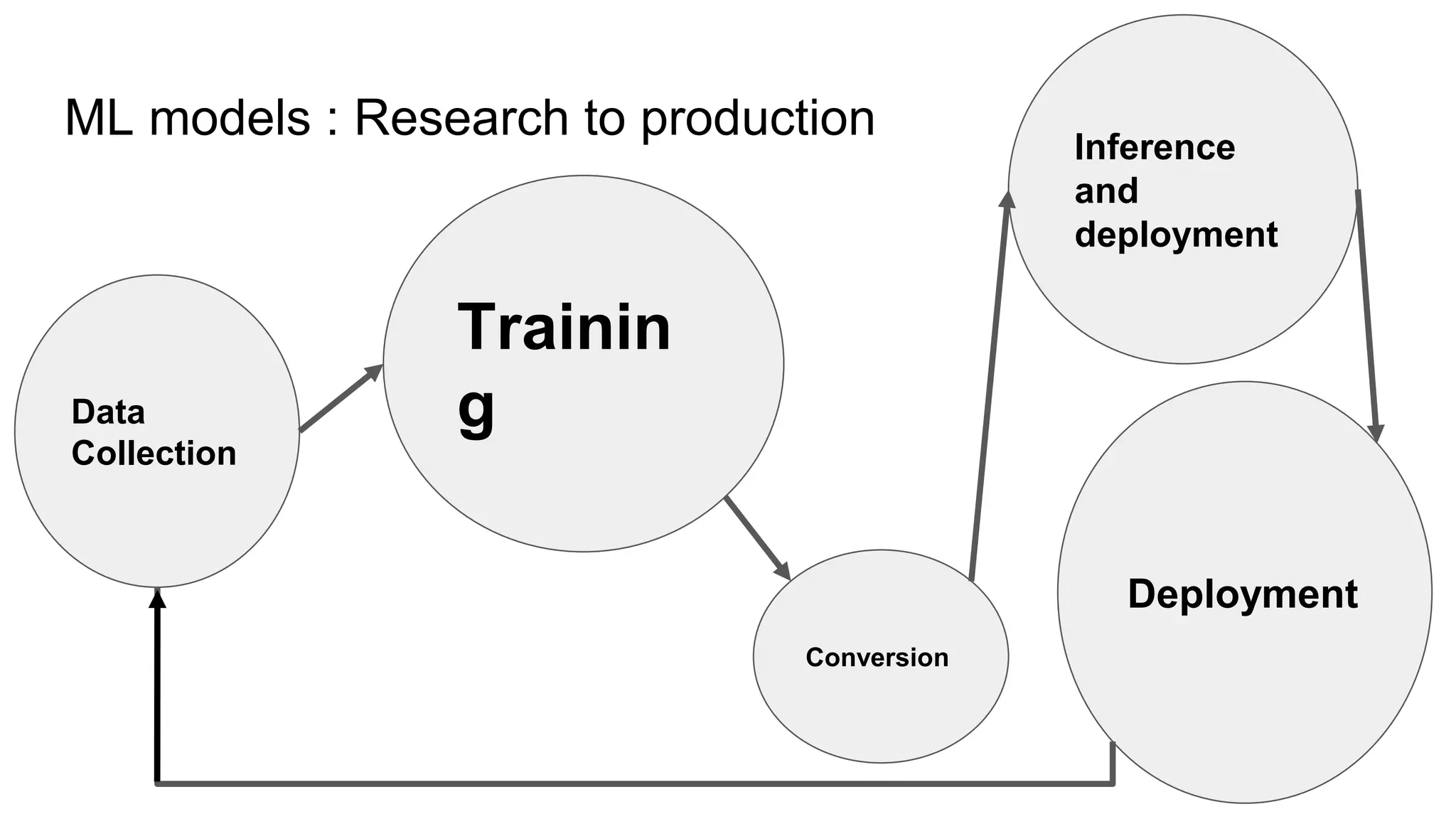
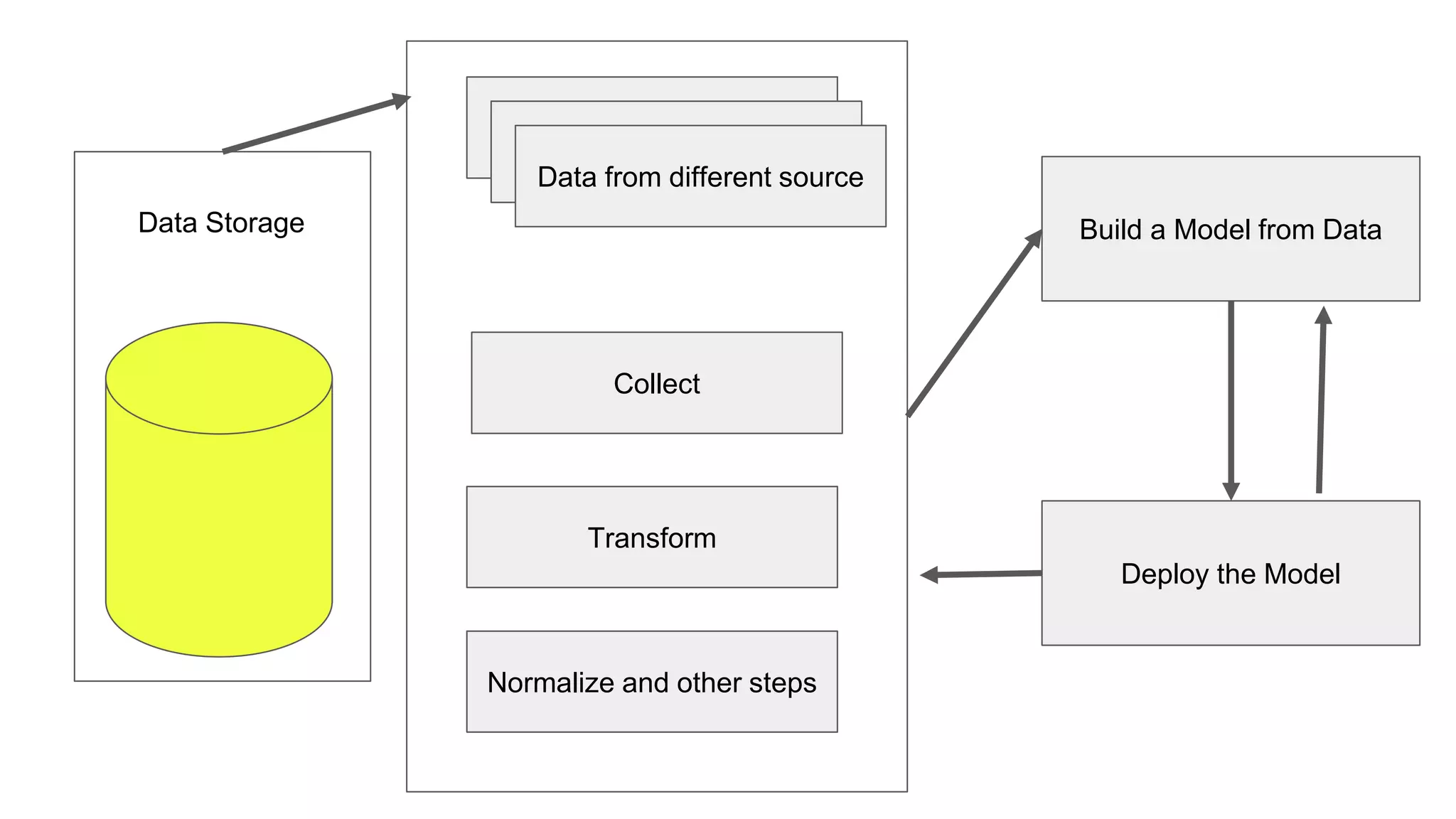
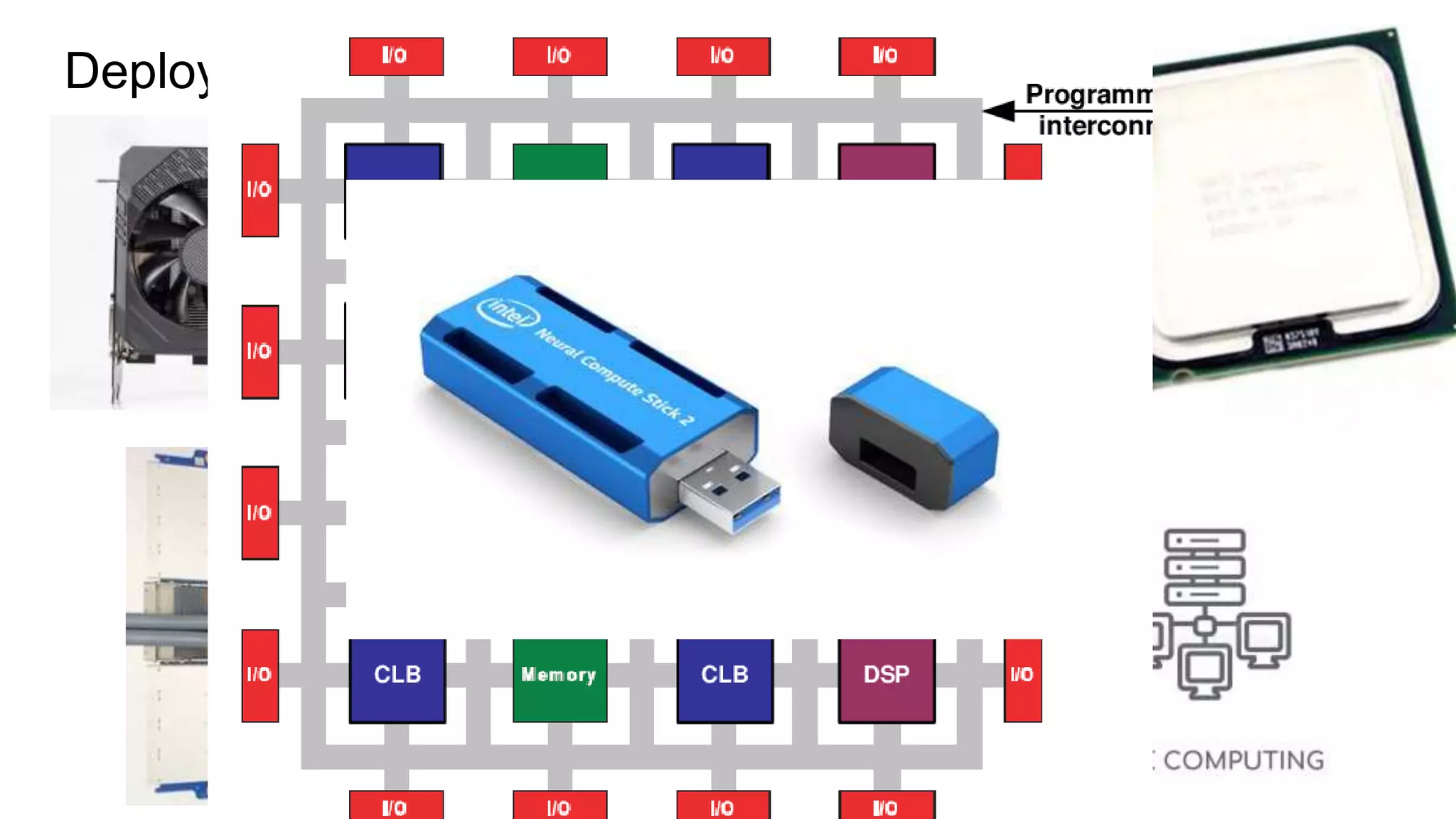
