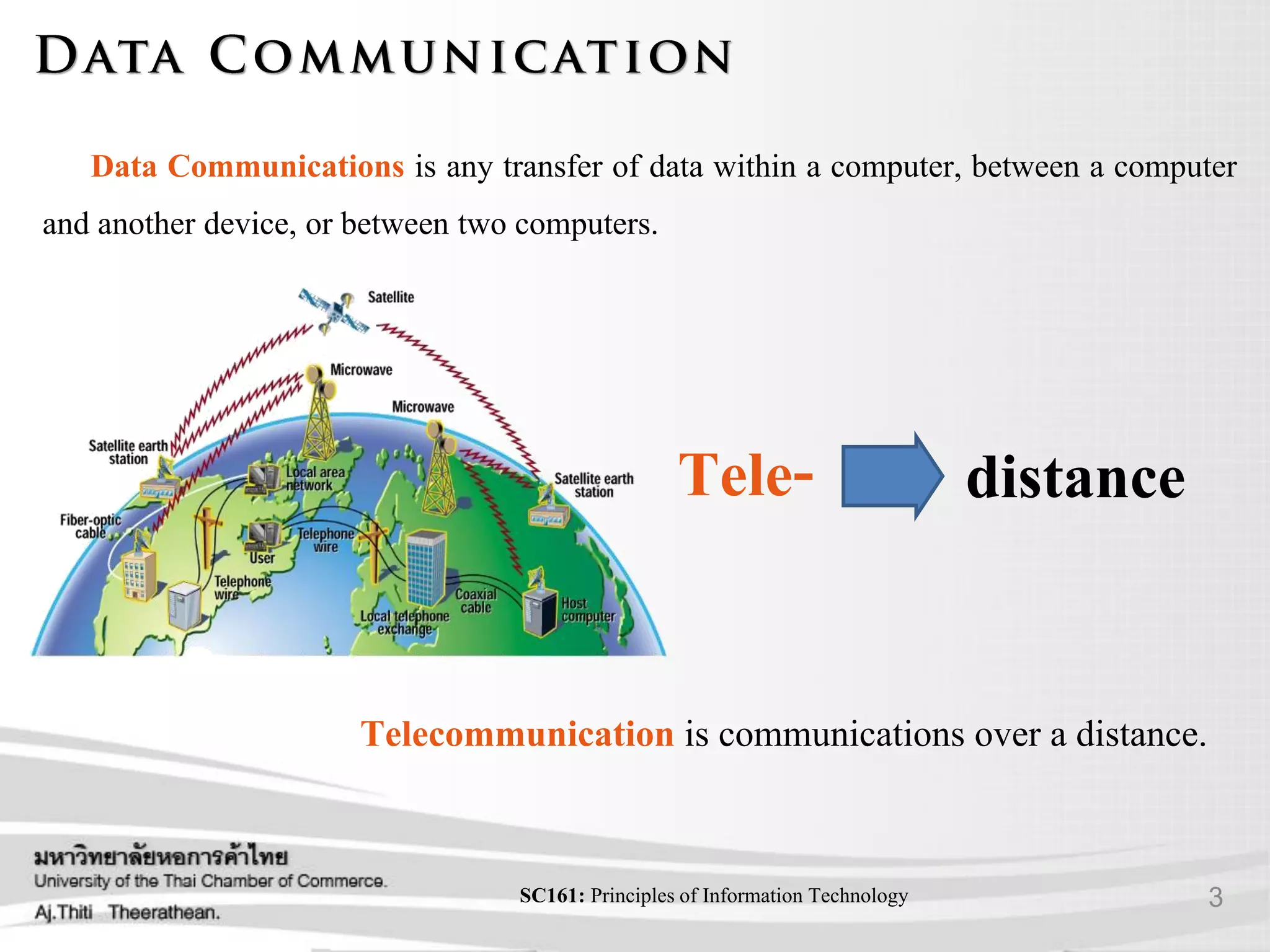
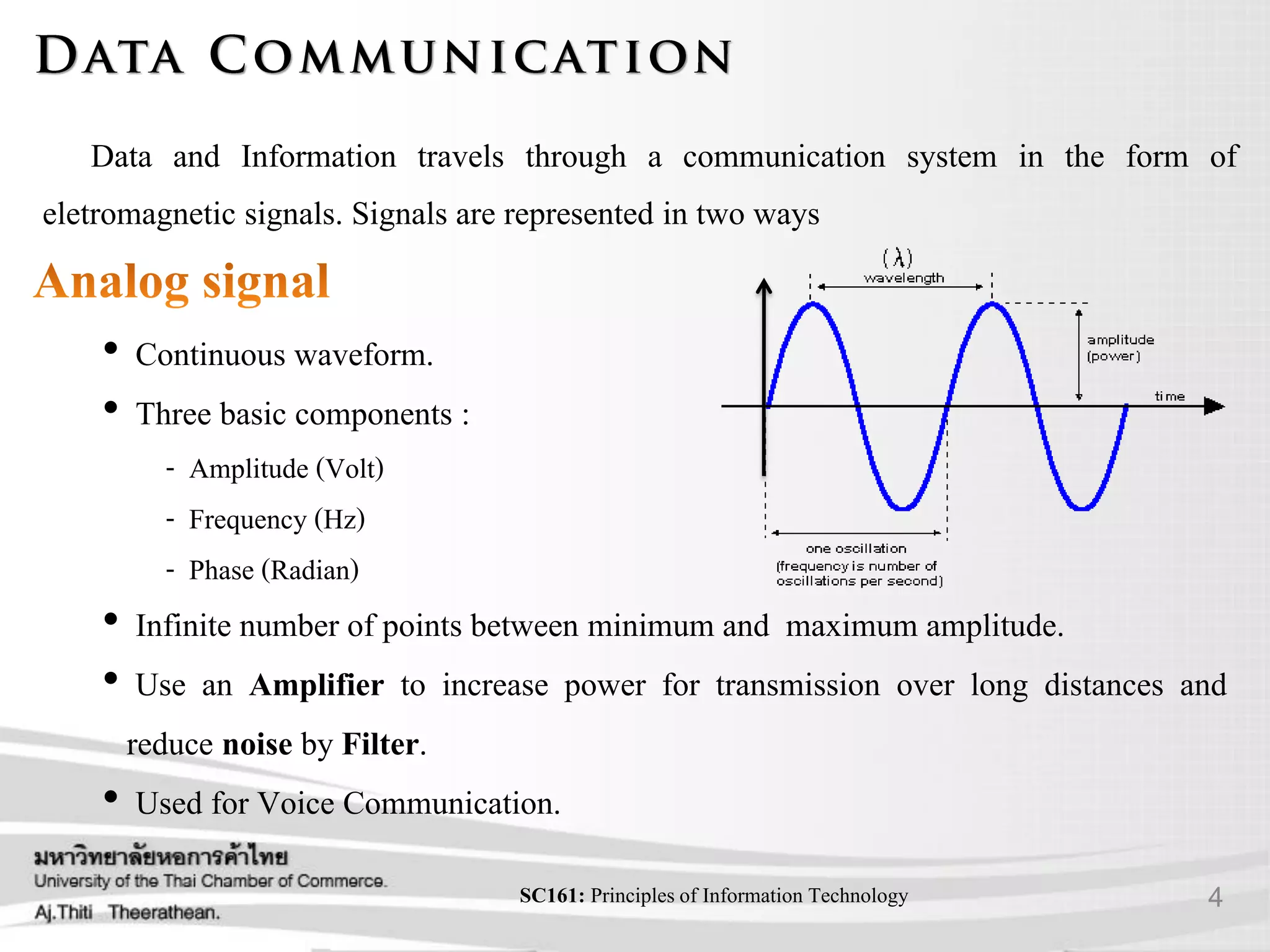
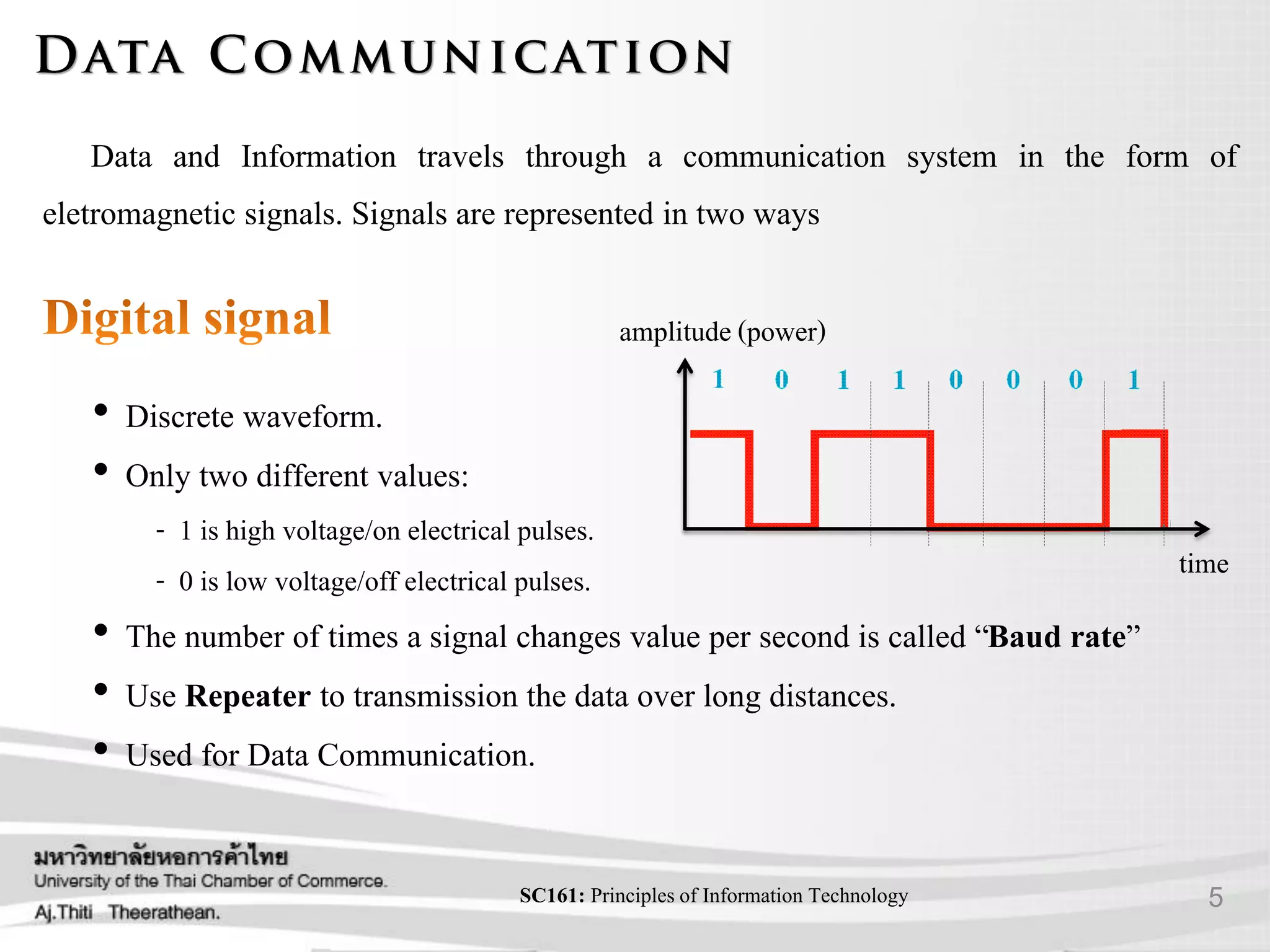
This document provides an overview