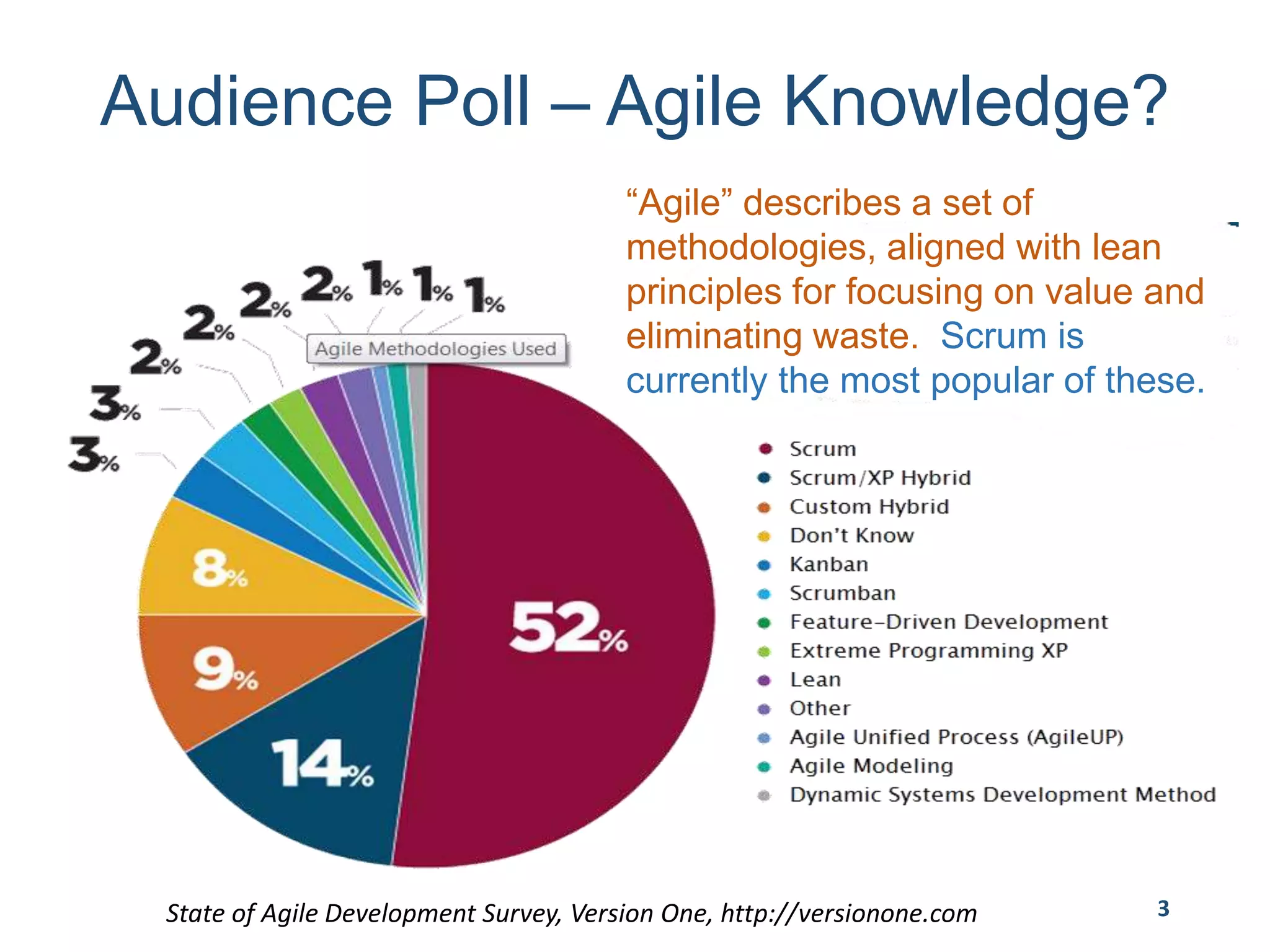
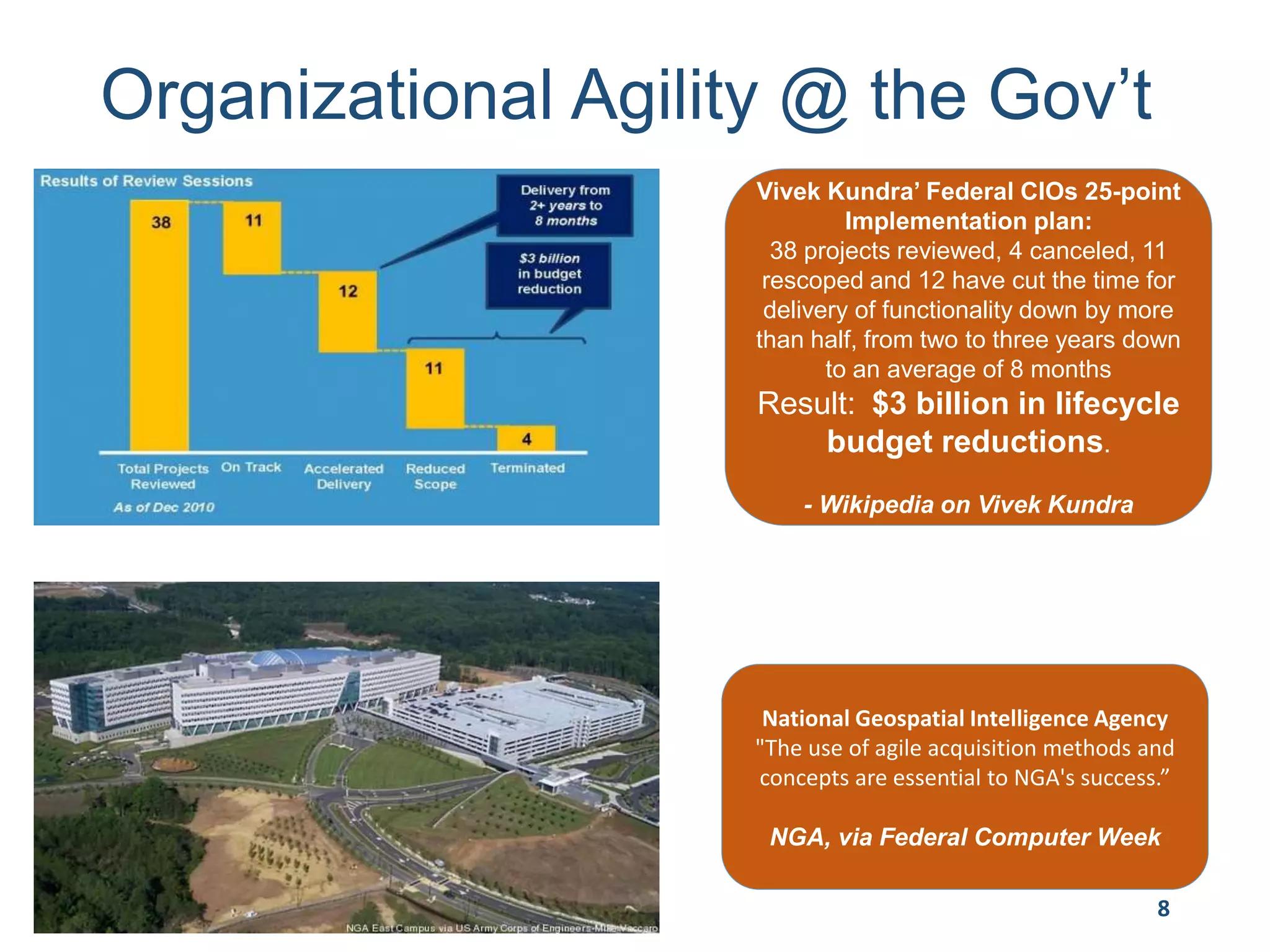
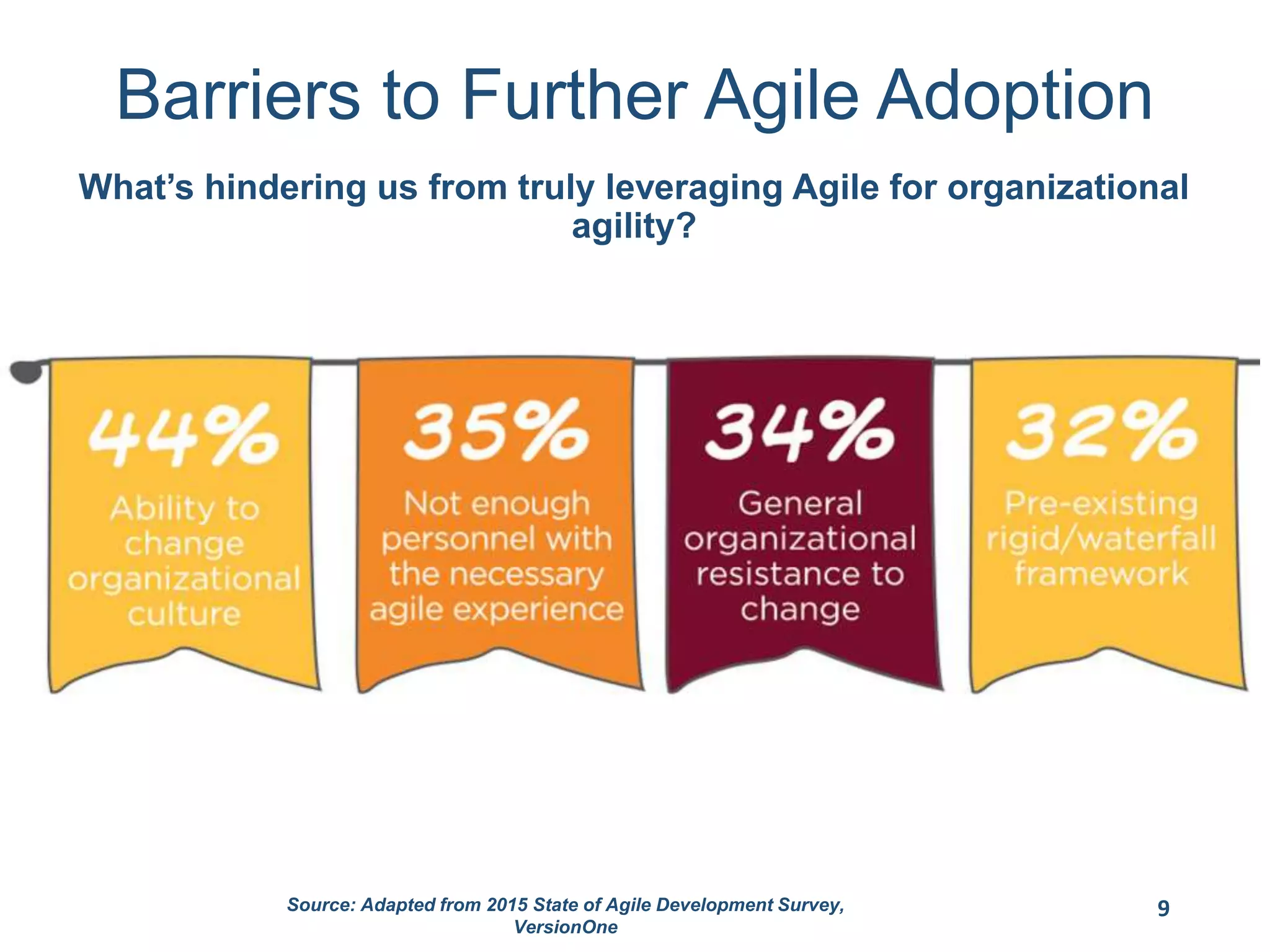
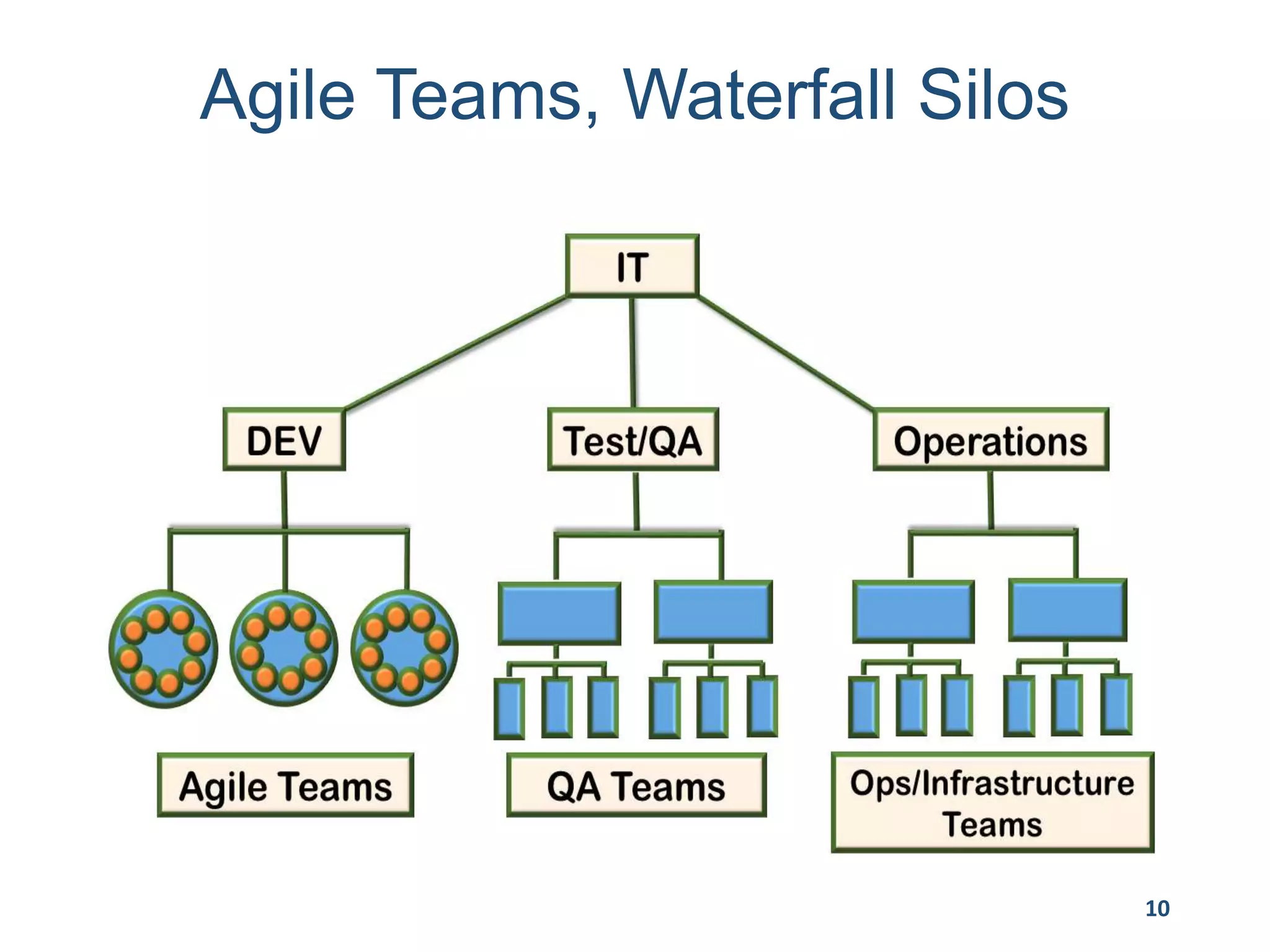
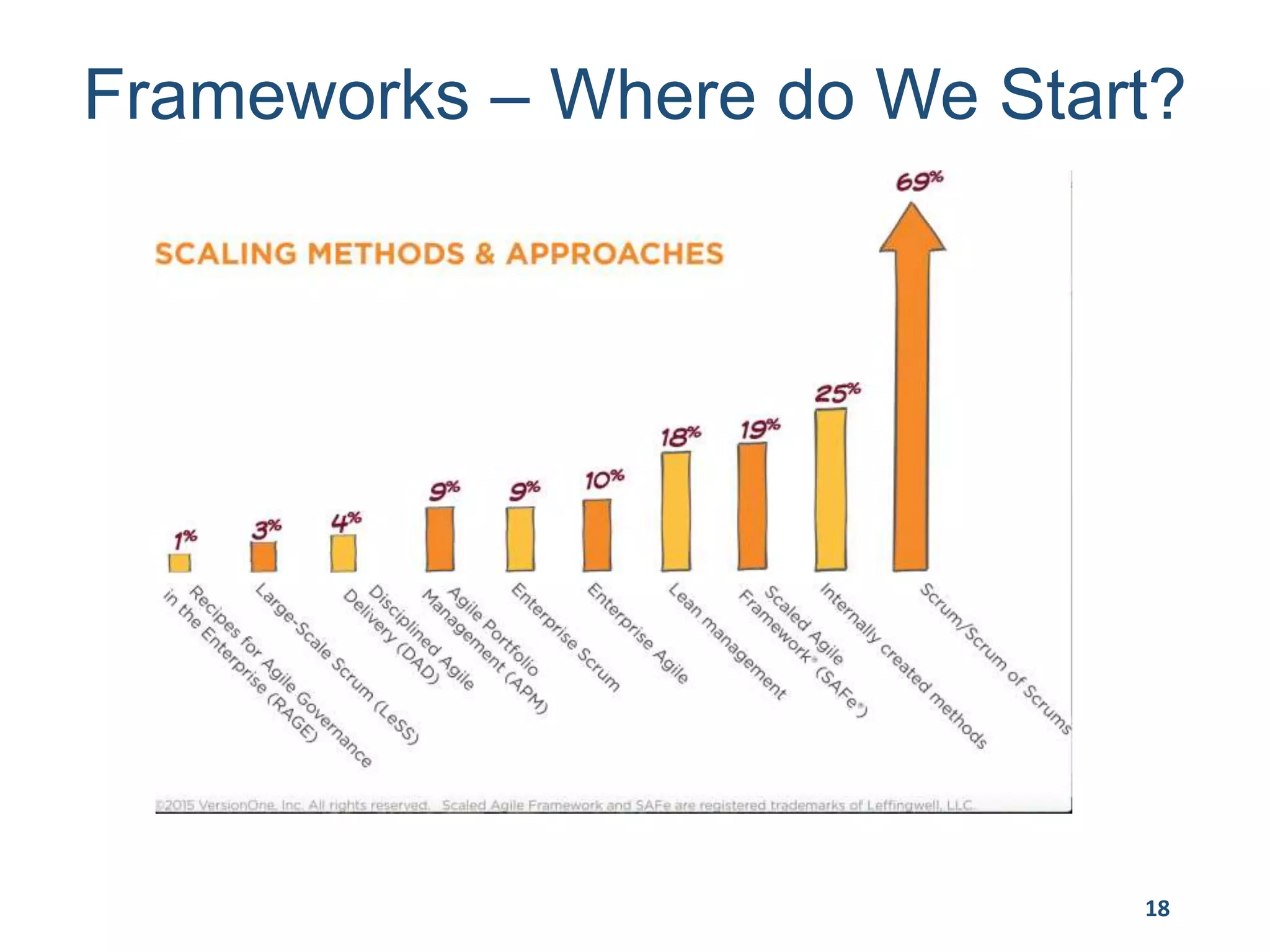
