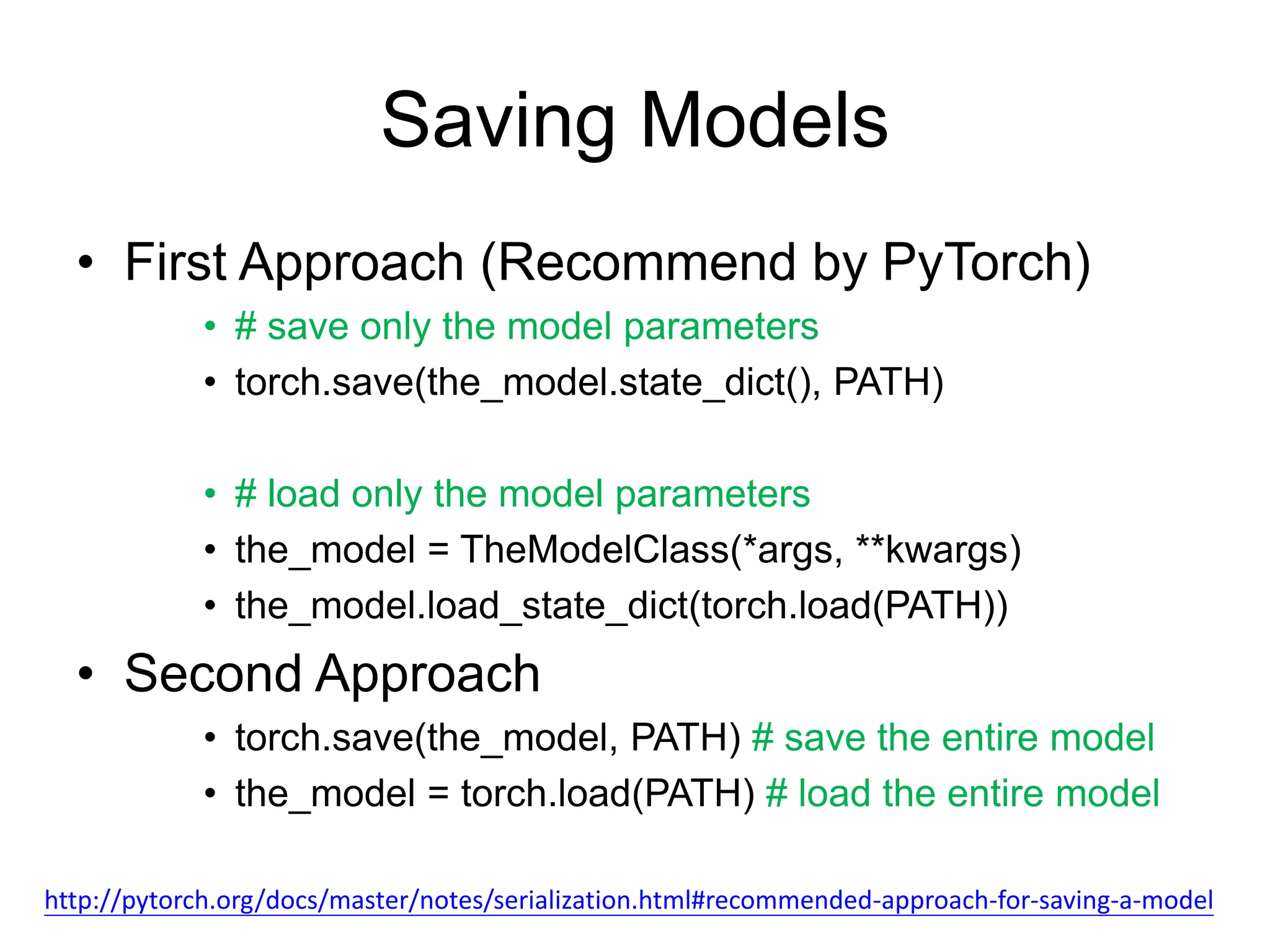
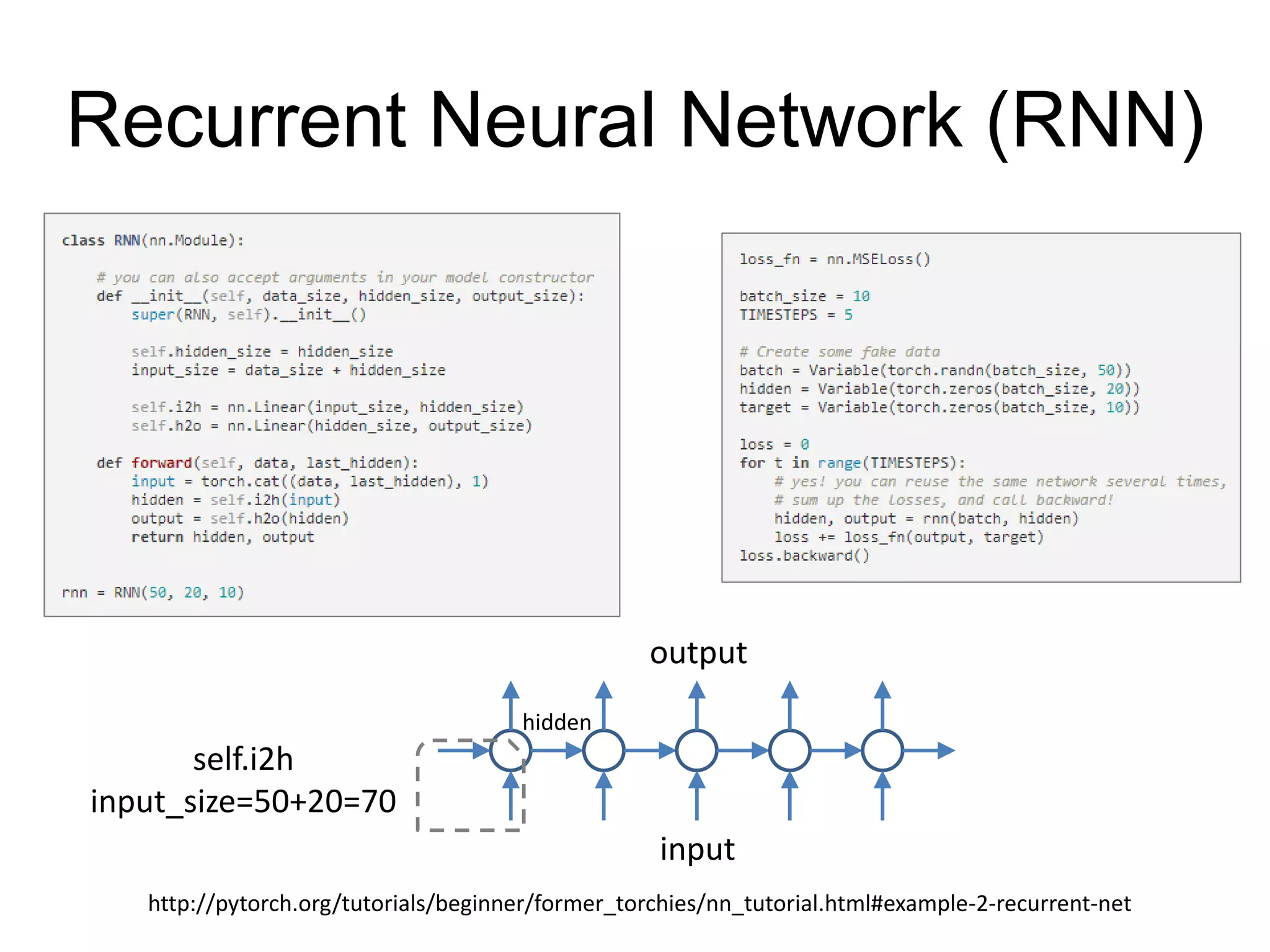
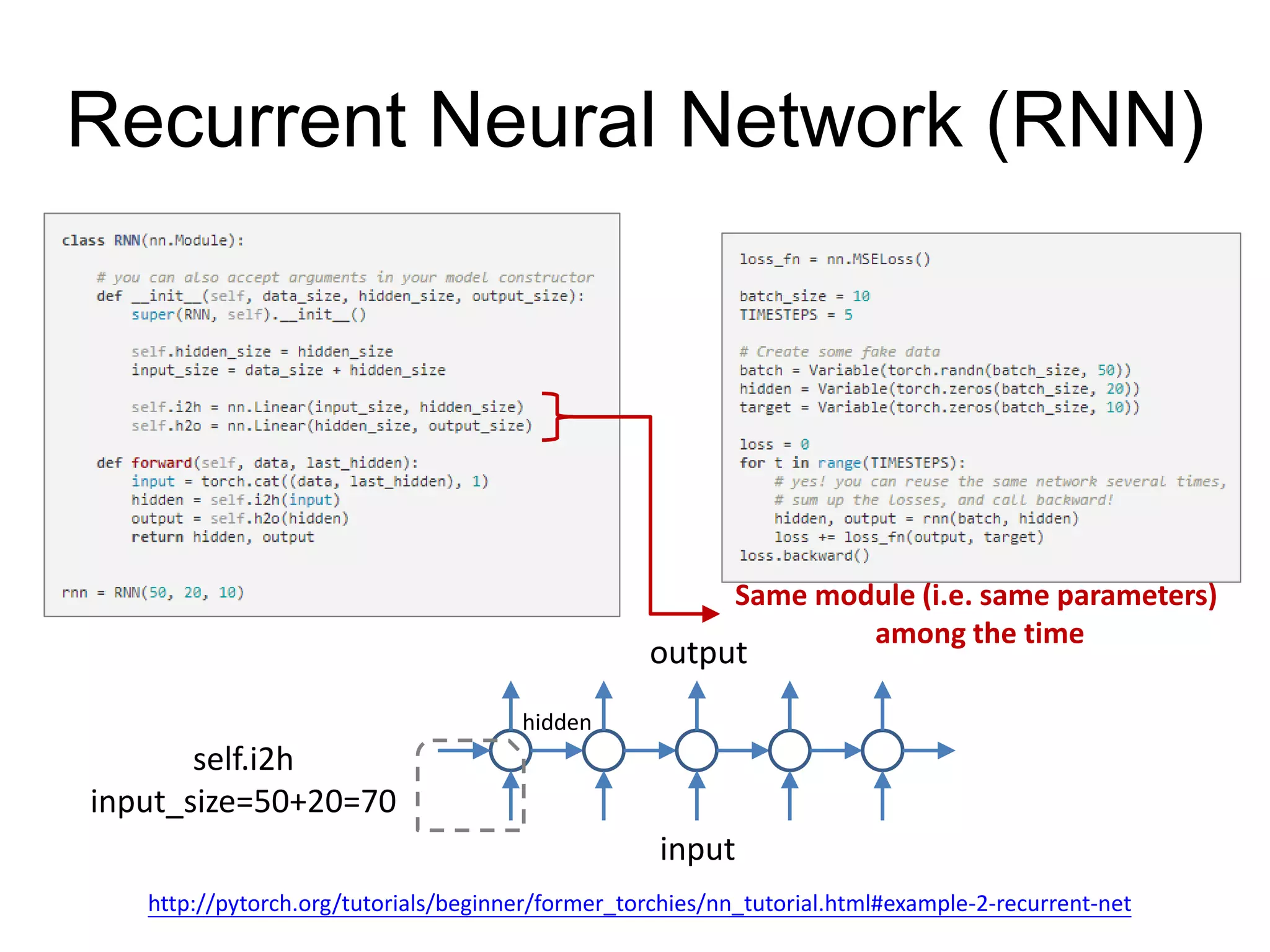
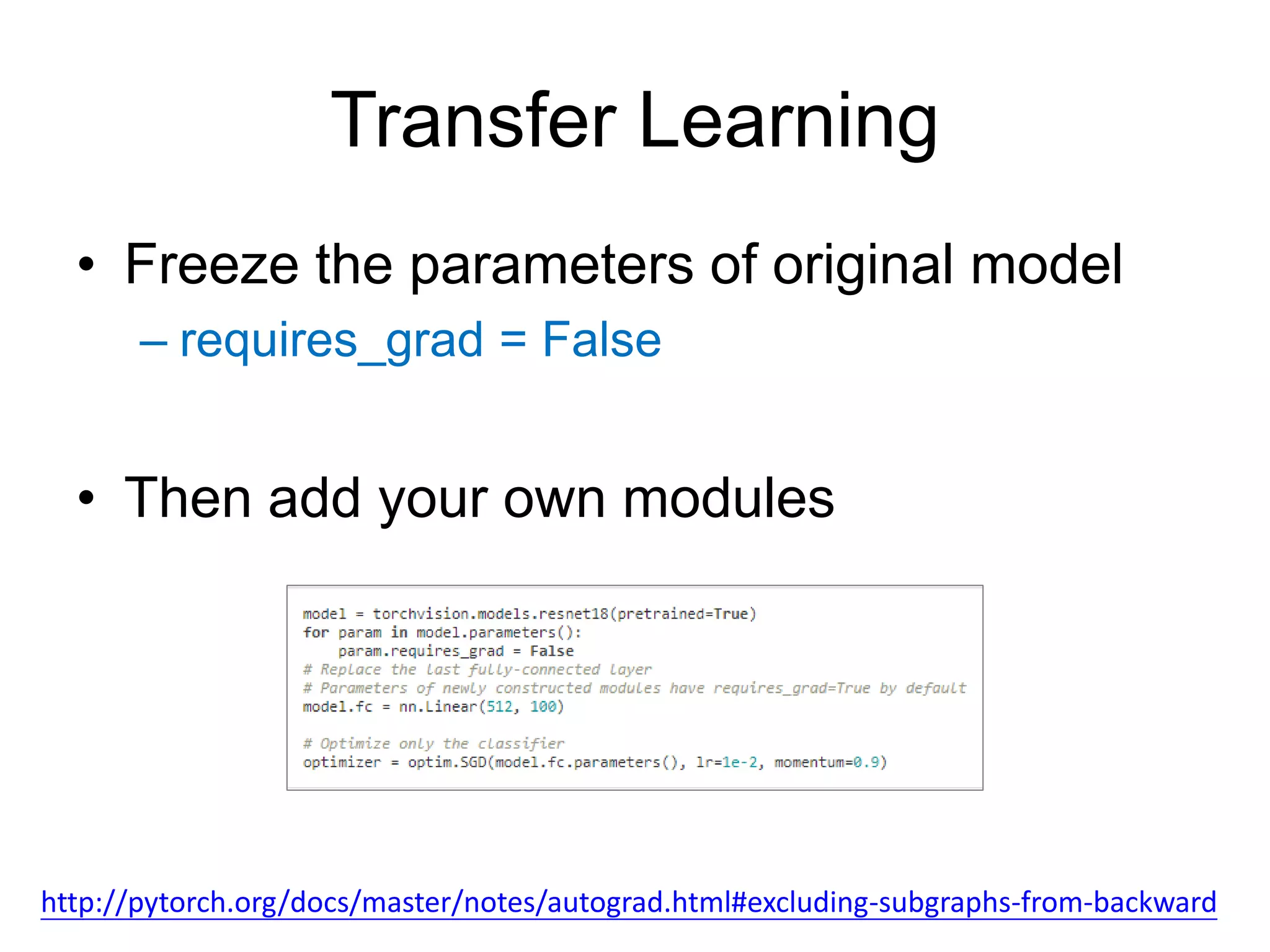
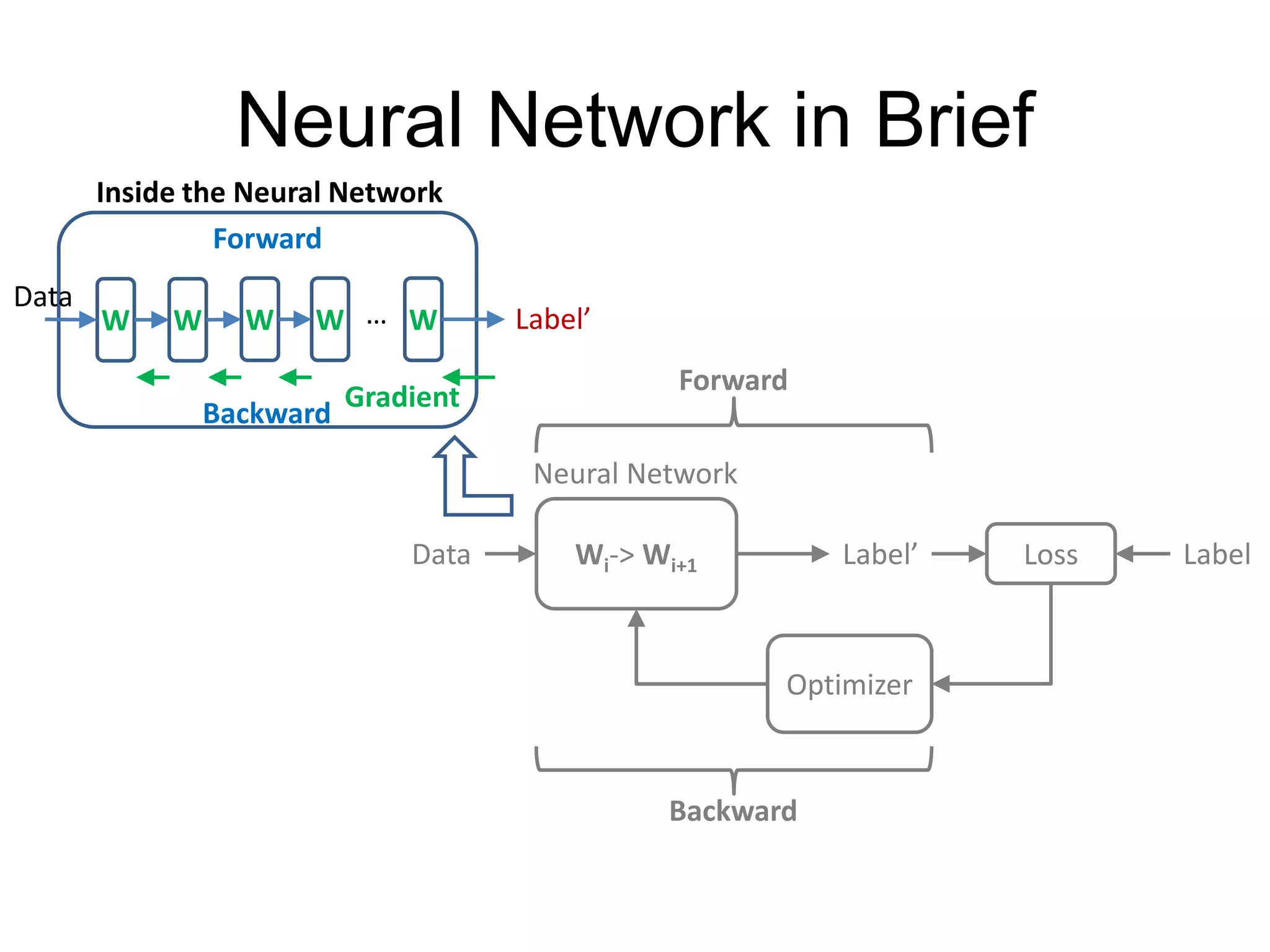
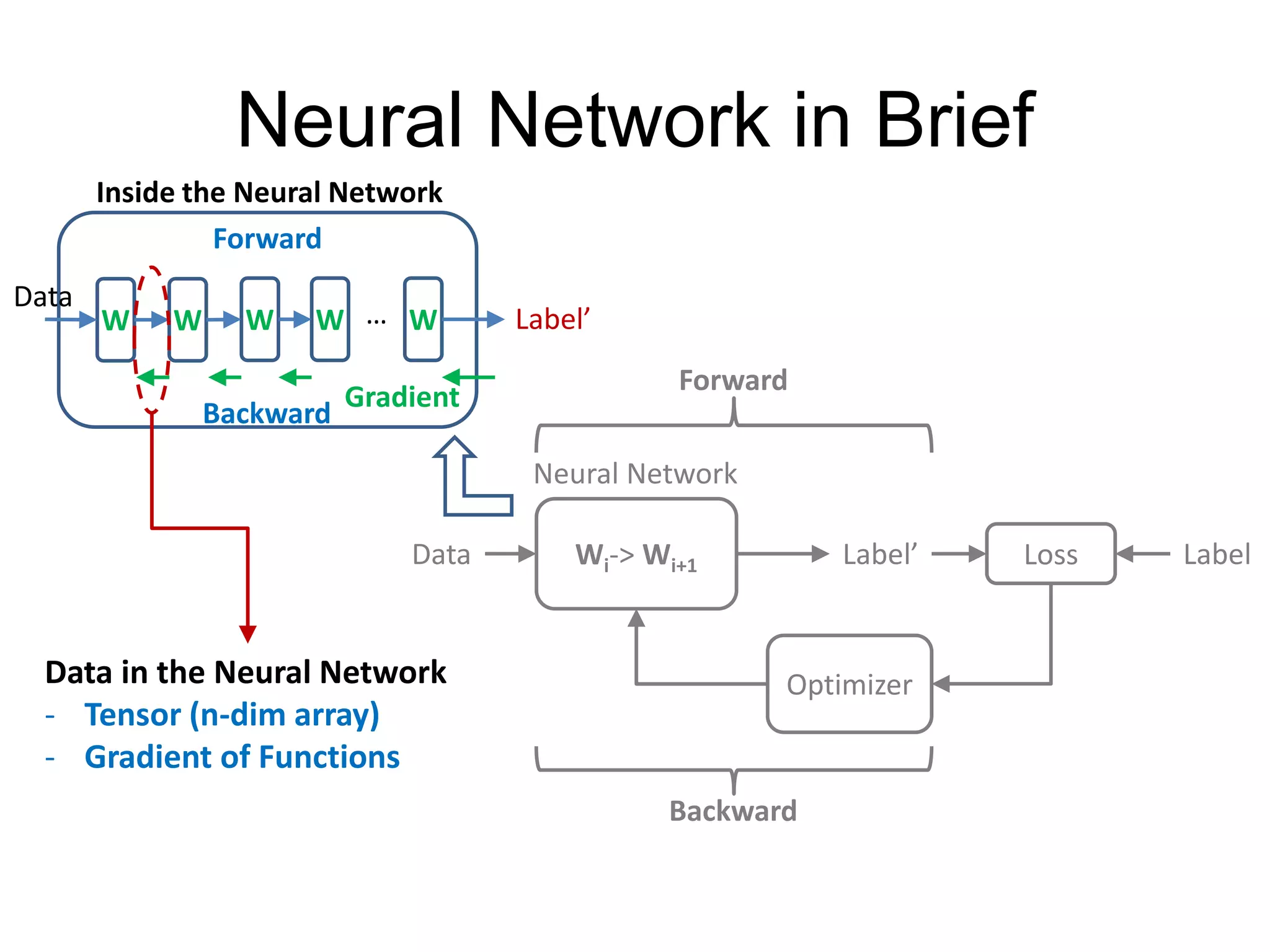
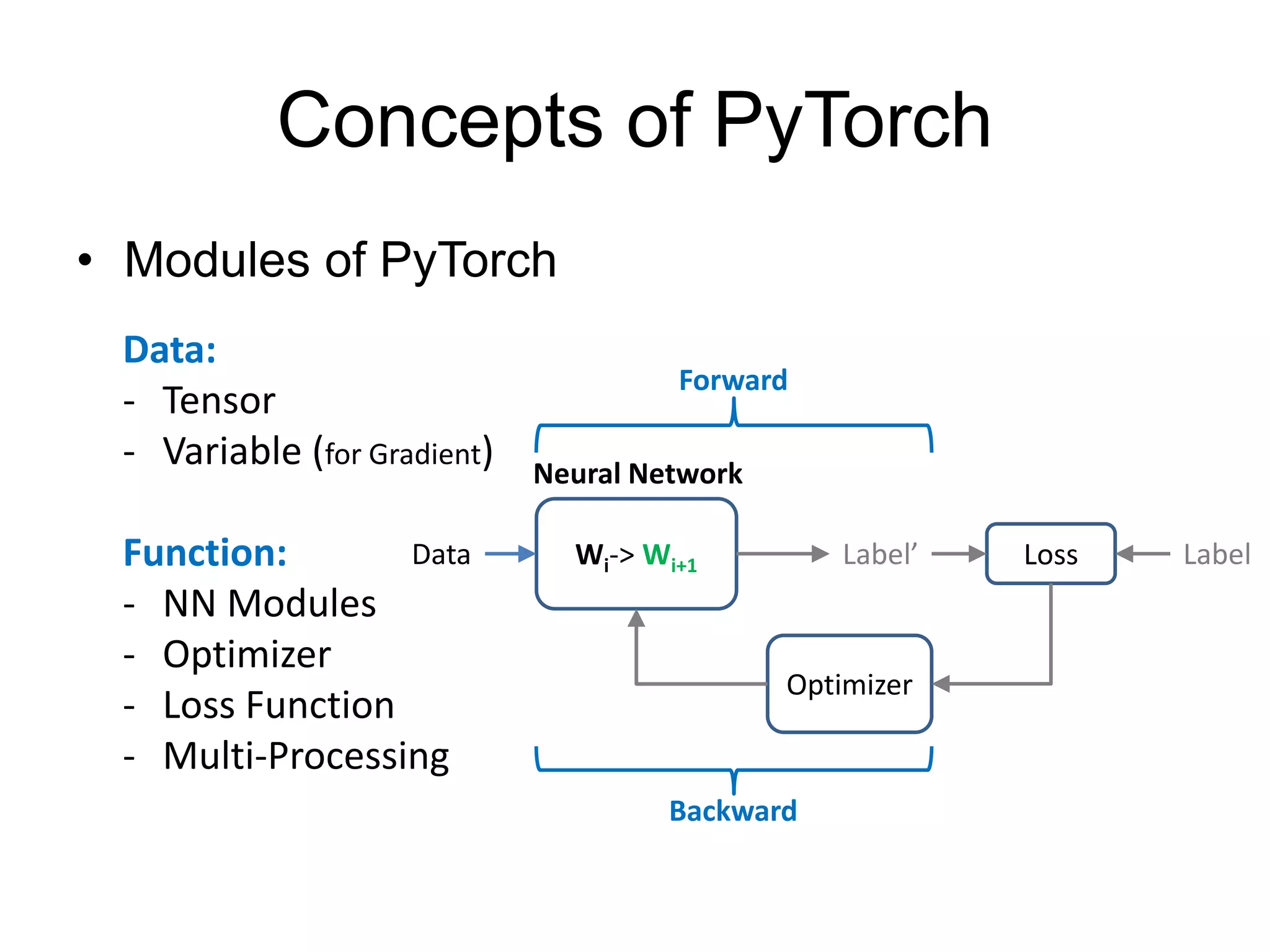
