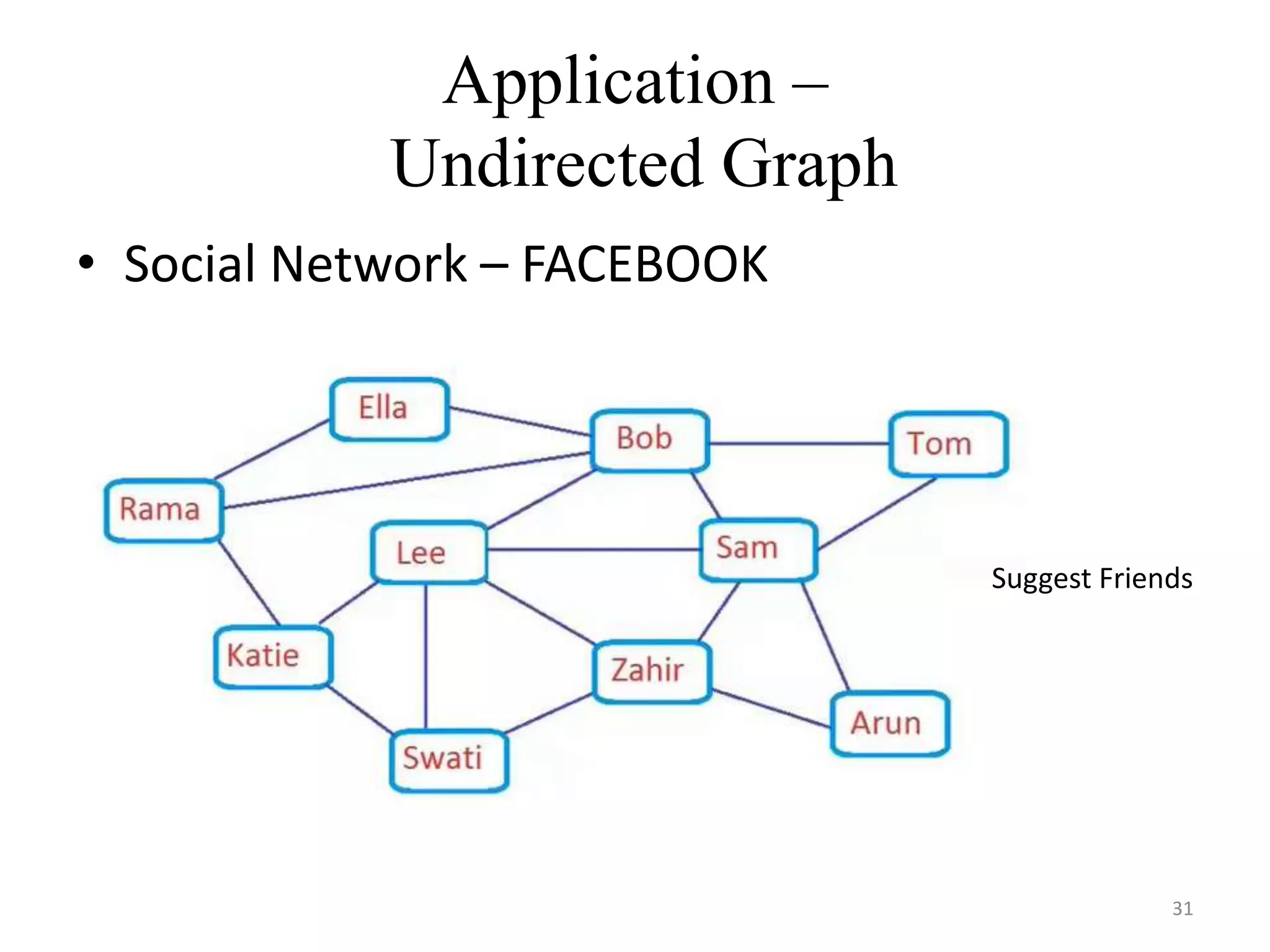
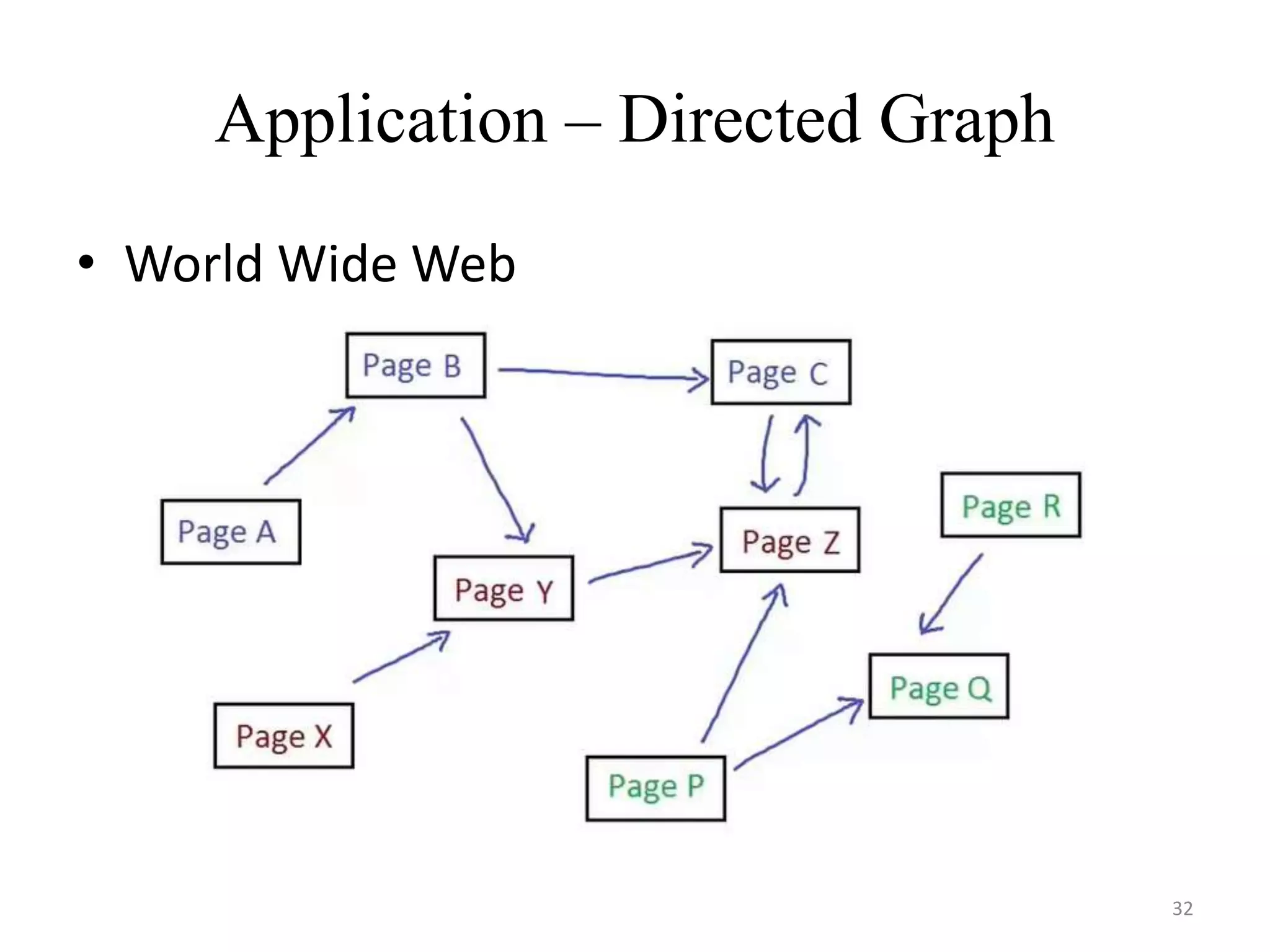
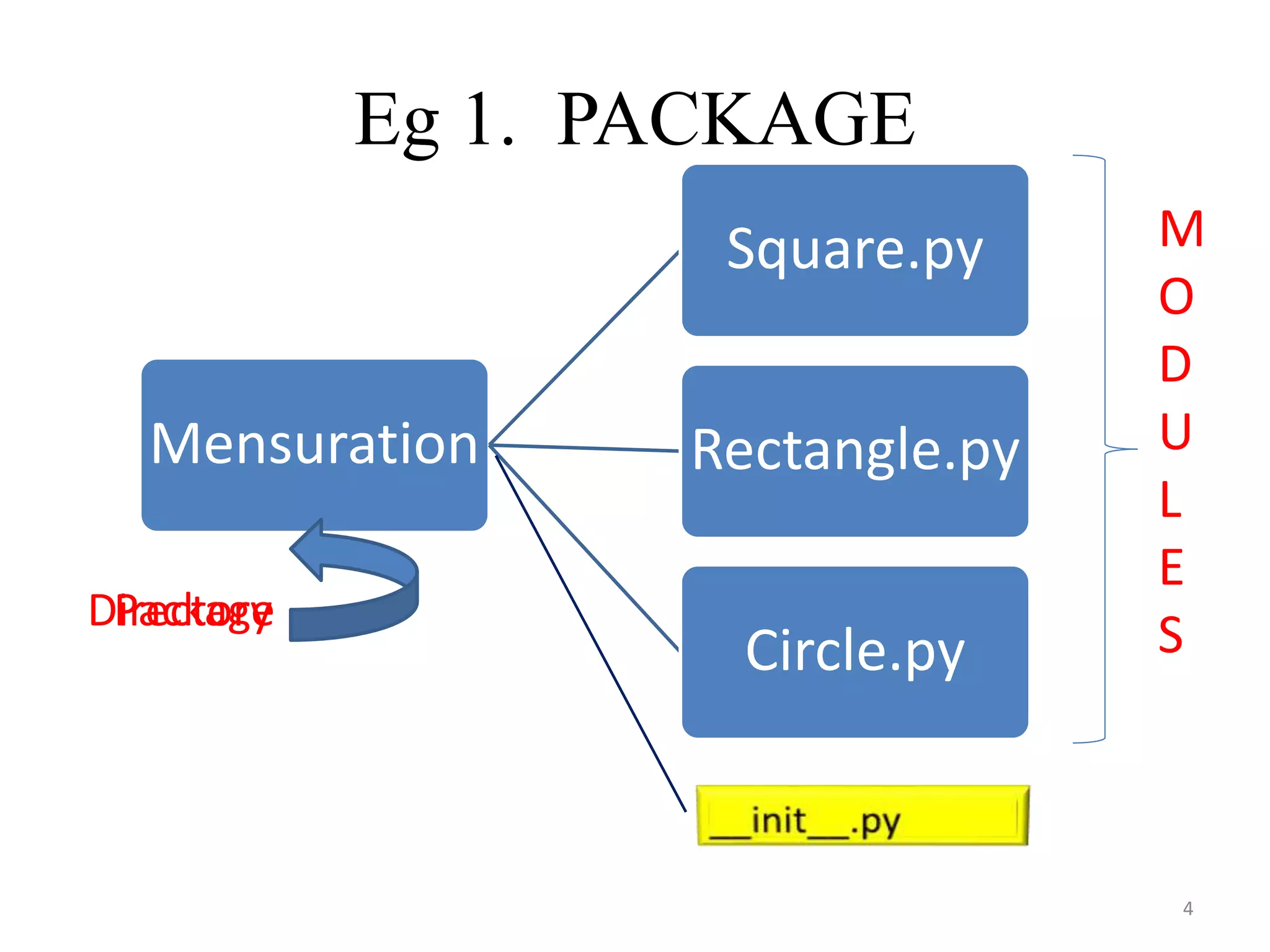
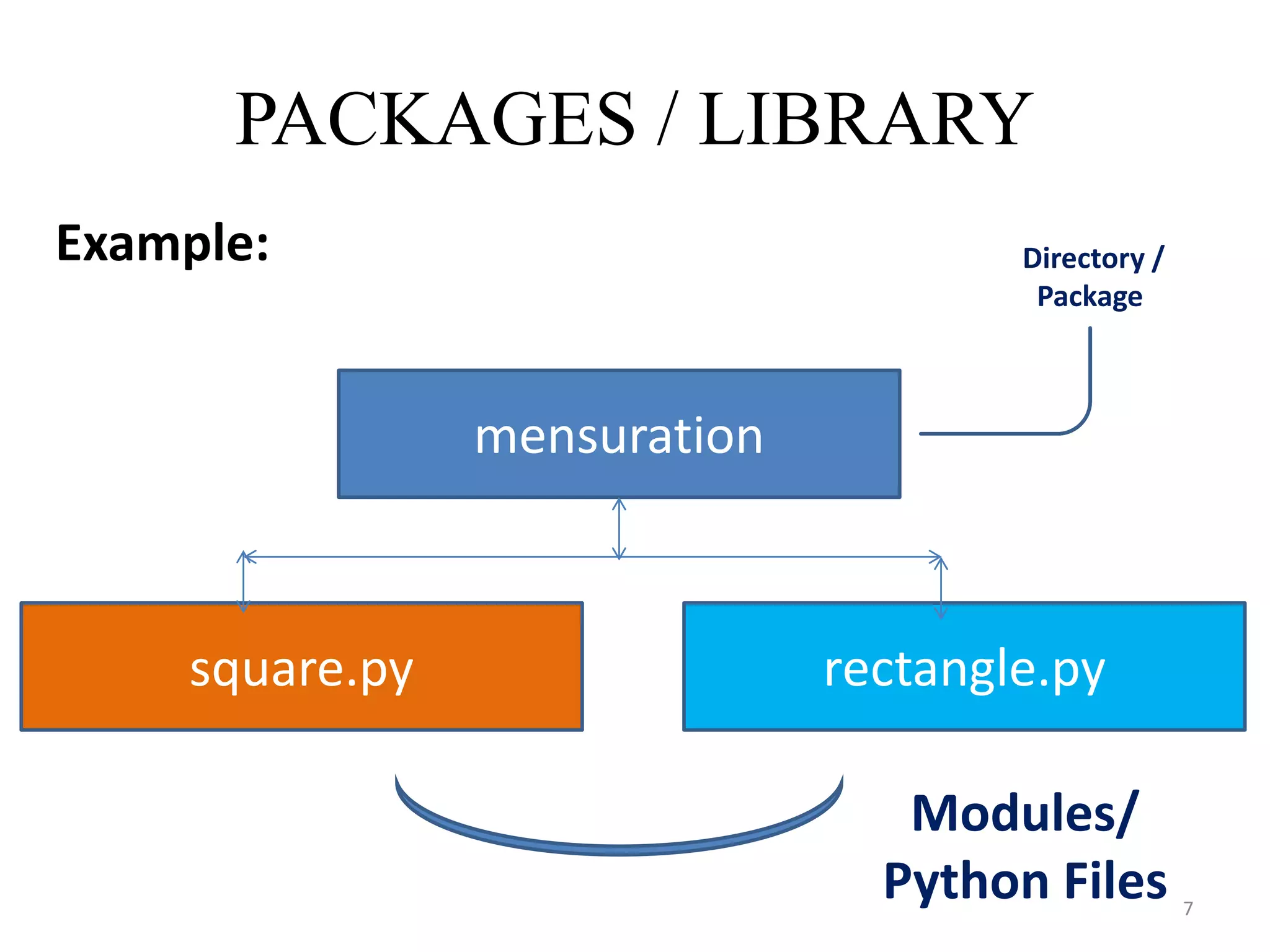