of data communication and networking concepts including:
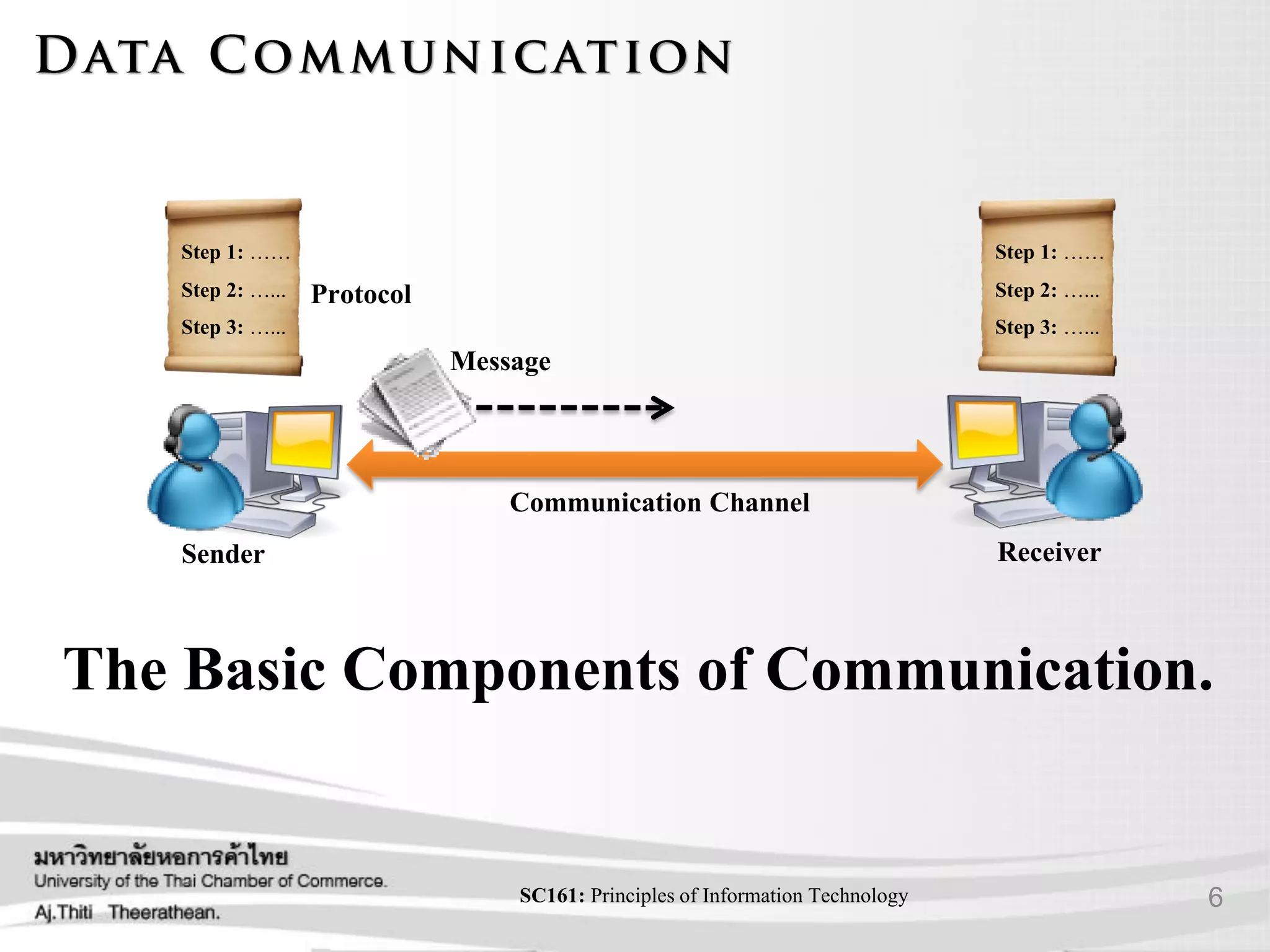
- The basic components of communication systems including