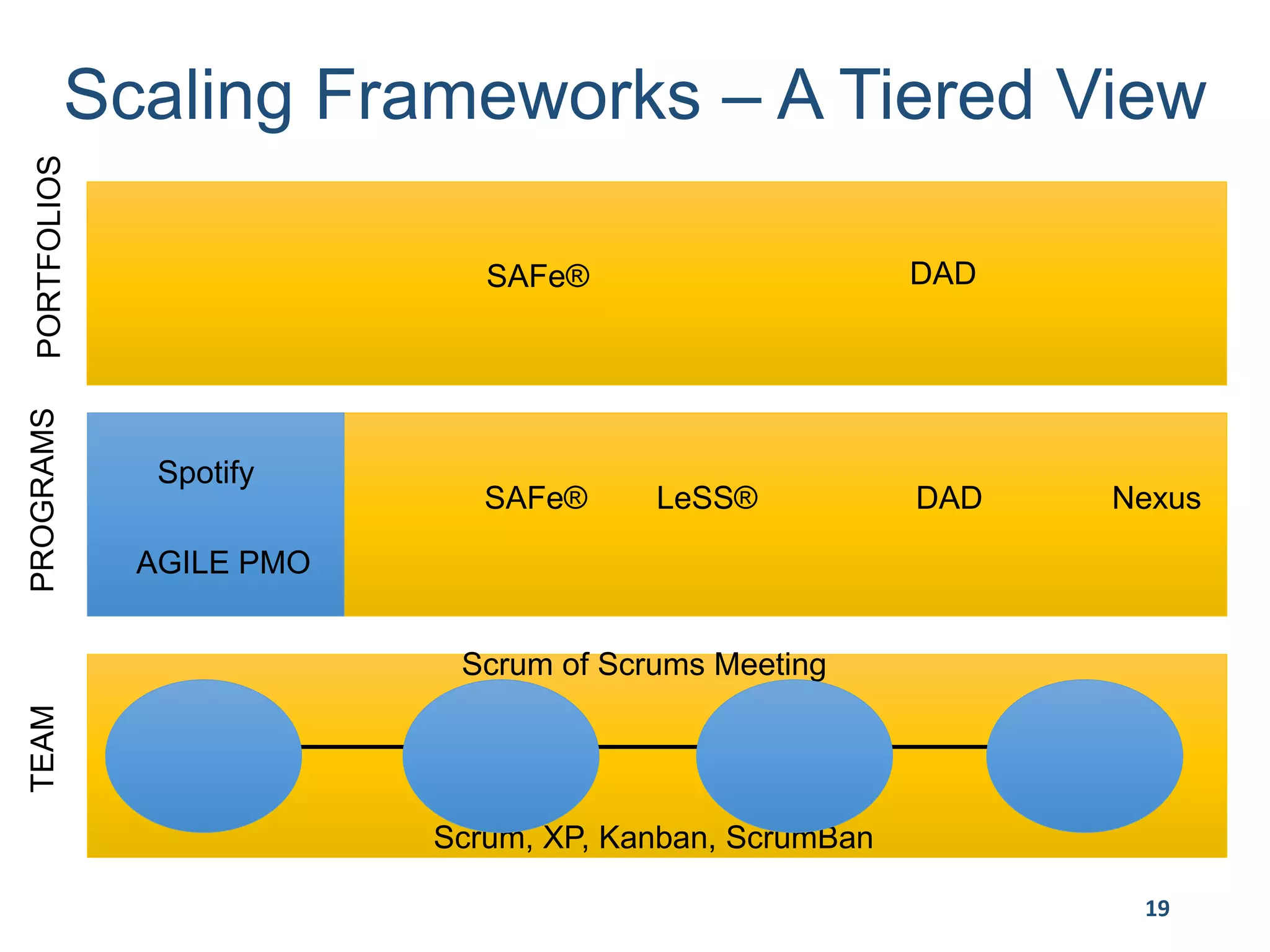
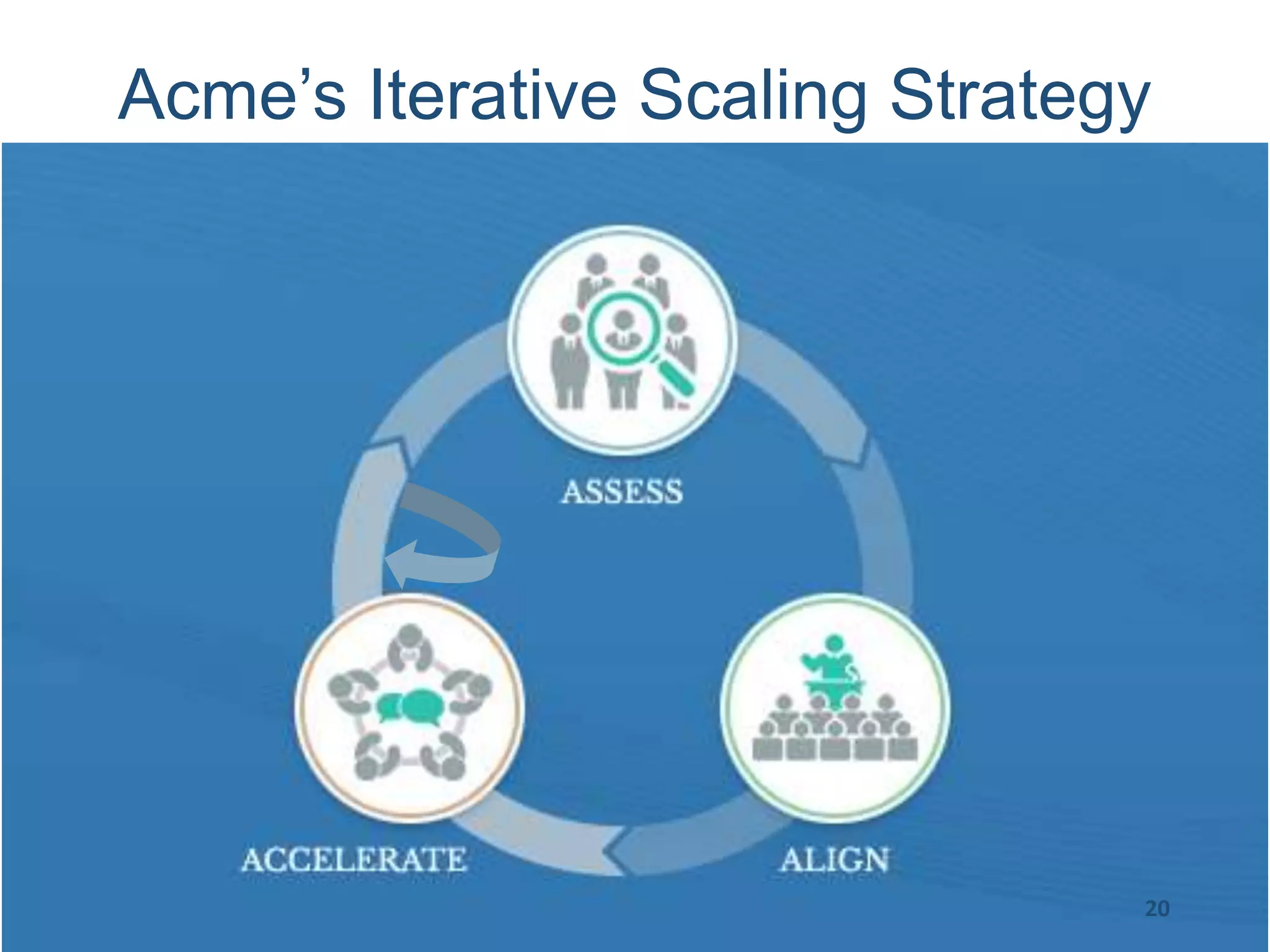
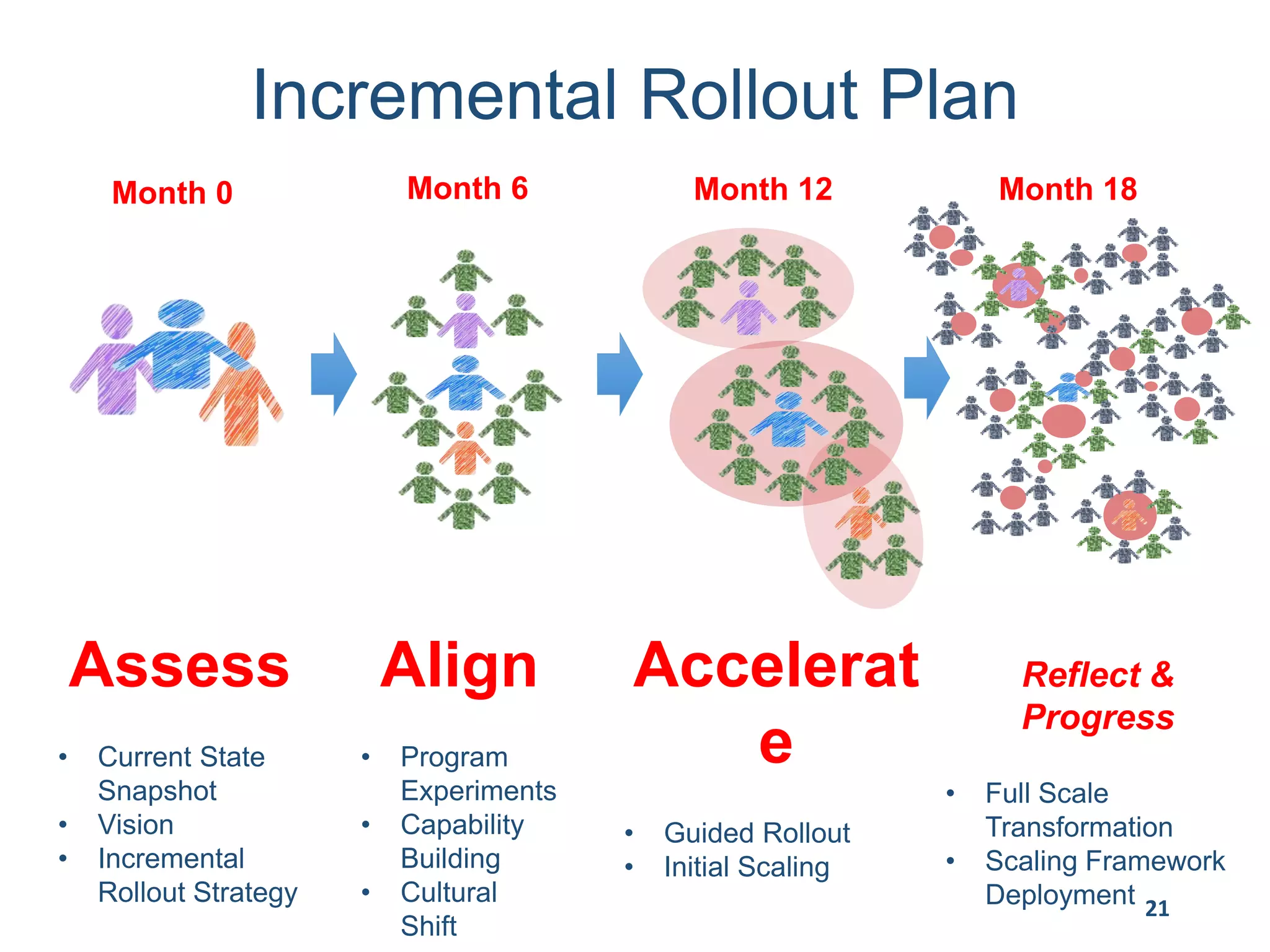
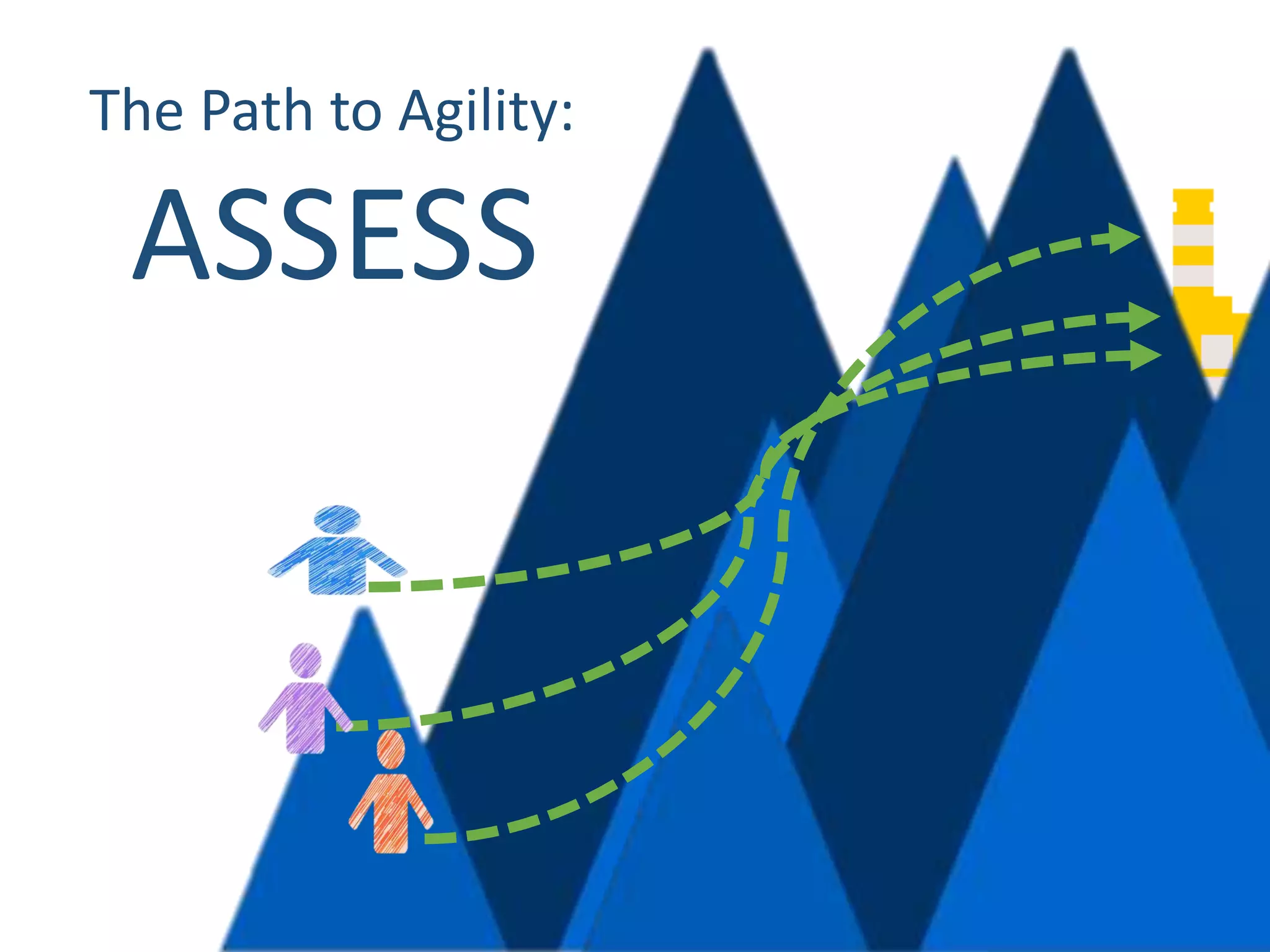
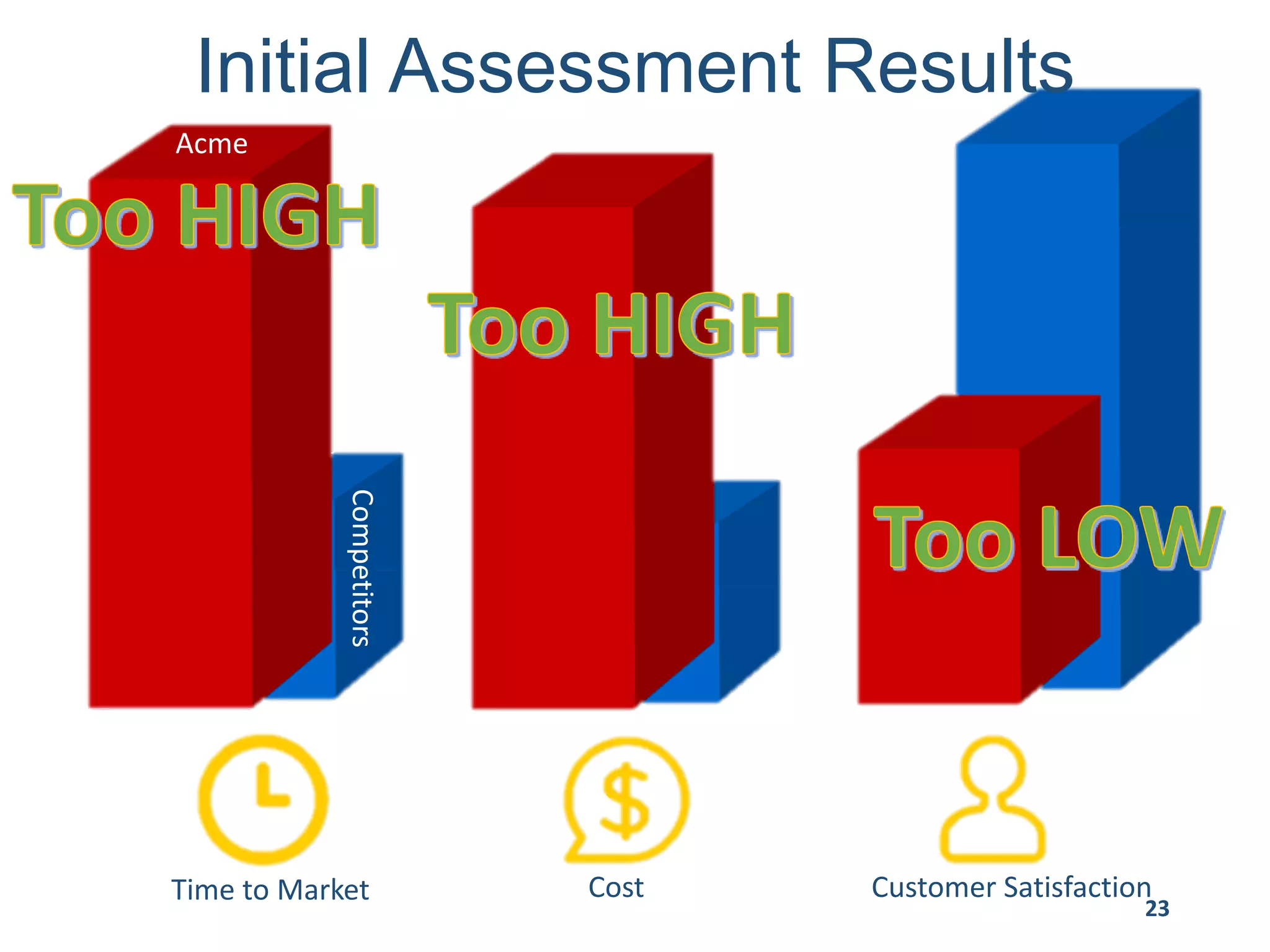
