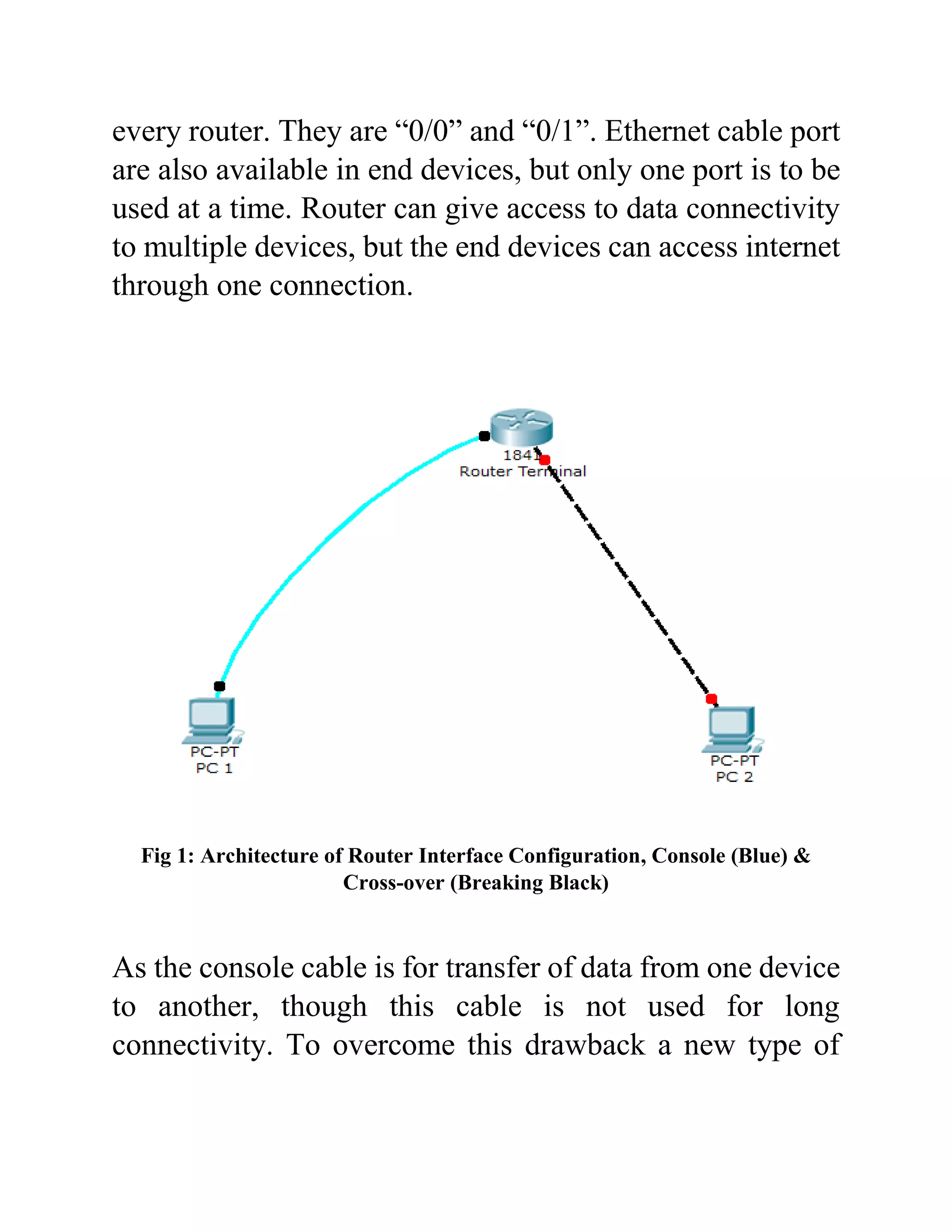
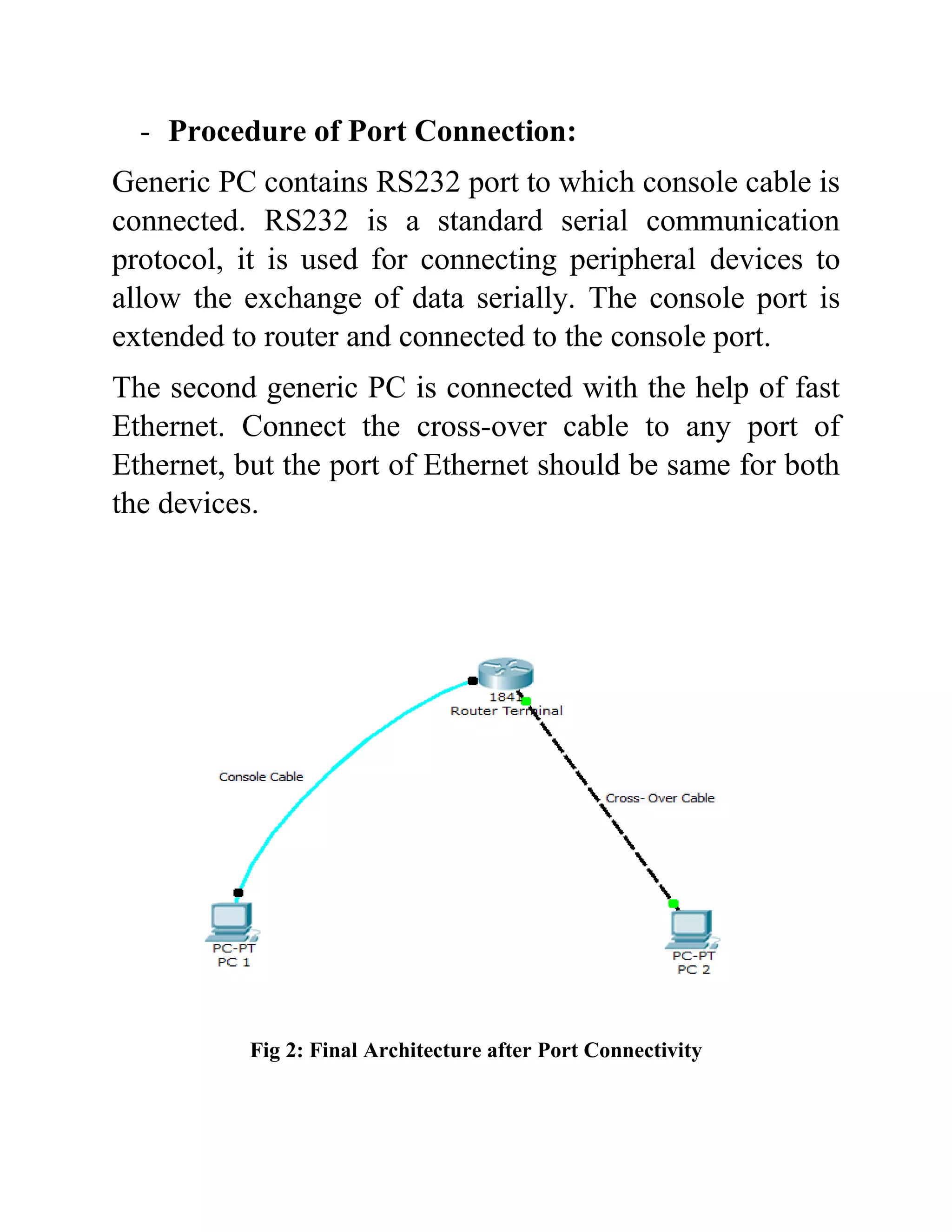
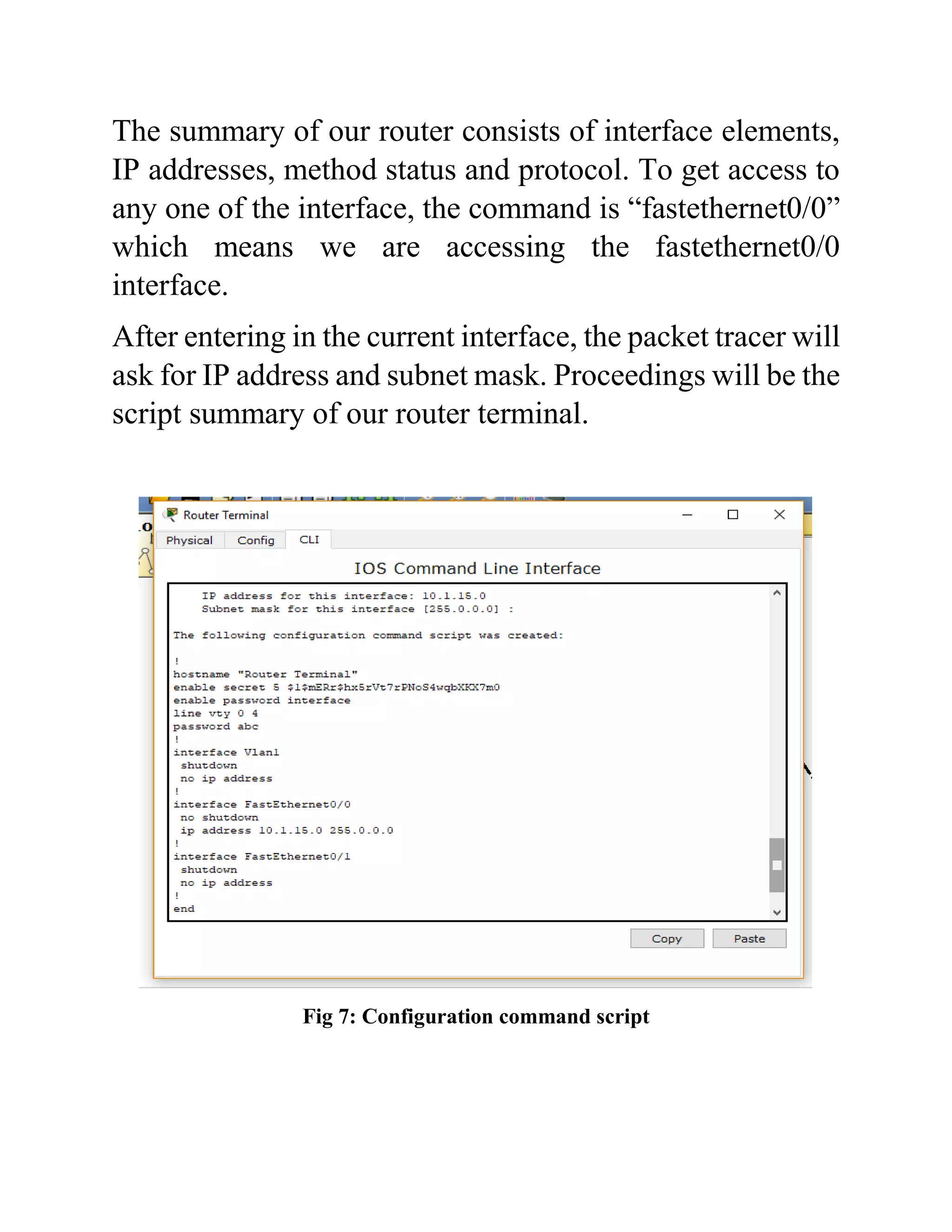