senders, channels, and receivers.
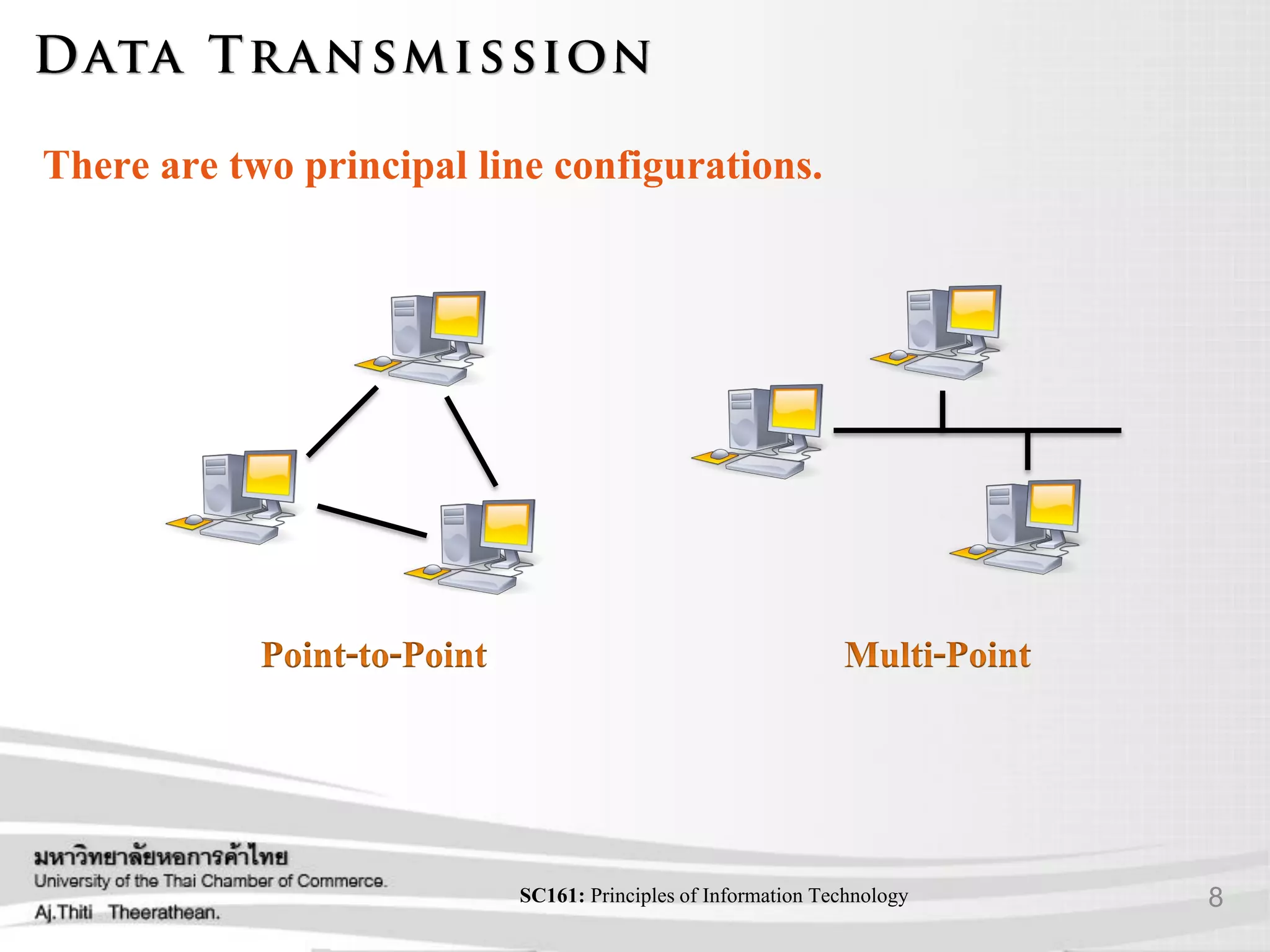
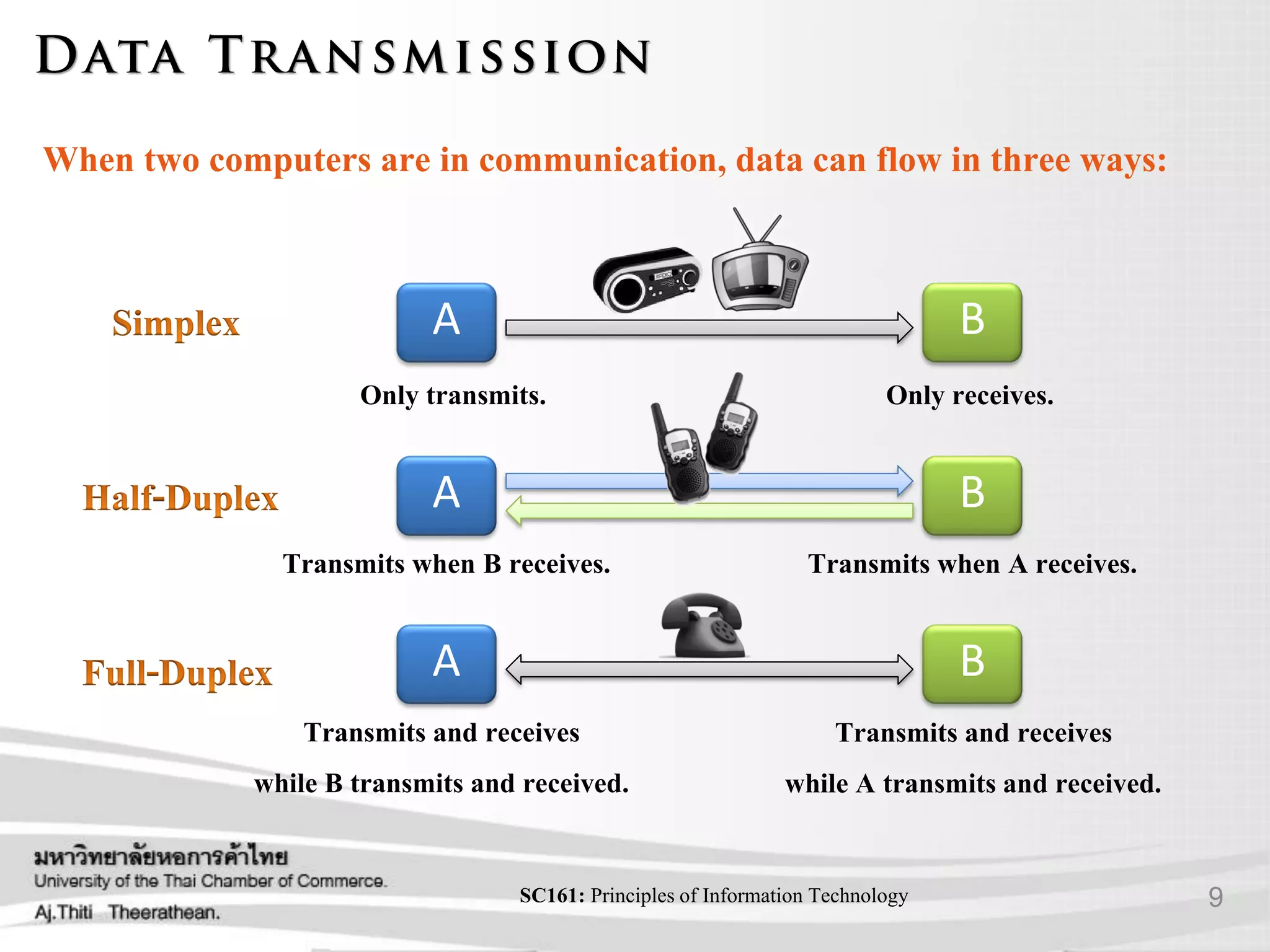
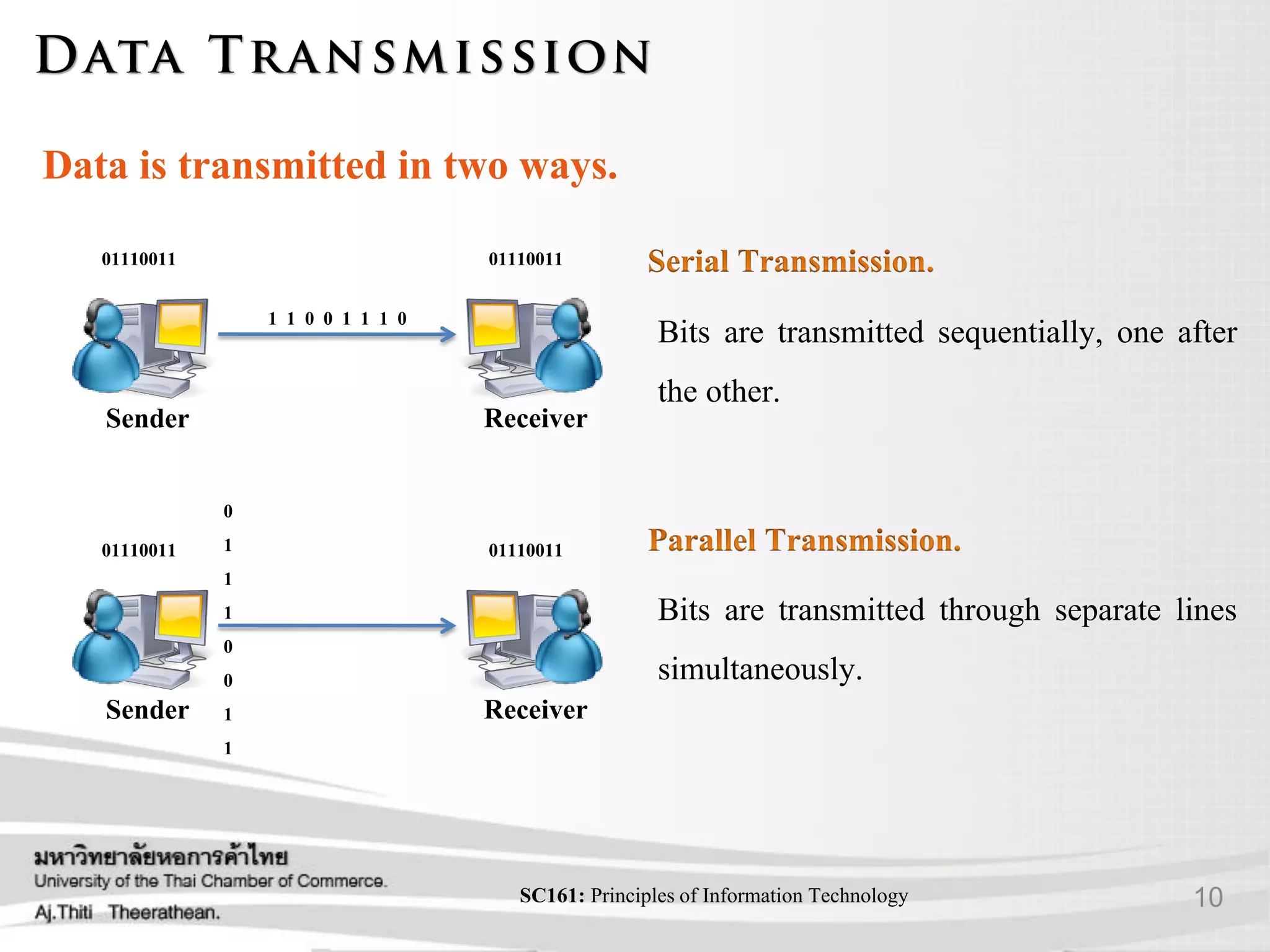
