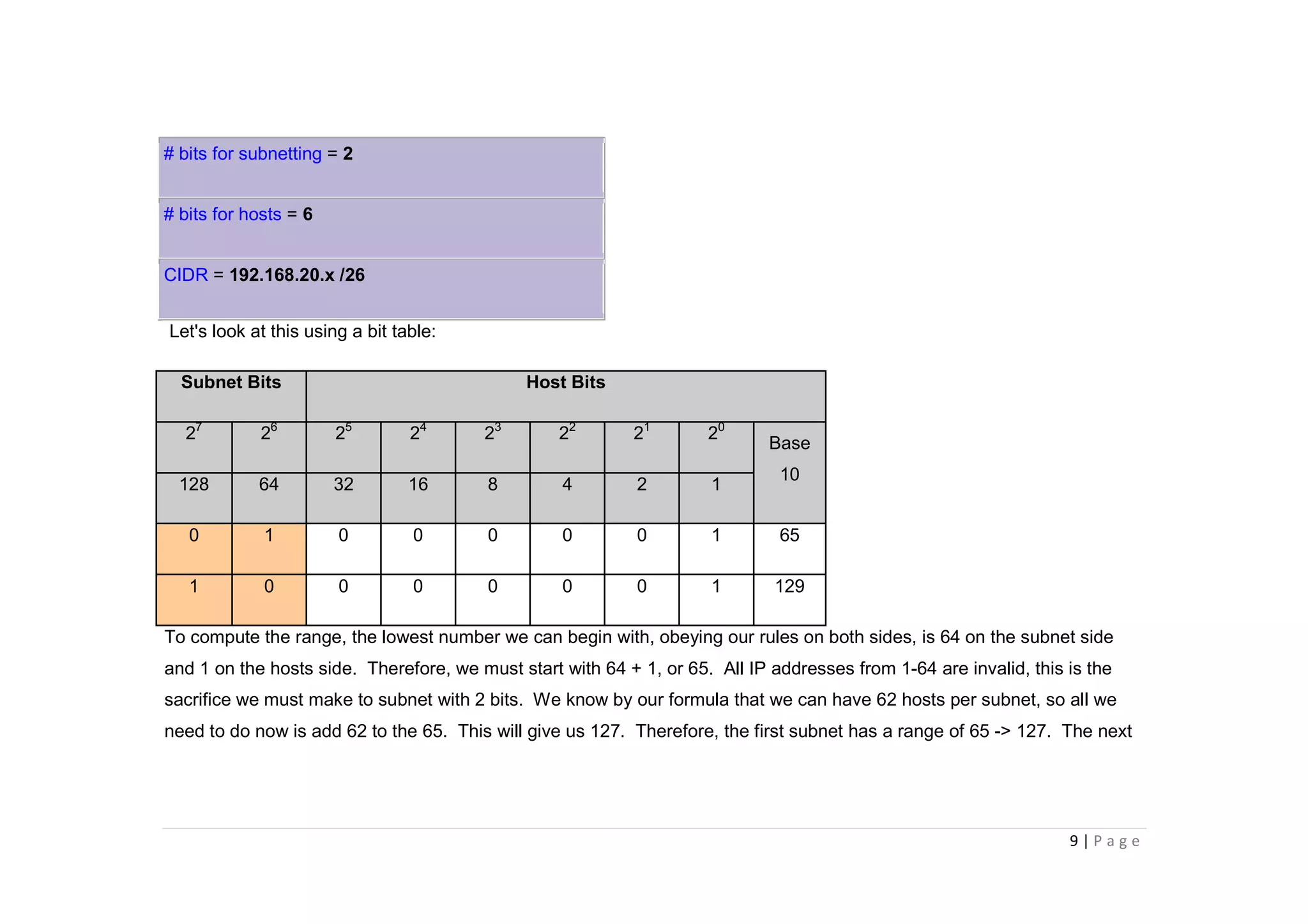
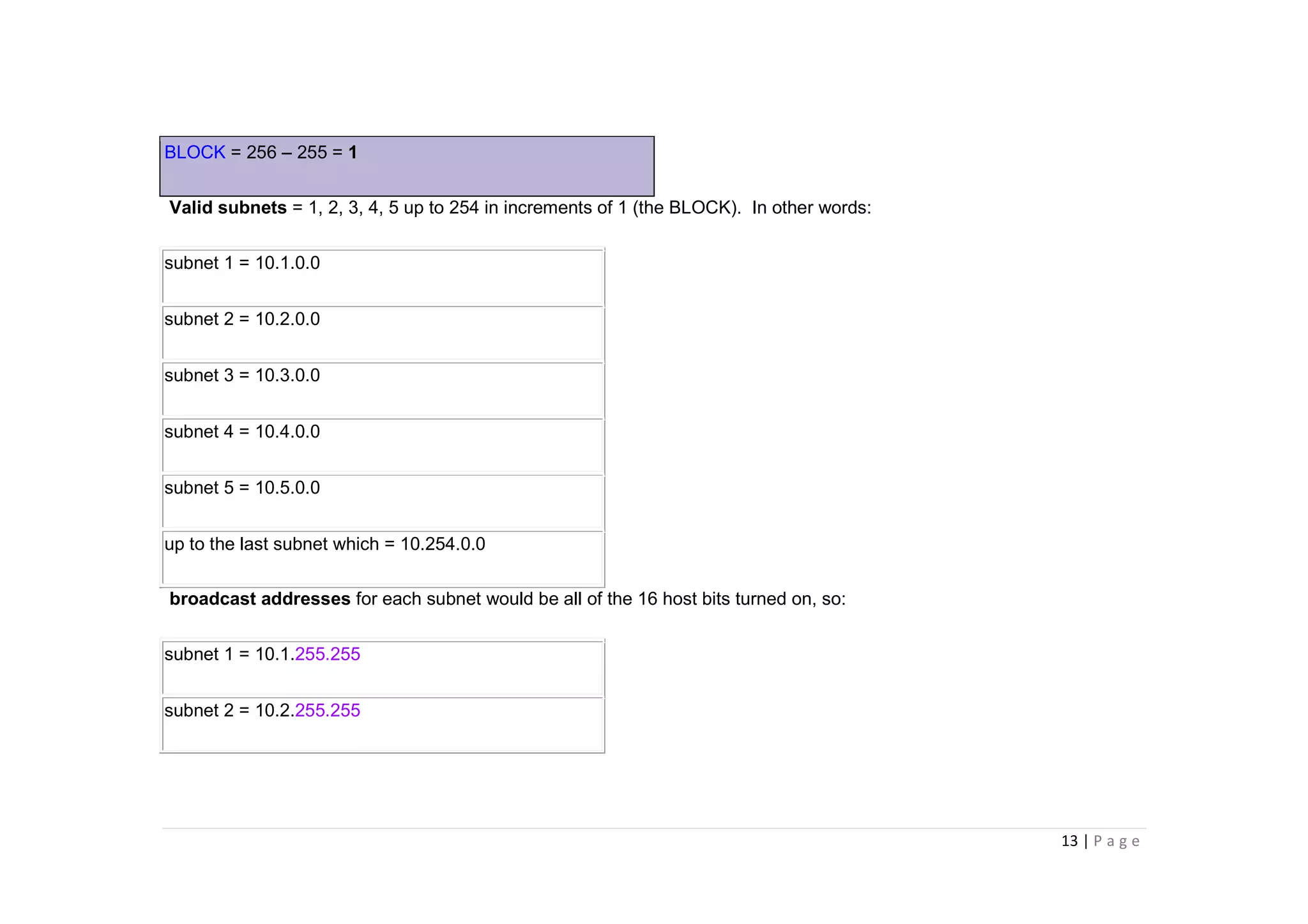
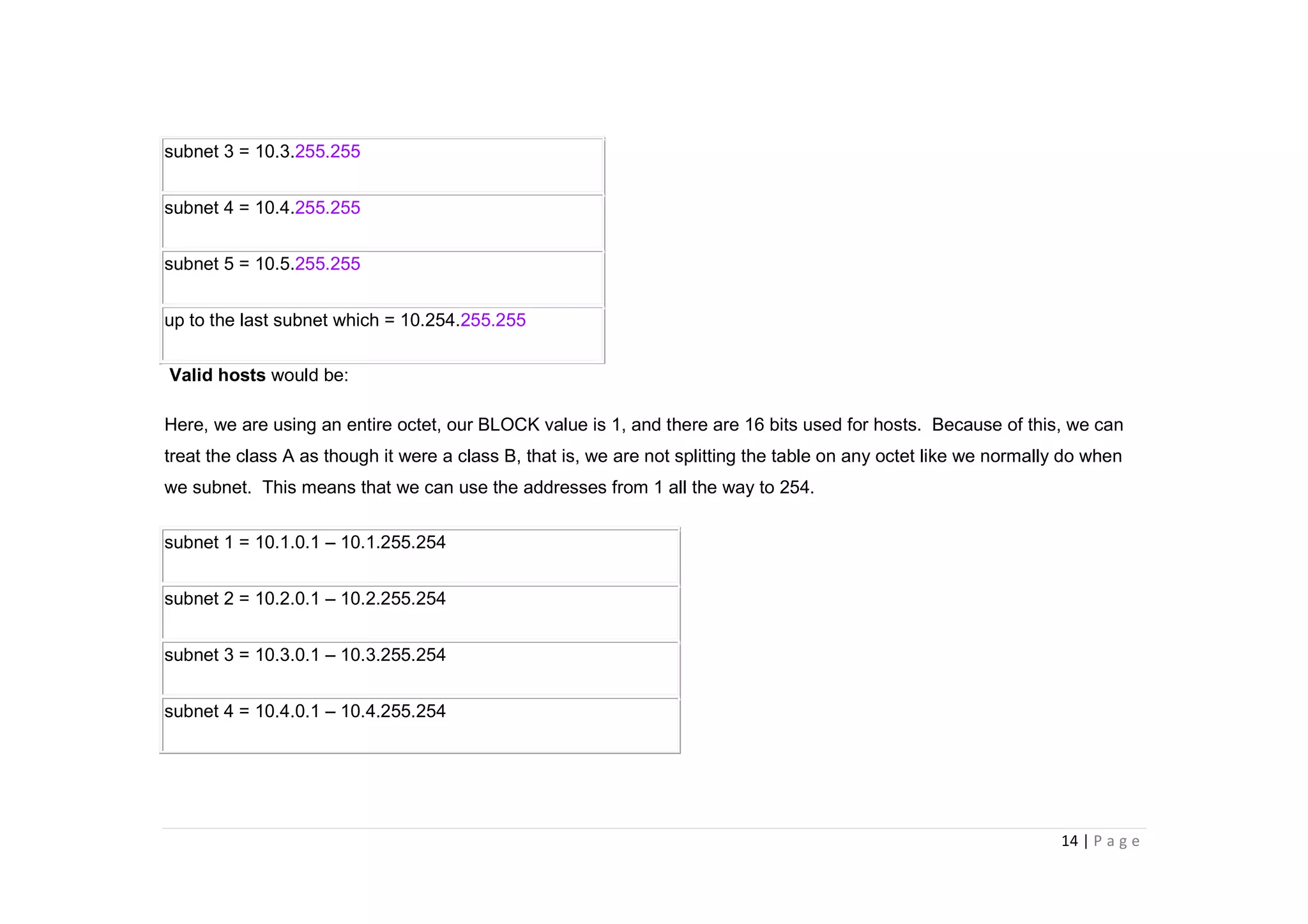
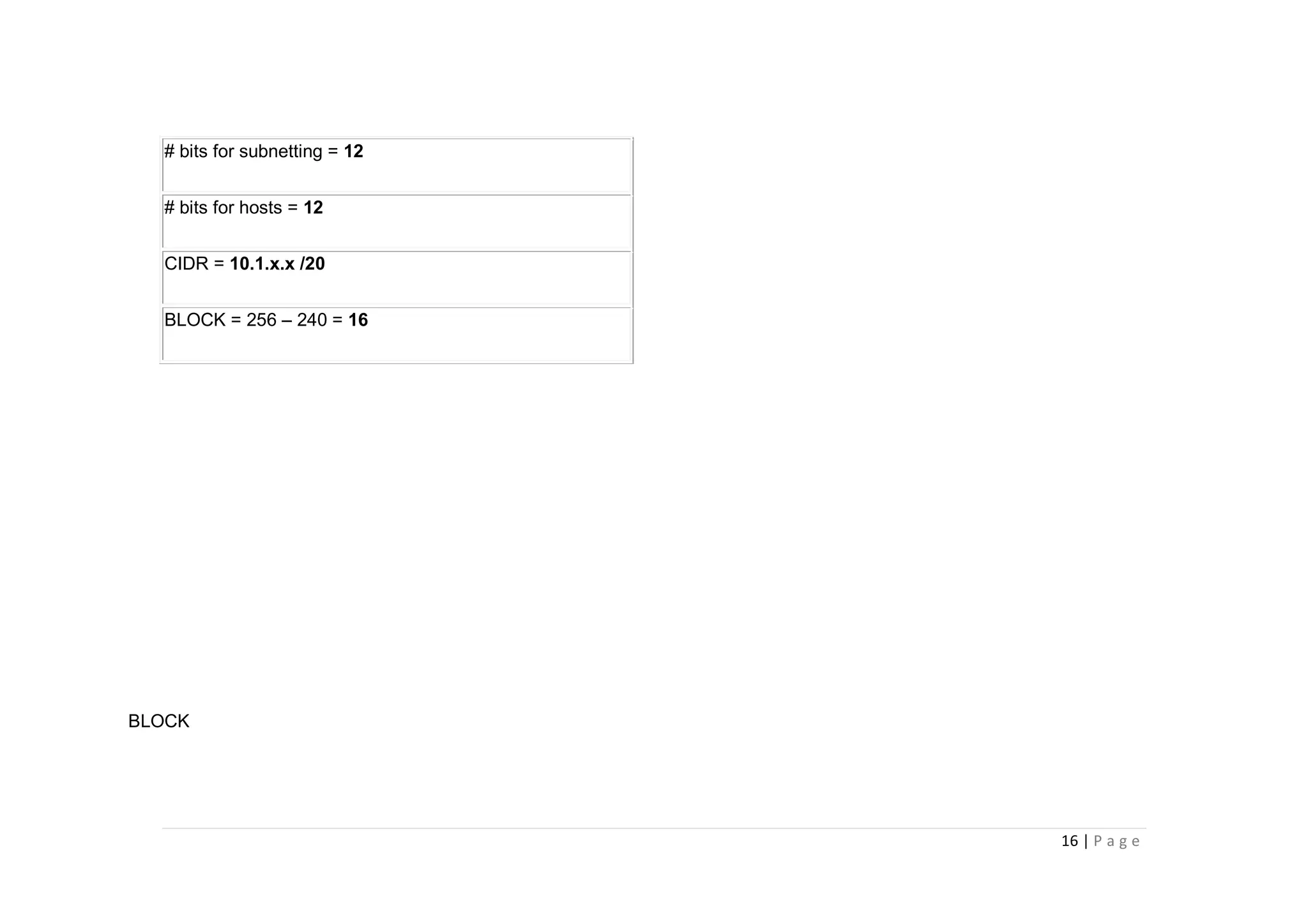
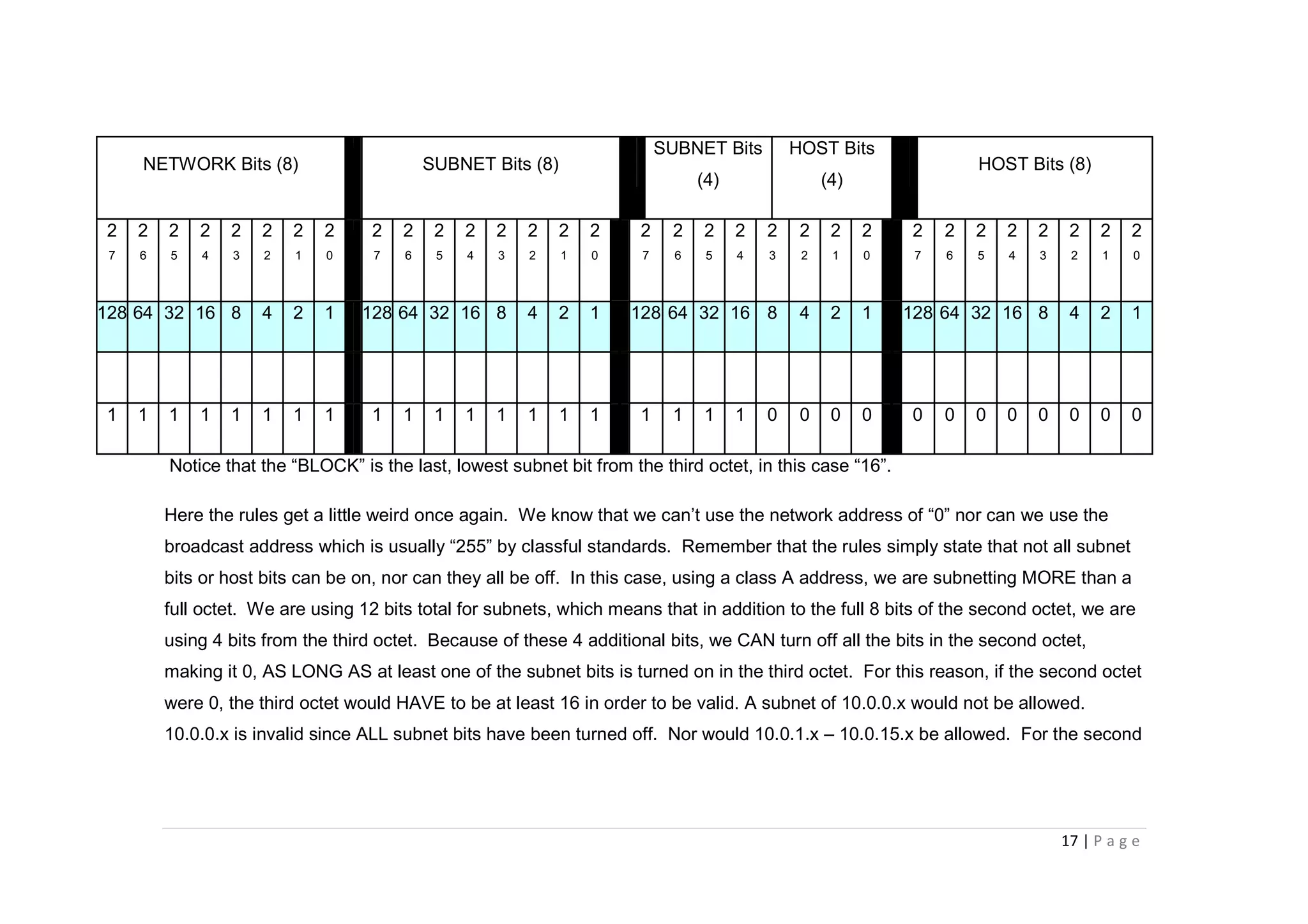