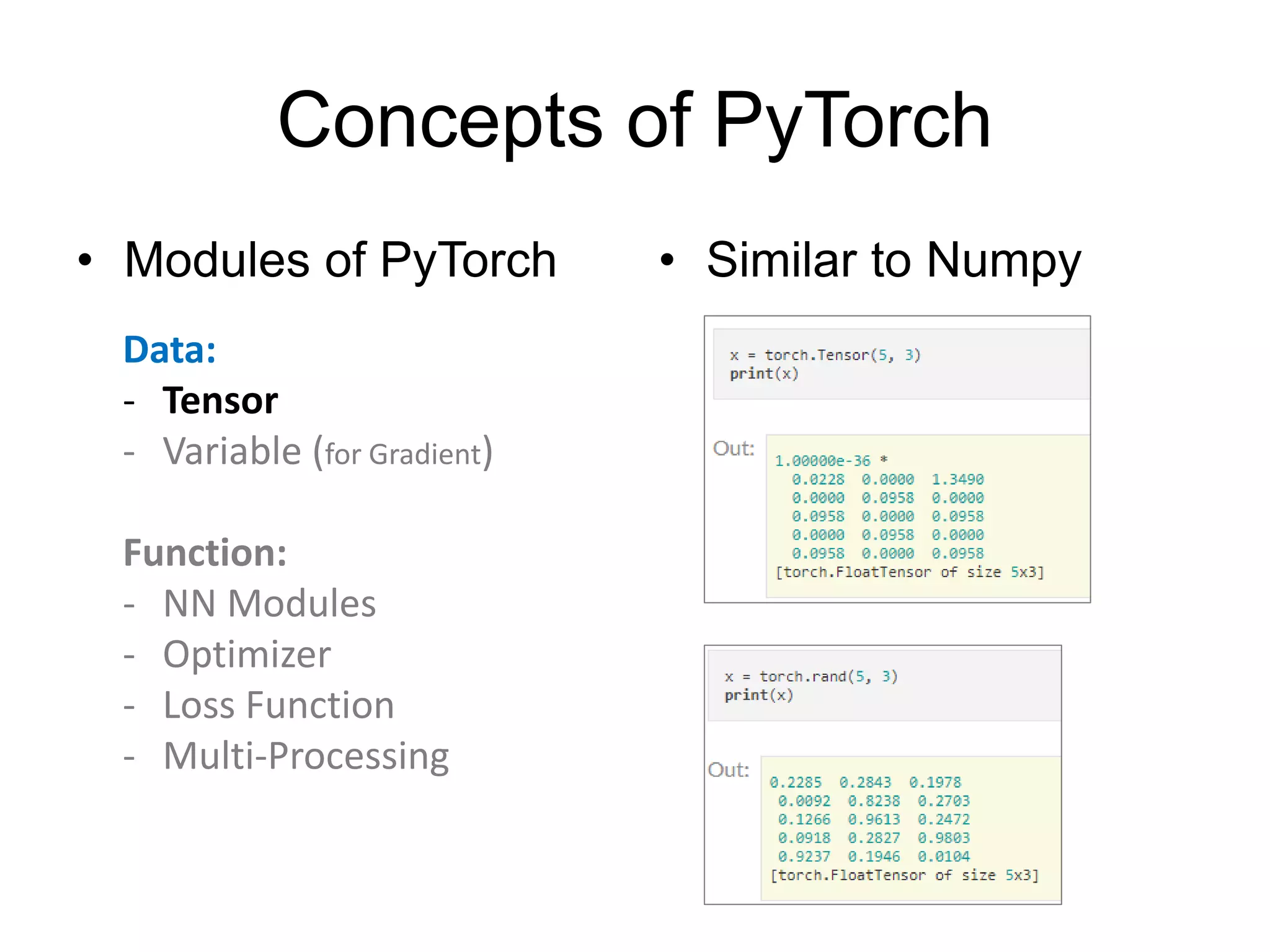
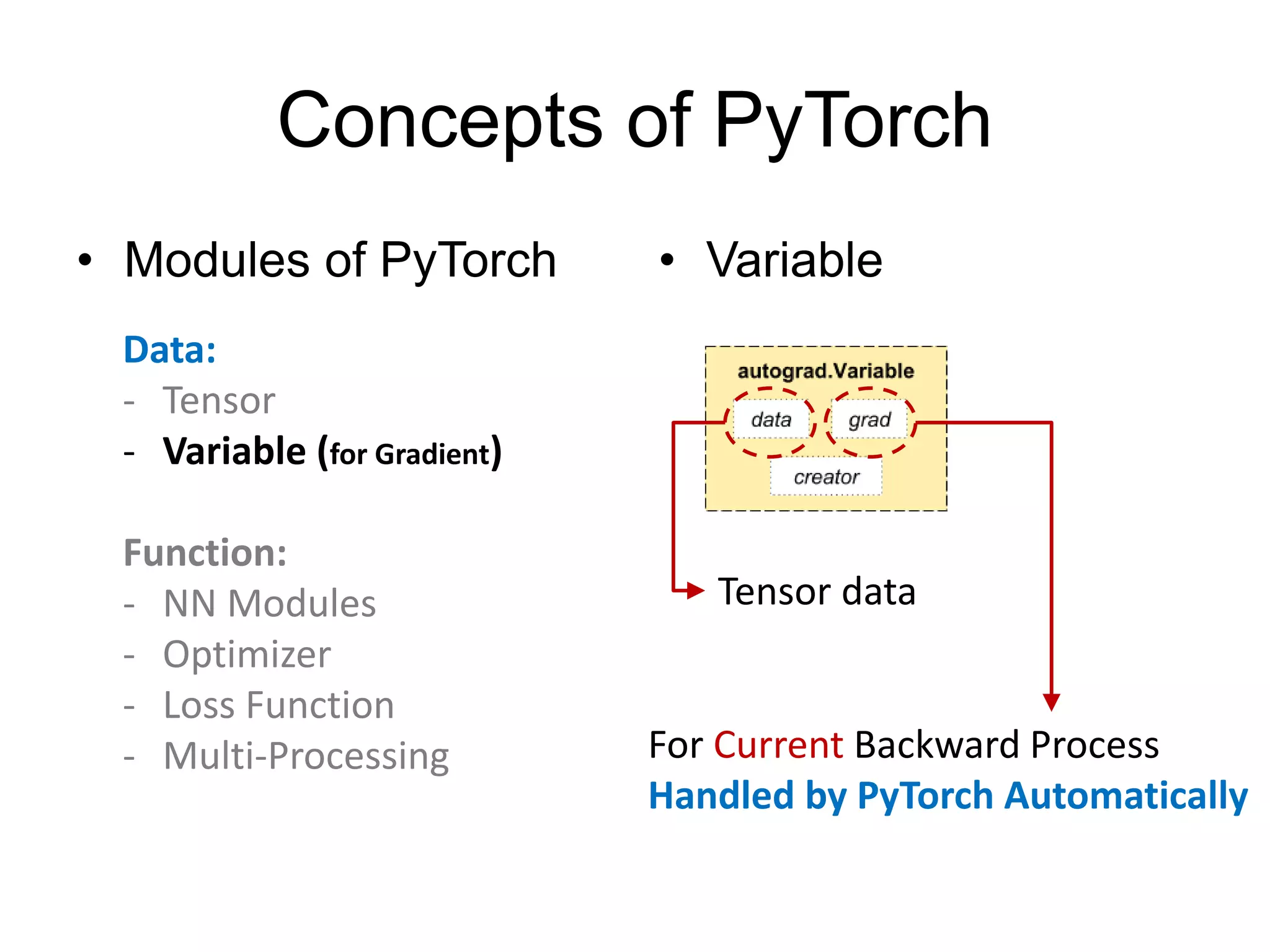
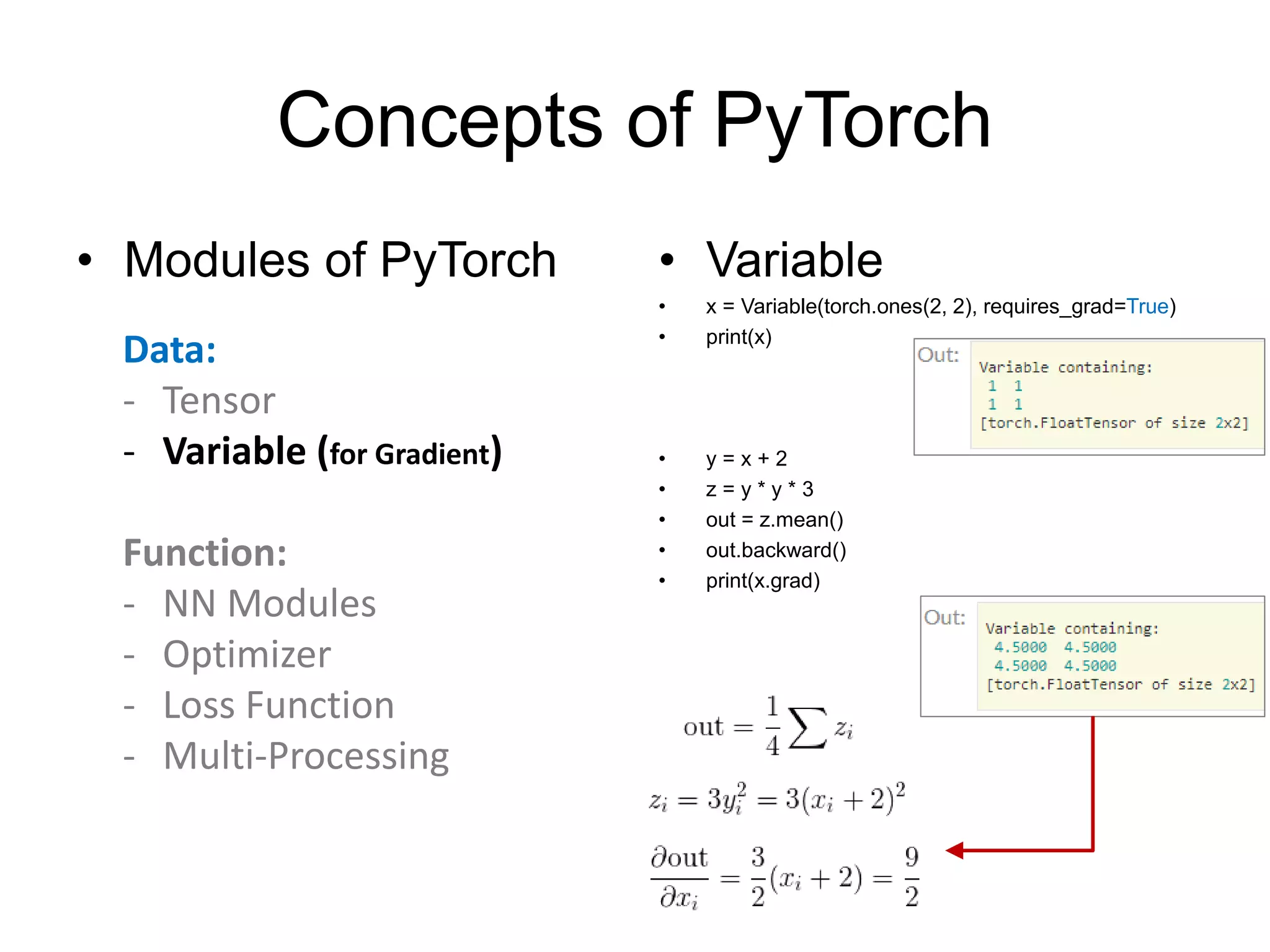
This document is a comprehensive tutorial on PyTorch, covering its core concepts, modules, and installation instructions. It details the building blocks of neural networks, including tensors, automatic differentiation, and the specific PyTorch libraries for neural networks and optimization. The tutorial also includes practical guidelines for using the library, including examples for defining and building networks.
