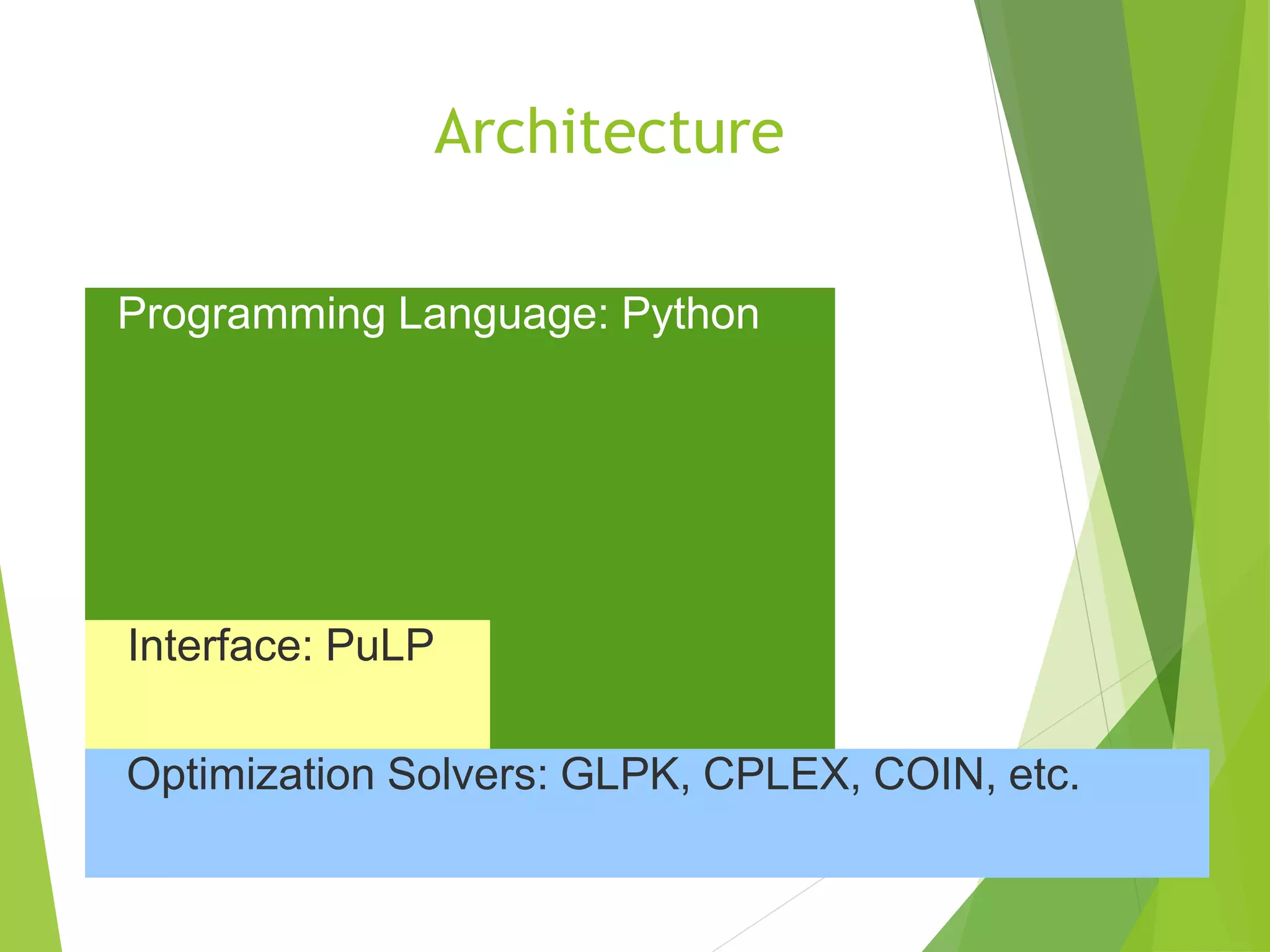
The document provides a comprehensive overview of a Python programming tutorial, covering topics such as program structure, data types, flow control, functions, and object-oriented programming. It includes specific details about the Pulp optimization library and its solvers like GLPK and CPLEX for linear programming. Additionally, contact information and training location are mentioned for potential participants interested in Python training in Bangalore.