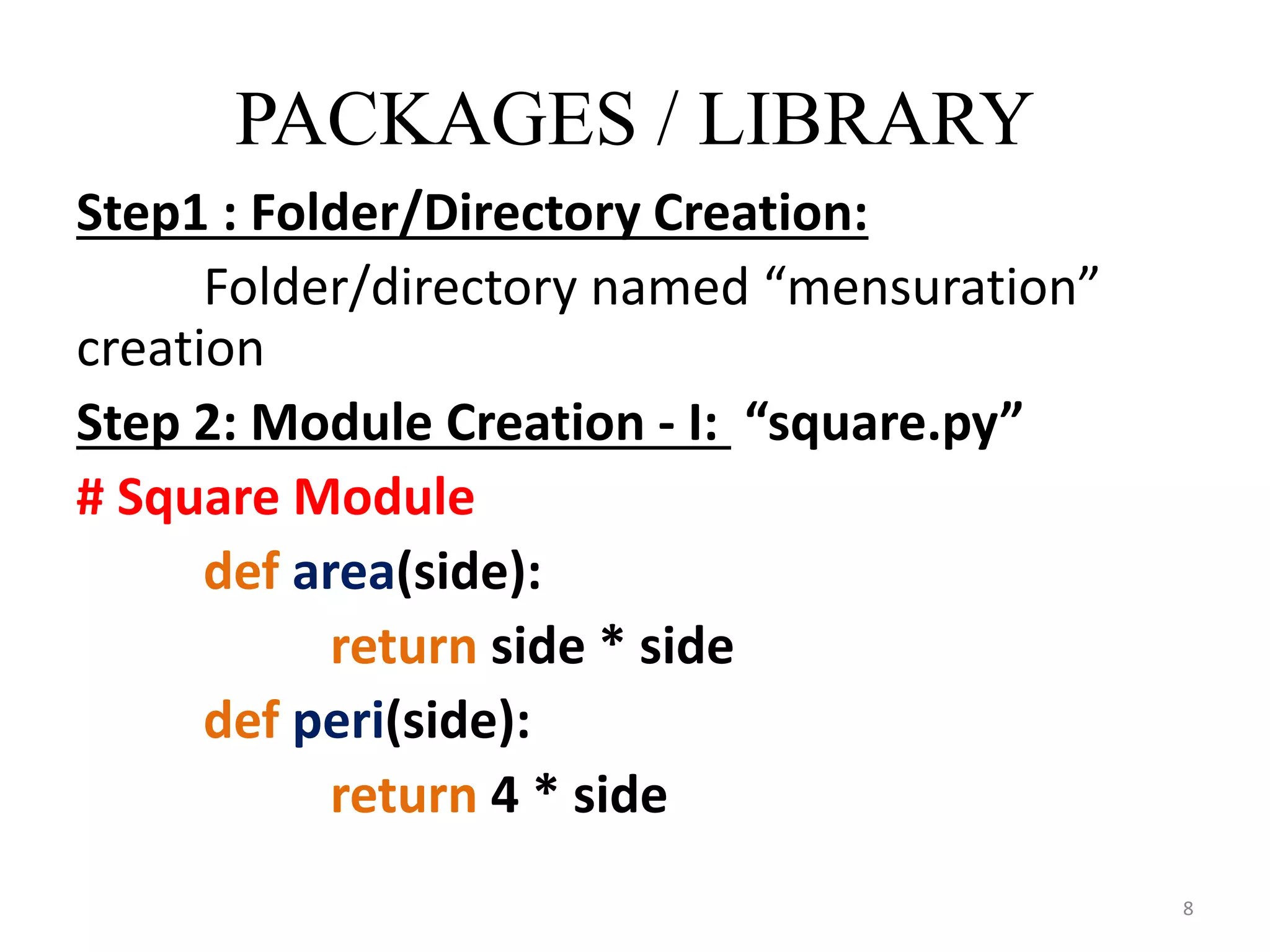
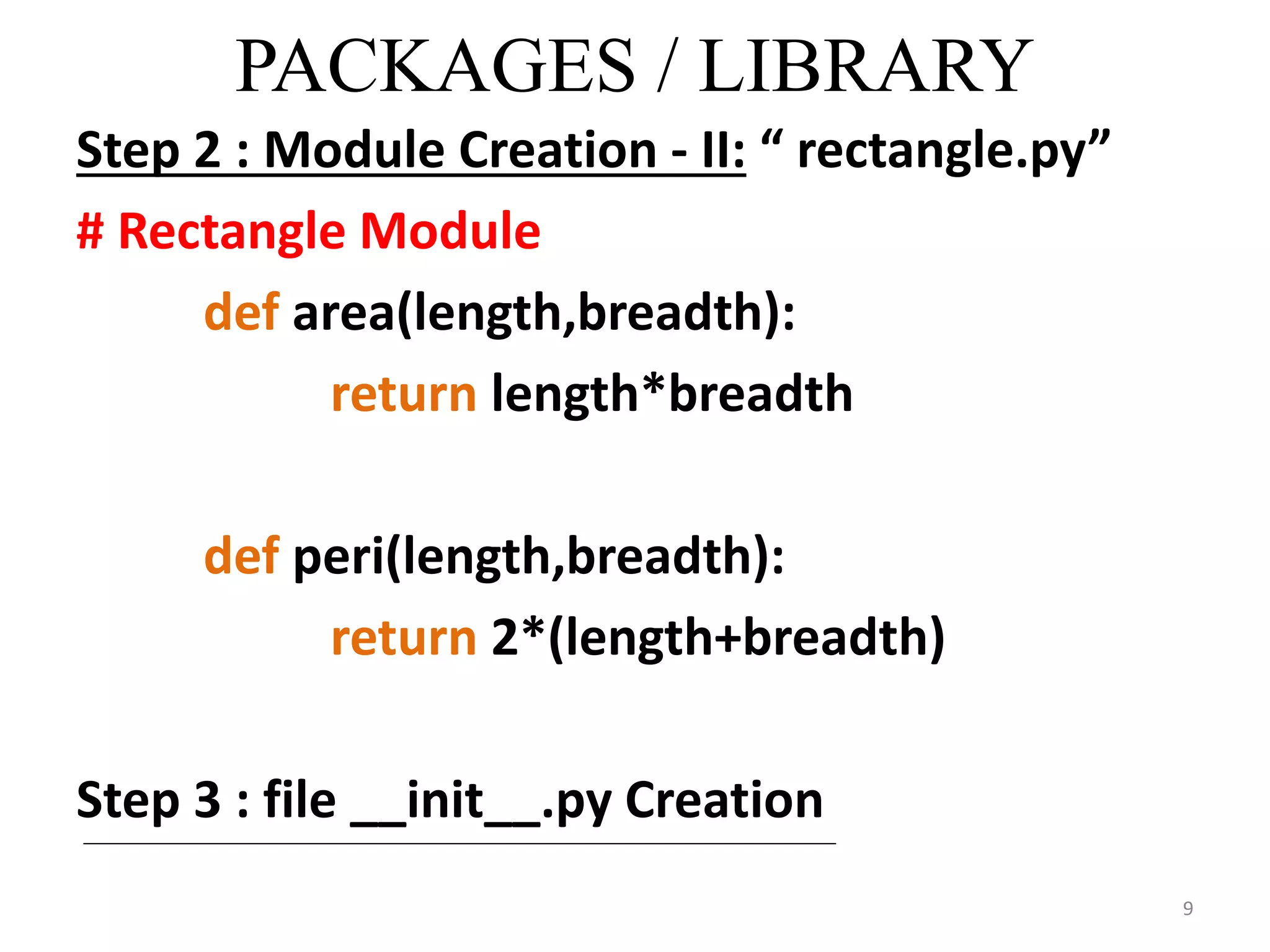
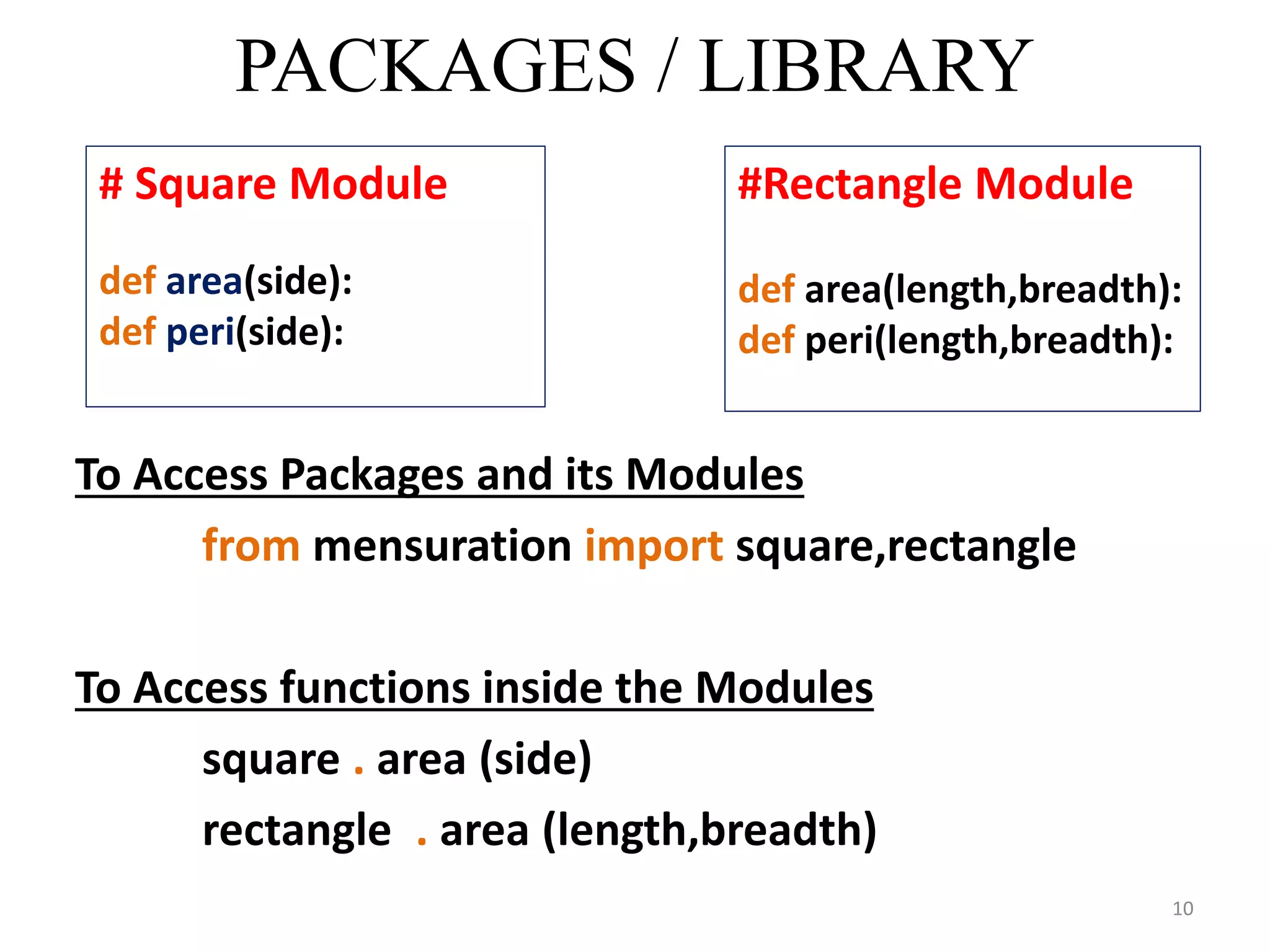
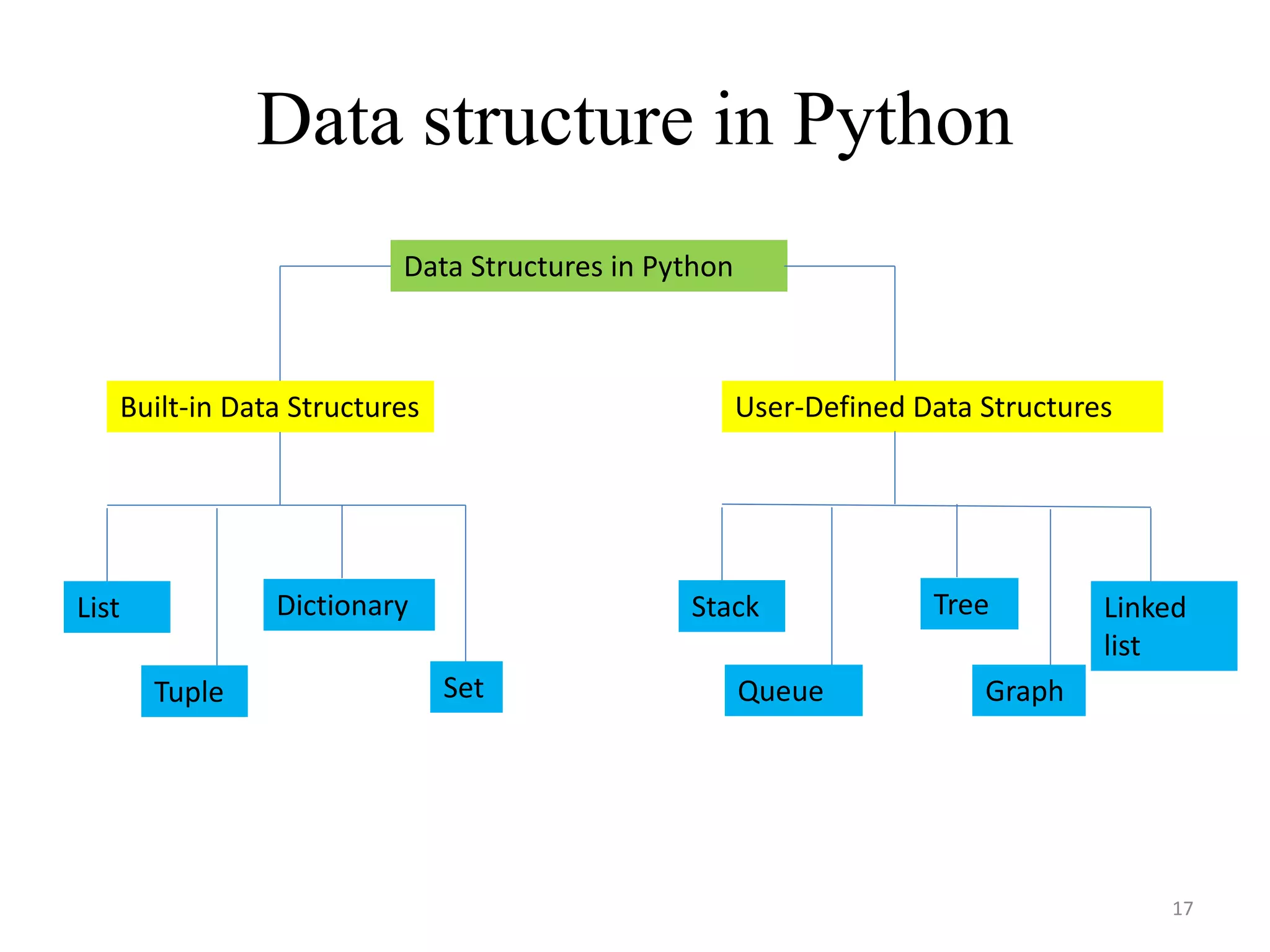
