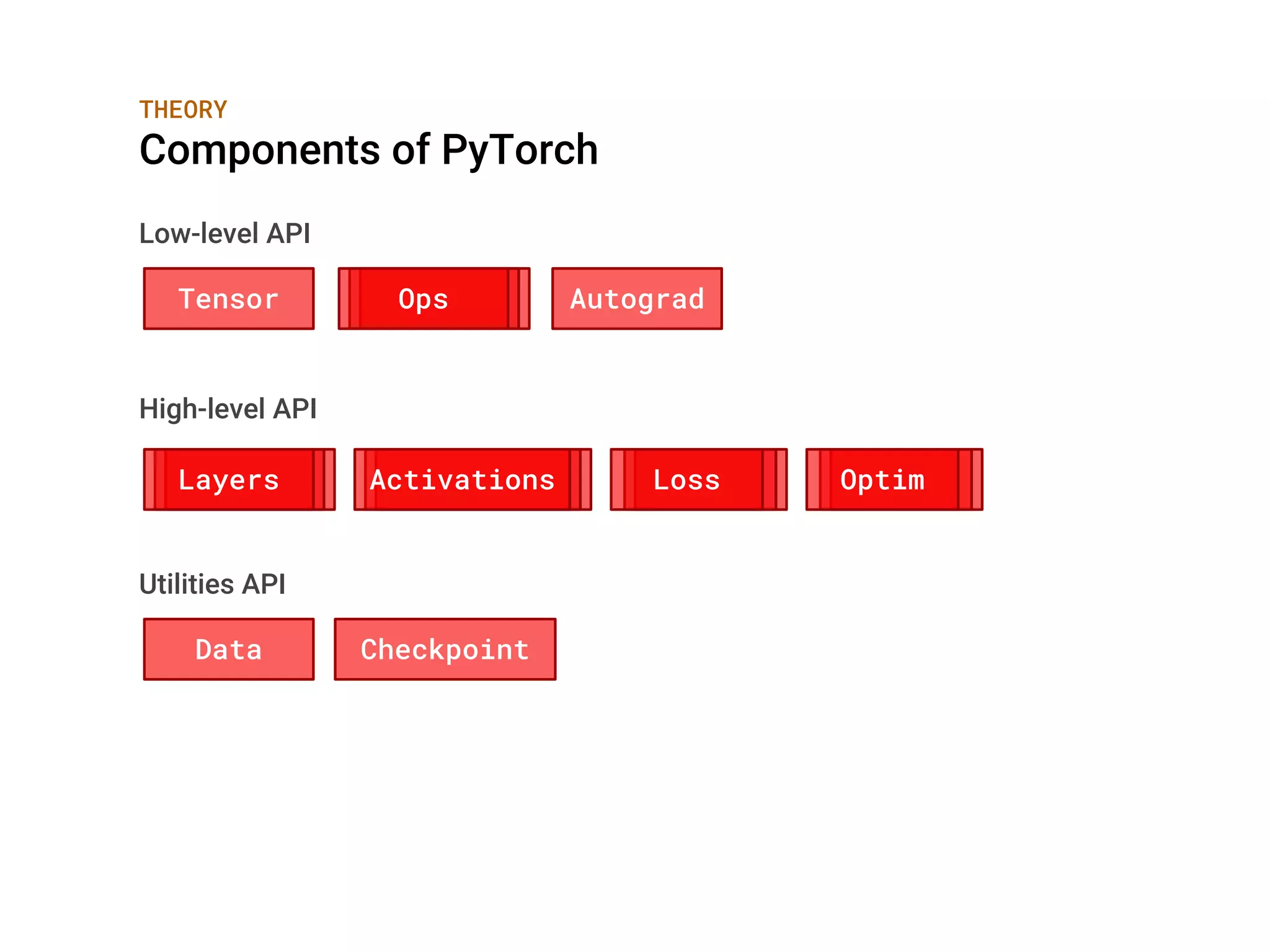
The document is a guide on using PyTorch for deep learning, presented by Bayu Aldi Yansyah at PyCon Indonesia in 2018. It covers both theoretical concepts and practical implementations of neural networks, detailing components like tensors, operations, layers, activation functions, and loss functions. Key takeaways emphasize PyTorch's intuitive nature and ease of use with standard Python.