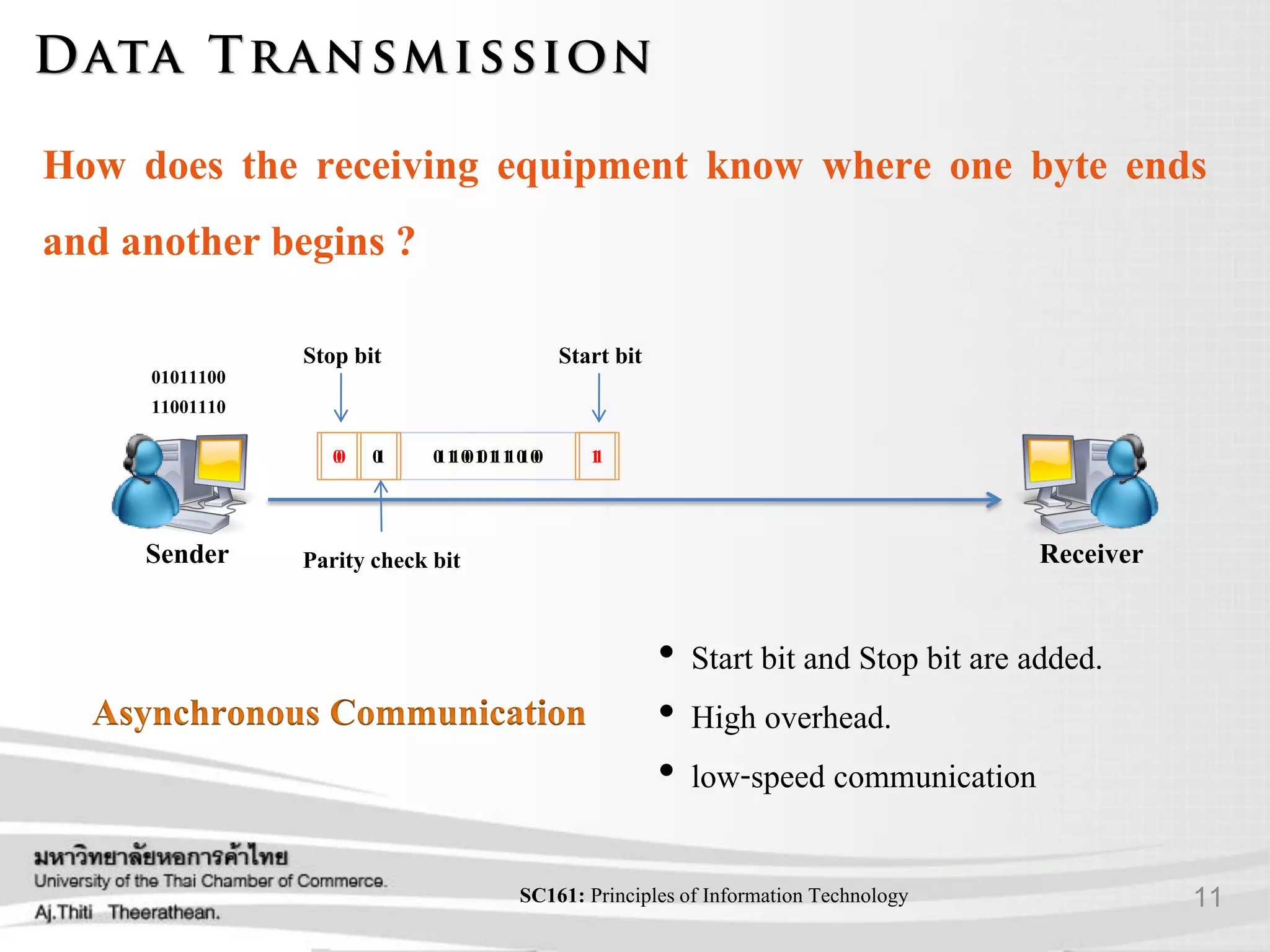
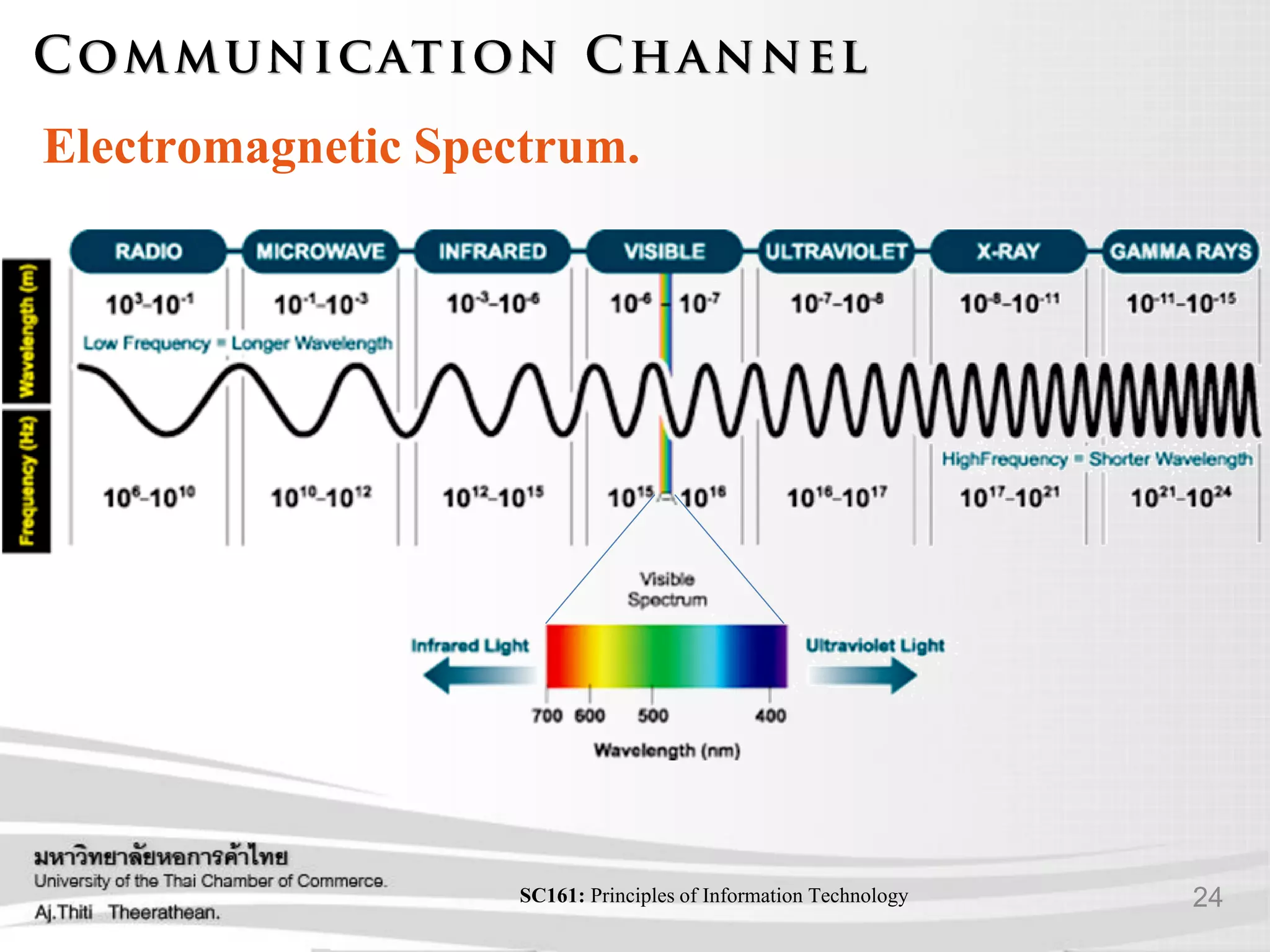
- Different types of communication signals and how data is transmitted.
