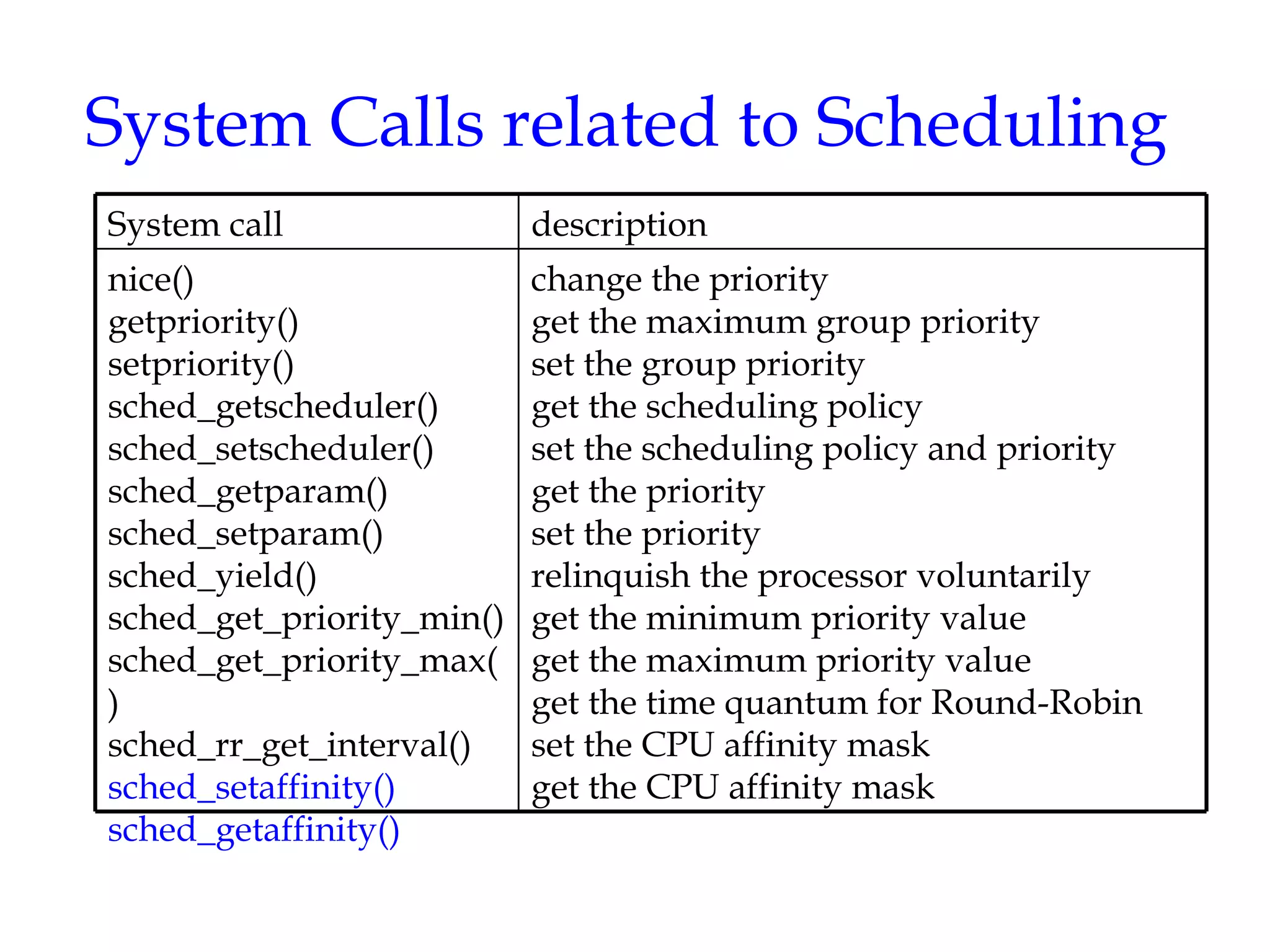
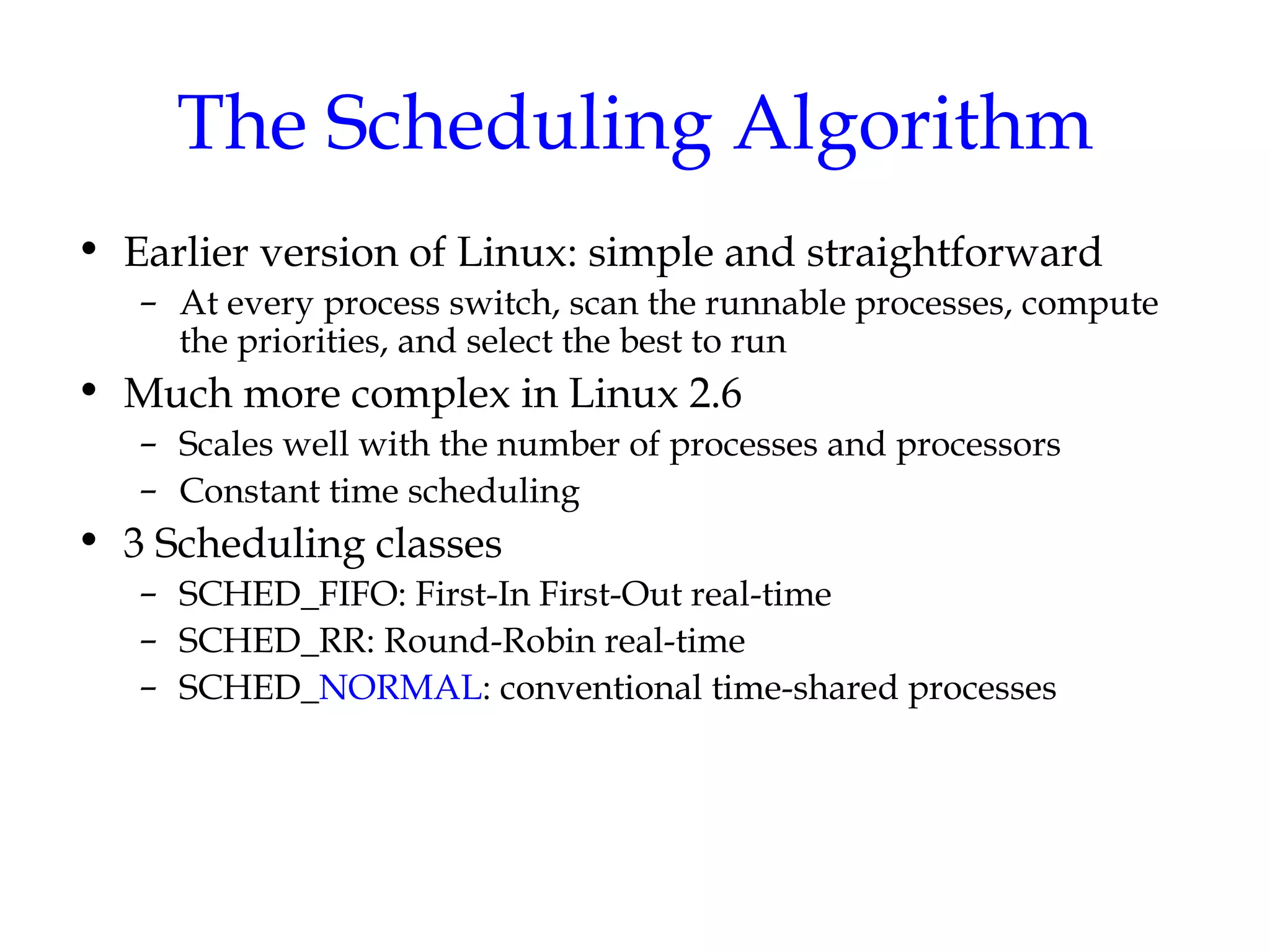
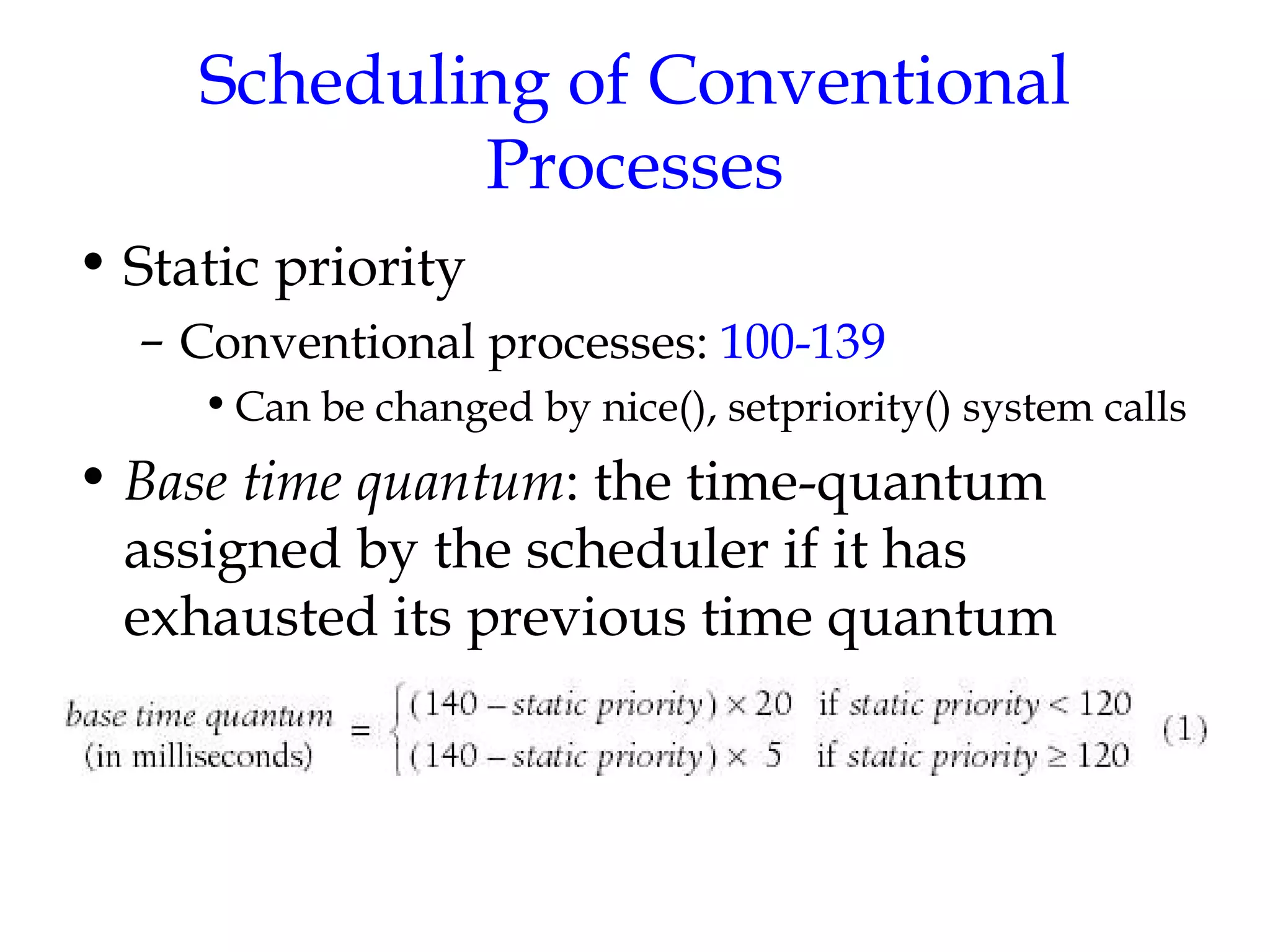
