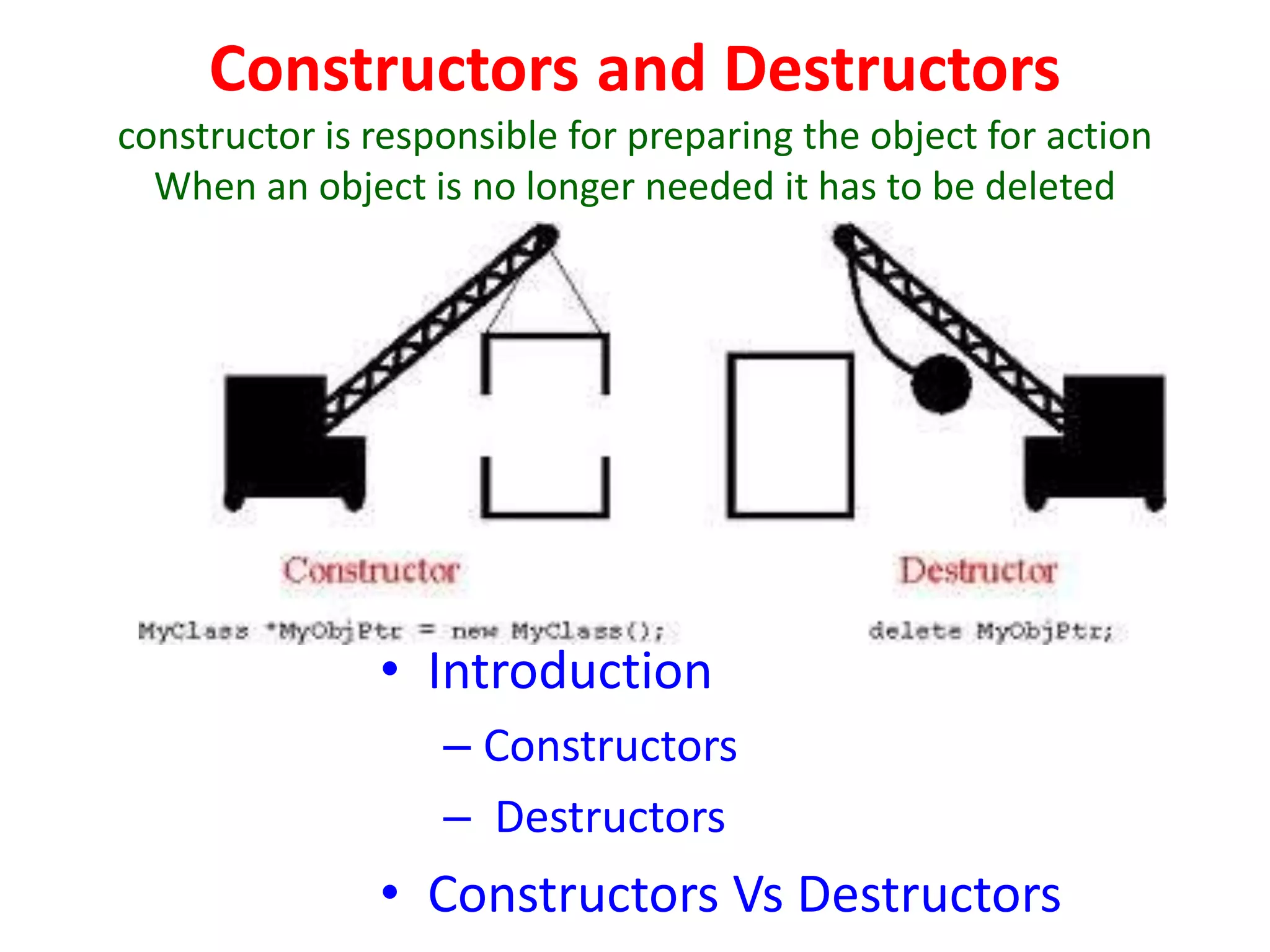
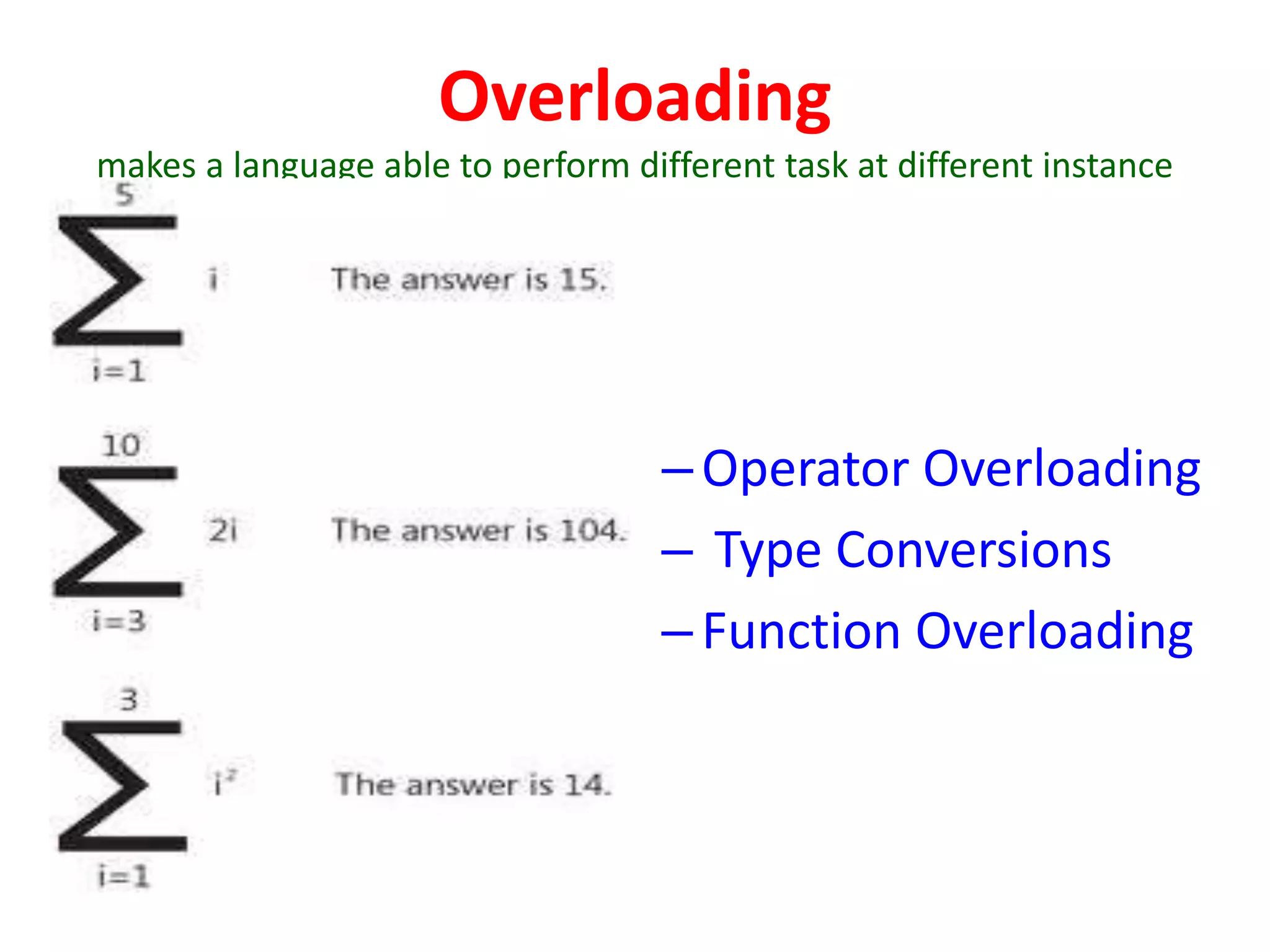
The document provides a syllabus covering 5 units of study in C++ programming over 150 minutes. Unit 1 covers basic C++ concepts like variables, operators, functions and pointers. Unit 2 discusses classes, objects, constructors, inheritance and polymorphism. Unit 3 covers working with files. Unit 4 addresses data structures like stacks, queues, linked lists. Unit 5 presents trees and graphs concepts. The syllabus outlines the key topics in each unit to help students organize the material.