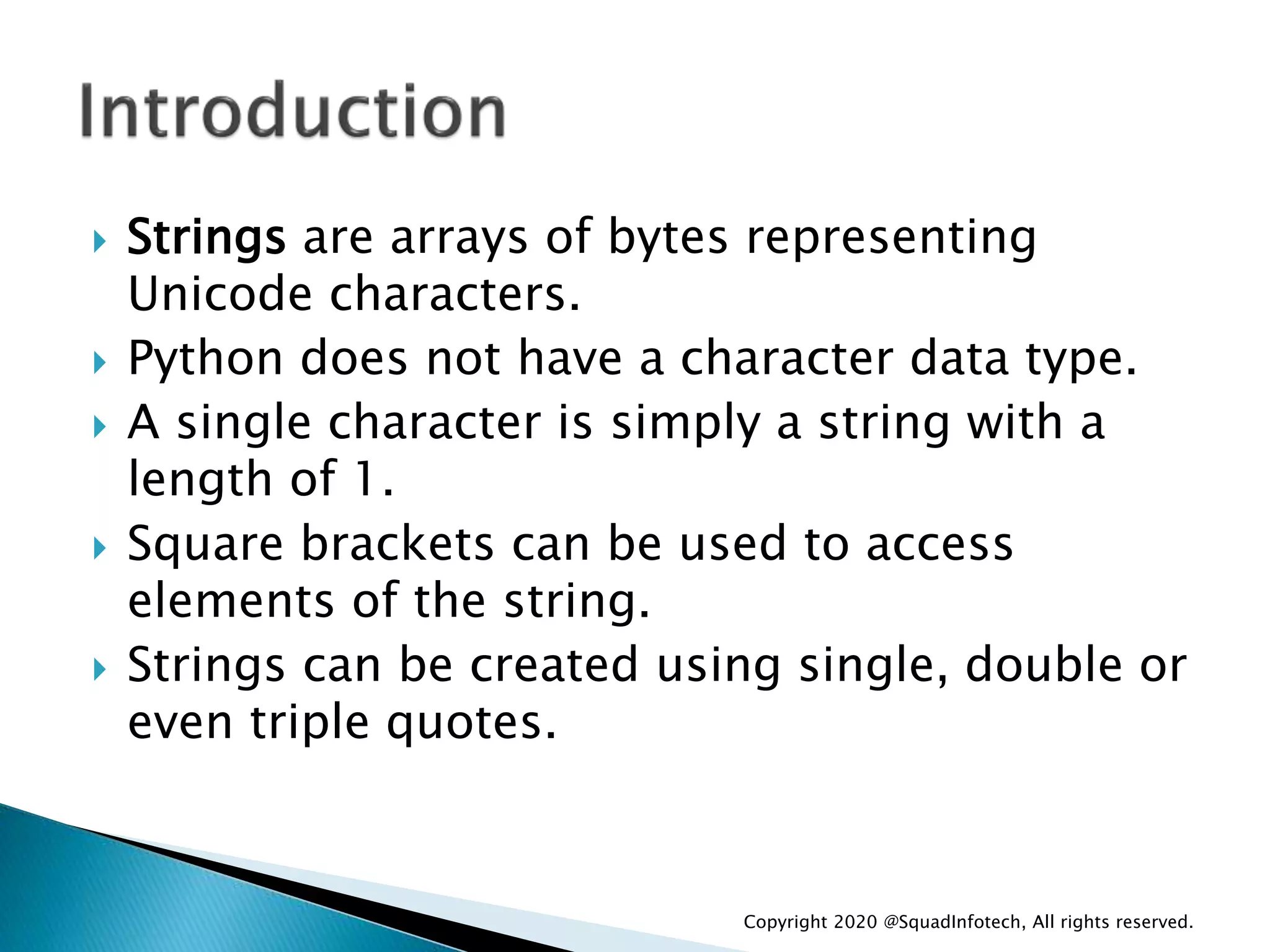
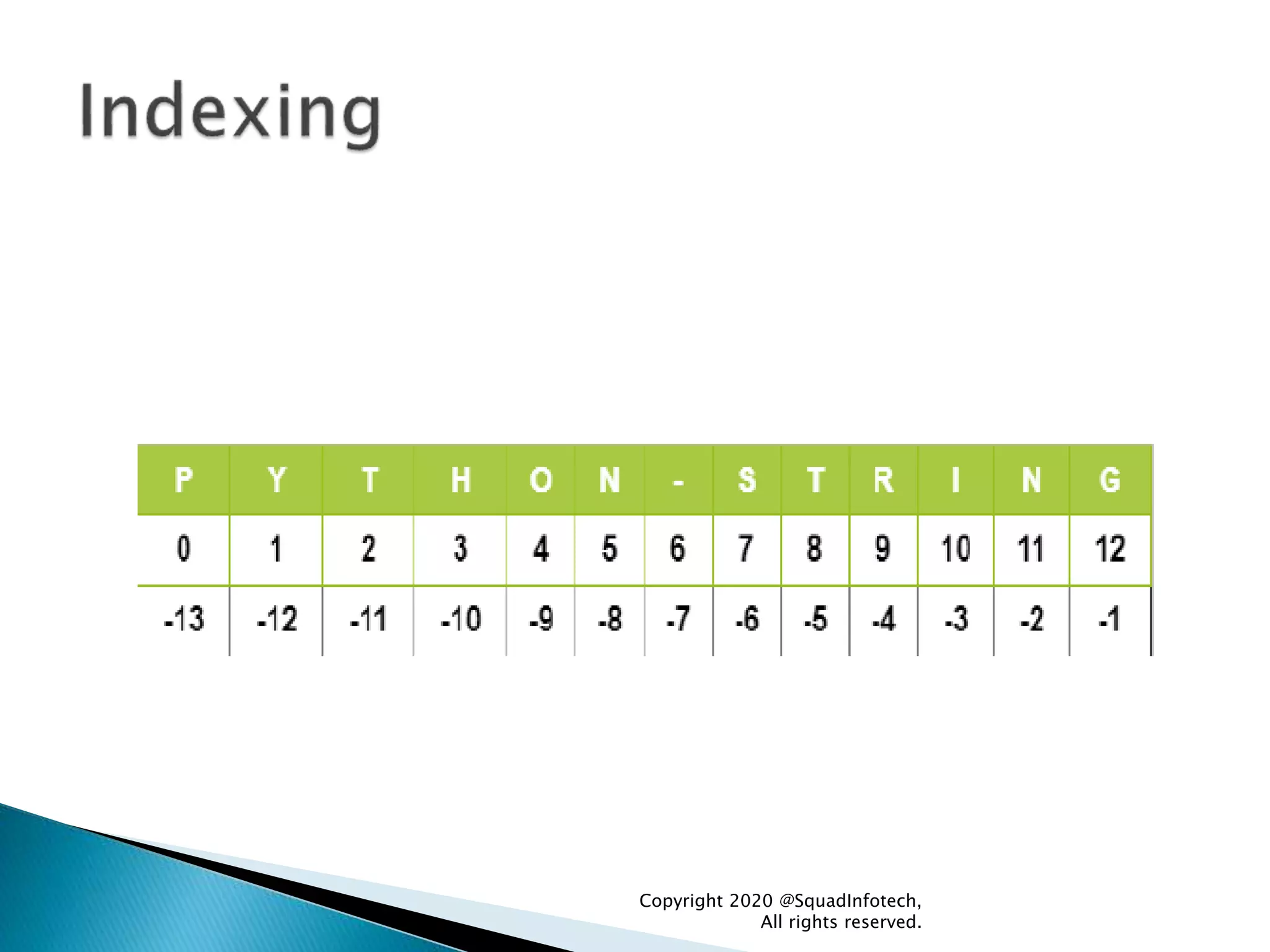
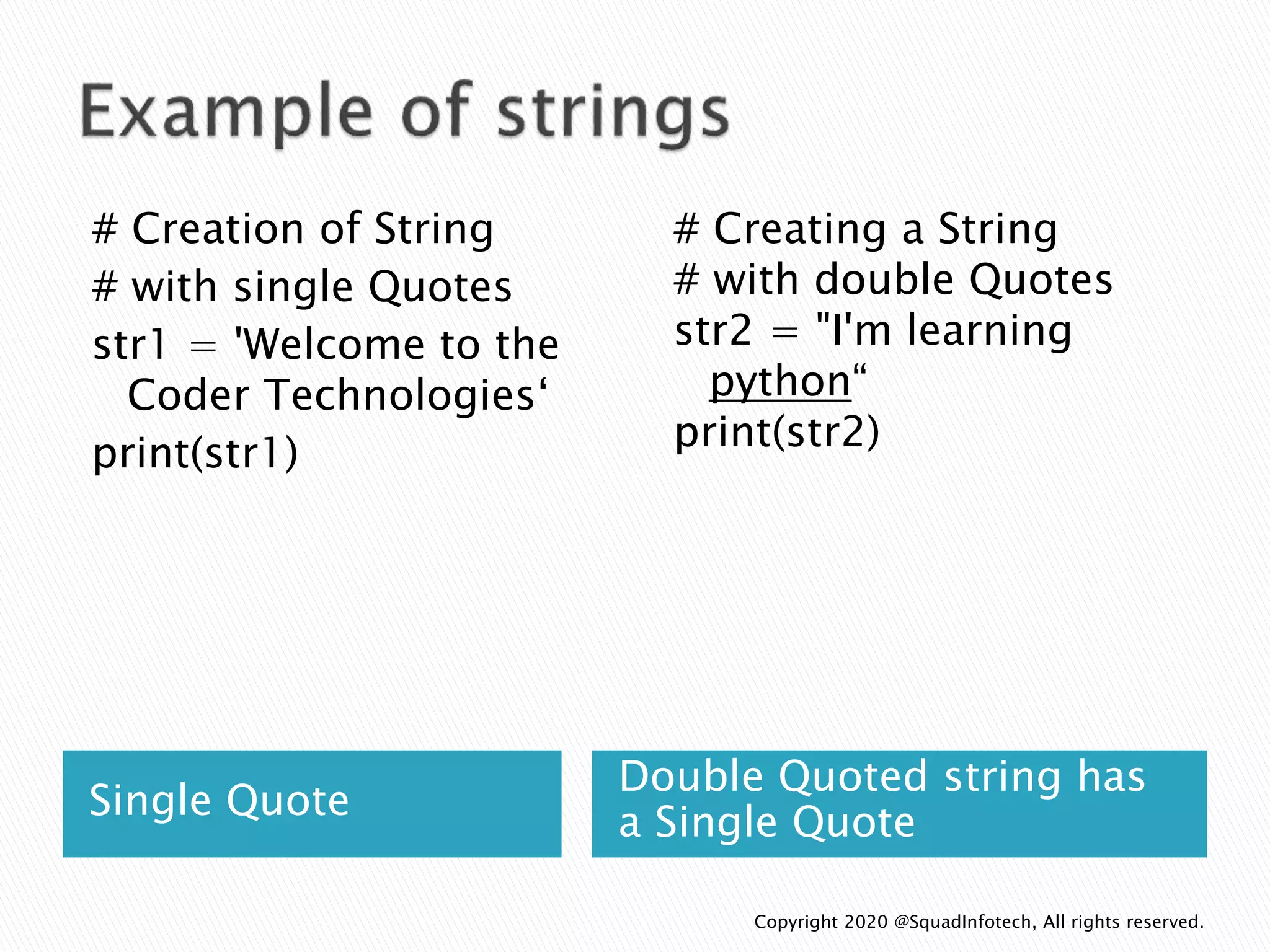
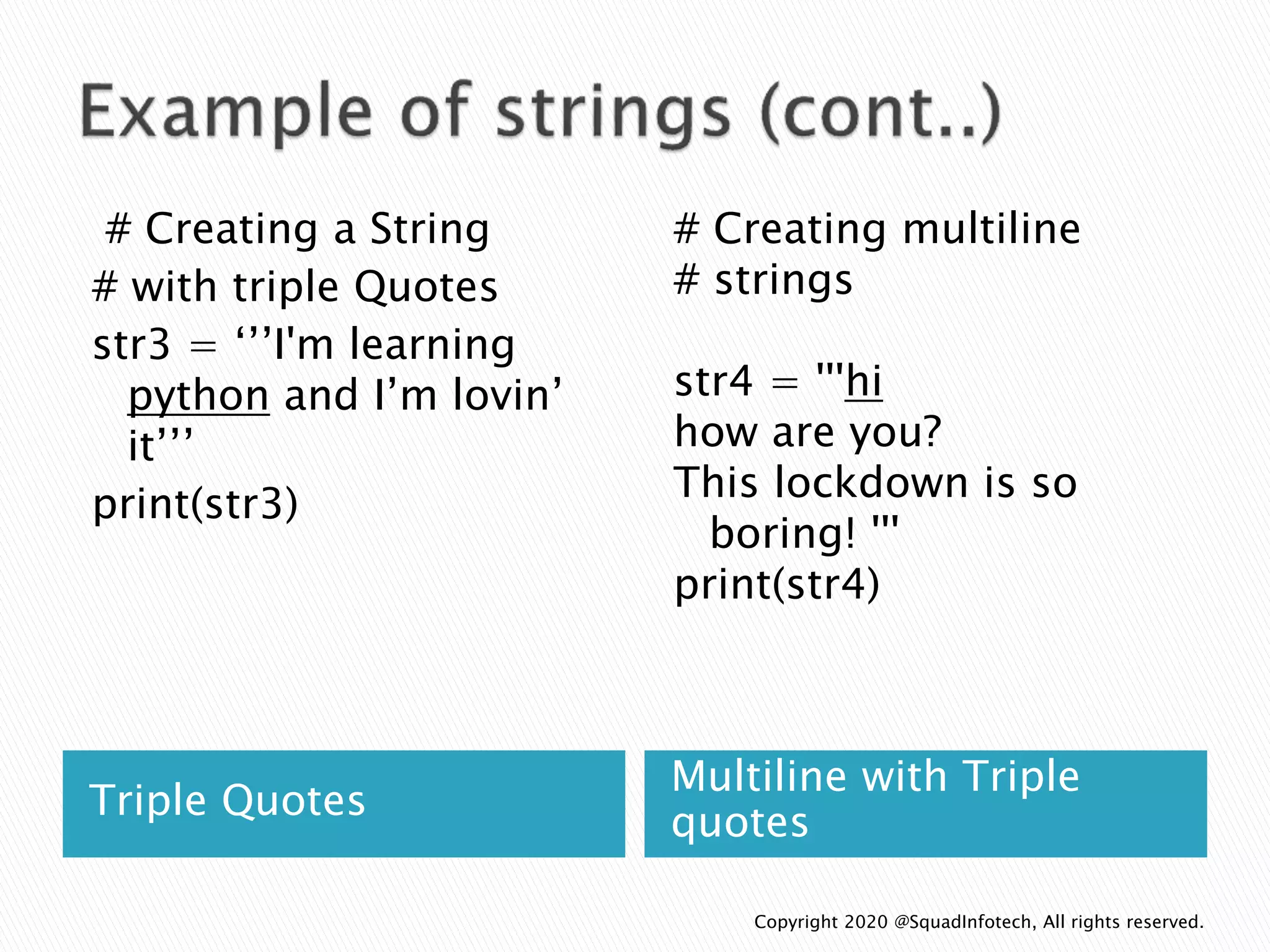