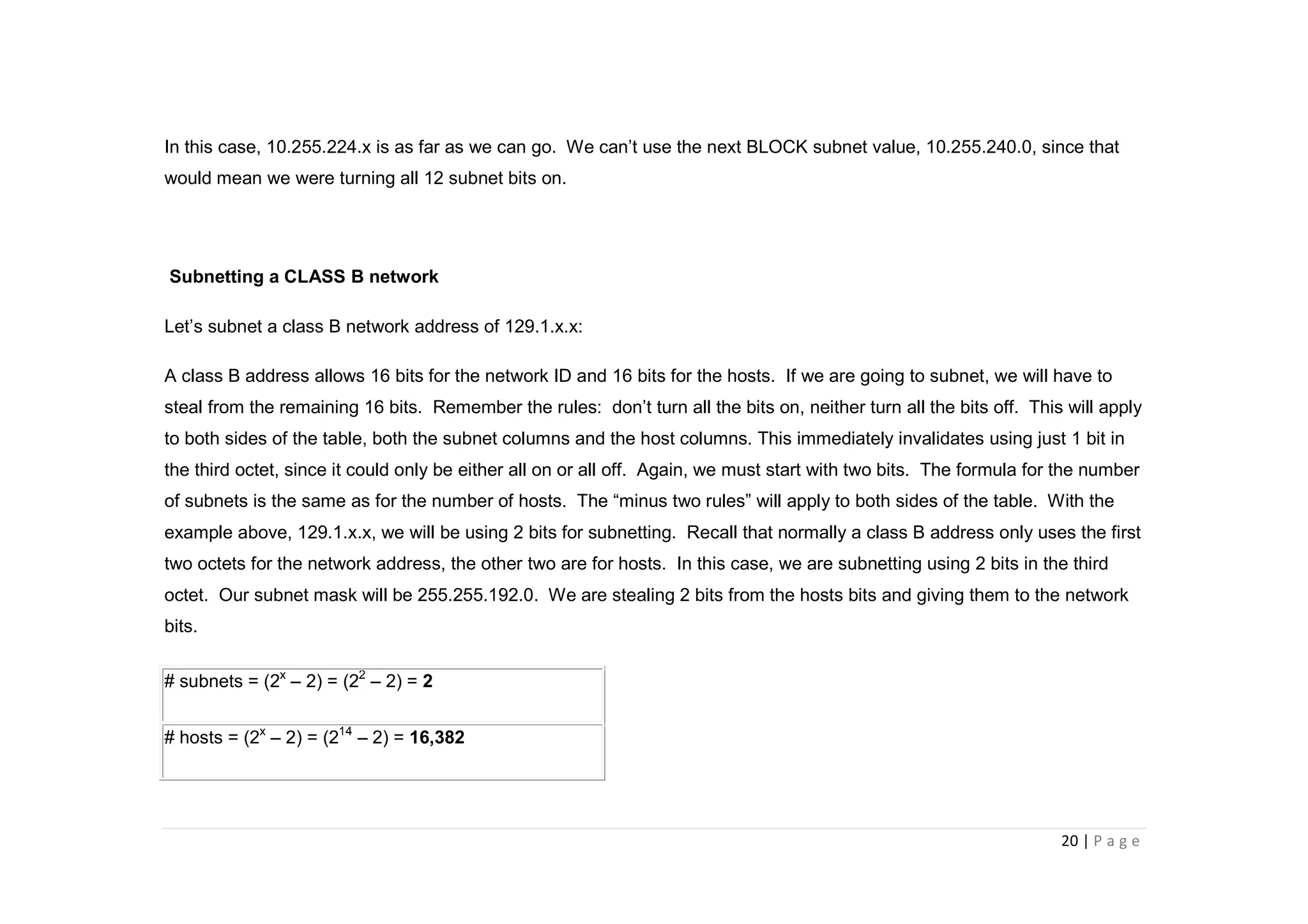
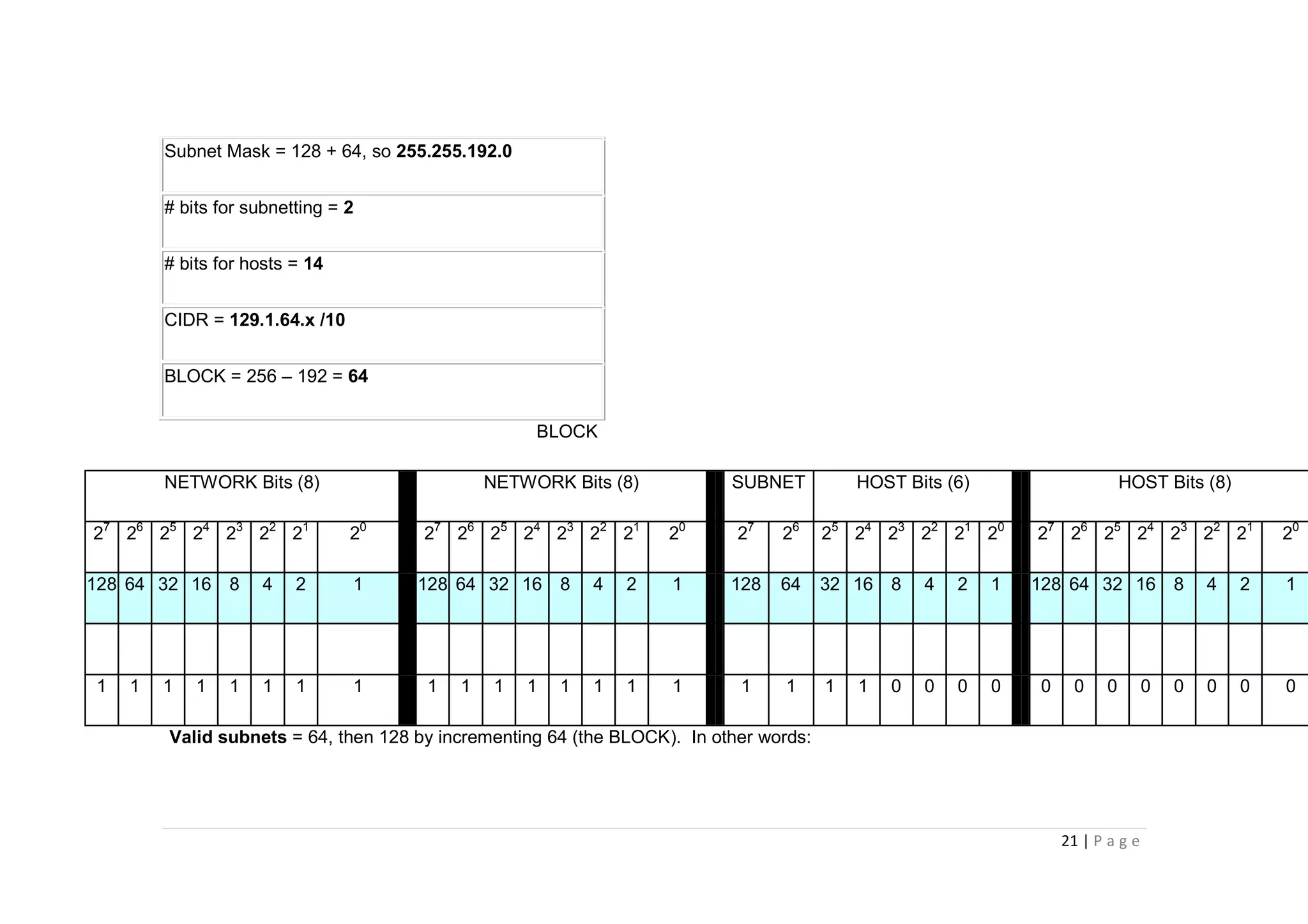
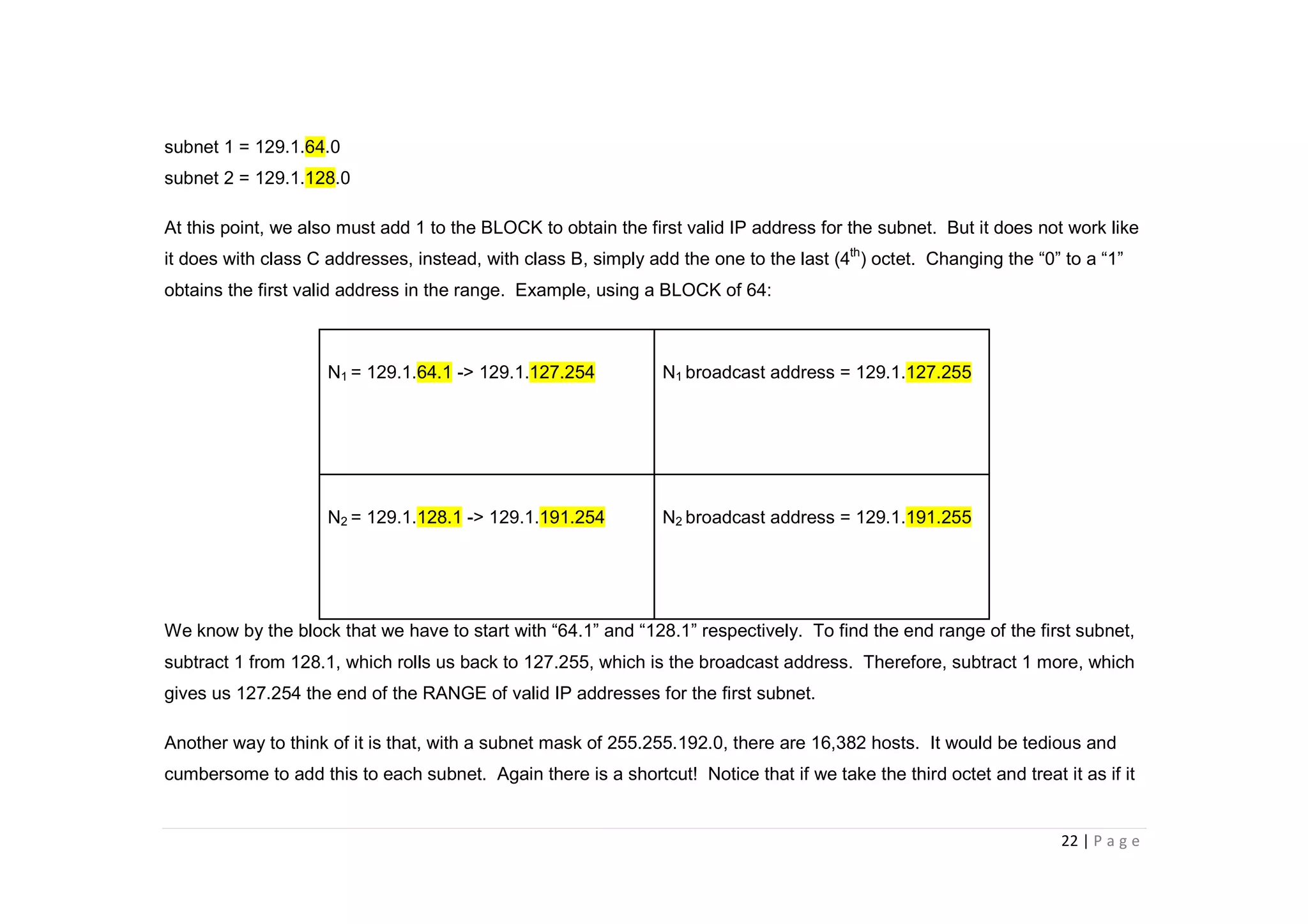
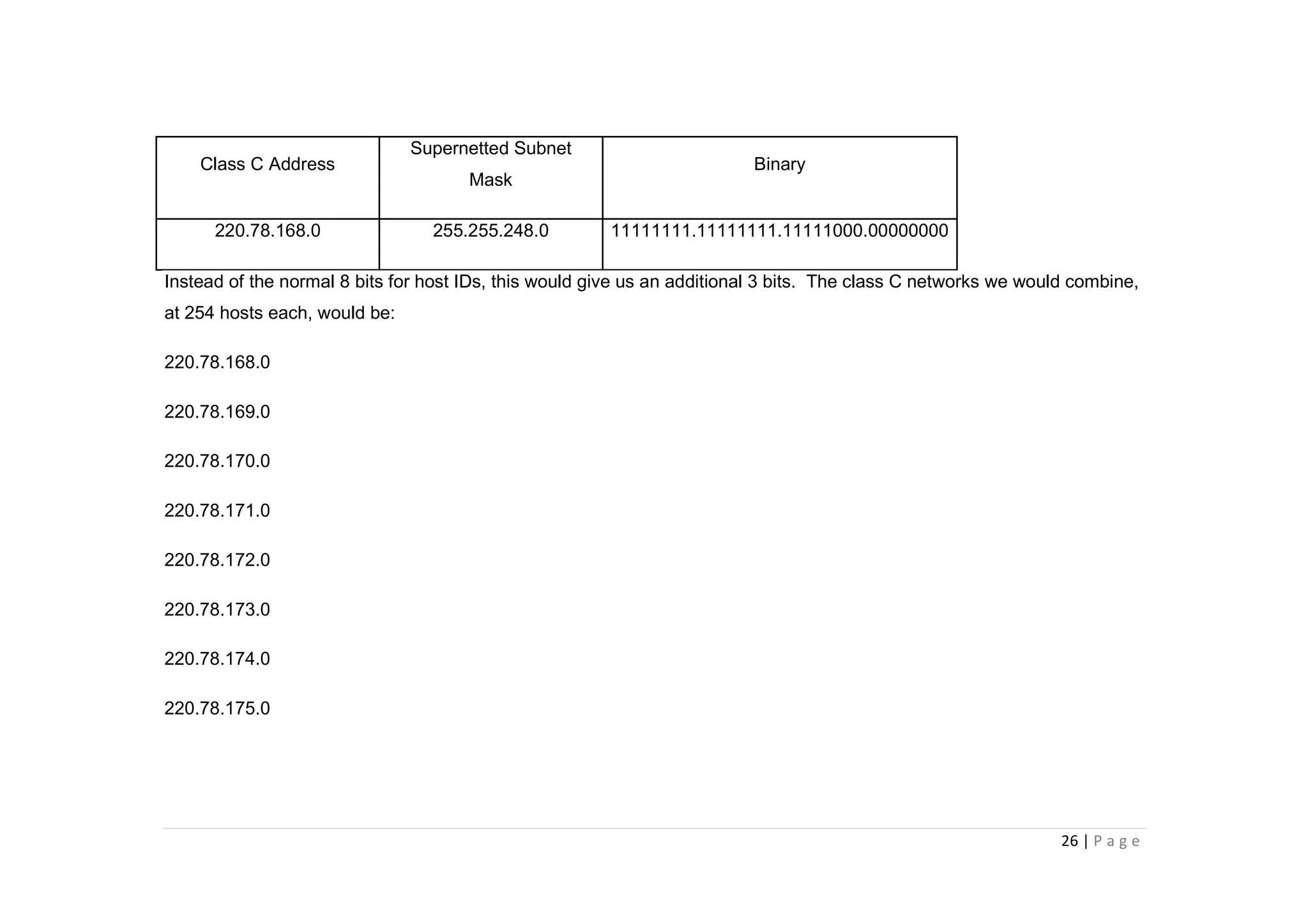
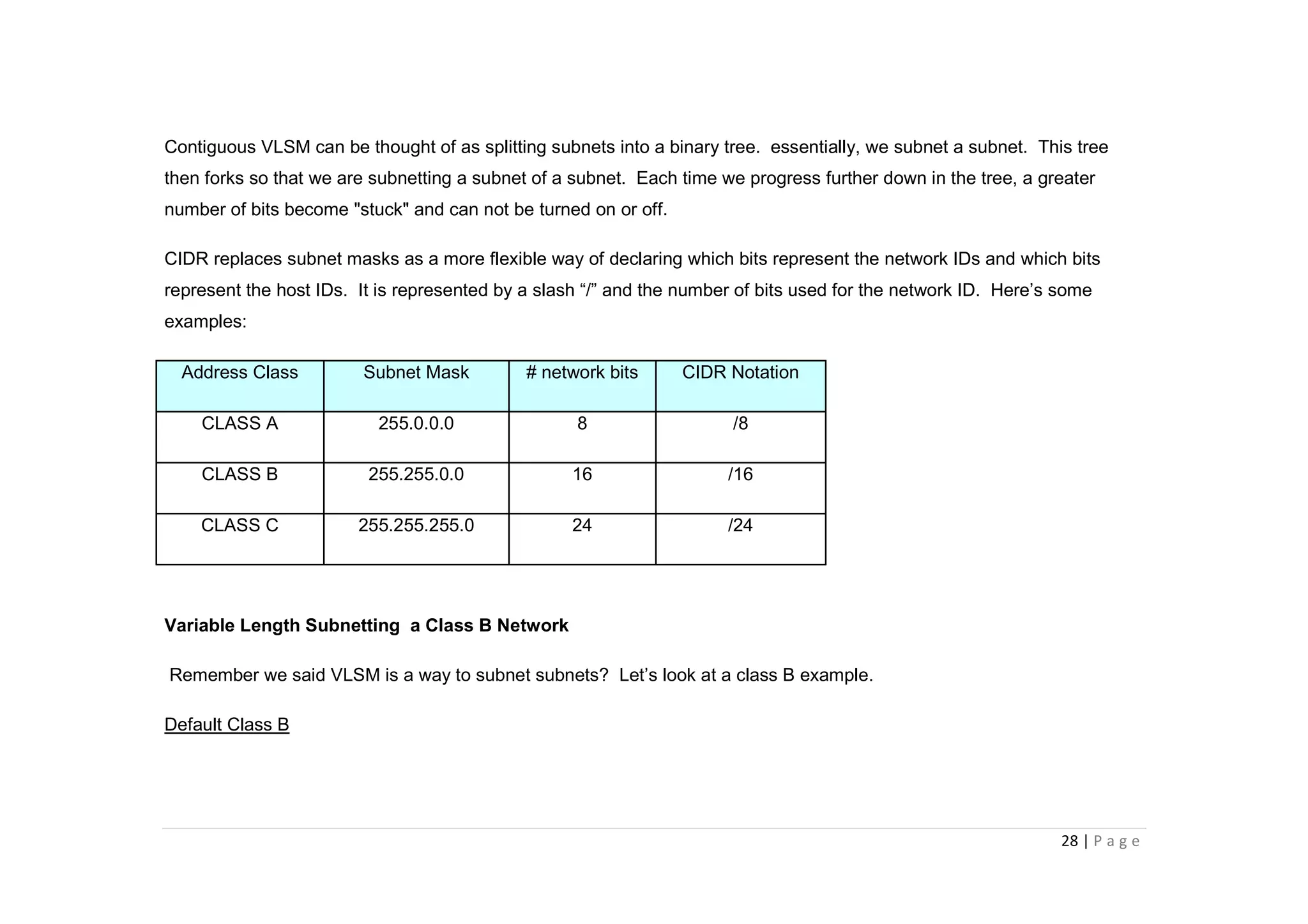