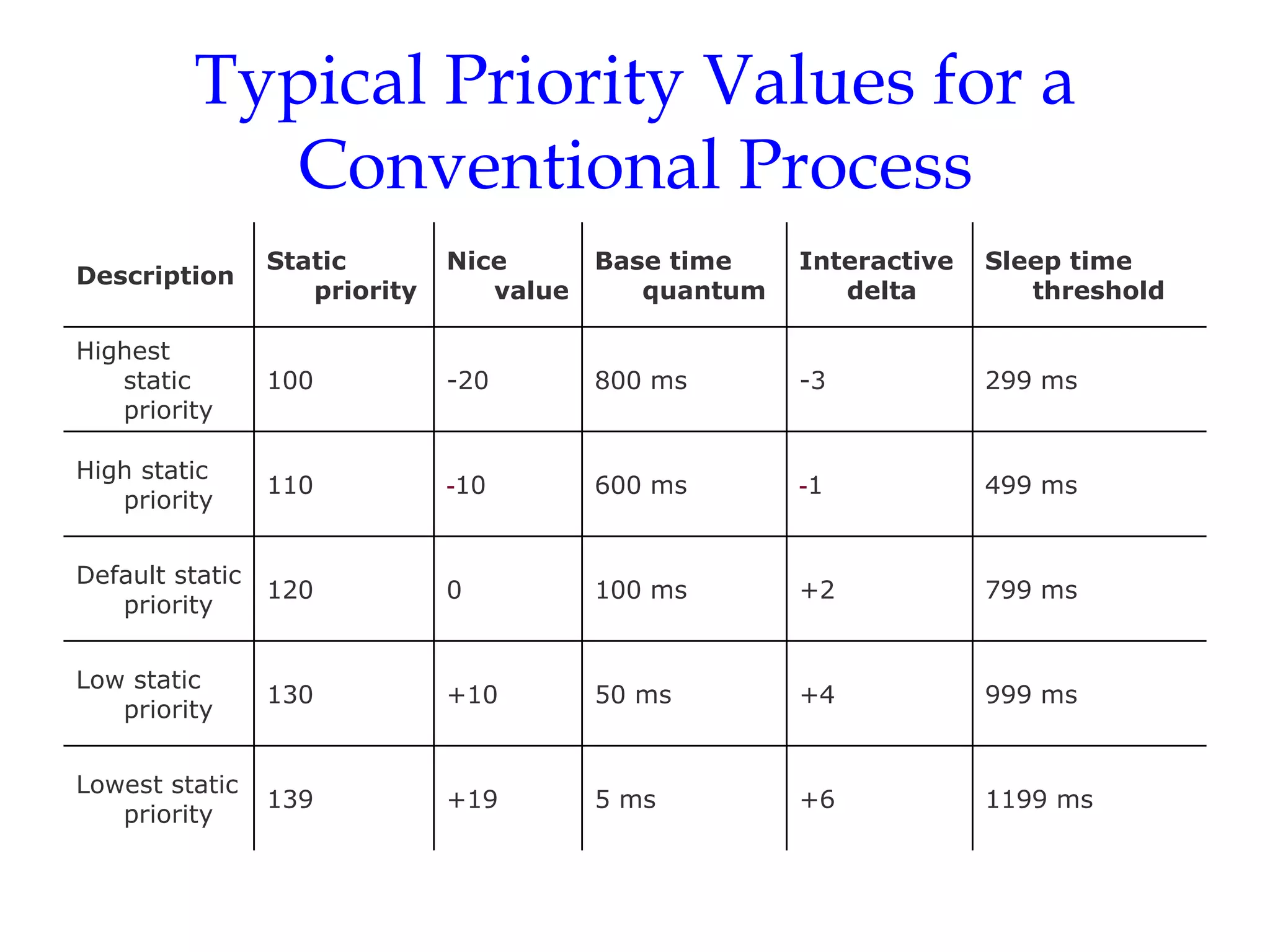
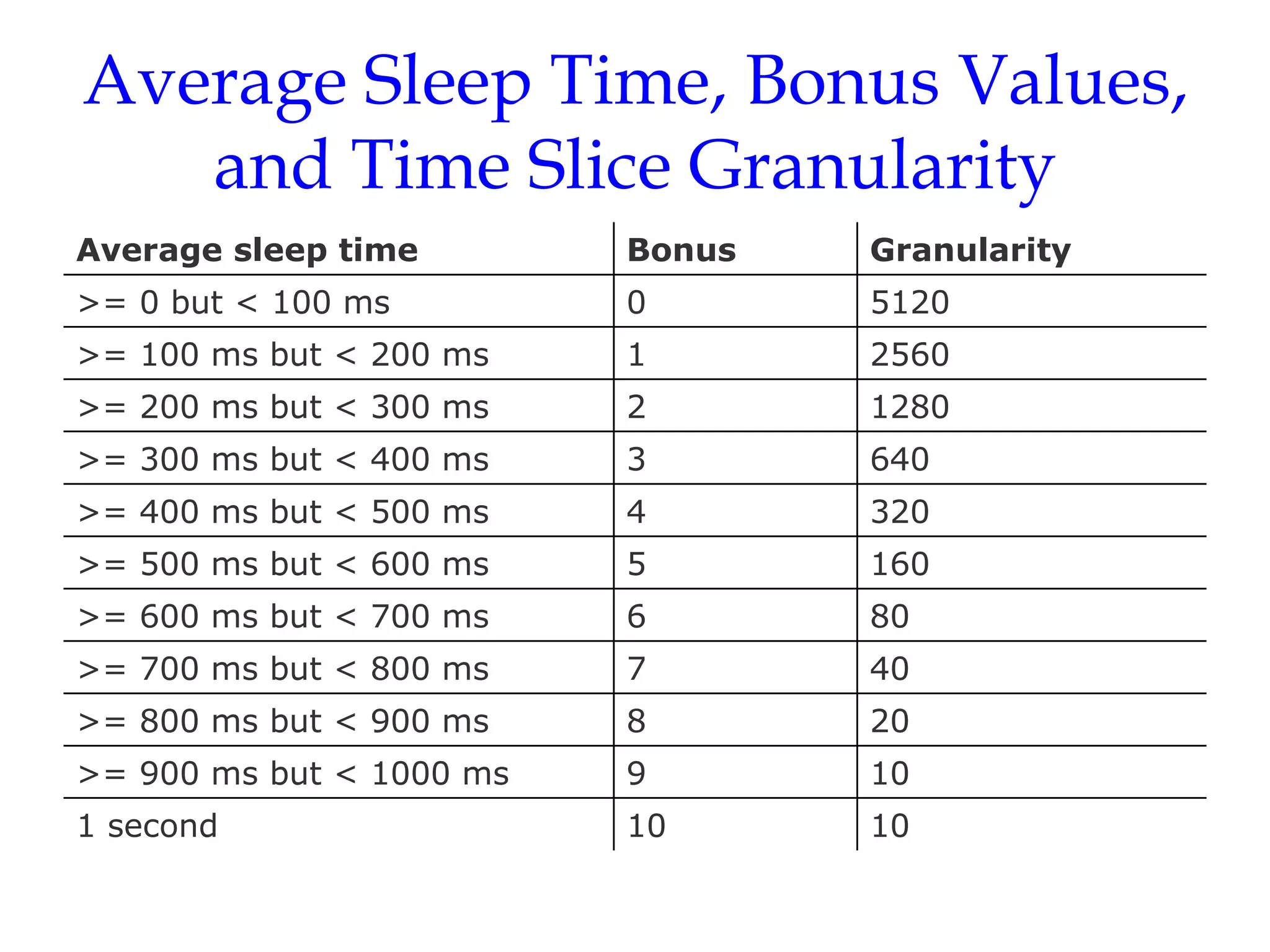