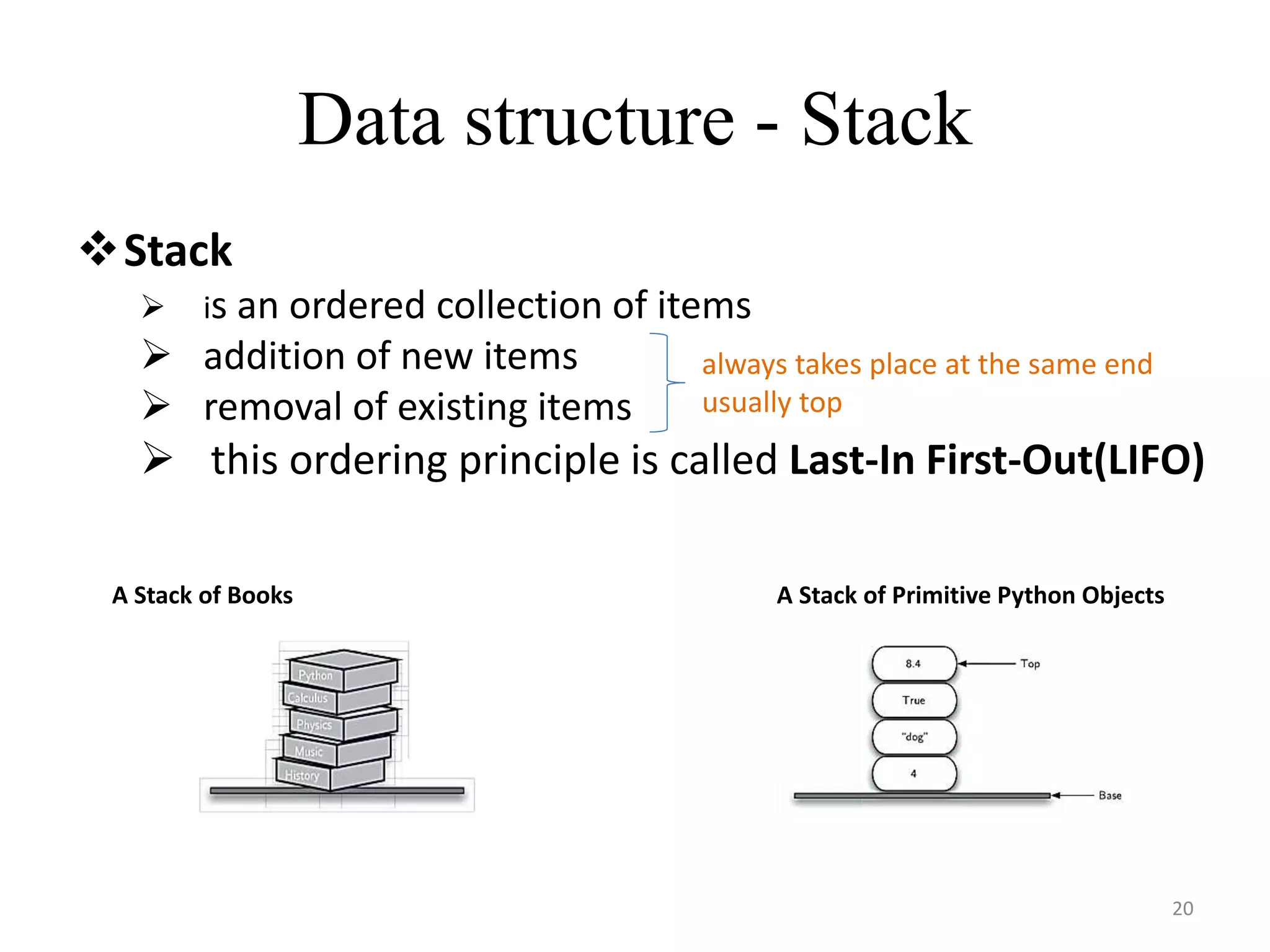
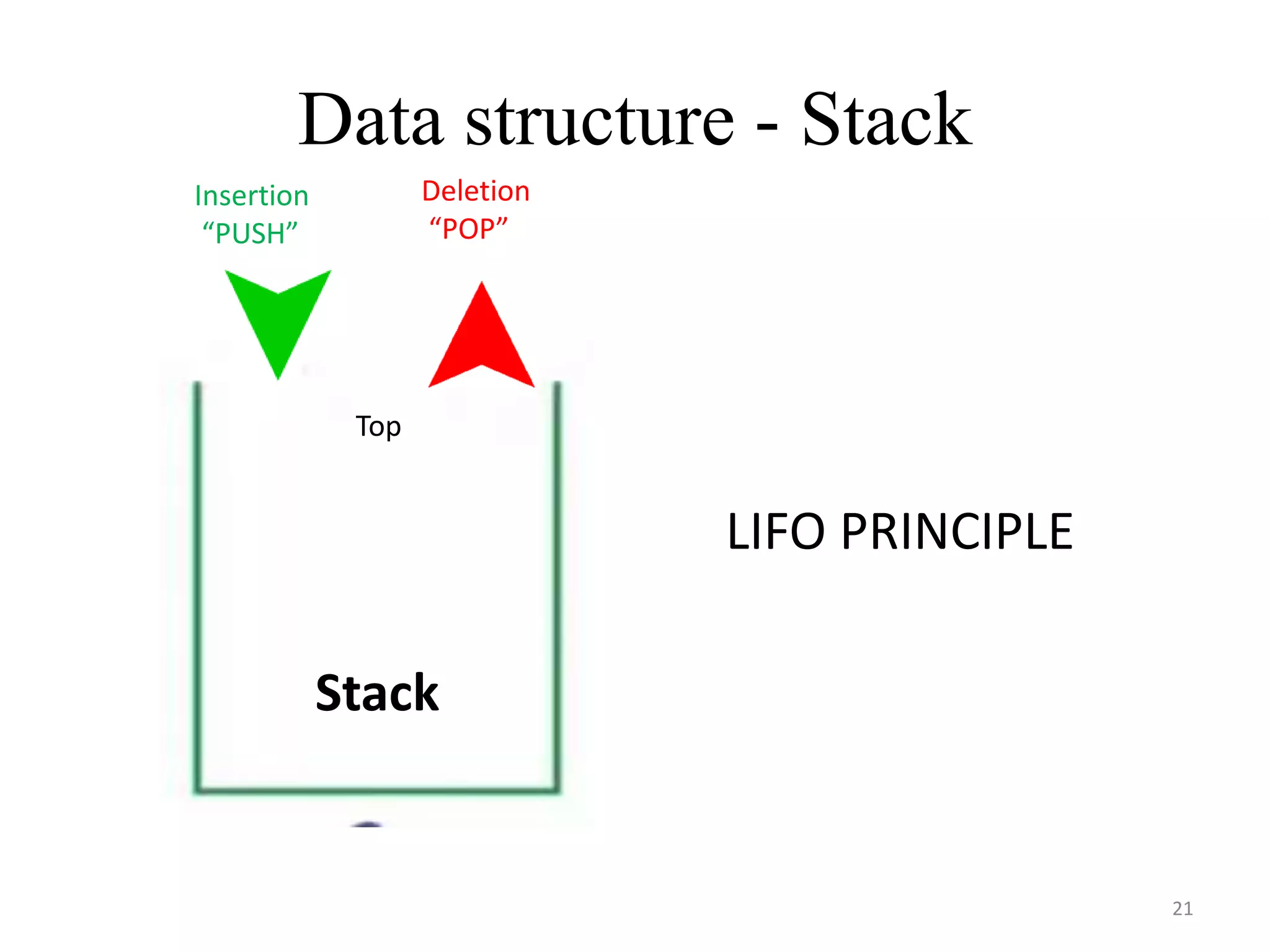
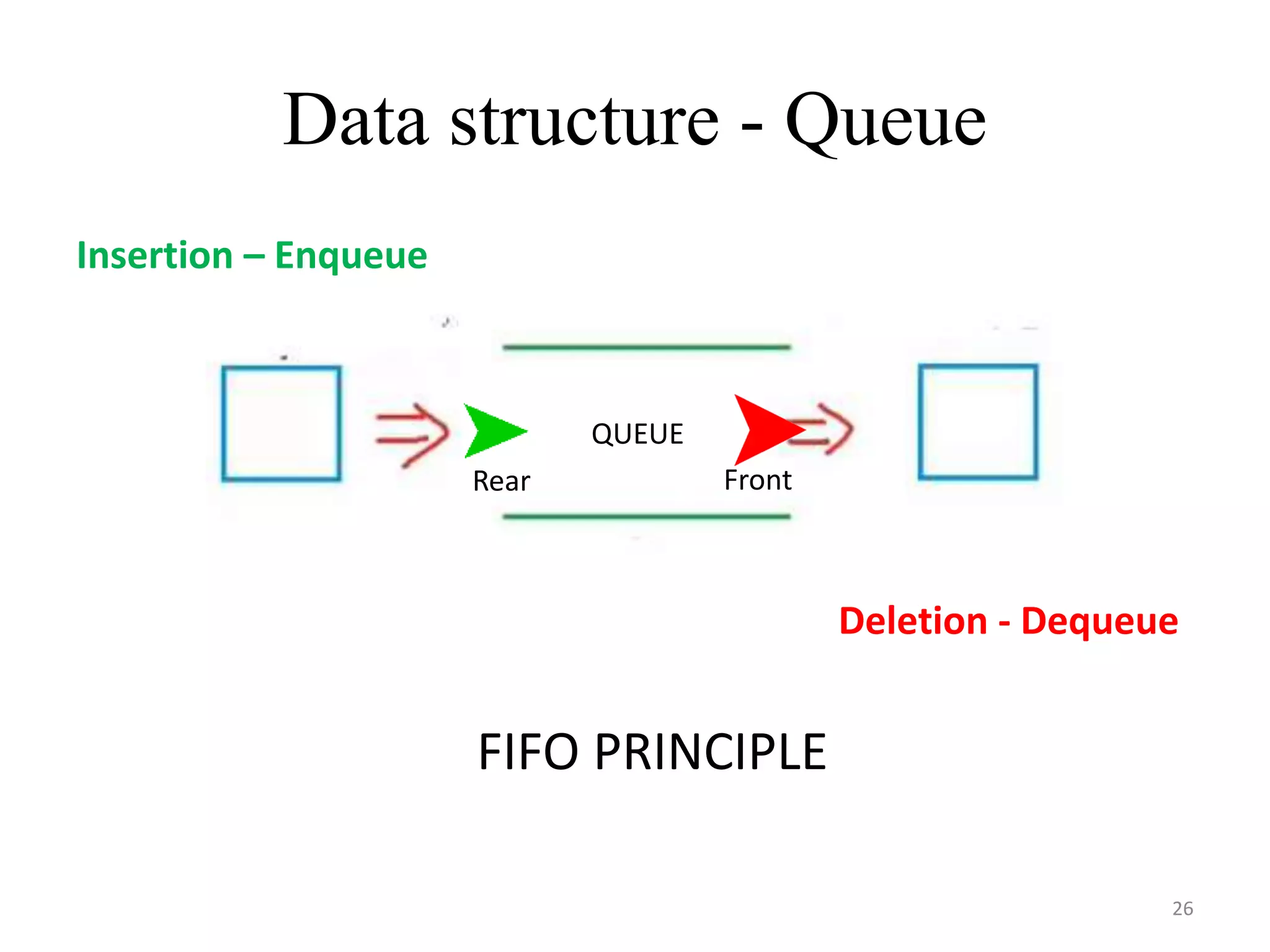
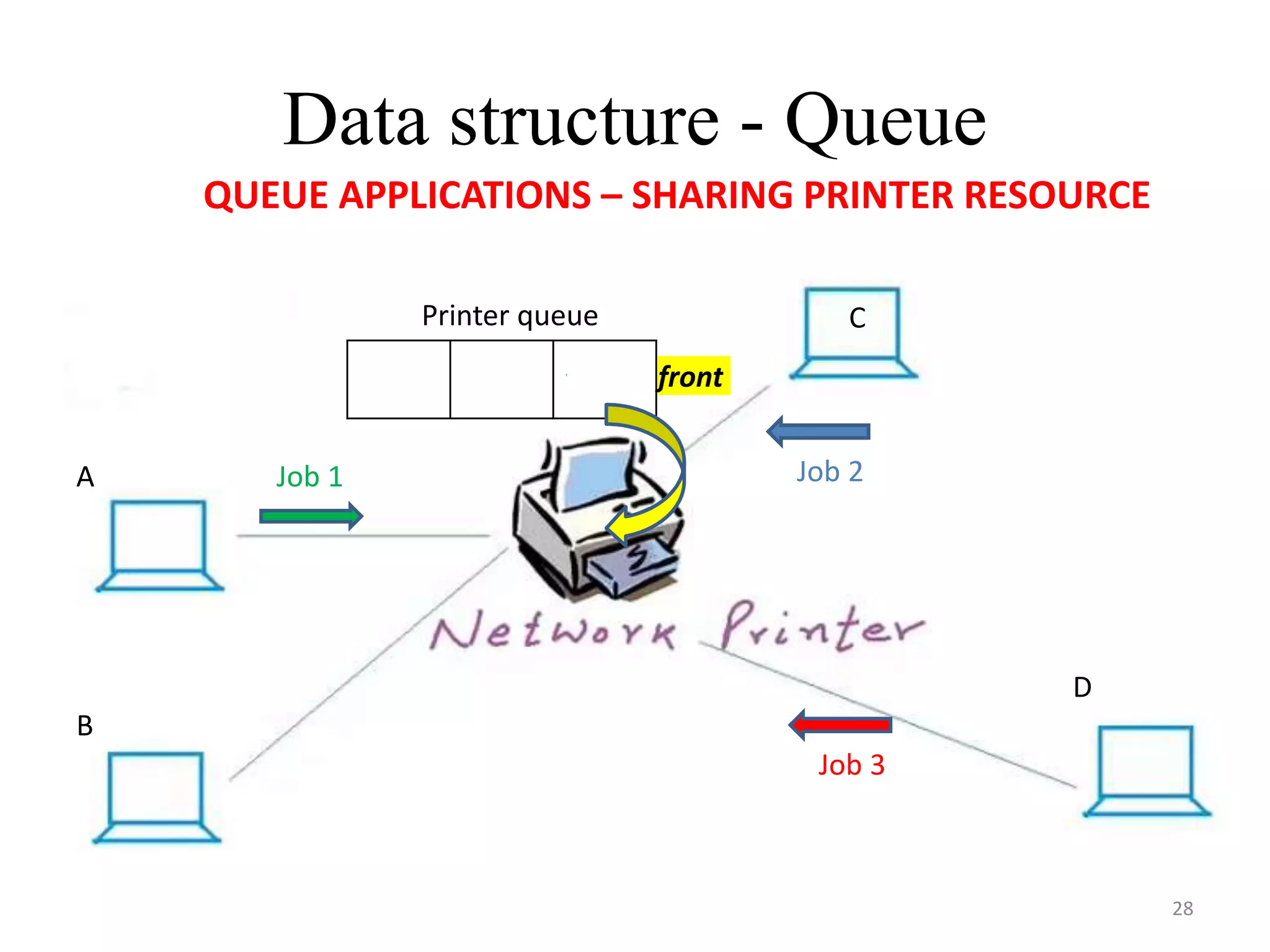
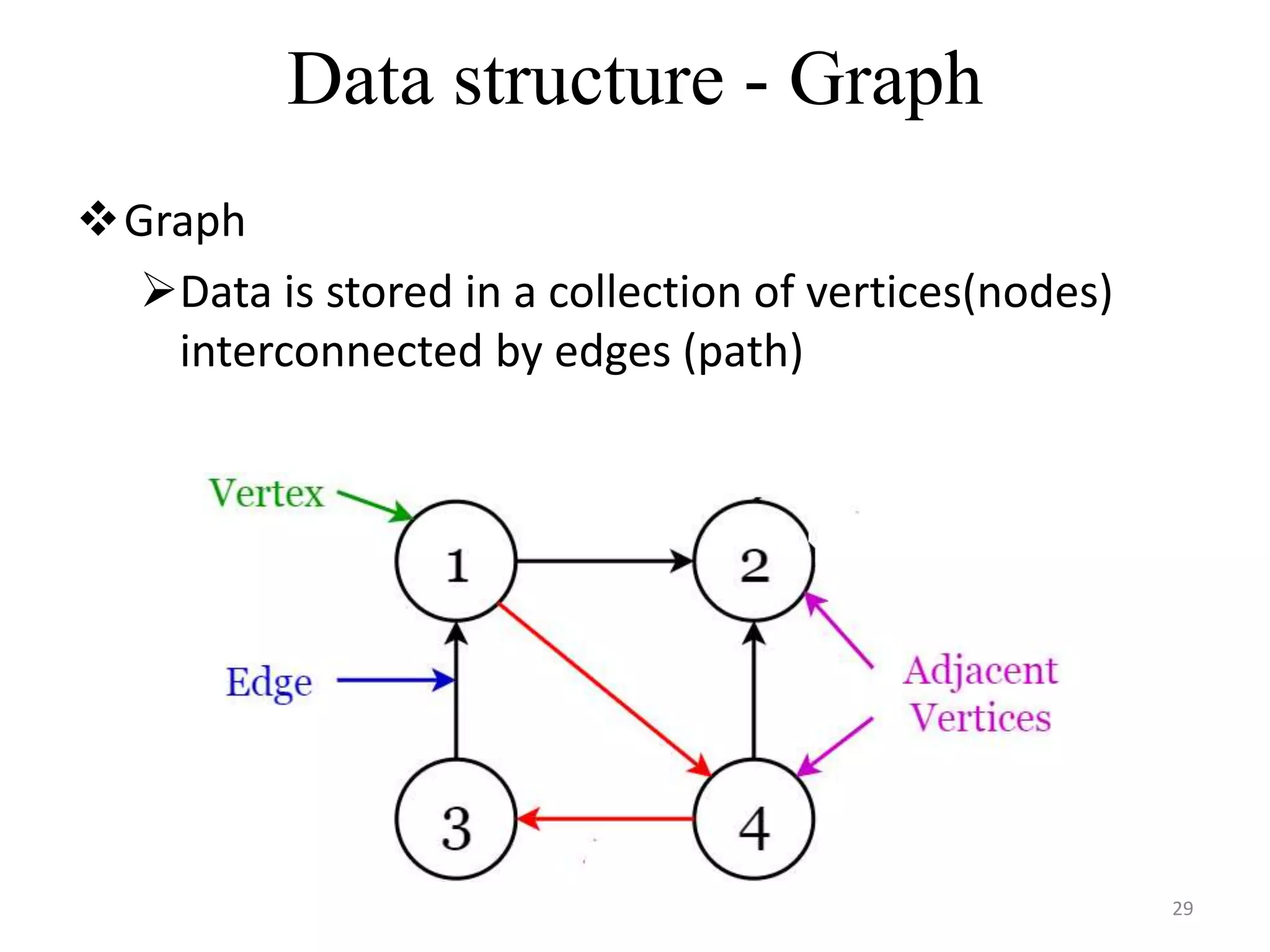
This document discusses packages and data structures in Python. It defines that a Python package is a directory containing sub-packages, modules, and an __init__.py file. It describes how to create packages by making directories, adding modules within them, and including an __init__.py file. Common data structures in Python like lists, tuples, and dictionaries are built-in, while stacks, queues, trees and graphs can be user-defined. The document provides examples of implementing stacks and queues using lists in Python and describes their applications. It also gives an overview of graphs and shows an example of representing a graph using a dictionary in Python.












