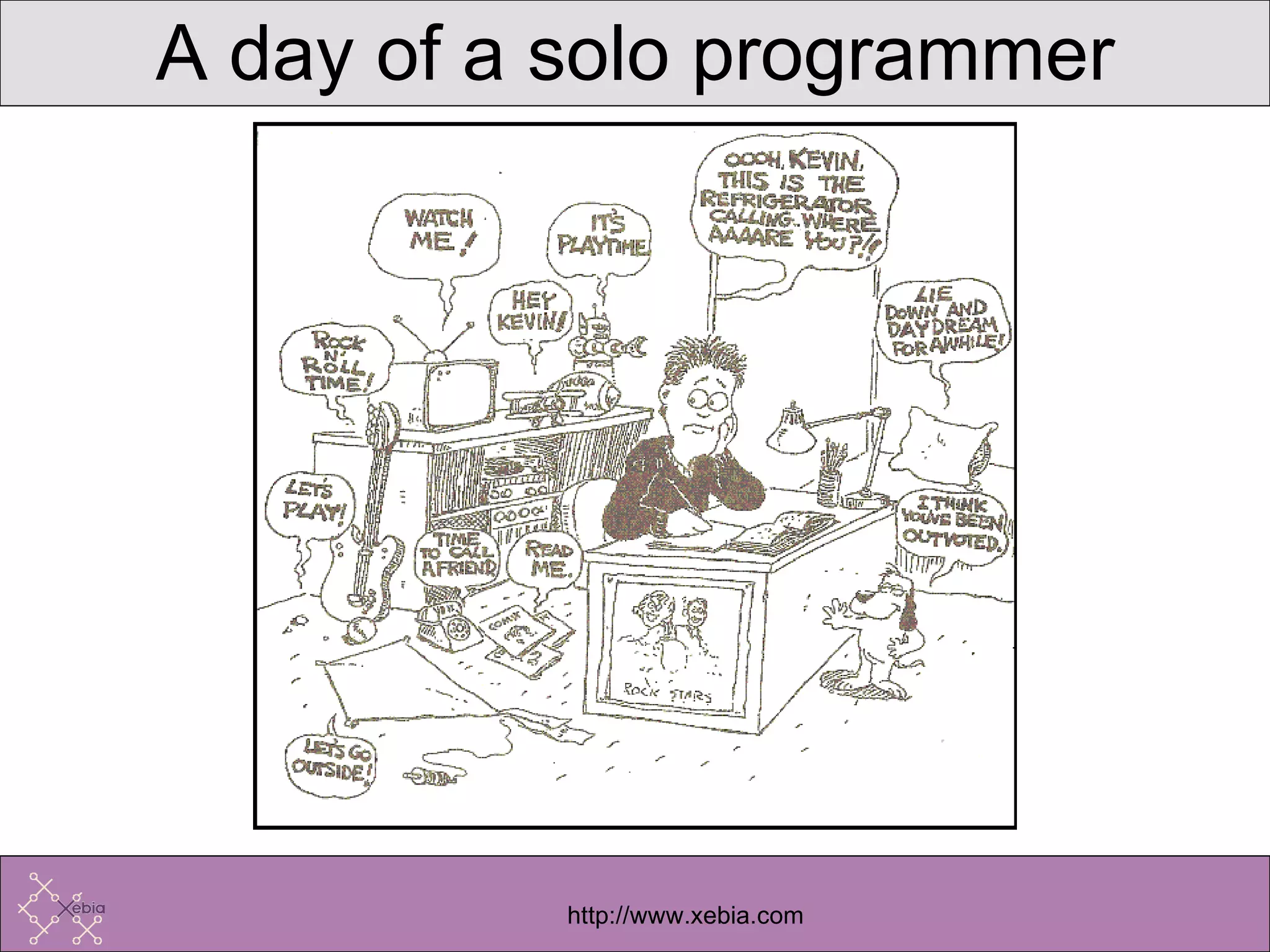
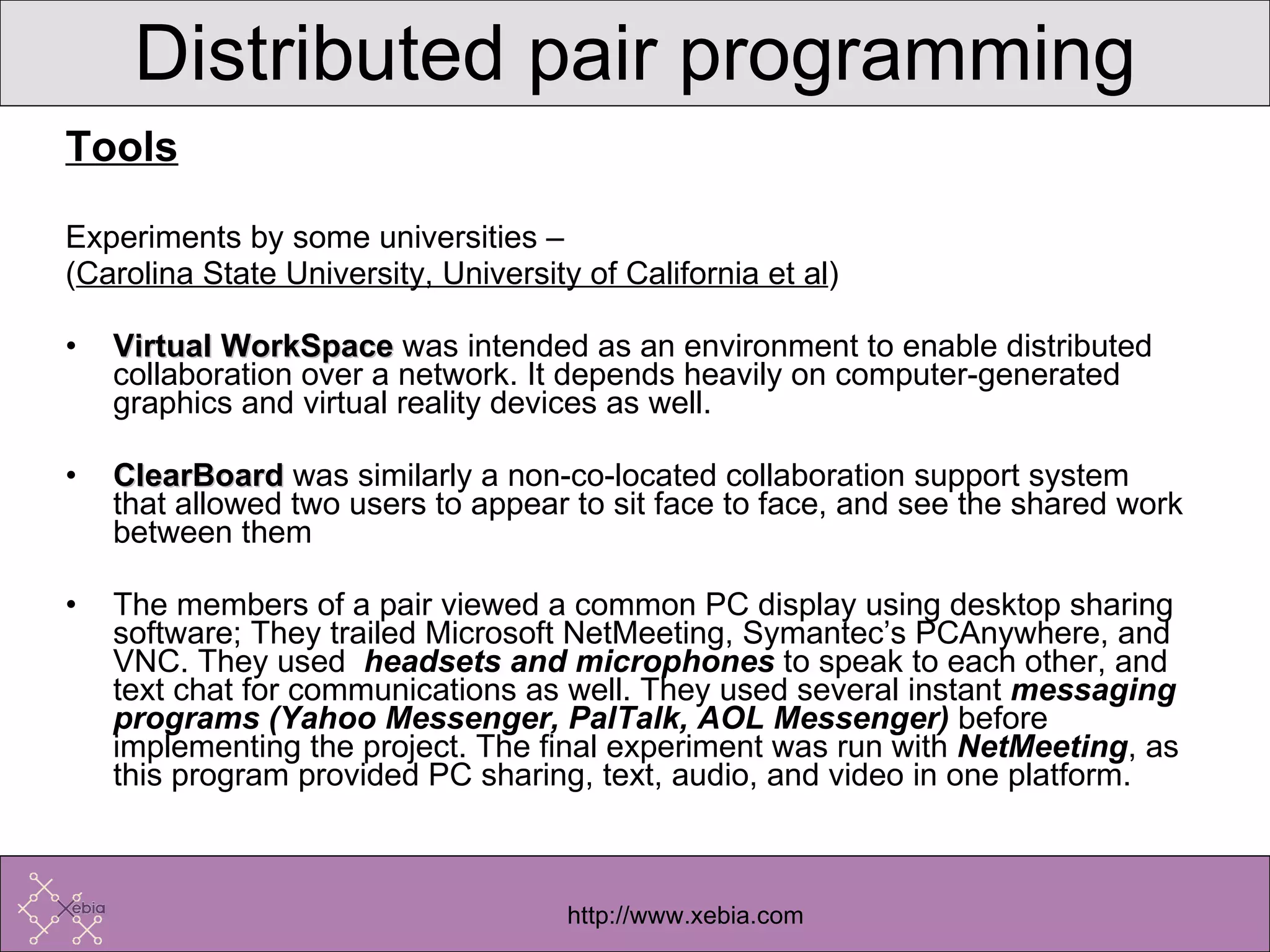
Collaborative programming involves two programmers working side-by-side on design, coding, and testing of software. It transforms solitary work into a cooperative effort. Pair programming minimizes distractions, catches errors earlier, and promotes knowledge sharing, leading to increased productivity compared to individual work. While cultural and psychological challenges exist, distributed pair programming tools can enable effective collaboration even when programmers are in different locations.