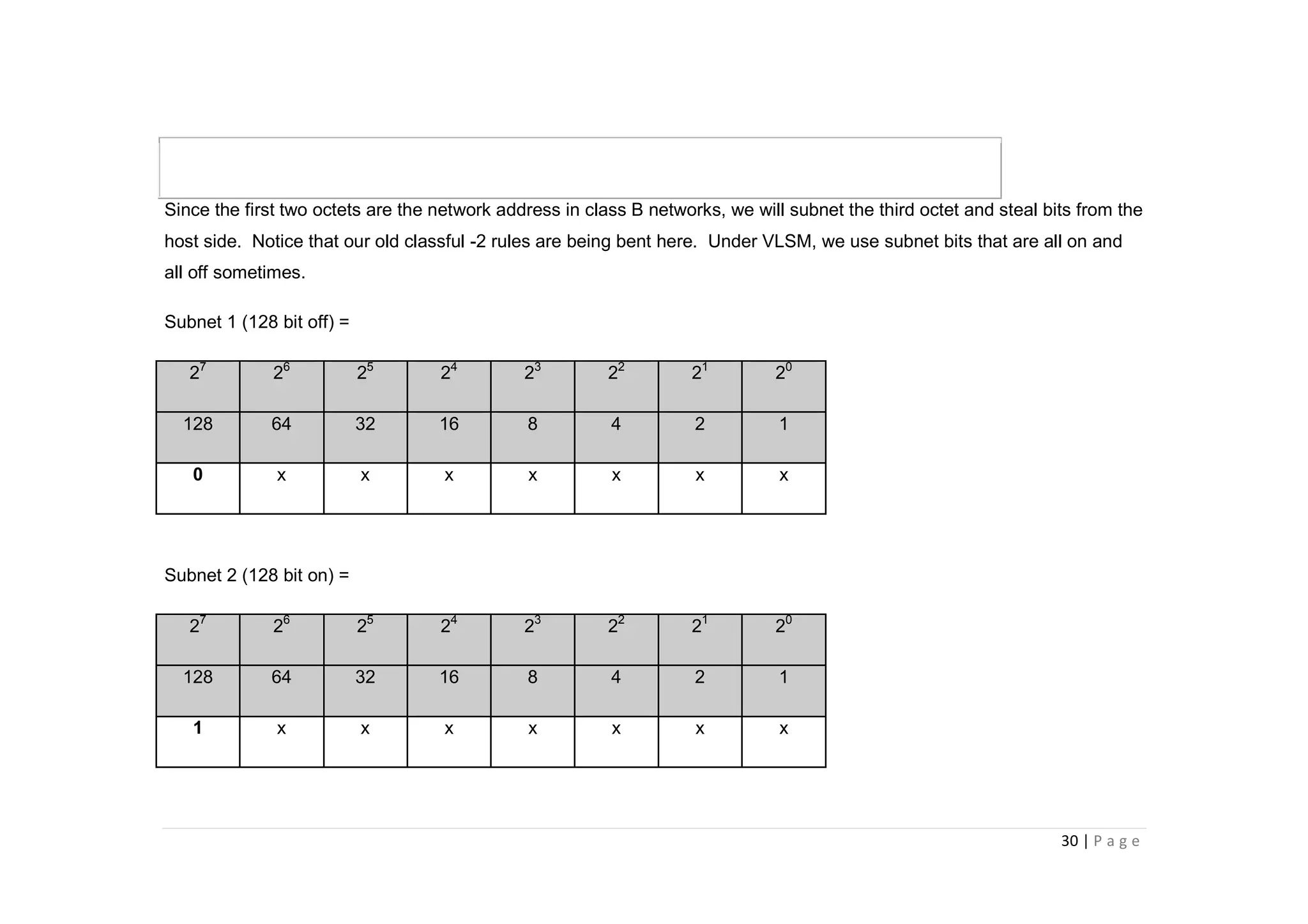
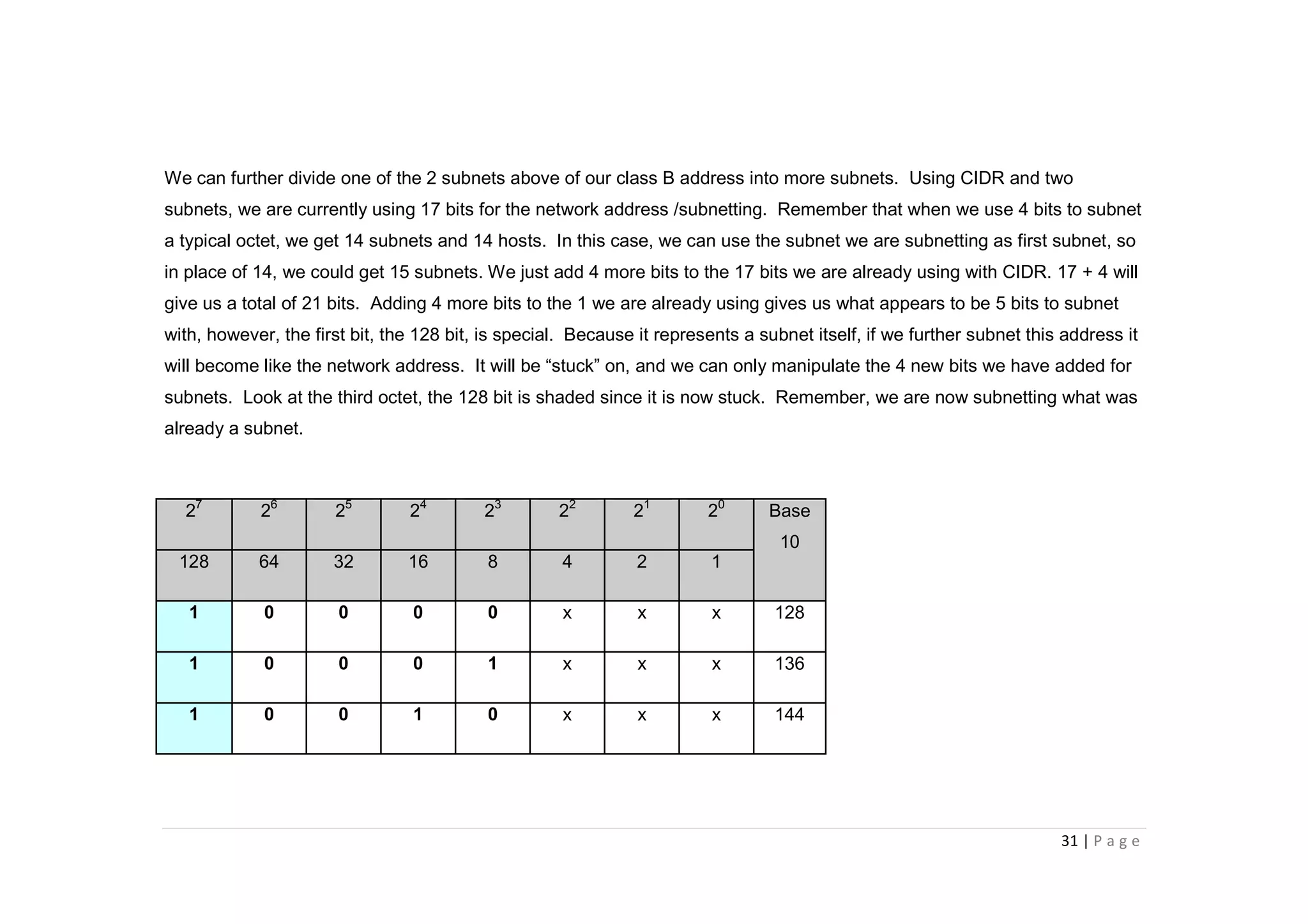
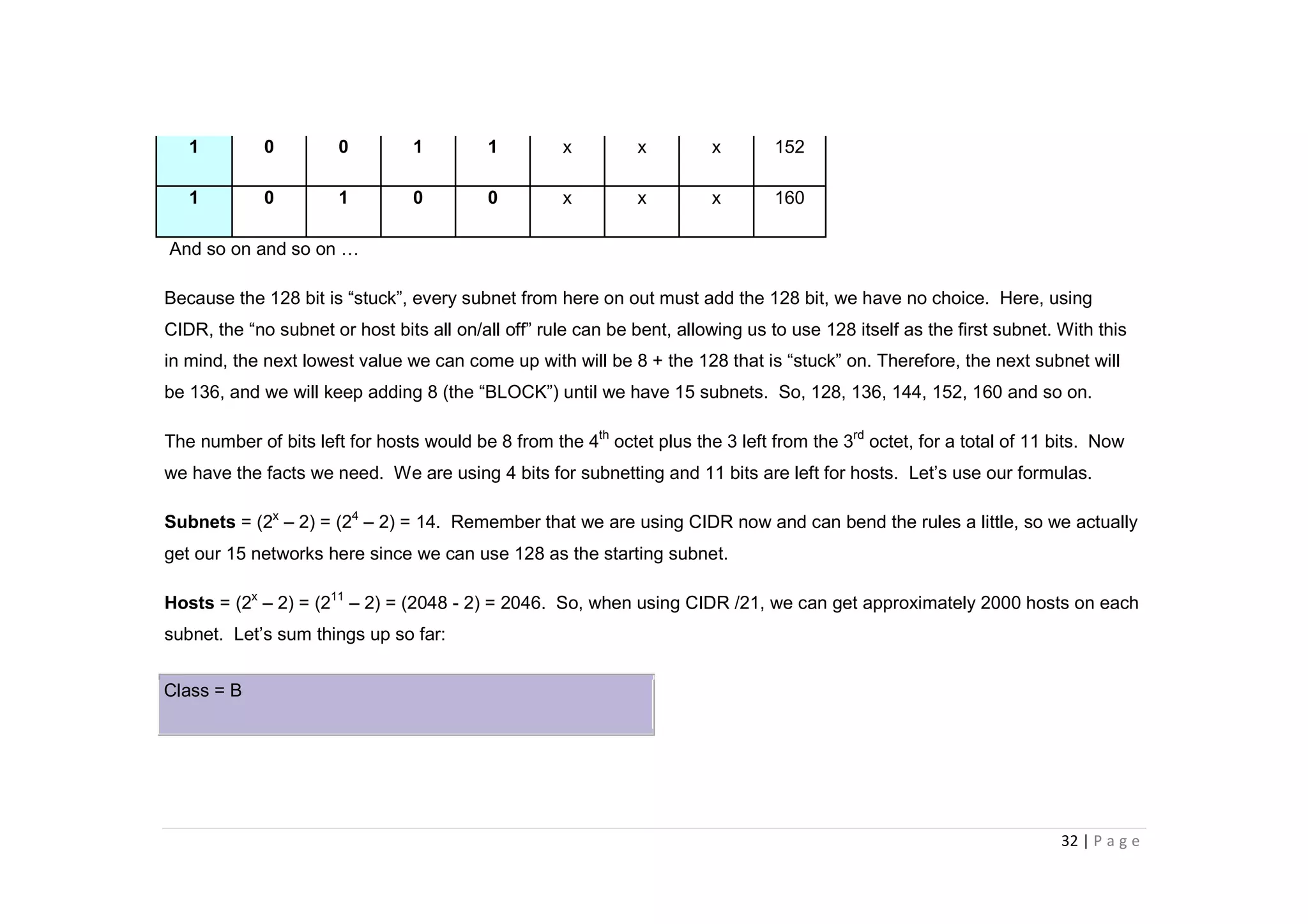
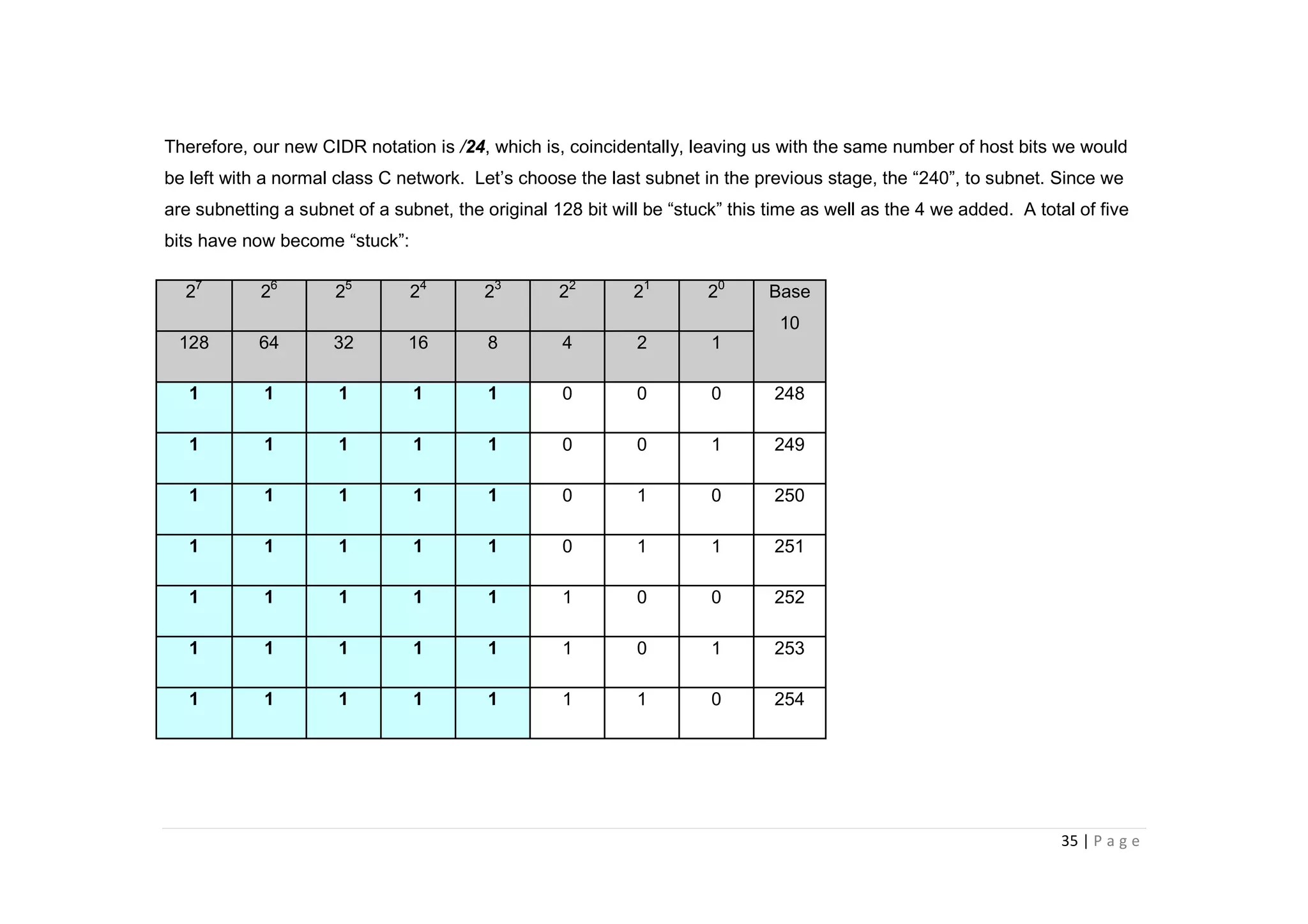
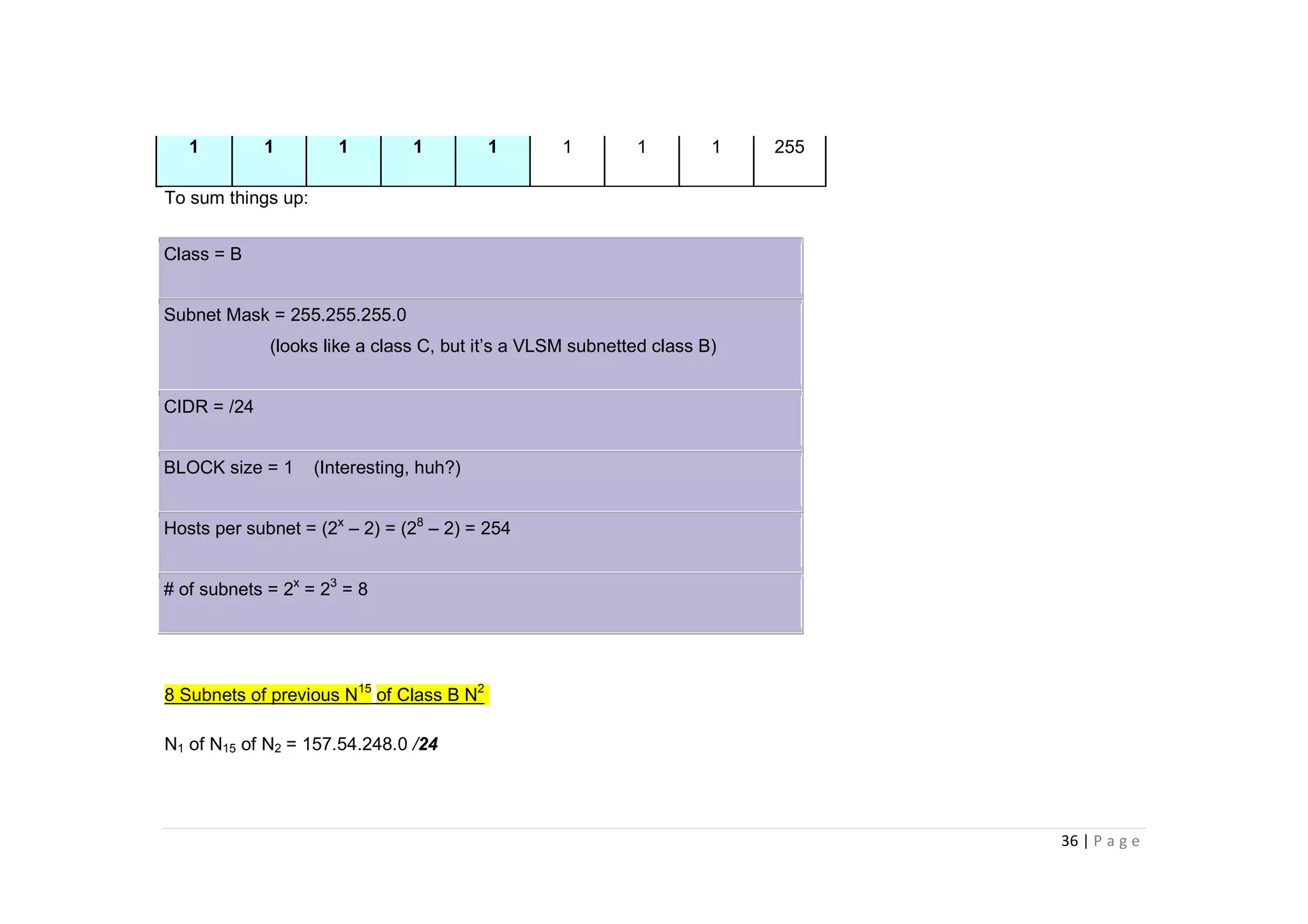