![THEORY - LOW LEVEL API
Tensors
torch.Tensor are generalizations of a matrix that can be indexed in more
than 2 dimensions.
Creating a torch.Tensor
Tensors can be created from Python lists with the torch.Tensor() function.
import torch
vector_data = [0.0, 1.0, 0.0]
vector = torch.Tensor(vector)
matrix_data = [[1.0., 0.0, 0.0], [0.0, 1.0, 0.0]]
matrix = torch.Tensor(matrix_data)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchfordeeplearningpractitioners-181105141725/75/PyTorch-for-Deep-Learning-Practitioners-6-2048.jpg)


![THEORY - LOW LEVEL API
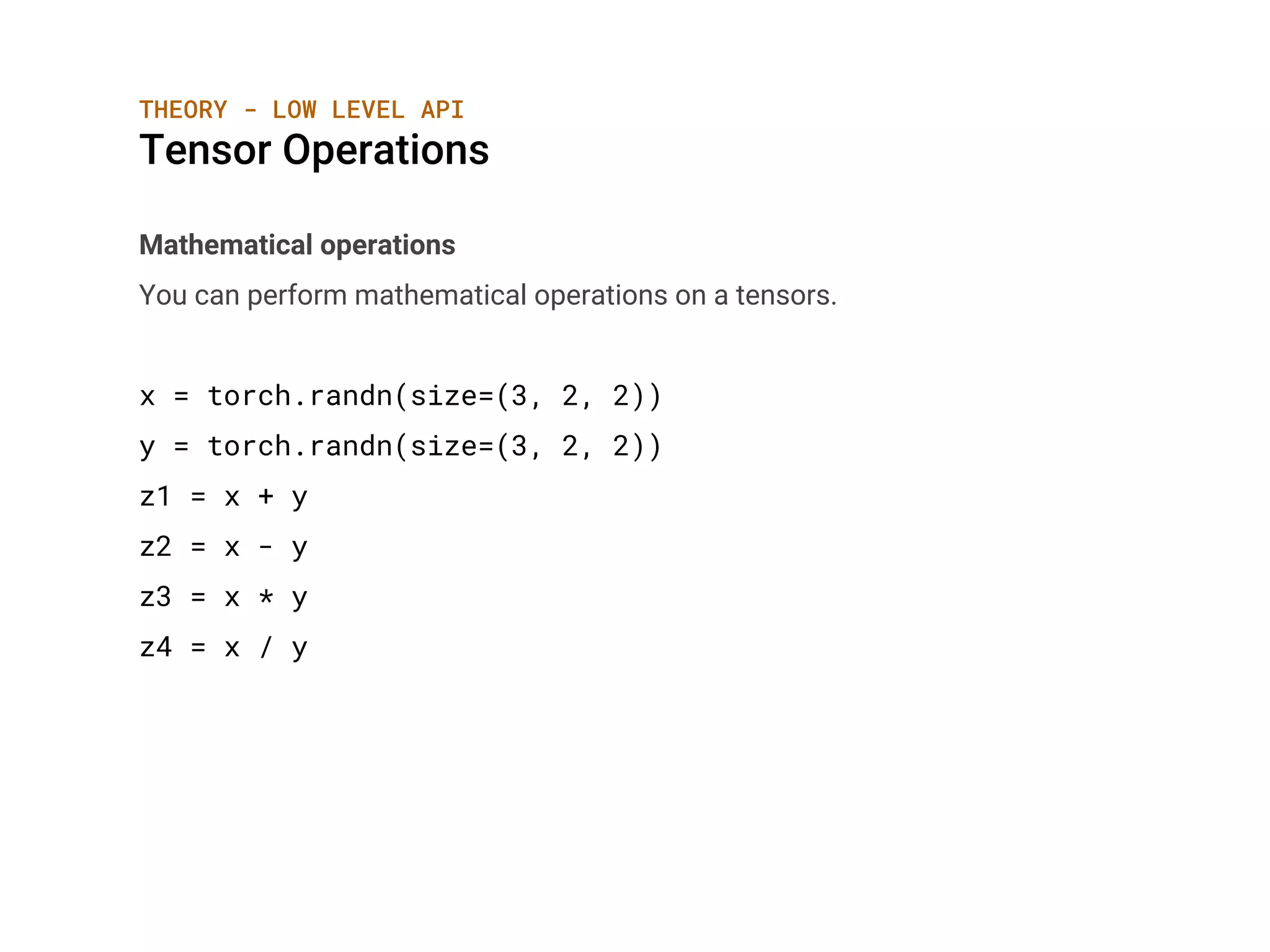
Tensor Operations
Beyond Mathematical operations
You can perform indexing, slicing, joining, mutating operations on a tensors.