![PyTorch Tutorial
-NTU Machine Learning Course-
Lyman Lin 林裕訓
Nov. 03, 2017
lymanblue[at]gmail.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171102090953/75/PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-1-2048.jpg)


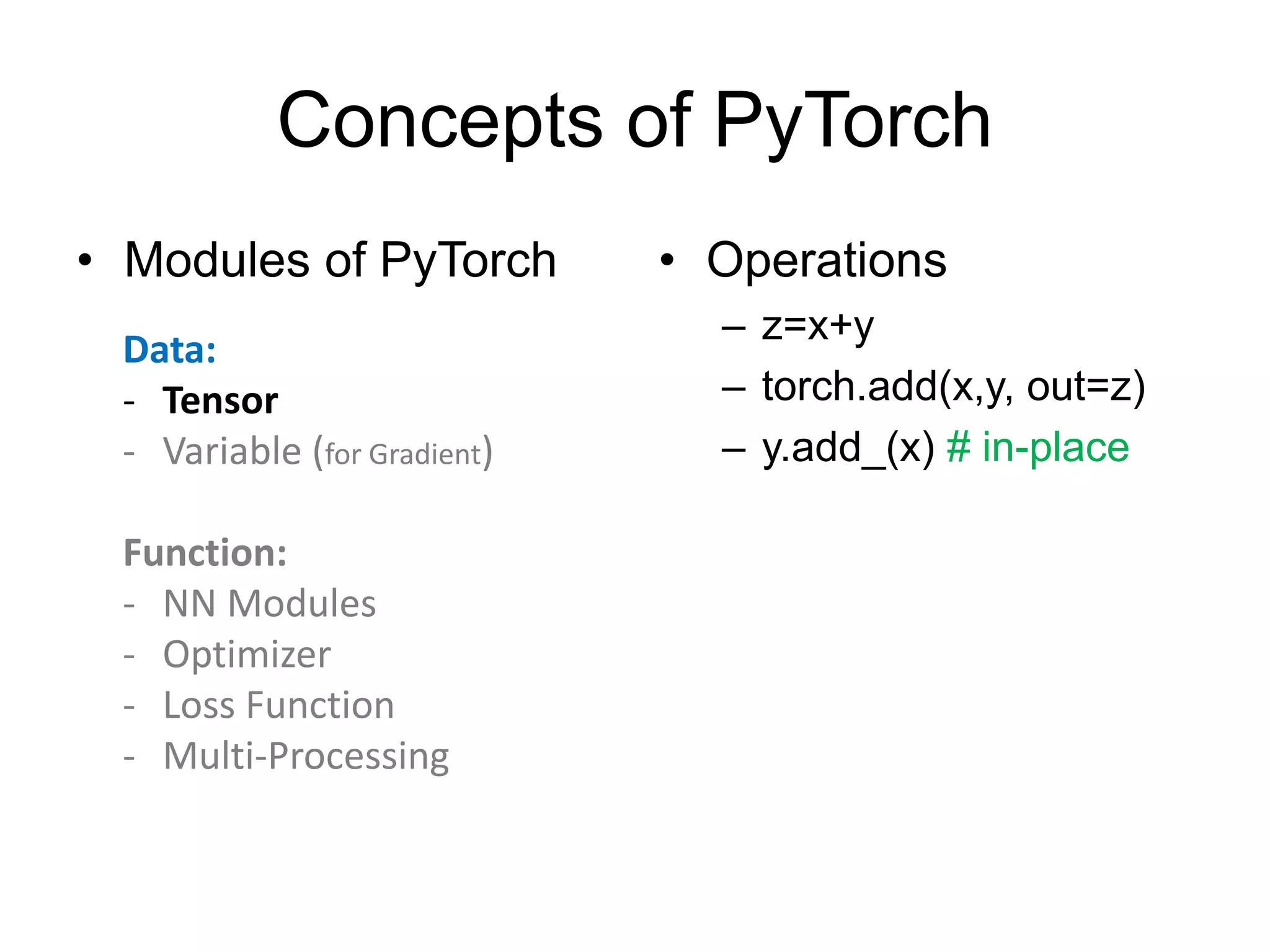
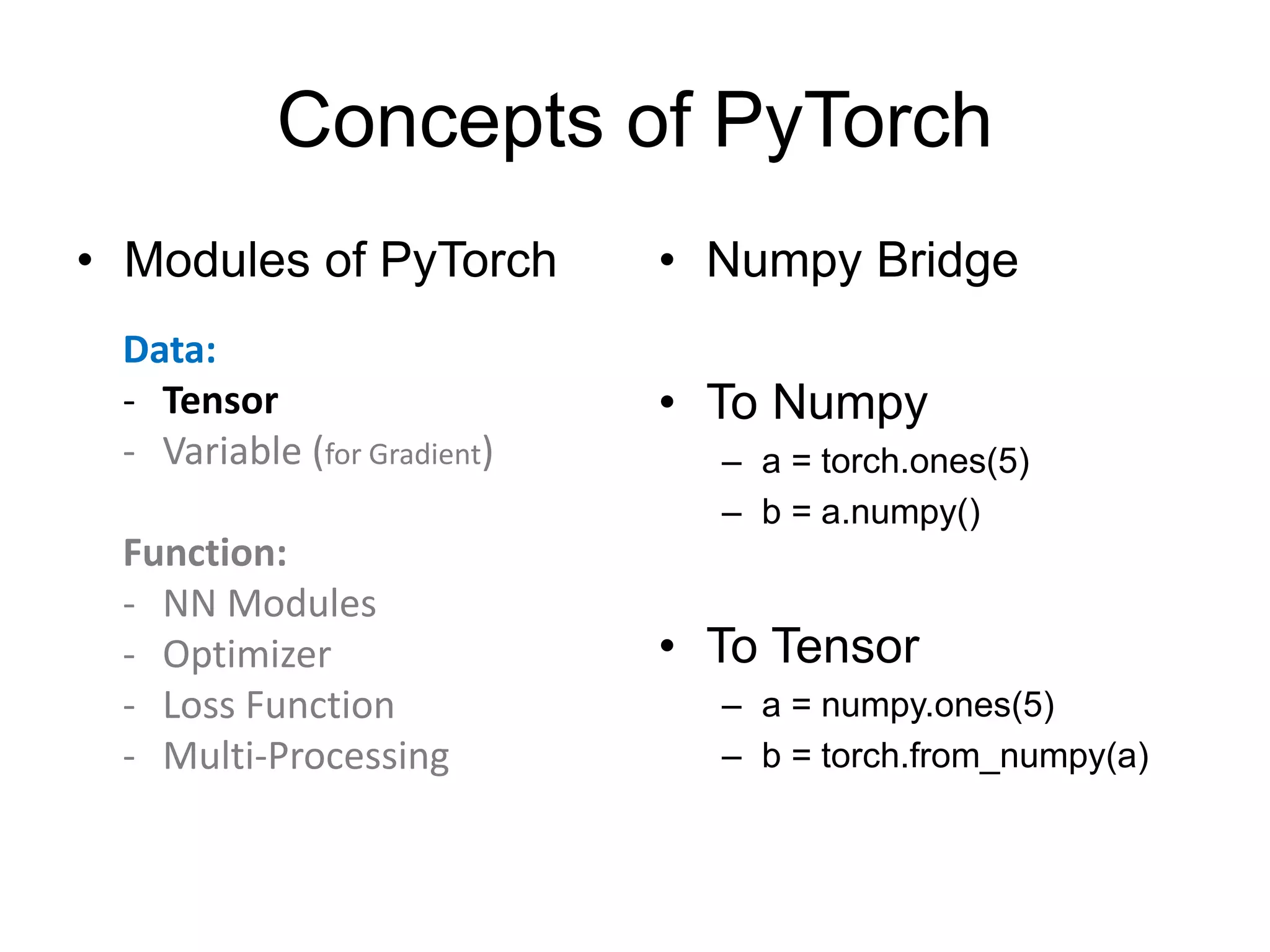
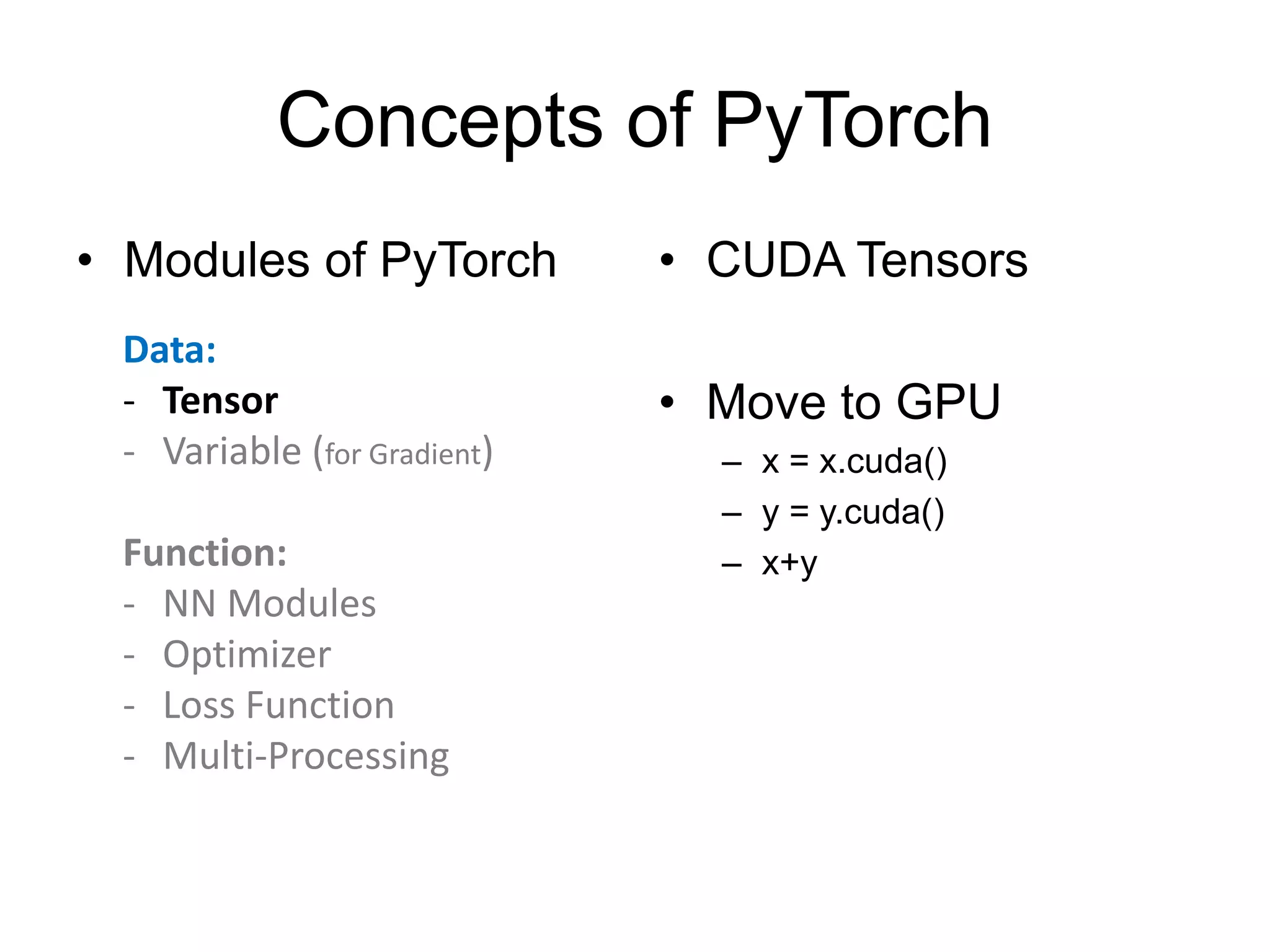
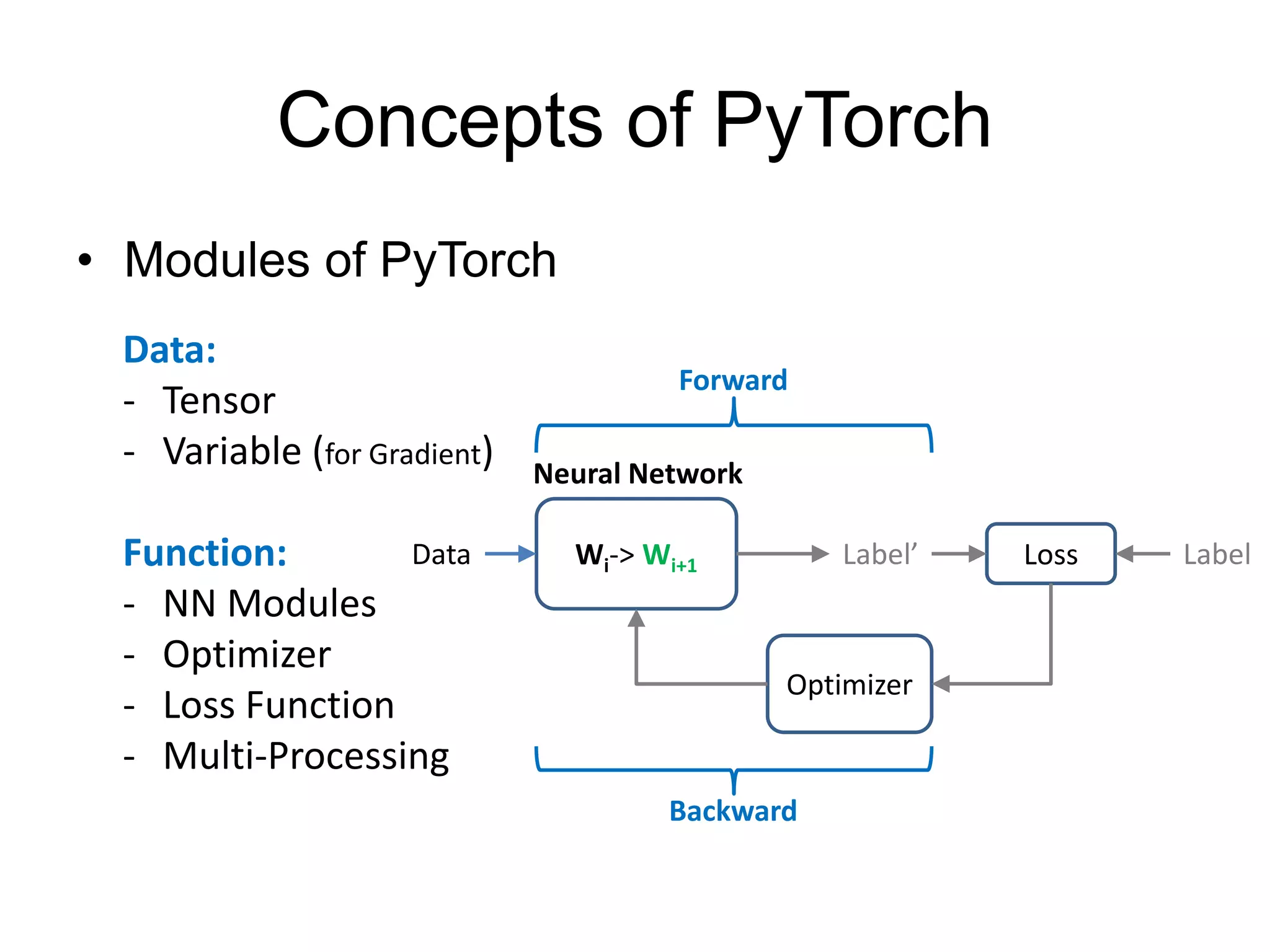
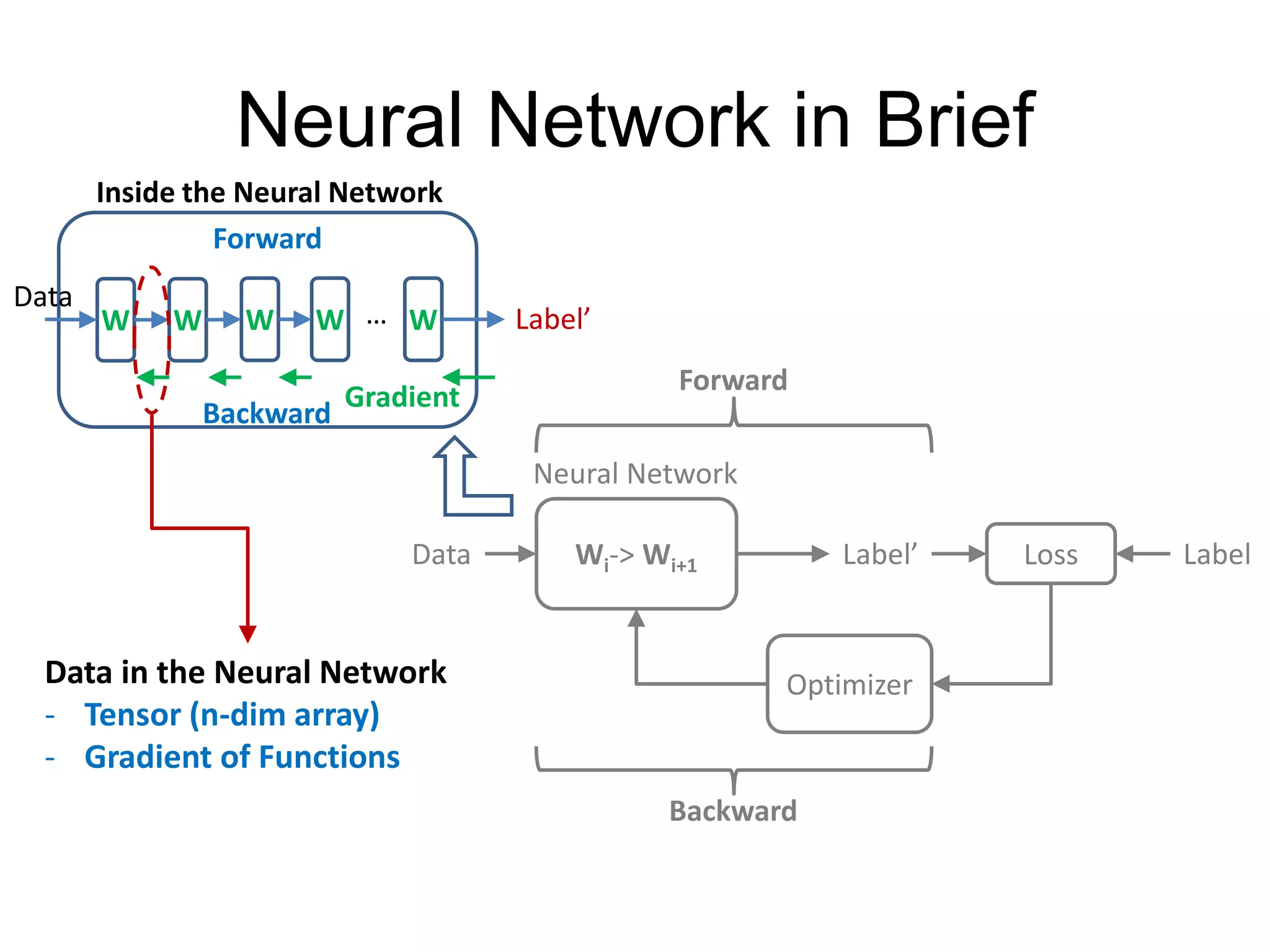
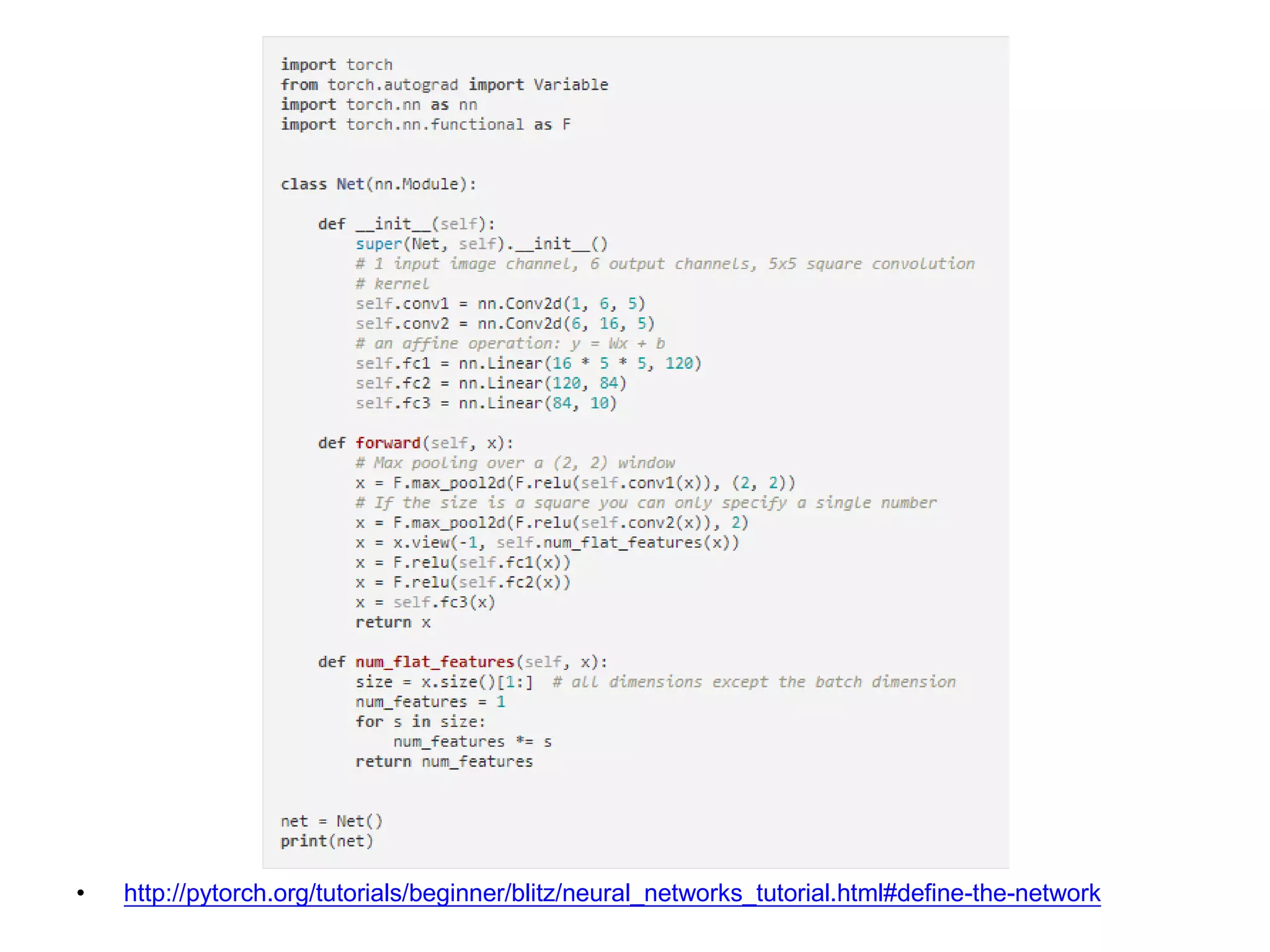

![• http://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/blitz/neural_networks_tutorial.html#define-the-network
conv1
x
relu
pooling
conv2
relu
pooling
fc1
relu
fc2
relu
fc3
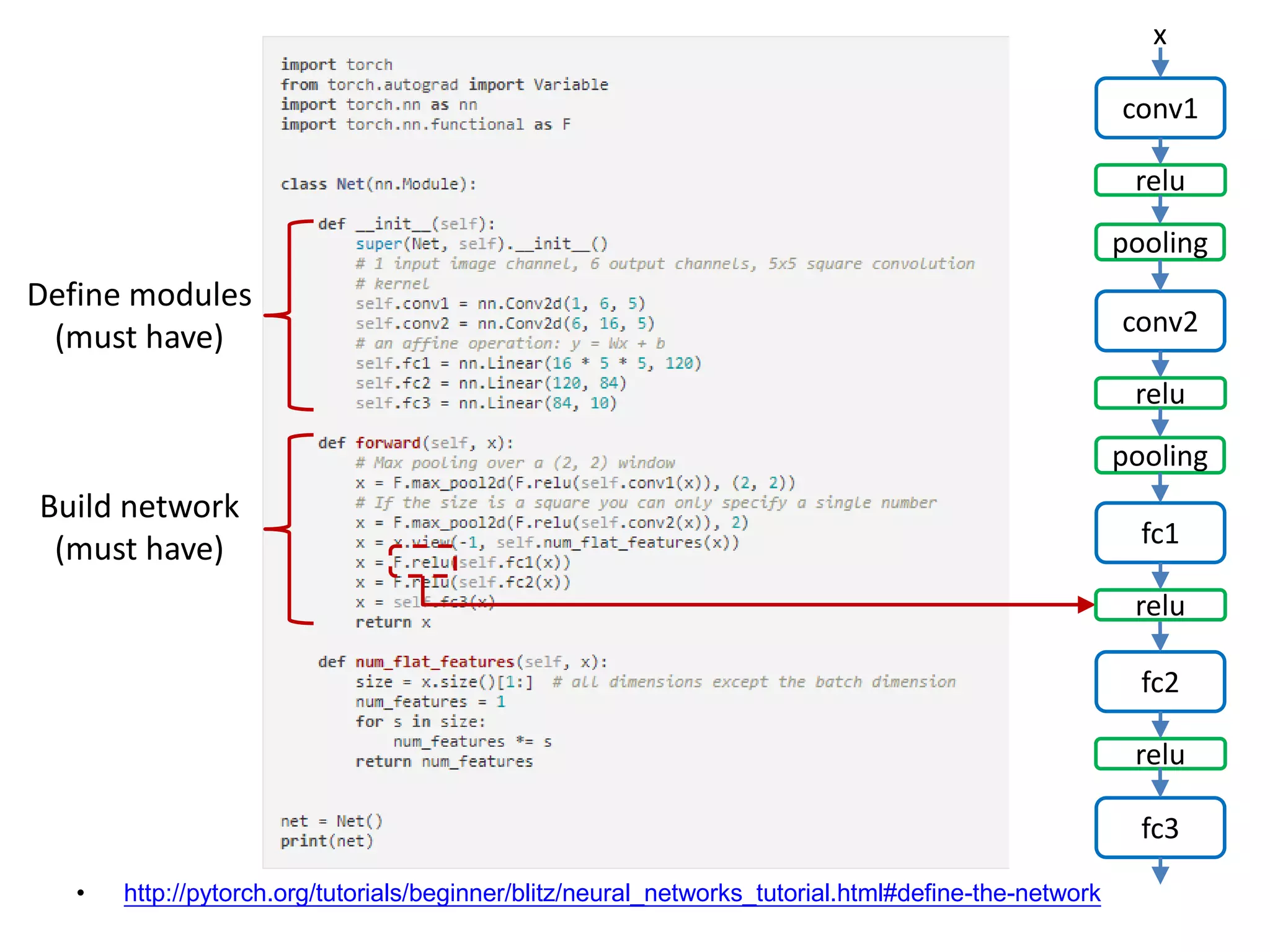
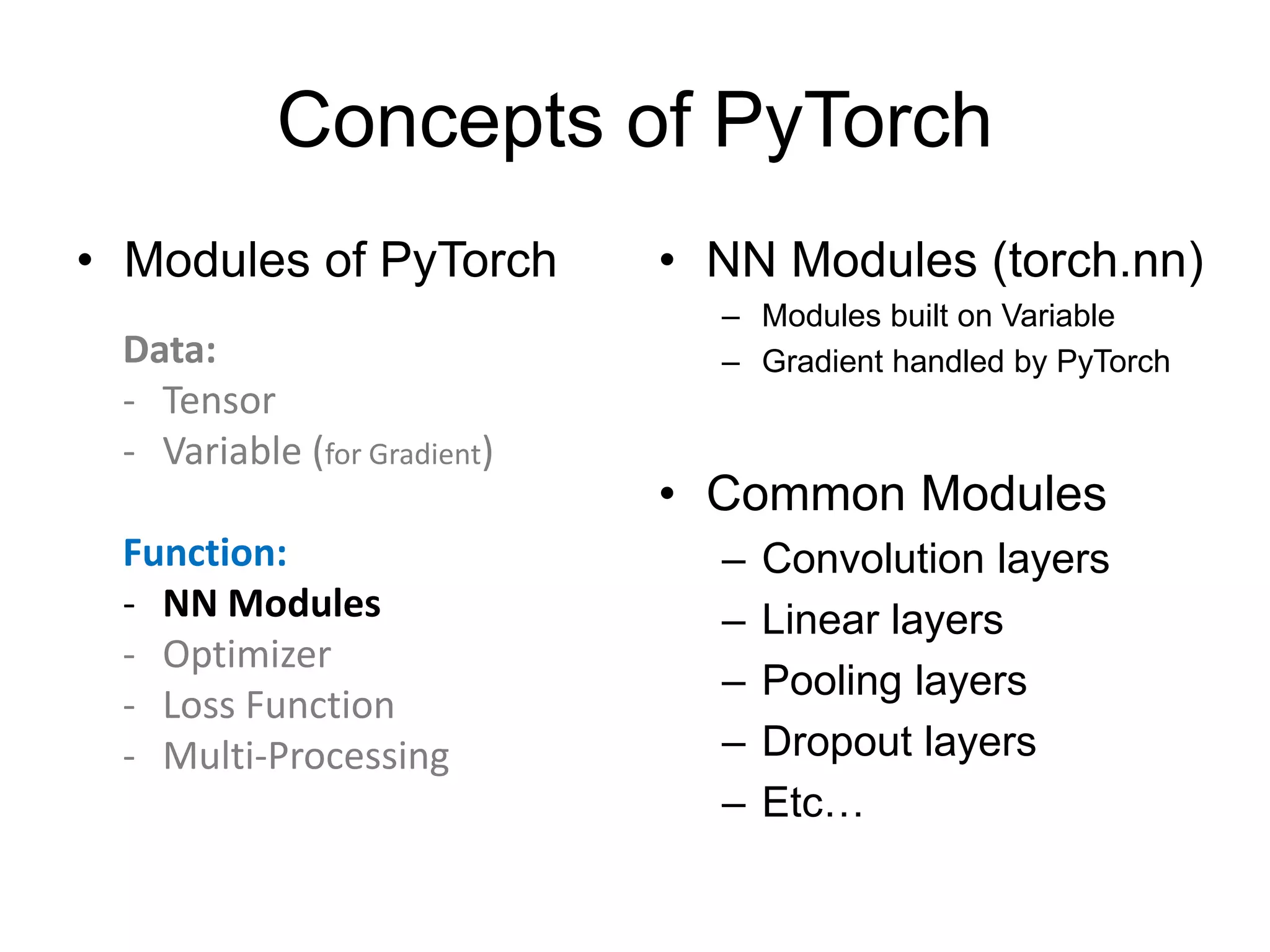
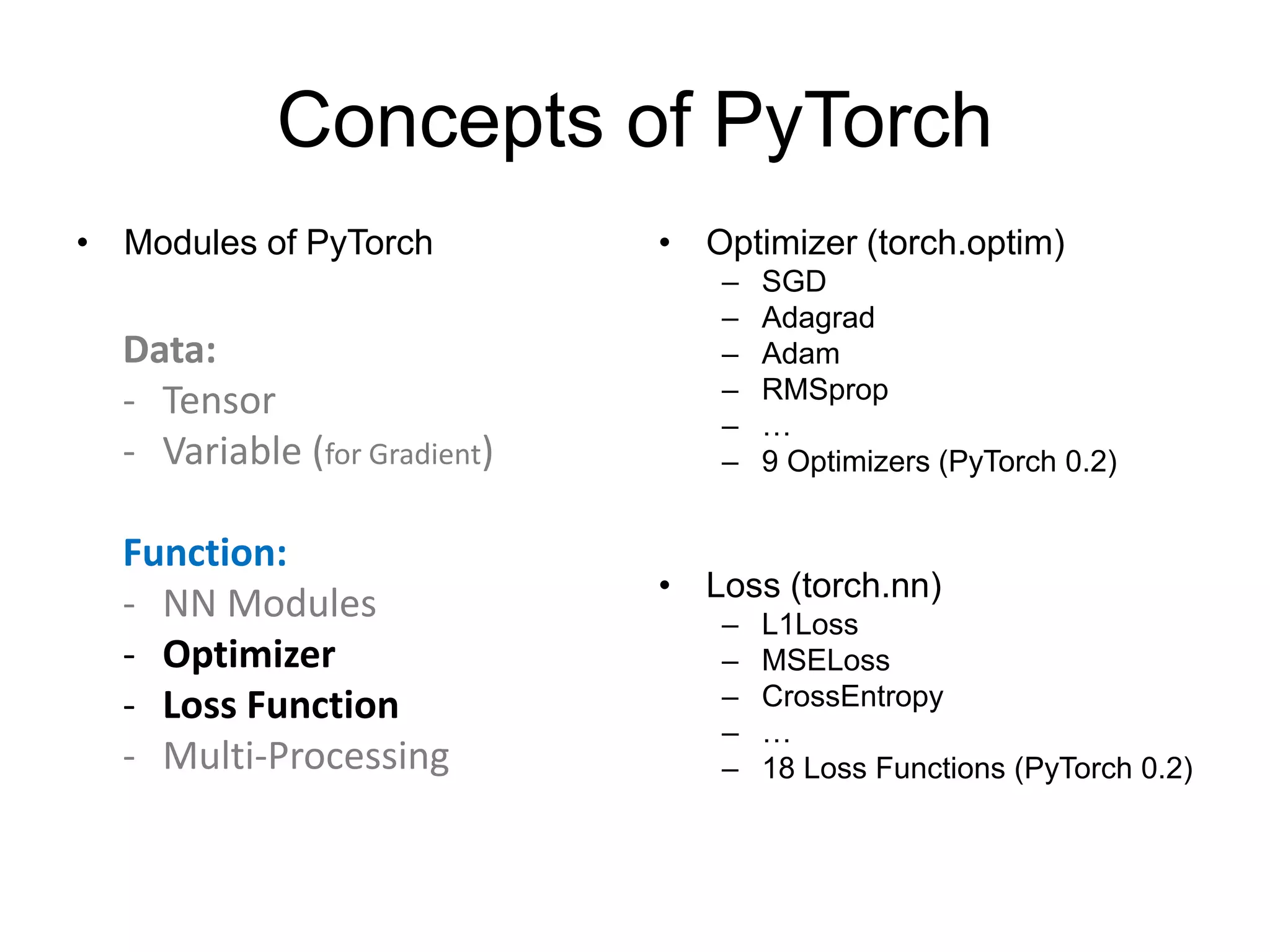
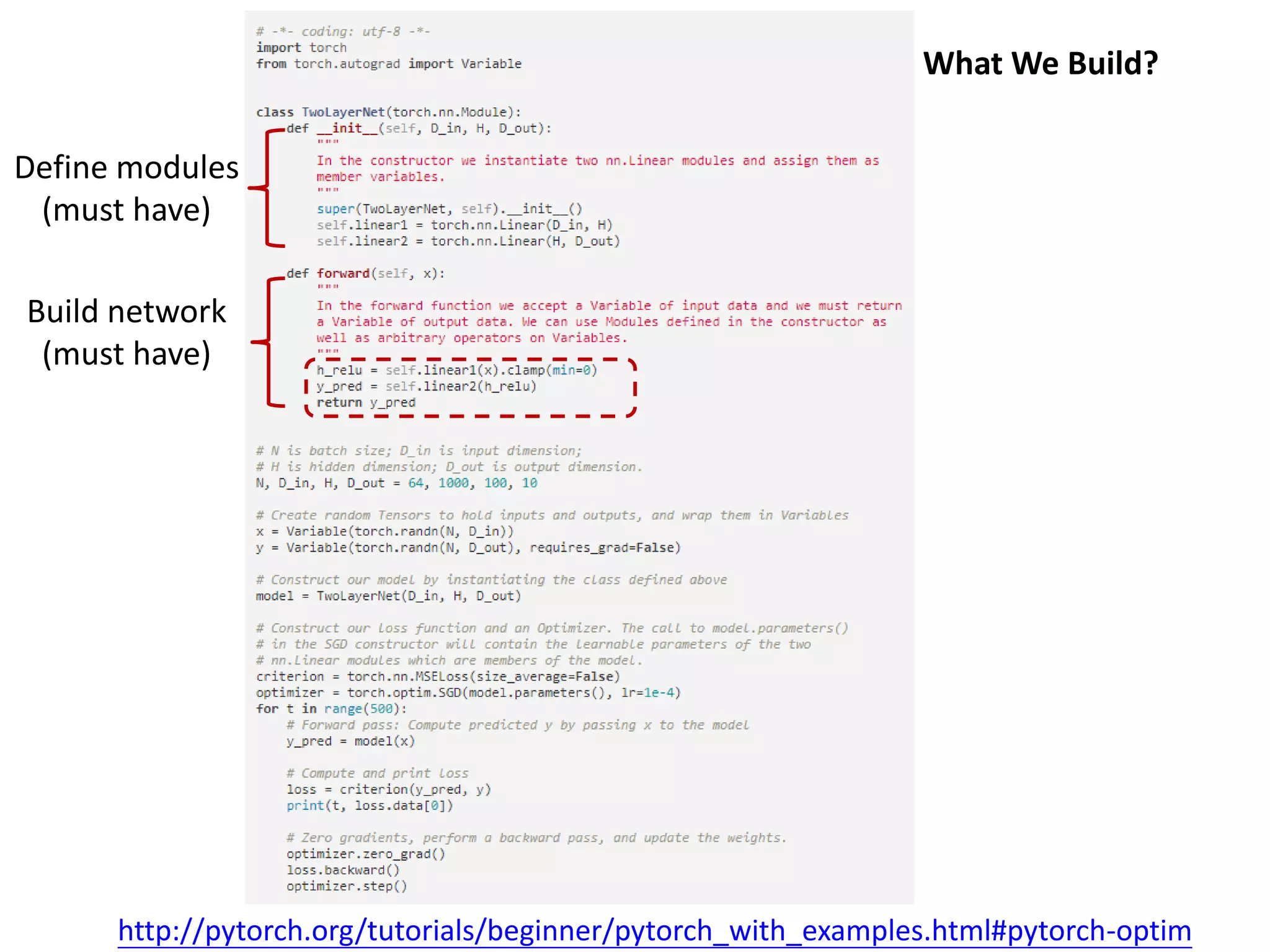
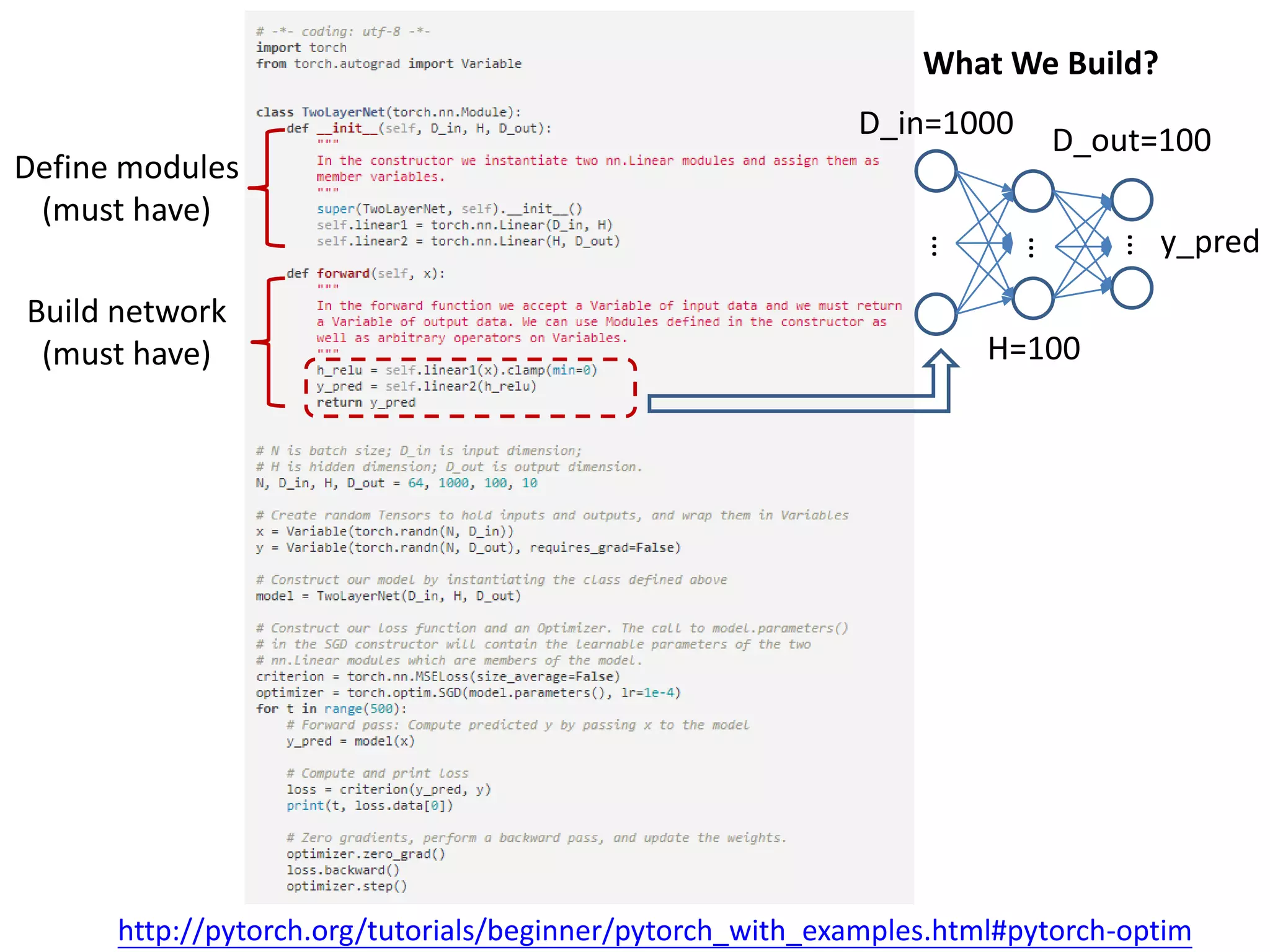
Define modules
(must have)
Build network
(must have)
[Channel, H, W]: 1x32x32->6x28x28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171102090953/75/PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-24-2048.jpg)
![• http://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/blitz/neural_networks_tutorial.html#define-the-network
conv1
x
relu
pooling
conv2
relu
pooling
fc1
relu
fc2
relu
fc3
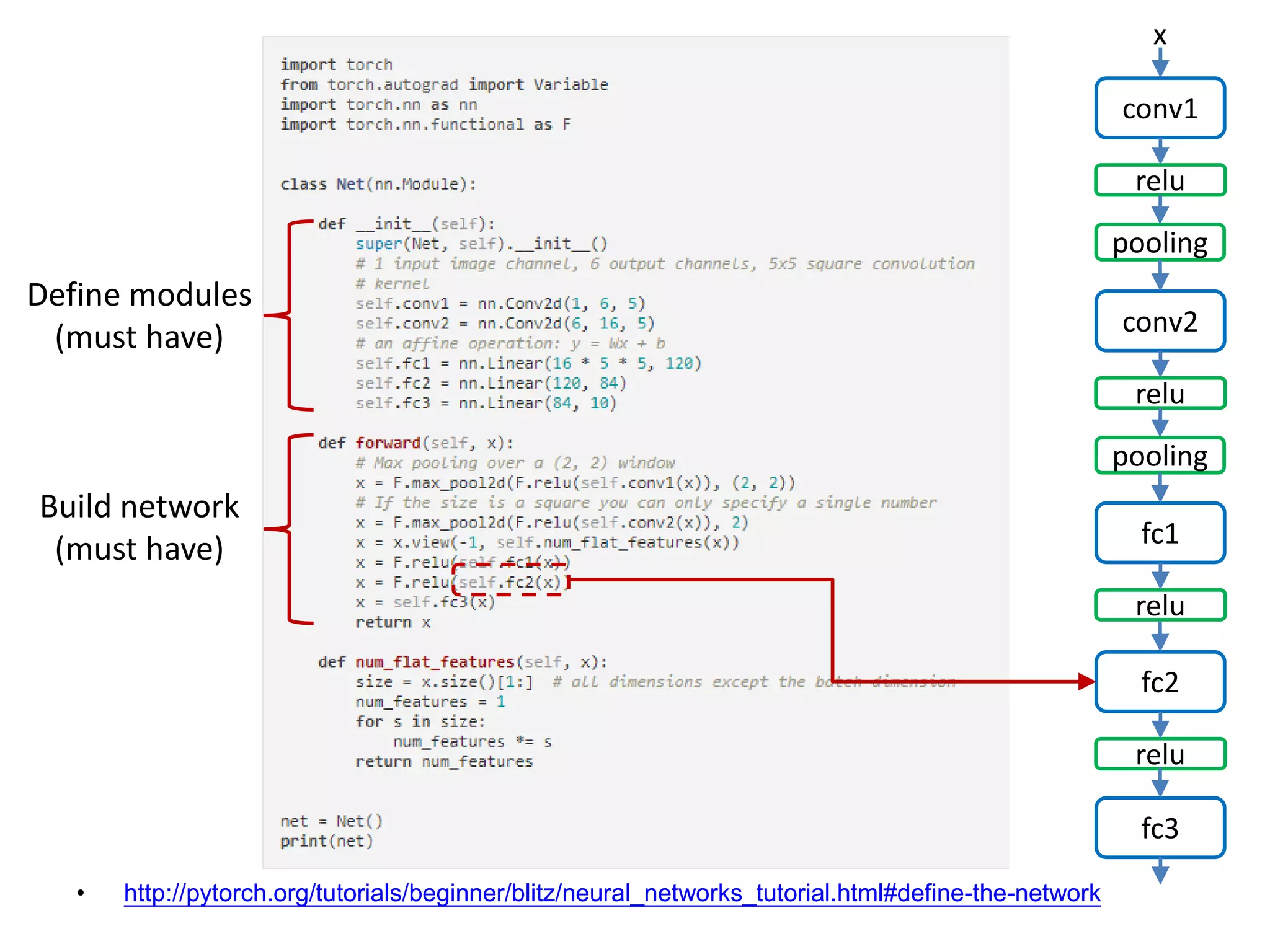
Define modules
(must have)
Build network
(must have)
[Channel, H, W]: 6x28x28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171102090953/75/PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-25-2048.jpg)
![• http://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/blitz/neural_networks_tutorial.html#define-the-network
conv1
x
relu
pooling
conv2
relu
pooling
fc1
relu
fc2
relu
fc3
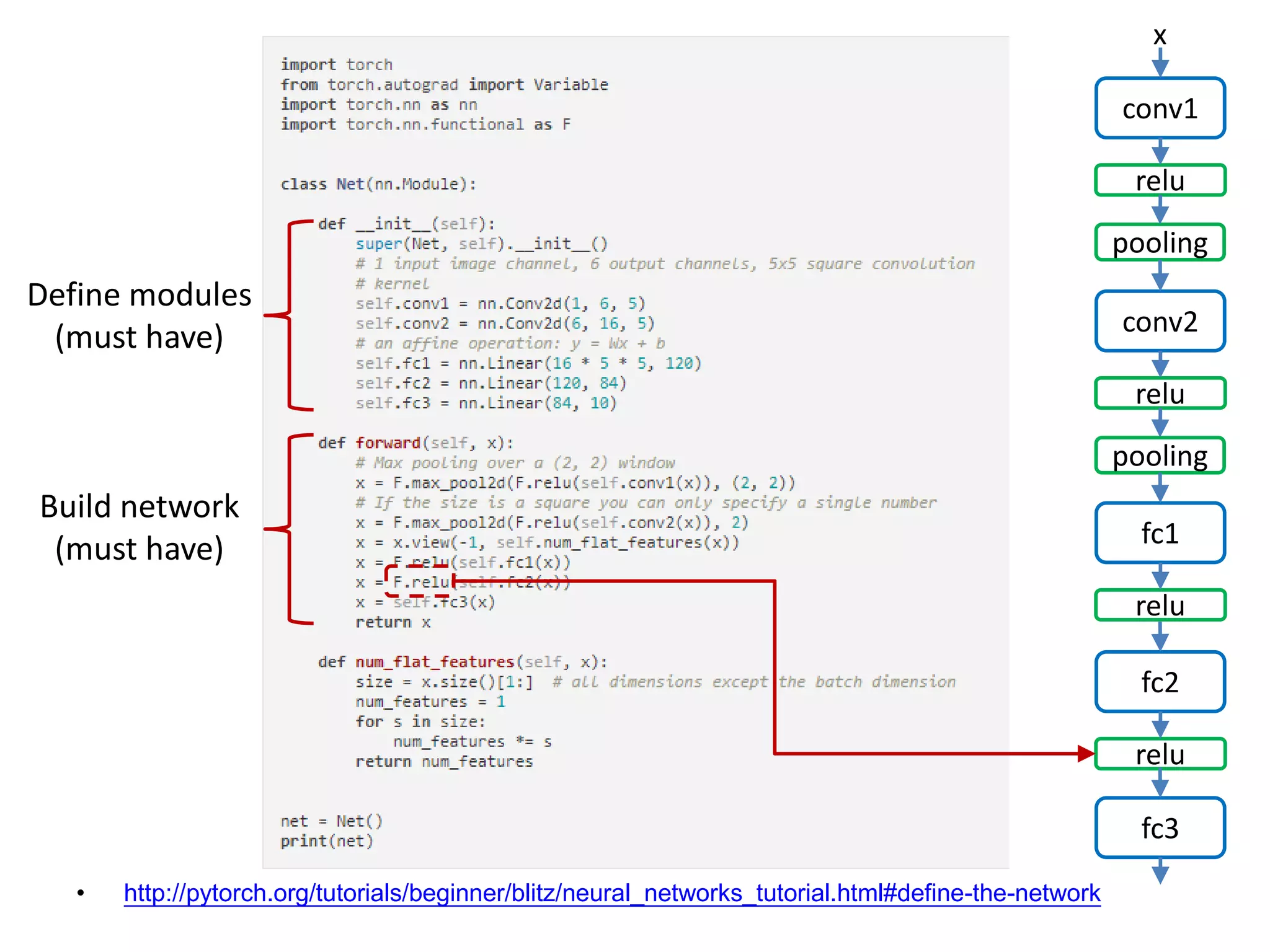
Define modules
(must have)
Build network
(must have)
[Channel, H, W]: 6x28x28 -> 6x14x14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171102090953/75/PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-26-2048.jpg)