![Python: High-Level Data Type
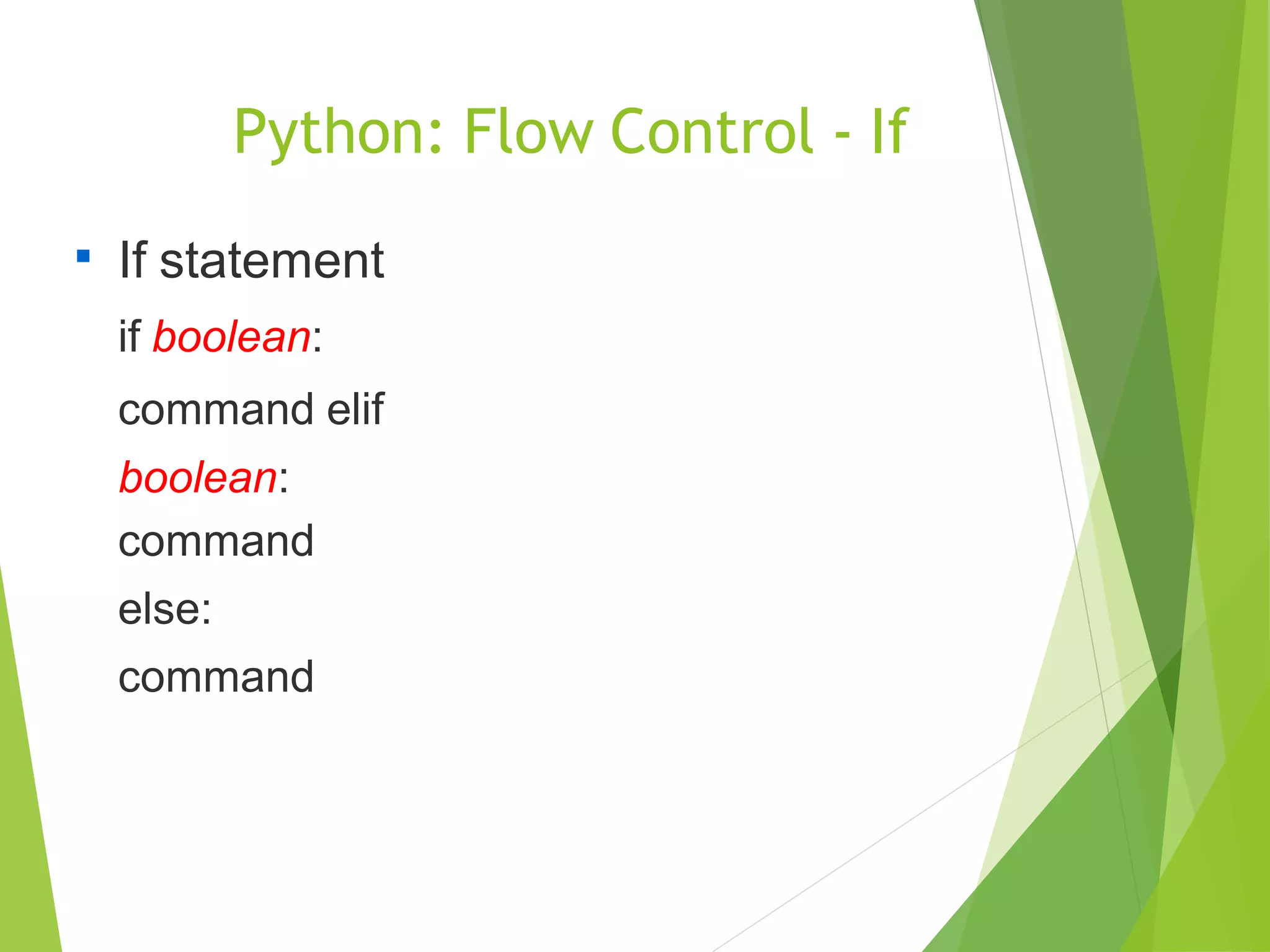
Lt(list): [ d1, d2, …, dn ]
Ex: [ 1, 3.14, True, 'a', [1], (2,3), {'B+':3.5} ]
Tuple (tuple): ( d1, d2, ..., dn, )
Ex: ( 1, 3.14, True, 'a', [1], (2,3), {'B+':3.5} )
Dictionary (dict): { k1:v1 , k2:v2 , ..., kn:vn }
Ex: { 'A':4 , 'B+':3.5 , 3:'B' }
Set (set): set([ d1, d2, ..., dn ])
Ex: set([ 4, 3.5, 