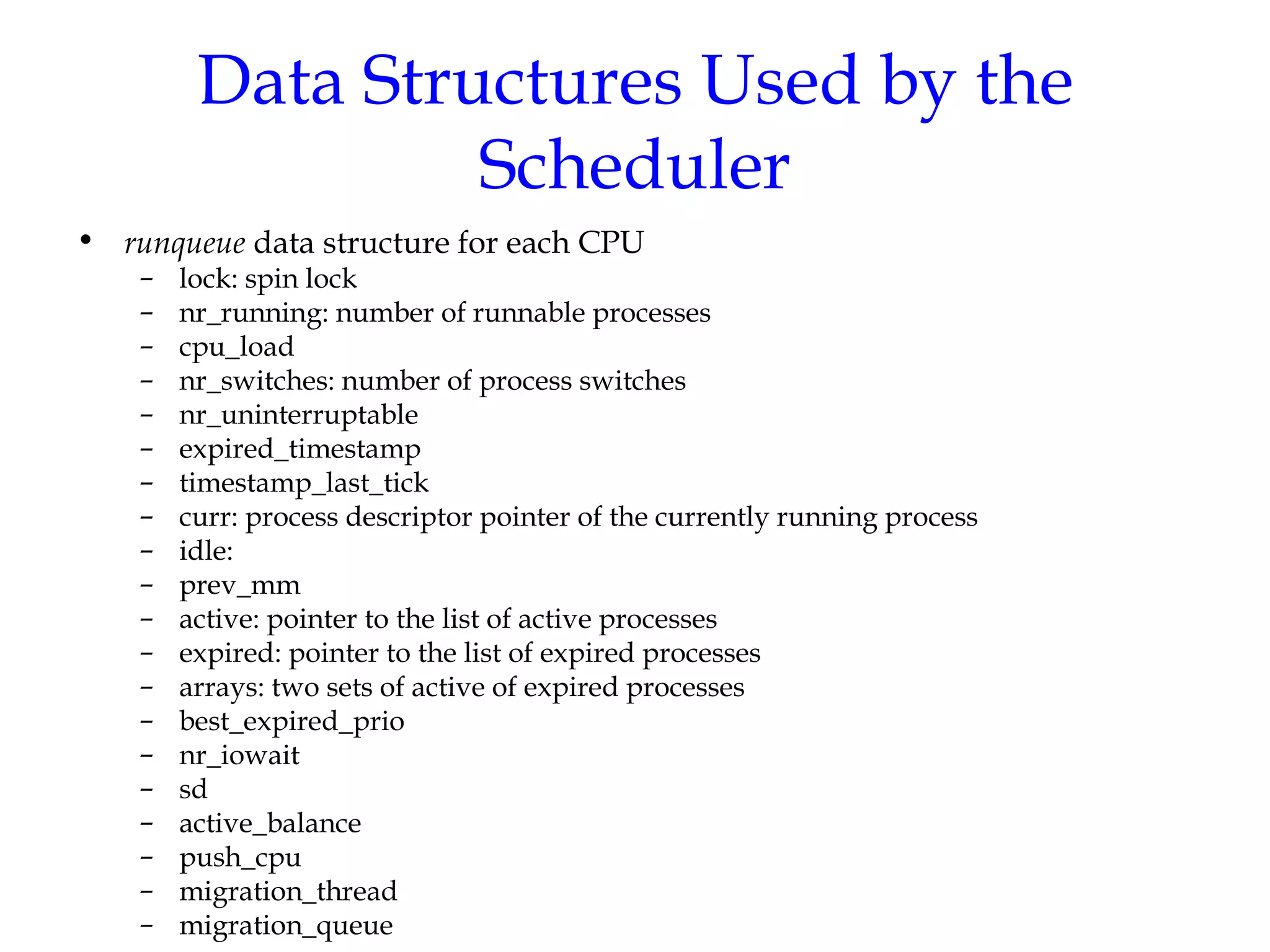
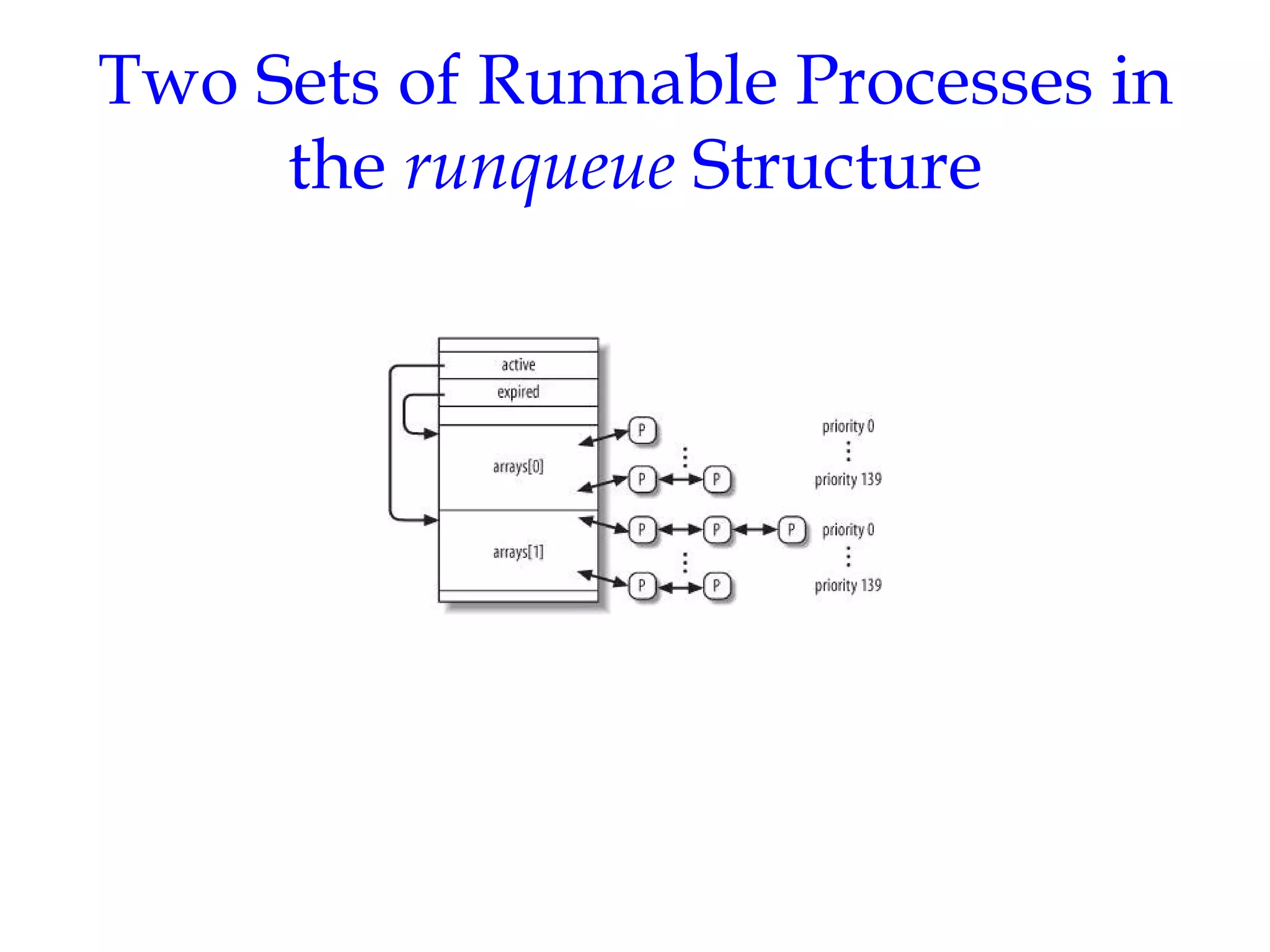
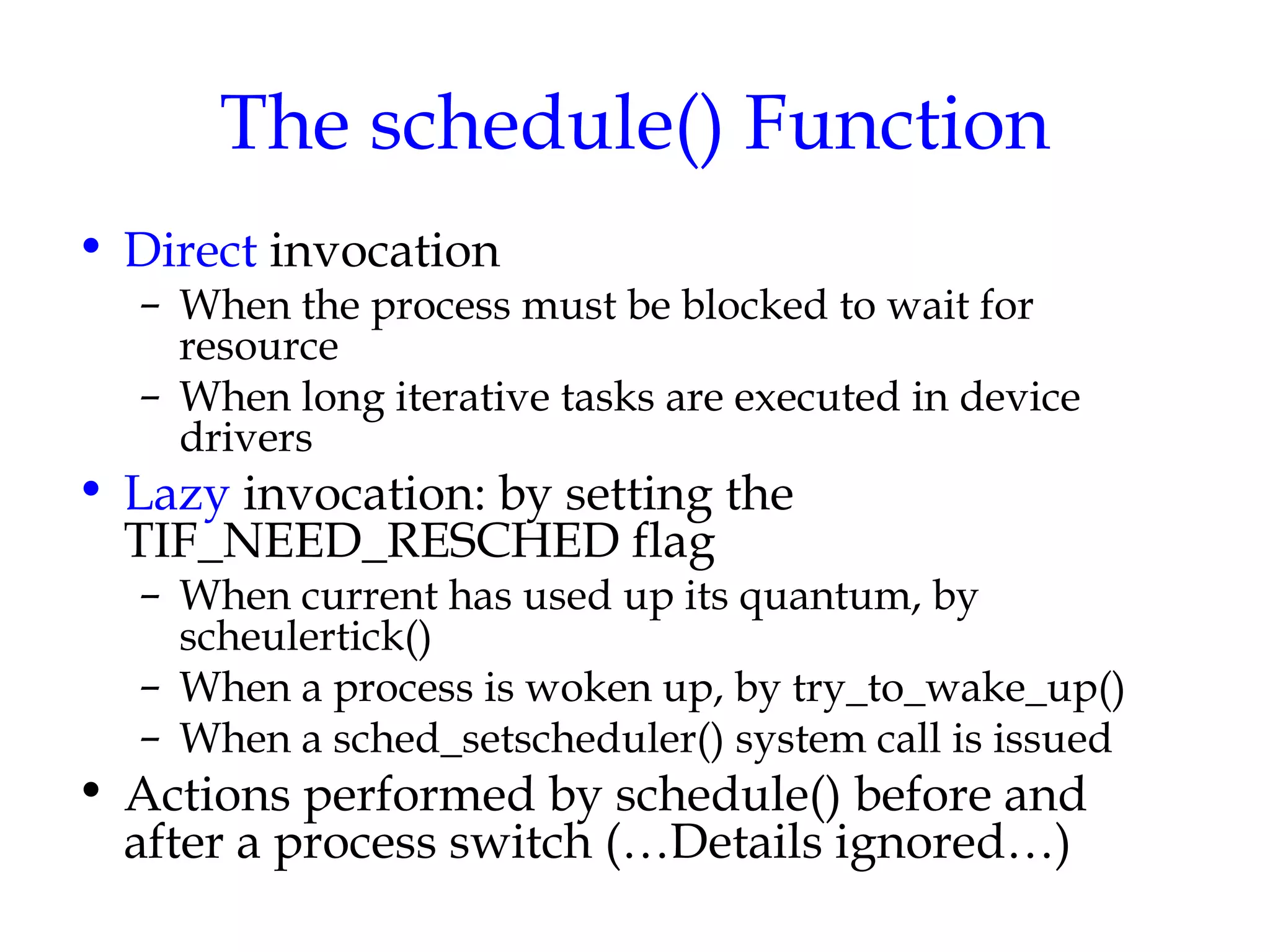
