The document discusses various types and constructs in Scala, including static and trait types, type parameters, compound and structural types, and phantom types. It illustrates type variance, type bounds, and higher-kinded types, explaining concepts through numerous code examples. The presentation focuses on type linearization, ad-hoc polymorphism, and type classes, providing a comprehensive overview of Scala's type system.











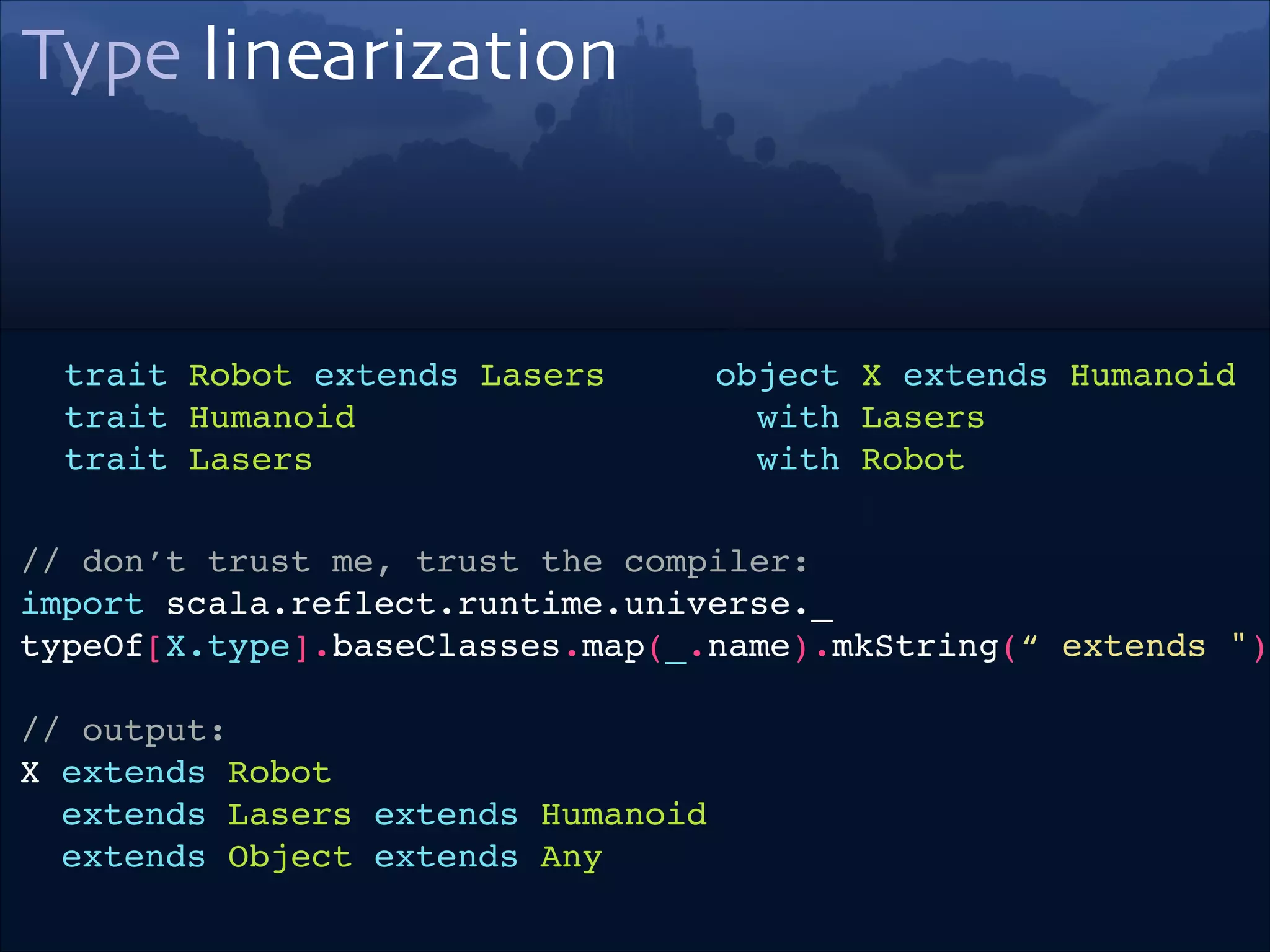
![Type linearization
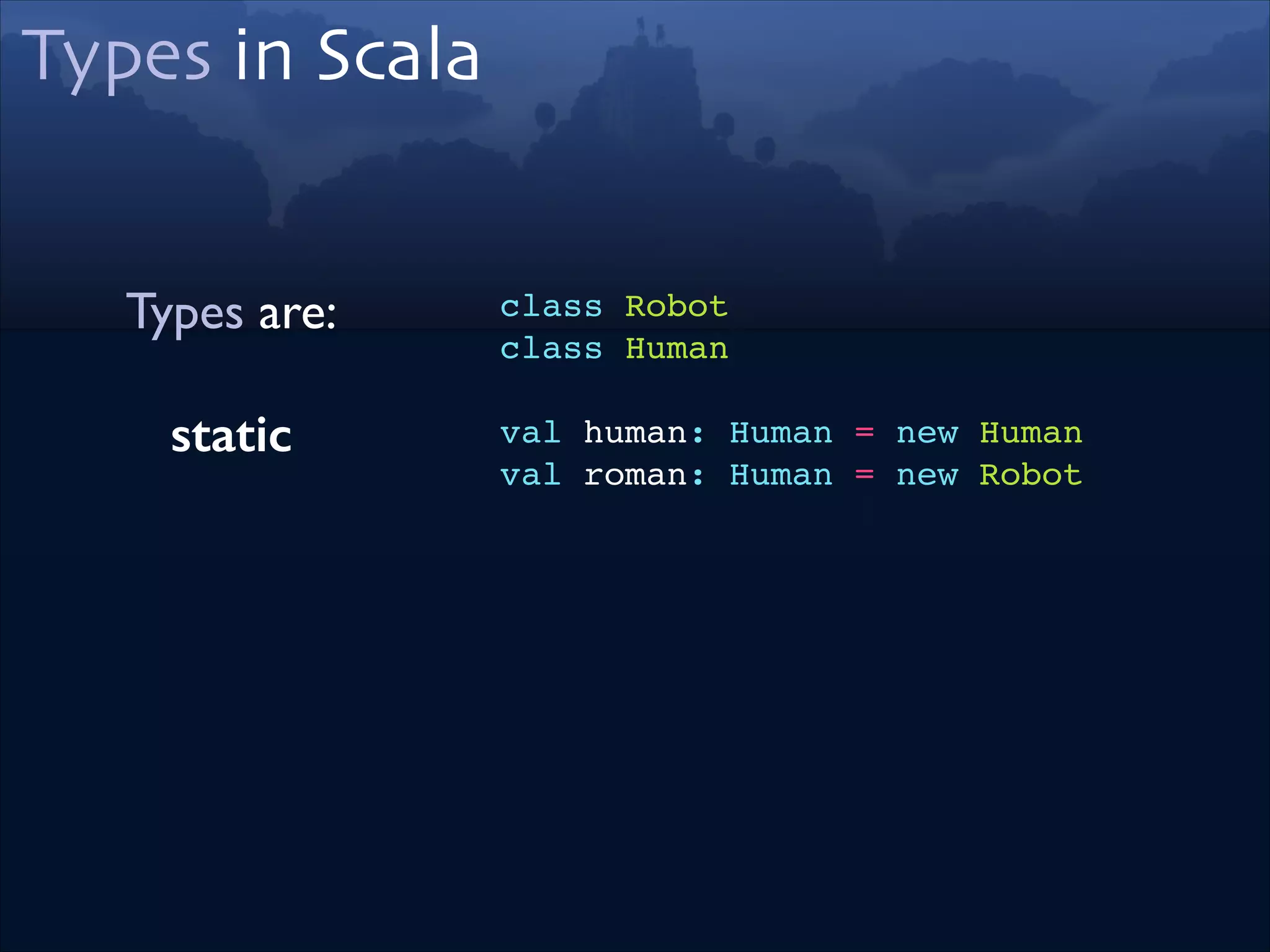
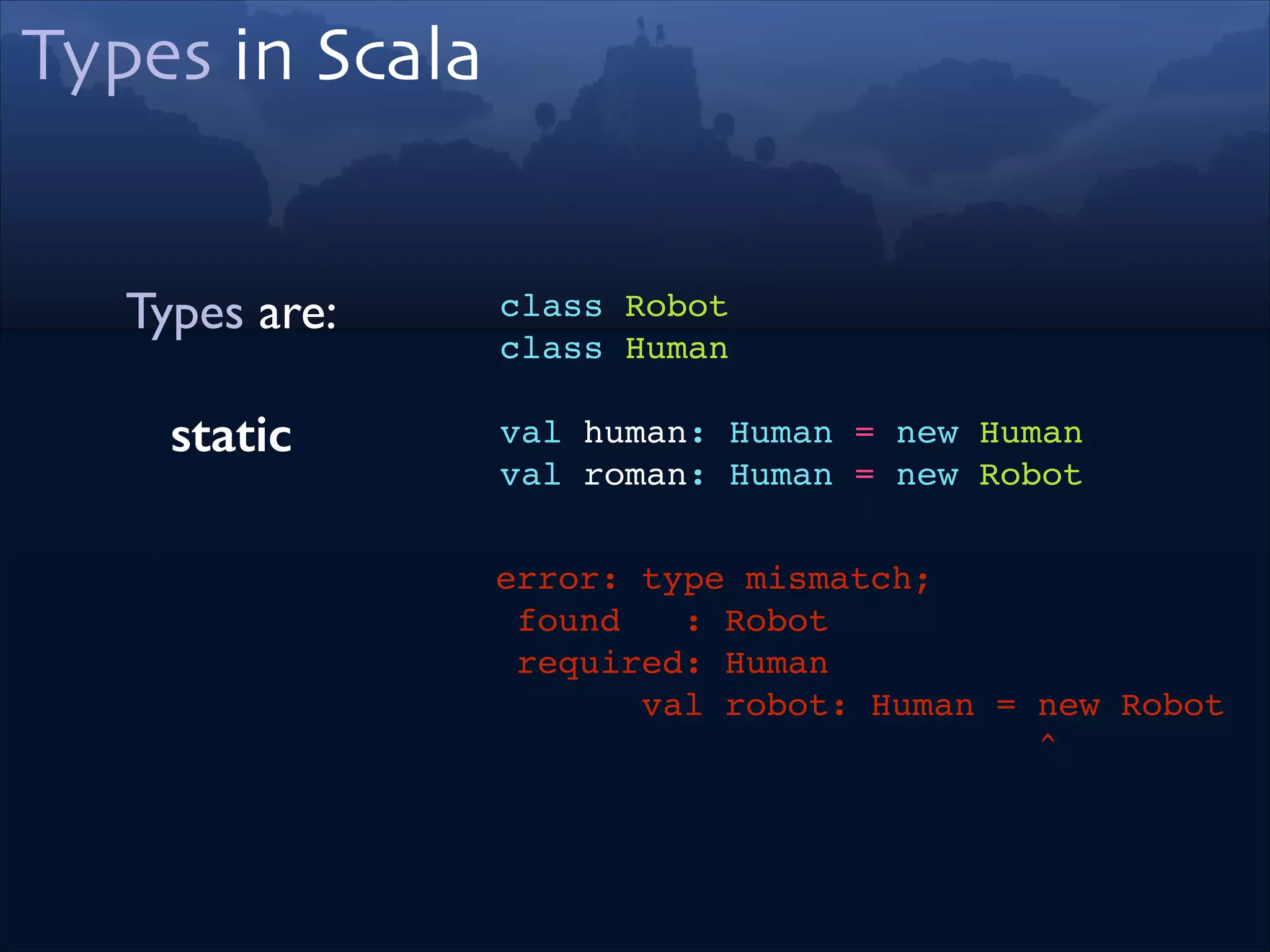
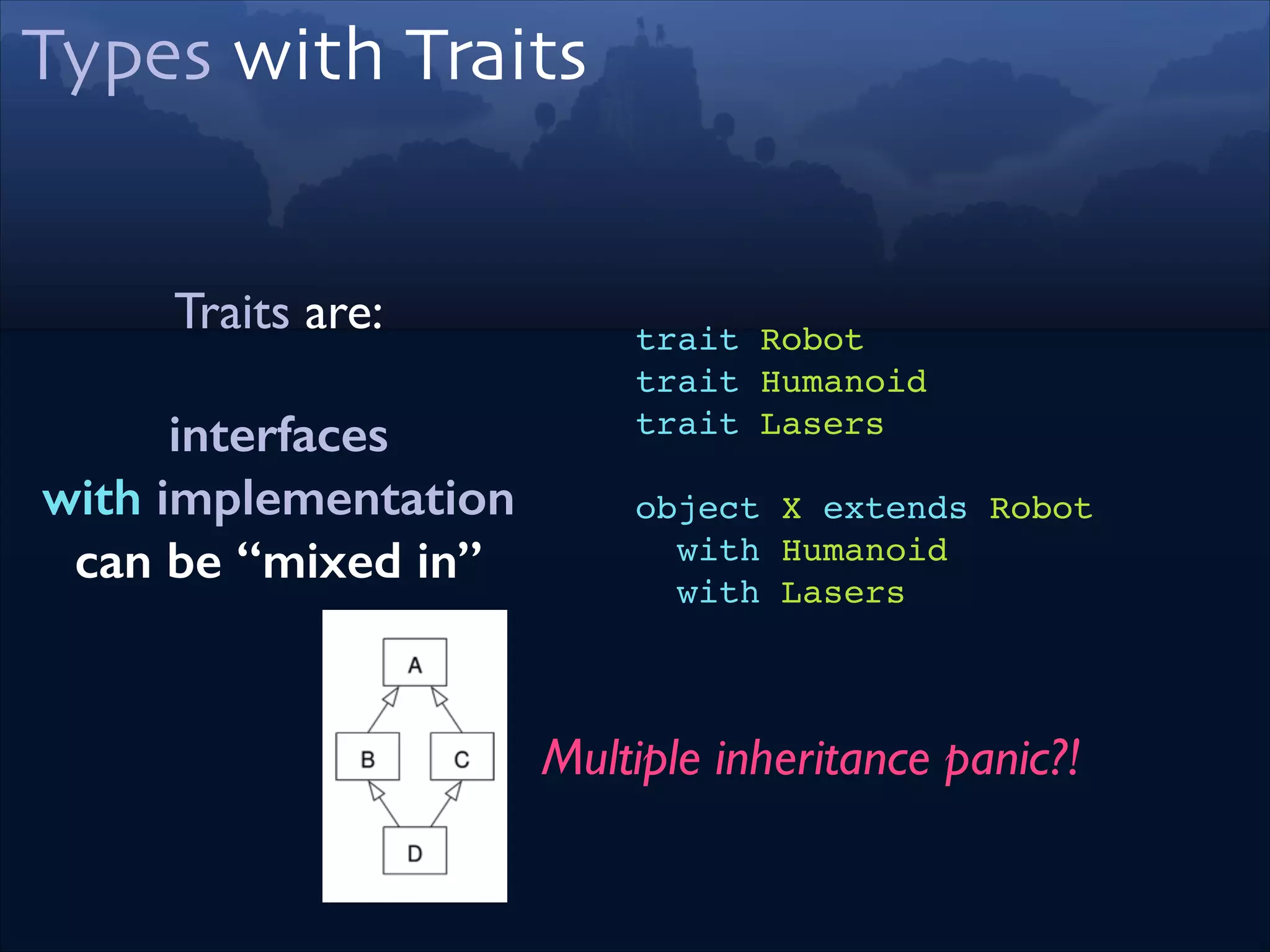
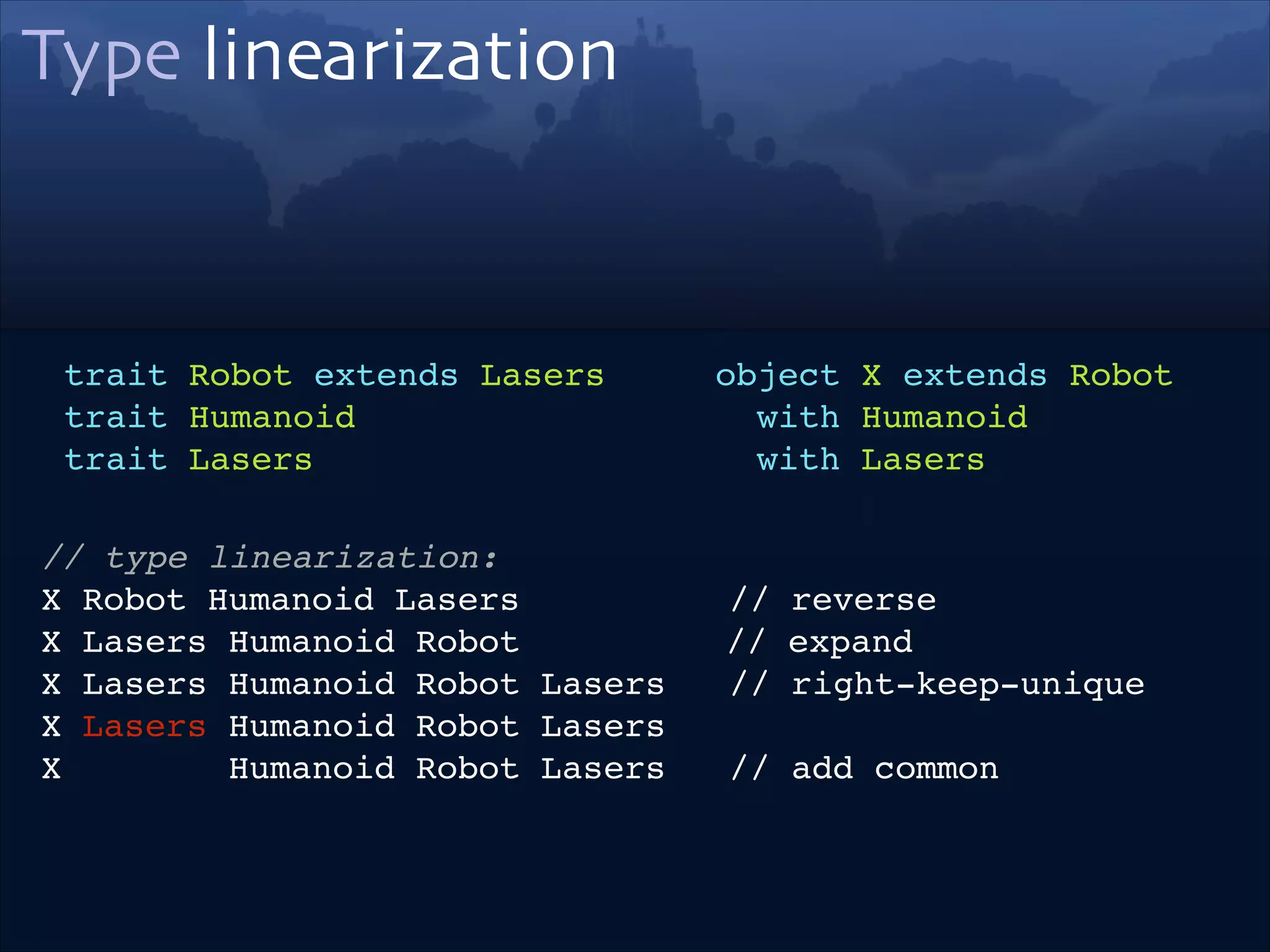
