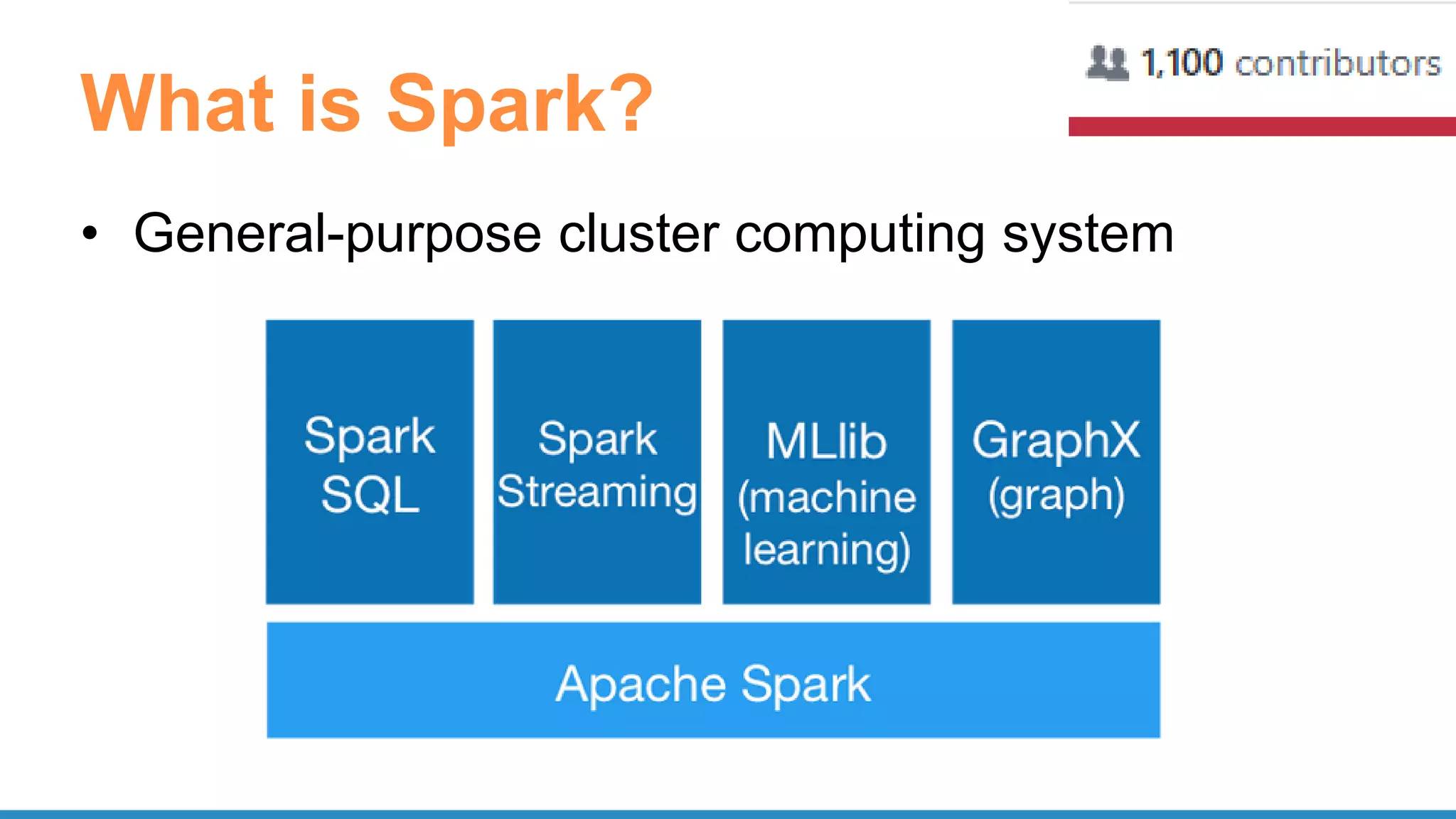
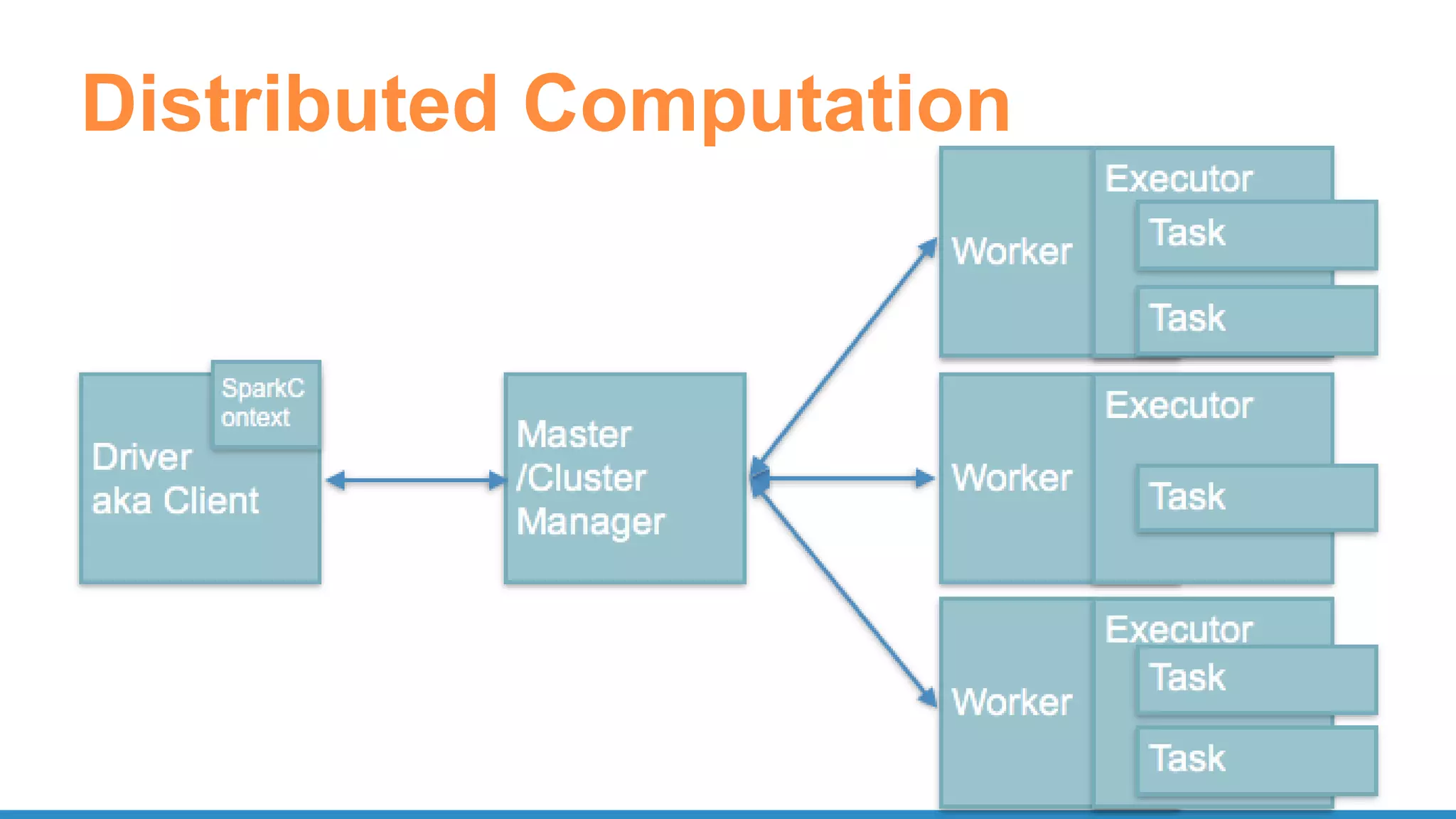
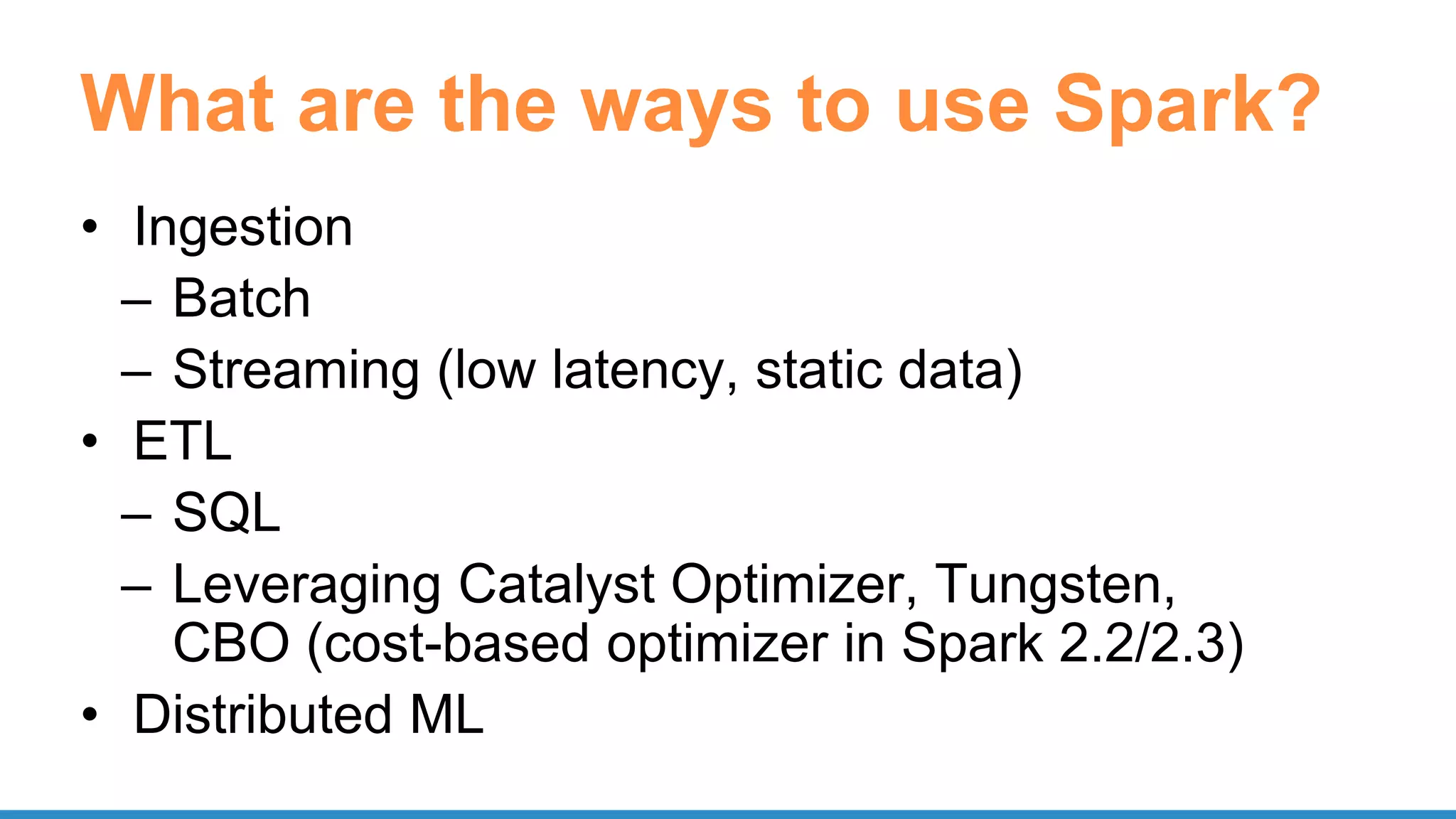
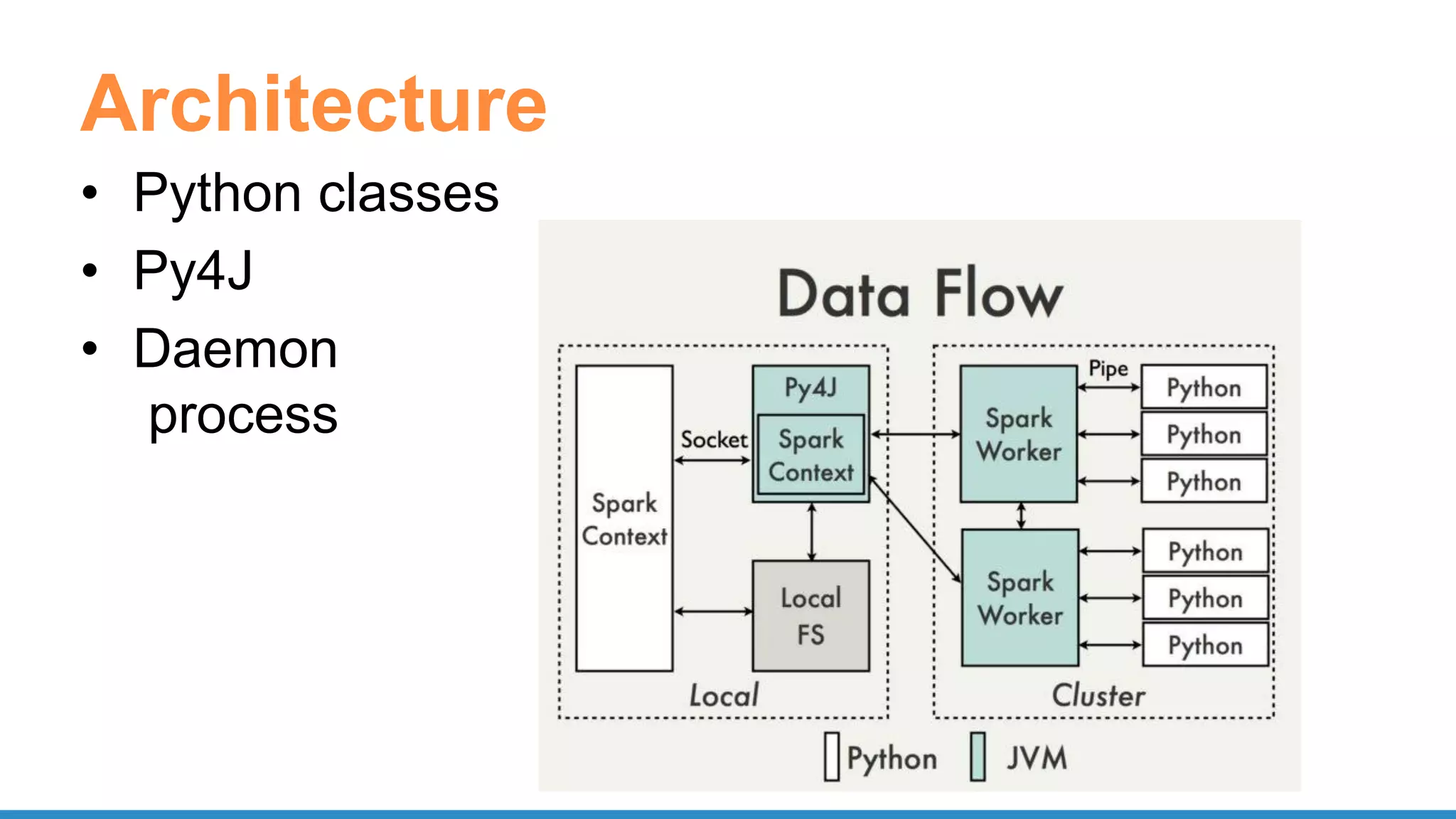
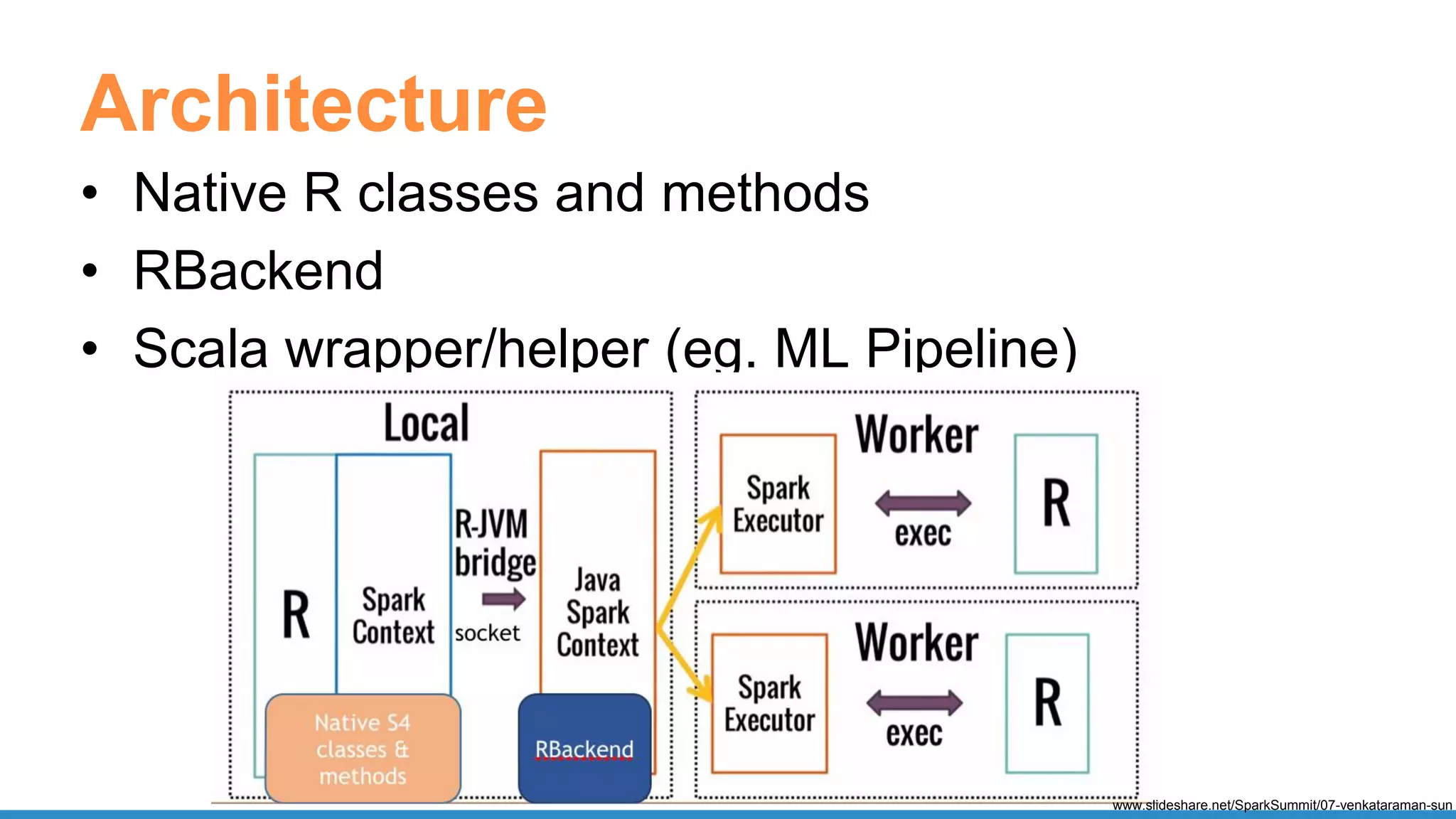
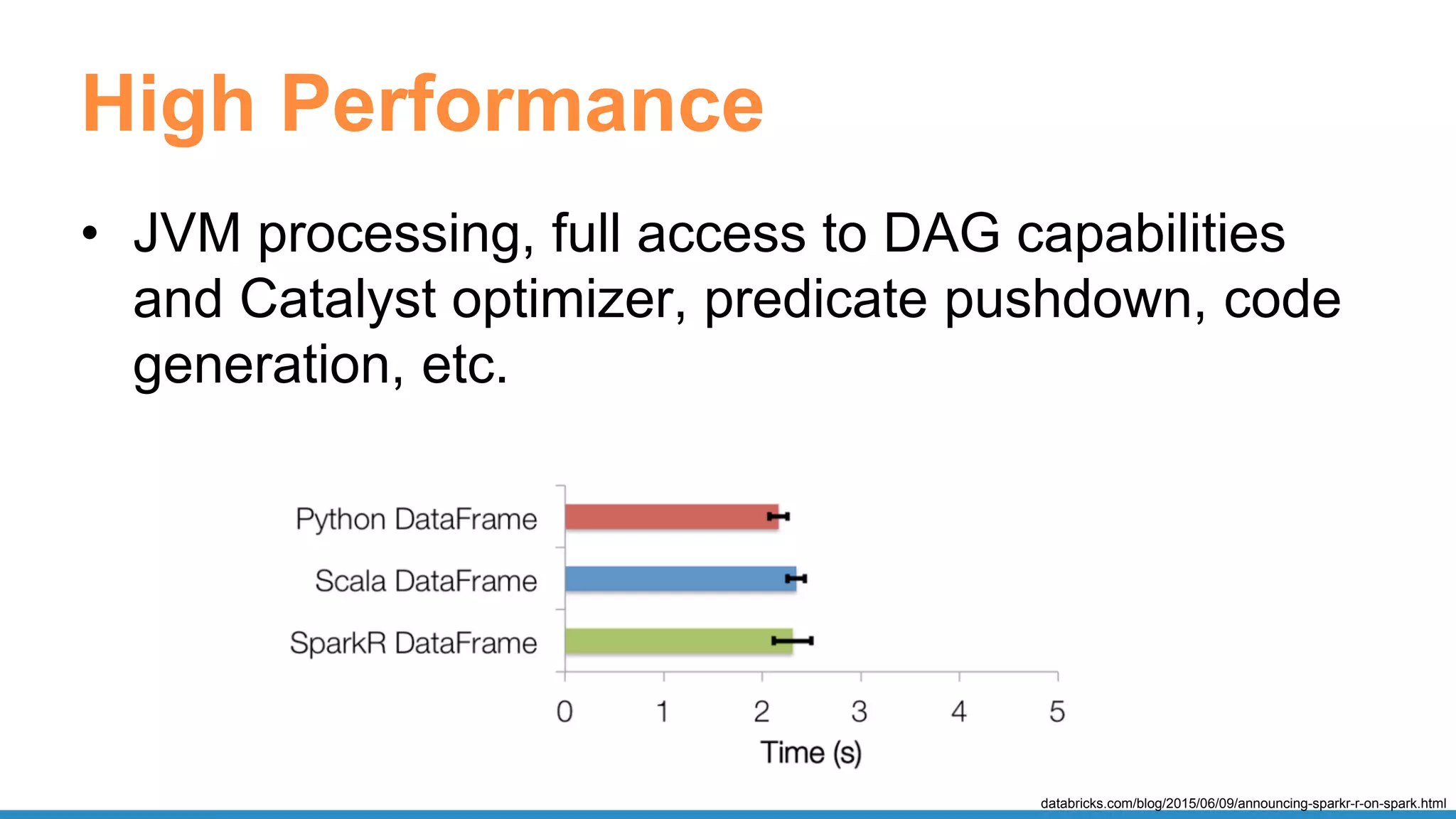