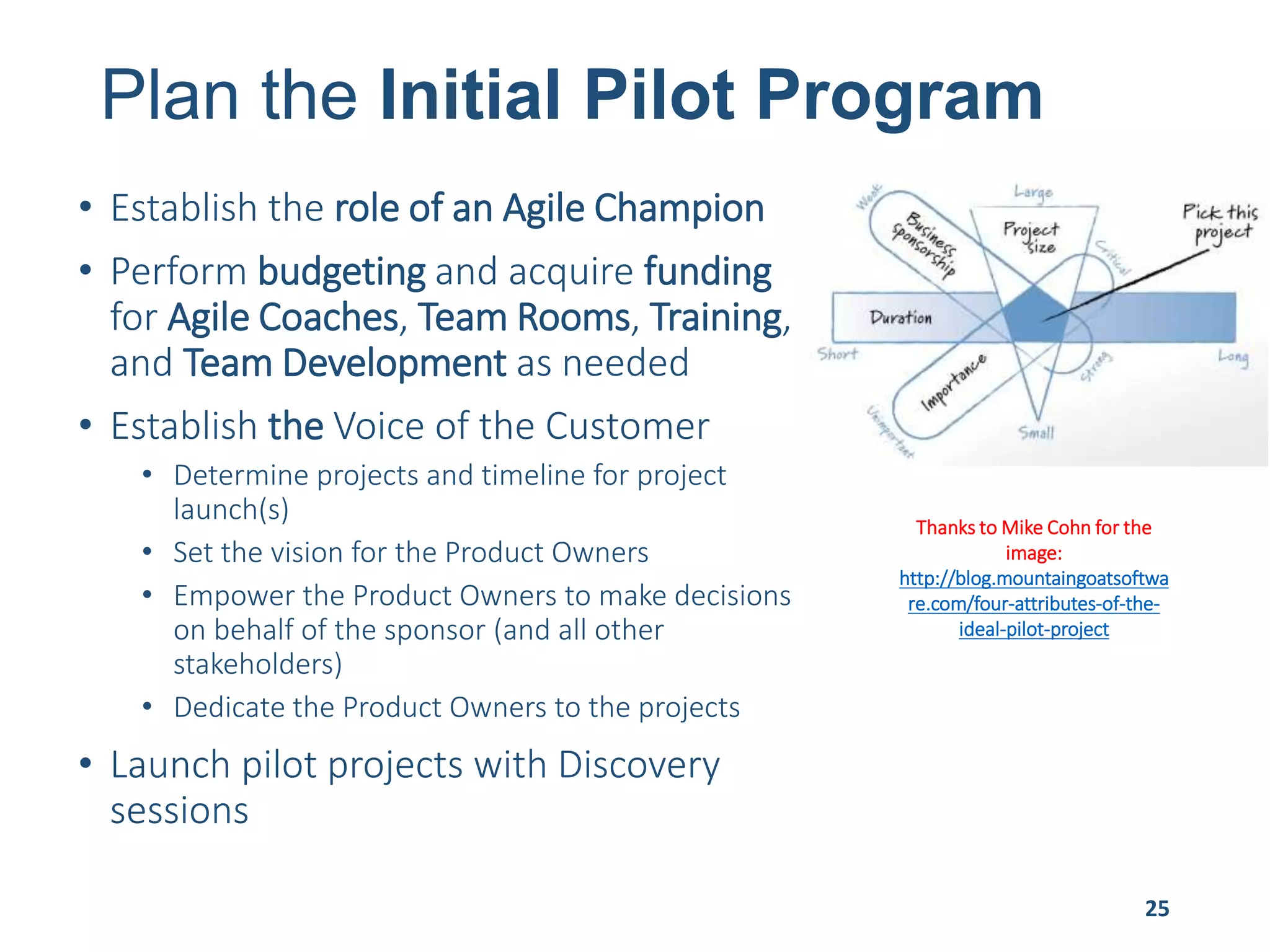
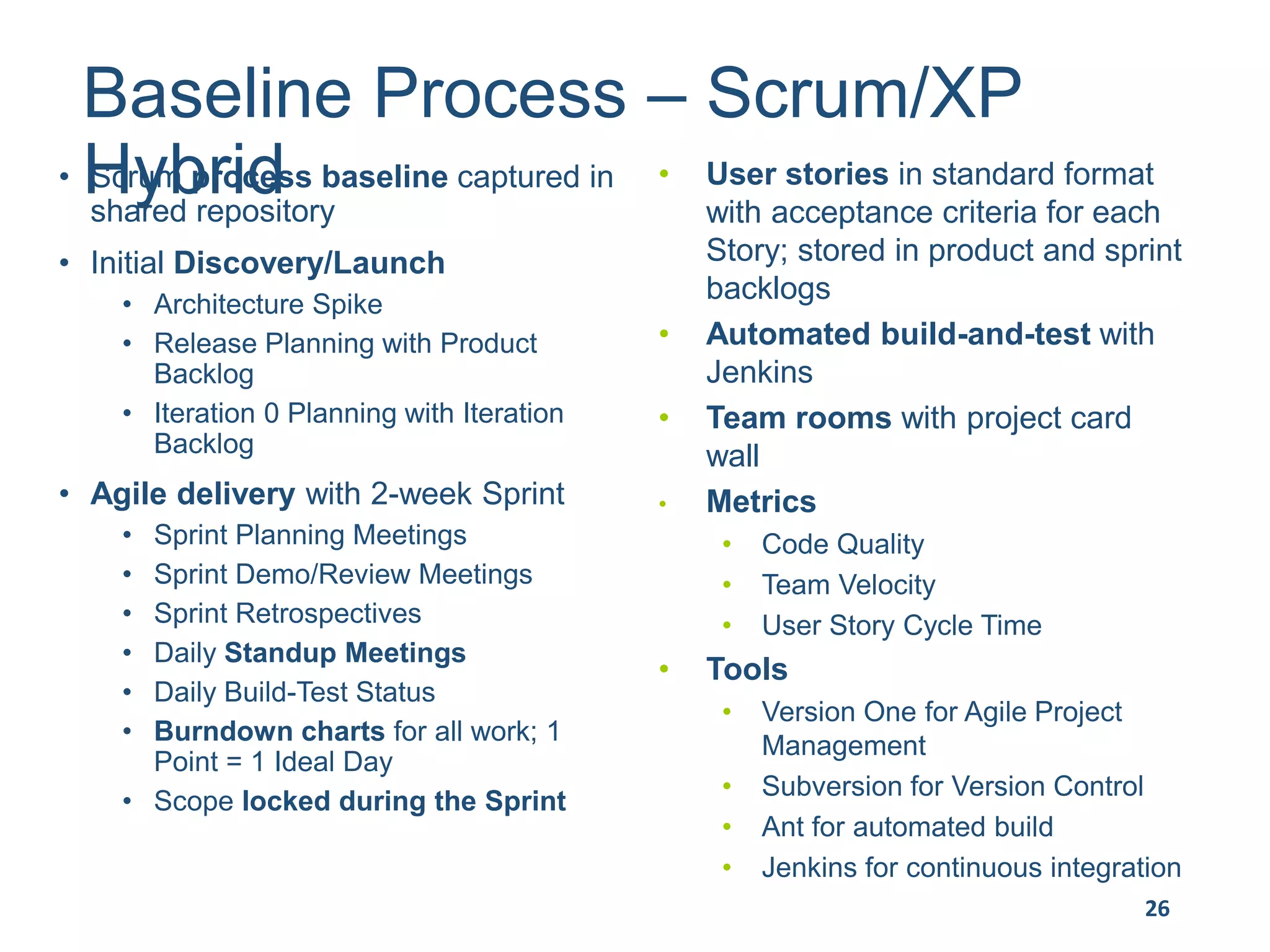
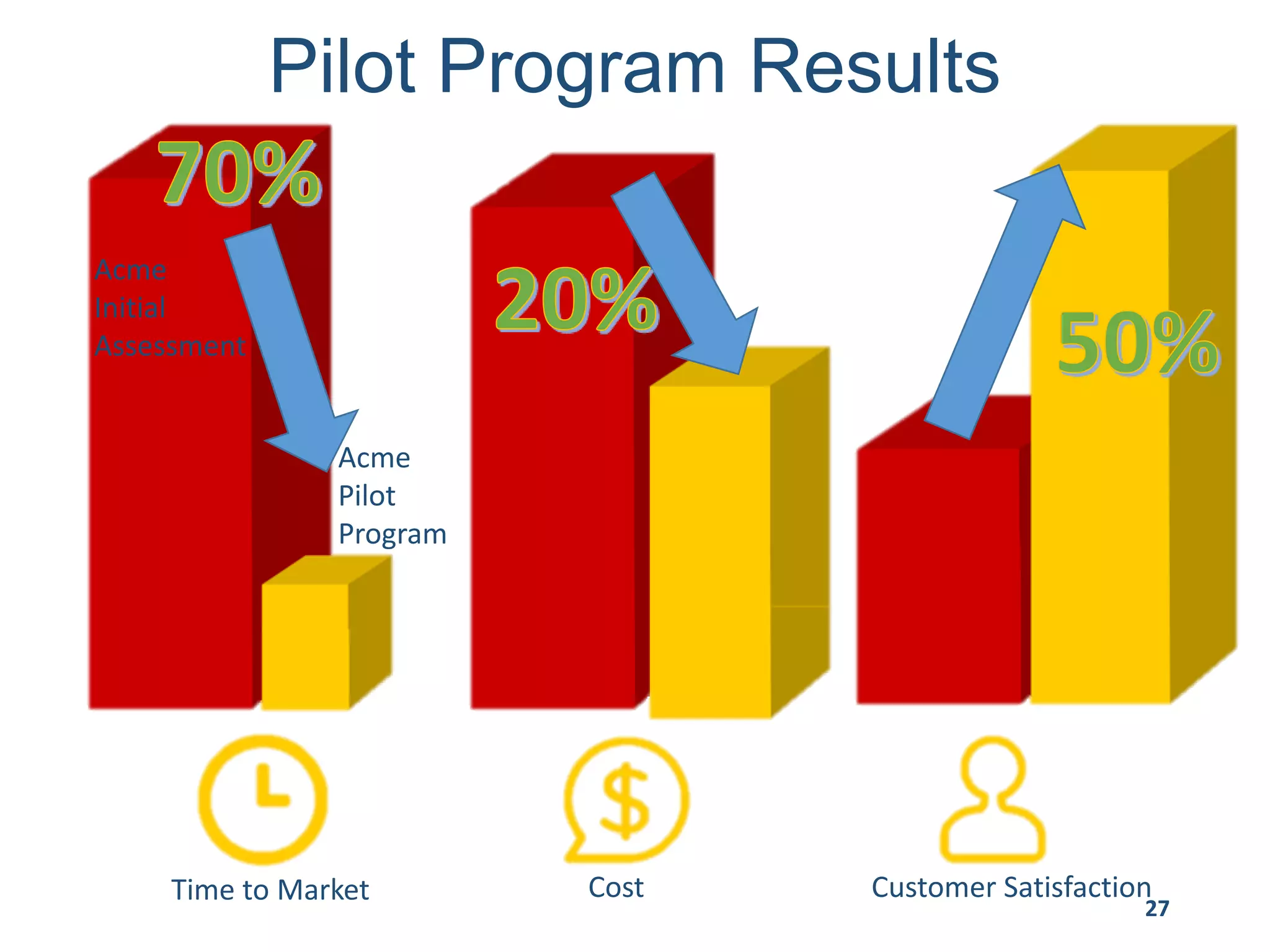
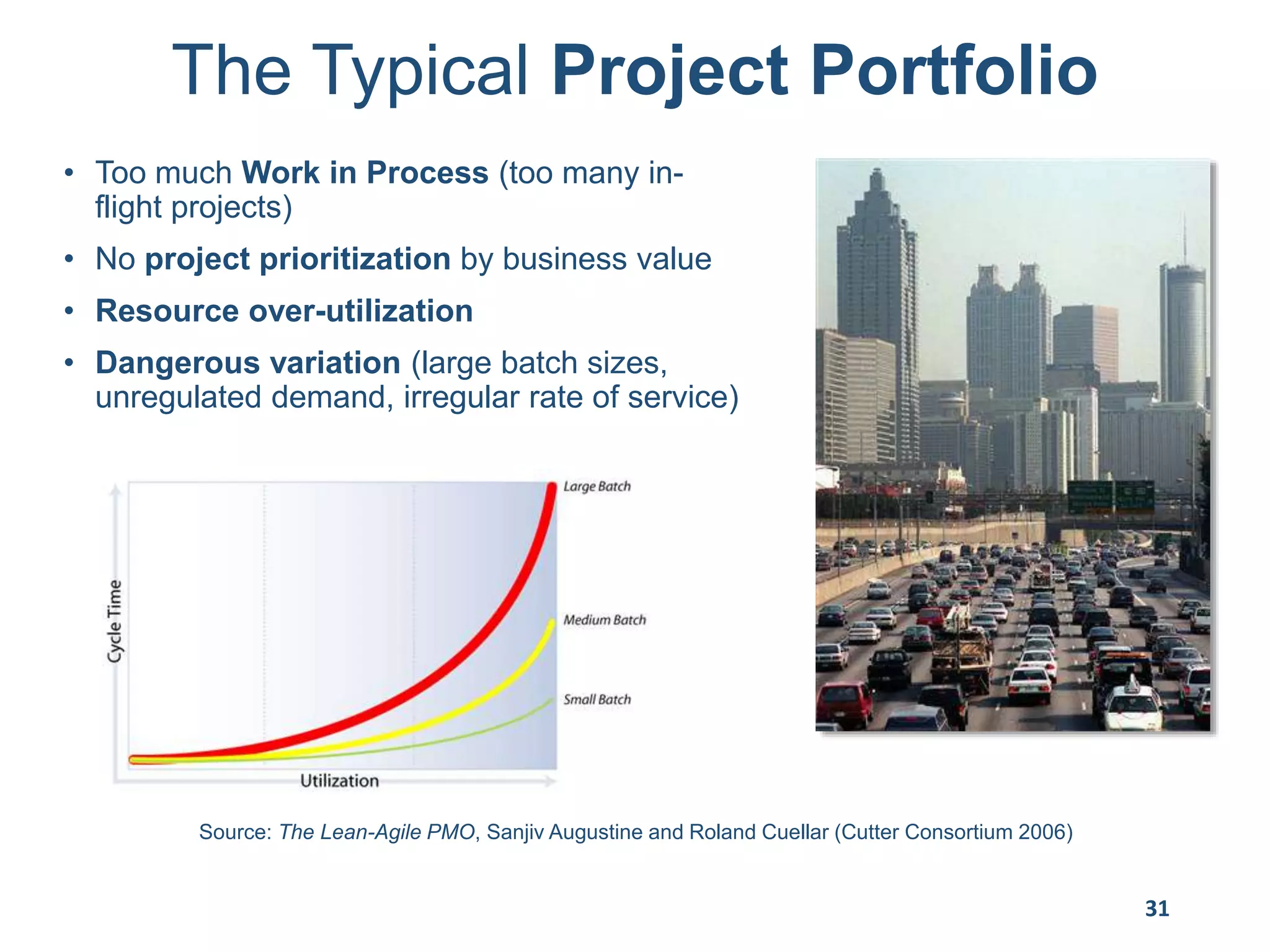
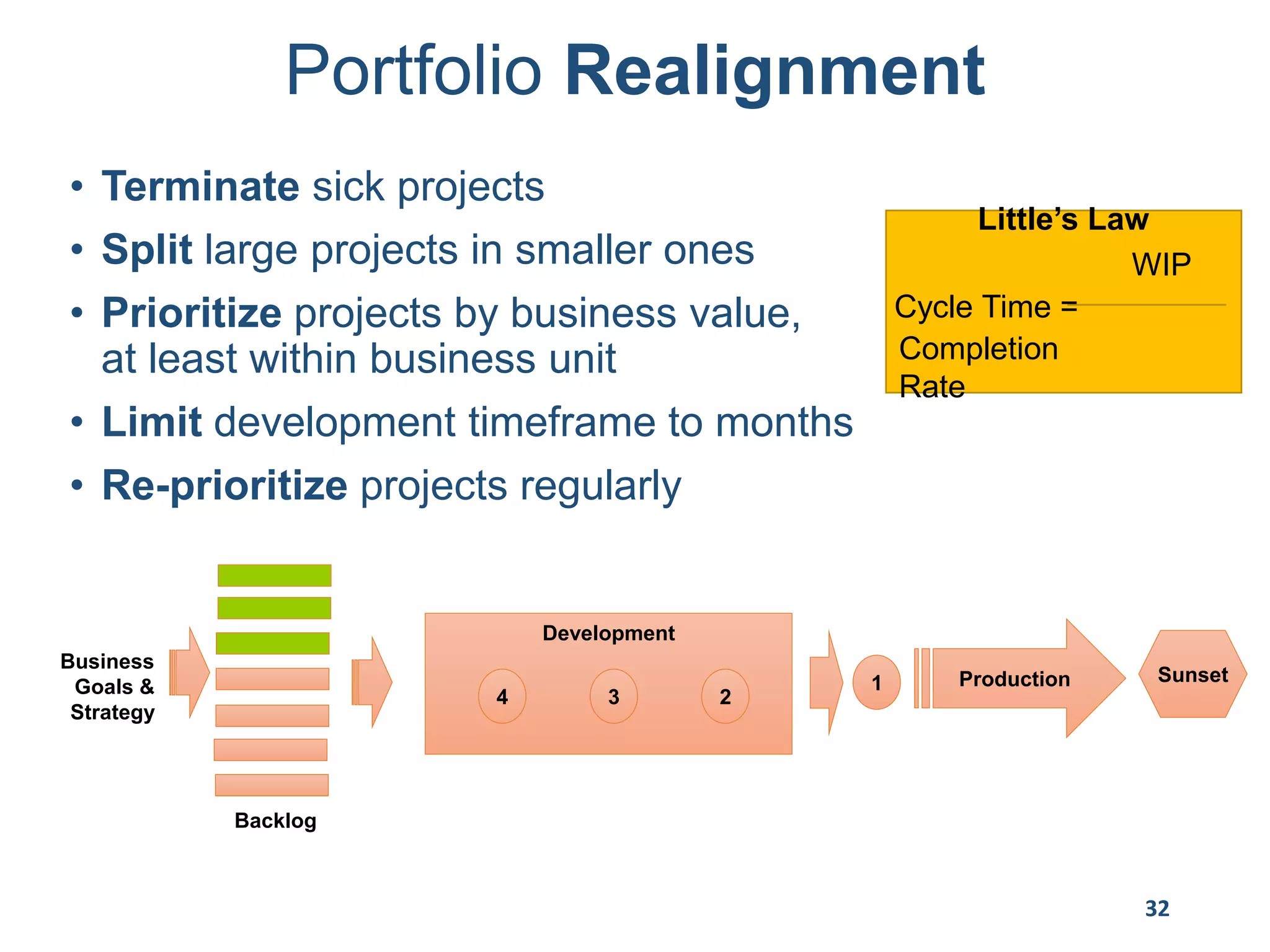
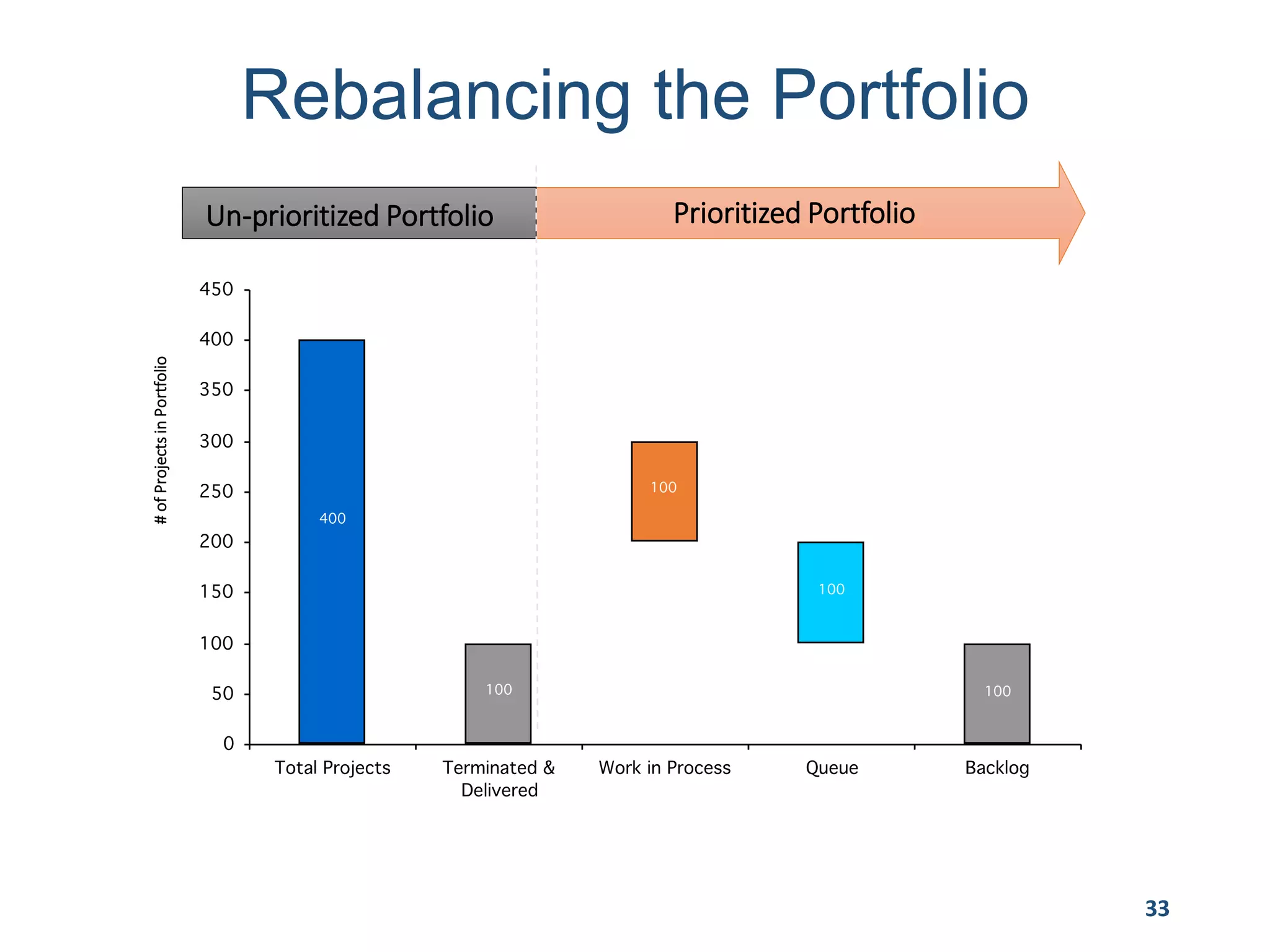