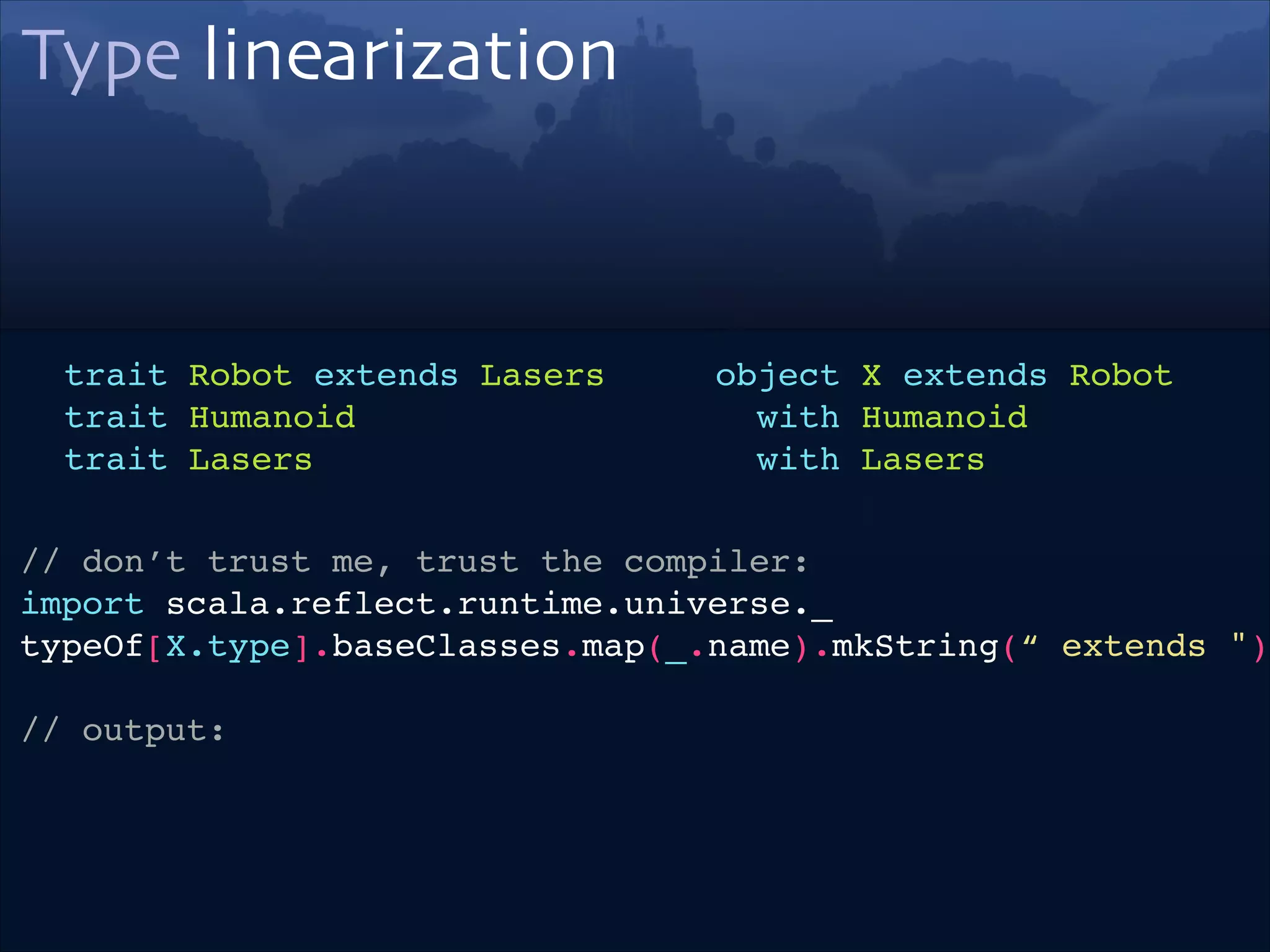
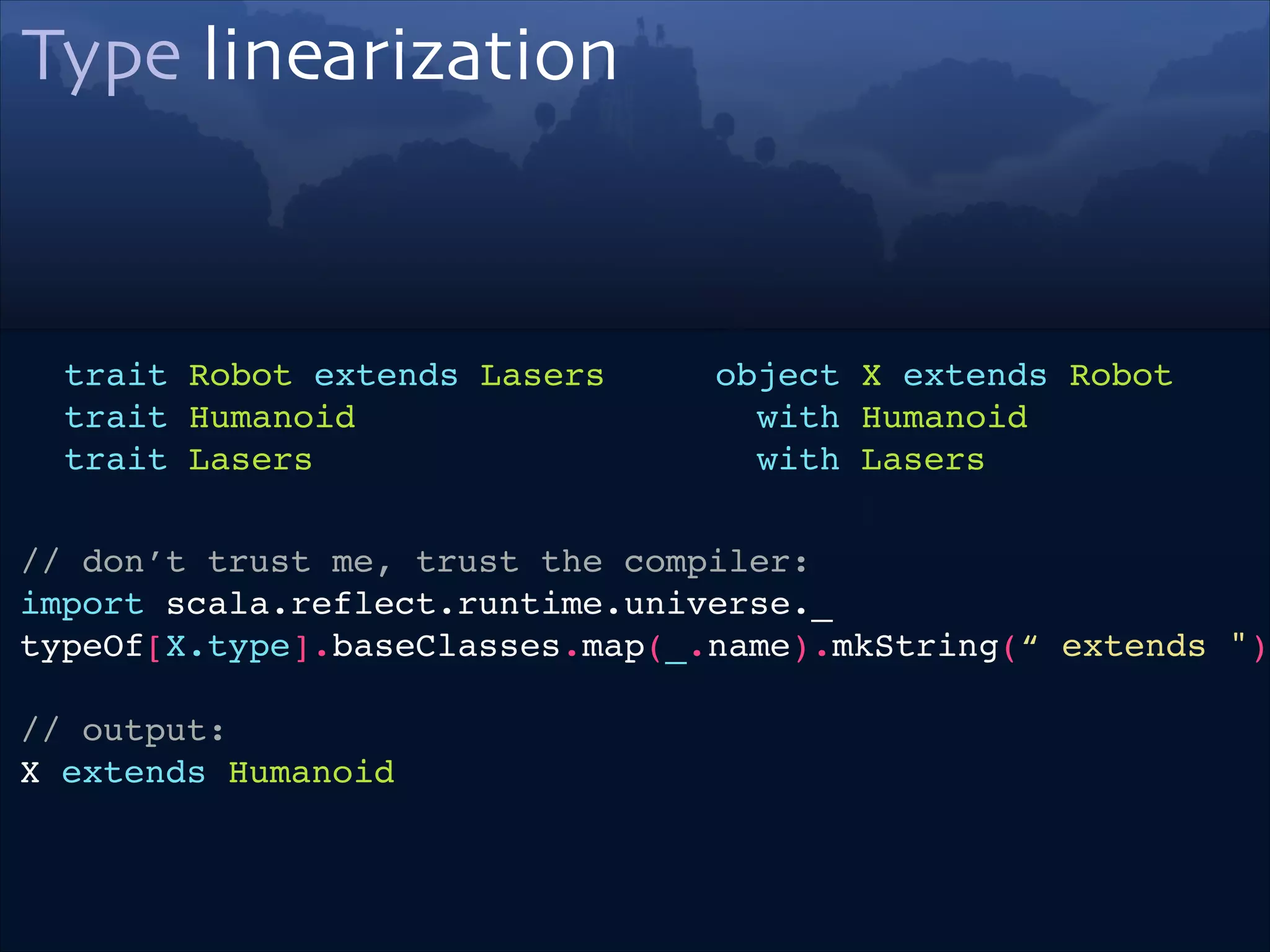
trait Robot extends Lasers!
trait Humanoid!
trait Lasers
object X extends Robot !
with Humanoid!
with Lasers
// don’t trust me, trust the compiler:!
import scala.reflect.runtime.universe._!
typeOf[X.type].baseClasses.map(_.name).mkString(“ extends ")!
!
// output:!
