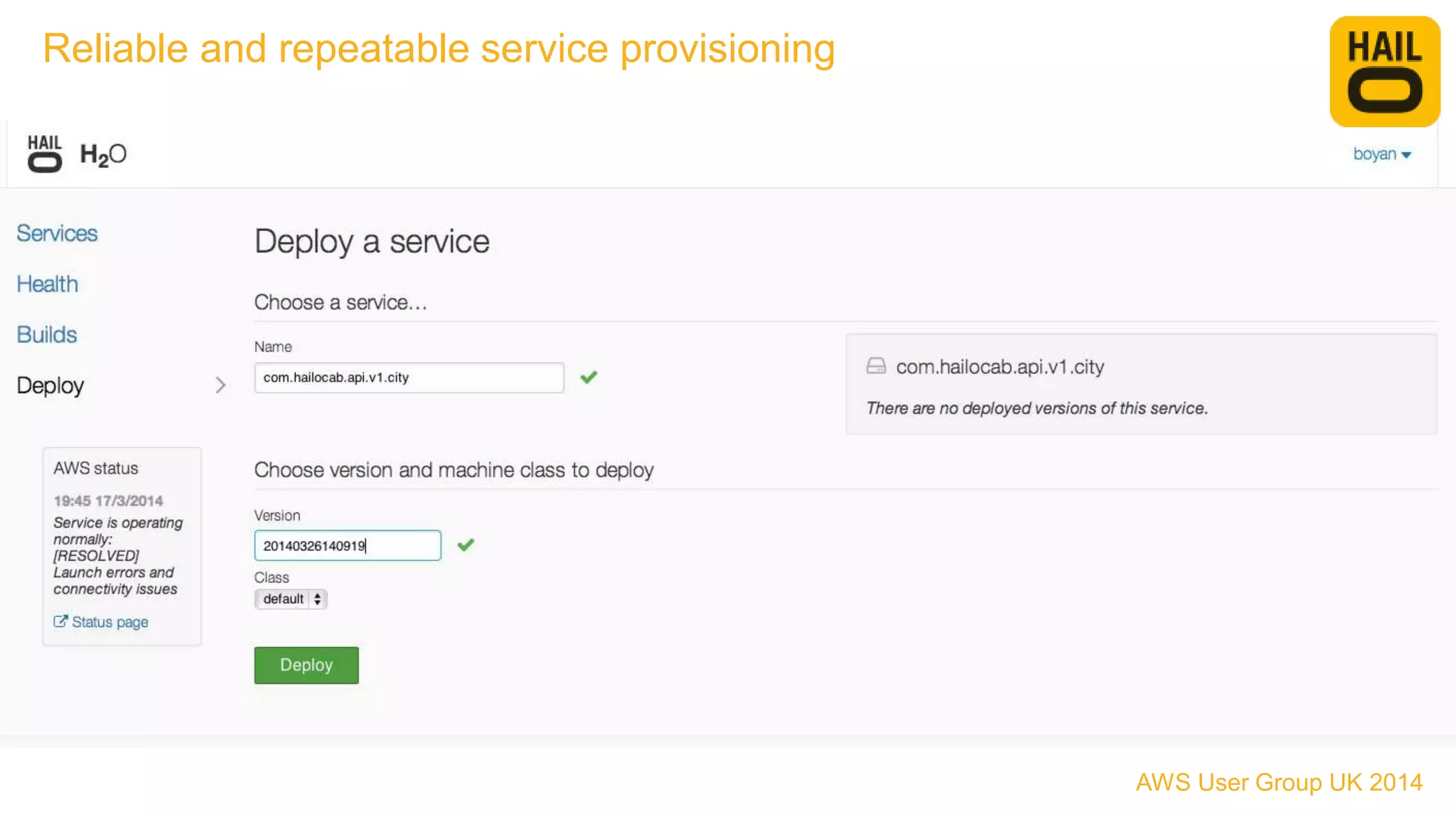
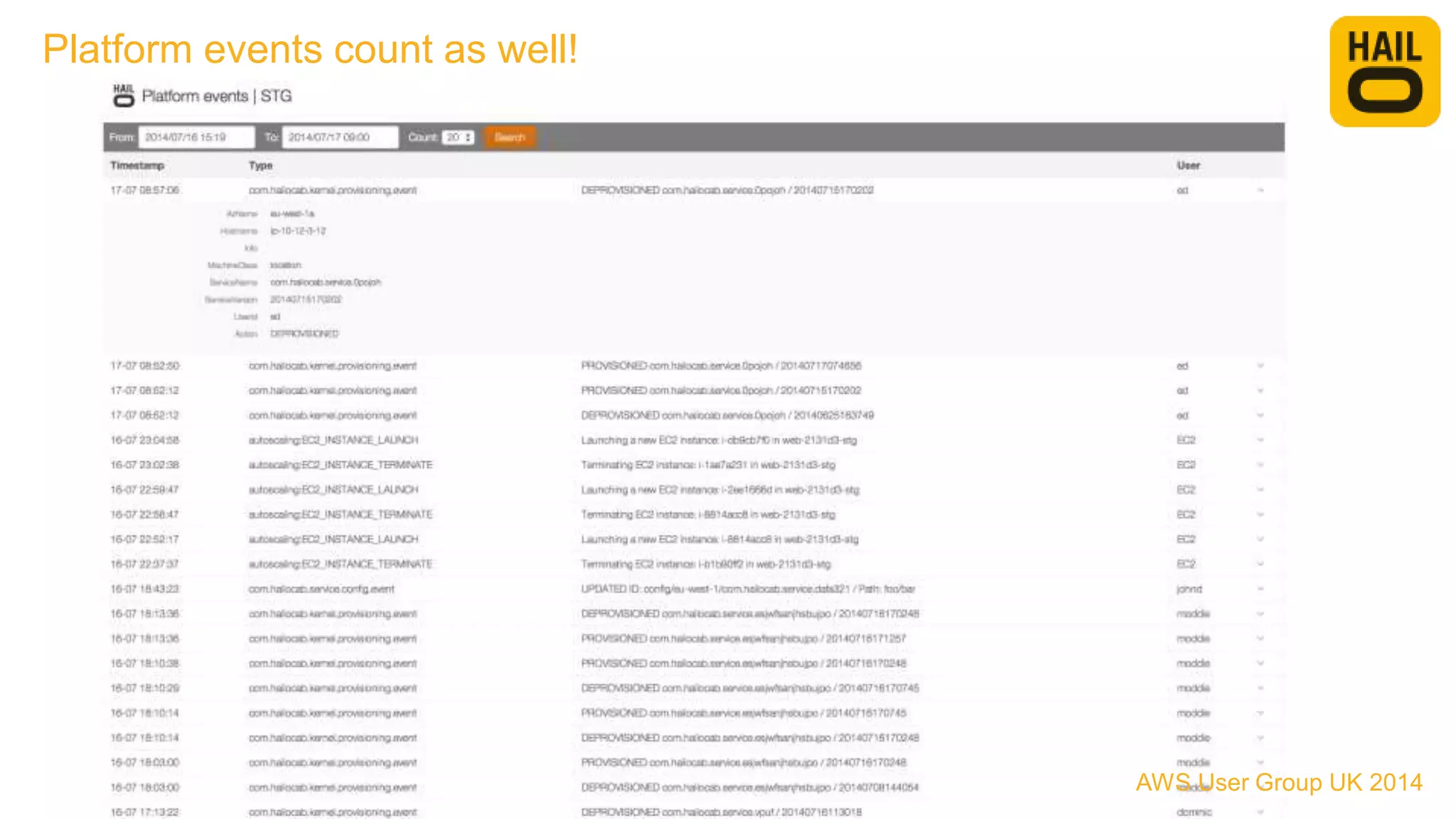
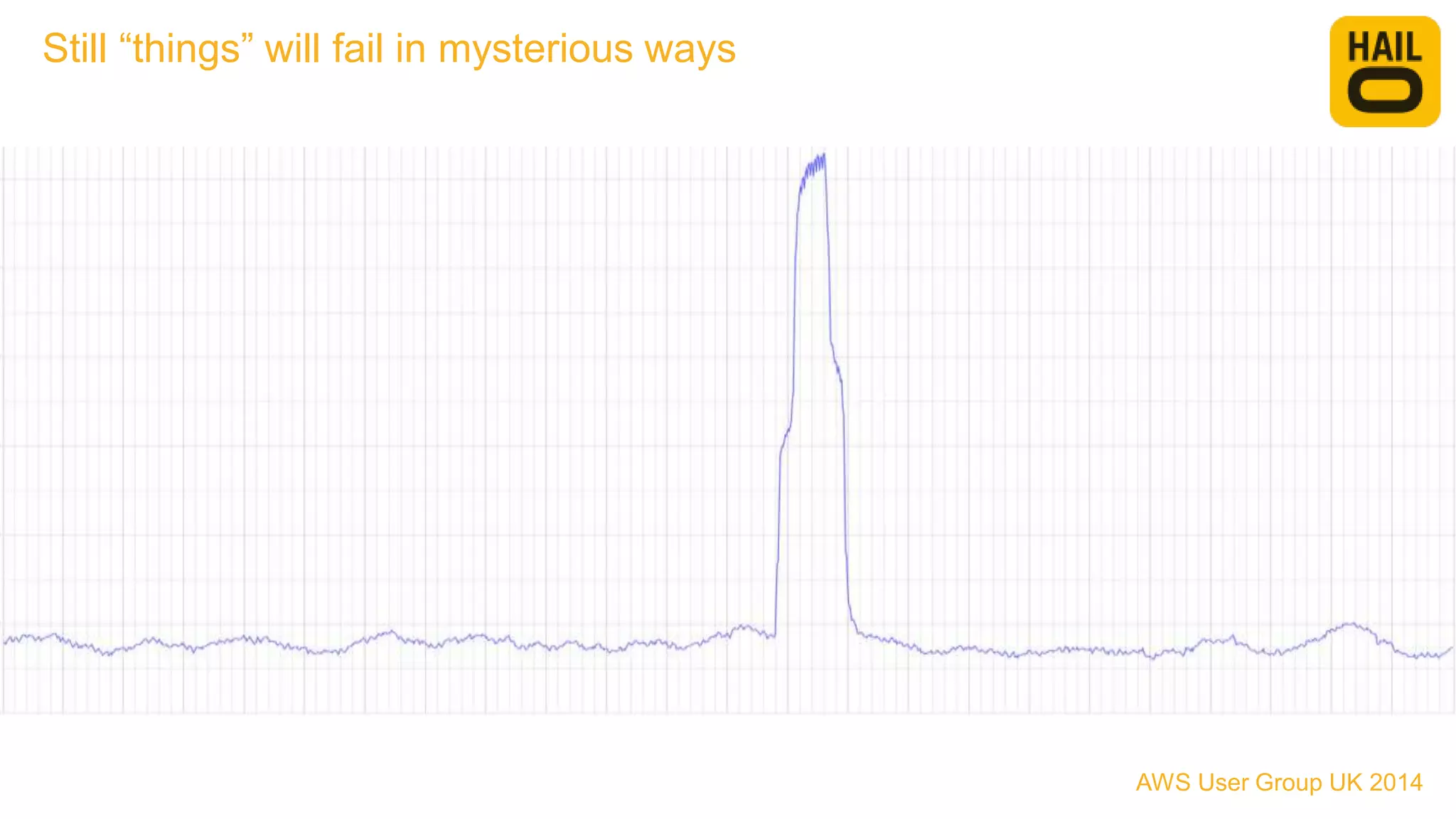
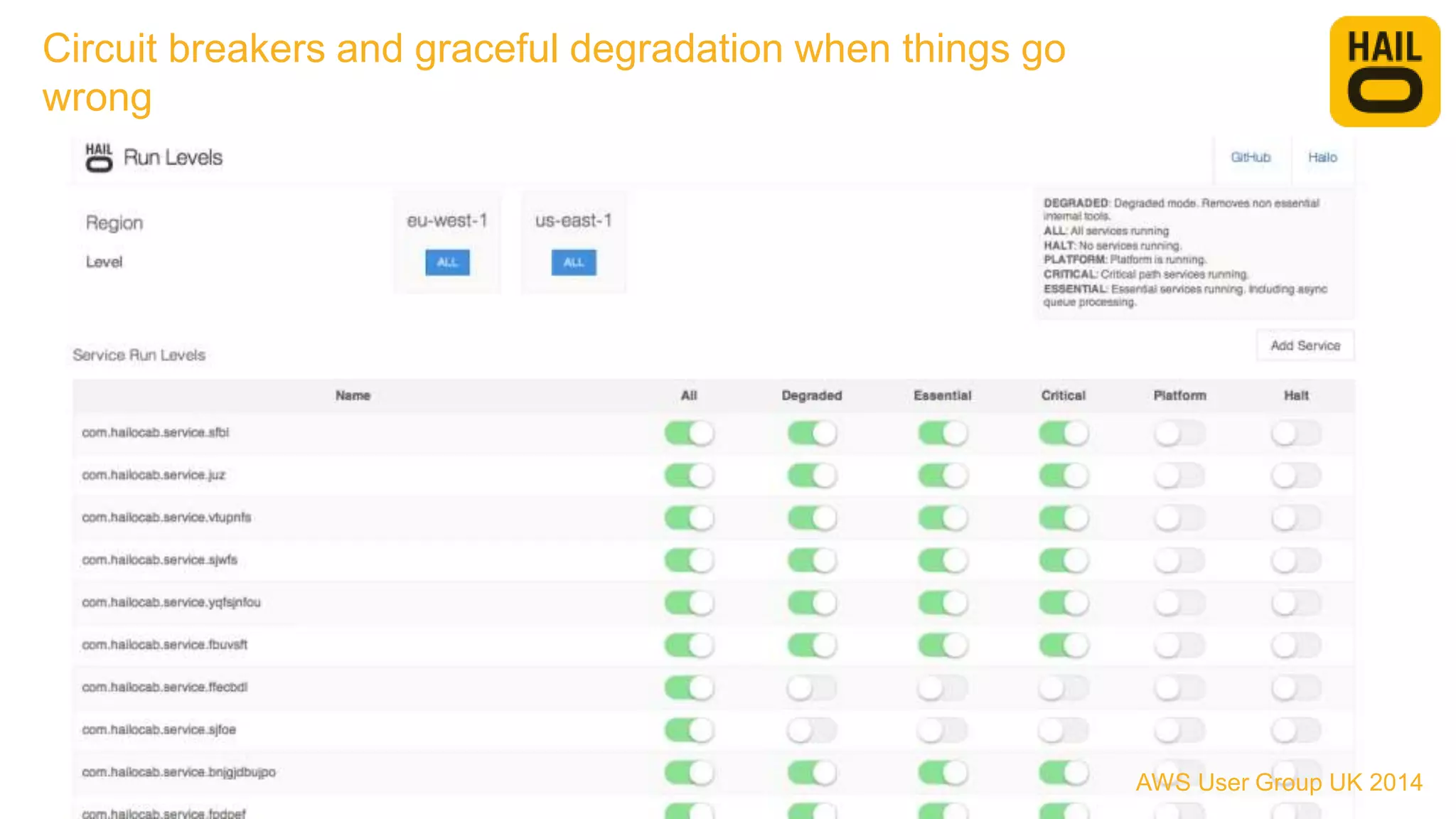
The document outlines the evolution of Hailo's architecture from a monolithic structure to a micro-services architecture on AWS, driven by increased user demand and operational challenges. It discusses the specific technologies used, such as Go and Java, as well as the benefits and drawbacks of the new architecture, including improved scalability and deployment speed. Additionally, it highlights the ongoing complexities and risks associated with managing distributed services and orchestration layers.