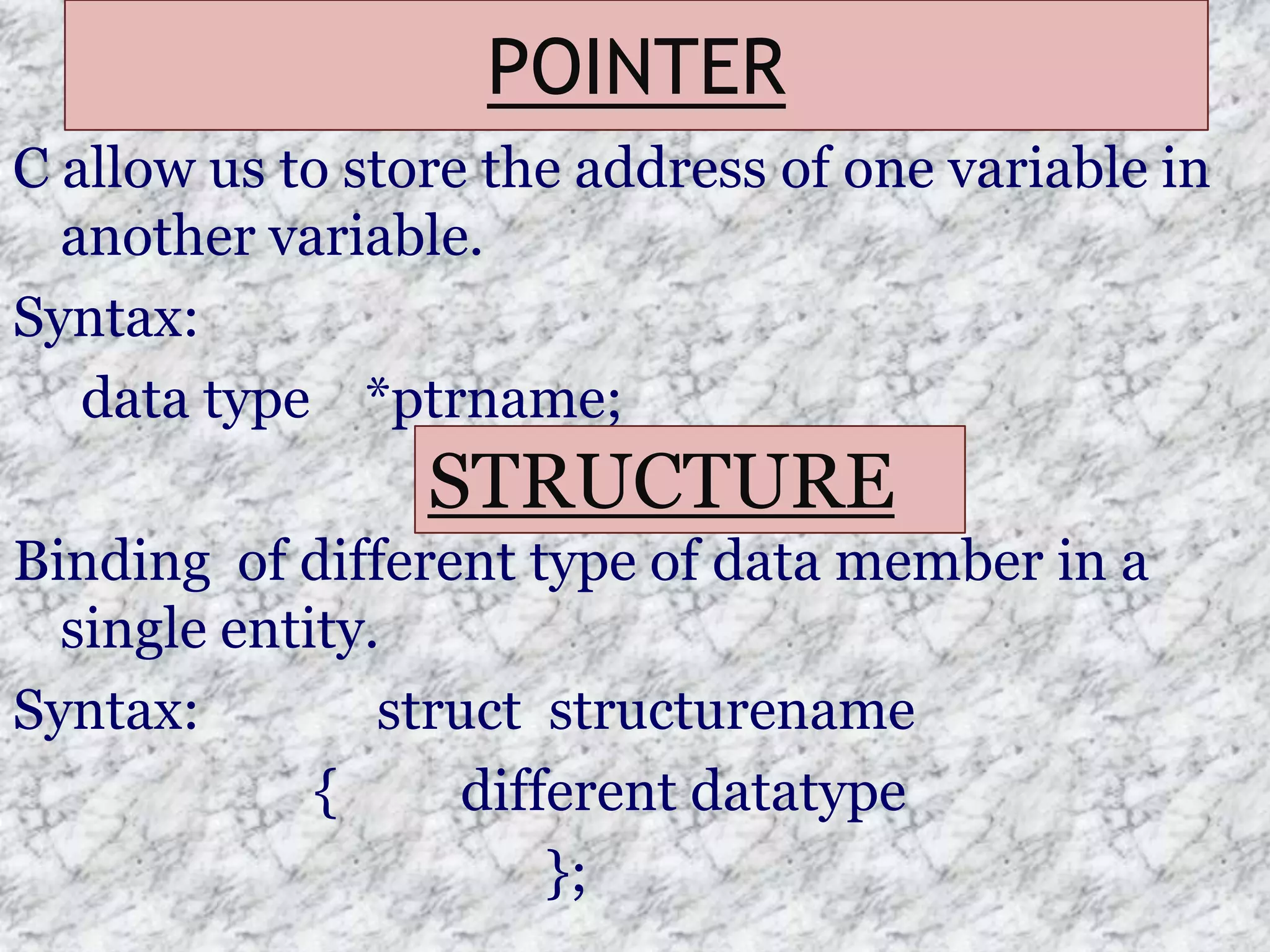
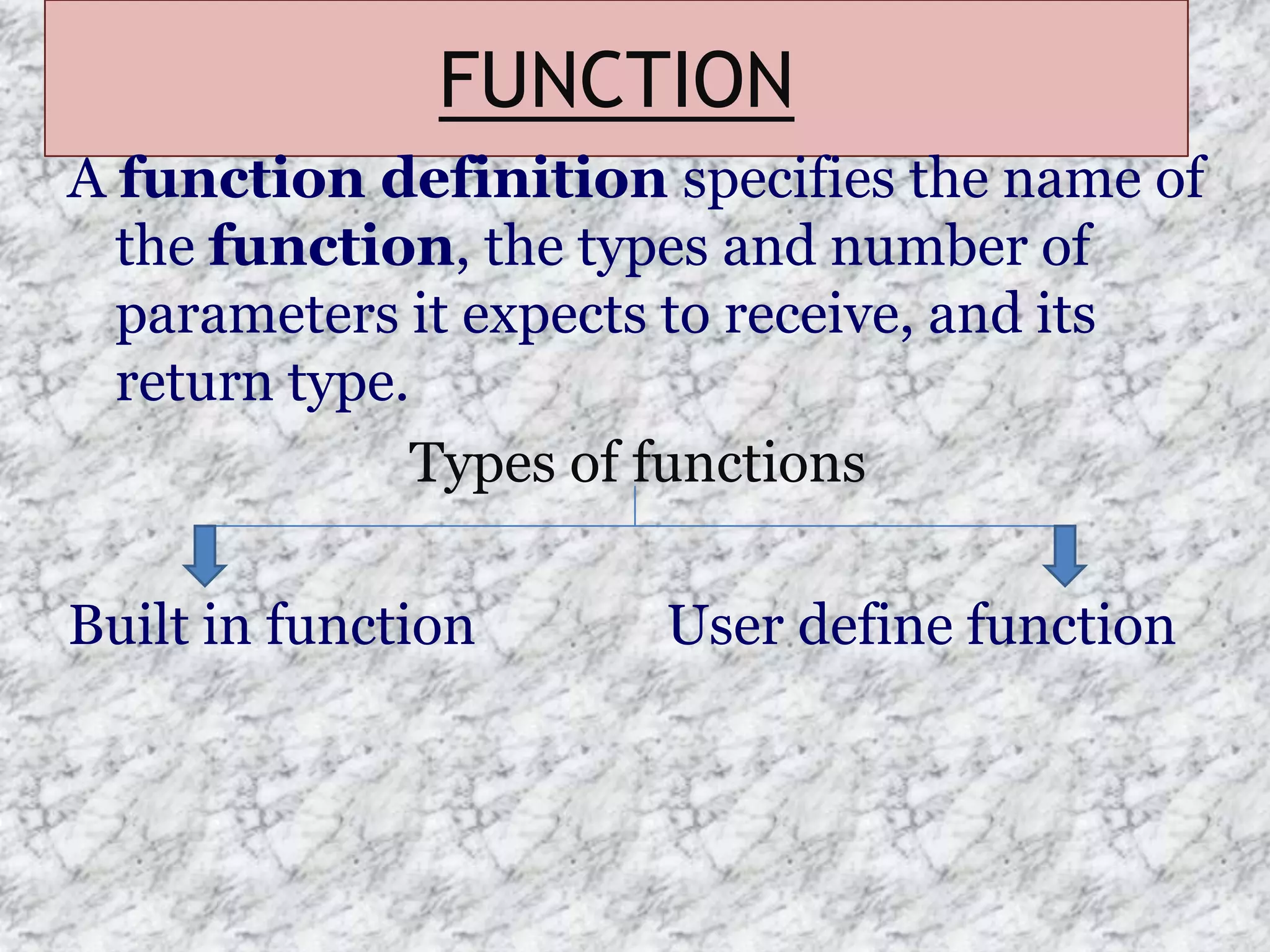
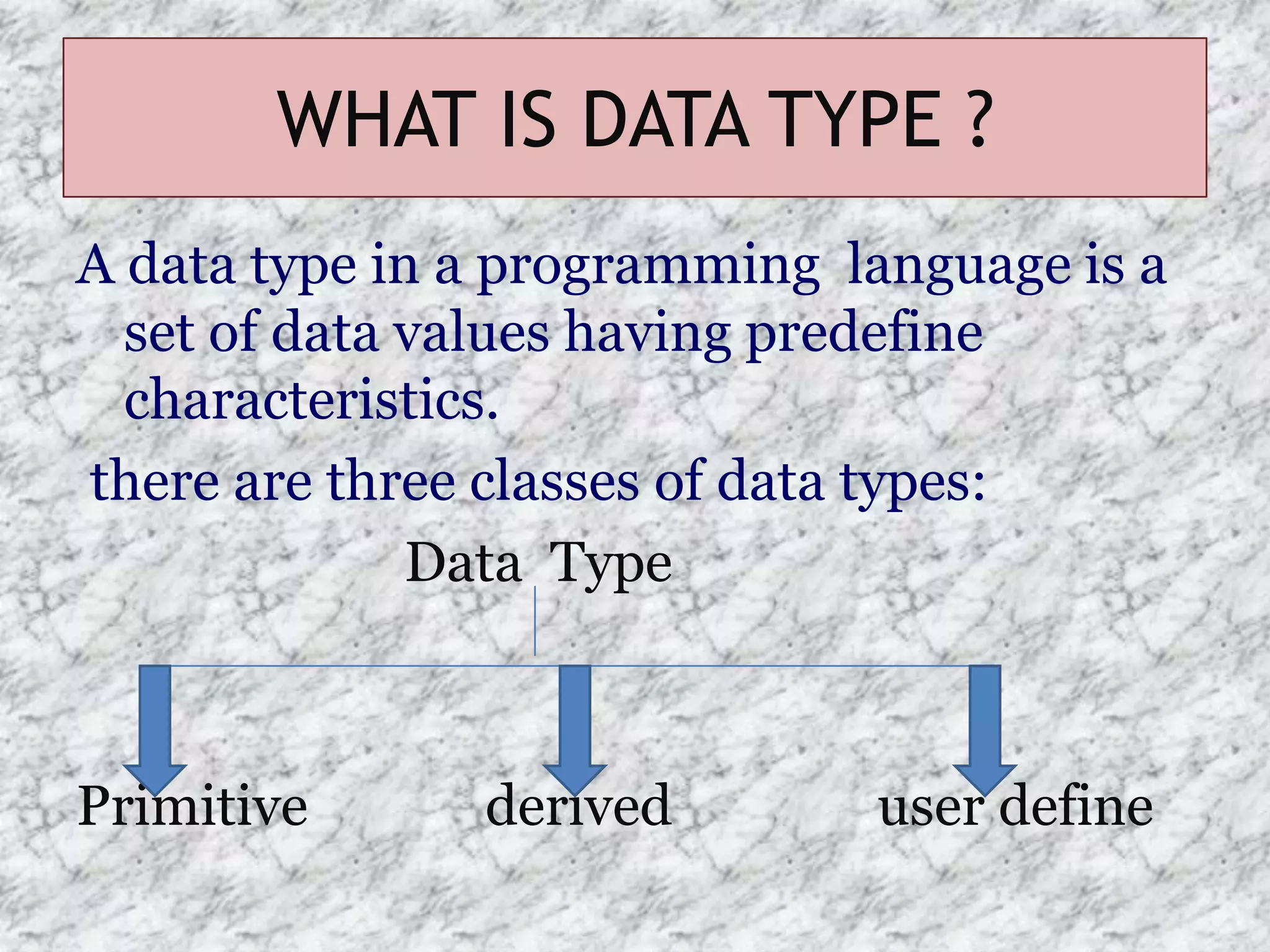
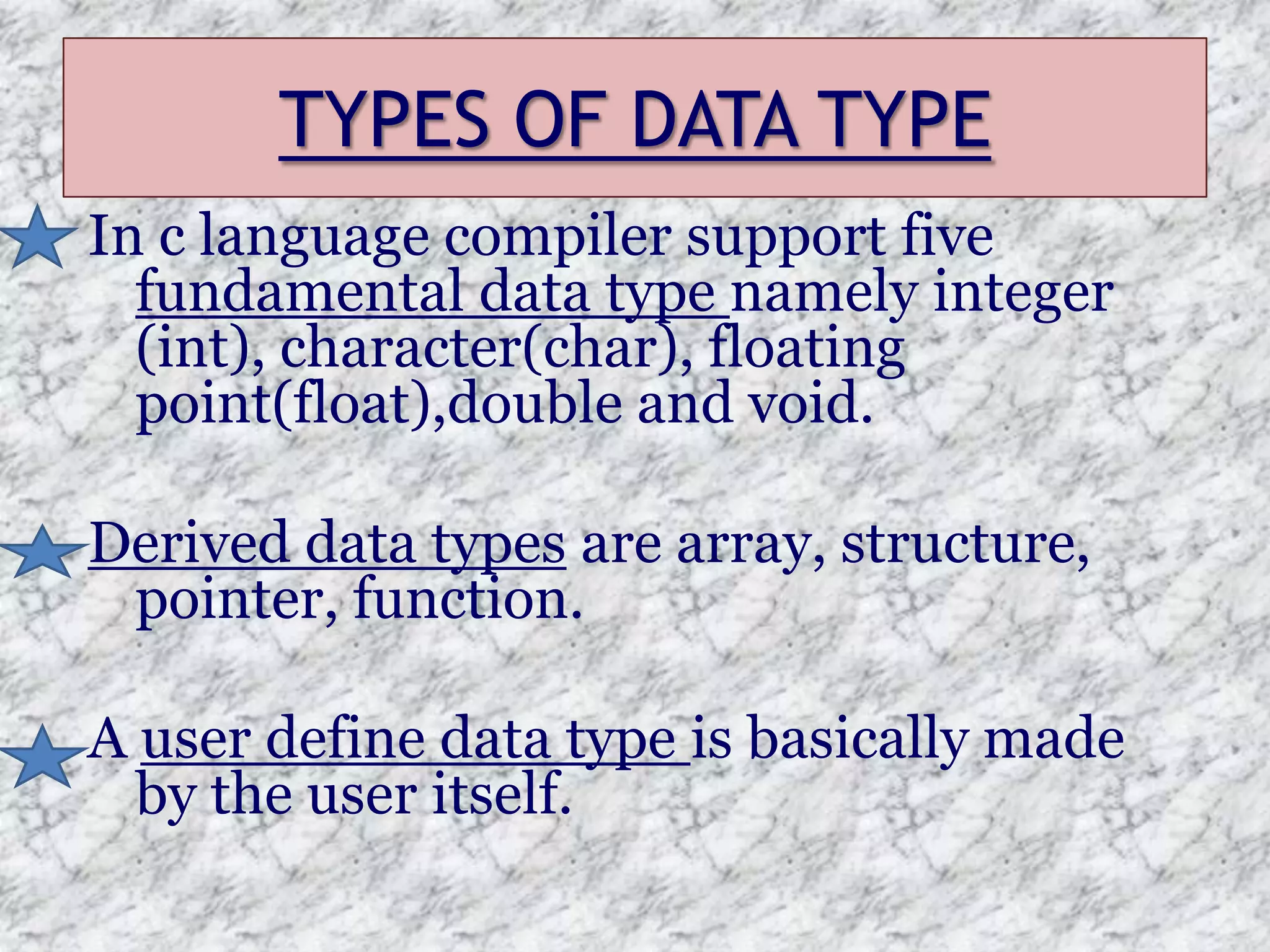