X extends Humanoid !
extends Robot extends Lasers !
extends Object extends Any!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-16-2048.jpg)

![Type linearization
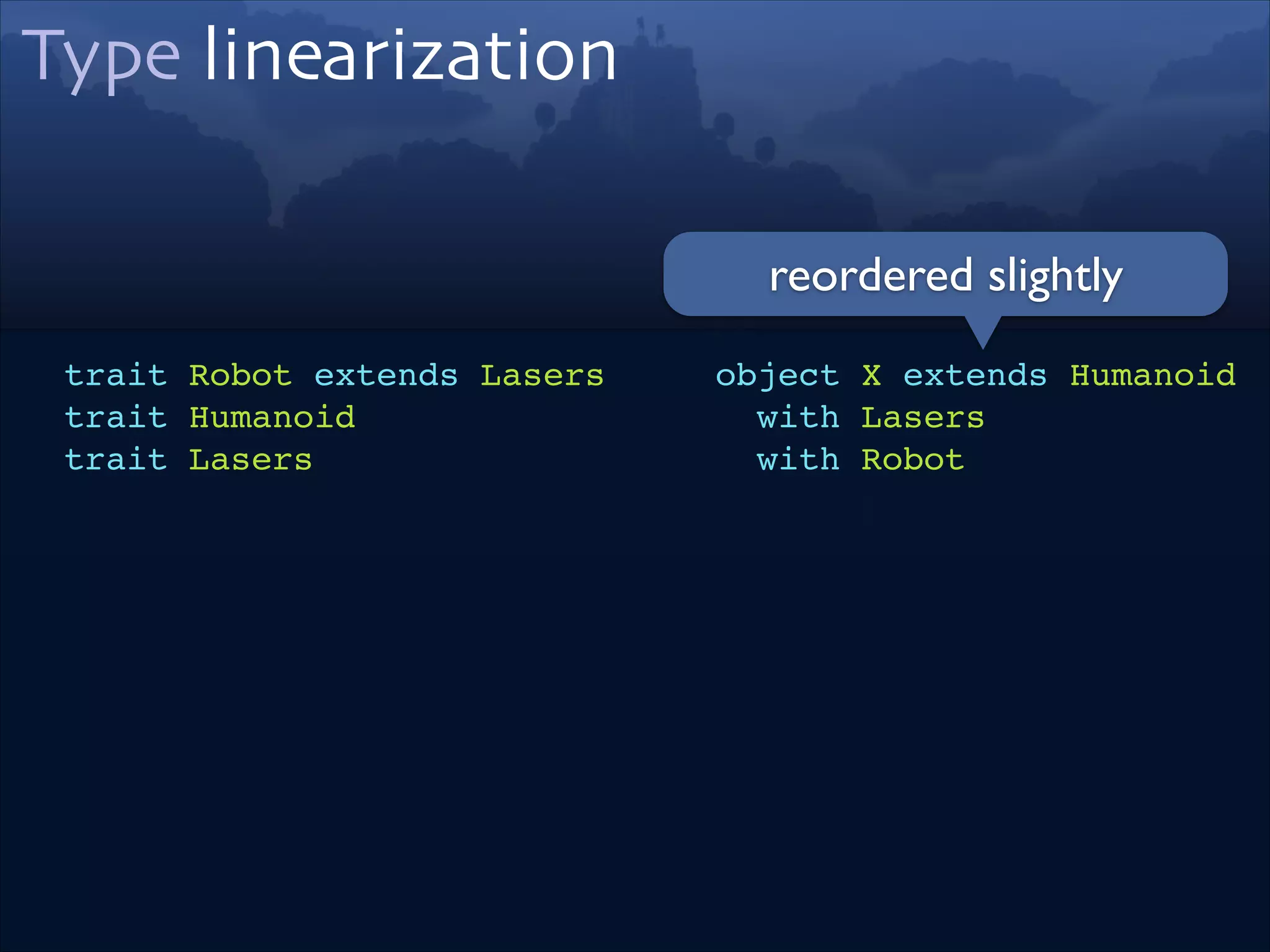
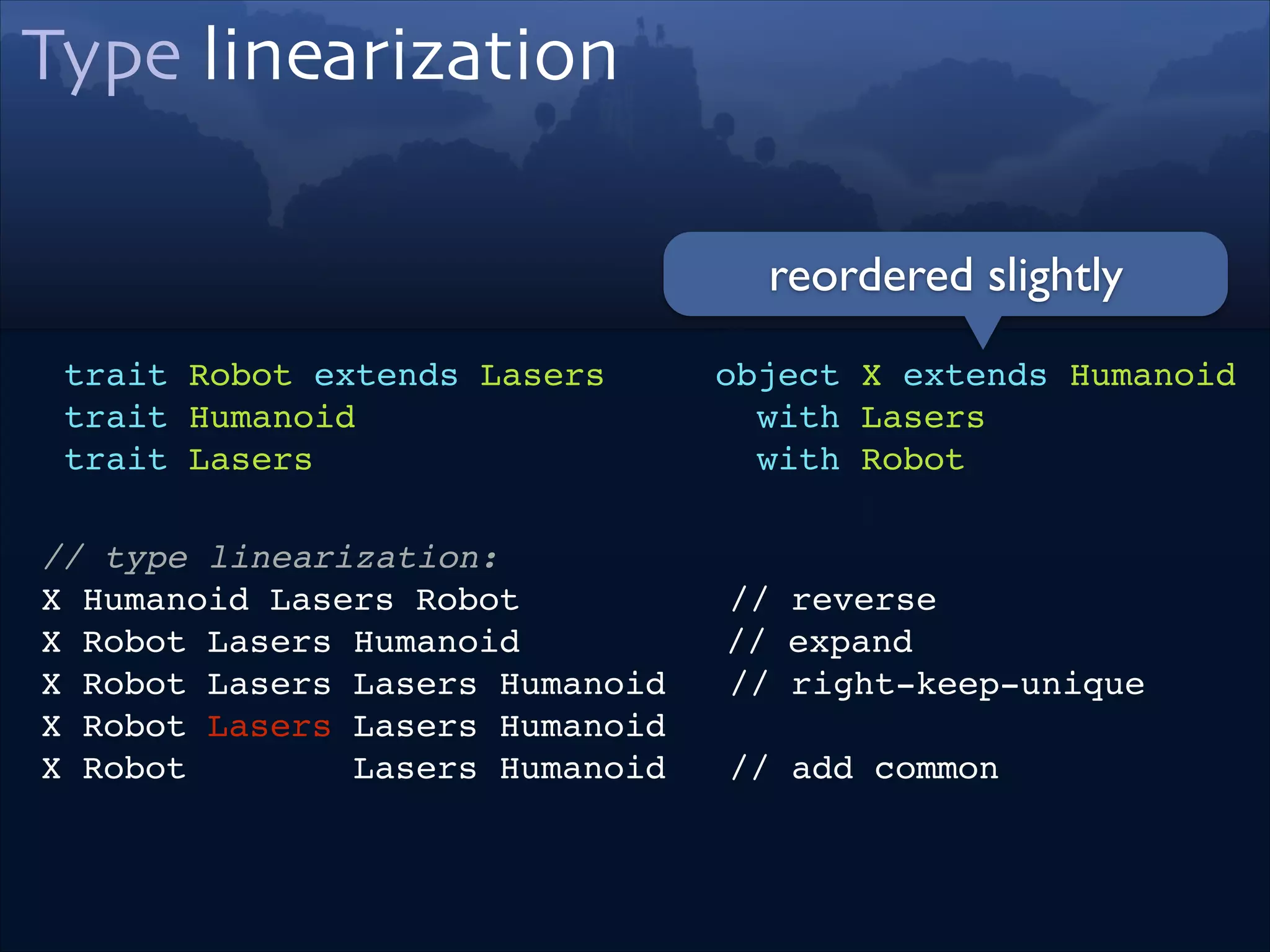
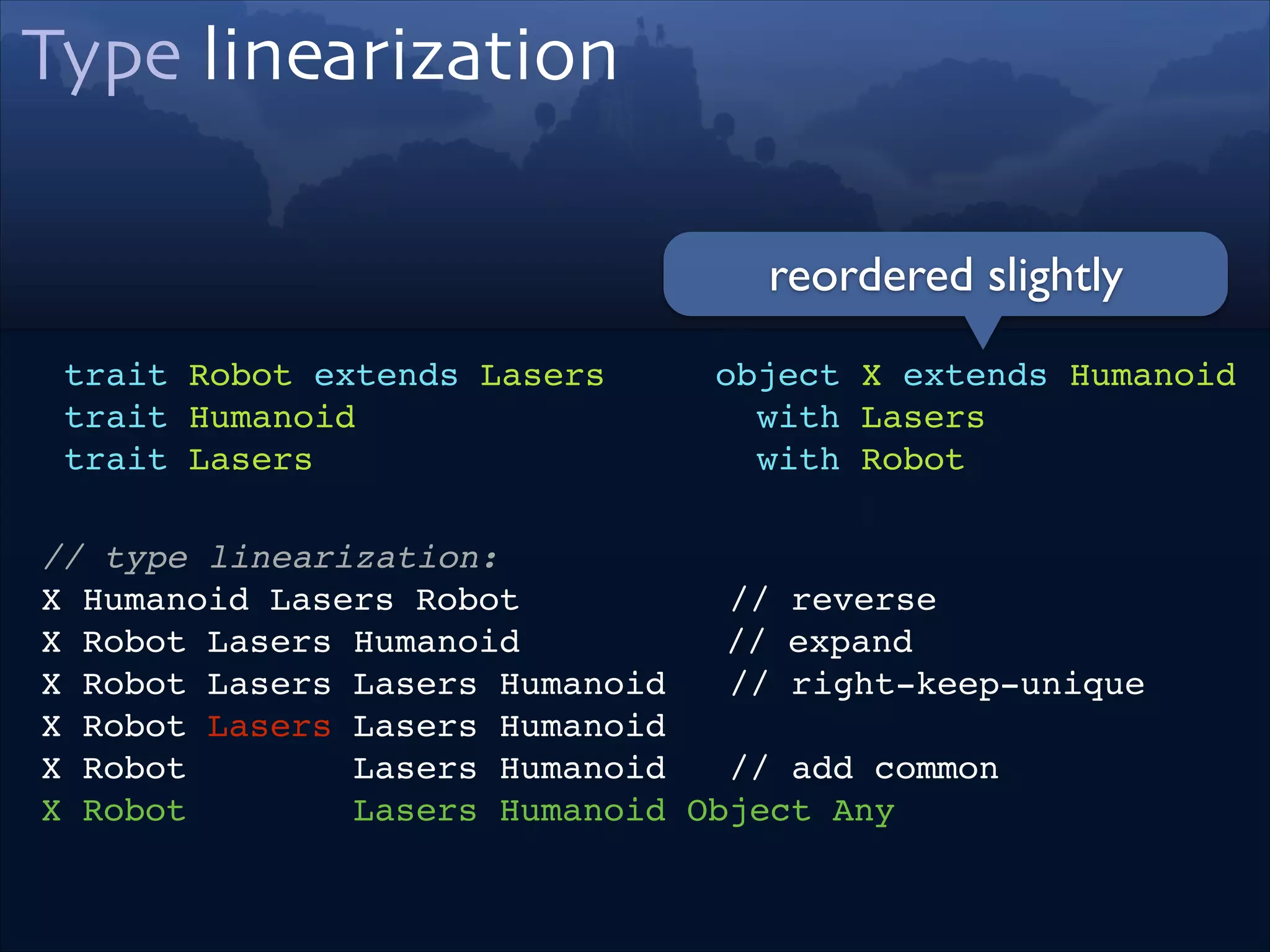
trait Robot extends Lasers!