For example:
# Indexing
x = torch.randn(size=(1, 3))
x[0]
# Joining (Concatenation)
xx = torch.cat((x, x))
See the documentation for a complete list of the massive number of operations
available to you.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchfordeeplearningpractitioners-181105141725/75/PyTorch-for-Deep-Learning-Practitioners-10-2048.jpg)
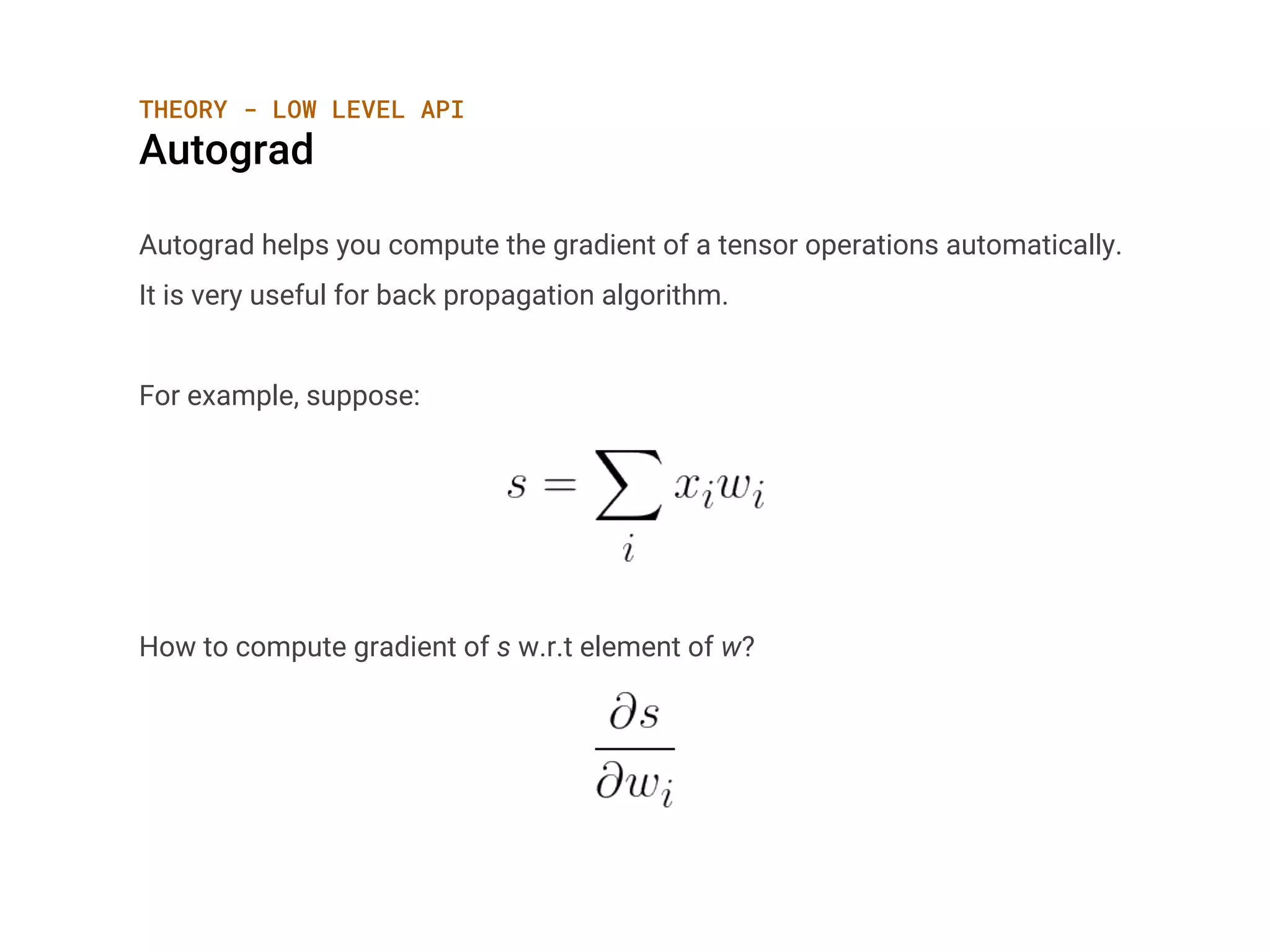
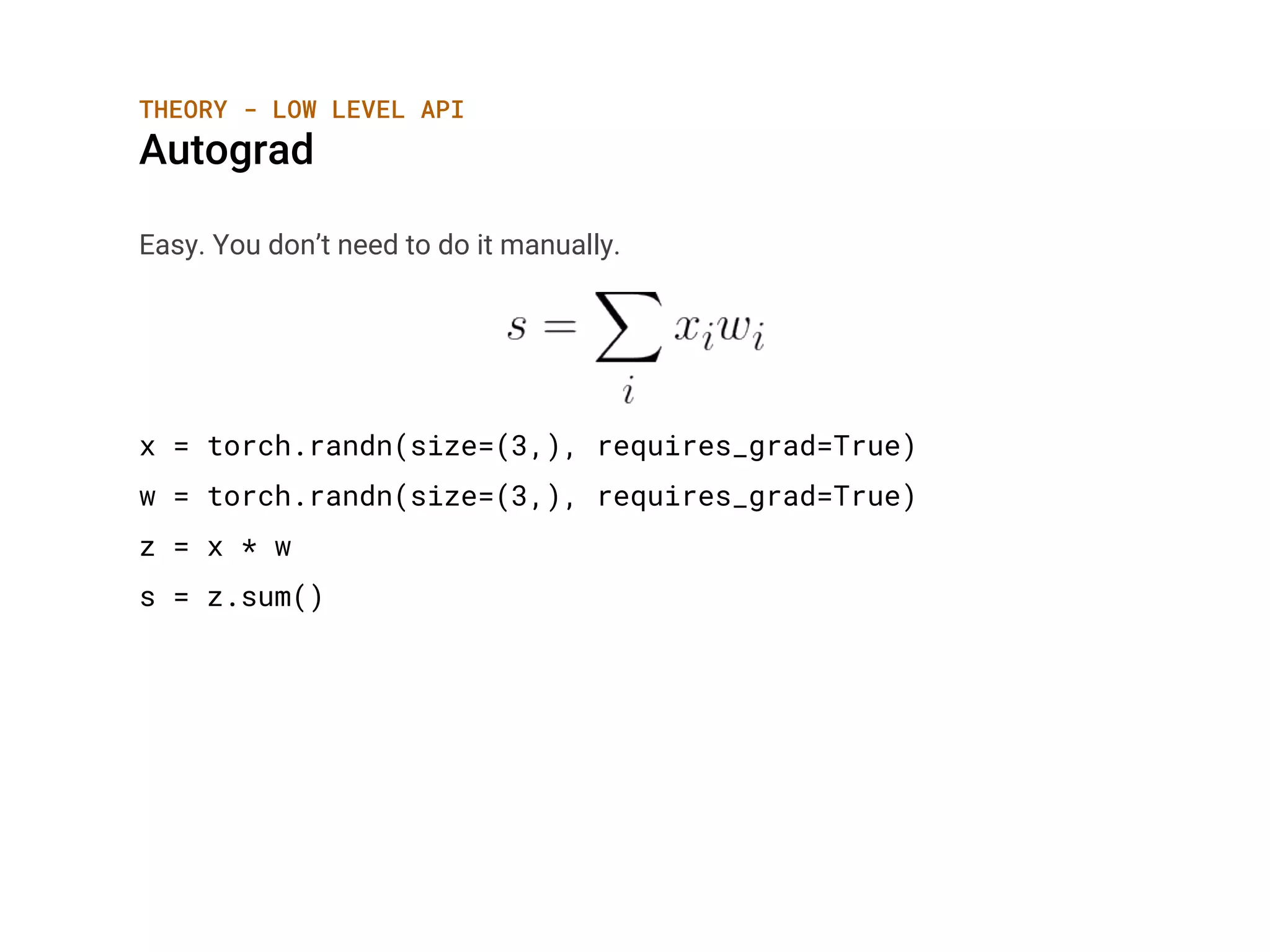
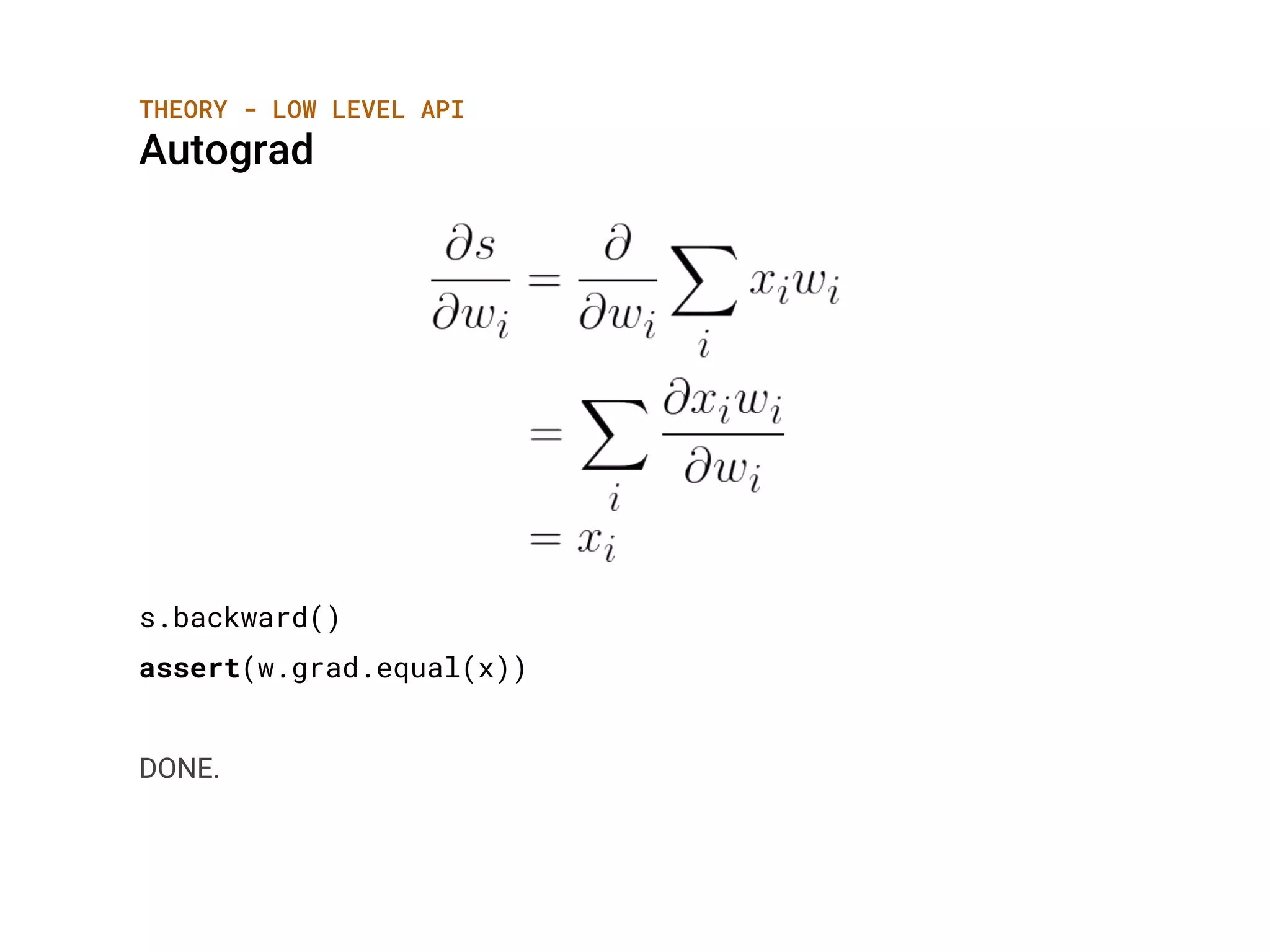


![THEORY - HIGH LEVEL API
Activation Functions
Softmax
Applies the Softmax function to an n-dimensional input Tensor rescaling them
so that the elements of the n-dimensional output Tensor lie in the range (0,1)
and sum to 1.
s = nn.Softmax(dim=2)
x = torch.Tensor([1, 2])
output = s(x)
See the documentation for a other layers.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pytorchfordeeplearningpractitioners-181105141725/75/PyTorch-for-Deep-Learning-Practitioners-17-2048.jpg)