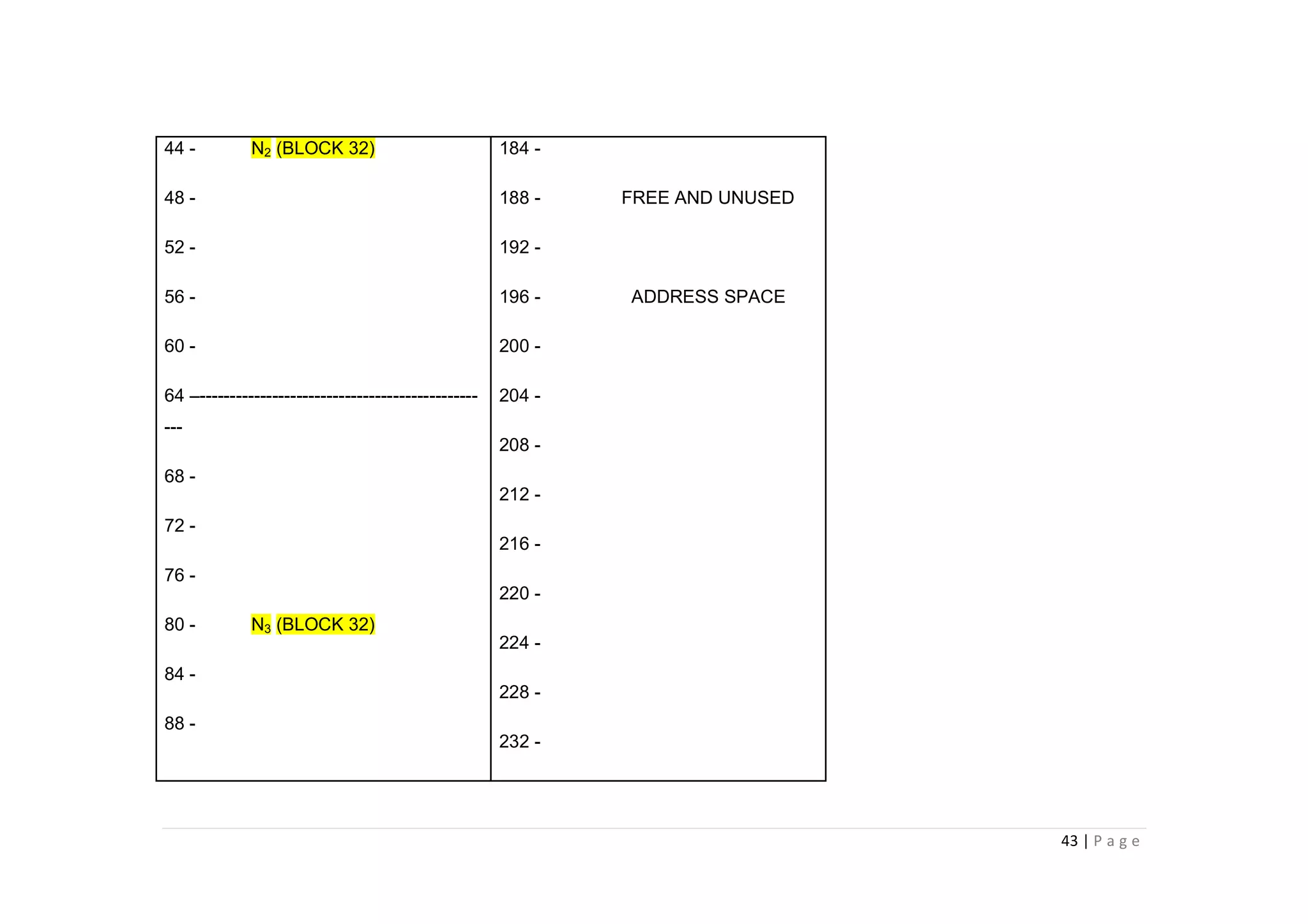
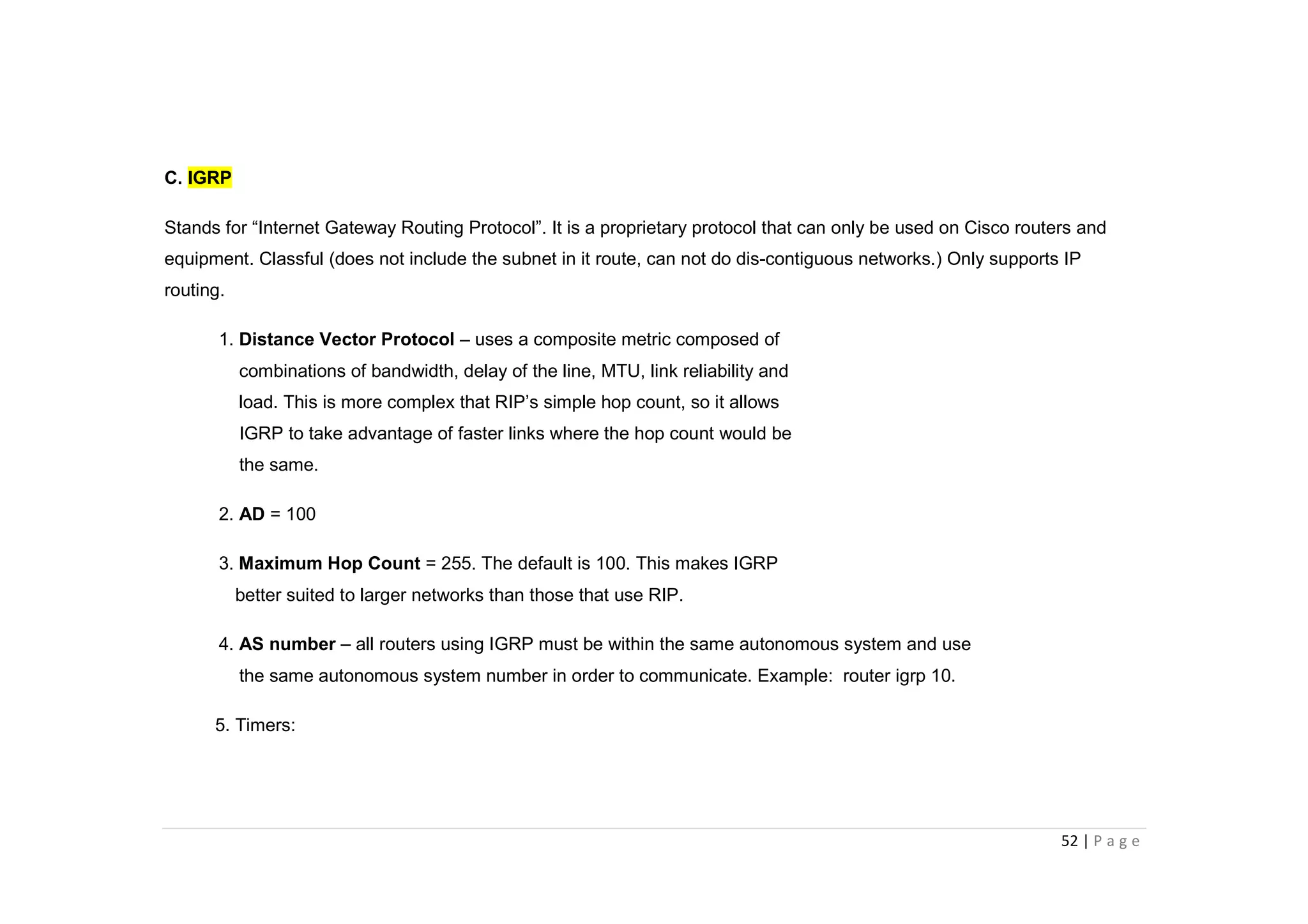
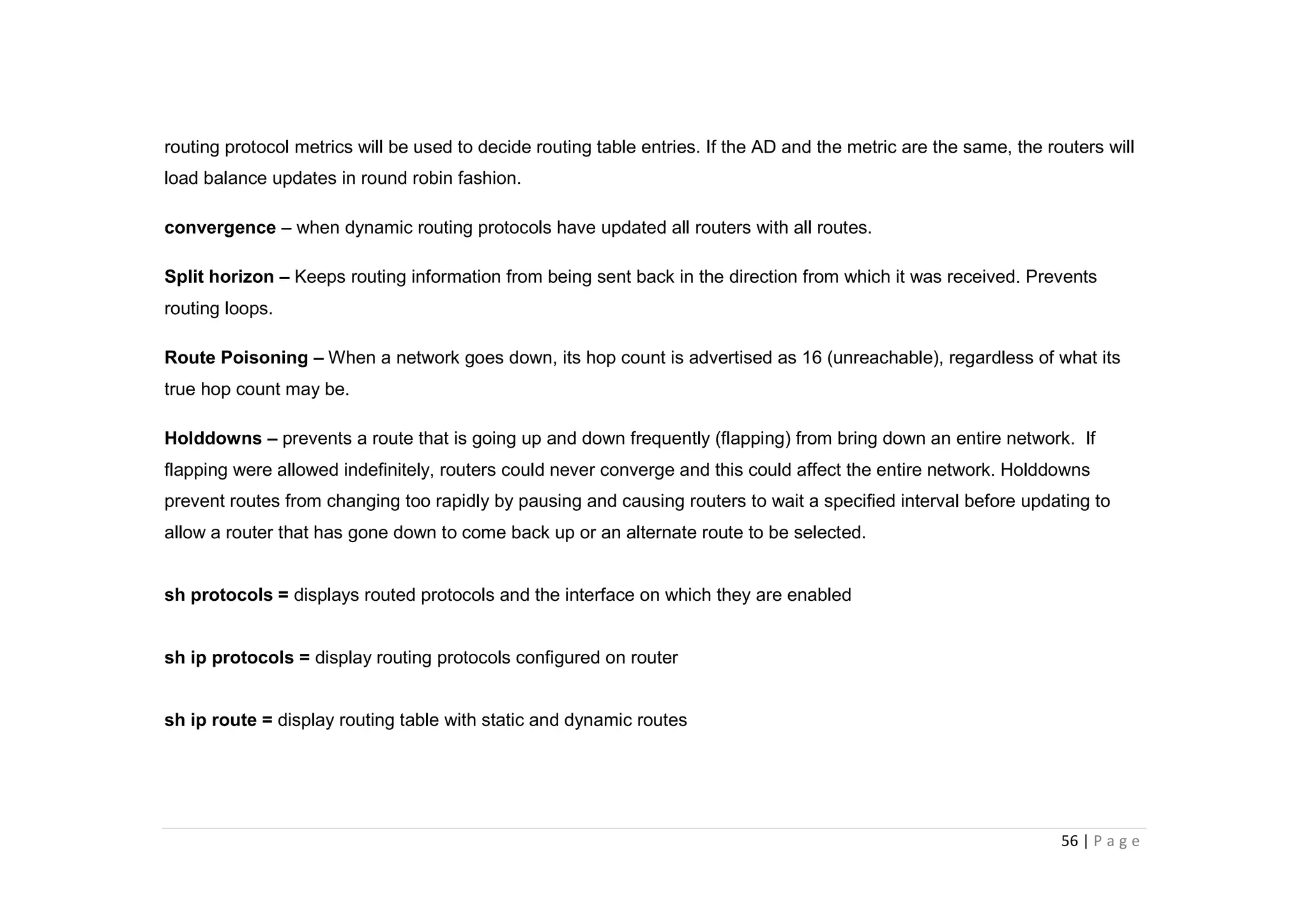
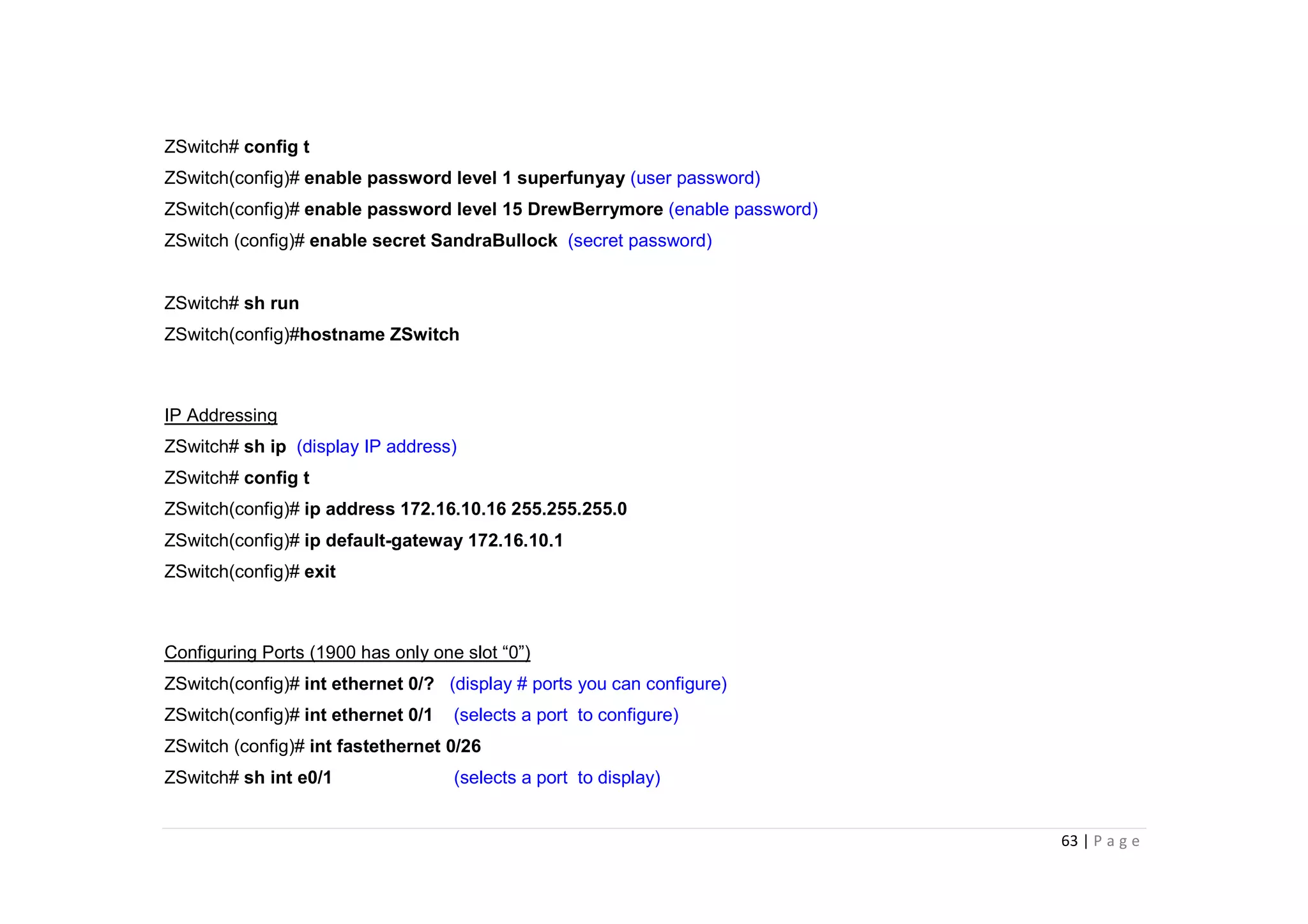
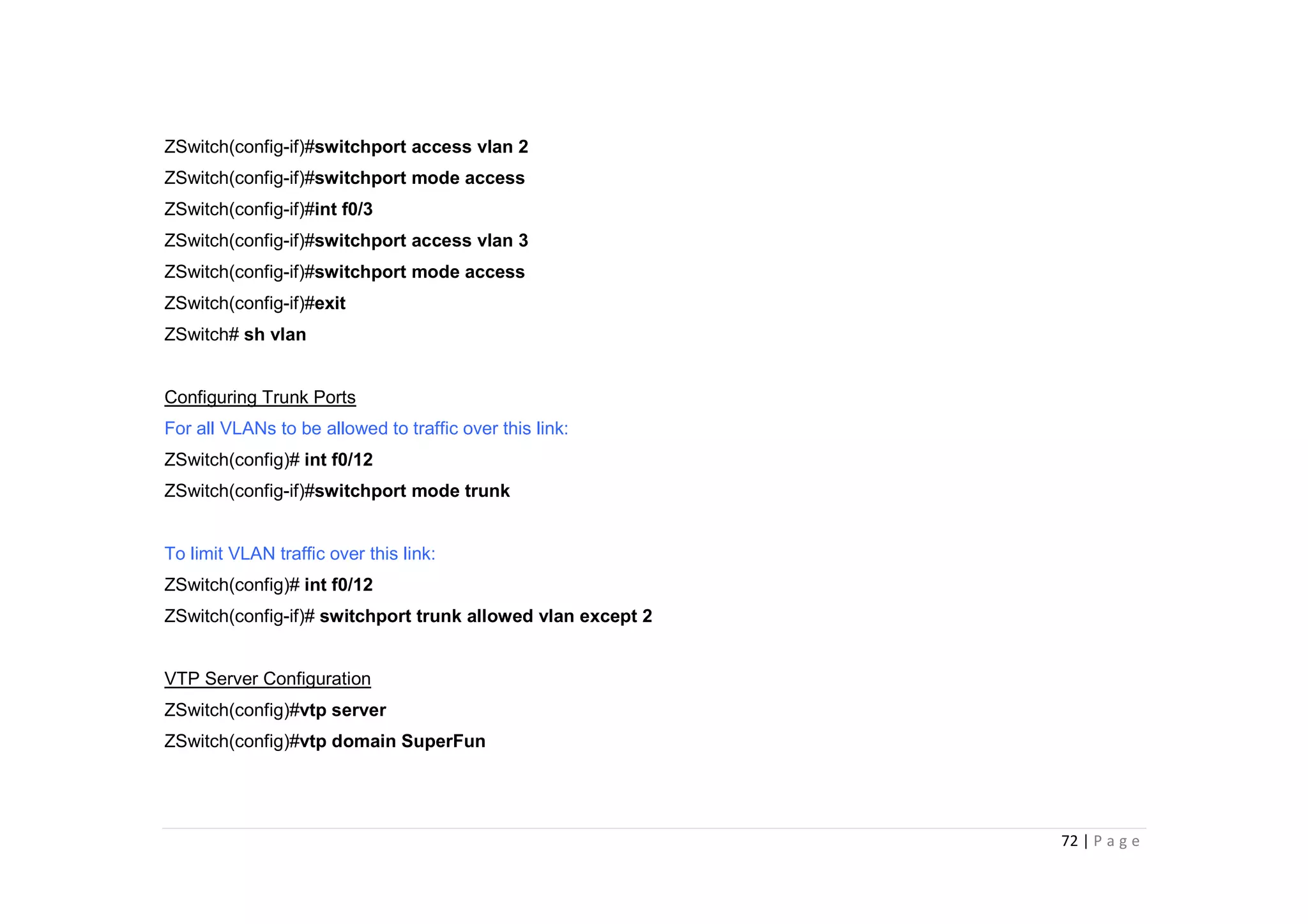