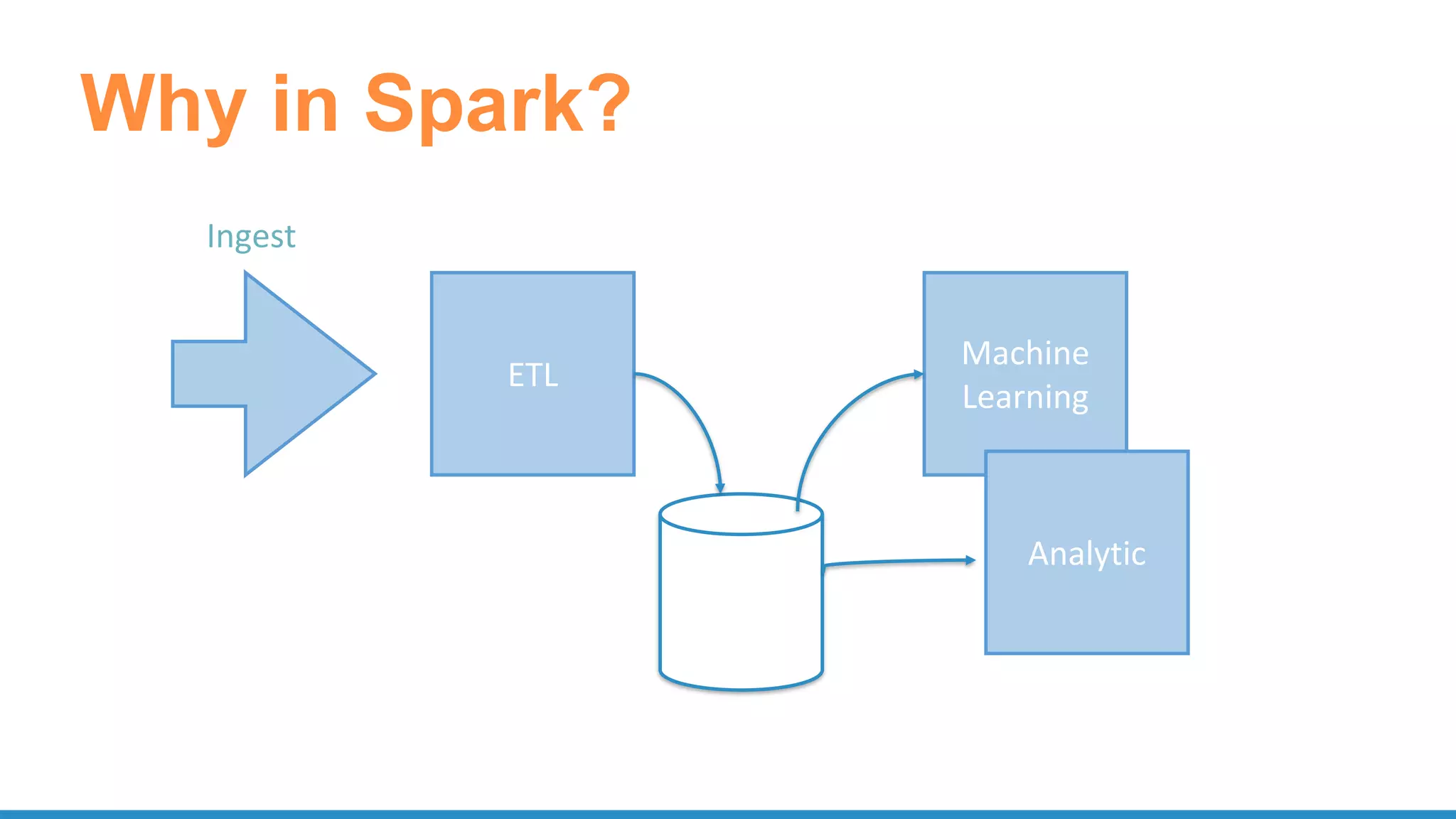
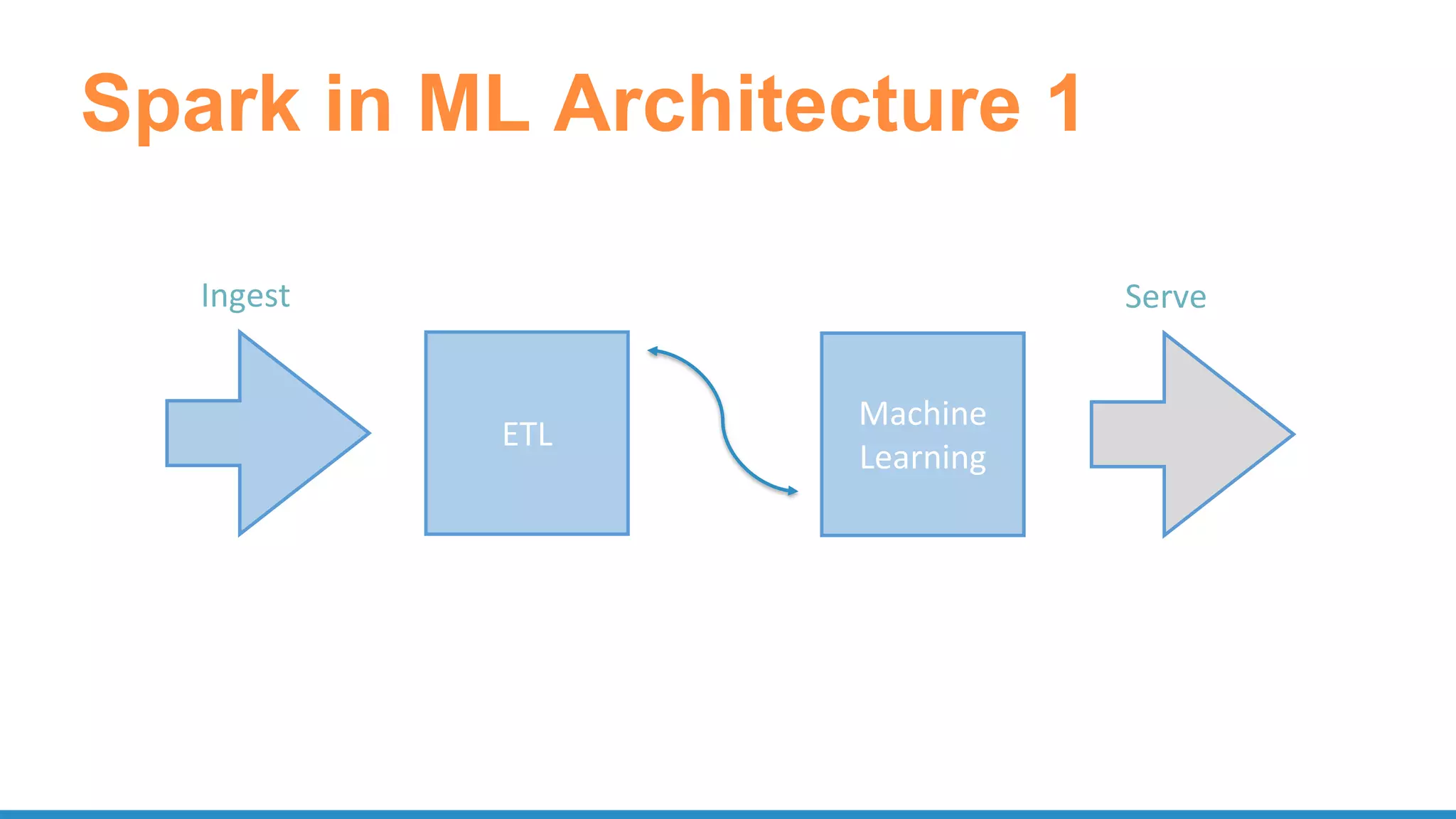
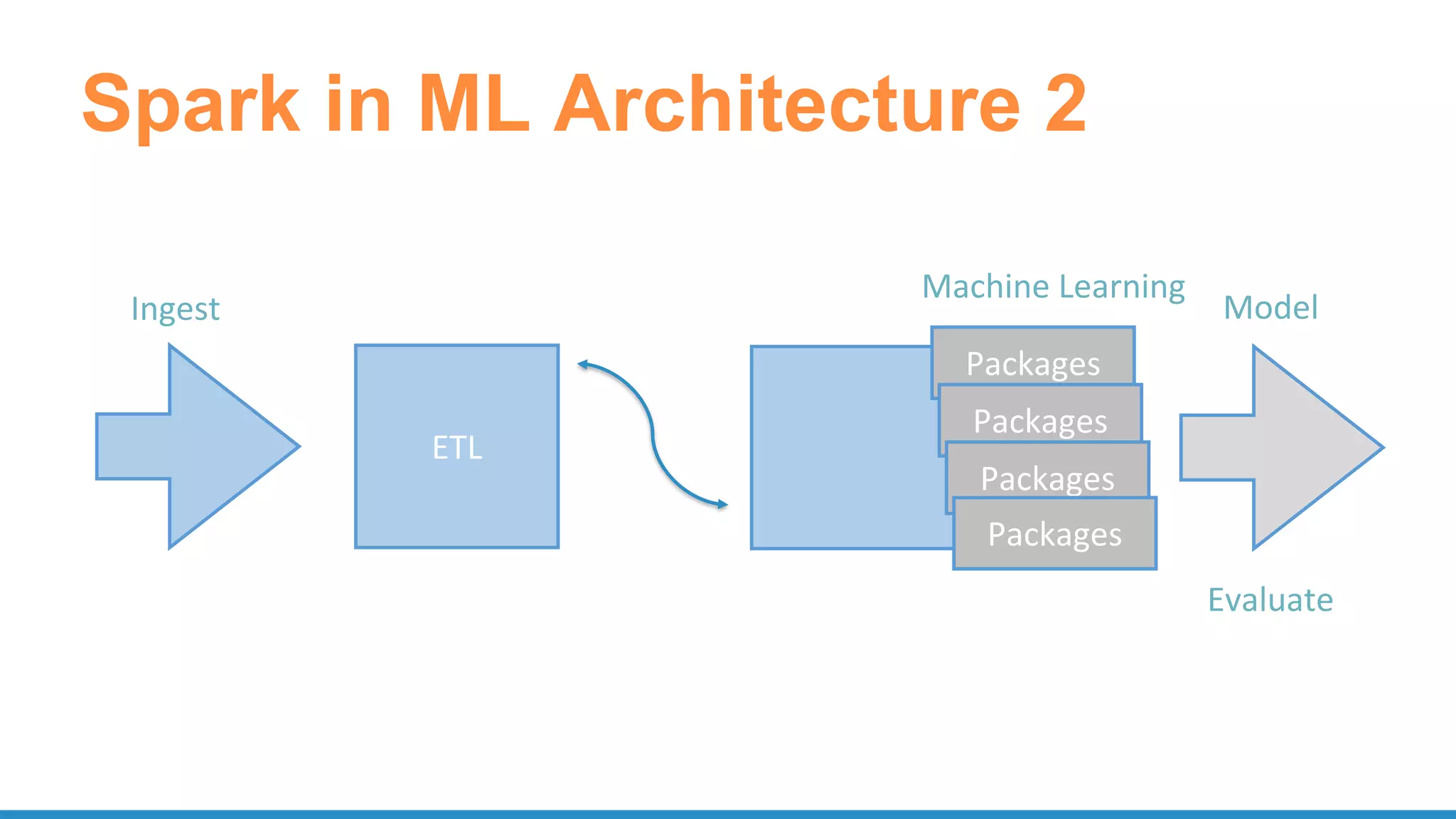
The document outlines the use of Apache Spark for scalable data science applications in Python and R, covering various aspects such as machine learning, data ingestion, and ETL processes. It highlights the architecture and tools available for integrating Spark with popular ML libraries and emphasizes the Spark ML pipeline for efficient model training and evaluation. Additionally, it discusses advanced functionalities such as vectorized user-defined functions (UDFs) and options for implementing deep learning with libraries like BigDL and TensorFrames.









