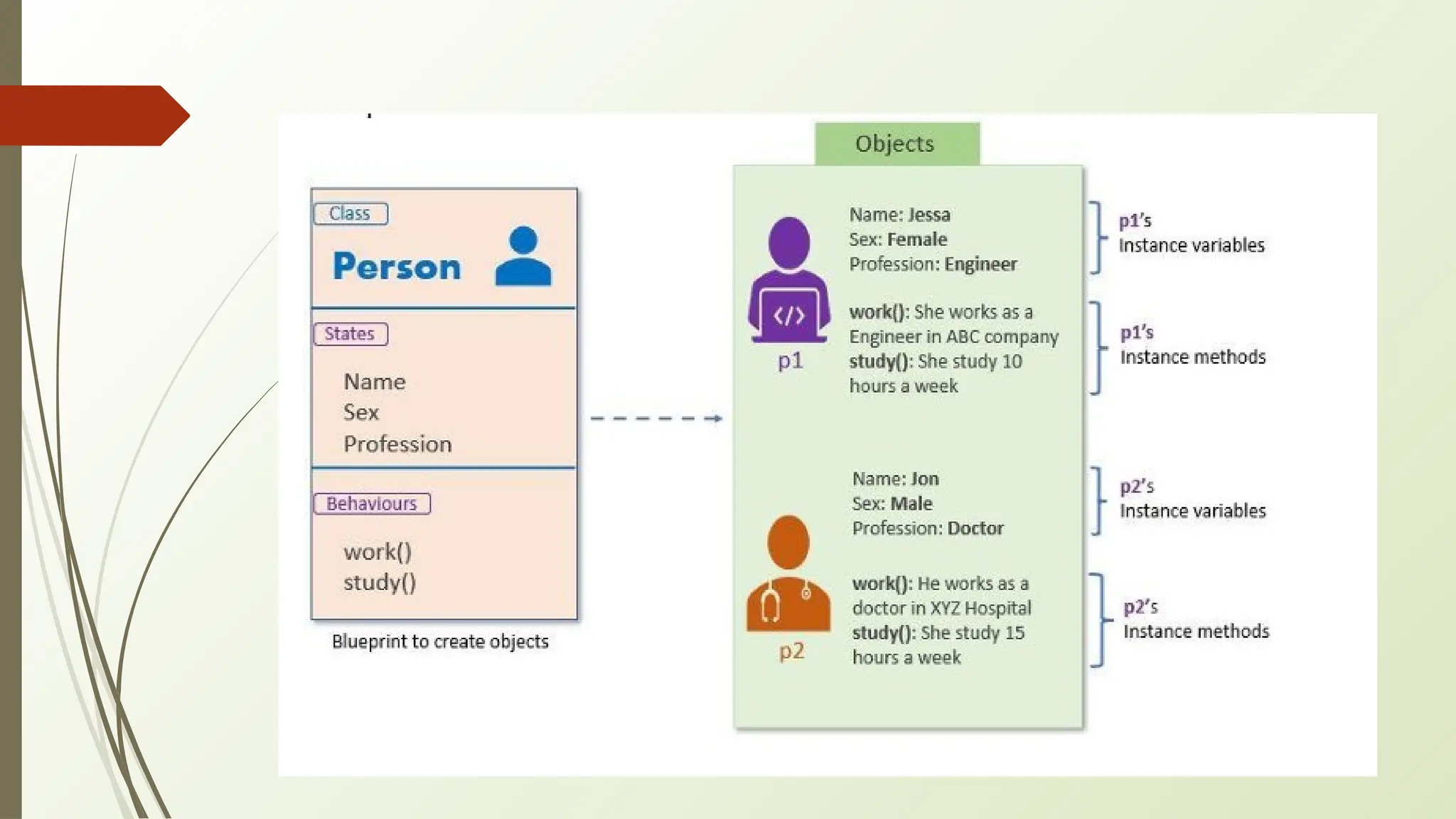