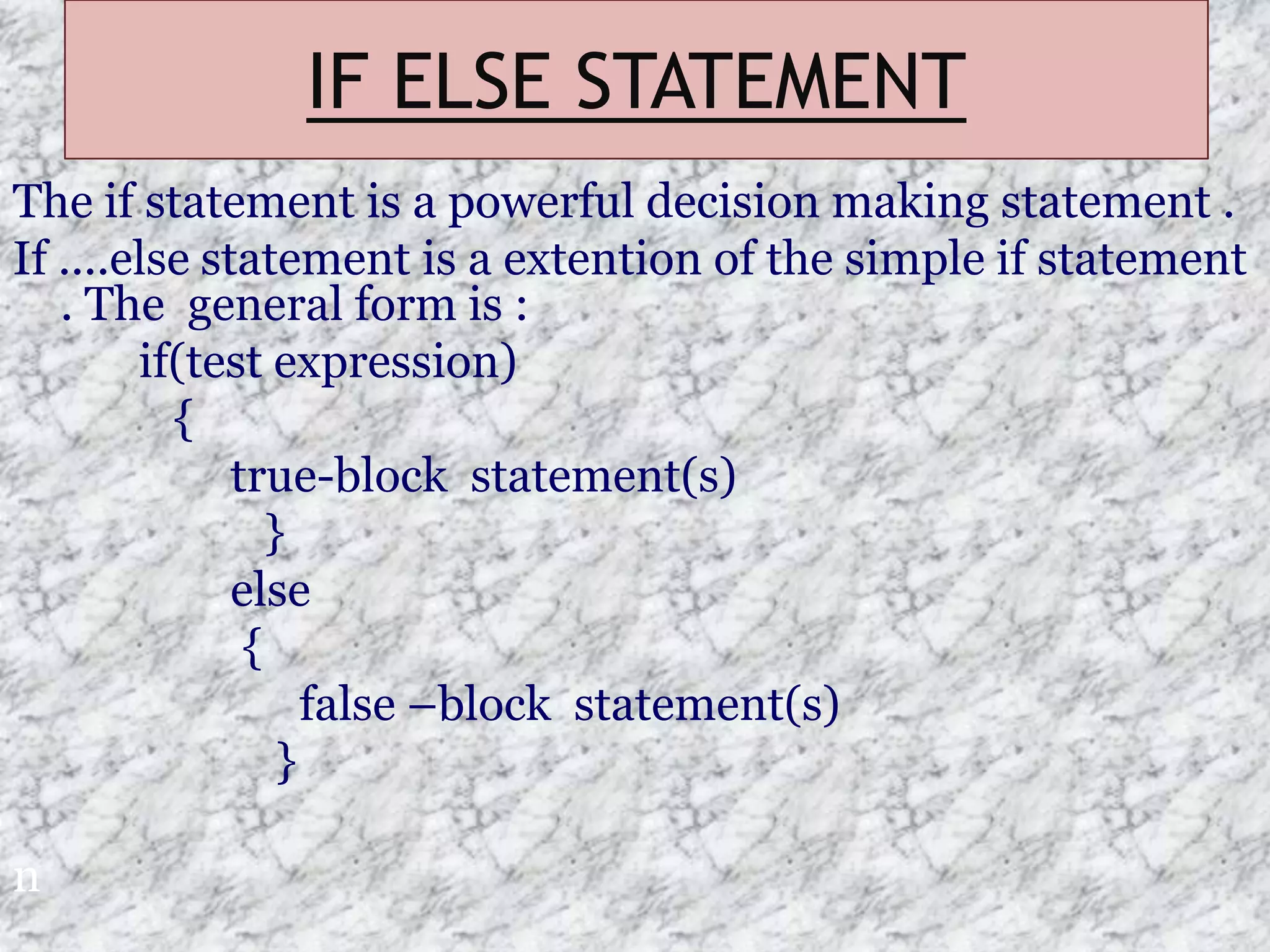
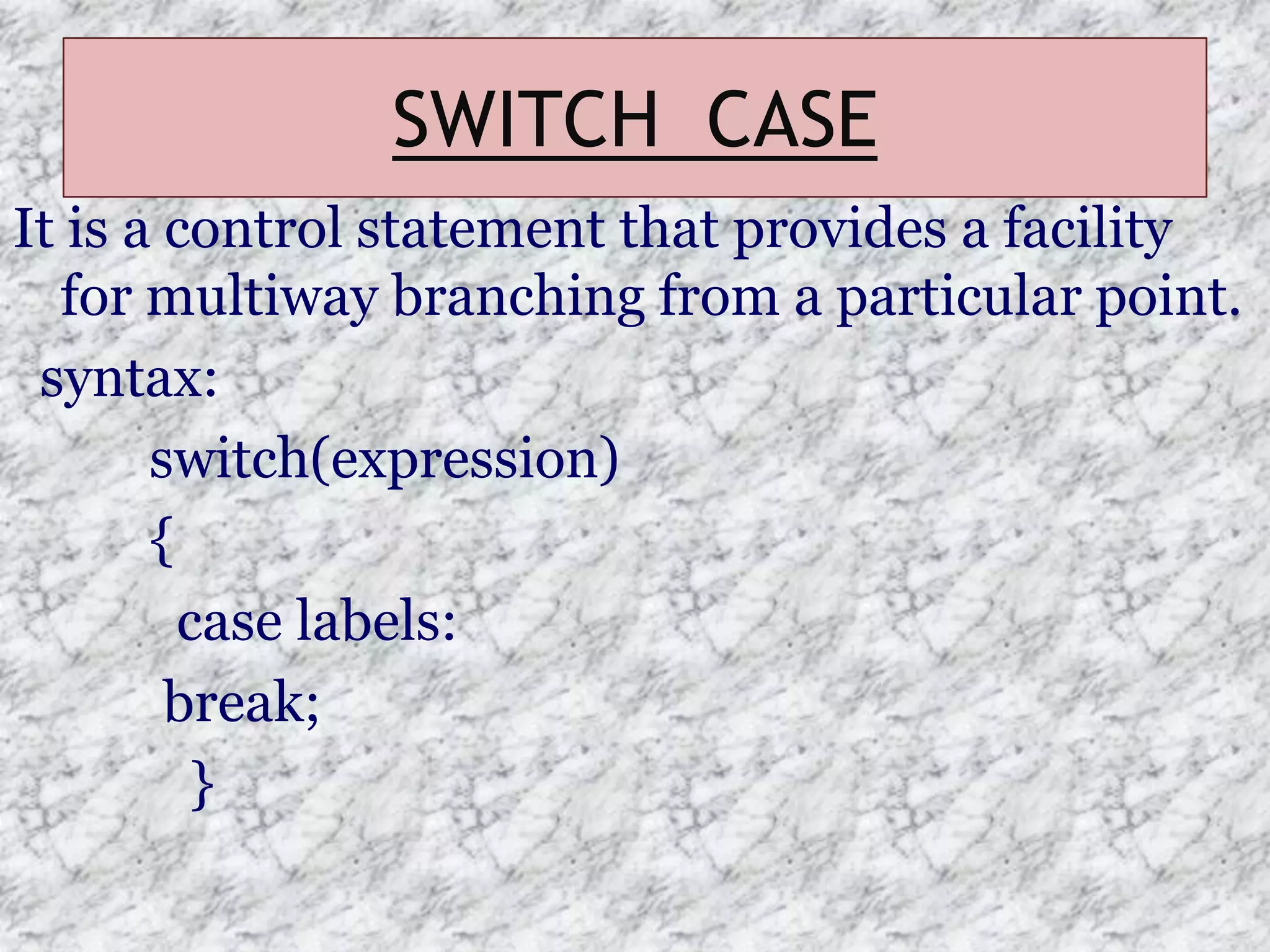
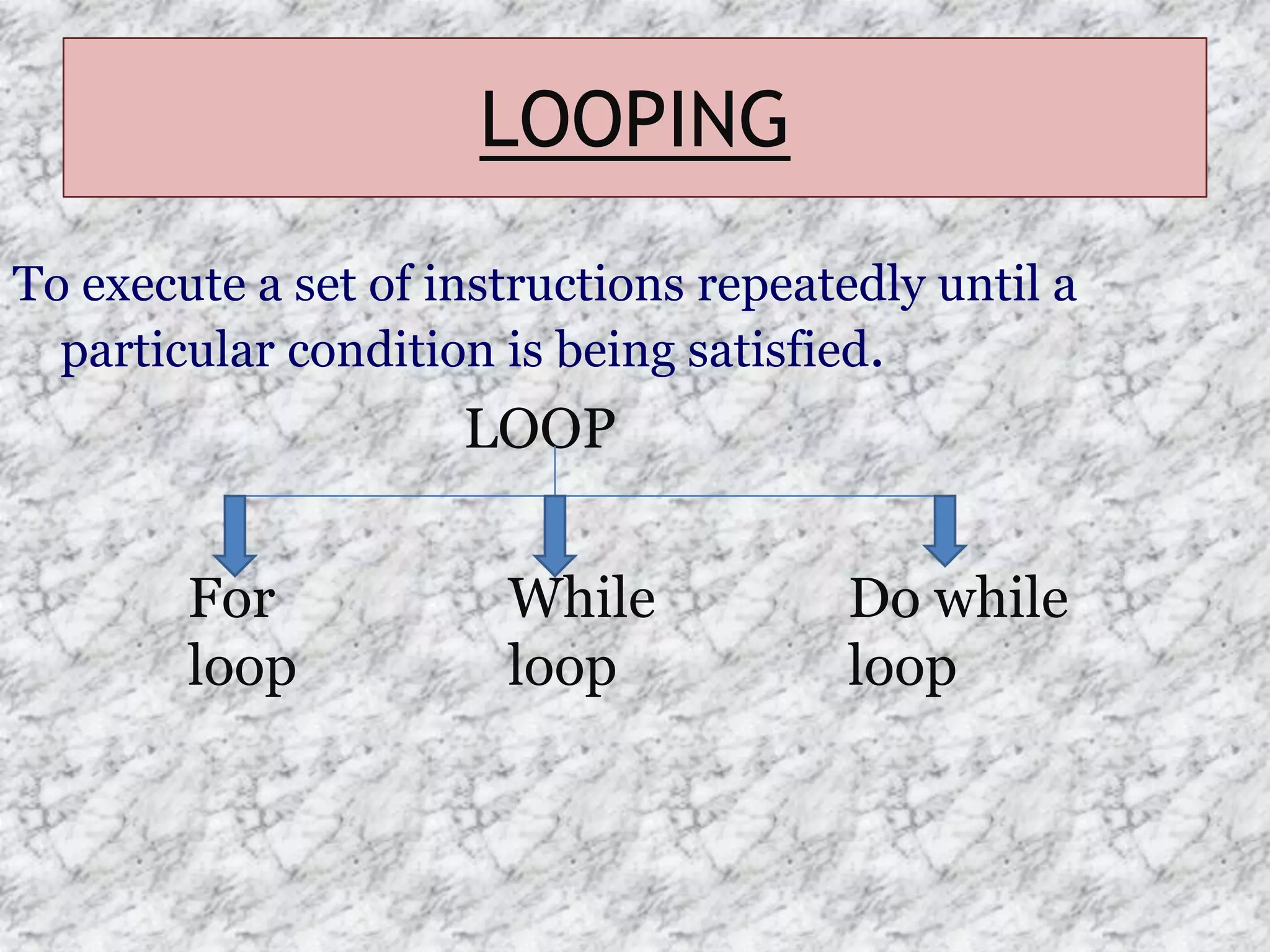
The document provides an introduction to the C programming language, outlining its key characteristics, structure, data types, control structures like if/else and switch statements, looping, arrays, pointers, structures, and functions. It describes C as a structured, low-level language developed in 1969-1973, and covers basic data types like int, char, and float, as well as derived types like arrays and pointers.





![ARRAY
An array is a collection of elements of the same
data type.
Syntax :
data type arrayname[size];
Type of array
1 dimensional 2 dimensional Multi-dimensional](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/overviewofclanguage-121225023819-phpapp01/75/Overview-of-c-language-13-2048.jpg)