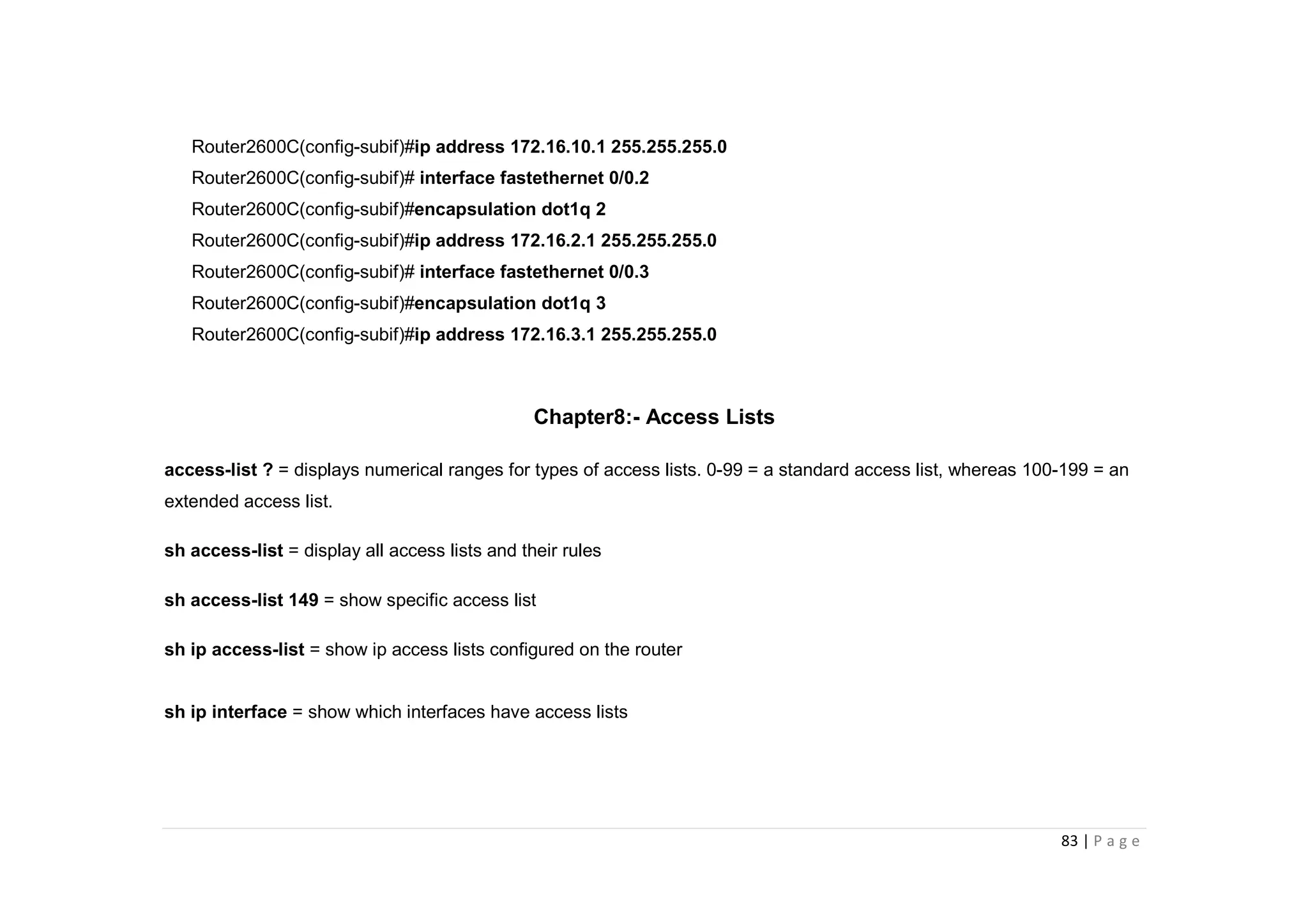
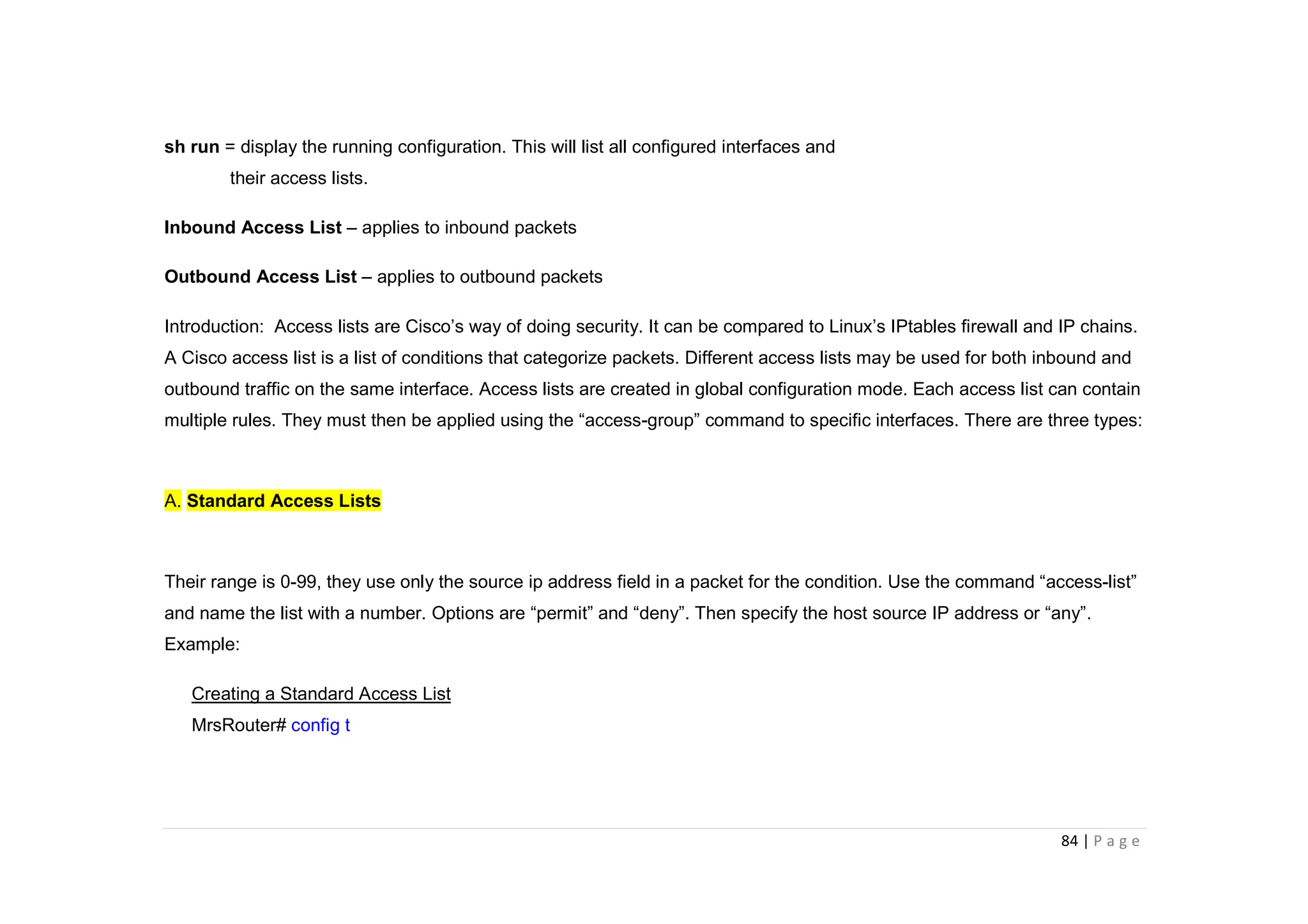
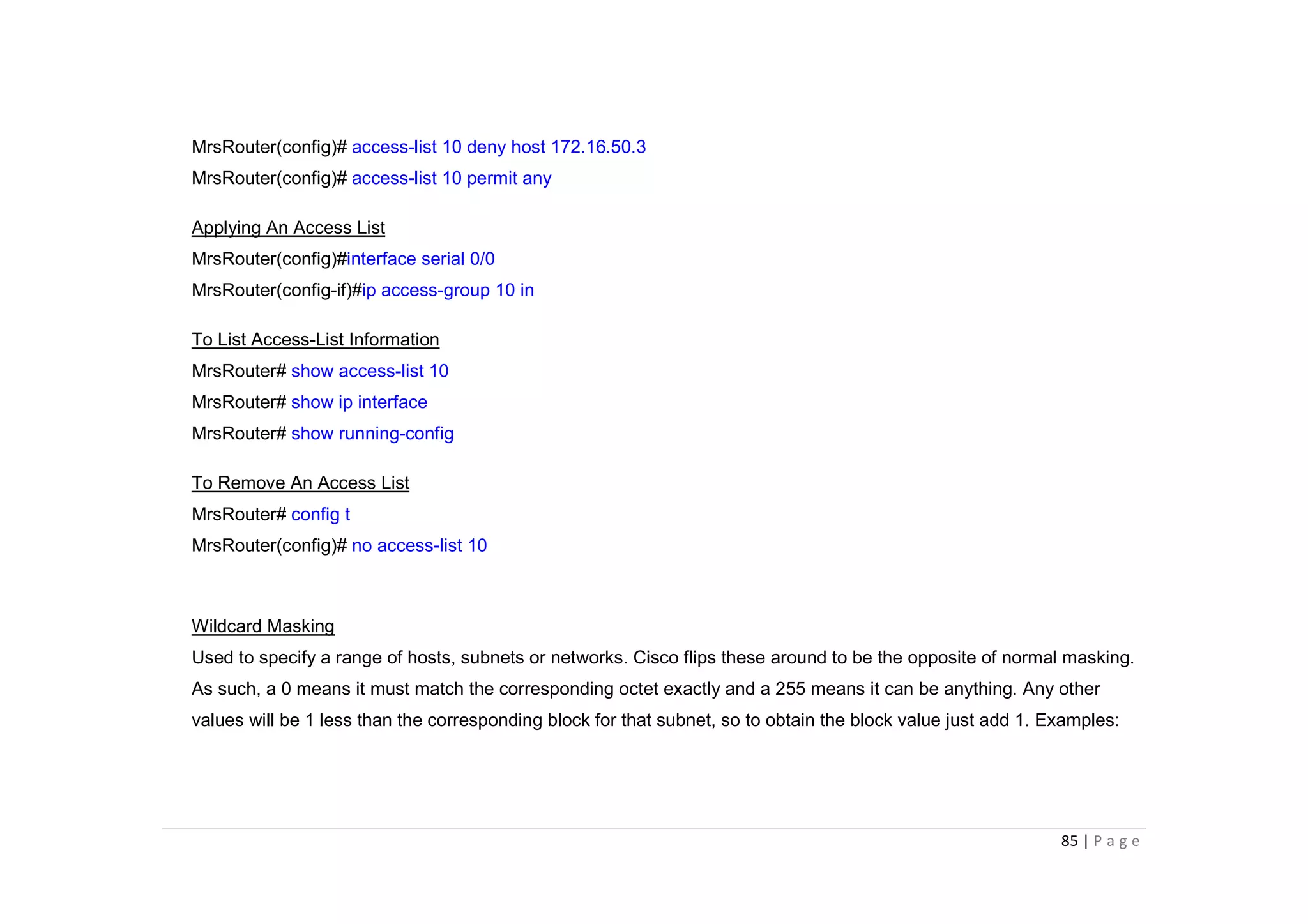
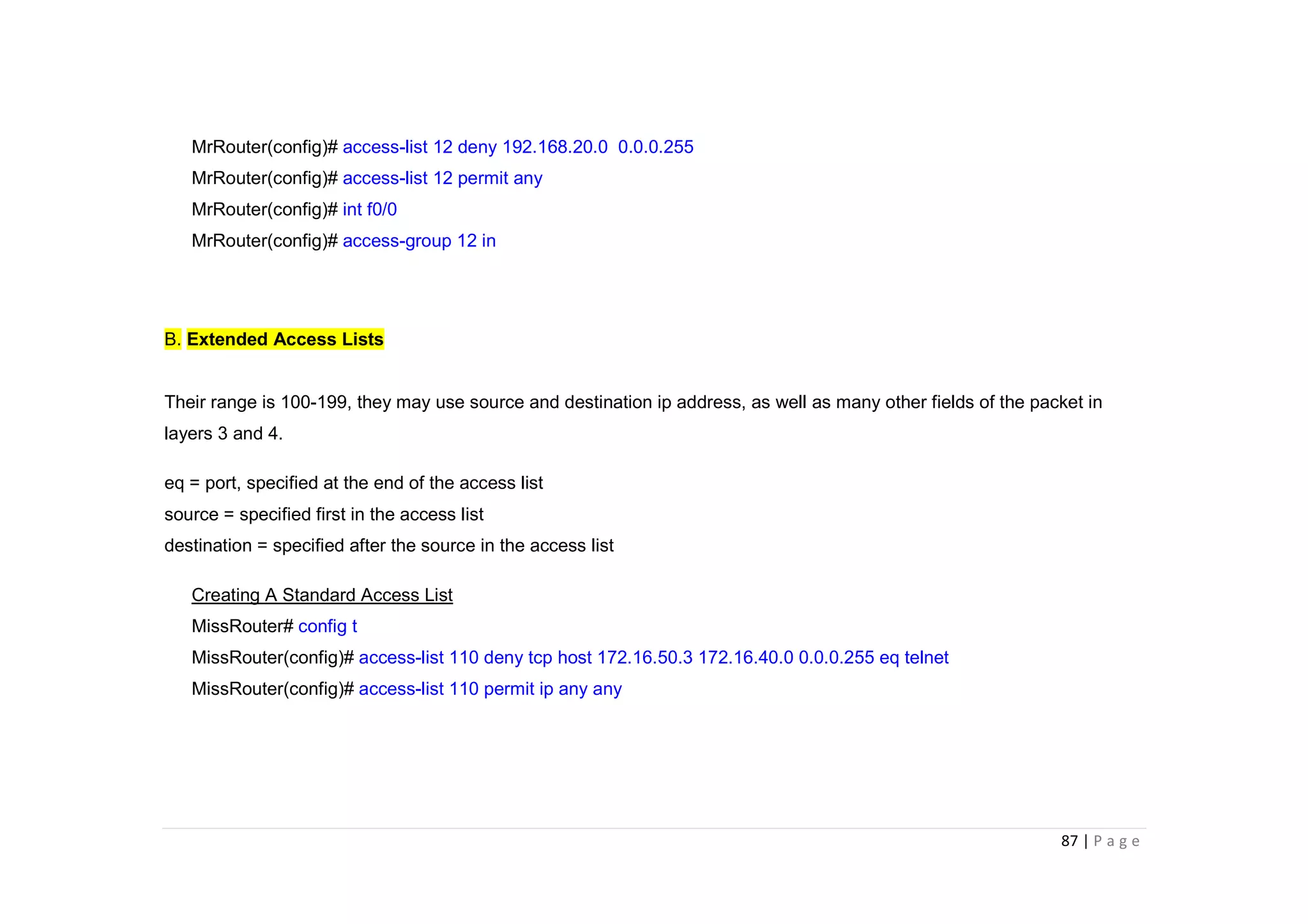
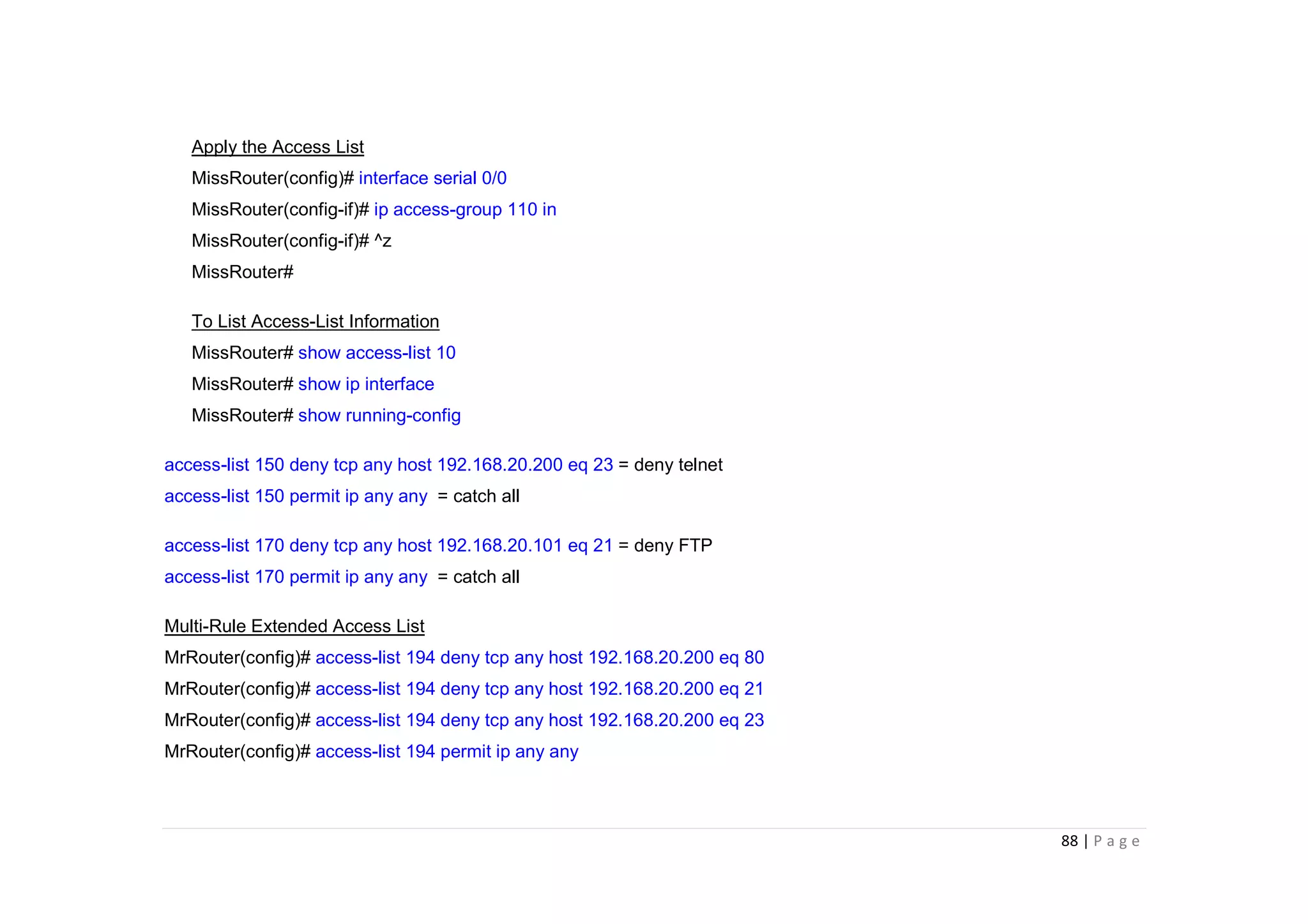