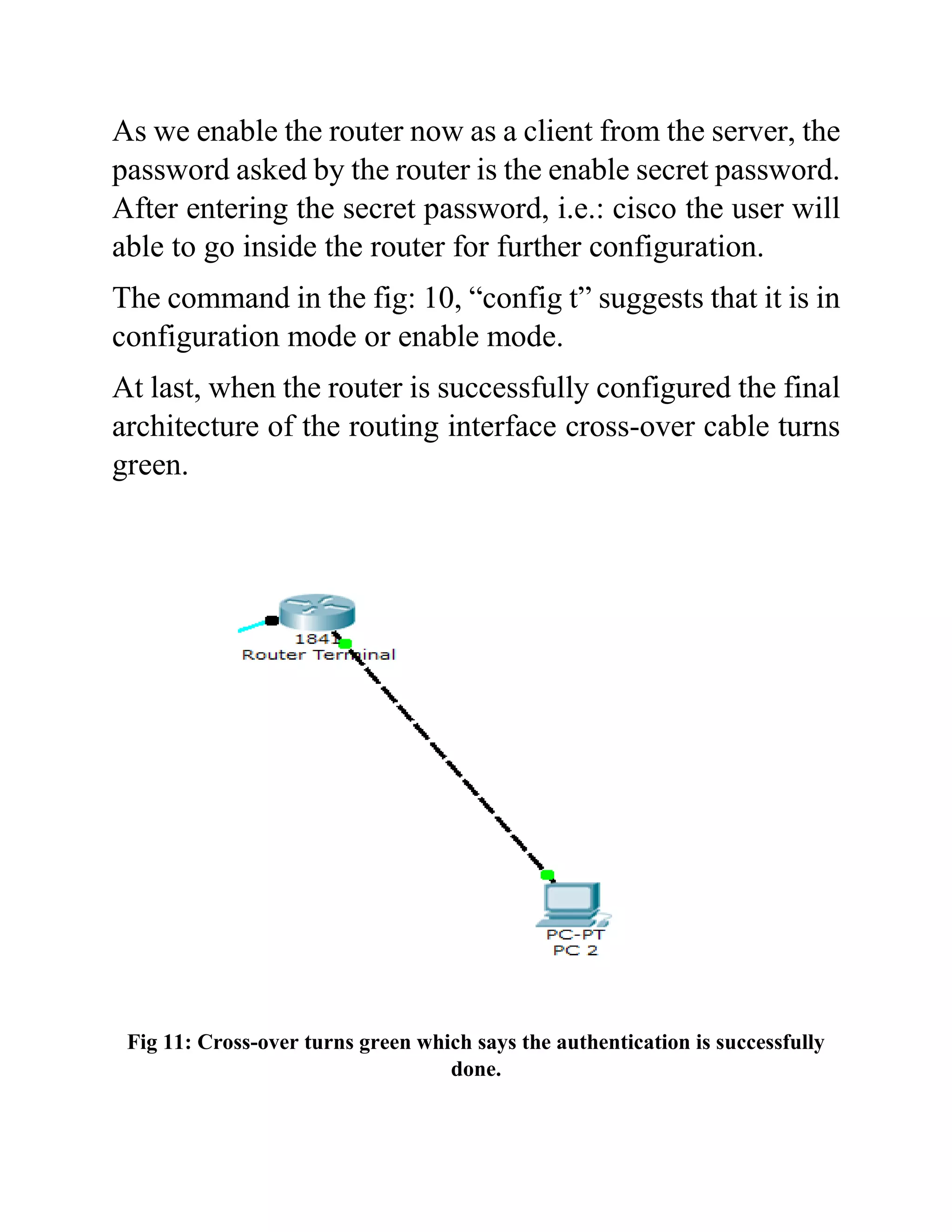
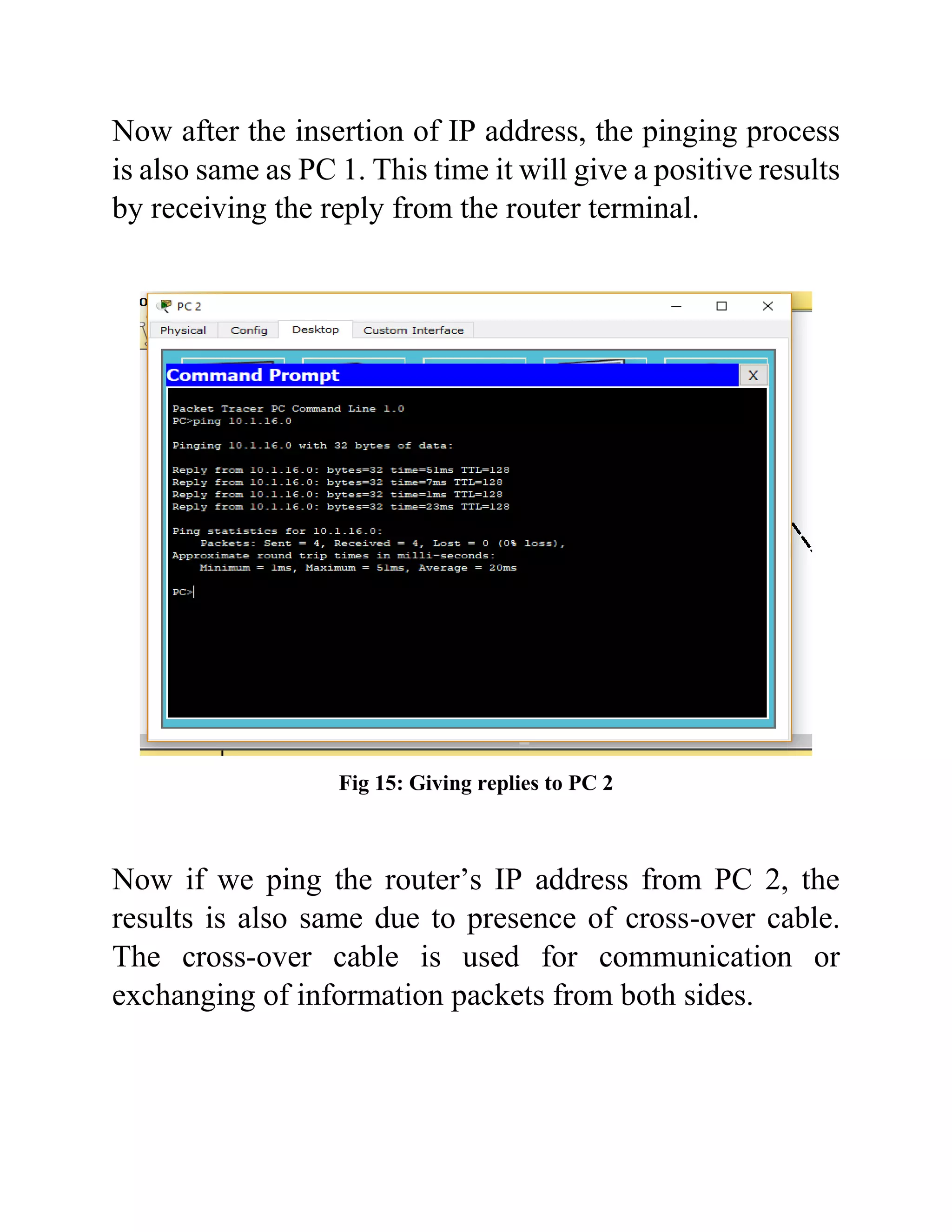
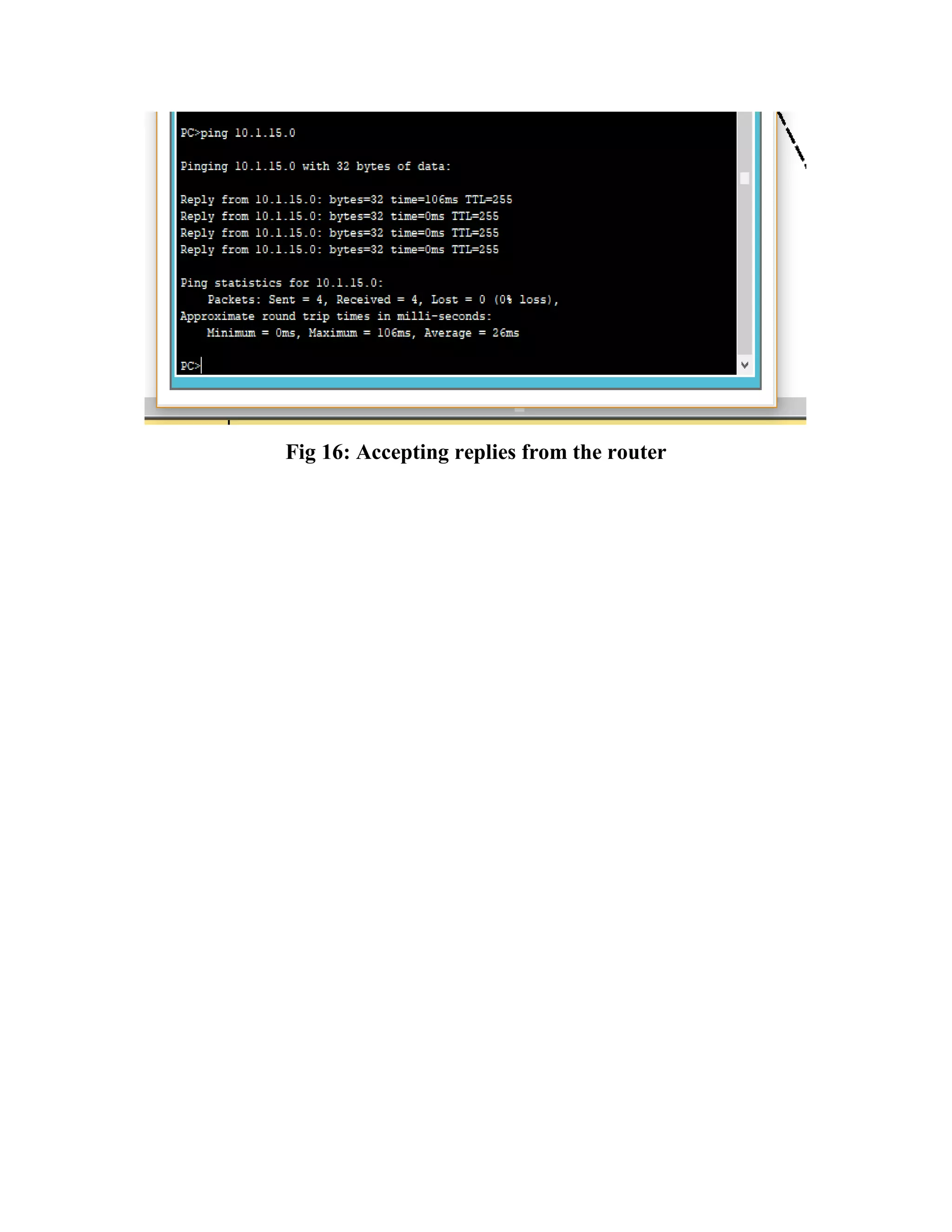
The document outlines the configuration of routing interfaces using Cisco Packet Tracer with an emphasis on connecting various devices to a router. It details the architecture, implementation processes, and testing, including using console and crossover cables for device communication. The conclusion emphasizes that end devices cannot communicate without a router, and that proper cable connections and IP configurations are critical for successful data transfer.