![• http://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/blitz/neural_networks_tutorial.html#define-the-network
conv1
x
relu
pooling
conv2
relu
pooling
fc1
relu
fc2
relu
fc3
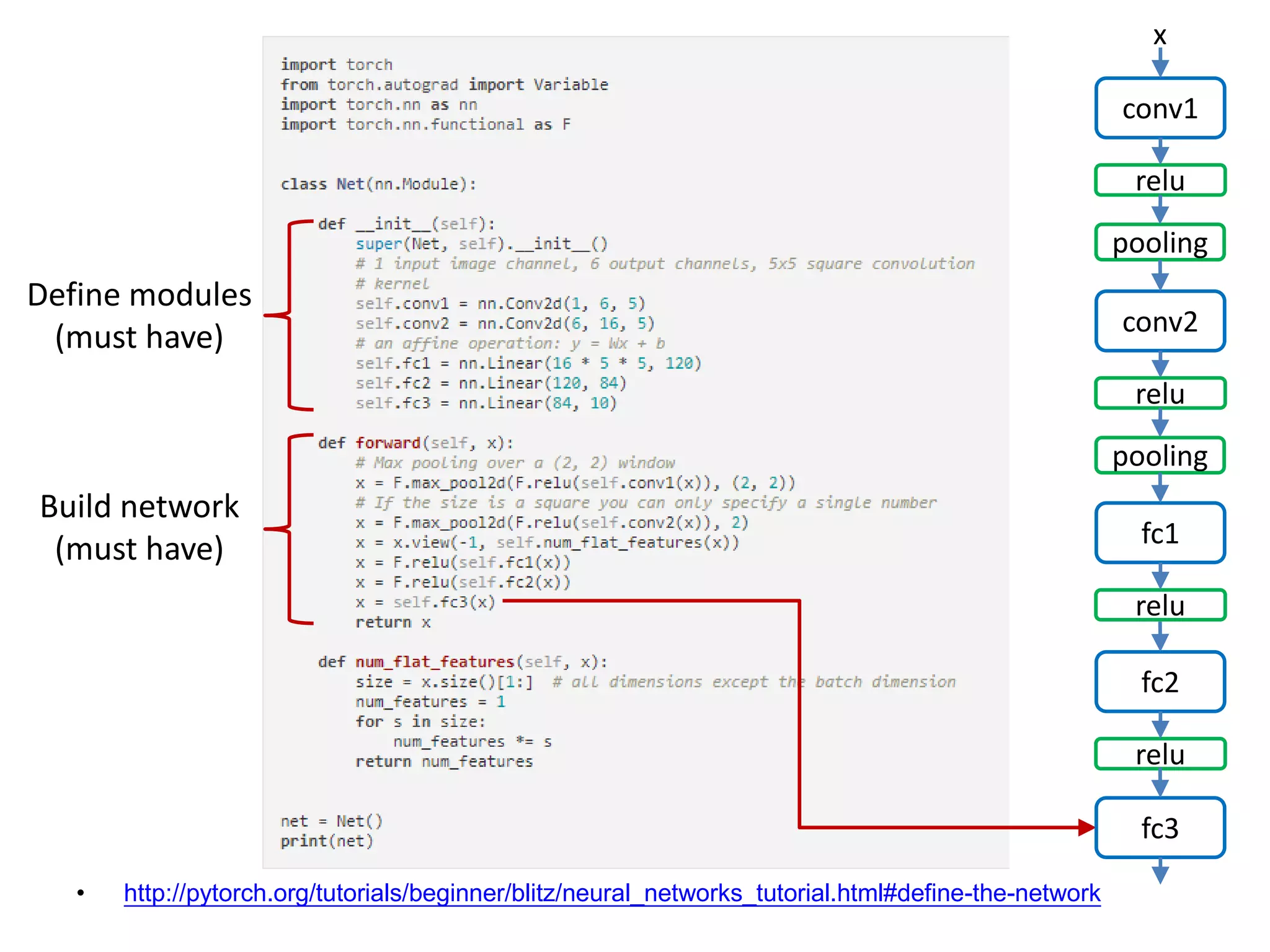
Define modules
(must have)
Build network
(must have)
[Channel, H, W]: 6x14x14 -> 16x10x10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171102090953/75/PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-27-2048.jpg)
![• http://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/blitz/neural_networks_tutorial.html#define-the-network
conv1
x
relu
pooling
conv2
relu
pooling
fc1
relu
fc2
relu
fc3
Define modules
(must have)
Build network
(must have)
[Channel, H, W]: 16x10x10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171102090953/75/PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-28-2048.jpg)
![• http://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/blitz/neural_networks_tutorial.html#define-the-network
conv1
x
relu
pooling
conv2
relu
pooling
fc1
relu
fc2
relu
fc3
Define modules
(must have)
Build network
(must have)
[Channel, H, W]: 16x10x10 -> 16x5x5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171102090953/75/PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-29-2048.jpg)
![• http://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/blitz/neural_networks_tutorial.html#define-the-network
conv1
x
relu
pooling
conv2
relu
pooling
fc1
relu
fc2
relu
fc3
Flatten the Tensor
Define modules
(must have)
Build network
(must have)
16x5x5
Tensor: [Batch N, Channel, H, W]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171102090953/75/PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-30-2048.jpg)

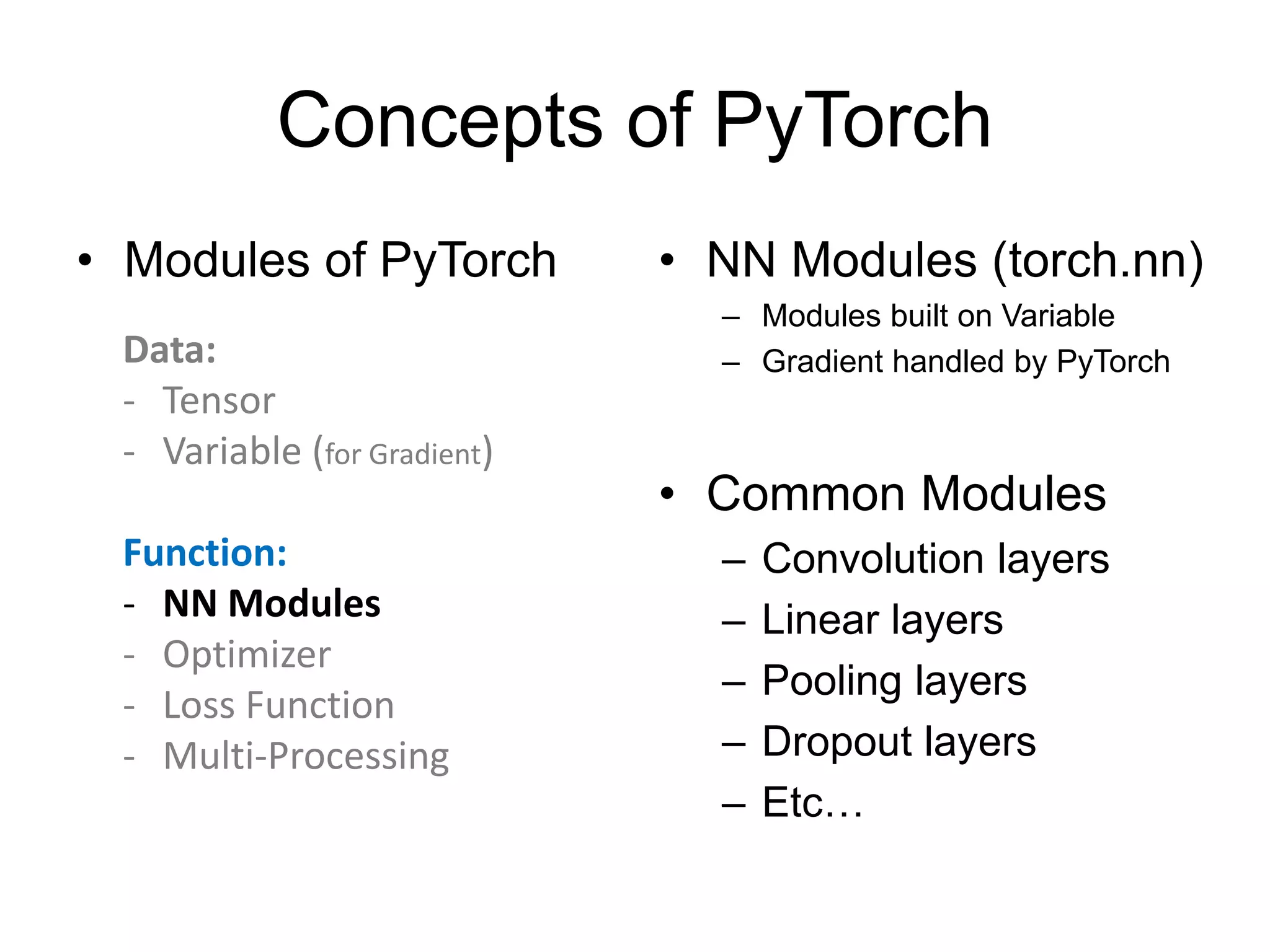
![NN Modules
• Convolution Layer
– N-th Batch (N), Channel (C)
– torch.nn.Conv1d: input [N, C, W] # moving kernel in 1D