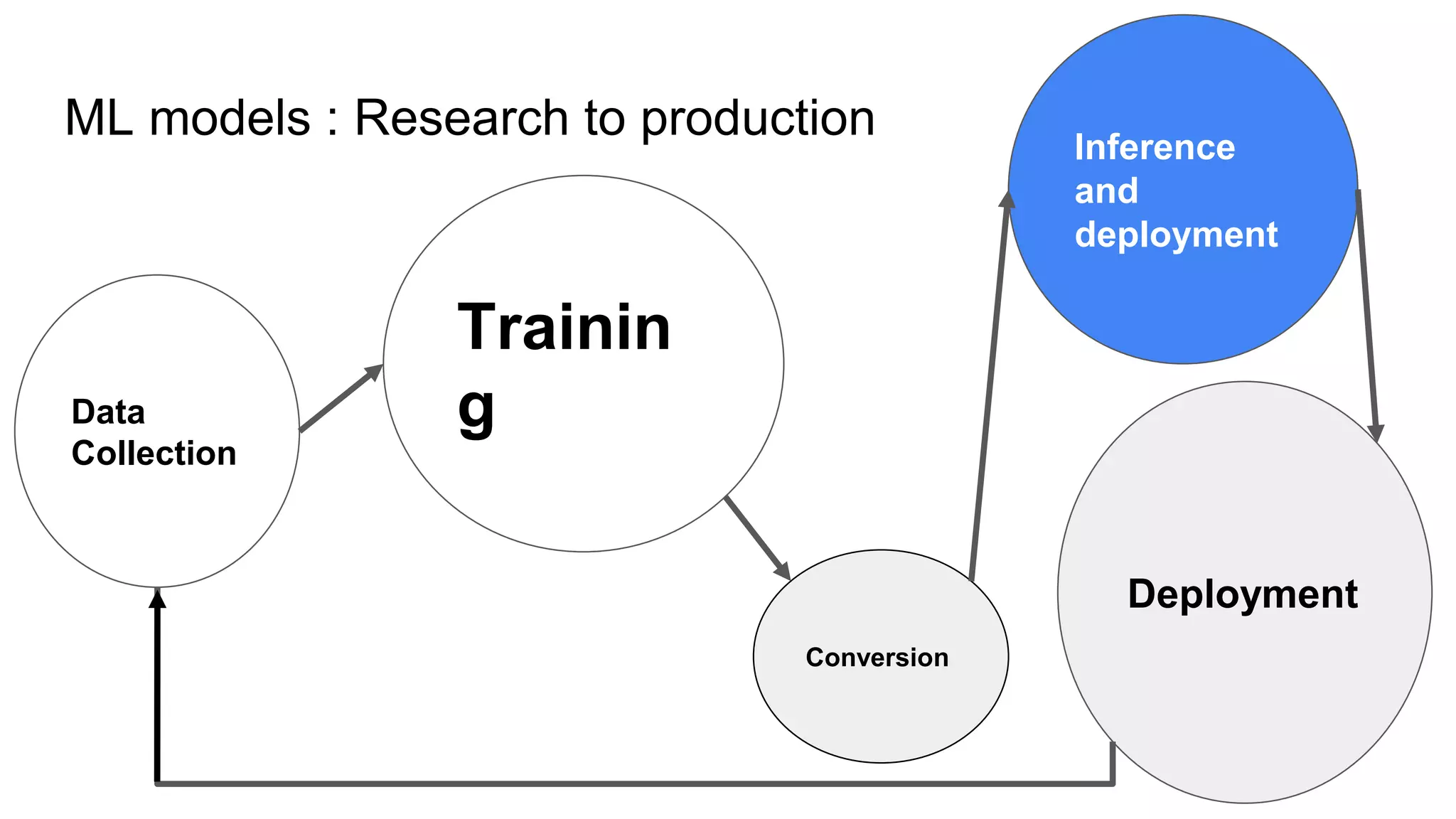
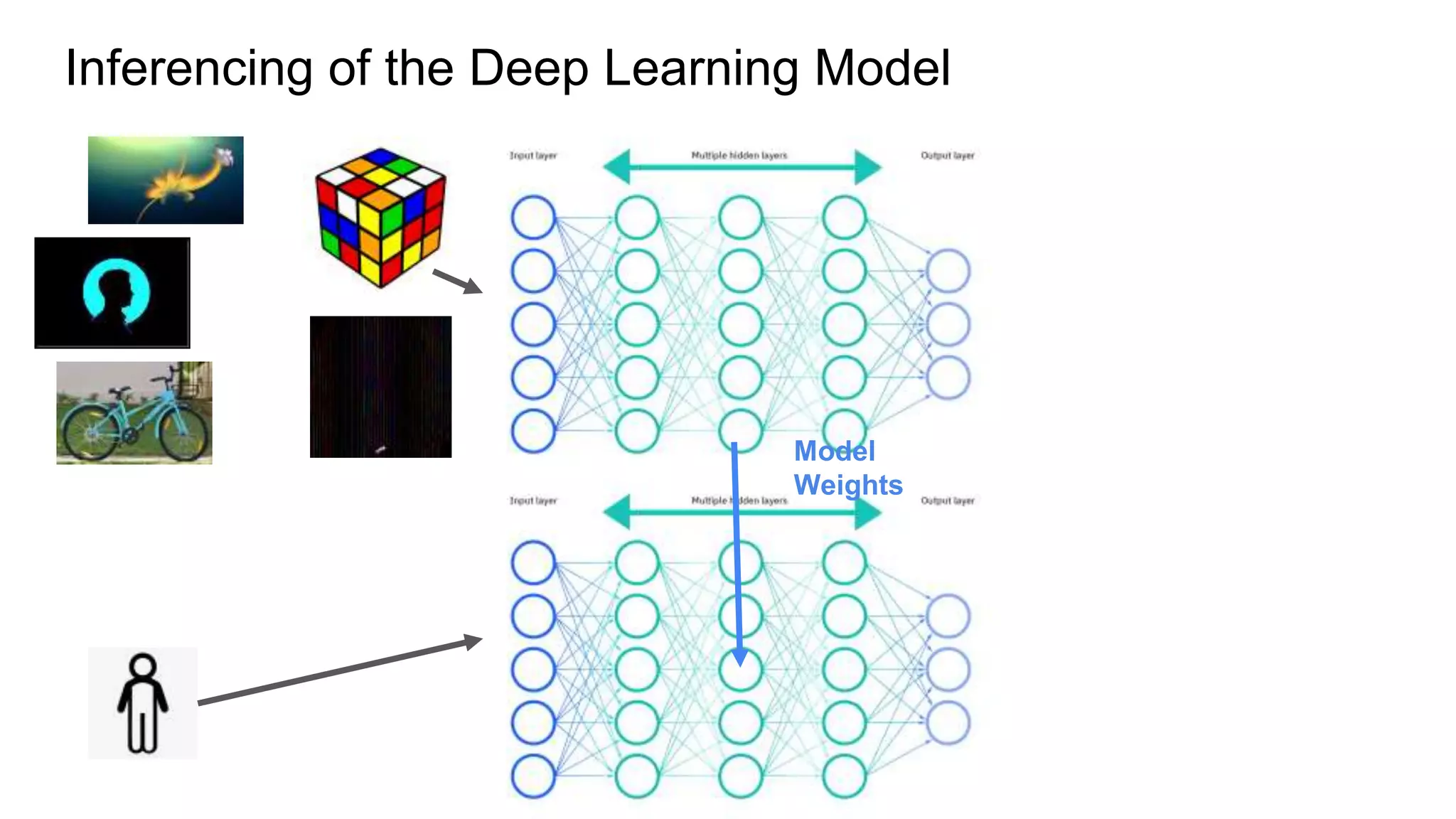
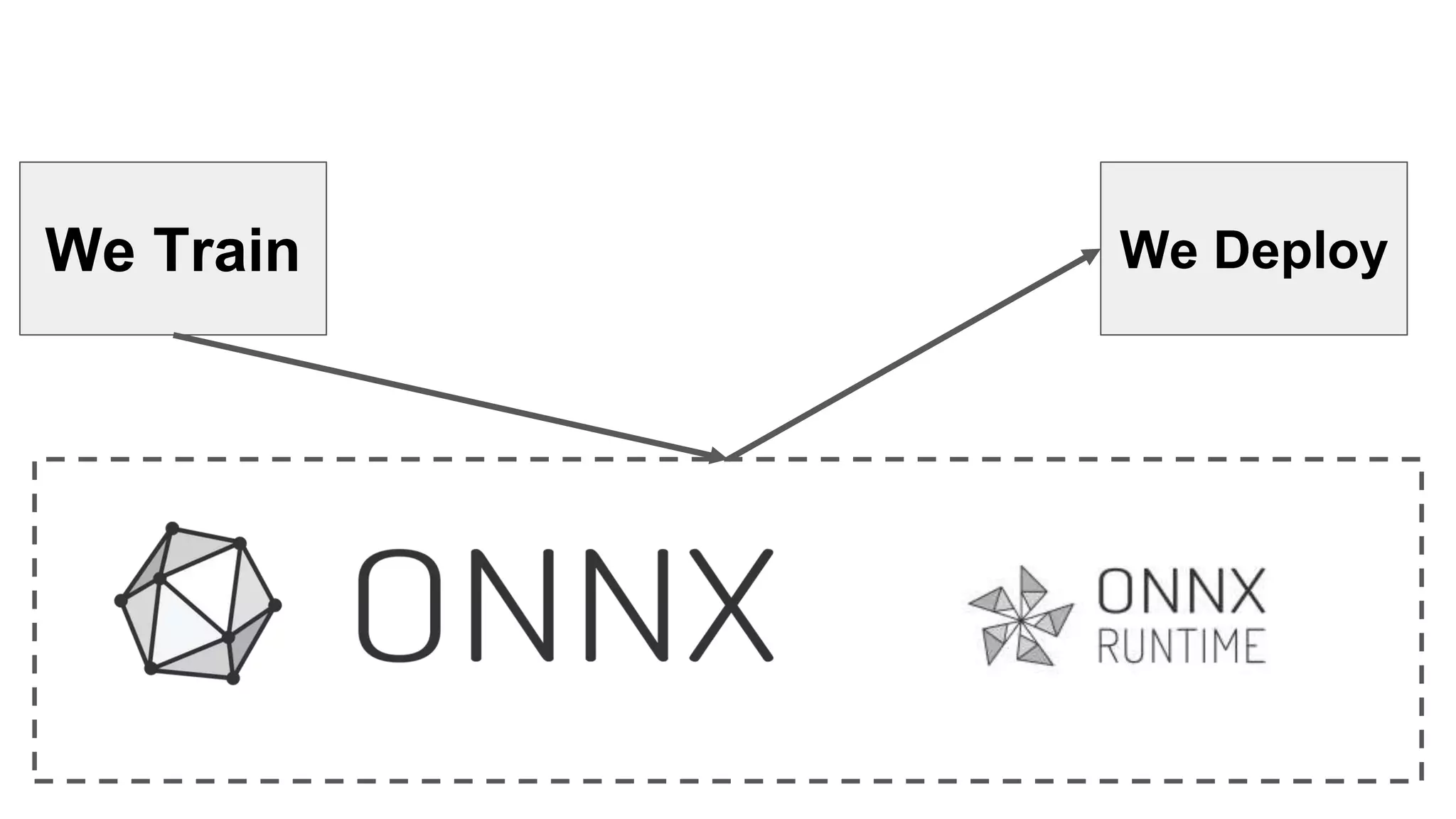
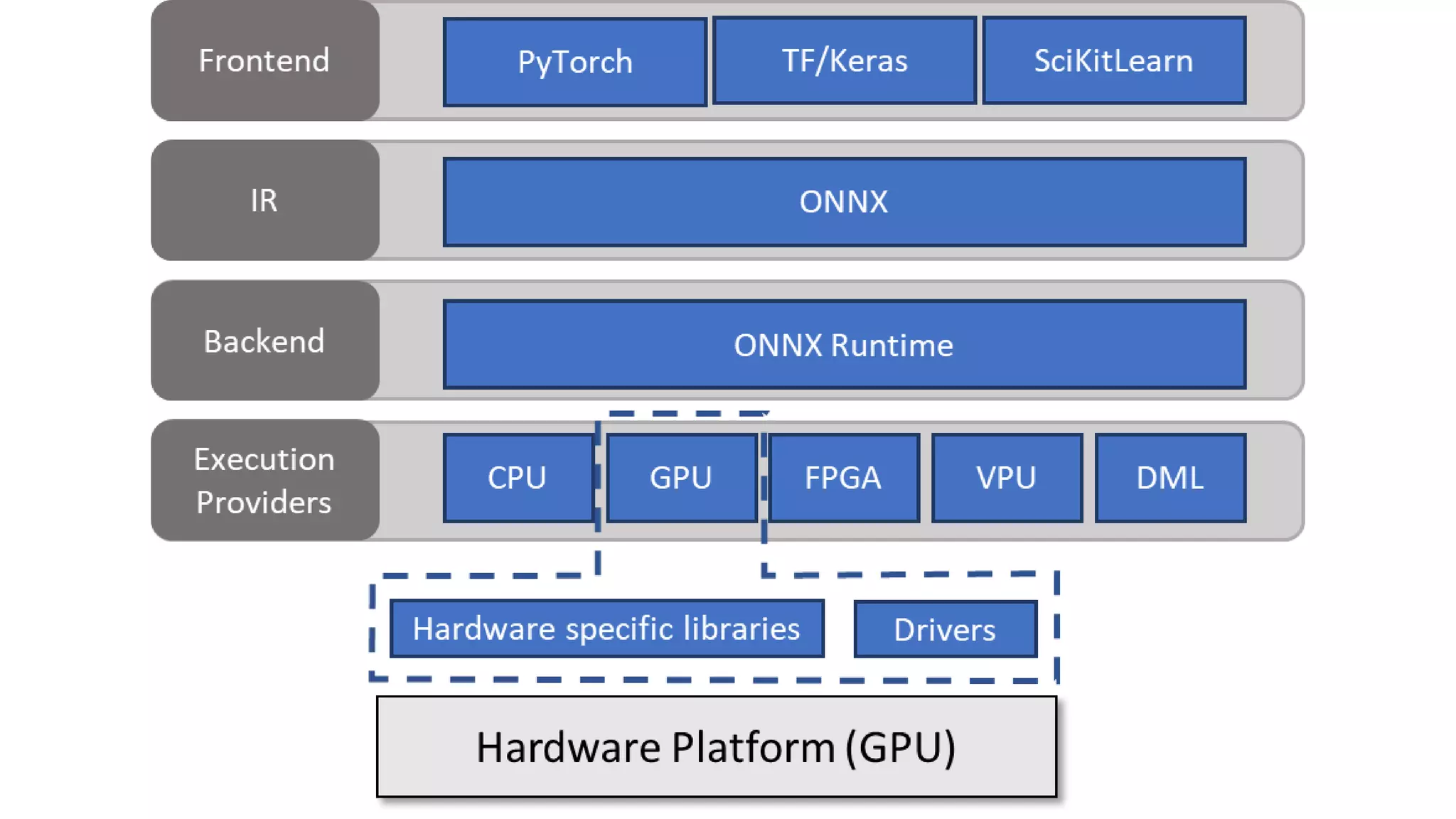