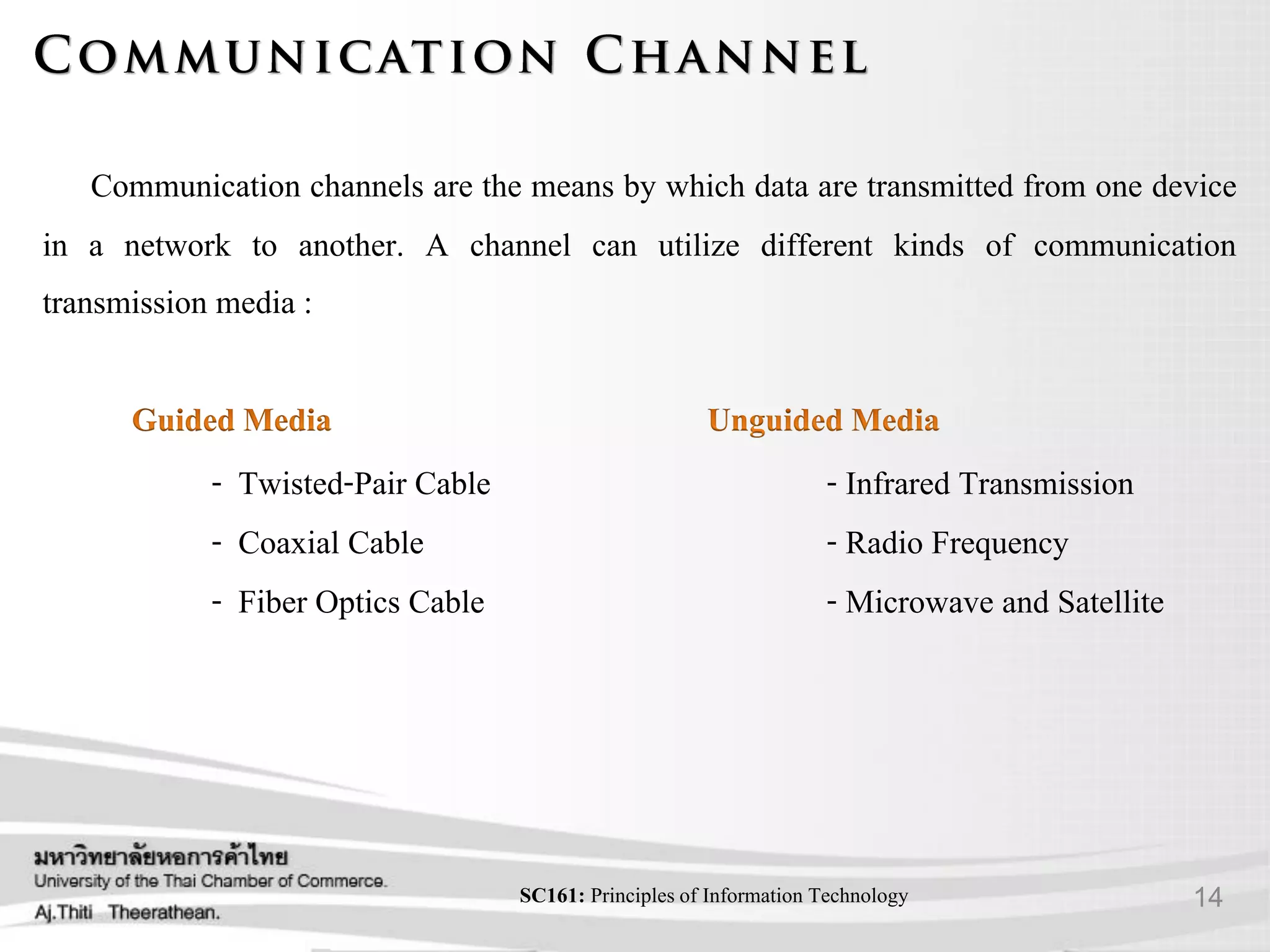
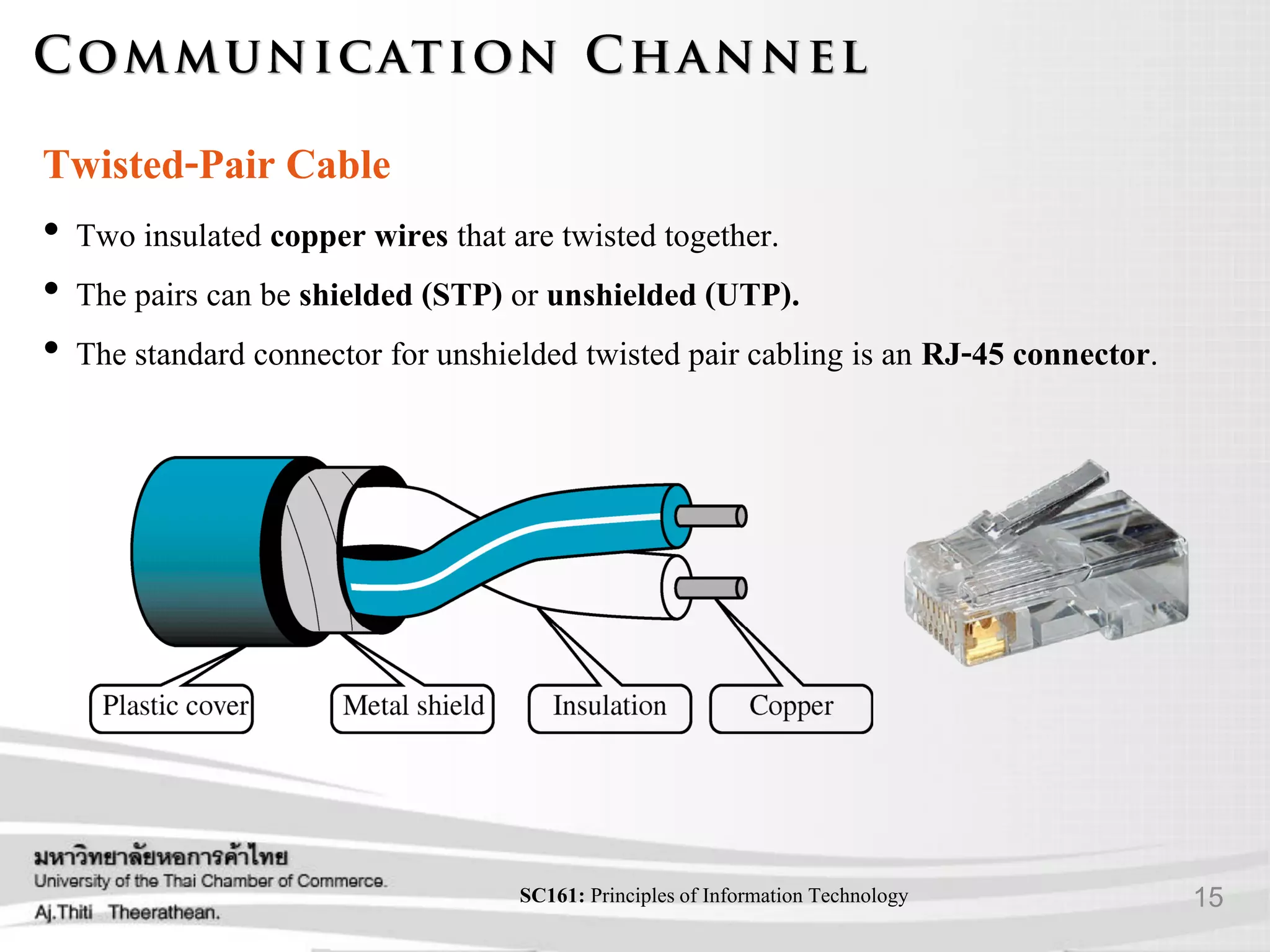
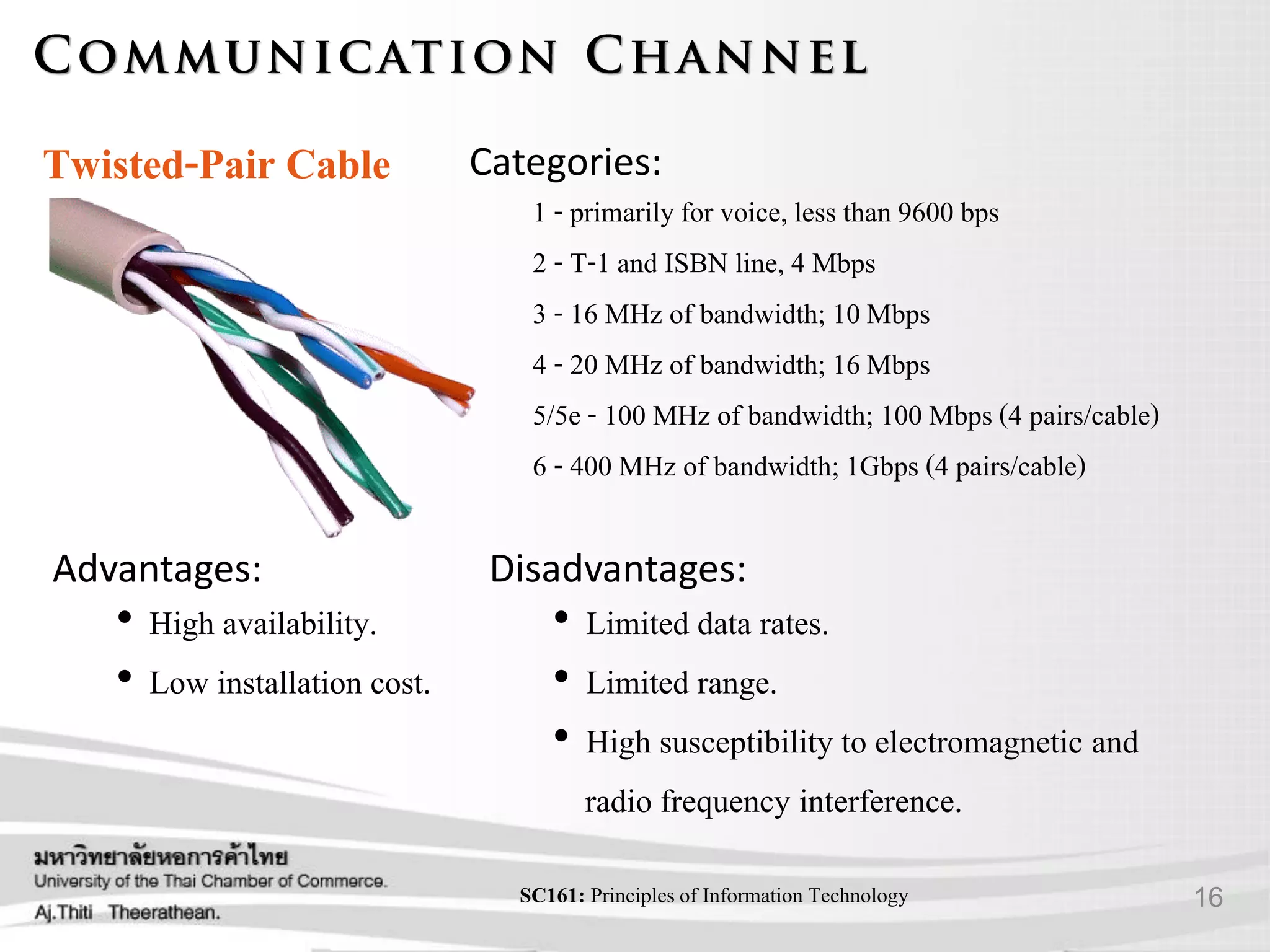
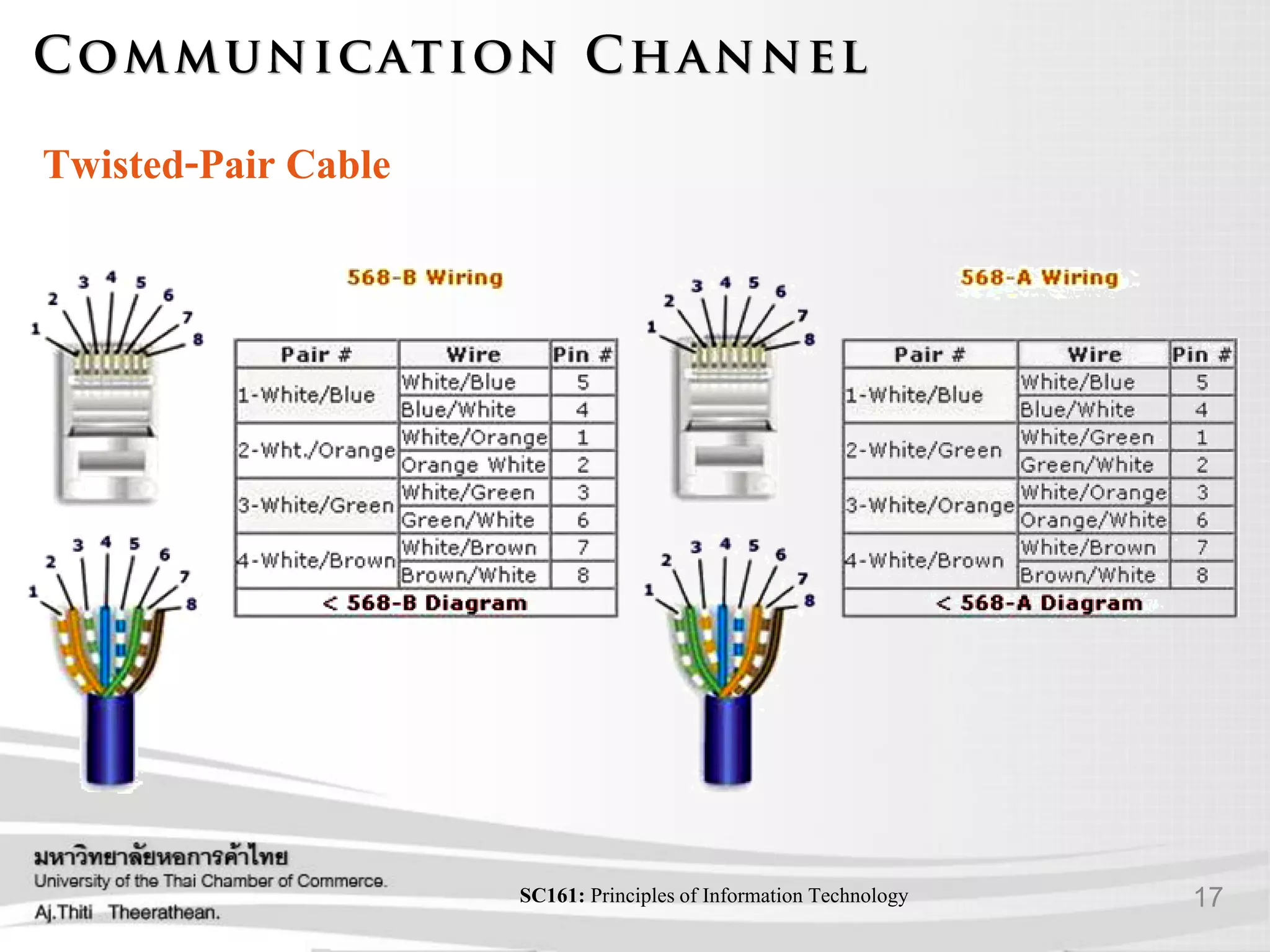