– torch.nn.Conv2d: input [N, C, H, W] # moving kernel in 2D
– torch.nn.Conv3d: input [N, C, D, H, W] # moving kernel in 3D
– Example:
– torch.nn.conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=16, kernel_size=3, padding=1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171102090953/75/PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-37-2048.jpg)
![NN Modules
• Convolution Layer
– N-th Batch (N), Channel (C)
– torch.nn.Conv1d: input [N, C, W] # moving kernel in 1D
– torch.nn.Conv2d: input [N, C, H, W] # moving kernel in 2D
– torch.nn.Conv3d: input [N, C, D, H, W] # moving kernel in 3D
Hin
Input for Conv2d
Win
Cin
*: convolution](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171102090953/75/PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-38-2048.jpg)
![NN Modules
• Convolution Layer
– N-th Batch (N), Channel (C)
– torch.nn.Conv1d: input [N, C, W] # moving kernel in 1D
– torch.nn.Conv2d: input [N, C, H, W] # moving kernel in 2D
– torch.nn.Conv3d: input [N, C, D, H, W] # moving kernel in 3D
Hin
Input for Conv2d
k
k
Win
Cin
Cin
*
1st kernel
*: convolution](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171102090953/75/PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-39-2048.jpg)
![NN Modules
• Convolution Layer
– N-th Batch (N), Channel (C)
– torch.nn.Conv1d: input [N, C, W] # moving kernel in 1D
– torch.nn.Conv2d: input [N, C, H, W] # moving kernel in 2D
– torch.nn.Conv3d: input [N, C, D, H, W] # moving kernel in 3D
Hin
Input for Conv2d
k
k
Win
Cin
Cin
Hout
Wout
1
*
1st kernel
=
*: convolution](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171102090953/75/PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-40-2048.jpg)
![NN Modules
• Convolution Layer
– N-th Batch (N), Channel (C)
– torch.nn.Conv1d: input [N, C, W] # moving kernel in 1D
– torch.nn.Conv2d: input [N, C, H, W] # moving kernel in 2D