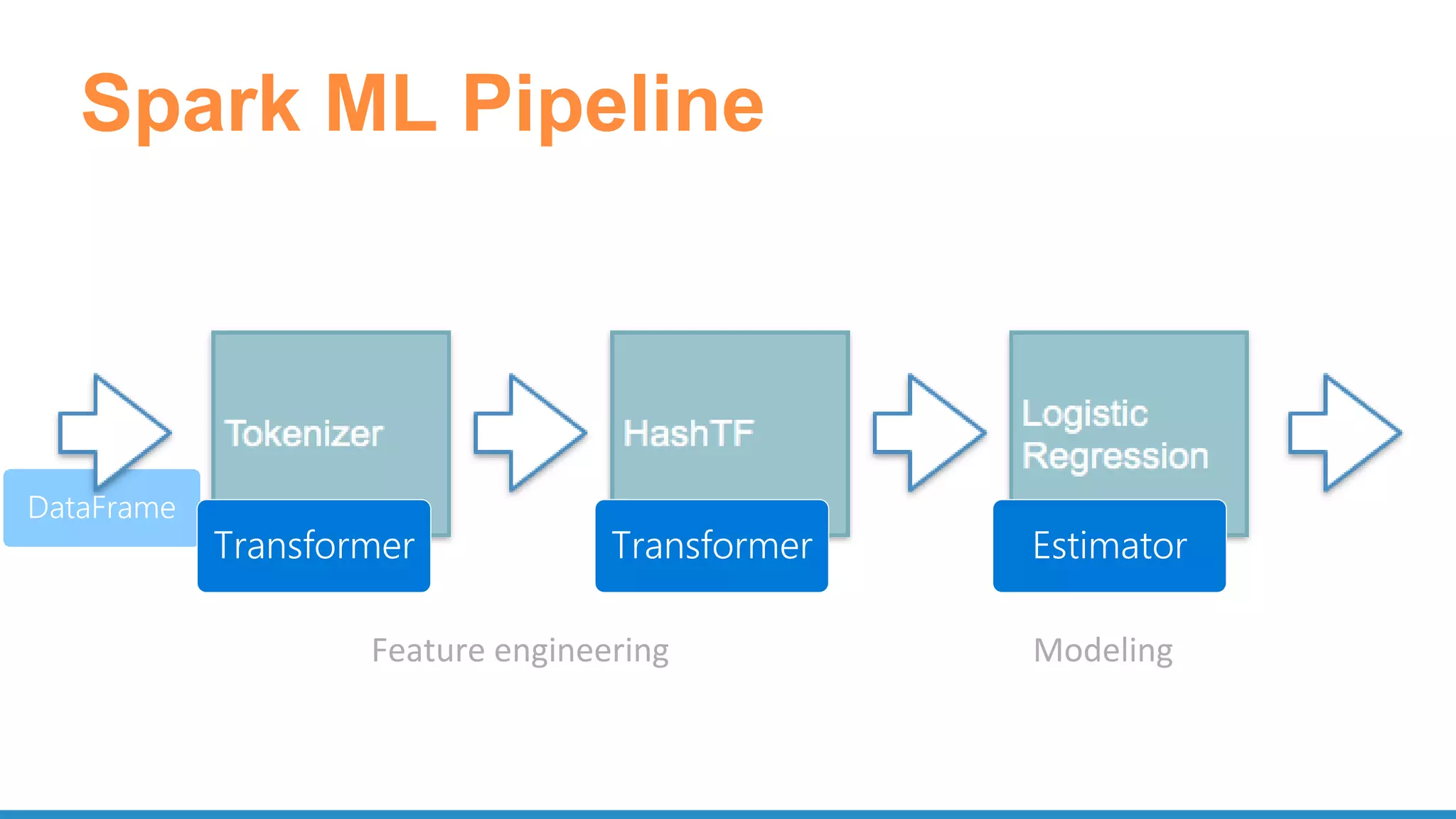

![PySpark ML Pipline Model
tokenizer = Tokenizer(inputCol="text", outputCol="words")
hashingTF = HashingTF(inputCol=tokenizer.getOutputCol(),
outputCol="features")
lr = LogisticRegression(maxIter=10, regParam=0.001)
pipeline = Pipeline(stages=[tokenizer, hashingTF, lr])
# Fit the pipeline to training documents.
model = pipeline.fit(training)
prediction = model.transform(test)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pydatascalabledatasciencepythonrspark-170708220340/75/Scalable-Data-Science-in-Python-and-R-on-Apache-Spark-25-2048.jpg)

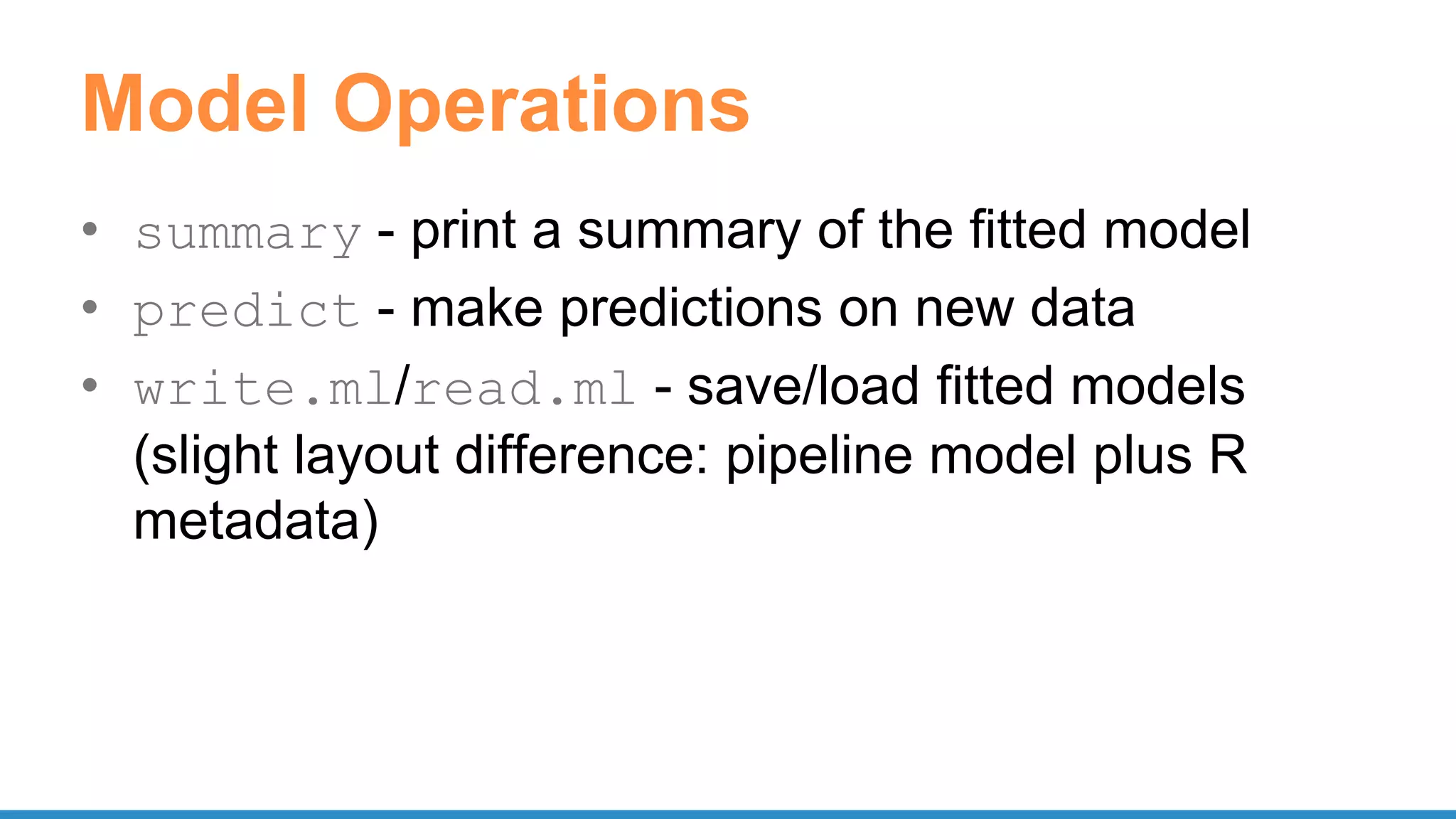
![UDF
• Register function to use in SQL
– spark.udf.register("stringLengthInt", lambda x:
len(x), IntegerType())
spark.sql("SELECT stringLengthInt('test')")
• Function on RDD
– rdd.map(lambda l: str(l.e)[:7])
– rdd.mapPartitions(lambda x: [(1,), (2,), (3,)])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pydatascalabledatasciencepythonrspark-170708220340/75/Scalable-Data-Science-in-Python-and-R-on-Apache-Spark-28-2048.jpg)