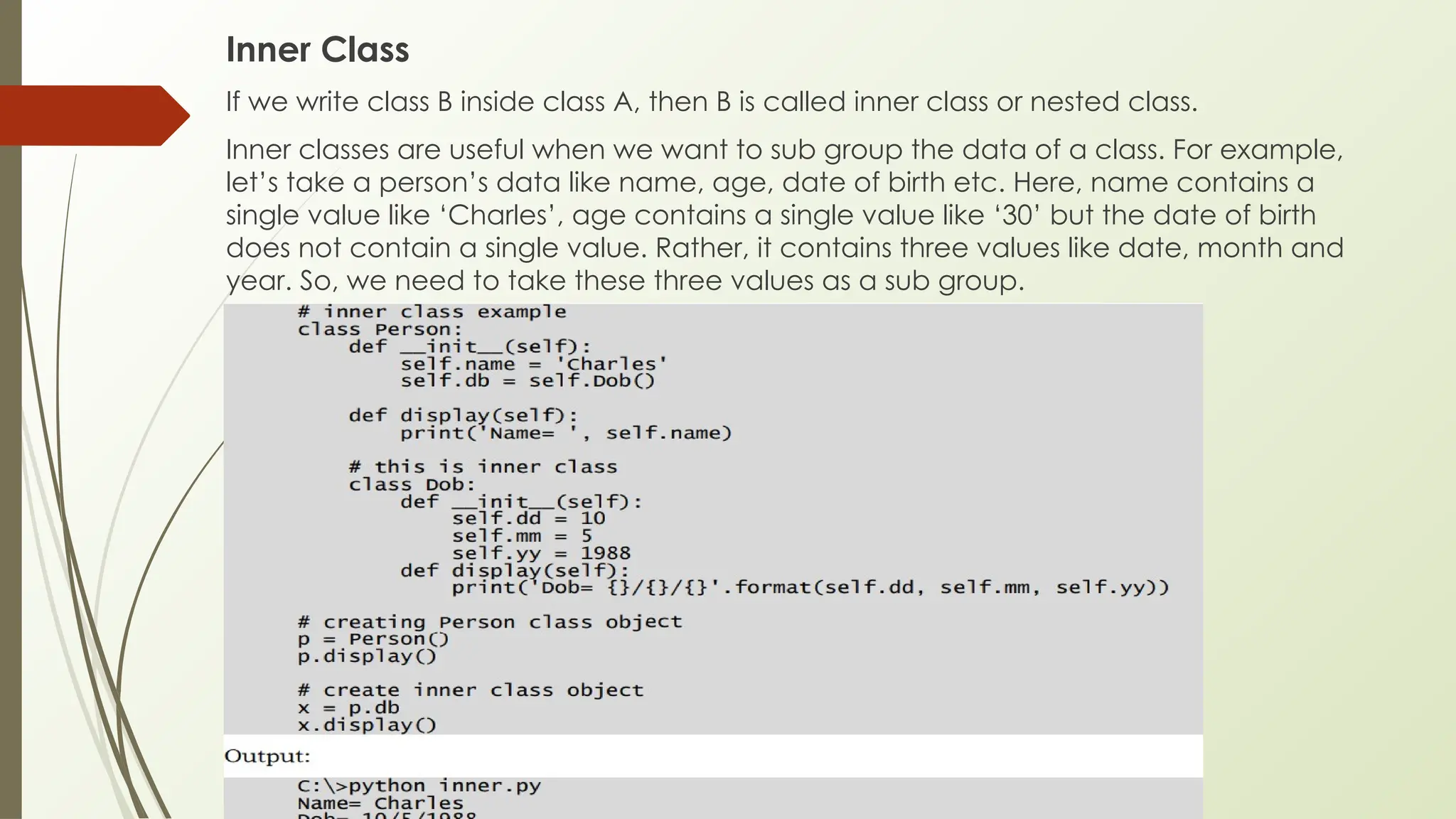