'B'])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-171220133716/75/Python-Training-Tutorial-for-Frreshers-9-2048.jpg)
![Python: List Comprehensions
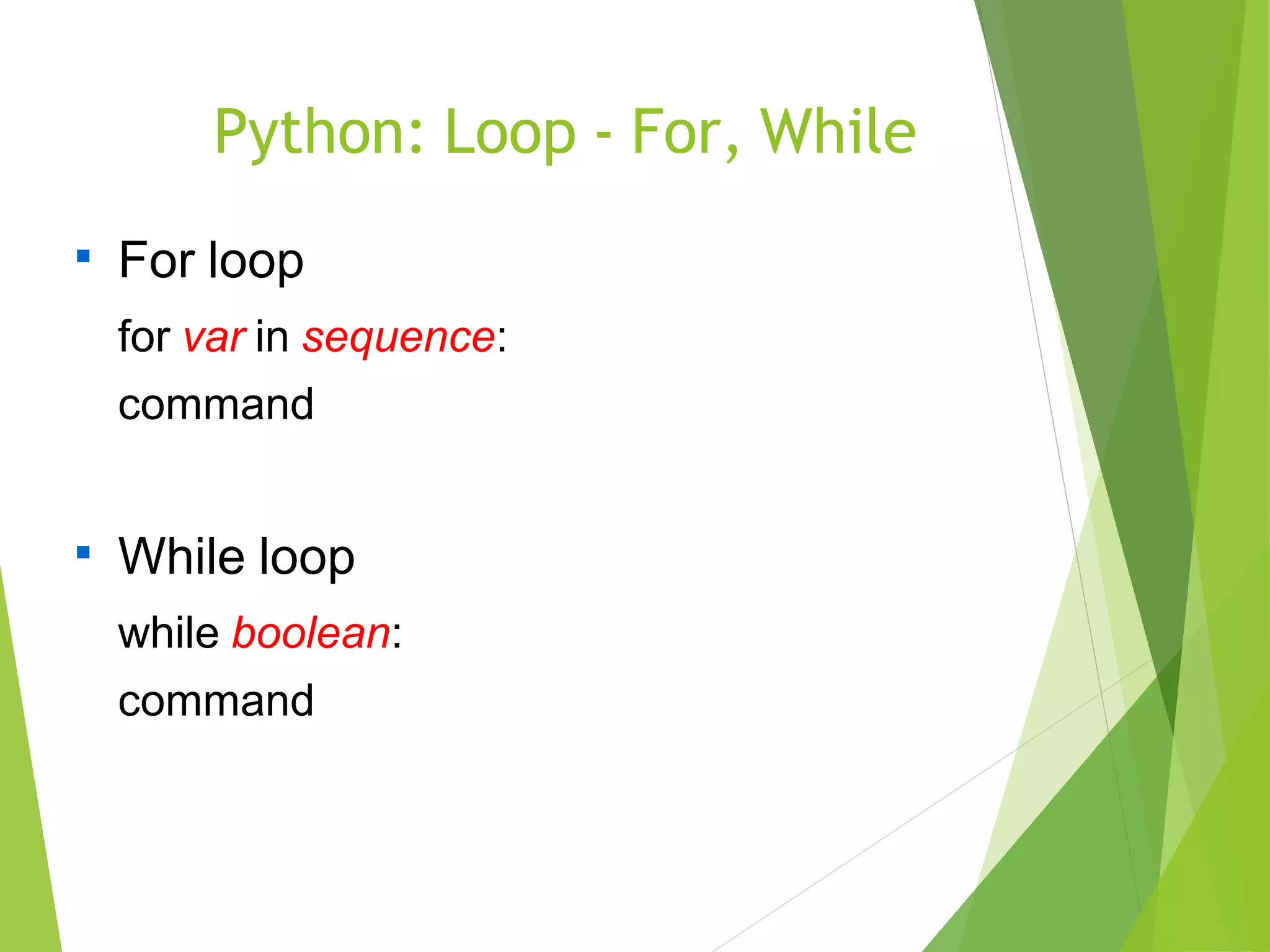
>>>[ i for i in range(5)]
→ [ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 ]
>>>[ i for i in range(5) if i <> 3 ]
→ [ 0, 1, 2, 4 ]
>>>[ (i, j) for i in range(3) for j in range(i) ]
→ [ (1,0), (2,0), (2,1) ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-171220133716/75/Python-Training-Tutorial-for-Frreshers-12-2048.jpg)