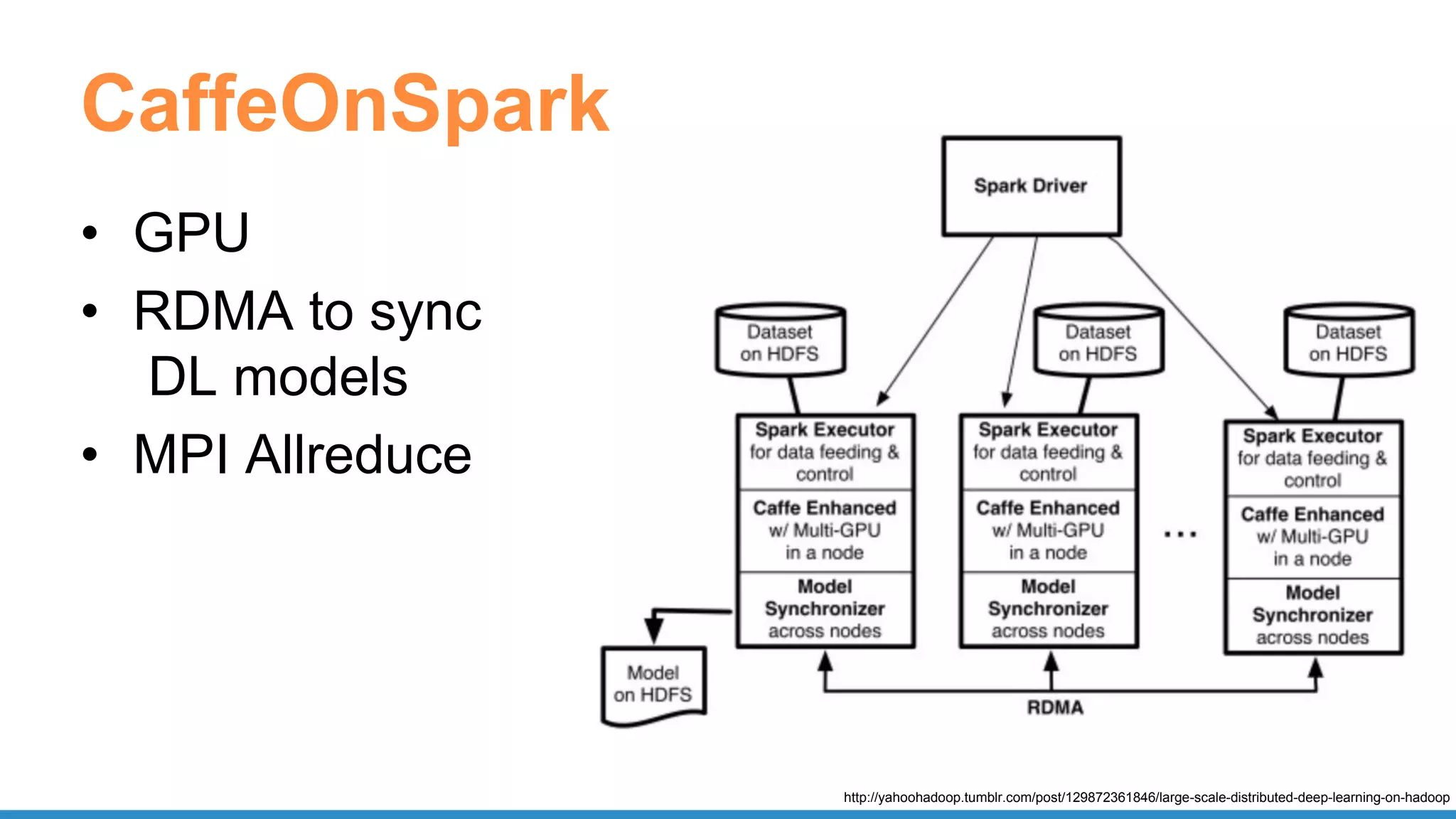
![CaffeOnSpark
def get_predictions(sqlContext, images, model, imagenet, lstmnet, vocab):
rdd = images.mapPartitions(lambda im: predict_caption(im, model, imagenet,
lstmnet, vocab))
...
return sqlContext.createDataFrame(rdd, schema).select("result.id",
"result.prediction")
def predict_caption(list_of_images, model, imagenet, lstmnet, vocab):
out_iterator = []
ce = CaptionExperiment(str(model),str(imagenet),str(lstmnet),str(vocab))
for image in list_of_images:
out_iterator.append(ce.getCaption(image))
return iter(out_iterator)
https://github.com/yahoo/CaffeOnSpark/blob/master/caffe-grid/src/main/python/examples/ImageCaption.py](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pydatascalabledatasciencepythonrspark-170708220340/75/Scalable-Data-Science-in-Python-and-R-on-Apache-Spark-34-2048.jpg)
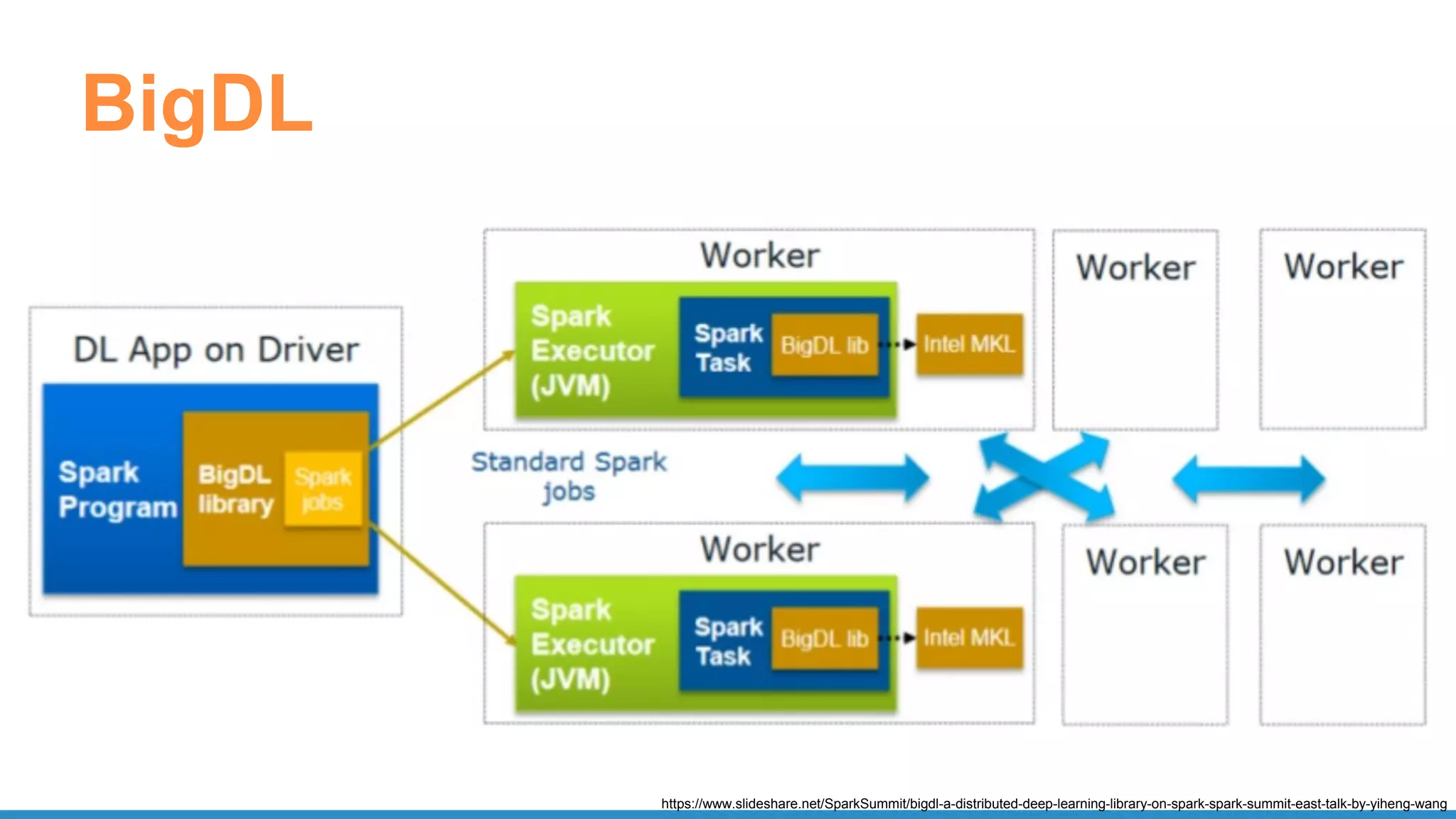

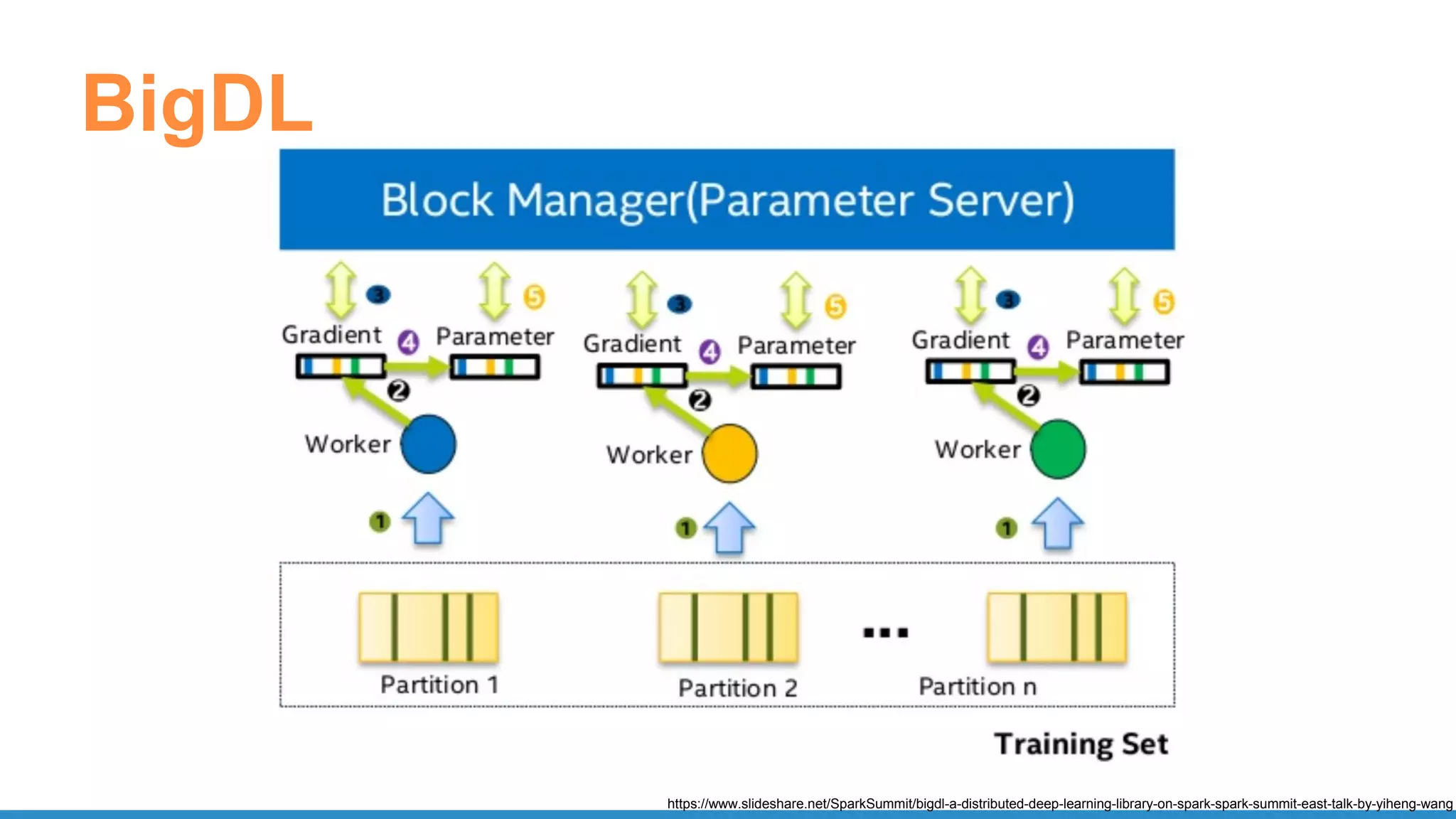
![BigDL - CNN MNIST
def build_model(class_num):
model = Sequential() # Create a LeNet model
model.add(Reshape([1, 28, 28]))
model.add(SpatialConvolution(1, 6, 5, 5).set_name('conv1'))