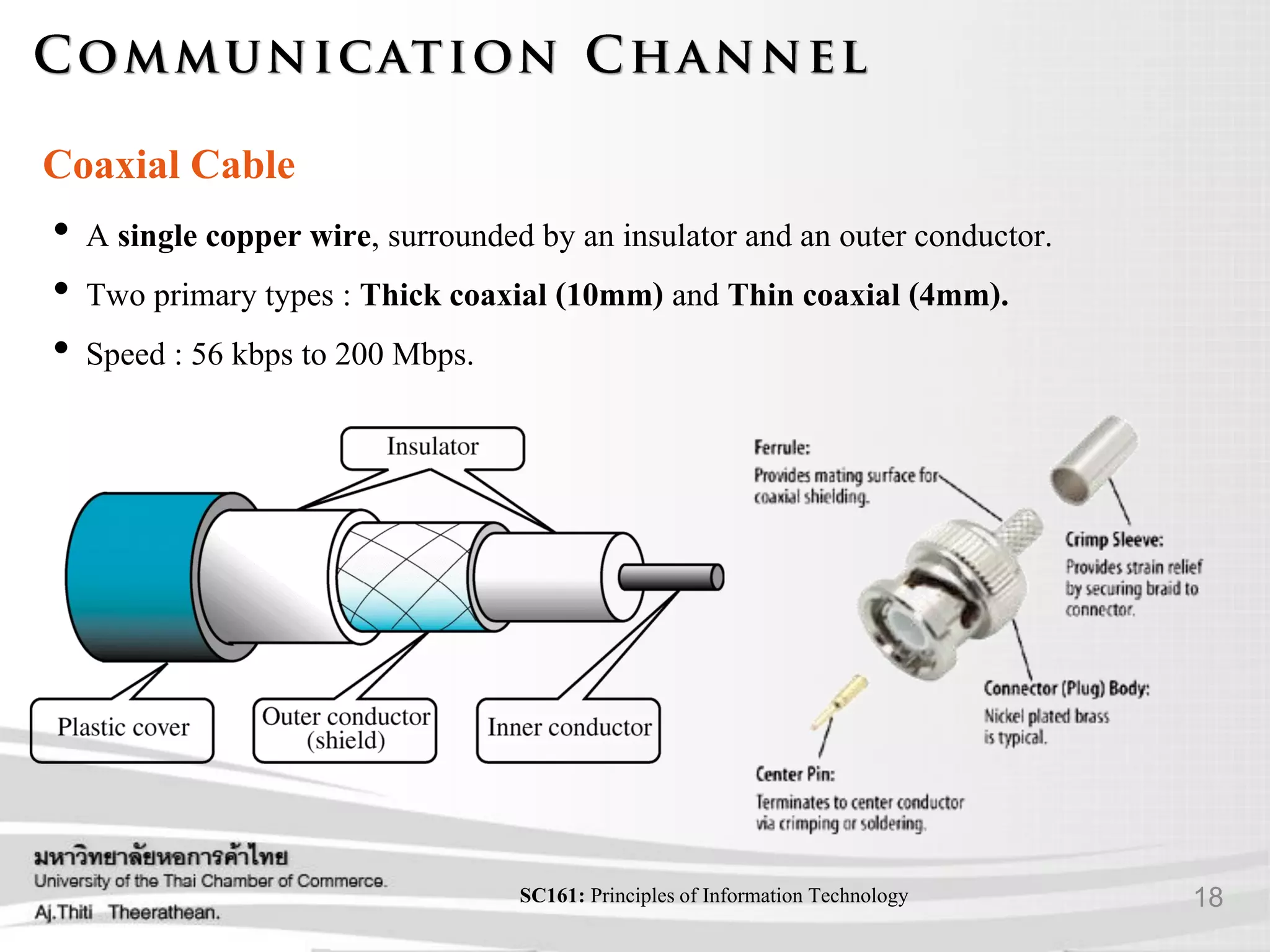
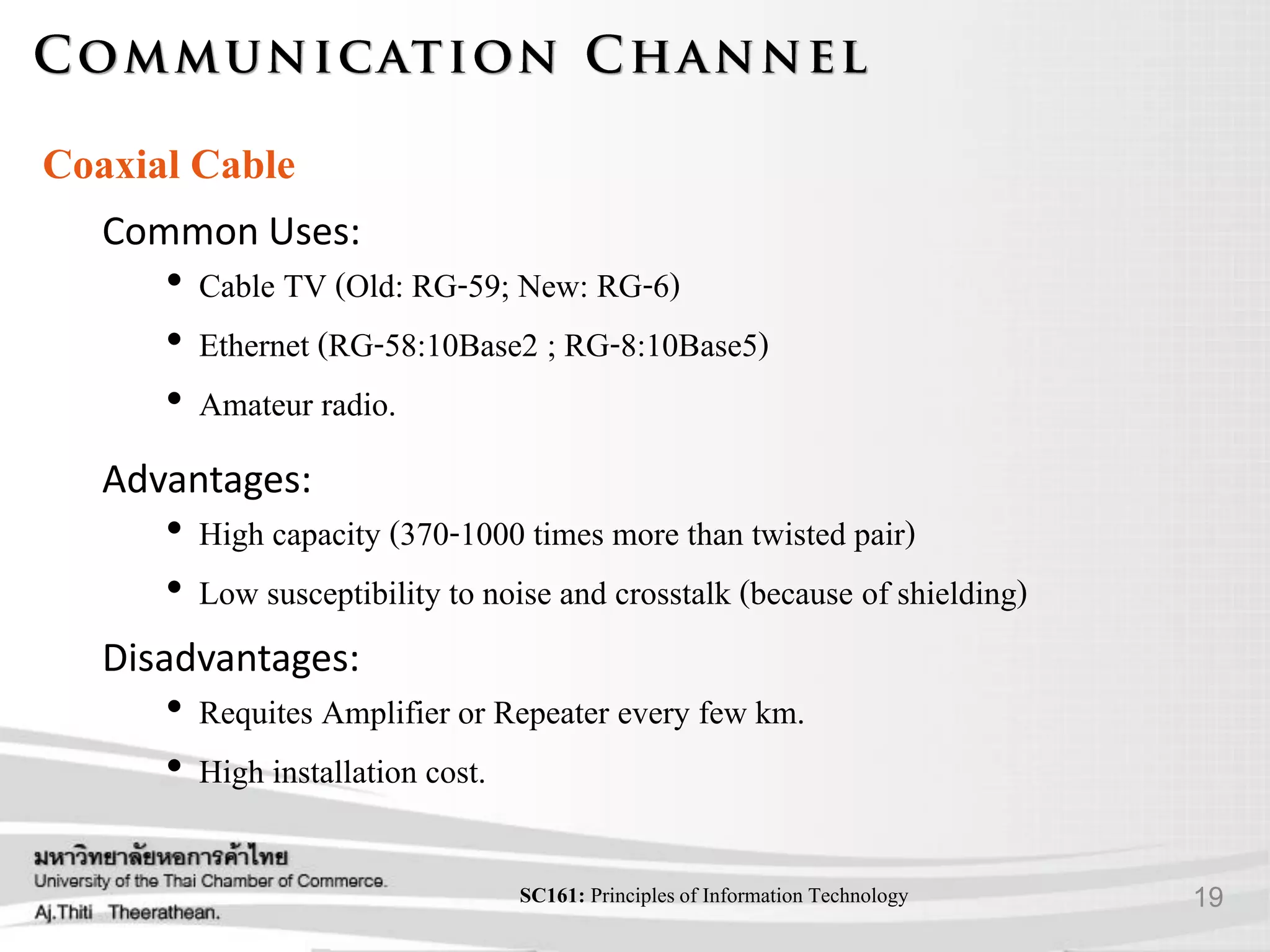
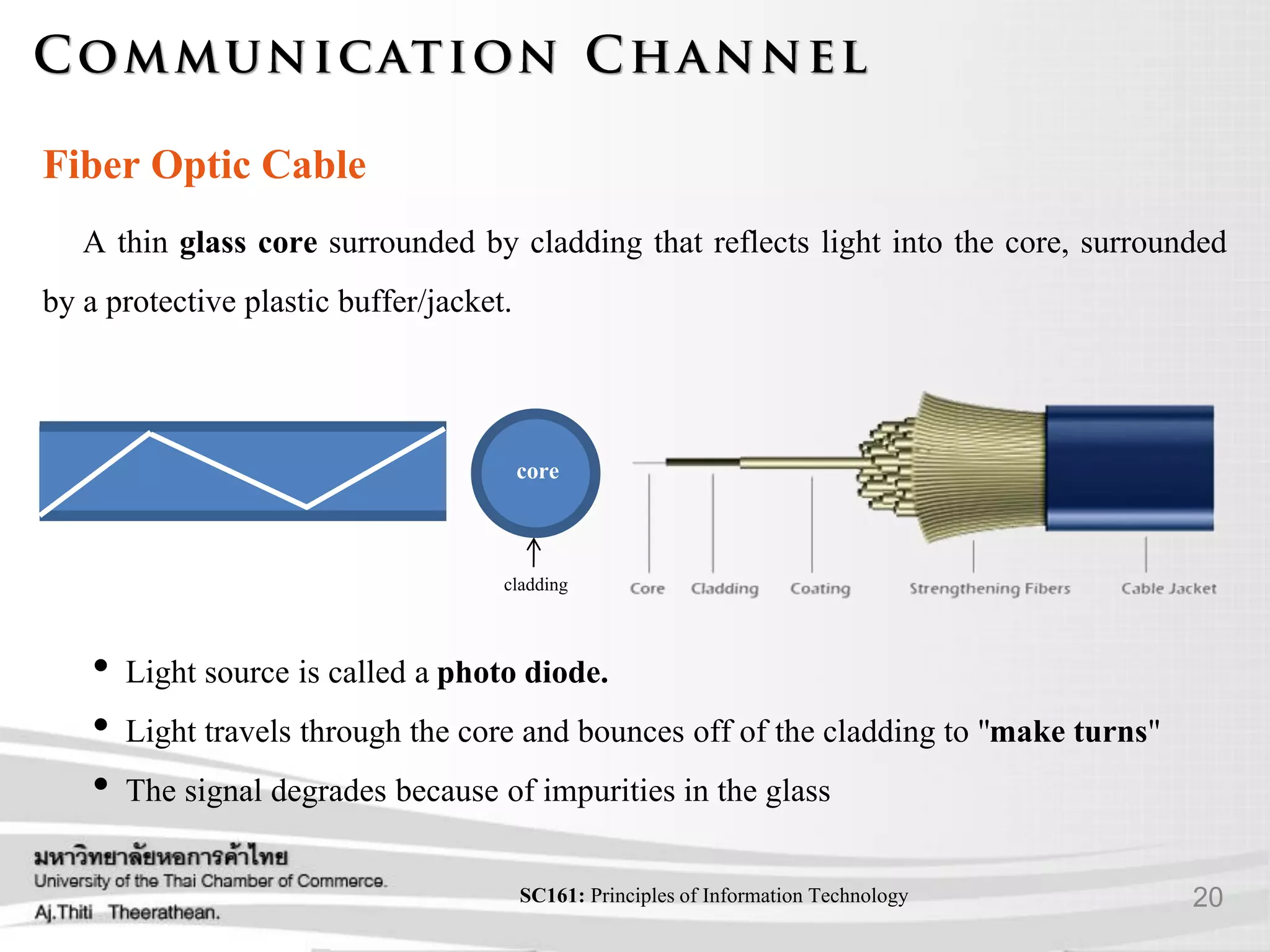
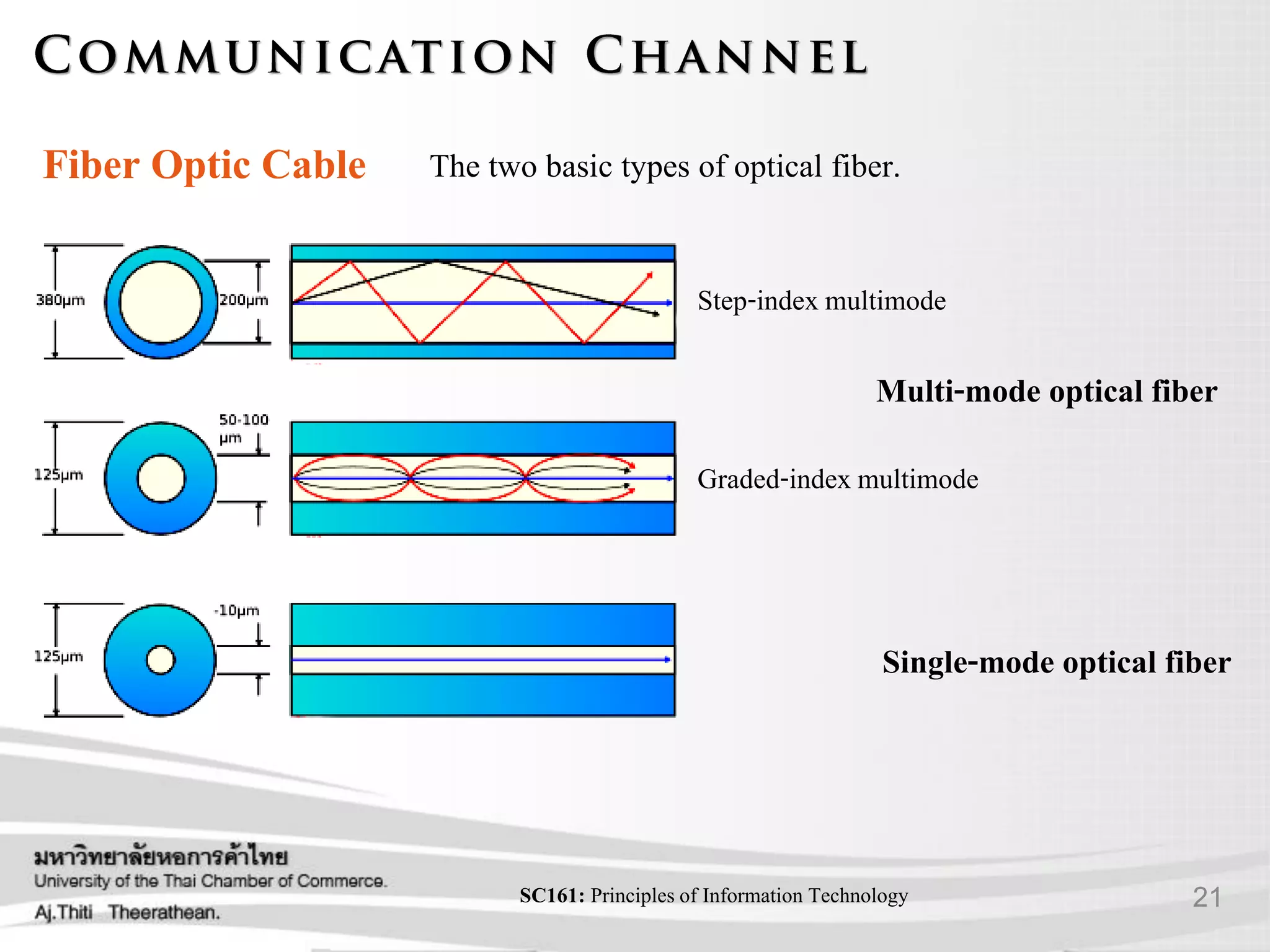