![Stack using LIST in Python
Example:
# empty stack
stack = [ ]
# push operation # pop operation
23
OUTPUT
stack.append(10) stack =[10]
stack.append(20) stack =[10,20]
stack.append(30) stack =[10,20,30]
OUTPUT
stack.pop() stack =[10,20,30]
stack.pop() stack =[10,20]
top
top
top
top
top](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/packagesdatastructures-210805141549/75/Packages-and-Datastructures-Python-23-2048.jpg)
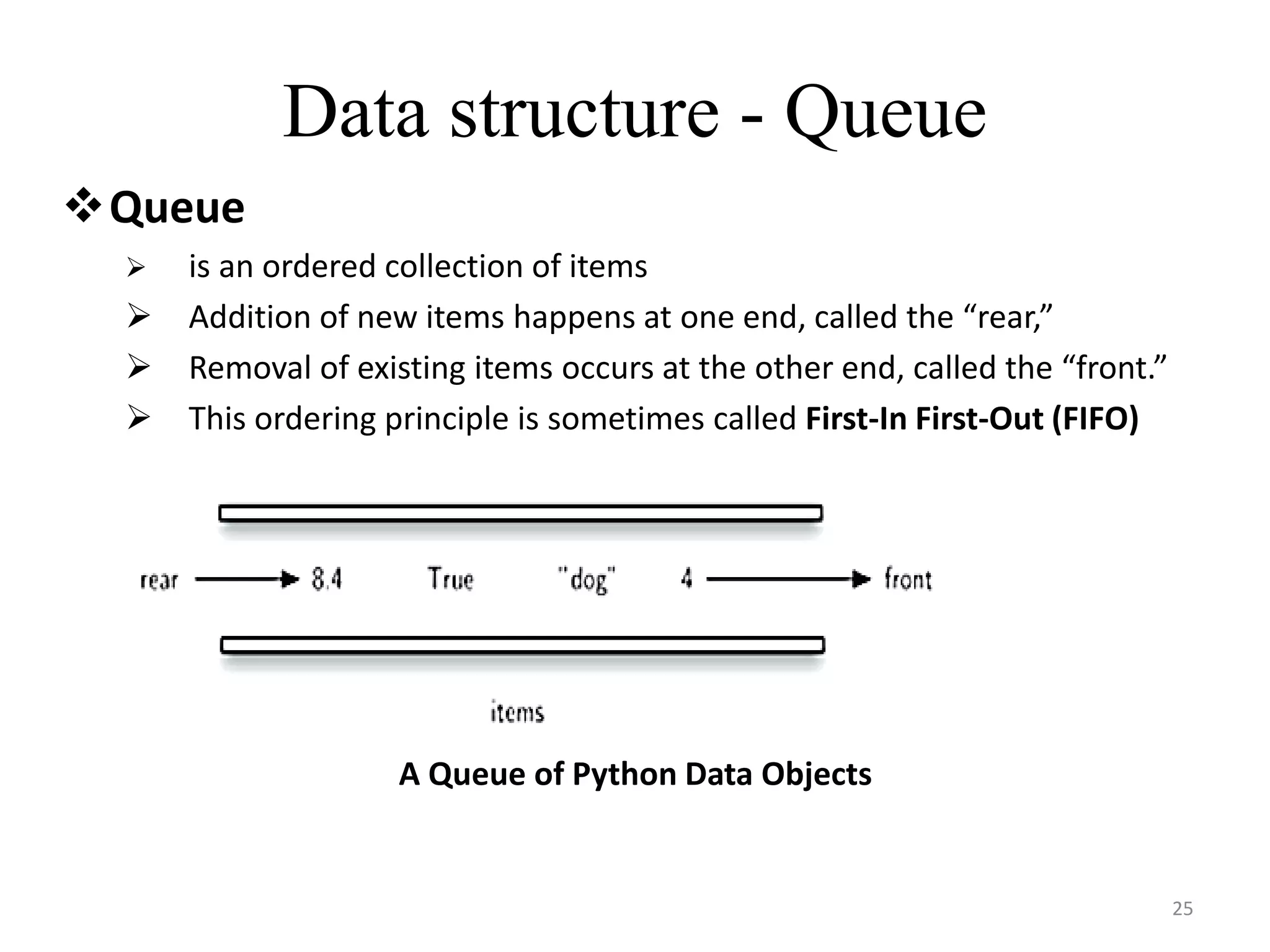
![Queue using LIST in Python
Example:
# empty queue
queue = [ ]
# enqueue operation # dequeue operation
27
OUTPUT
queue.append(10) queue =[10]
queue.append(20) queue =[10,20]
queue.append(30) queue =[10,20,30]
OUTPUT
queue.pop(0) queue =[10,20,30]
queue.pop(0) queue =[20,30]
rear
rear
front
front
rear](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/packagesdatastructures-210805141549/75/Packages-and-Datastructures-Python-27-2048.jpg)
![Graph using DICTIONARY
Example:
# GRAPH structure
graph = { “a”:[“d”], “b”:[“c”],“c”:[“d”,”e”],
“d”: [“a”,”c”] ,”e”:[“c”]}
30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/packagesdatastructures-210805141549/75/Packages-and-Datastructures-Python-30-2048.jpg)