![PuLP: Results
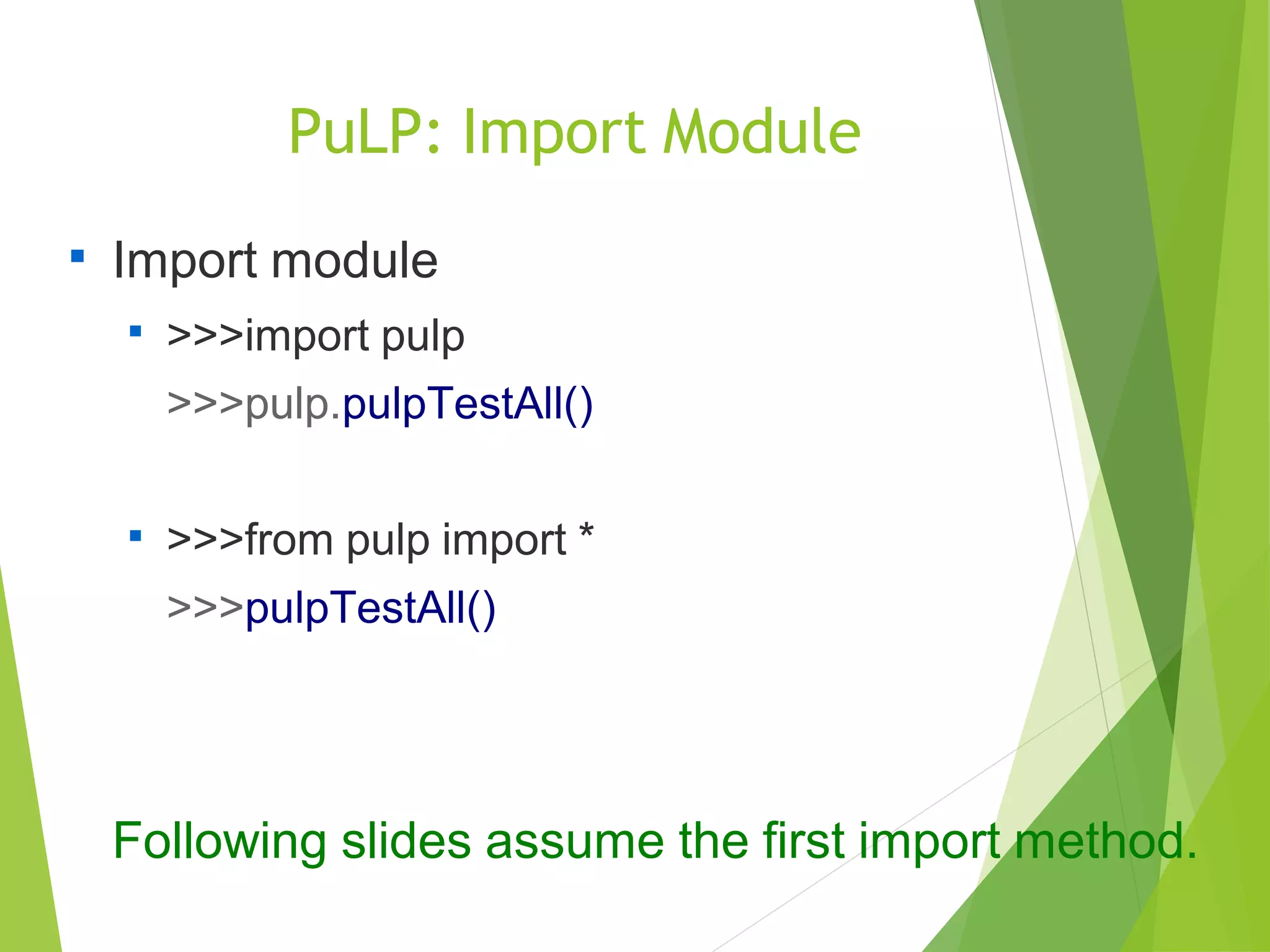
Check status: pulp.LpStatus[PB.status]
Ex: pulp.LpStatus[prob.status]
Optimal cost: pulp.value(PB.objective)
Ex: pulp.value(prob.objective)
Optimal solution: DV.varValue
Ex: x1.varValue
or pulp.value(x1)
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-171220133716/75/Python-Training-Tutorial-for-Frreshers-21-2048.jpg)
