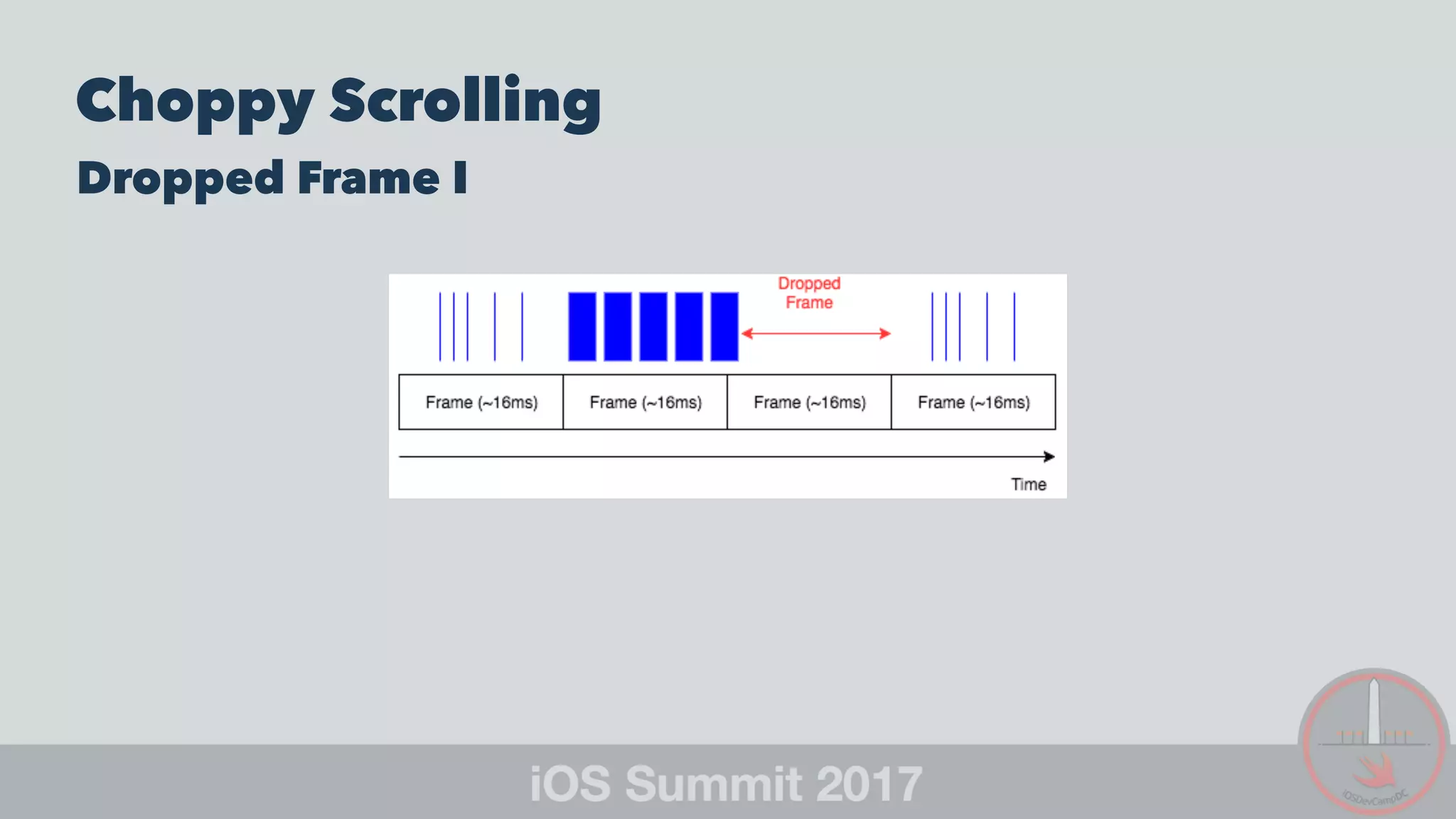
This document provides strategies for optimizing UICollectionView scrolling performance. It recommends:
1. Asynchronously fetching and caching user data and images to avoid blocking the main thread.
2. Implementing cell reuse and prefetching to efficiently render cells.
3. Calculating optimal cell sizes and handling orientation changes to maintain smooth scrolling.
4. Using opaque layers and avoiding gradients to improve cell rendering speed.