trait Humanoid!
trait Lasers
object X extends Humanoid!
with Lasers!
with Robot
// don’t trust me, trust the compiler:!
import scala.reflect.runtime.universe._!
typeOf[X.type].baseClasses.map(_.name).mkString(“ extends ")!
!
// output:!
X extends Robot !
extends Lasers extends Humanoid!
extends Object extends Any!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-18-2048.jpg)







![!
Type Parameters
[Type Variance]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-29-2048.jpg)
![!
Type Parameters
[Type Variance]
<: Type Bounds >:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-30-2048.jpg)
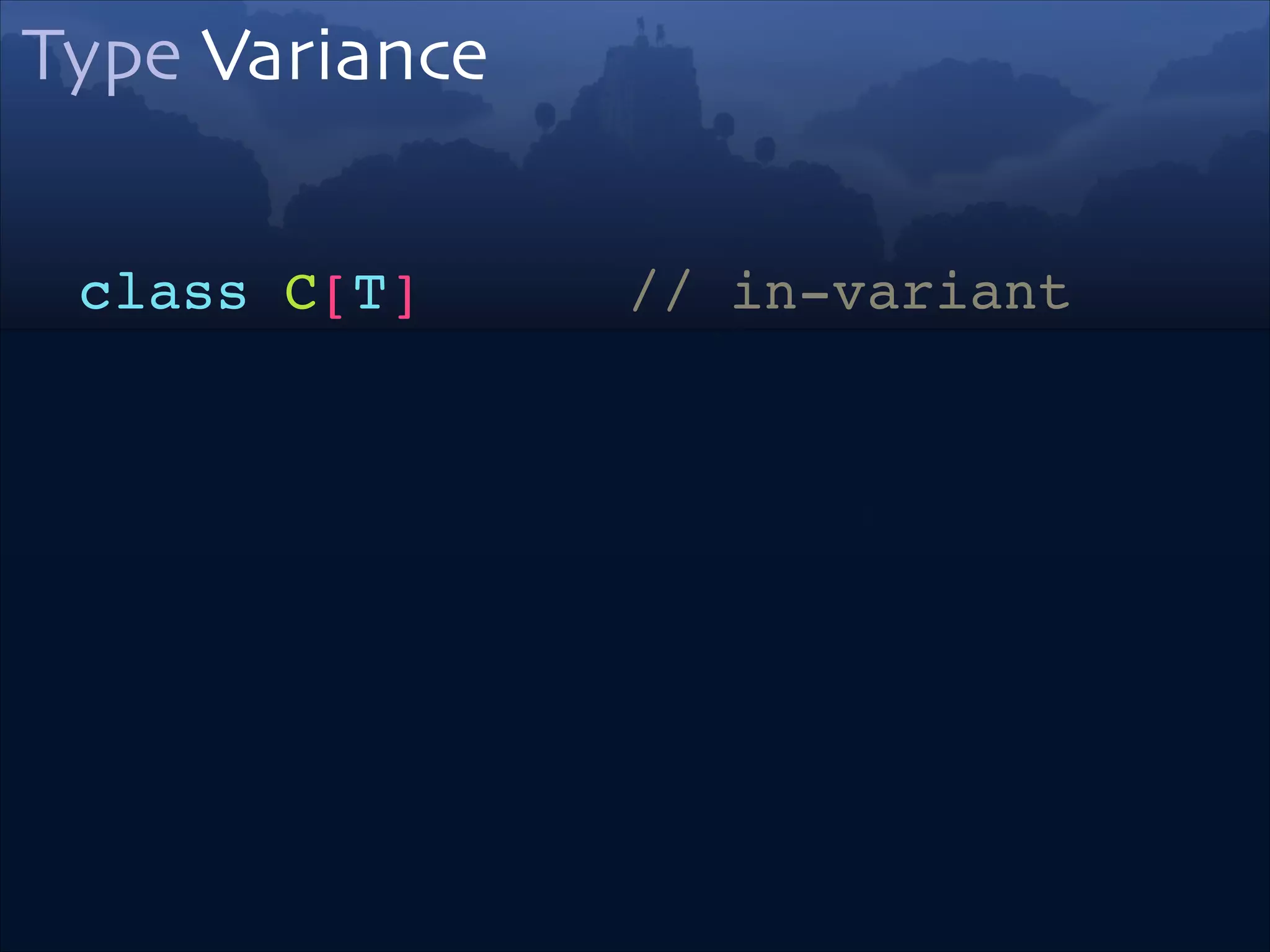
![Type Parameters
type constructor
class C[T]
type parameter](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-31-2048.jpg)
![Type Variance
class C[T] // in-variant!
class C[+T] // co-variant!
class C[-T] // contra-variant!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-32-2048.jpg)
![Type Variance
class C[T]
// in-variant
val x: C[Parent] = new C[Parent]!
!
val x: C[Parent] = new C[Bottom]!
error: type mismatch; found: C[Bottom] required: C[Parent]!
Note: Bottom <: Parent, but class C is invariant in type A.!
You may wish to define A as +A instead. (SLS 4.5)!
!
val x: C[Bottom] = new C[Parent]!
error: type mismatch; found: C[Parent] required: C[Bottom]!
Note: Parent >: Bottom, but class C is invariant in type A.!
You may wish to define A as -A instead. (SLS 4.5)!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-34-2048.jpg)
![Type Variance
class C[+T]
// co-variant
val x: C[Parent] = new C[Parent]!
!
val x: C[Parent] = new C[Bottom]!
!
val x: C[Bottom] = new C[Parent]!
error: type mismatch; found: C[Parent] required: C[Bottom]!
!
!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-35-2048.jpg)
![Type Variance
class C[-T]
// contra-variant
val x: C[Parent] = new C[Parent]!
!
val x: C[Parent] = new C[Bottom]!
error: type mismatch; found: C[Bottom] required: C[Parent]!
!
val x: C[Bottom] = new C[Parent]!
!