– torch.nn.Conv3d: input [N, C, D, H, W] # moving kernel in 3D
Hin
Input for Conv2d
k
k
Win
Cin
Cin
Hout
Wout
1
*
1st kernel
=
*: convolution
k=3d=1
s=1, moving step size
p=1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171102090953/75/PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-41-2048.jpg)
![NN Modules
• Convolution Layer
– N-th Batch (N), Channel (C)
– torch.nn.Conv1d: input [N, C, W] # moving kernel in 1D
– torch.nn.Conv2d: input [N, C, H, W] # moving kernel in 2D
– torch.nn.Conv3d: input [N, C, D, H, W] # moving kernel in 3D
Hin
Input for Conv2d
k
k
Win
Cin
Cin
Hout
Wout
1
*
1st kernel
=
*: convolution
k=3d=1
p=1
p=1
s=1, moving step size](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171102090953/75/PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-42-2048.jpg)
![NN Modules
• Convolution Layer
– N-th Batch (N), Channel (C)
– torch.nn.Conv1d: input [N, C, W] # moving kernel in 1D
– torch.nn.Conv2d: input [N, C, H, W] # moving kernel in 2D
– torch.nn.Conv3d: input [N, C, D, H, W] # moving kernel in 3D
Hin
Input for Conv2d
k
k
Win
Cin
Cin
Hout
Wout
1
*
1st kernel
=
*: convolution
k=3d=1
p=1
k=3
p=1
s=1, moving step size](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171102090953/75/PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-43-2048.jpg)
![NN Modules
• Convolution Layer
– N-th Batch (N), Channel (C)
– torch.nn.Conv1d: input [N, C, W] # moving kernel in 1D
– torch.nn.Conv2d: input [N, C, H, W] # moving kernel in 2D
– torch.nn.Conv3d: input [N, C, D, H, W] # moving kernel in 3D
Hin
Input for Conv2d
k
k
Win
Cin
Cin
Hout
Wout
1
*
1st kernel
=
*: convolution
k=3d=1
p=1
k=3
s=1
p=1
s=1, moving step size](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171102090953/75/PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-44-2048.jpg)
![NN Modules
• Convolution Layer
– N-th Batch (N), Channel (C)
– torch.nn.Conv1d: input [N, C, W] # moving kernel in 1D