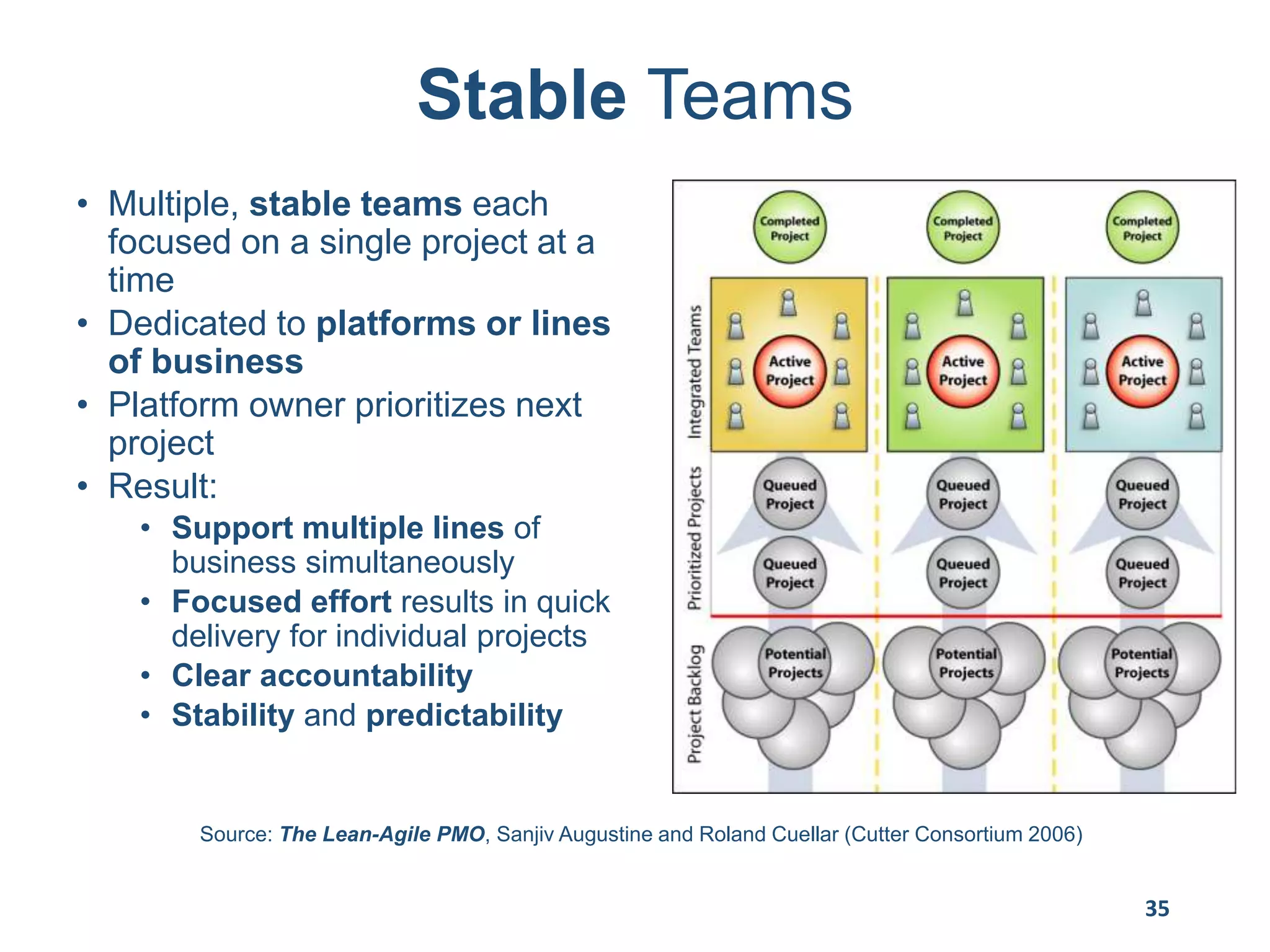
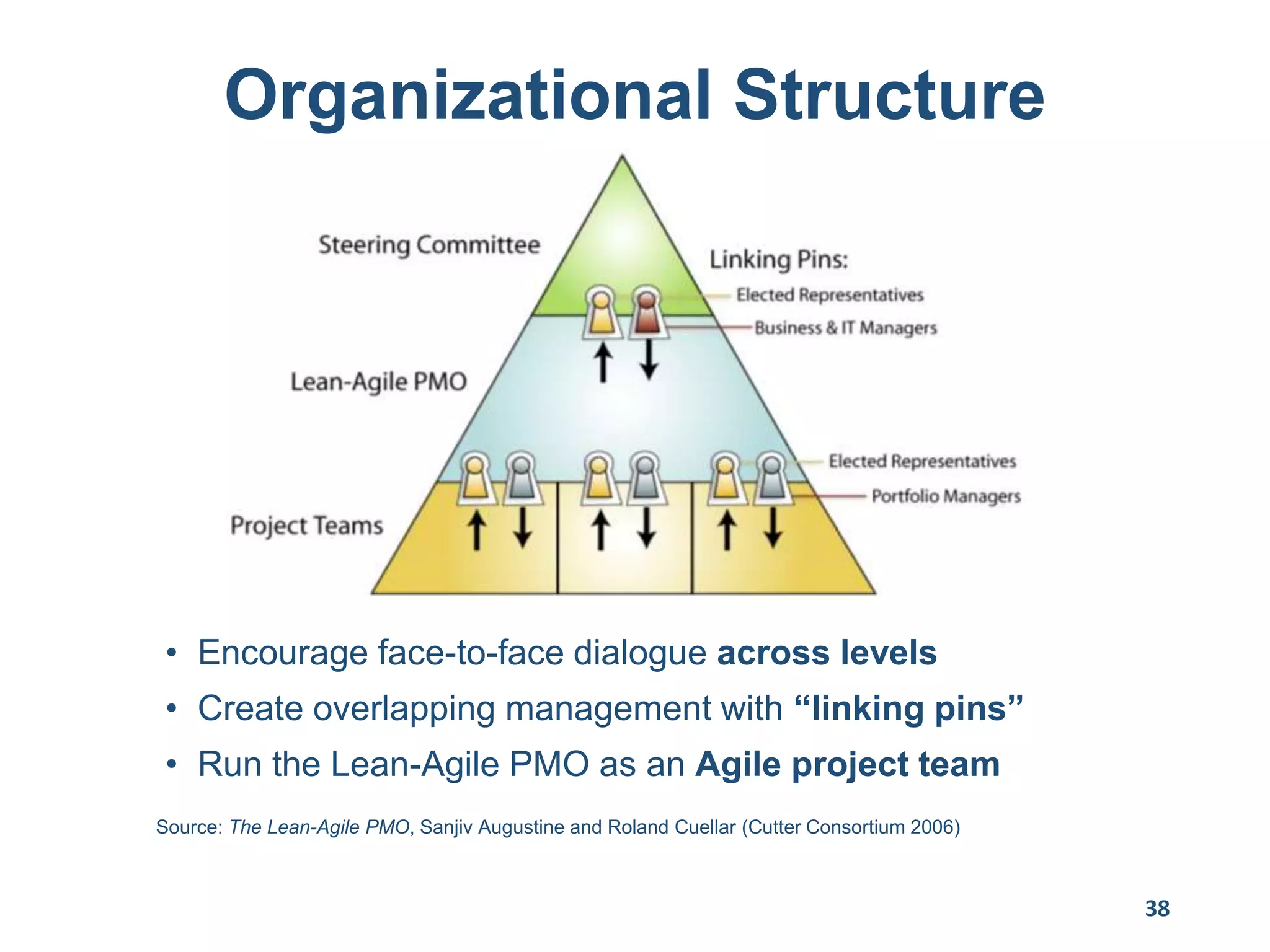
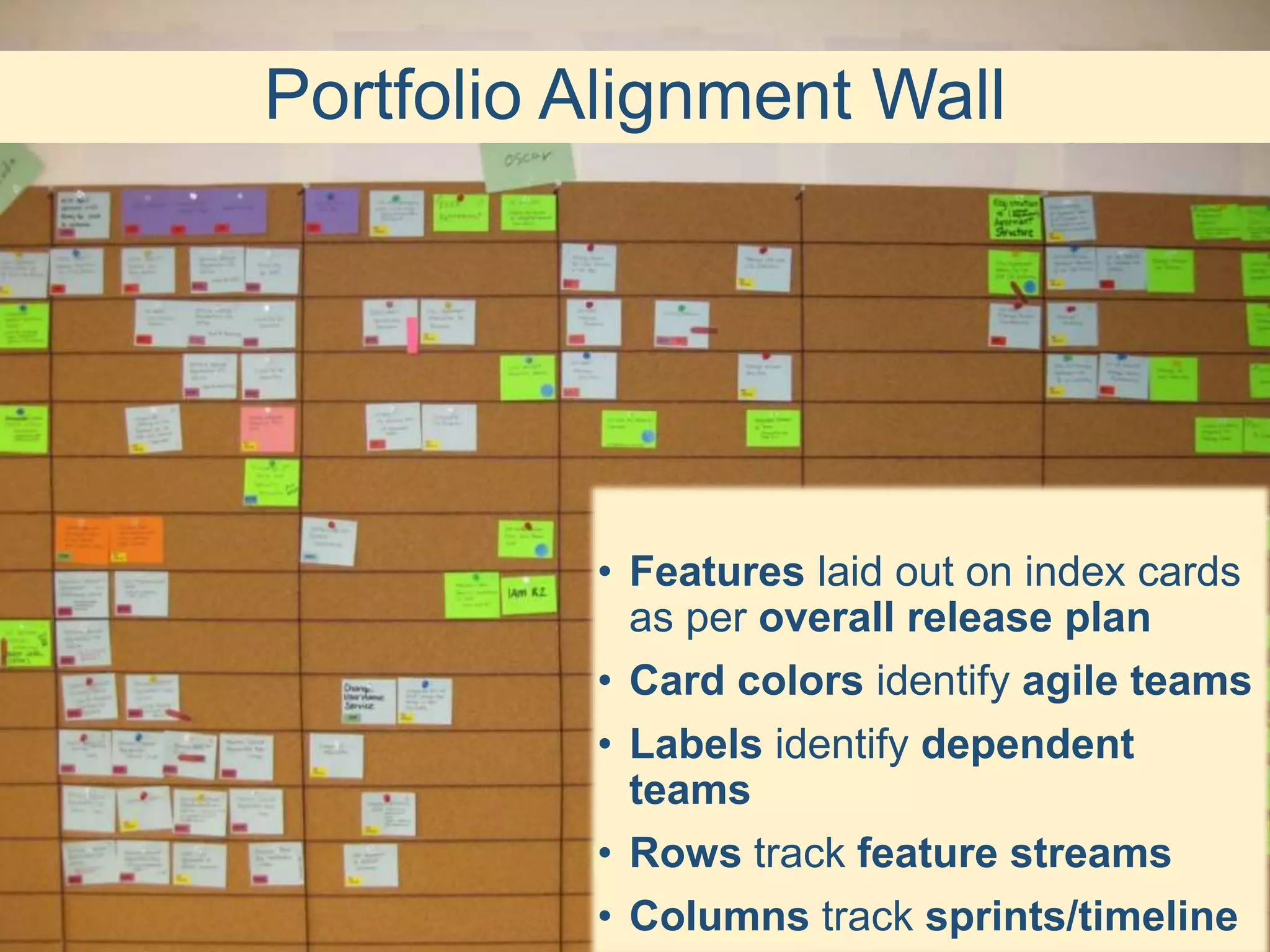
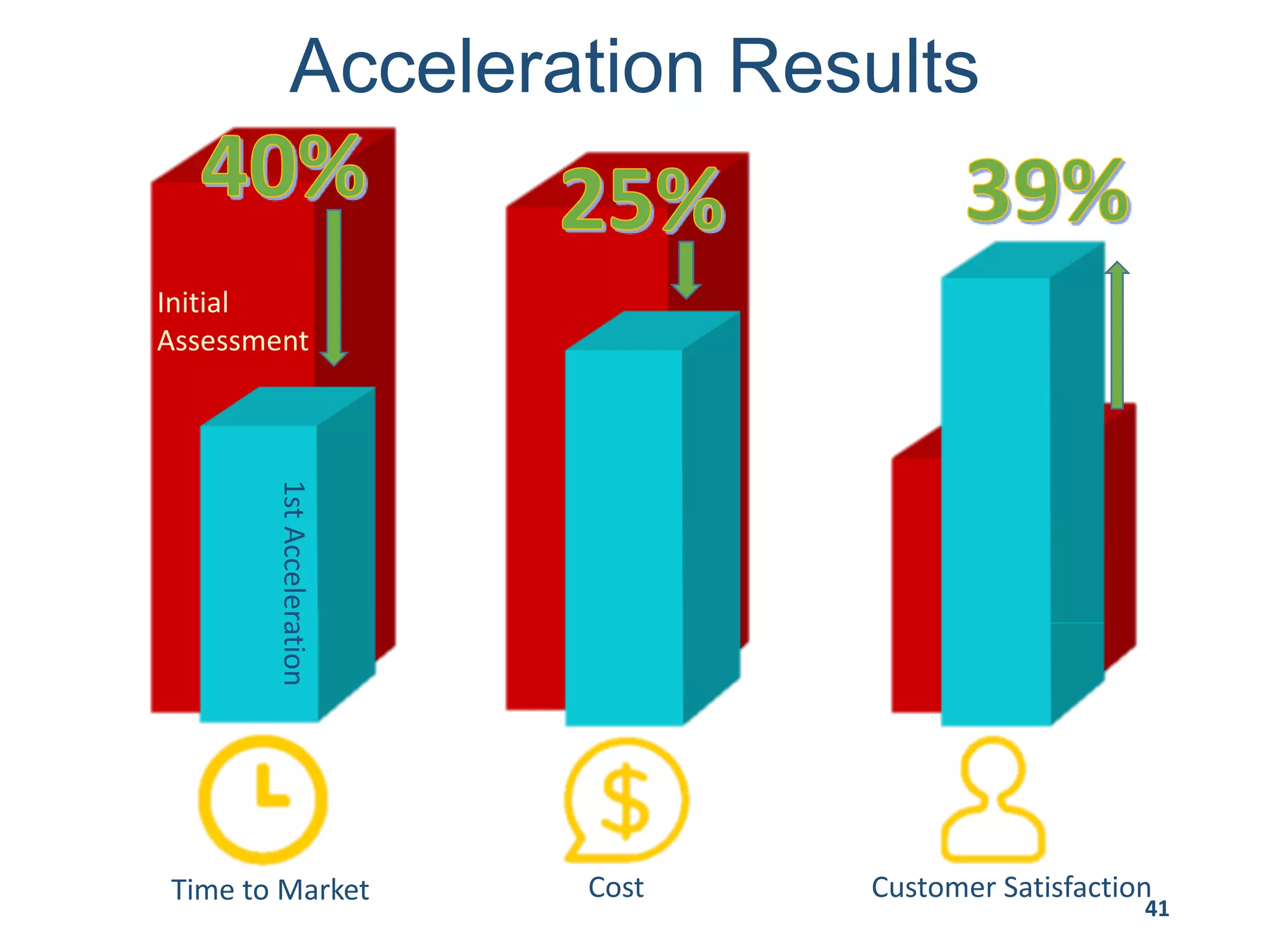
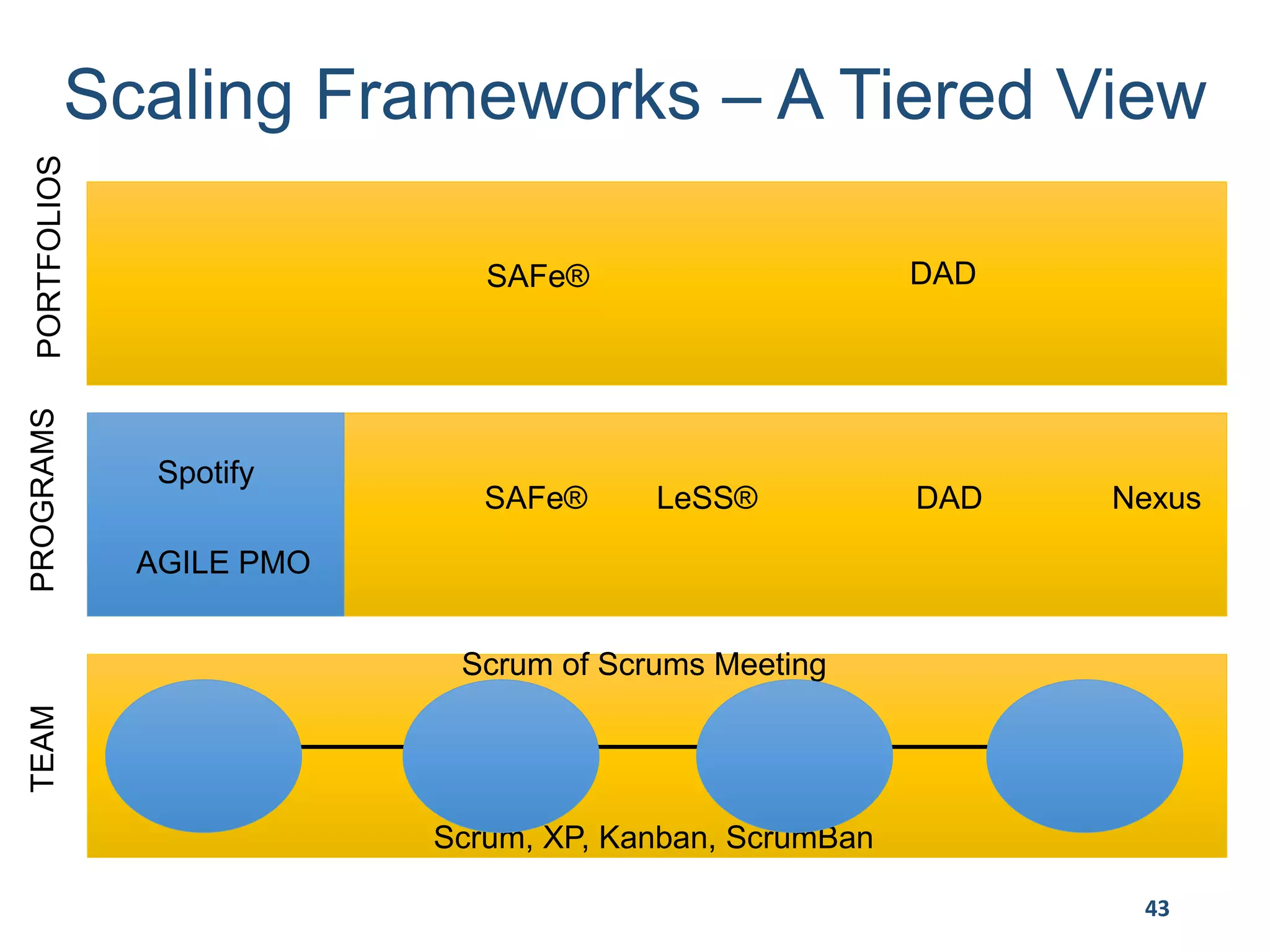