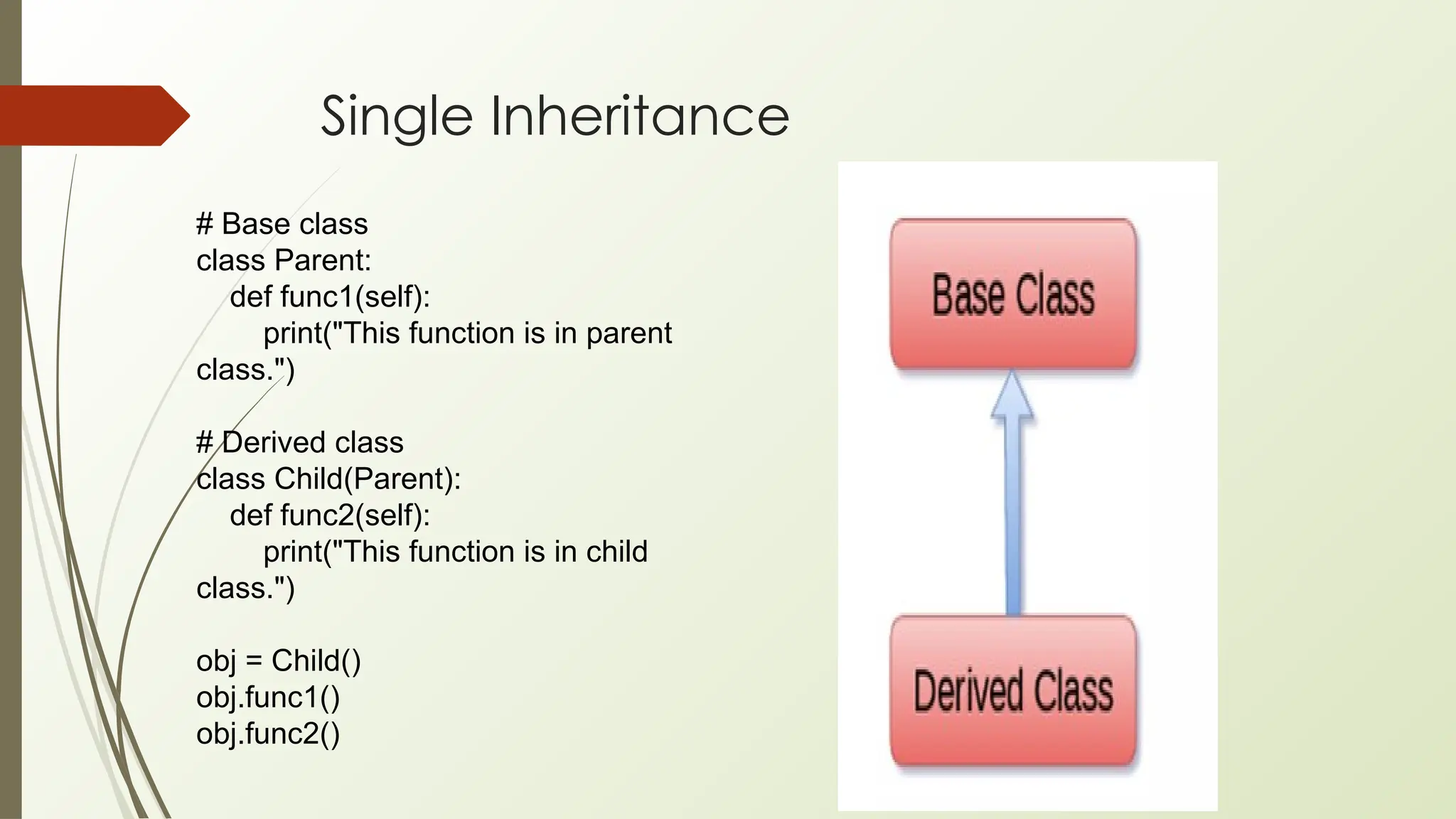