– torch.nn.Conv2d: input [N, C, H, W] # moving kernel in 2D
– torch.nn.Conv3d: input [N, C, D, H, W] # moving kernel in 3D
Hin
Input for Conv2d
k
k
Win
Cin
Cin
Hout
Wout
1
*
1st kernel
Cout-th kernel
k
k
Cin
Hout
Wout
1
*
=
=
*: convolution
… …](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171102090953/75/PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-45-2048.jpg)
![NN Modules
• Convolution Layer
– N-th Batch (N), Channel (C)
– torch.nn.Conv1d: input [N, C, W] # moving kernel in 1D
– torch.nn.Conv2d: input [N, C, H, W] # moving kernel in 2D
– torch.nn.Conv3d: input [N, C, D, H, W] # moving kernel in 3D
Hin
Input for Conv2d
k
k
Win
Cin
Cin
Hout
Wout
1
*
1st kernel
Cout-th kernel
k
k
Cin
Hout
Wout
1
*
=
=
Hout
Wout
Cout
*: convolution
… …](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171102090953/75/PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-46-2048.jpg)
![NN Modules
• Convolution Layer
– N-th Batch (N), Channel (C)
– torch.nn.Conv1d: input [N, C, W] # moving kernel in 1D
– torch.nn.Conv2d: input [N, C, H, W] # moving kernel in 2D
– torch.nn.Conv3d: input [N, C, D, H, W] # moving kernel in 3D
Hin
Input for Conv2d
k
k
Win
Cin
Cin
*
1st kernel
Cout-th kernel
k
k
Cin
*
*: convolution
…
# of parameters](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171102090953/75/PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-47-2048.jpg)
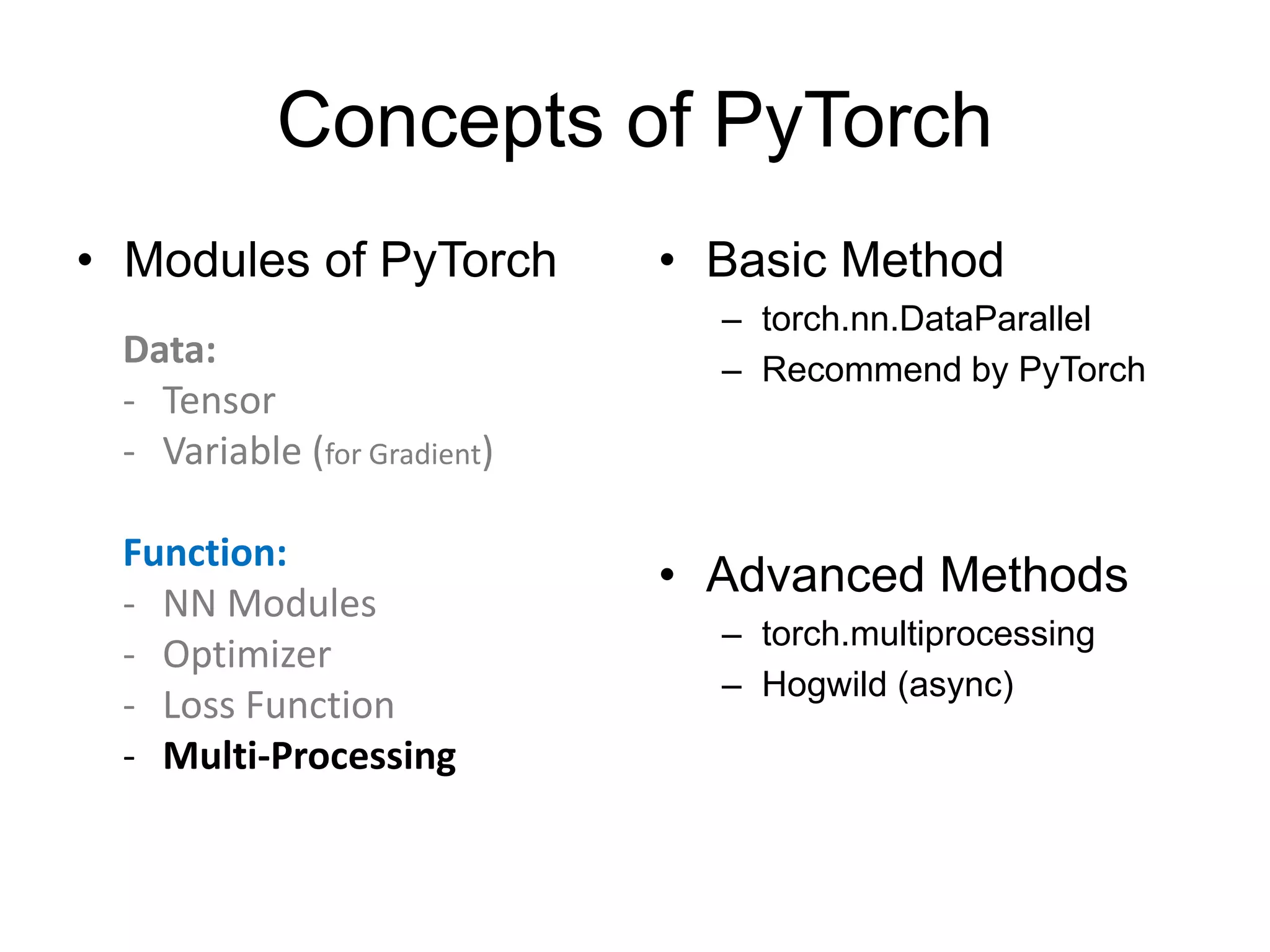
![Multi-GPU Processing
• torch.nn.DataParallel
– gpu_id = '6,7‘
– os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = gpu_id
– net = torch.nn.DataParallel(model, device_ids=[0, 1, 2])
– output = net(input_var)
• Important Notes:
– Device_ids must start from 0
– (batch_size/GPU_size) must be integer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchtutorial-2017-1103-171102090953/75/PyTorch-Tutorial-for-NTU-Machine-Learing-Course-2017-58-2048.jpg)