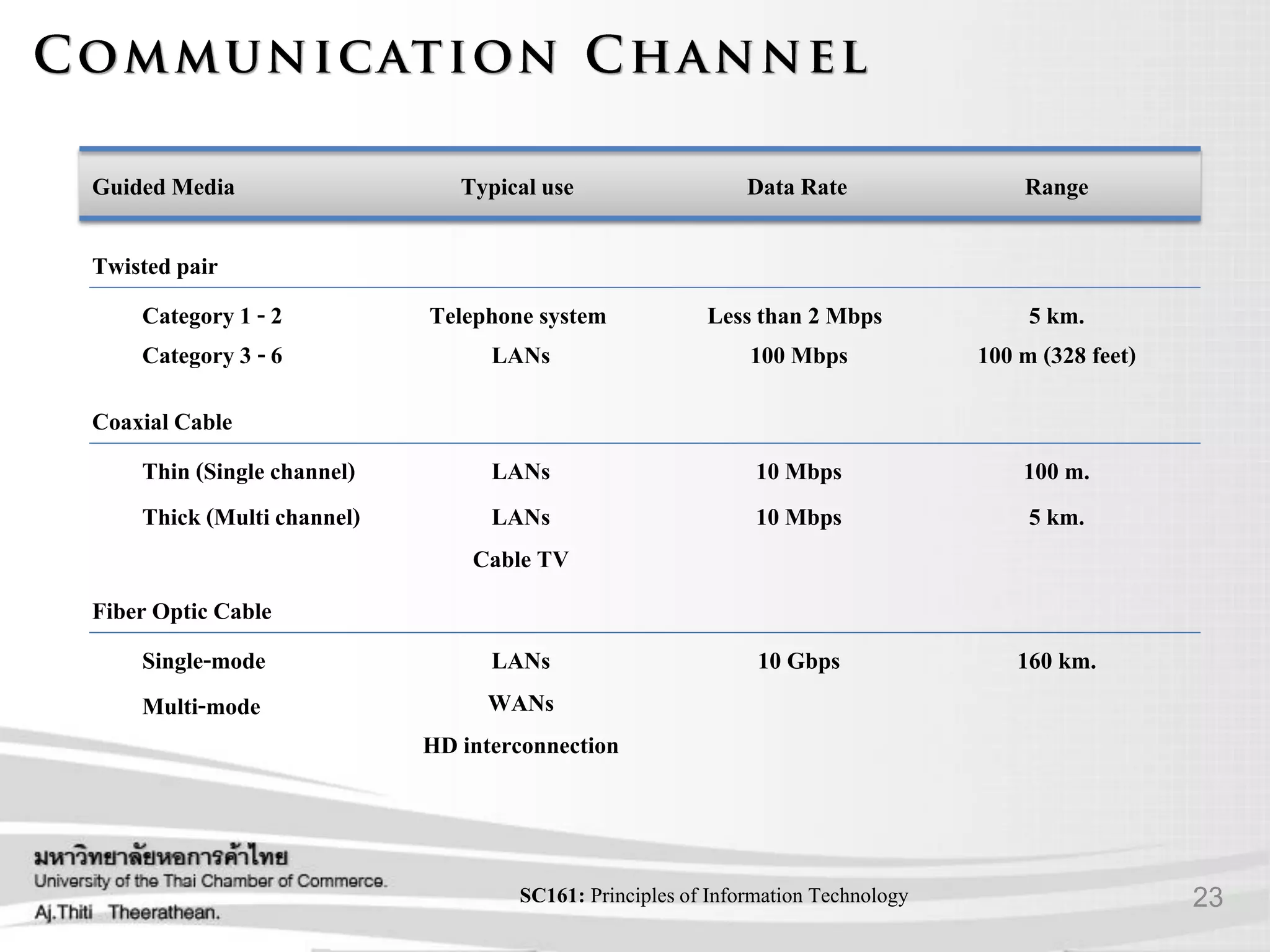
- Various transmission media including guided media like twisted pair cable, coaxial cable, and fiber