model.add(Tanh())
model.add(SpatialMaxPooling(2, 2, 2, 2).set_name('pool1'))
model.add(Tanh())
model.add(SpatialConvolution(6, 12, 5, 5).set_name('conv2'))
model.add(SpatialMaxPooling(2, 2, 2, 2).set_name('pool2'))
model.add(Reshape([12 * 4 * 4]))
model.add(Linear(12 * 4 * 4, 100).set_name('fc1'))
model.add(Tanh())
model.add(Linear(100, class_num).set_name('score'))
model.add(LogSoftMax())
return model
https://github.com/intel-analytics/BigDL-Tutorials/blob/master/notebooks/neural_networks/cnn.ipynb
lenet_model = build_model(10)
state = {"learningRate": 0.4,
"learningRateDecay": 0.0002}
optimizer = Optimizer(
model=lenet_model,
training_rdd=train_data,
criterion=ClassNLLCriterion(),
optim_method="SGD",
state=state,
end_trigger=MaxEpoch(20),
batch_size=2048)
trained_model = optimizer.optimize()
predictions = trained_model.predict(test_data)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pydatascalabledatasciencepythonrspark-170708220340/75/Scalable-Data-Science-in-Python-and-R-on-Apache-Spark-38-2048.jpg)
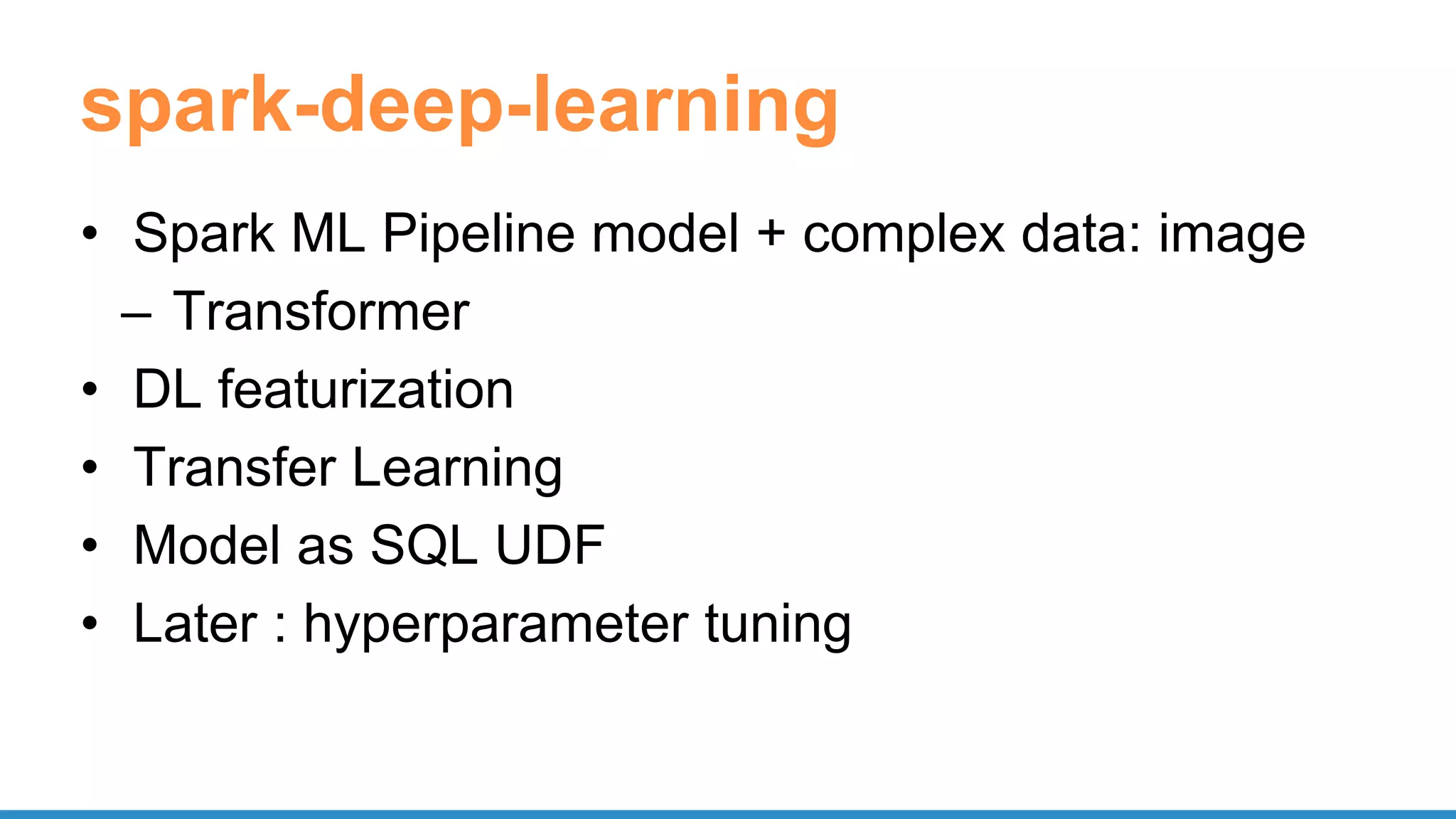
![spark-deep-learning