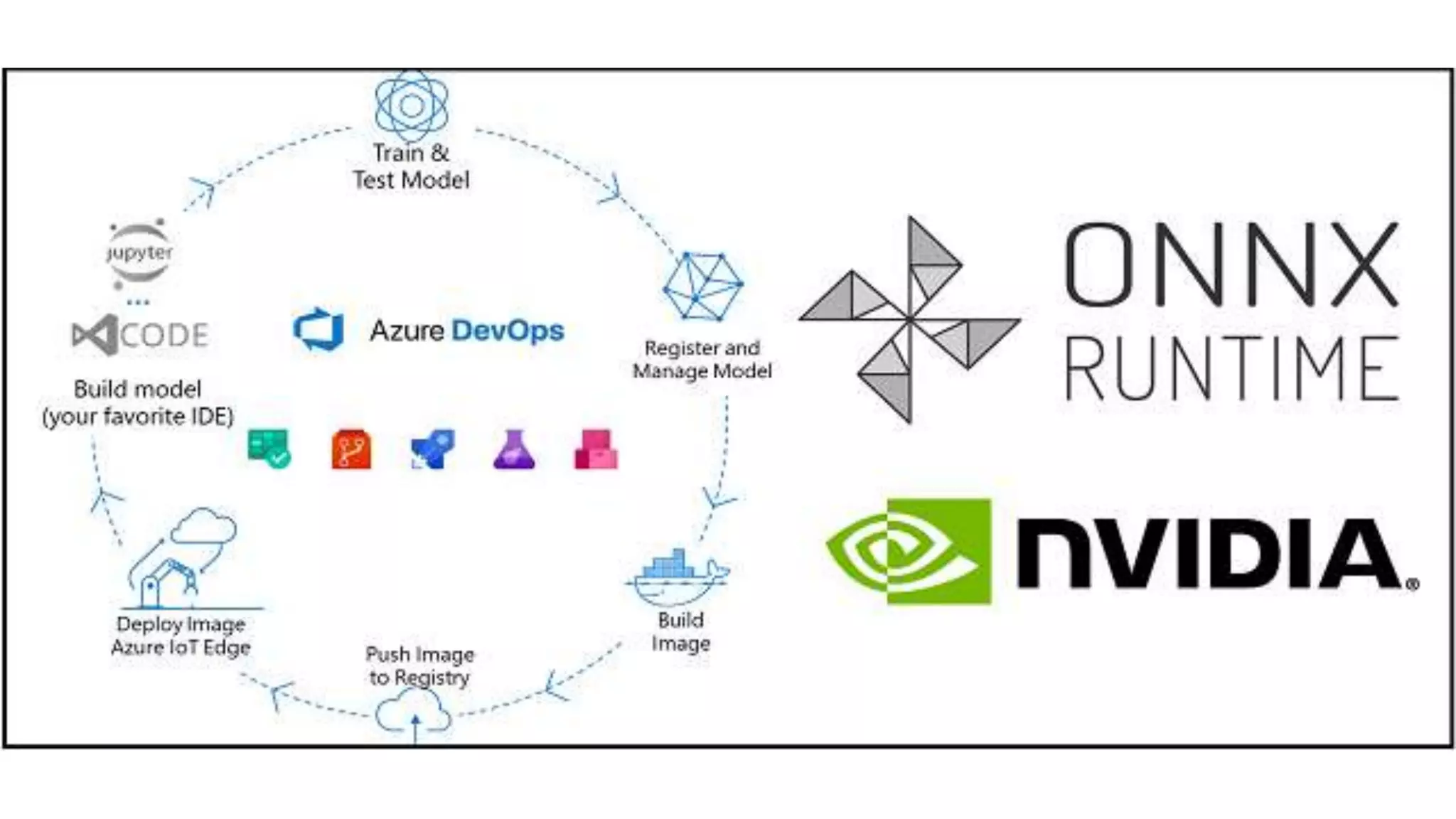
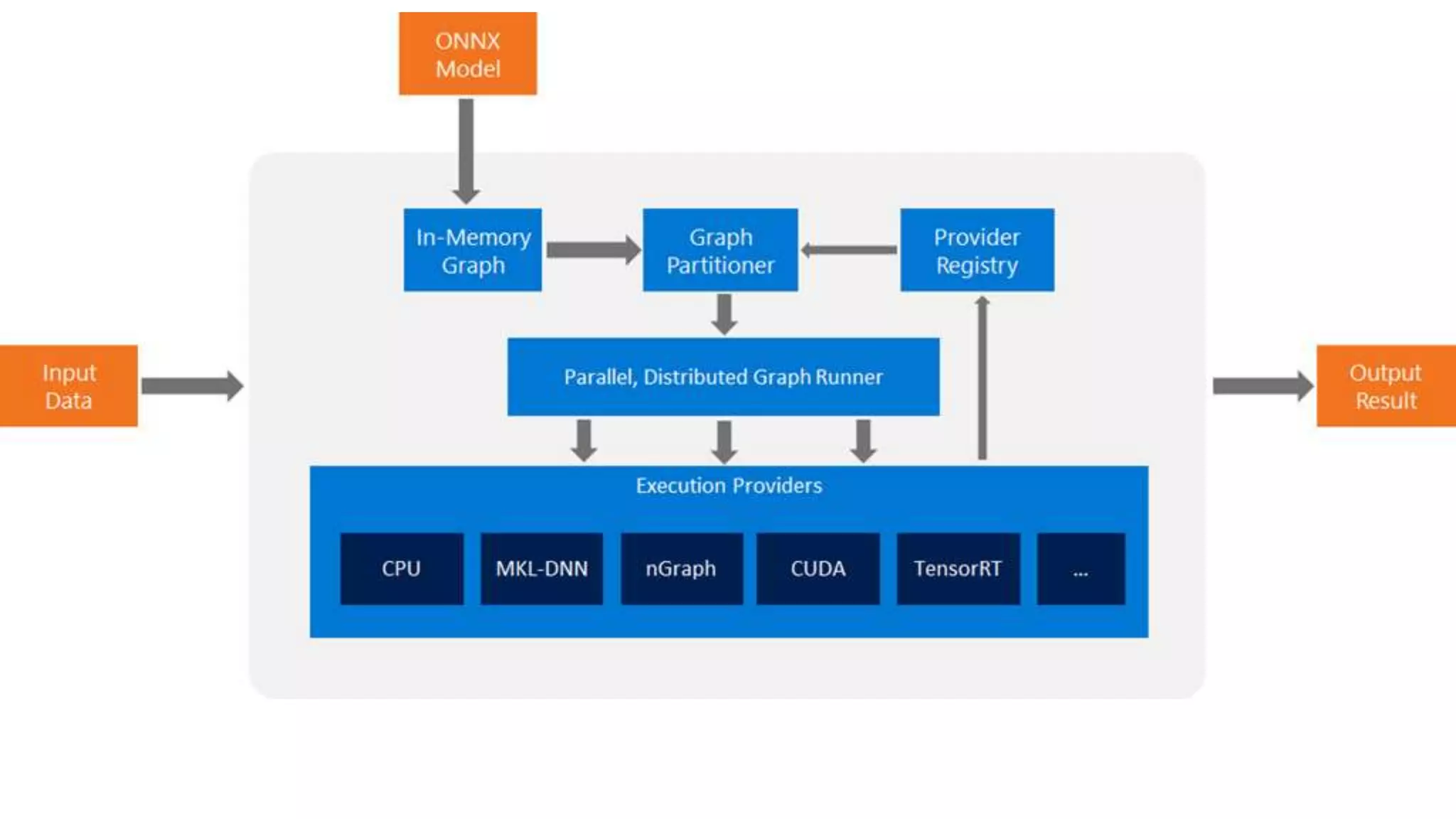
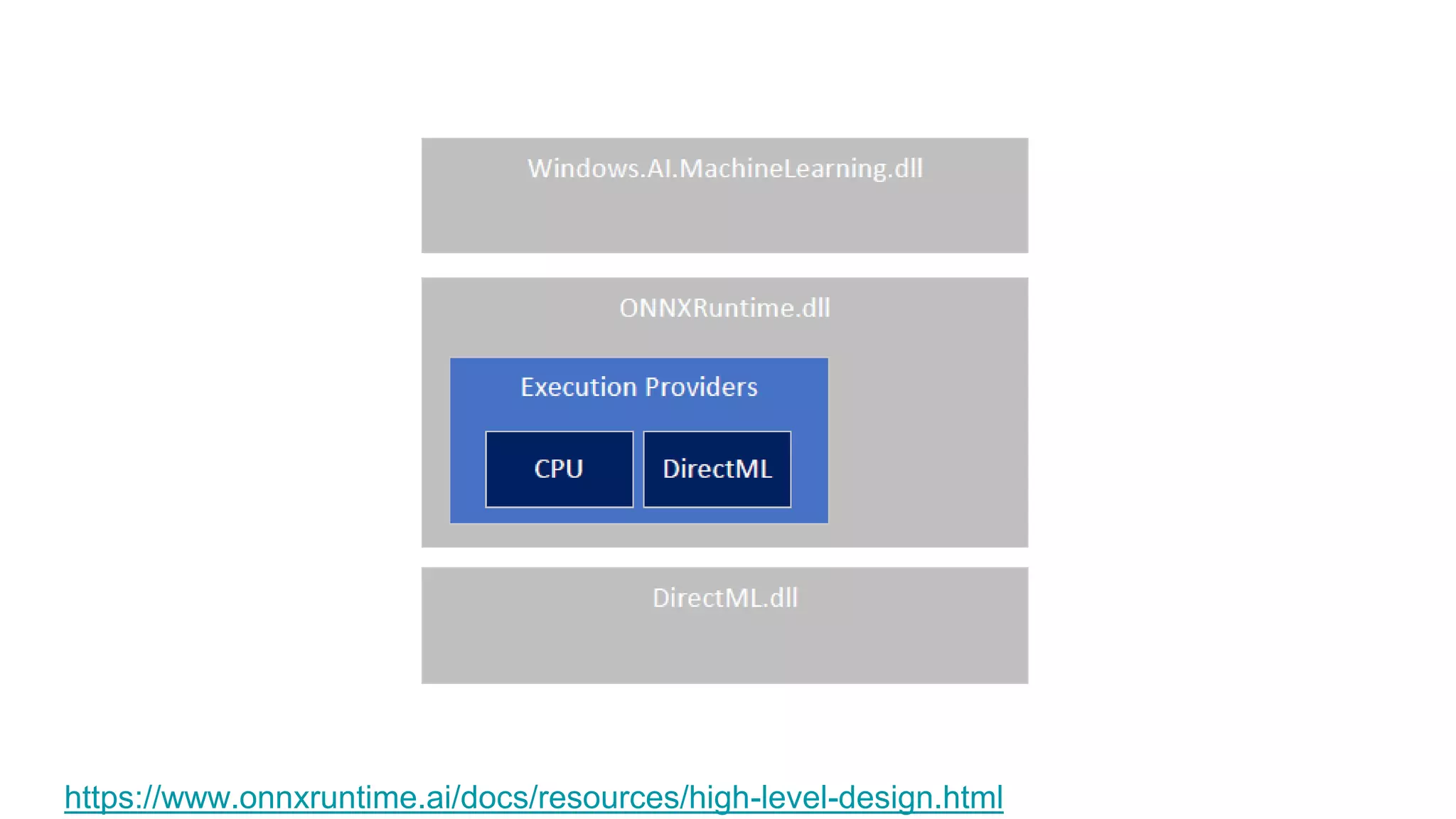