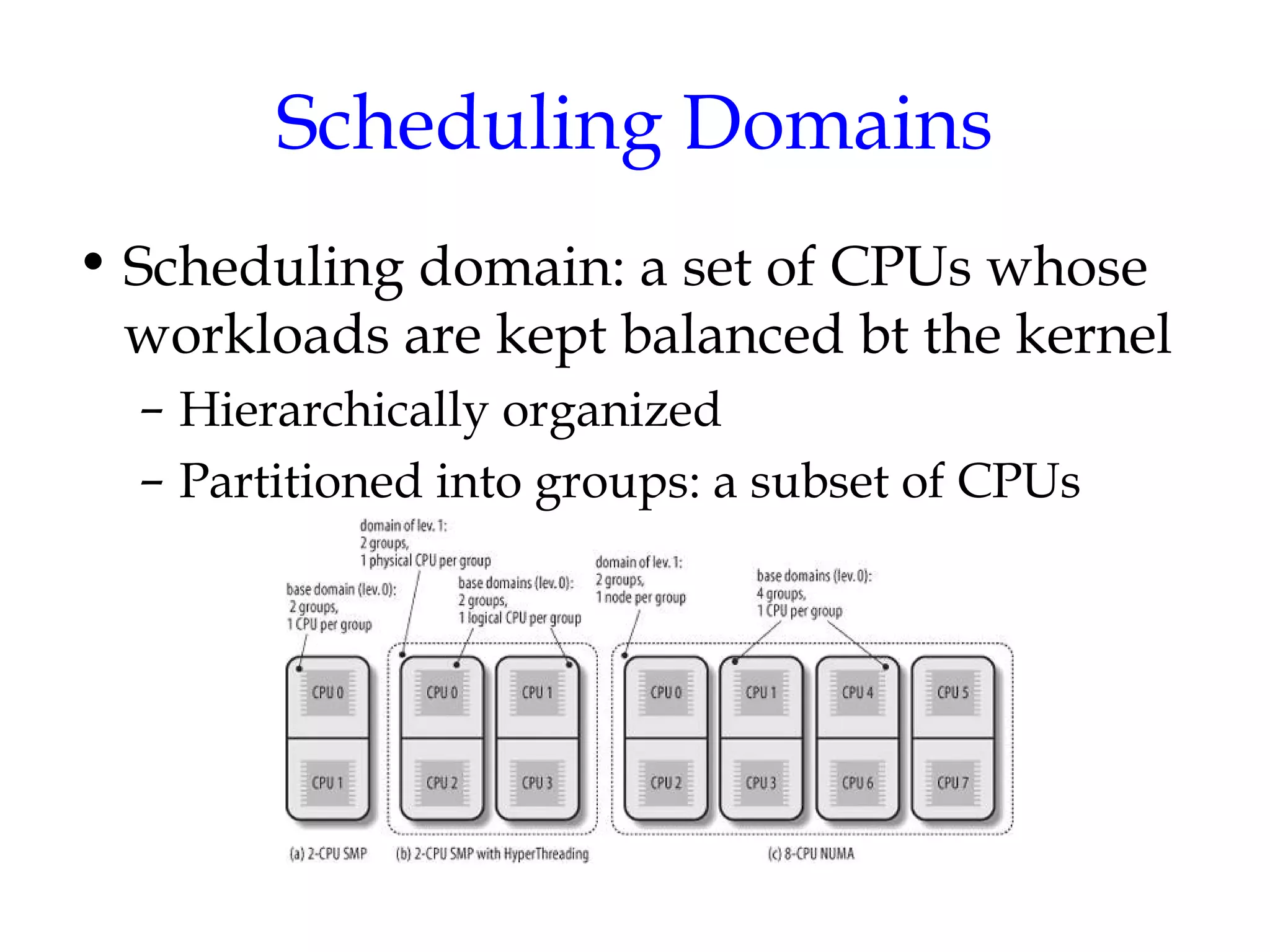
Linux uses a preemptive multilevel feedback queue scheduling algorithm. Processes have both static priorities based on nice values and dynamic priorities based on recent CPU usage. The scheduler selects from two lists of active and expired processes using their dynamic priorities. It also performs load balancing across CPU runqueues to improve performance on multiprocessor systems. System calls like setpriority(), sched_setscheduler(), and sched_yield() allow modifying process priorities and scheduling policies.