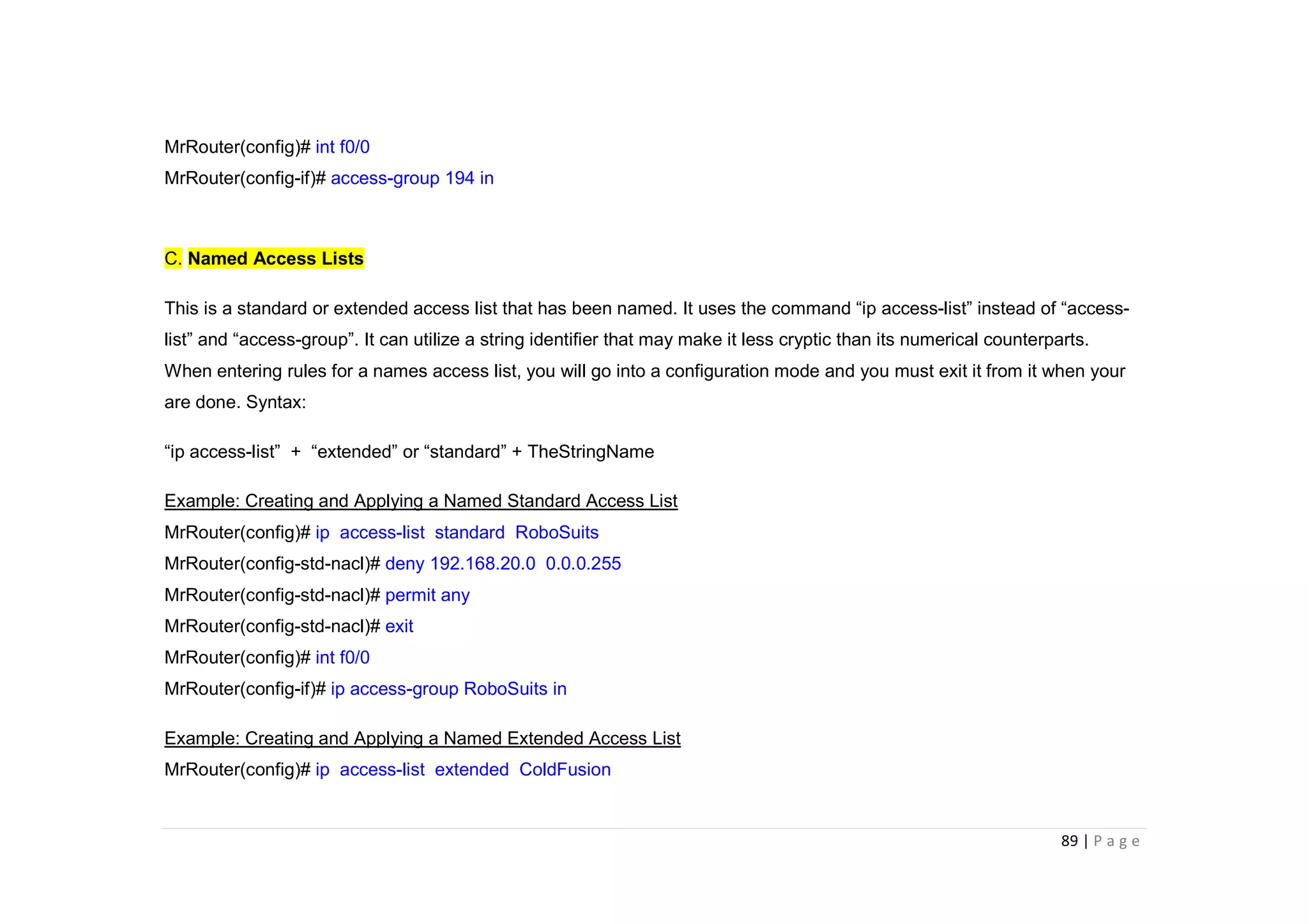
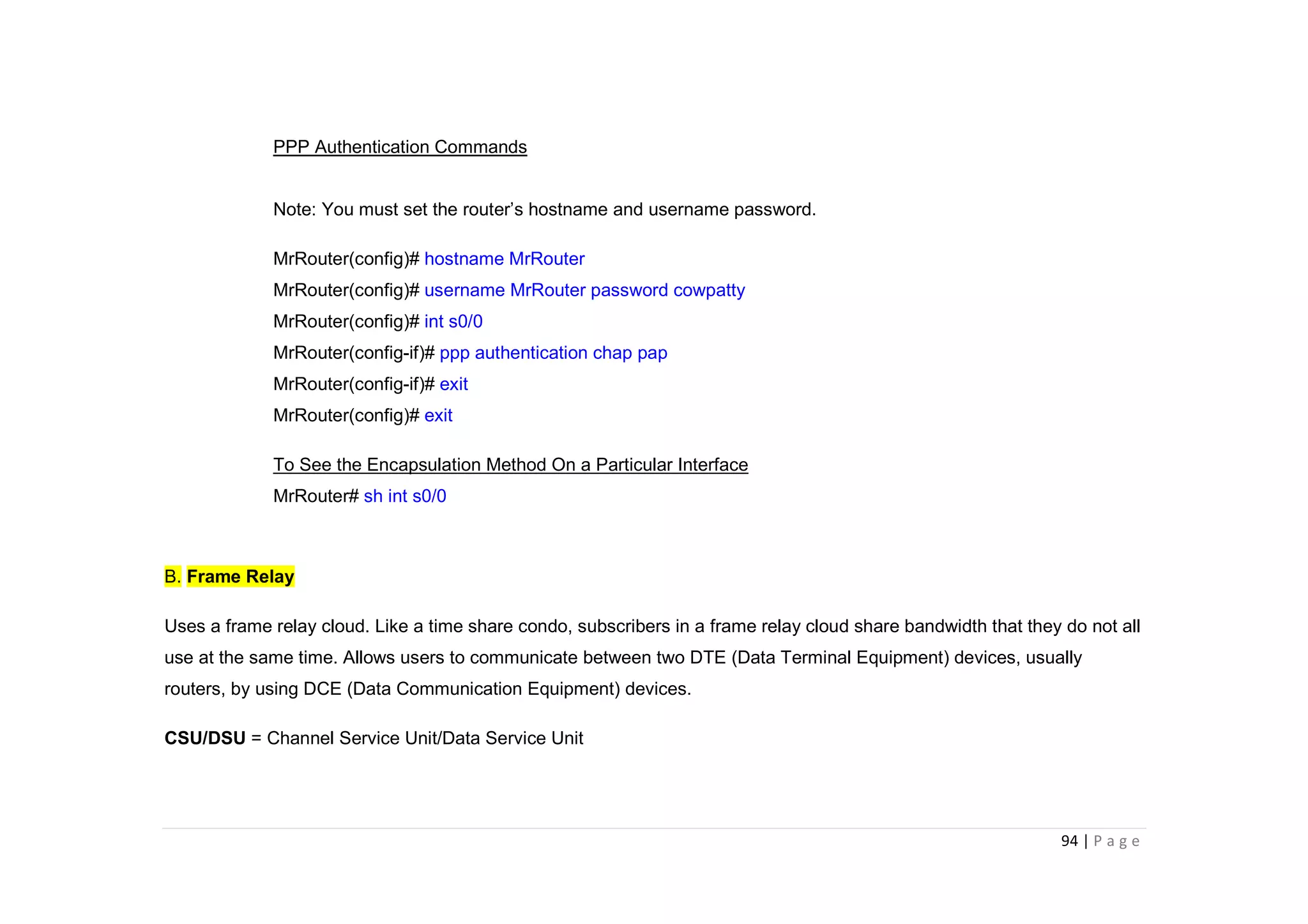
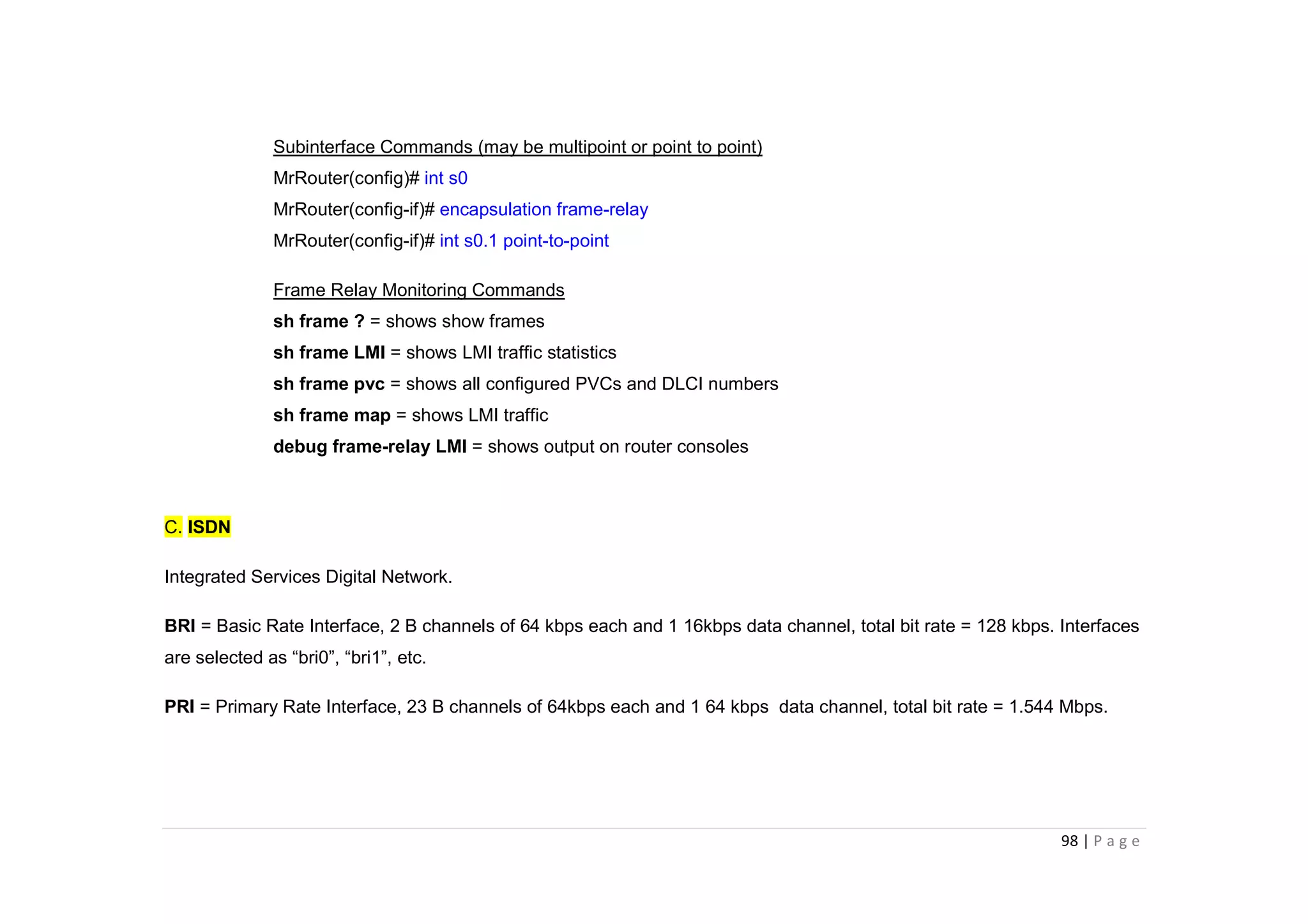
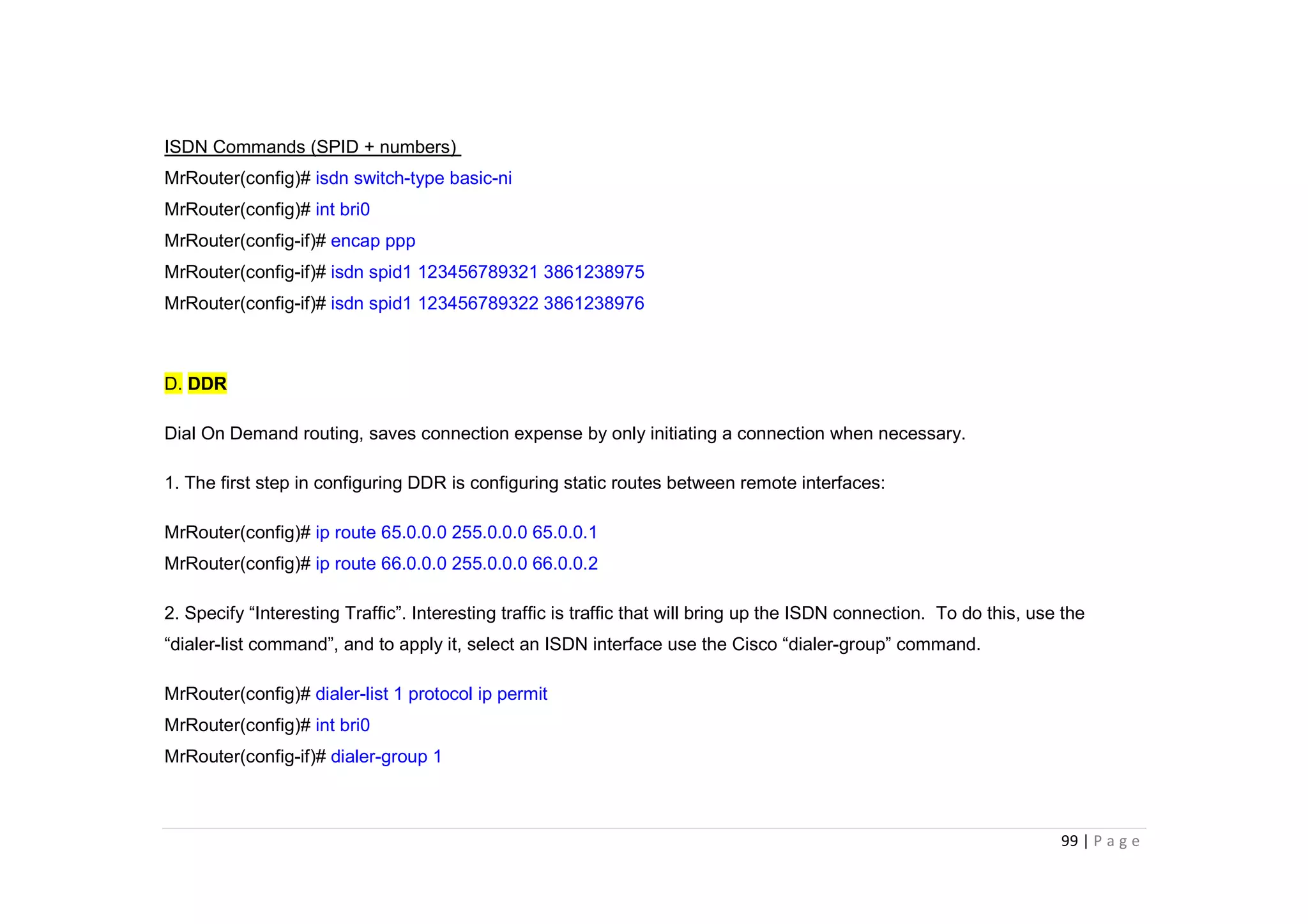
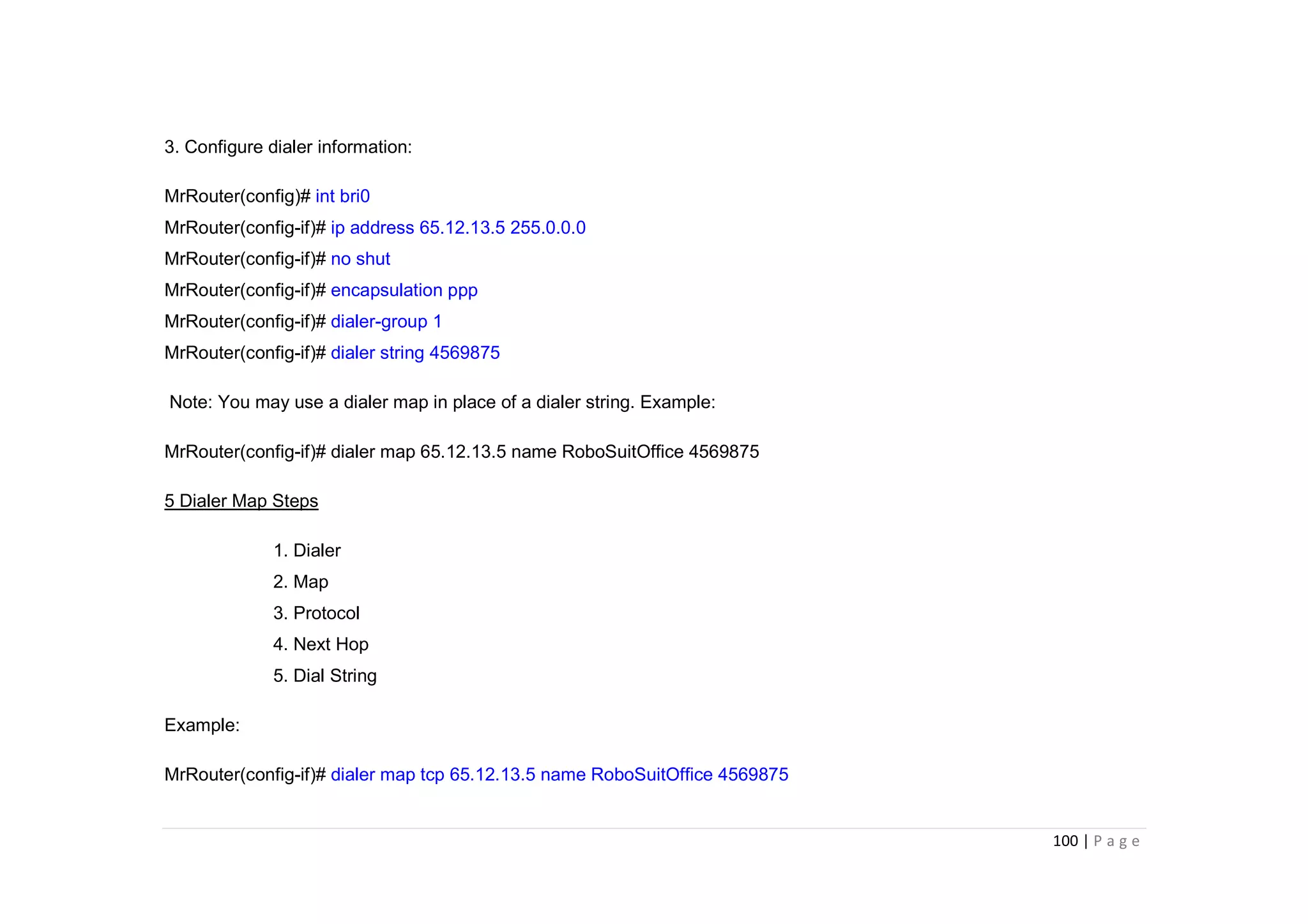