!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-36-2048.jpg)




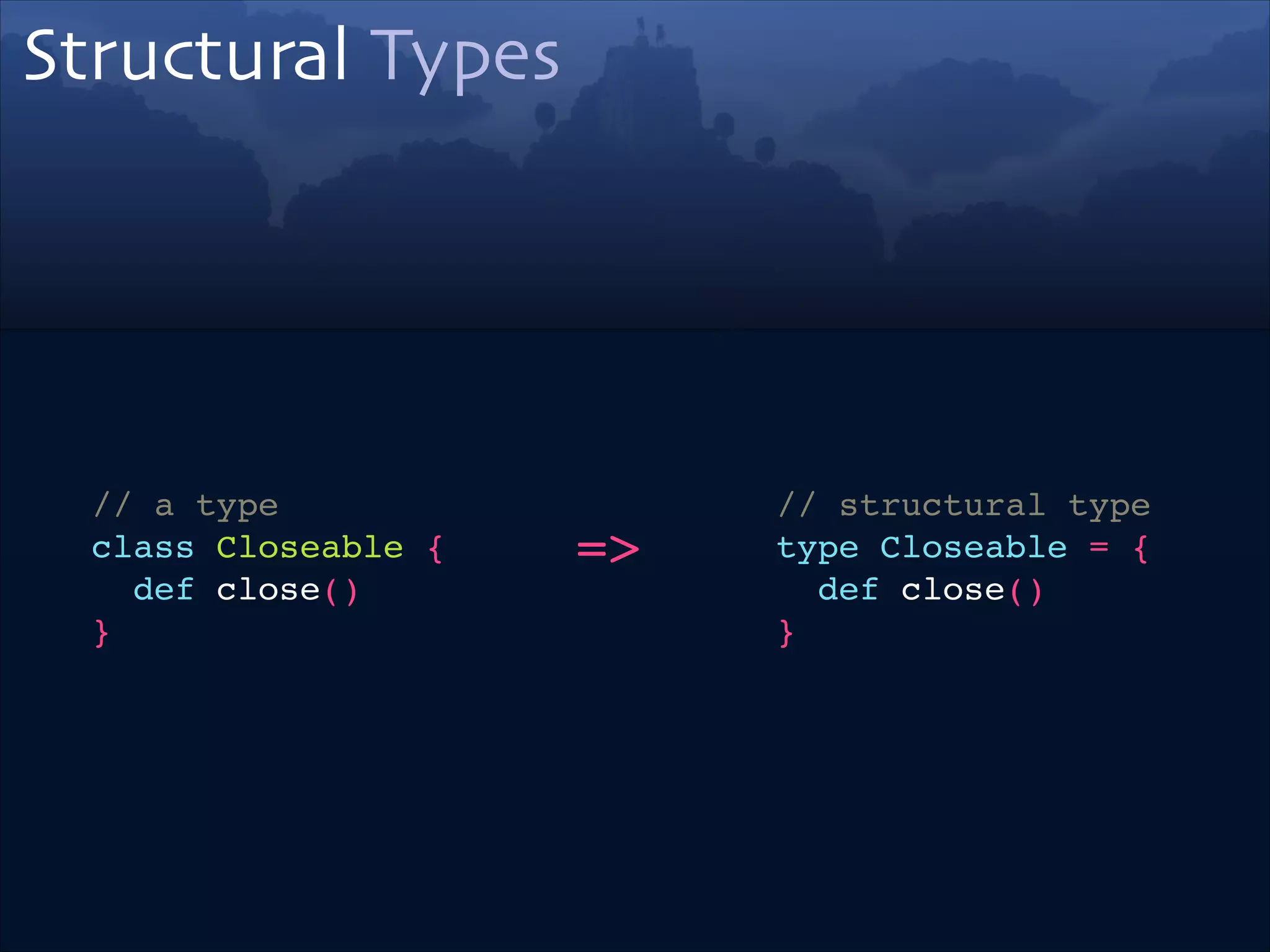
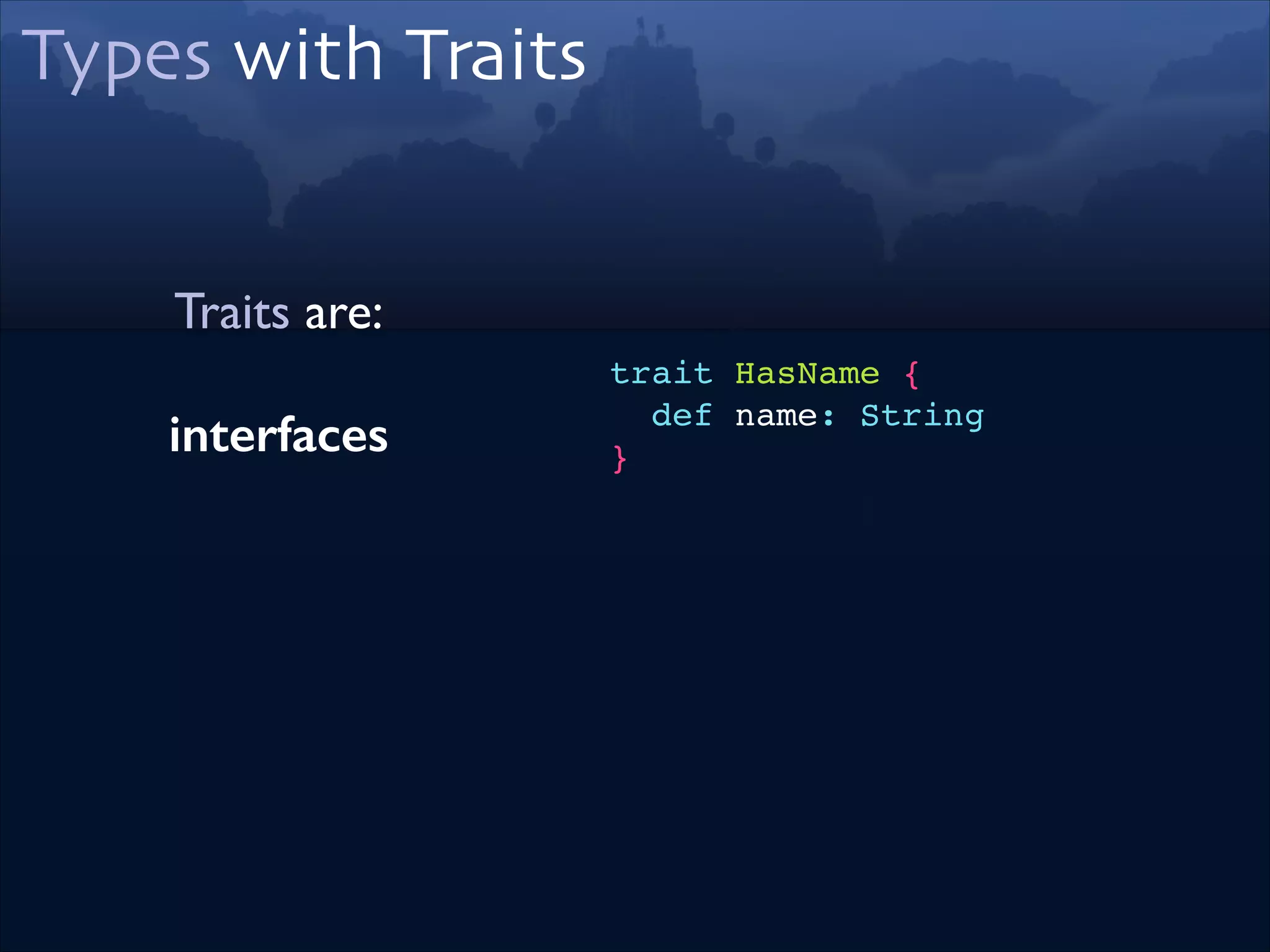
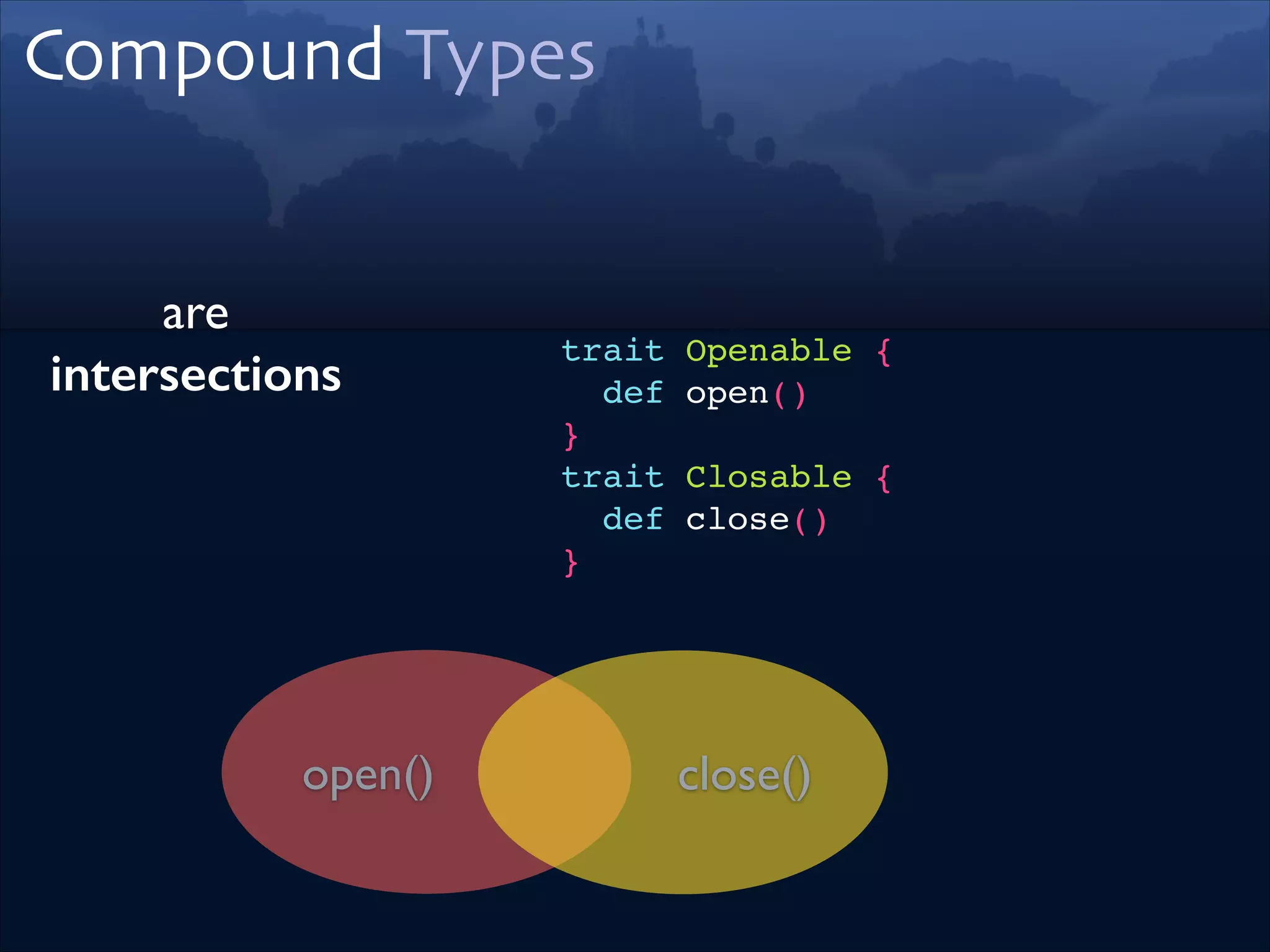
![Type Member
Same goal as
Type Parameter
if List was using Type Params
trait StringList!
extends List[String]
=>
trait StringList !
extends List {!
type A = String!
