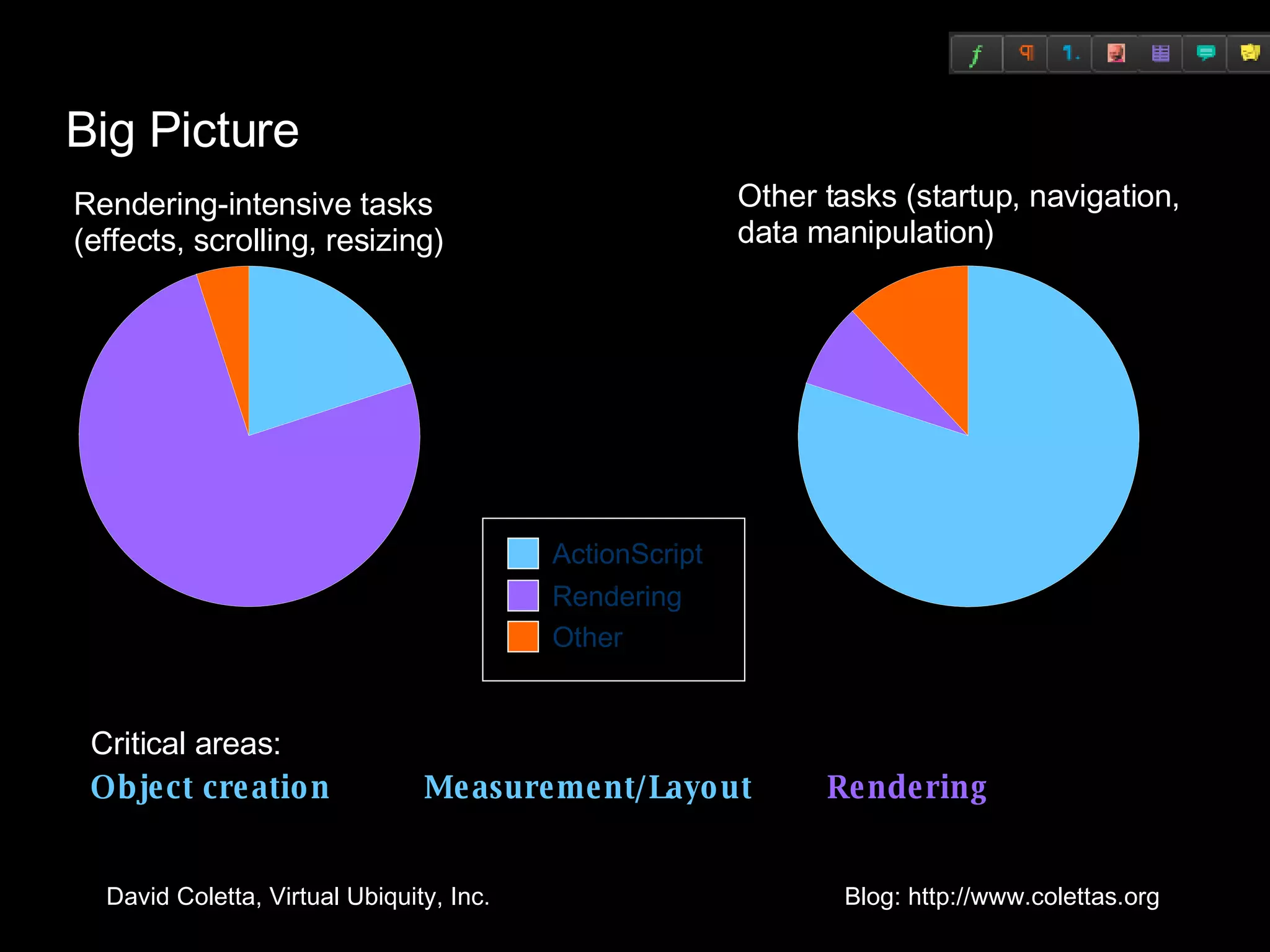
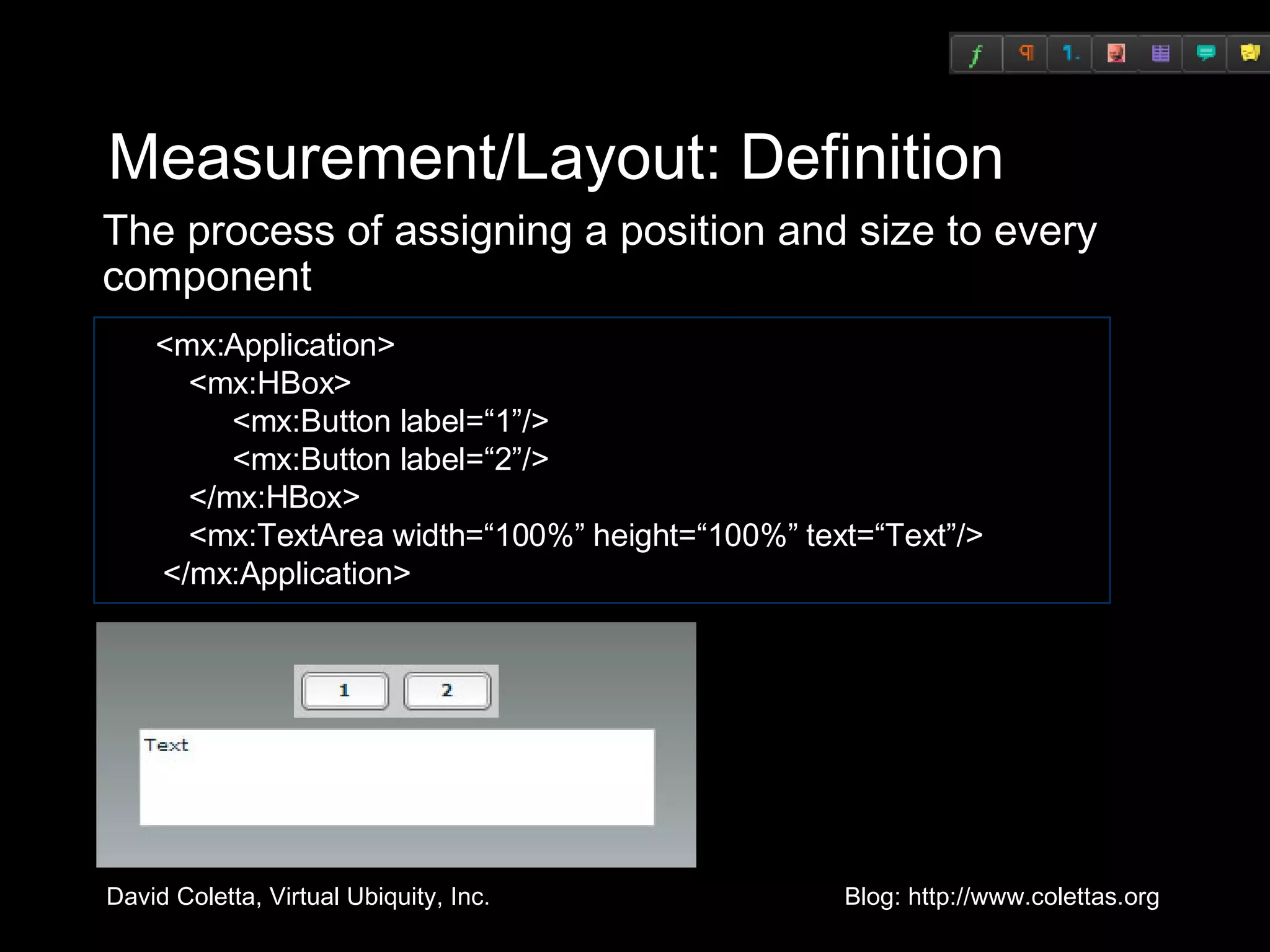
The document summarizes techniques for optimizing Flex applications. It discusses improving actual performance through techniques like finding cheaper algorithms, precomputing values, and reducing garbage collection load. It also discusses improving perceived performance by doing work in the background and showing progress. The document provides case studies and examples of optimizing object creation, measurement/layout, and rendering in Flex applications.
![Optimizing Flex Applications David Coletta Virtual Ubiquity, Inc. [email_address] Blog: http://www.colettas.org](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optimizing-flex-applications4291/75/Optimizing-Flex-Applications-1-2048.jpg)

























![How the Profiler Works Uses new Player APIs 10 ms sampling interval Computes cumulative values Records internal Player actions (e.g., [keyboardEvent], [mark], [sweep])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optimizing-flex-applications4291/75/Optimizing-Flex-Applications-29-2048.jpg)