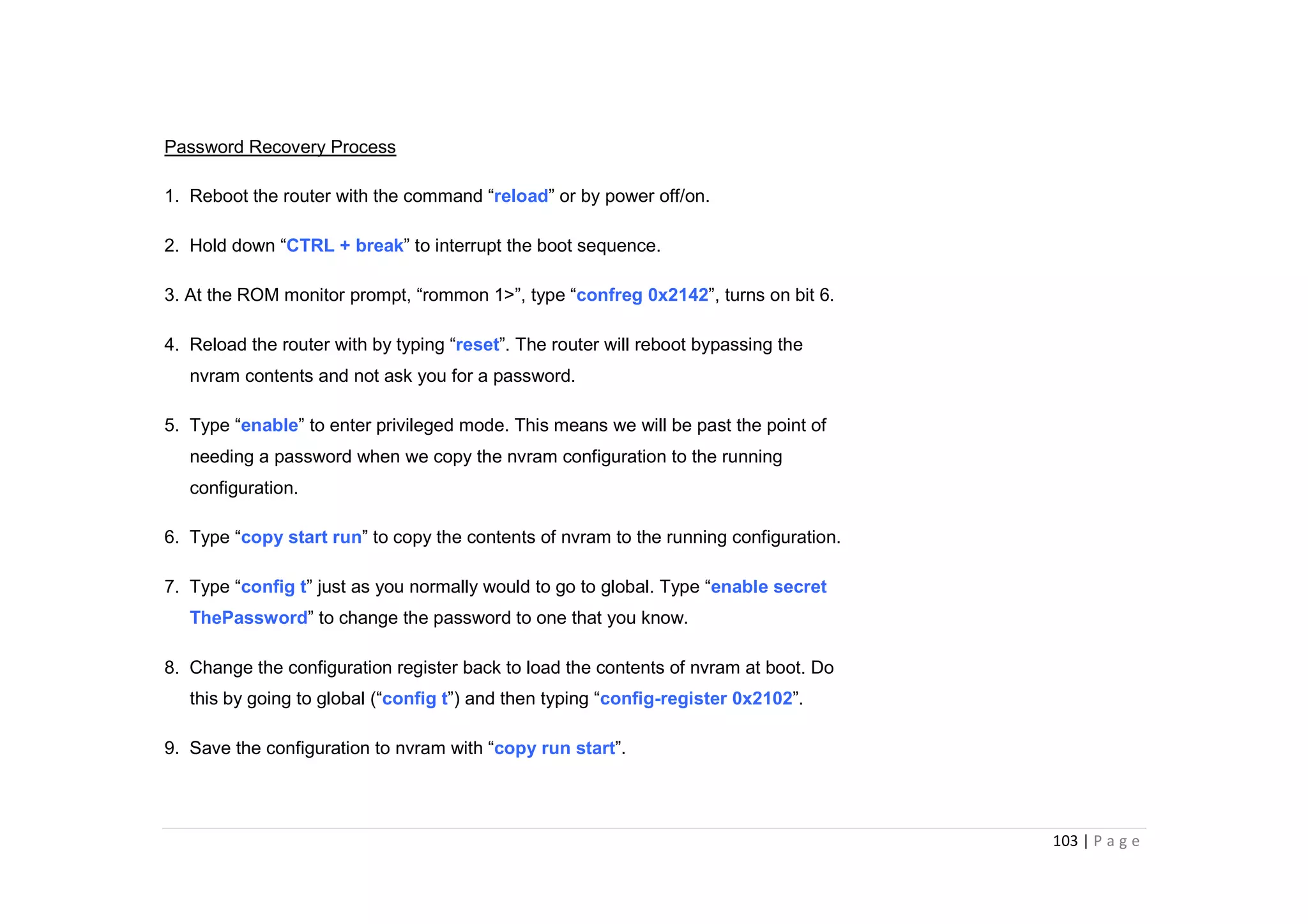
- The document discusses classful IP addressing and subnetting. It provides examples of subnetting Class A, B, and C networks using different numbers of subnet bits.