optic cable as well as unguided media like wireless transmission.
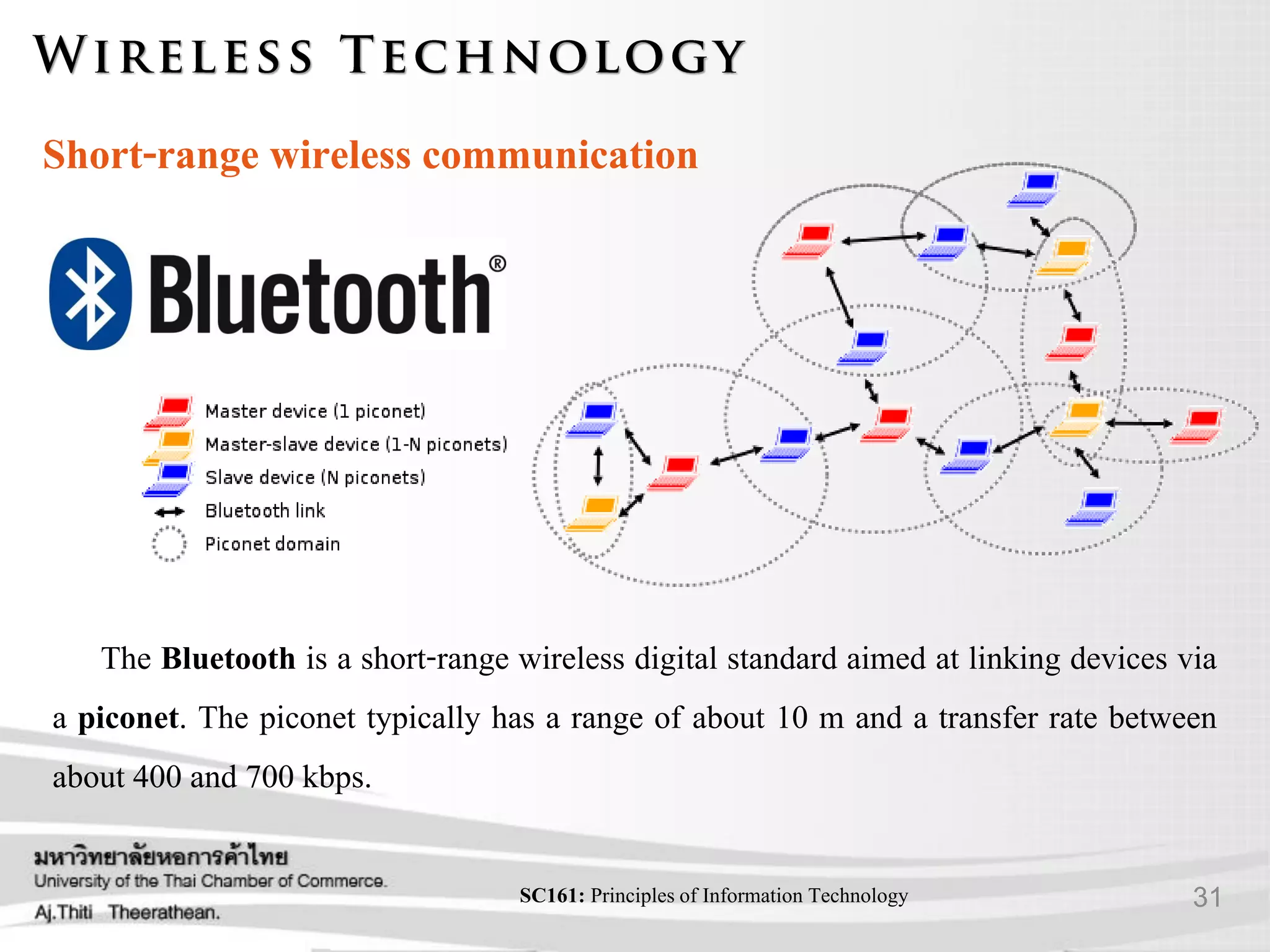
- Short-range and long-distance wireless technologies.