The document discusses Python programming language. Some key points:
- Python was invented by Guido Van Rossum and is a combination of various programming languages.
- It is a general purpose, high-level programming language that is interpreted, interactive, object-oriented and extensible.
- Python can be used for web applications, desktop applications, data analysis, artificial intelligence, and more. Popular companies that use Python include Google, YouTube, and NASA.
- Python code is portable and can run on various platforms. It has a simple syntax and is easy to learn.










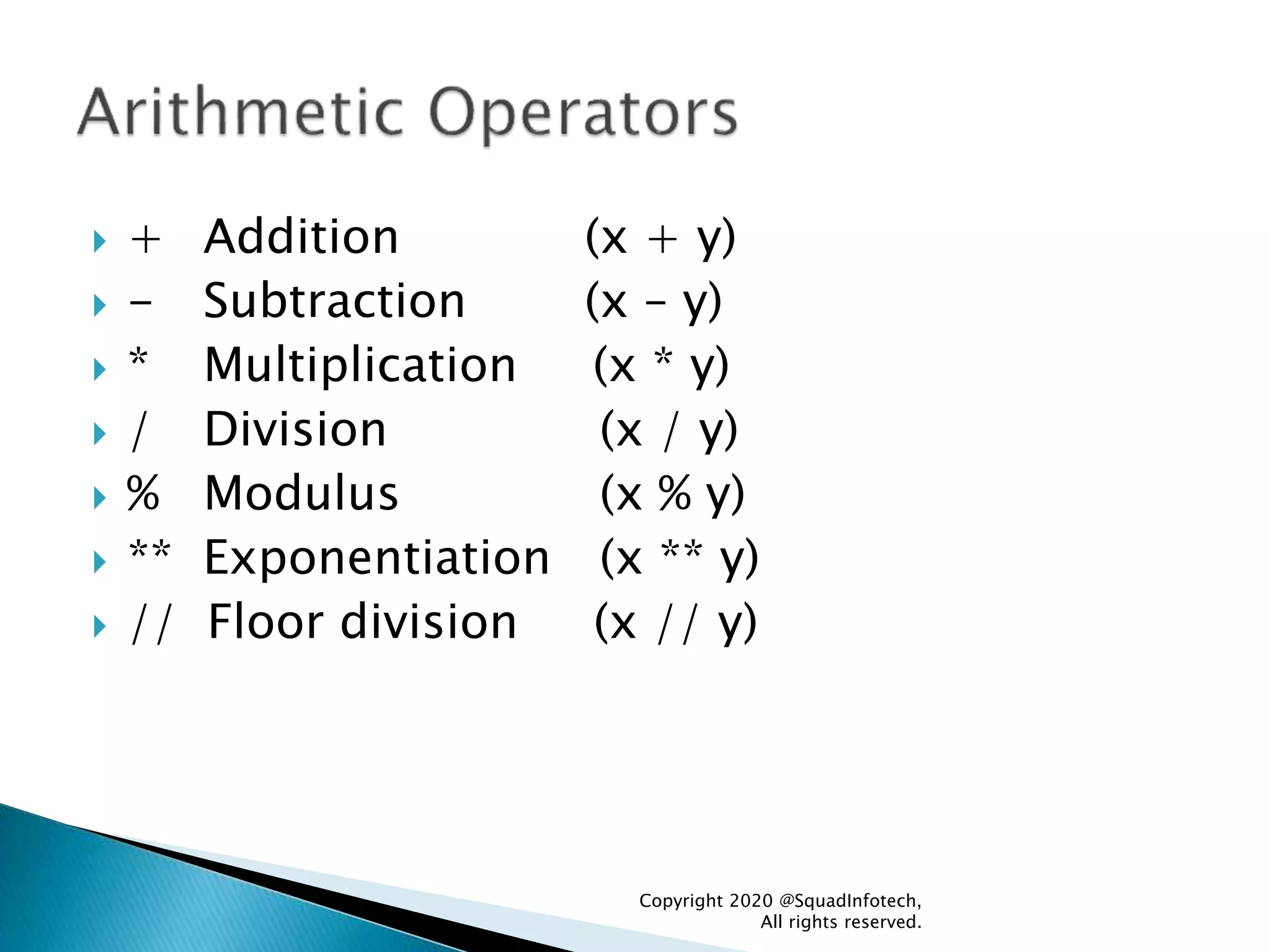
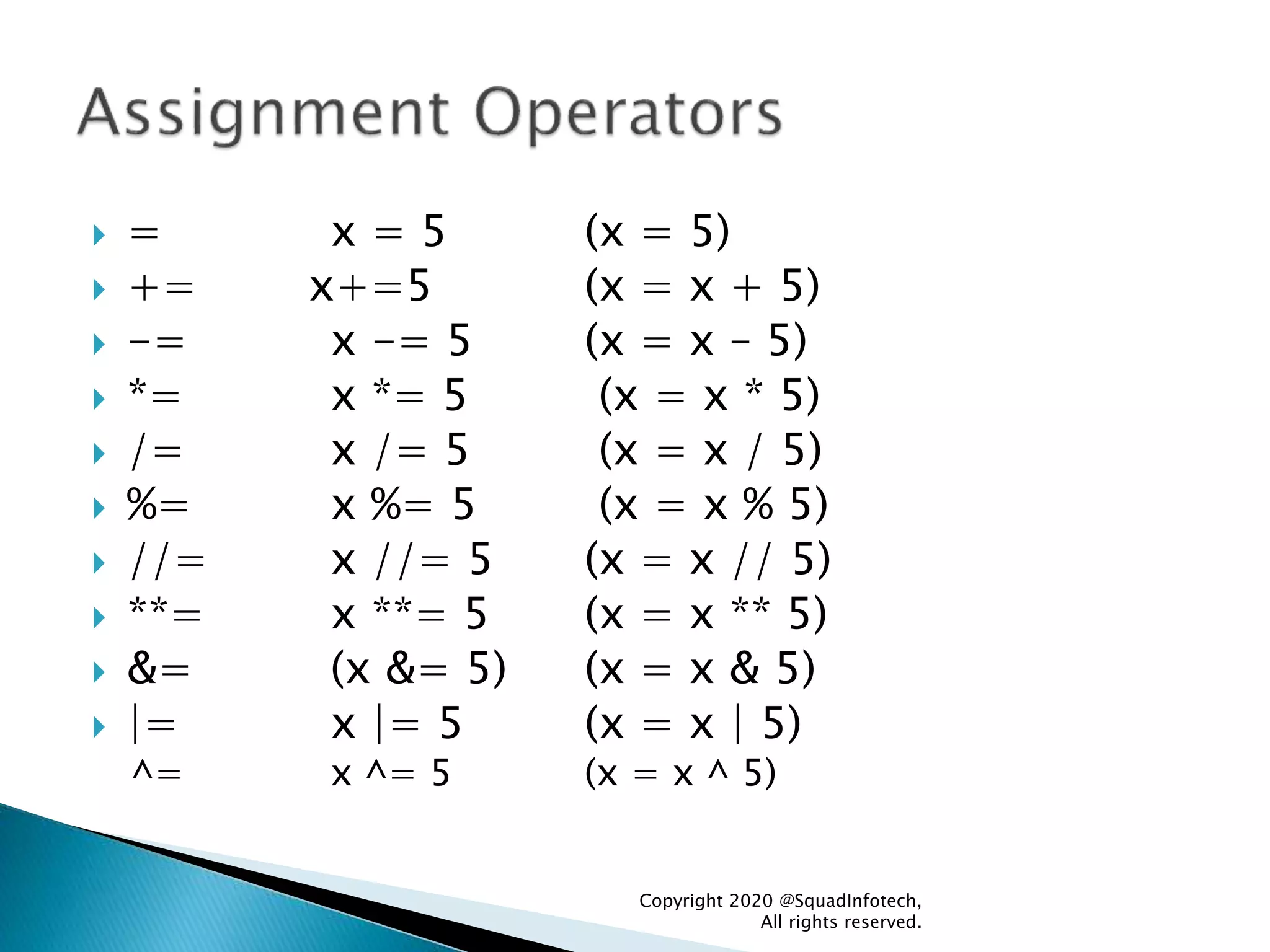
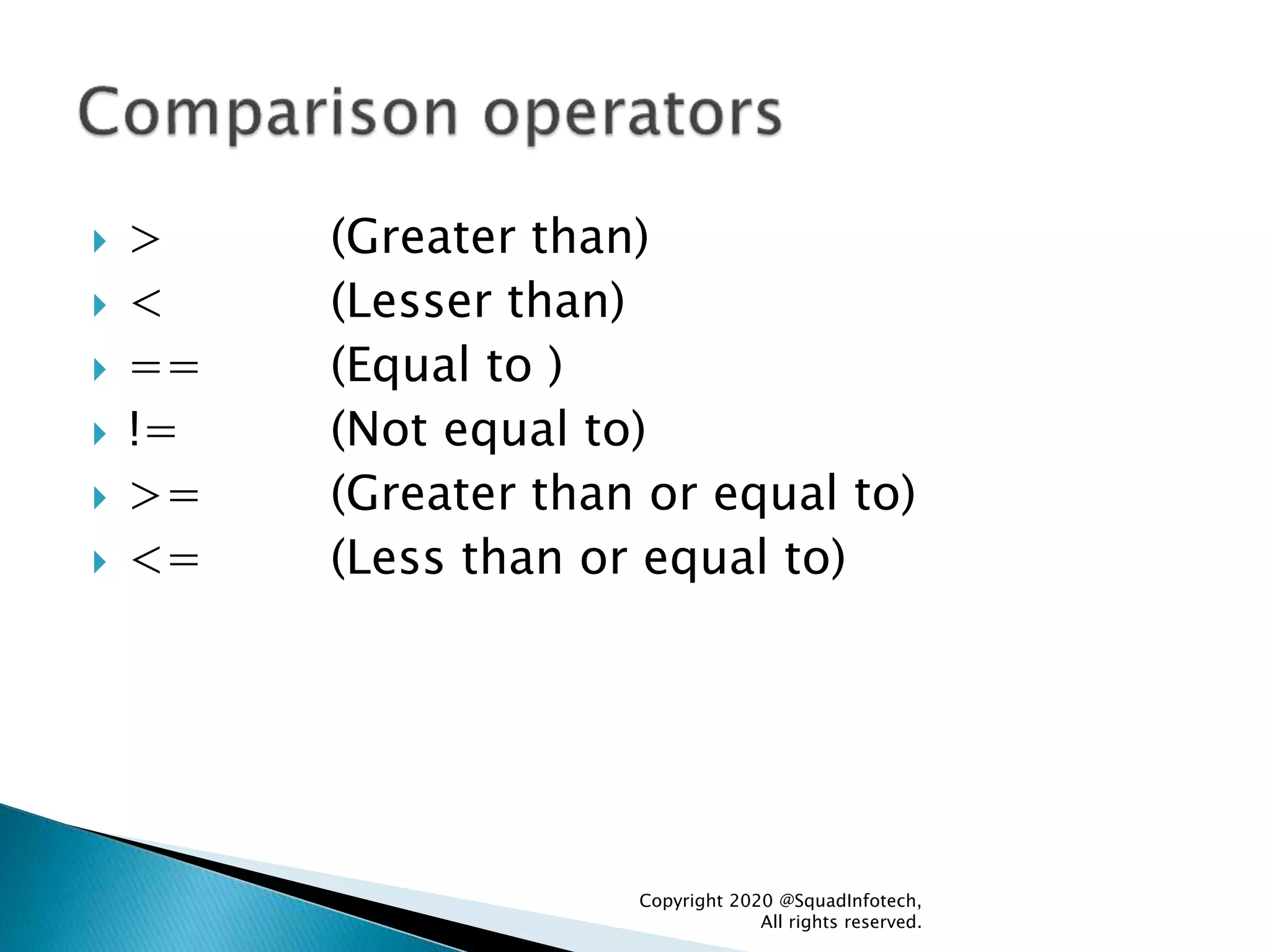





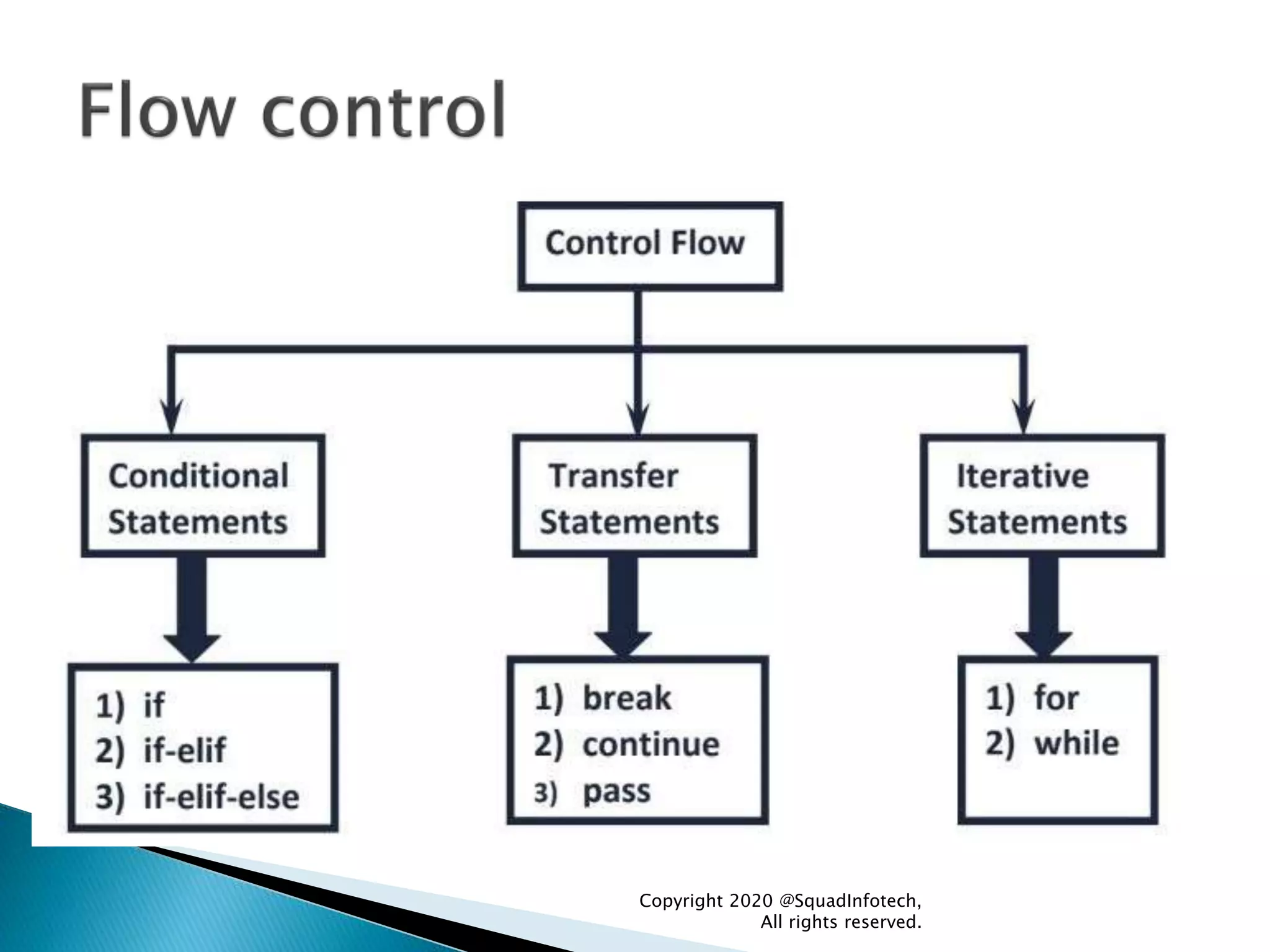
