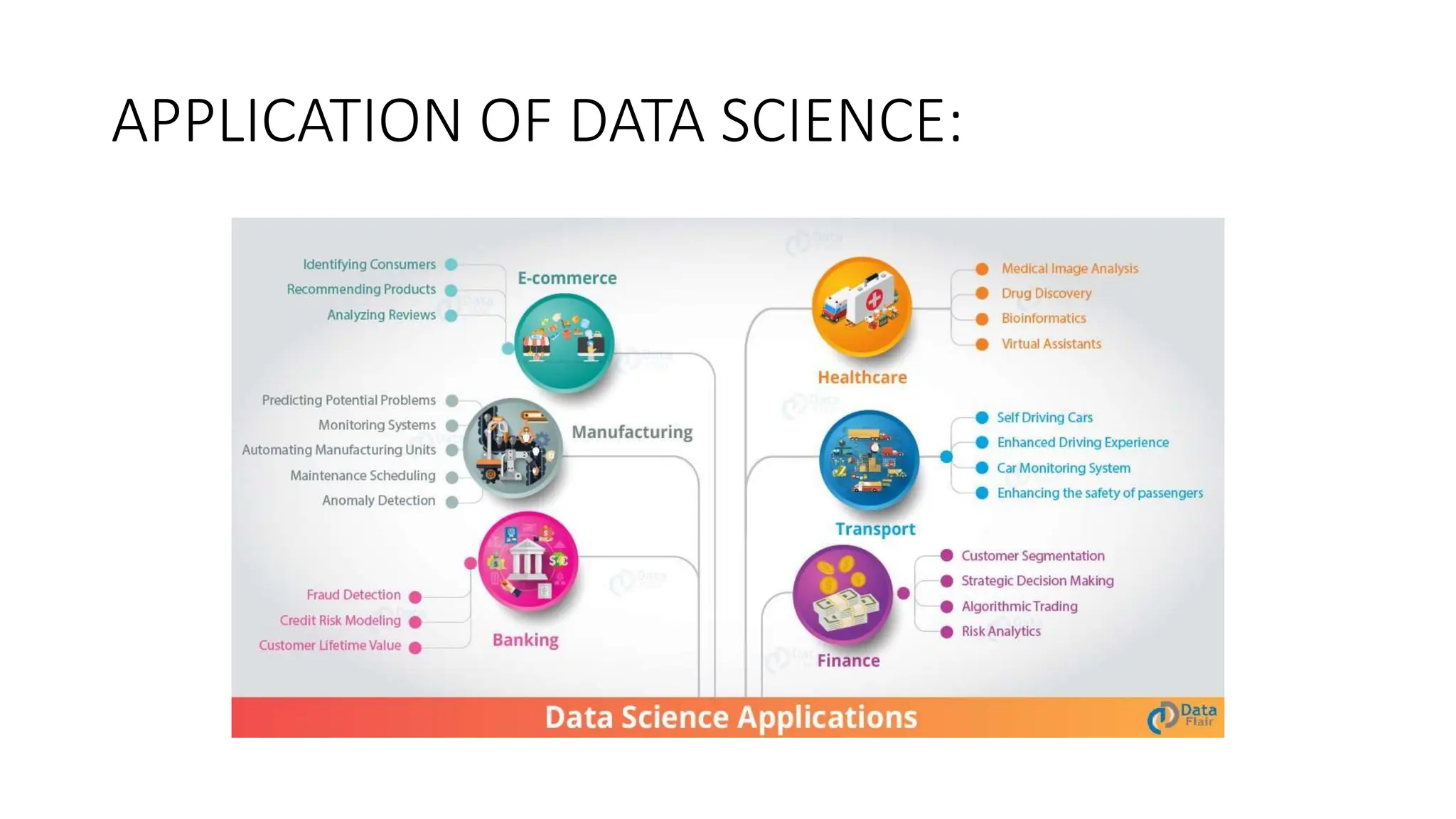
The document discusses a seminar on data science with Python. It defines data science as using insights from data to help business leaders make better decisions. Python is described as a popular and free tool for data analysis, visualization, and machine learning tasks in data science. The seminar covers Python basics like data types, looping, and libraries like NumPy for mathematics and Pandas for working with table-like data. Real-world applications of data science are also mentioned.








![LIST
• Collection comma-separated values (items) between square brackets
• Contain same or different types
• Mutable behavior Values can add, remove, update/replace the value, slice and dice the members
Example:
list1 = ['physics', 'chemistry', 1997, 2000];
list2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/khushbujain-240104033029-ddef5819/75/presentation-on-data-science-with-python-9-2048.jpg)
![TUPLE
• A tuple is very similar to List A collection of items inside the parenthesis()
• Tuple is Immutable ( The value cannot be changed)
• Can slice and dice add elements and Delete the entire tuple
• Example:
• tup2 = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5 );
• tup3 = ("a", "b", "c", "d“);
• Accessing Values: print
"tup2[1:5]: “ Output:
• tup2[1:5]: [2, 3, 4, 5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/khushbujain-240104033029-ddef5819/75/presentation-on-data-science-with-python-10-2048.jpg)



![PYTHON LIBRARY : PANDAS
• It adds data structures and tools designed to work with table-like data (similar to table in SQL Server environment)
• It provides tools for data manipulation: selecting, reshaping, merging, sorting, slicing, aggregation etc.
• It also handles missing data
• EXAMPLE:
import numpy as np #importing numpy
import pandas as pd #importing pandas
arr=np.array([1,3,5,7,9]) #create arr array
s2=pd.Series(arr) #create pandas series s2
print(s2) #print s2
print(type(s2)) #print type of s2
Output:
0 1
1 3
2 5
3 7
4 9
dtype: int64
<class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/khushbujain-240104033029-ddef5819/75/presentation-on-data-science-with-python-14-2048.jpg)