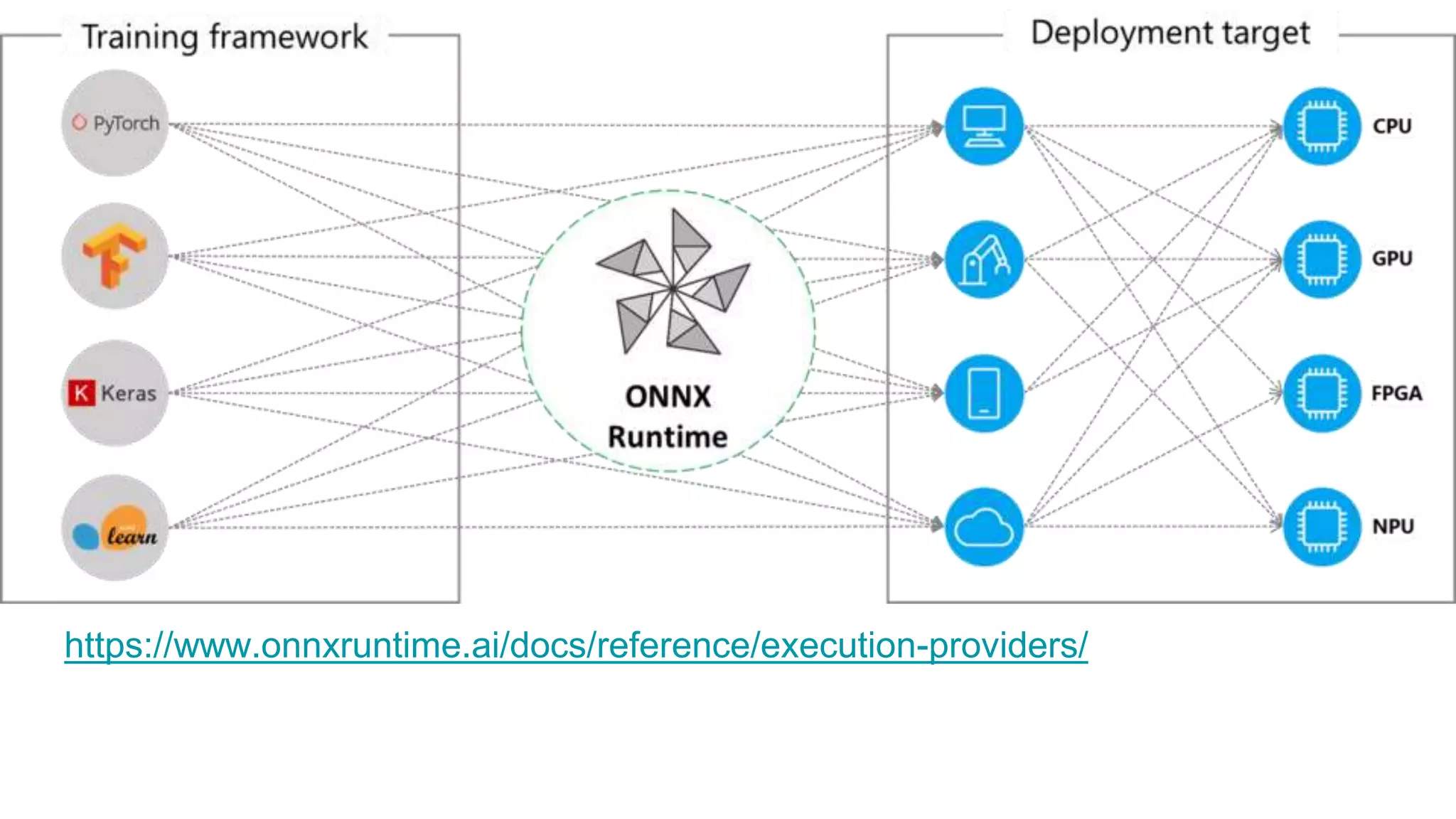
This document provides an overview of ONNX and ONNX Runtime. ONNX is an open format for machine learning models that allows models to be shared across different frameworks and tools. ONNX Runtime is a cross-platform open source inference engine that runs ONNX models. It supports hardware acceleration and has a modular design that allows for custom operators and execution providers to extend its capabilities. The document discusses how ONNX helps with deploying machine learning models from research to production and how ONNX Runtime performs high performance inference through optimizations and hardware acceleration.