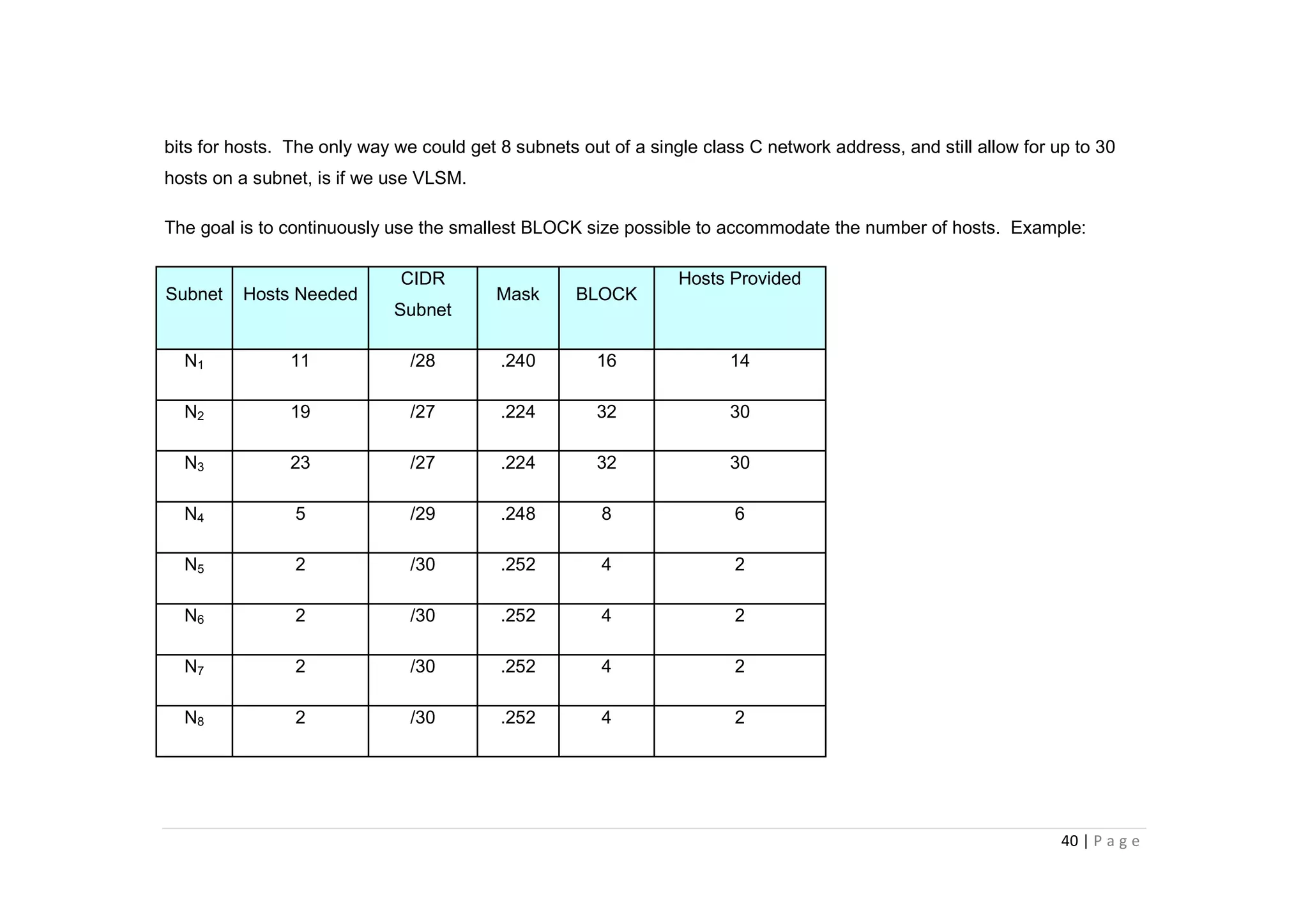
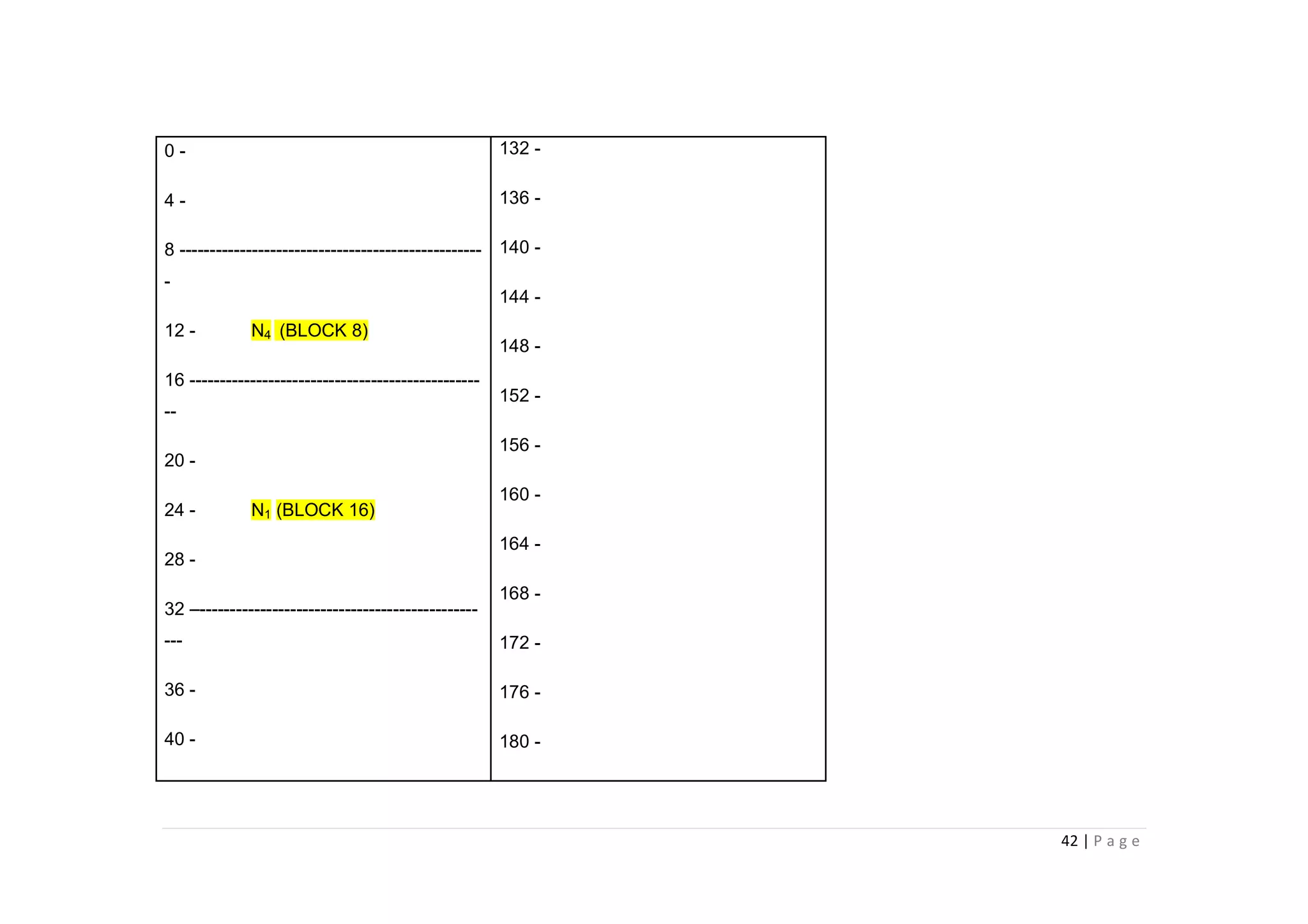
- The key steps in subnetting are determining the number of subnet and host bits, calculating the subnet range and broadcast addresses, and identifying valid host addresses within each subnet.
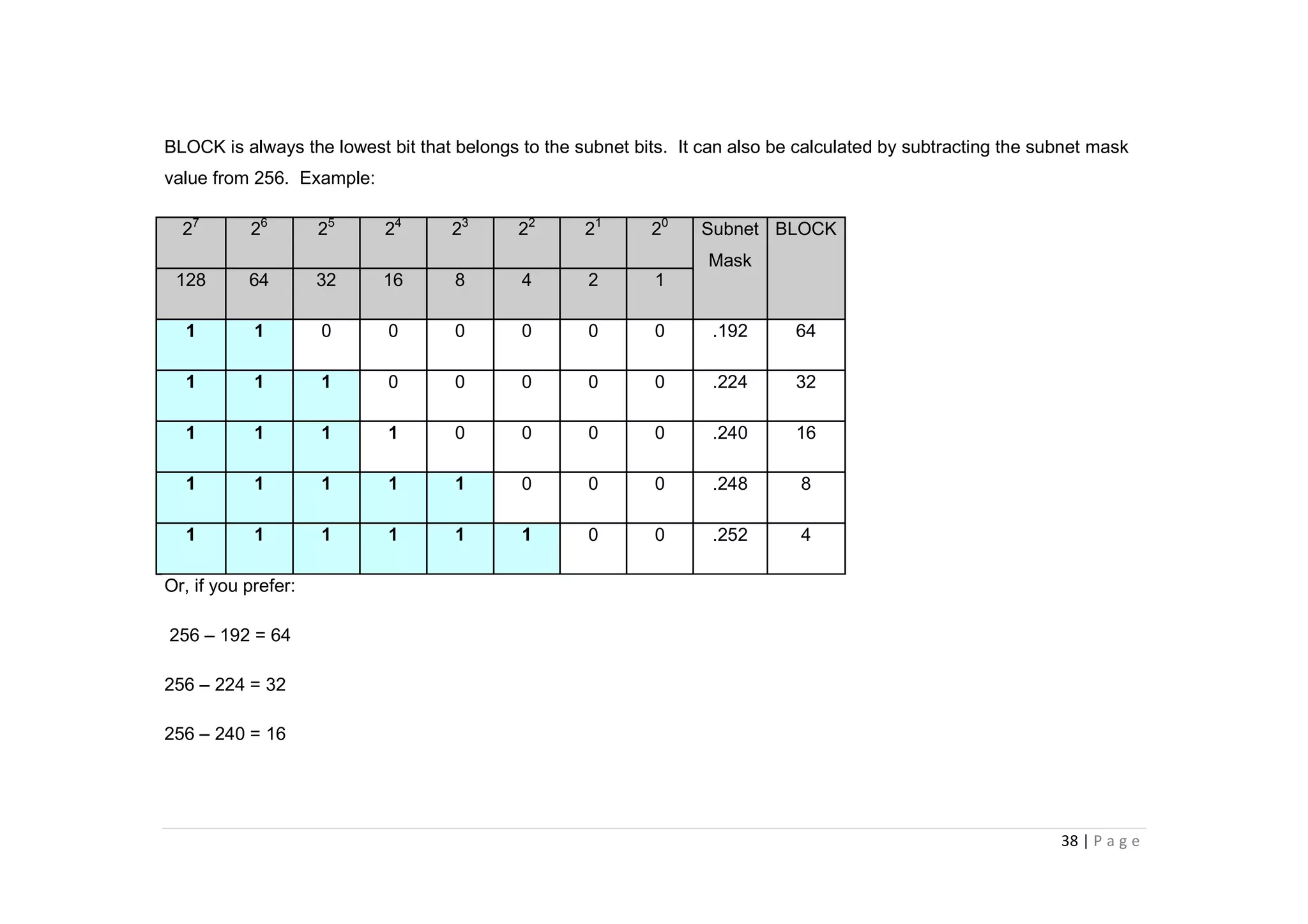
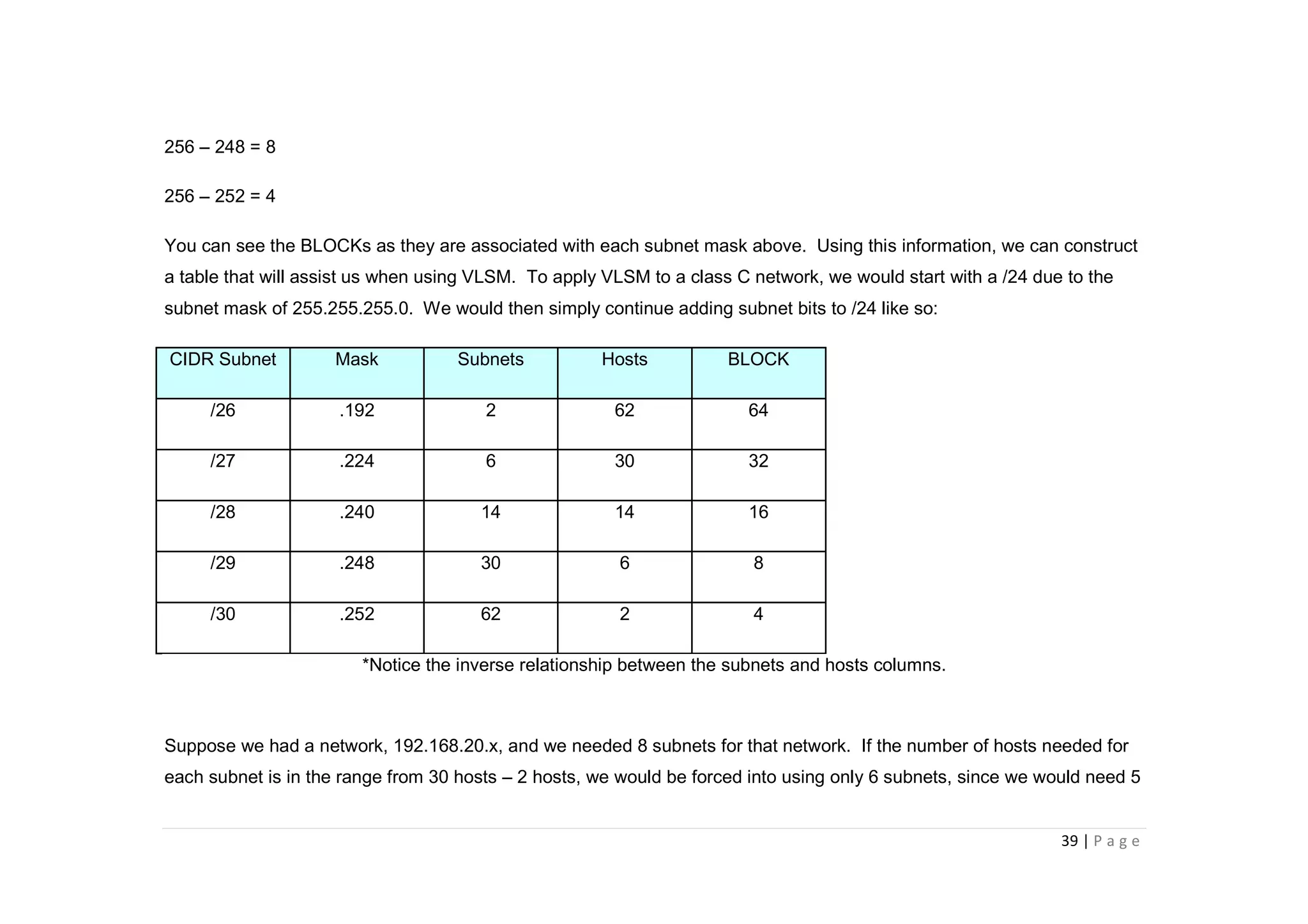
- A "block" shortcut can be used, where the block size is 256 minus the subnet mask, to quickly determine subnet ranges.