}
if List was using Type Members](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-43-2048.jpg)

![Without Type Alias
“1st” and “2nd” type param
ALL HOPE IS LOST!
object `bytes -> string` !
extends Builder[Array[Byte], String] {!
!
def make(in: Array[Byte]): String = new String(in)!
}!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-46-2048.jpg)
![Without Type Alias
“1st” and “2nd” type param
Some meaning is lost!
object `bytes -> string` !
extends Builder[Array[Byte], String] {!
!
def make(in: Array[Byte]): String = new String(in)!
}!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-47-2048.jpg)
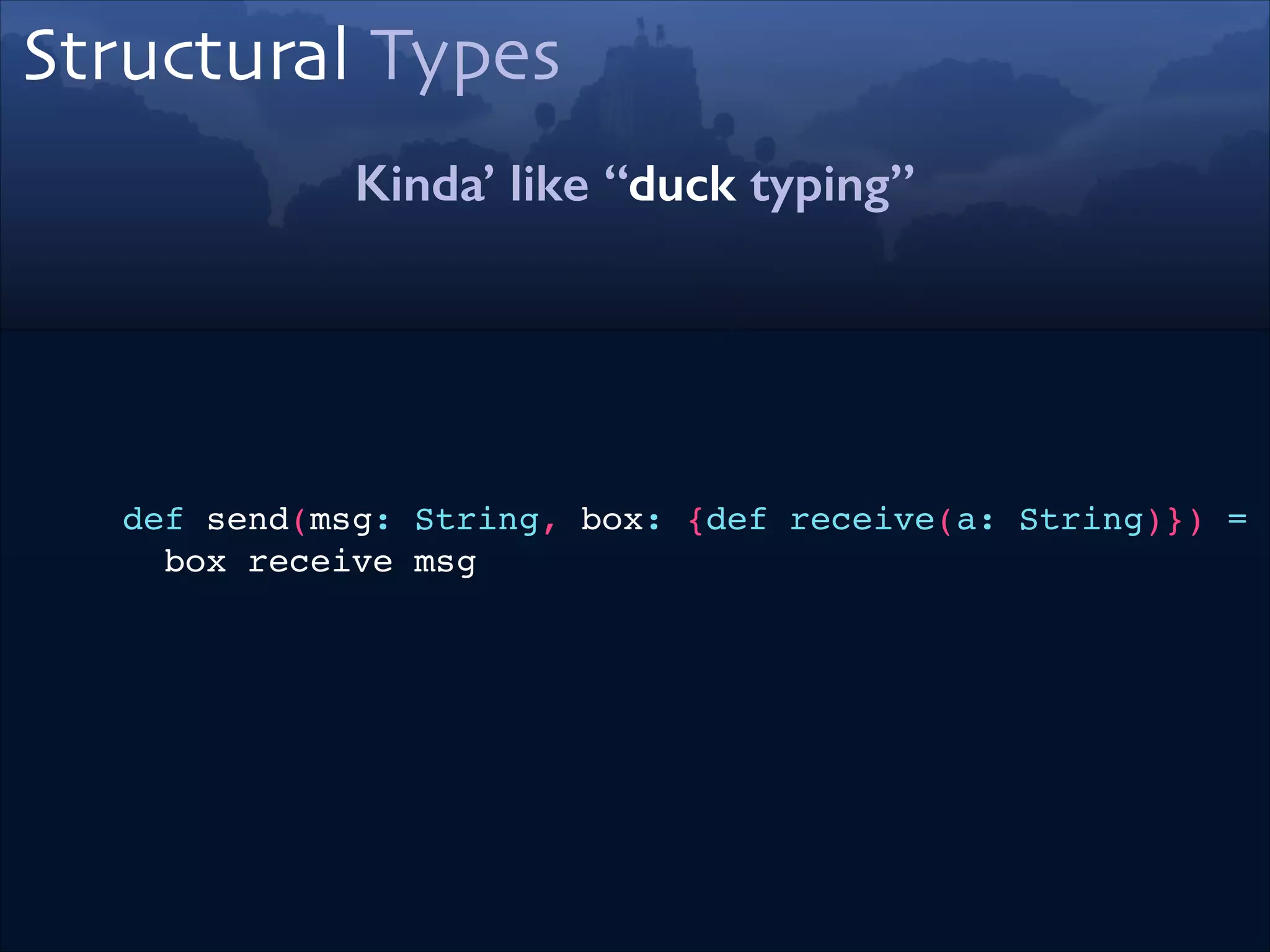
![Type Alias
From Type Parameter to Type Members
trait Builder[From, To]
=>
trait Builder {!
type From!
type To!
def make(in: From): To!
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-48-2048.jpg)
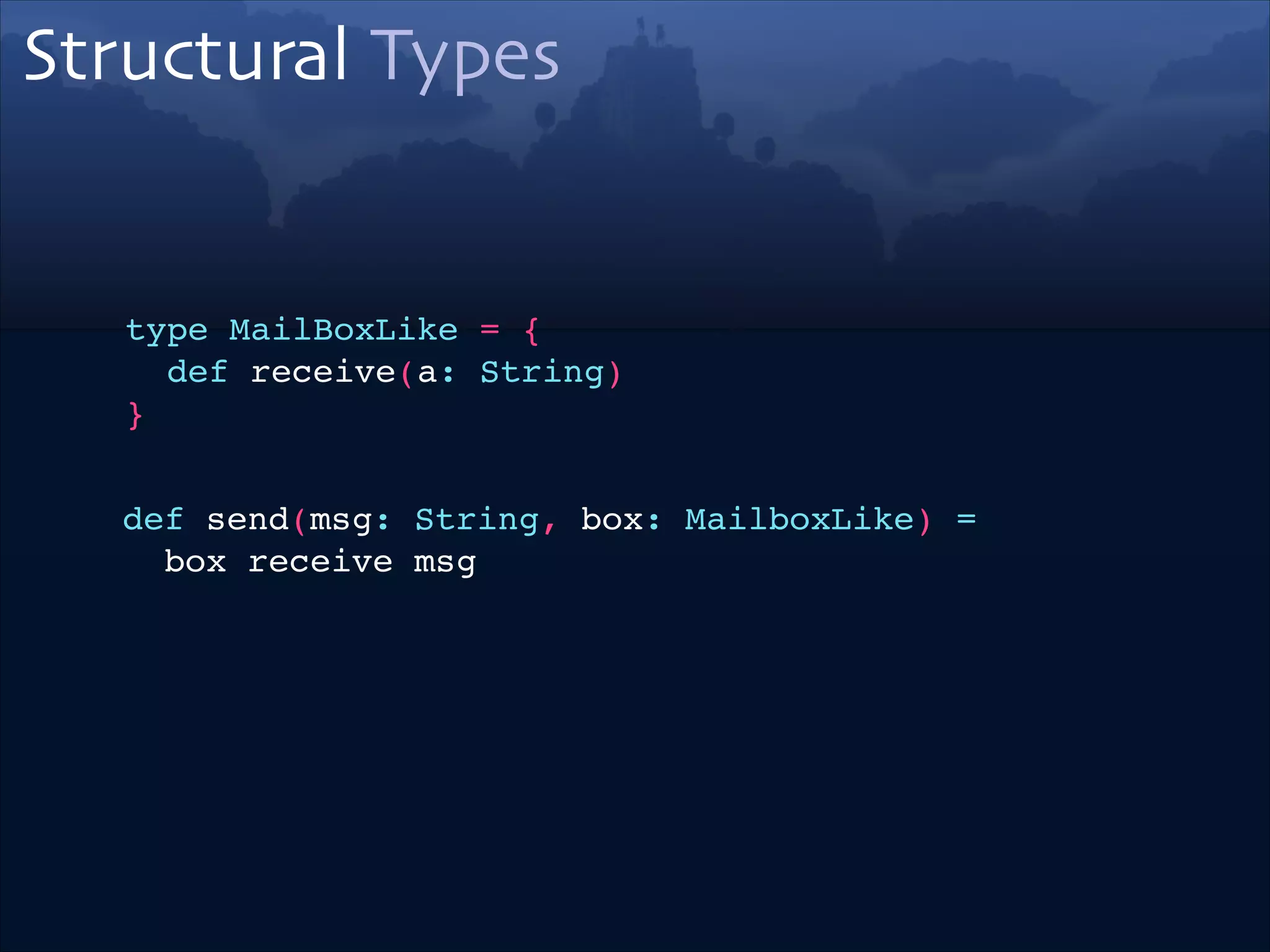
![Type Alias
trait Builder { type From; type To; def make(in: From): To }!
trait StringBuilder extends Builder {!
type To = String!
}
trait FromBytesBuilder extends Builder {!
type From = Array[Byte]!
}
object `bytes -> string` extends Builder!
with FromBytesBuilder!
with StringBuilder {!
!
def make(in: From): To = new String(in)!
}!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-49-2048.jpg)
![Type Alias
trait Builder { type From; type To; def make(in: From): To }!
object `bytes -> string` extends Builder {!
type From = Array[Bytes]!
type To = String!
!
def make(in: From): To = new String(in)!
}!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-50-2048.jpg)
![Phantom Types
Marker traits:
sealed trait DoorState!
final class Open
extends DoorState!
final class Closed extends DoorState!
trait Door[State <: DoorState] {!
!
def open[T >: State <: Closed](): Door[Open] !