predictor = DeepImagePredictor(inputCol="image",
outputCol="predicted_labels", modelName="InceptionV3")
predictions_df = predictor.transform(df)
featurizer = DeepImageFeaturizer(modelName="InceptionV3")
p = Pipeline(stages=[featurizer, lr])
sparkdl.registerKerasUDF("img_classify",
"/mymodels/dogmodel.h5")
SELECT image, img_classify(image) label FROM images](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pydatascalabledatasciencepythonrspark-170708220340/75/Scalable-Data-Science-in-Python-and-R-on-Apache-Spark-43-2048.jpg)

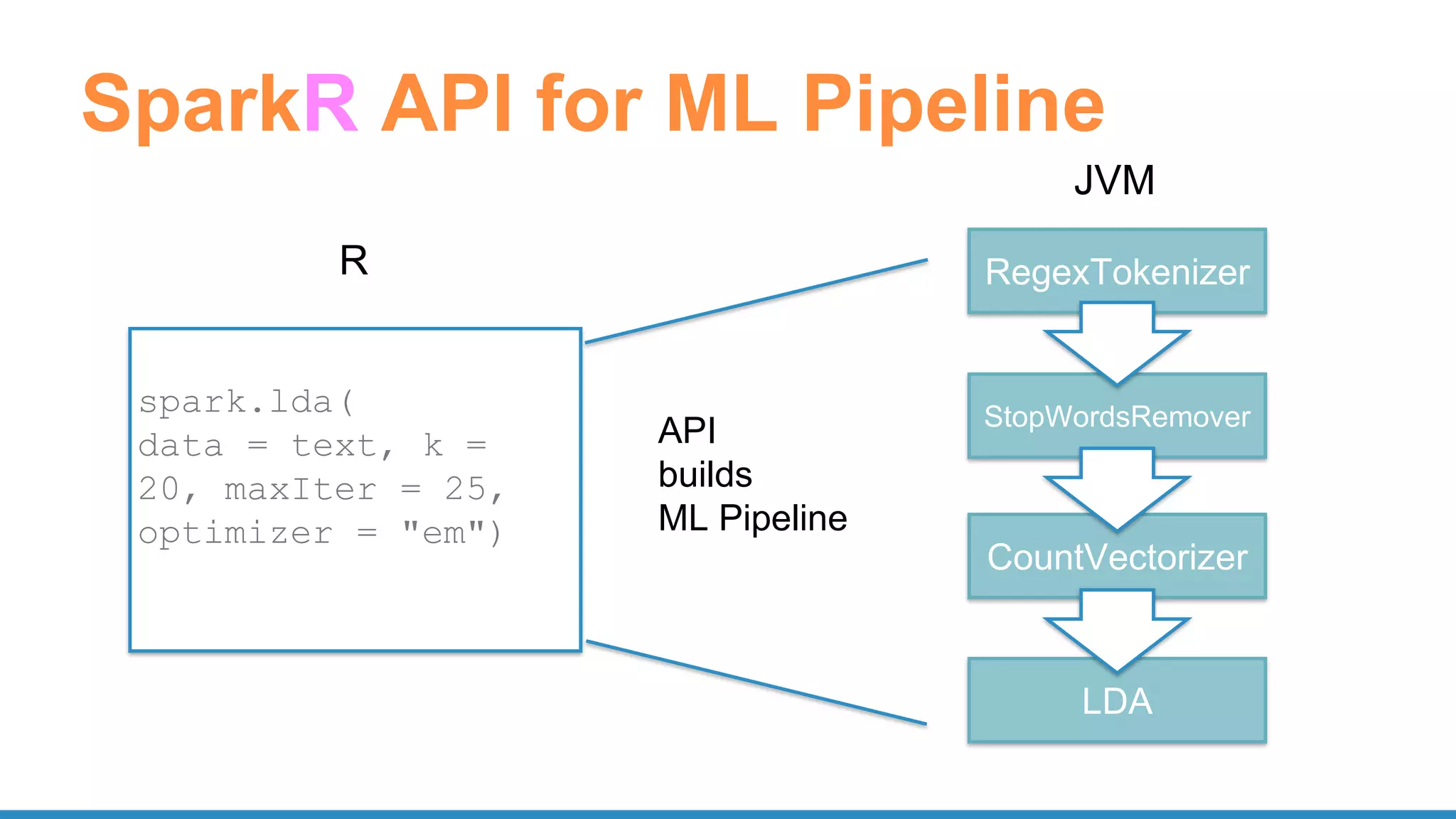

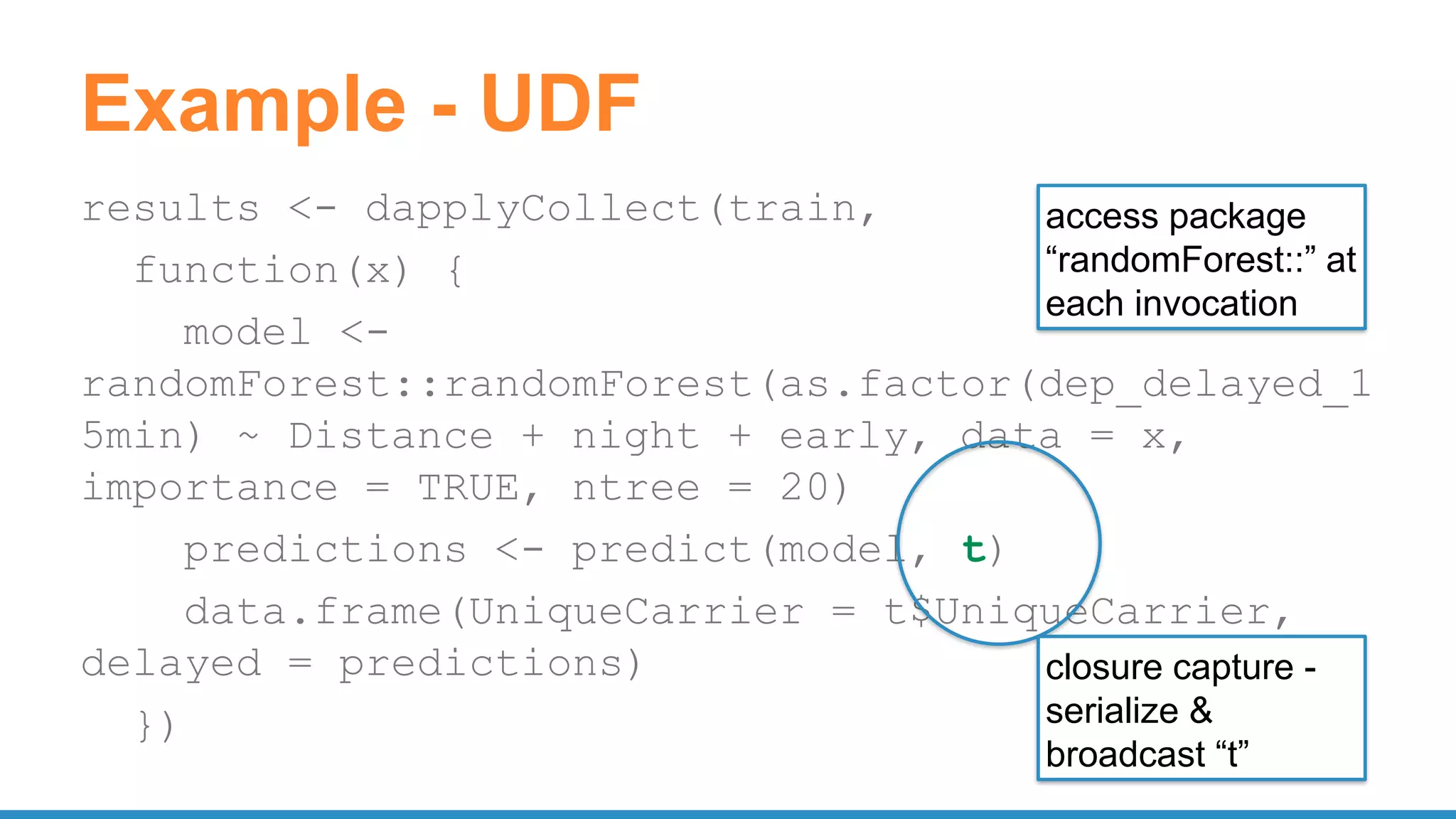



![UDF: model training tensorflow
train <- function(step) {
library(tensorflow)
sess <- tf$InteractiveSession()
...
result <- sess$run(list(merged, train_step),
feed_dict = feed_dict(TRUE))
summary <- result[[1]]
train_writer$add_summary(summary, step)
step
}
spark.lapply(1:20000, train)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pydatascalabledatasciencepythonrspark-170708220340/75/Scalable-Data-Science-in-Python-and-R-on-Apache-Spark-64-2048.jpg)