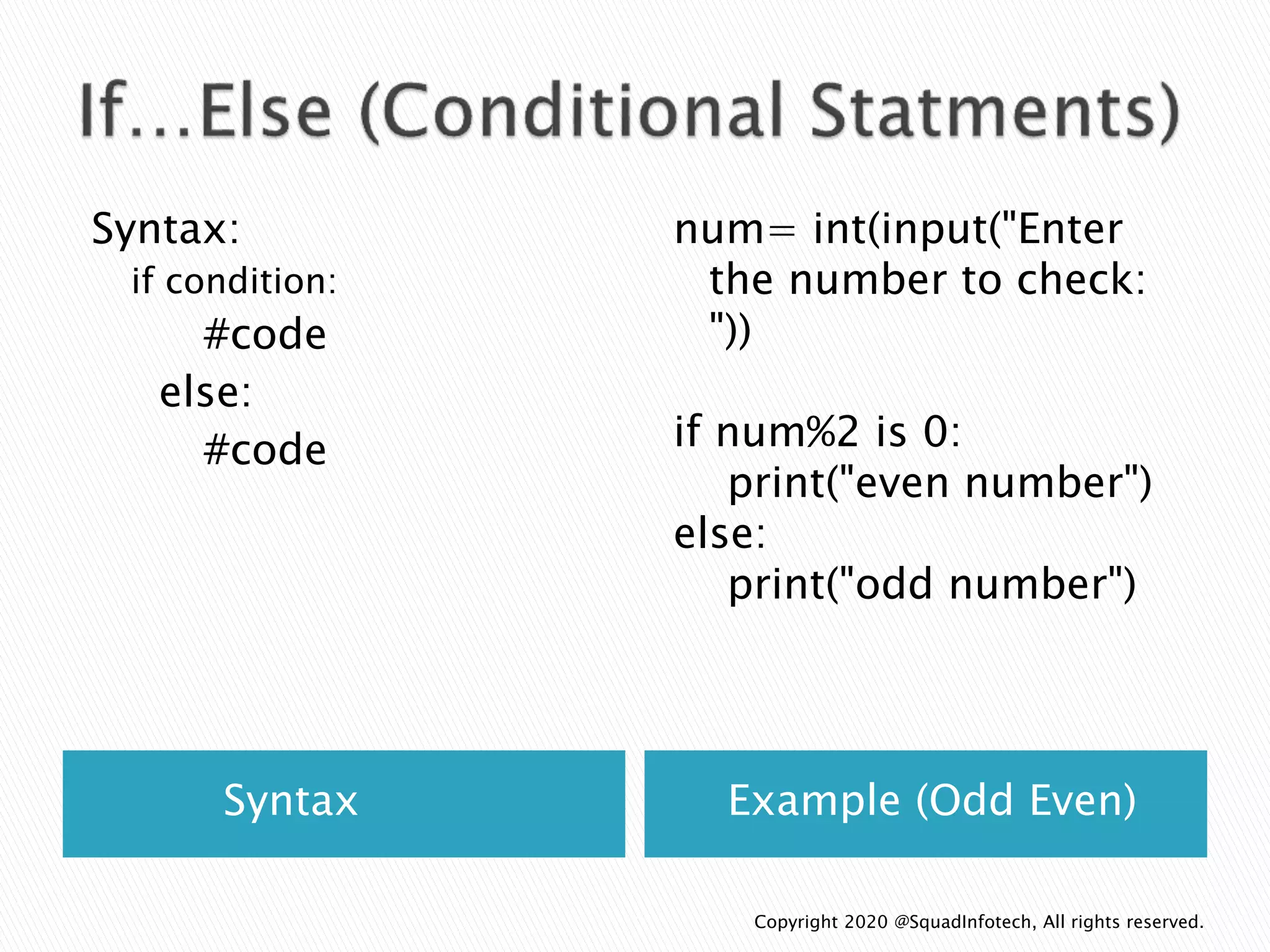
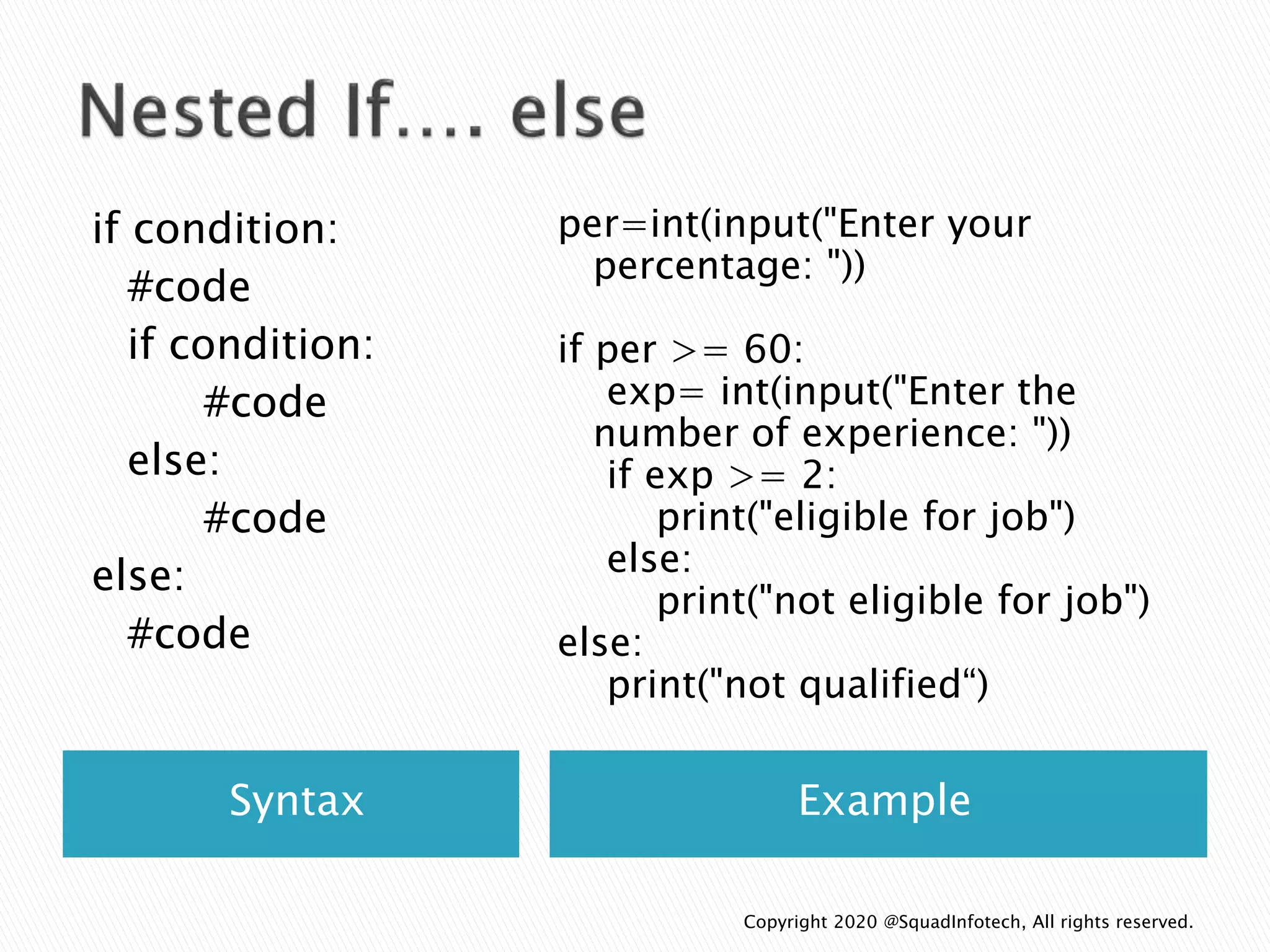
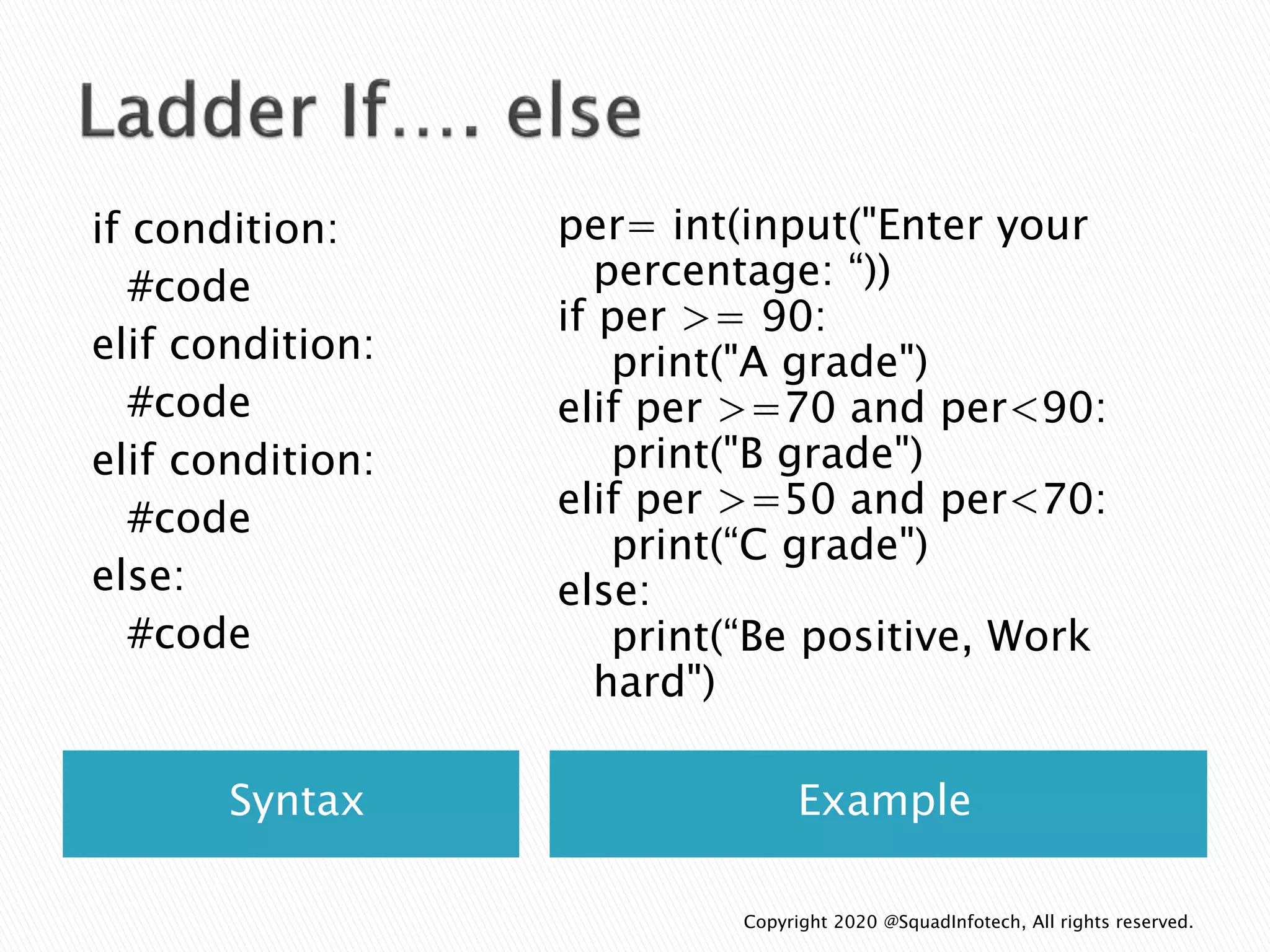
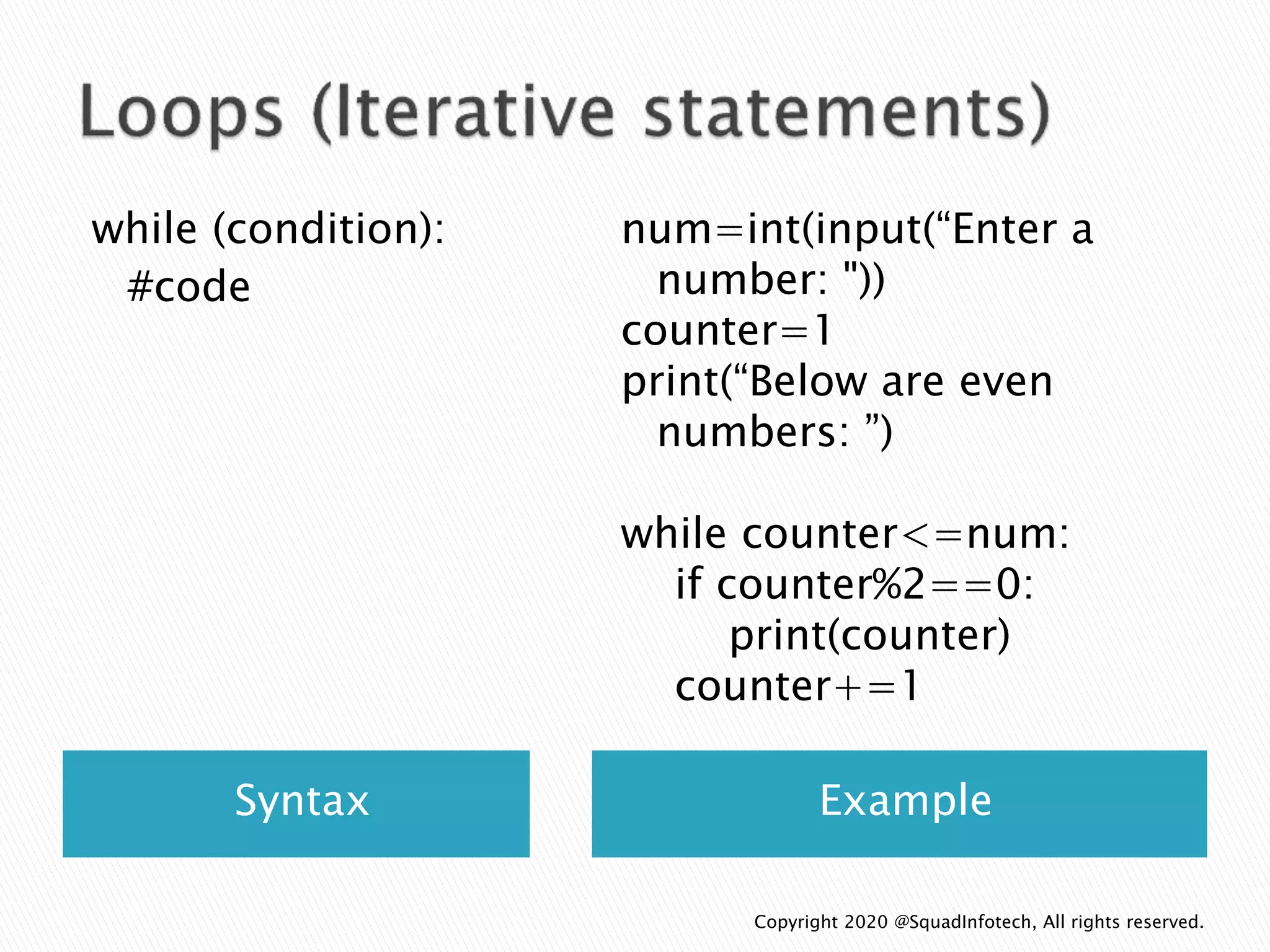
![Syntax Example
for counter in range
(lower limit,
upper limit,
[increment factor]):
#code
for i in range(1,5):
# default increment is1
print(i)
for i in range(5,0,-1):
#decrementing by -1
print(i, end=“ ”)
Copyright 2020 @SquadInfotech, All rights reserved.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonbasics-200828121723/75/Python-basics-28-2048.jpg)