!
!
def close[T >: State <: Open](): Door[Closed]!
!
}!
!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-54-2048.jpg)
![Phantom Types
Only slide in this talk with implementation!
class Door[State <: DoorState] private () {!
!
def open[T >: State <: Closed]() = !
this.asInstanceOf[Door[Open]]!
!
def close[T >: State <: Open]() =
this.asInstanceOf[Door[Closed]]!
!
}!
!
object Door { def apply() = new Door[Closed] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-55-2048.jpg)
![Phantom Types
Marker traits:
sealed trait DoorState!
final class Open
extends DoorState!
final class Closed extends DoorState!
class Door[State <: DoorState] private () {!
!
def open[T >: State <: Closed]() = !
this.asInstanceOf[Door[Open]]!
!
def stop[T >: State <: Open]() =
!
this.asInstanceOf[Door[Closed]]!
}!
!
object Door { def apply() = new Door[Closed] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-56-2048.jpg)
![Phantom Types
Marker traits:
sealed trait DoorState!
final class Open
extends DoorState!
final class Closed extends DoorState!
class Door[State <: DoorState] private () {!
!
def open[T >: State <: Closed]() = !
this.asInstanceOf[Door[Open]]!
!
def stop[T >: State <: Open]() =
!
this.asInstanceOf[Door[Closed]]!
}!
!
object Door { def apply() = new Door[Closed] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-57-2048.jpg)
![Phantom Types
Marker traits:
sealed trait DoorState!
final class Open
extends DoorState!
final class Closed extends DoorState!
class Door[State <: DoorState] private () {!
!
def open[T >: State <: Closed]() = !
this.asInstanceOf[Door[Open]]!
!
def stop[T >: State <: Open]() =
!
this.asInstanceOf[Door[Closed]]!
}!
!
object Door { def apply() = new Door[Closed] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-58-2048.jpg)
![Phantom Types
Marker traits:
sealed trait DoorState!
final class Open
extends DoorState!
final class Closed extends DoorState!
class Door[State <: DoorState] private () {!
!
def open[T >: State <: Closed]() = !
this.asInstanceOf[Door[Open]]!
!
def stop[T >: State <: Open]() =
!
this.asInstanceOf[Door[Closed]]!
}!
!
object Door { def apply() = new Door[Closed] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-59-2048.jpg)
![Phantom Types
val closed = Door()!
// closed: Door[Closed]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-60-2048.jpg)
![Phantom Types
val closed = Door()!
// closed: Door[Closed]!
!
val opened = closed.open()!
// opened: Door[Open]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-61-2048.jpg)
![Phantom Types
val closed = Door()!
// closed: Door[Closed]!
!
val opened = closed.open()!
// opened: Door[Open]!
!
val closedAgain = opened.close()!
// closedAgain: Door[Closed]!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-62-2048.jpg)
![Phantom Types
val closed = Door()!
// closed: Door[Closed]!
!
val opened = closed.open()!
// opened: Door[Open]!
!
val closedAgain = opened.close()!
// closedAgain: Door[Closed]!
!
closed.close()!
error: type arguments [Closed] do not conform to method
close's type parameter bounds [T >: Closed <: Open]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-63-2048.jpg)
![Phantom Types
val closed = Door()!
// closed: Door[Closed]!
!
val opened = closed.open()!
// opened: Door[Open]!
!
val closedAgain = opened.close()!
// closedAgain: Door[Closed]!
!
closed.close()!
error: type arguments [Closed] do not conform to method
close's type parameter bounds [T >: Closed <: Open]!
!
opened.open()!
error: type arguments [Open] do not conform to method !
open's type parameter bounds [T >: Open <: Closed]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-64-2048.jpg)

![Kind: x -> x
Type Constructor
List[+A]!
scala> :kind -v List!
!
scala.collection.immutable.List's kind is F[+A]!
* -(+)-> *!
!
This is a type constructor: !
a 1st-order-kinded type.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-67-2048.jpg)
![Kind:
(x -> x) -> x
Higher Kind
import language.higherKinds!
!
class Functor[M[_]]!
scala> :kind -v Functor[List]!
!
Functor's kind is X[F[A]]!
(* -> *) -> *!
!
This is a type constructor that takes type constructor(s): !
a higher-kinded type](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-68-2048.jpg)
![Higher Kinded Types
import scala.language.higherKinds!
!
takes Type Constructor
trait Functor [F[_]] {!
def map[A,B] (fn: A => B)(fa: F[A]): F[B]!
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-69-2048.jpg)
![Higher Kinded Types
import scala.language.higherKinds!
!
trait Functor [F[_]] {!
def map[A,B] (fn: A => B)(fa: F[A]): F[B]!
}
trait Functor [List] {!
def map[Int,String] (fn: Int => String)!
(fa: List[Int]): List[String]!
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-70-2048.jpg)
![Higher Kinded Types
import scala.language.higherKinds!
!
trait Functor [F[_]] {!
def map[A,B] (fn: A => B)(fa: F[A]): F[B]!
}
val funct = new Functor[List] {!
def map[String, Int] !
(f: String => Int)!
(fa: List[String])!
: List[Int] = fa map f // cheating ;-)!
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-71-2048.jpg)
![Higher Kinded Types
import scala.language.higherKinds!
!
trait Functor [F[_]] {!
def map[A,B] (fn: A => B)(fa: F[A]): F[B]!
}
val funct = new Functor[List] {!
def map[String, Int] !
(f: String => Int)!
(fa: List[String]): List[Int] = !
! ! !!!
fa map f // cheating ;-)!
}
val f: Int => String = _.toString!
funct.map(f)(List(1, 2)) == List("1", "2")!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-72-2048.jpg)
![Power up: Ad-Hoc Polymorphism
trait Container[M[_]] { !
def put[A](x: A): M[A]; def get[A](m: M[A]): A !
}!
implicit val listContainer = new Container[List] { !
def put[A](x: A) = List(x)!
def get[A](m: List[A]) = m.head !
}!
!
implicit val optionContainer = new Container[Some] {!
def put[A](x: A) = Some(x);!
def get[A](m: Some[A]) = m.get !
}!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-73-2048.jpg)
![Power up: Ad-Hoc Polymorphism
trait Container[M[_]] { !
def put[A](x: A): M[A]; def get[A](m: M[A]): A !
}!
def tupleize[M[_]: Container, A, B]!
(fst: M[A], snd: M[B]) !
(implicit c: Container[M]): M[(A, B)] =
c.put(c.get(fst), c.get(snd))
tupleize(Some(1), Some(2))!
Some((1,2)): Some[(Int, Int)]!
!
tupleize(List(1), List(“2”))!
List((1,2)): List[(Int, String)]!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-74-2048.jpg)
![Power up: Ad-Hoc Polymorphism
trait Container[M[_]] { !
def put[A](x: A): M[A]; def get[A](m: M[A]): A !
}!
def tupleize[M[_]: Container, A, B]!
(fst: M[A], snd: M[B]) !
(implicit c: Container[M]): M[(A, B)] =
c.put(c.get(fst), c.get(snd))
tupleize(Some(1), Some(2))!
Some((1,2)): Some[(Int, Int)]!
!
tupleize(List(1), List(“2”))!
List((1,2)): List[(Int, String)]!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-75-2048.jpg)




![Type Class
// no type classes yet!
trait Writeable[Out] {!
def write: Out!
}!
!
case class Num(a: Int, b: Int) extends Writeable[Json] {!
def write = Json.toJson(this)!
}!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-81-2048.jpg)
![Type Class
trait Writes[In, Out] {
def write(in: In): Out!
}!
!
!
Separated “what” from “who”
trait Writeable[Self] {
def writeAs[Out]()!
(implicit writes: Writes[Self, Out]): Out =!
! ! ! !
writes write this!
}!
!
!
!
implicit val jsonNum = Writes[Num, Json] {!
! def write(n: Num) = Json.toJson(n)!
!
}!
!
case class Num(a: Int) extends Writeable[Num]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-82-2048.jpg)
![Type Class
trait Writes[In, Out] {
def write(in: In): Out!
}!
!
!
trait Writeable[Self] {
def writeAs[Out]()!
(implicit writes: Writes[Self, Out]): Out =!
! ! ! !
writes write this!
}!
Implicit parameter
!
!
!
implicit val jsonNum = Writes[Num, Json] {!
! def write(n: Num) = Json.toJson(n)!
!
}!
!
Implicit value
case class Num(a: Int) extends Writeable[Num]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-83-2048.jpg)
![Type Class
implicit val jsonNum = Writes[Num, Json] {
def (n1: Num, n2: Num) = n1.a < n1.!
}!
!
case class Num(a: Int) extends Writeable[Num]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-84-2048.jpg)
![Type Class
implicit val jsonNum = Writes[Num, Json] {
def (n1: Num, n2: Num) = n1.a < n1.!
}!
!
case class Num(a: Int) extends Writeable[Num]
you write:
val jsonNum = Num(12).writeAs[Json]()!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-85-2048.jpg)
![Type Class
implicit val jsonNum = Writes[Num, Json] {
def (n1: Num, n2: Num) = n1.a < n1.!
}!
!
case class Num(a: Int) extends Writeable[Num]
you write:
val jsonNum = Num(12).writeAs[Json]()!
compiler does:
val jsonNum = Num(12).writeAs[Json]()(jsonNum)!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-types-of-types-lambda-days-2014-short-140226180059-phpapp02/75/Scala-Types-of-Types-Lambda-Days-86-2048.jpg)