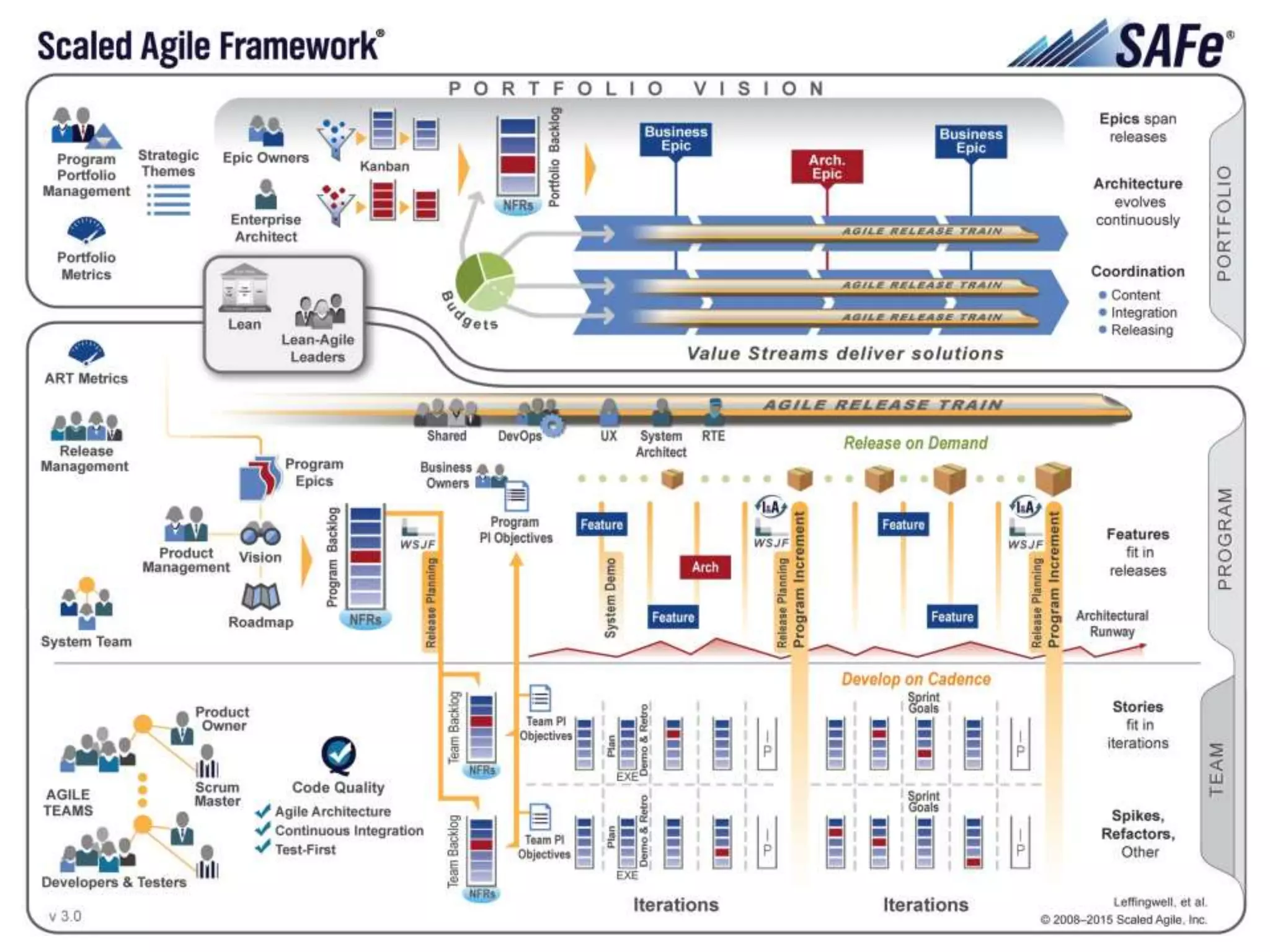
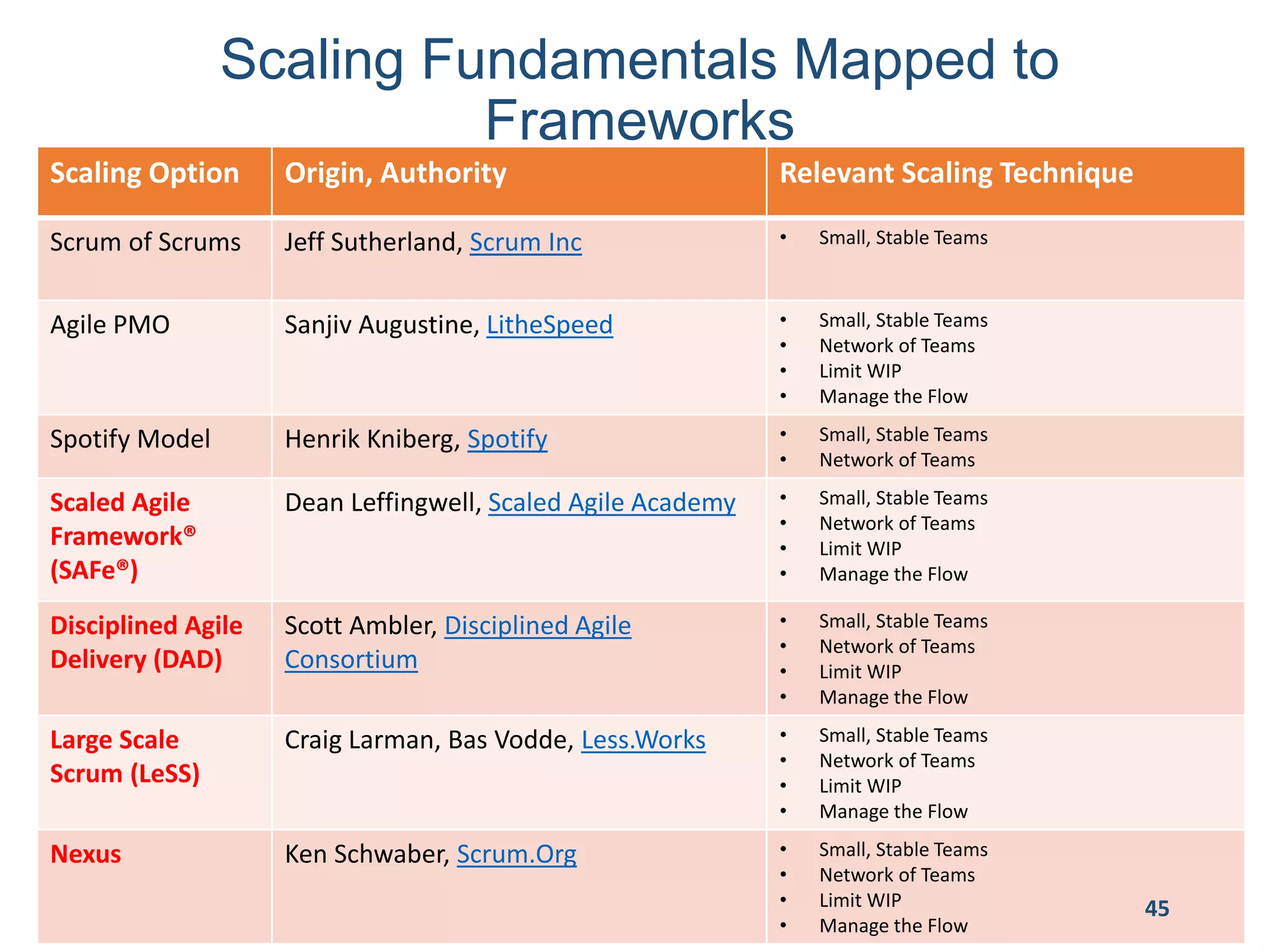
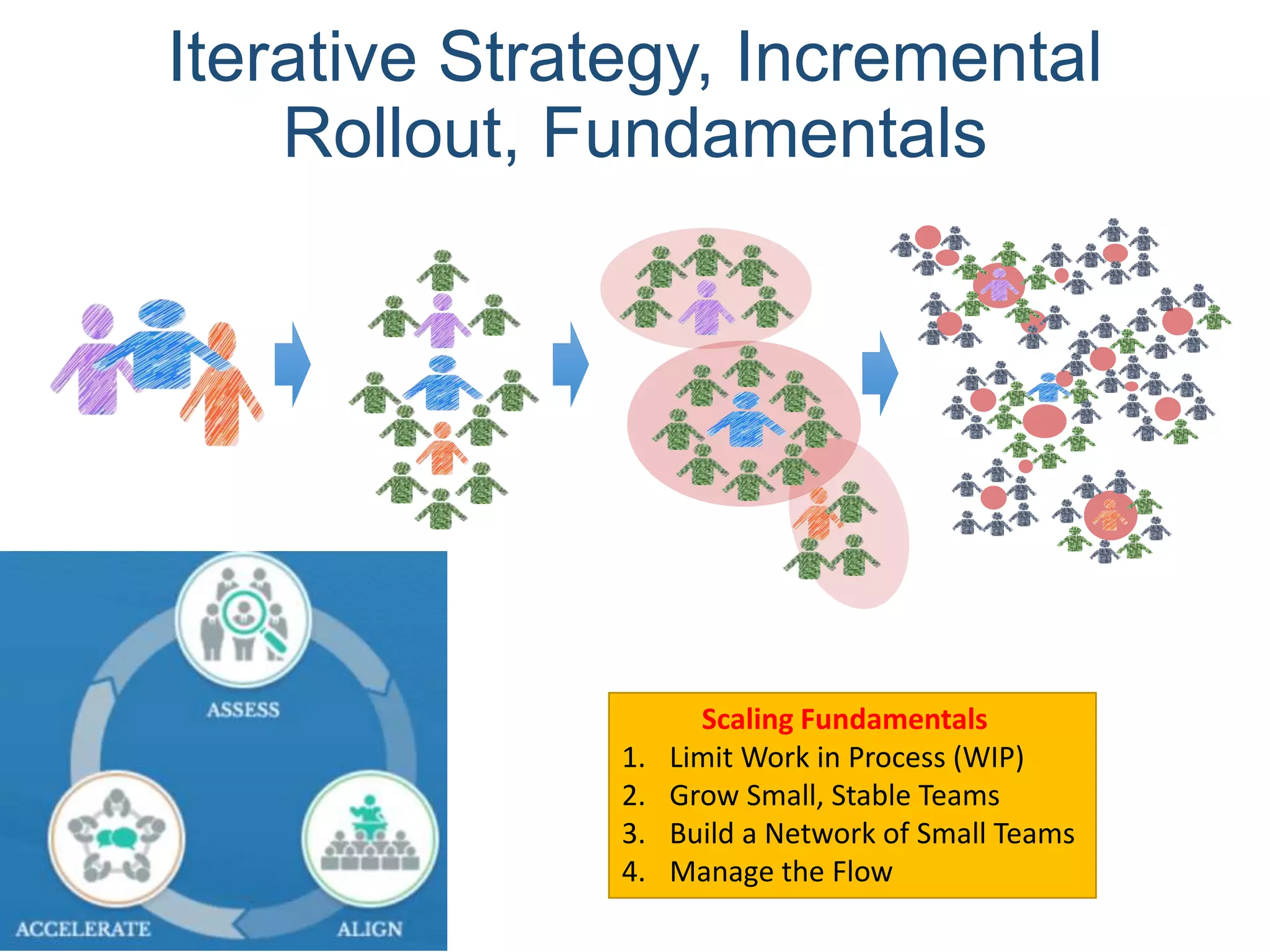
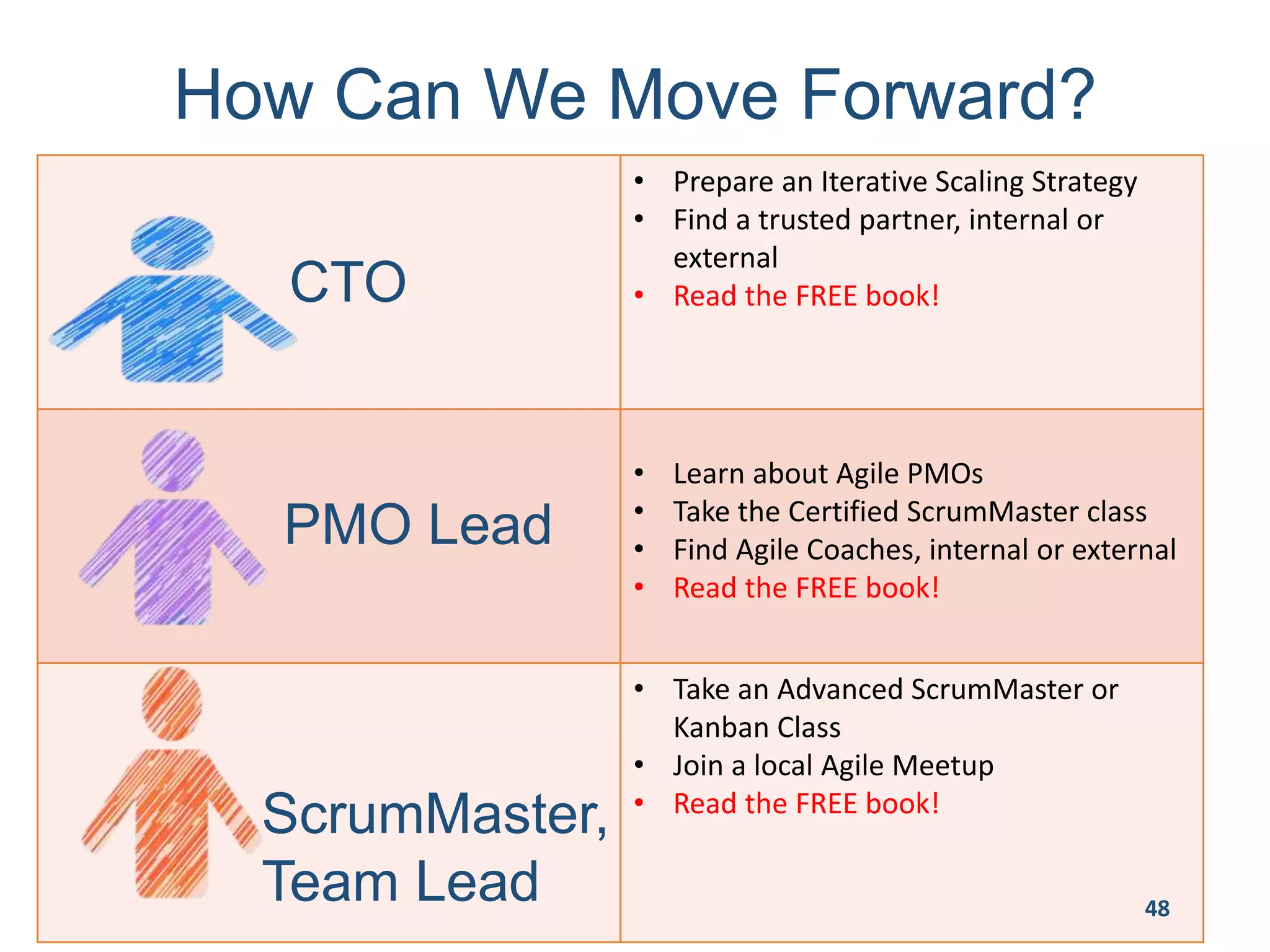
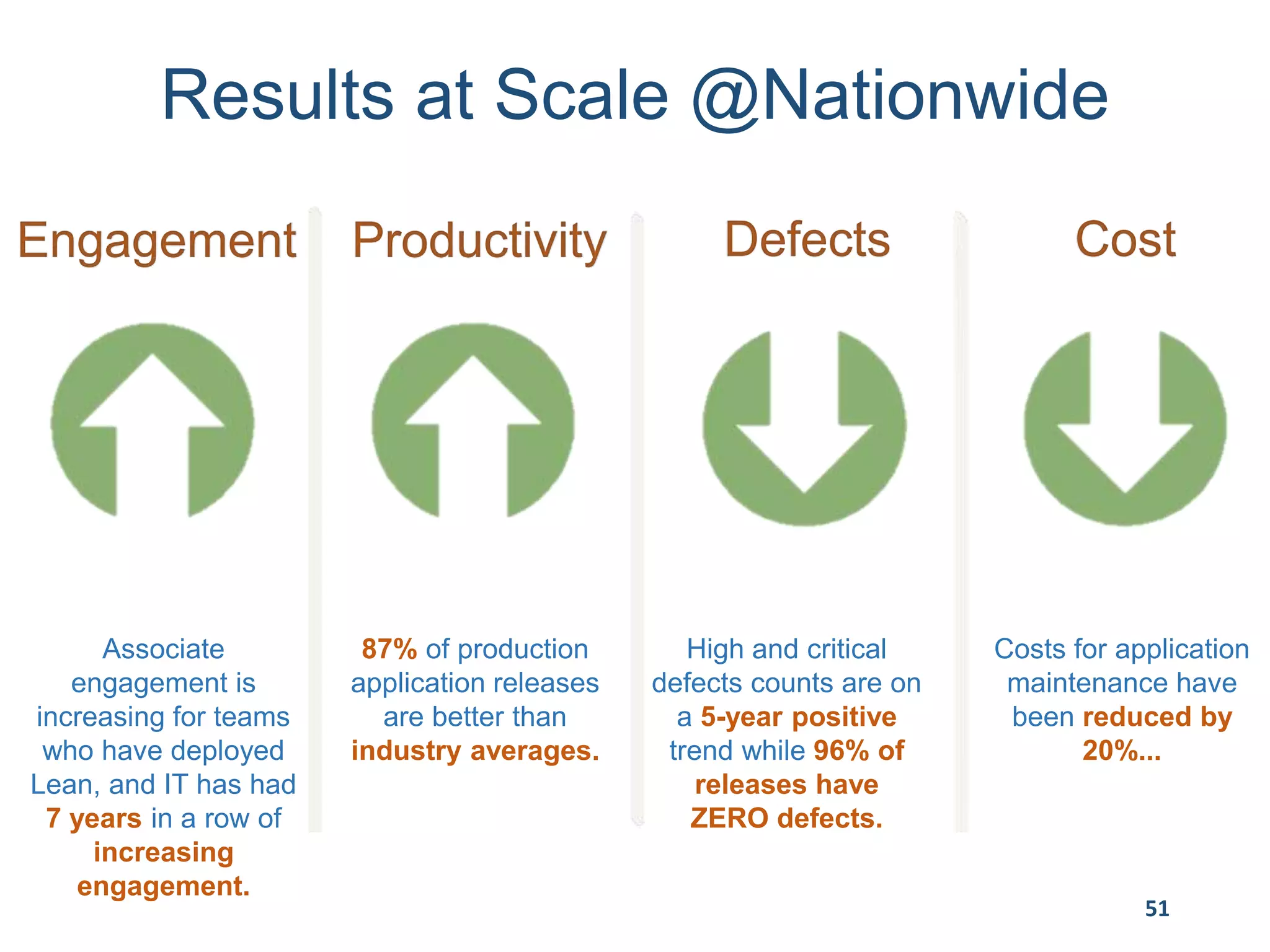
This document provides an overview of scaling agile development in an organization. It discusses why organizations scale agile, such as to improve organizational agility. It then outlines a four phase approach to jumpstarting scaling: assess the current state, align initiatives, accelerate progress incrementally, and reflect and progress further. Specific techniques are discussed for each phase, such as establishing agile champions, piloting programs, limiting work in process, growing stable teams, and selecting a scaling framework. The presentation concludes by emphasizing an iterative scaling strategy and finding support to move forward.