![User View Model Controller
Wrap and Cache View Model
class UserViewModelController {
private var viewModels: [UserViewModel?] = []
[...]
var viewModelsCount: Int {
return viewModels.count
}
func viewModel(at index: Int) -> UserViewModel? {
guard index >= 0 && index < viewModelsCount else { return nil }
return viewModels[index]
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optimizecollectionviewscrolling-170807121100/75/Optimize-CollectionView-Scrolling-10-2048.jpg)
![User View Model Controller
Asynchronous Data Fetch
func retrieveUsers(_ completionBlock: @escaping (_ success: Bool, _ error: NSError?) -> ()) {
let urlString = ... // Users Web Service URL
let session = URLSession.shared
guard let url = URL(string: urlString) else {
completionBlock(false, nil)
return
}
let task = session.dataTask(with: url) { [weak self] (data, response, error) in
guard let strongSelf = self else { return }
guard let jsonData = data, error == nil else {
completionBlock(false, error as NSError?)
return
}
if let users = UserViewModelController.parse(jsonData) {
strongSelf.viewModels = UserViewModelController.initViewModels(users)
completionBlock(true, nil)
} else {
completionBlock(false, NSError.createError(0, description: "JSON parsing error"))
}
}
task.resume()
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optimizecollectionviewscrolling-170807121100/75/Optimize-CollectionView-Scrolling-11-2048.jpg)
![User View Model Controller Extension
Parse JSON
private extension UserViewModelController {
static func parse(_ jsonData: Data) -> [User?]? {
do {
return try JSONDecoder().decode([User].self, from: jsonData)
} catch {
return nil
}
}
static func initViewModels(_ users: [User?]) -> [UserViewModel?] {
return users.map { user in
if let user = user {
return UserViewModel(user: user)
} else {
return nil
}
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optimizecollectionviewscrolling-170807121100/75/Optimize-CollectionView-Scrolling-12-2048.jpg)



![Customize the Cell
Subclass the Default Cell
class UserCell: UICollectionViewCell {
@IBOutlet weak var avatar: UIImageView!
@IBOutlet weak var username: UILabel!
@IBOutlet weak var role: UILabel!
func configure(_ viewModel: UserViewModel) {
UIImage.downloadImageFromUrl(viewModel.avatarUrl) { [weak self] (image) in
guard let strongSelf = self,
let image = image else {
return
}
strongSelf.avatar.image = image
}
username.text = viewModel.username
role.text = viewModel.roleText
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optimizecollectionviewscrolling-170807121100/75/Optimize-CollectionView-Scrolling-16-2048.jpg)
![Use Opaque Layers and Avoid Gradients
class UserCell: UICollectionViewCell {
@IBOutlet weak var avatar: UIImageView!
@IBOutlet weak var username: UILabel!
@IBOutlet weak var role: UILabel!
override func awakeFromNib() {
super.awakeFromNib()
setOpaqueBackground()
[...]
}
}
private extension UserCell {
static let DefaultBackgroundColor = UIColor.groupTableViewBackgroundColor
func setOpaqueBackground() {
alpha = 1.0
backgroundColor = UserCell.DefaultBackgroundColor
avatar.alpha = 1.0
avatar.backgroundColor = UserCell.DefaultBackgroundColor
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optimizecollectionviewscrolling-170807121100/75/Optimize-CollectionView-Scrolling-17-2048.jpg)





![Dynamically Adjust Cell Layout
Override apply(_:)
override func apply(_ layoutAttributes: UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes) {
super.apply(layoutAttributes)
// Customize the cell layout
[...]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optimizecollectionviewscrolling-170807121100/75/Optimize-CollectionView-Scrolling-23-2048.jpg)