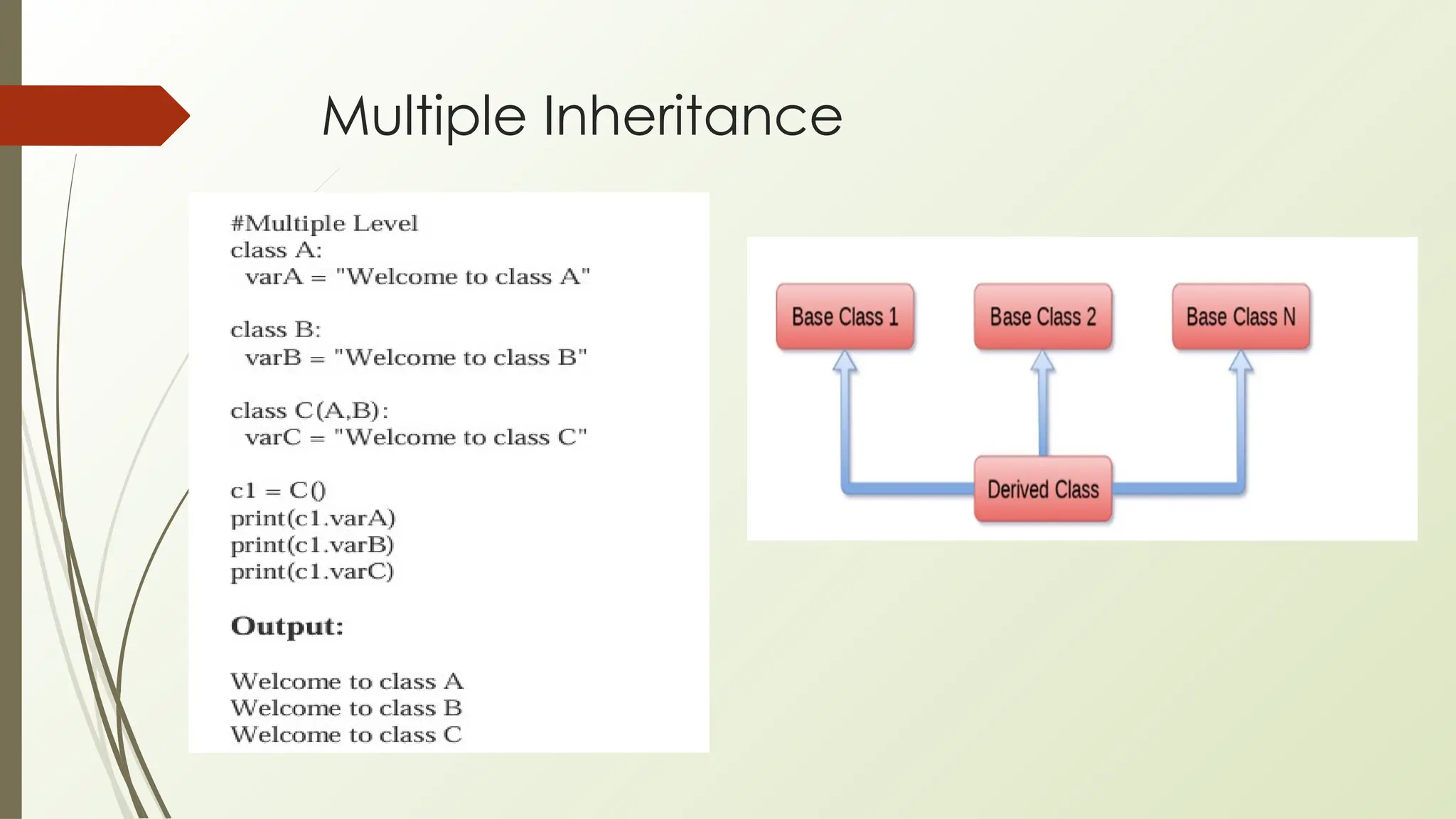
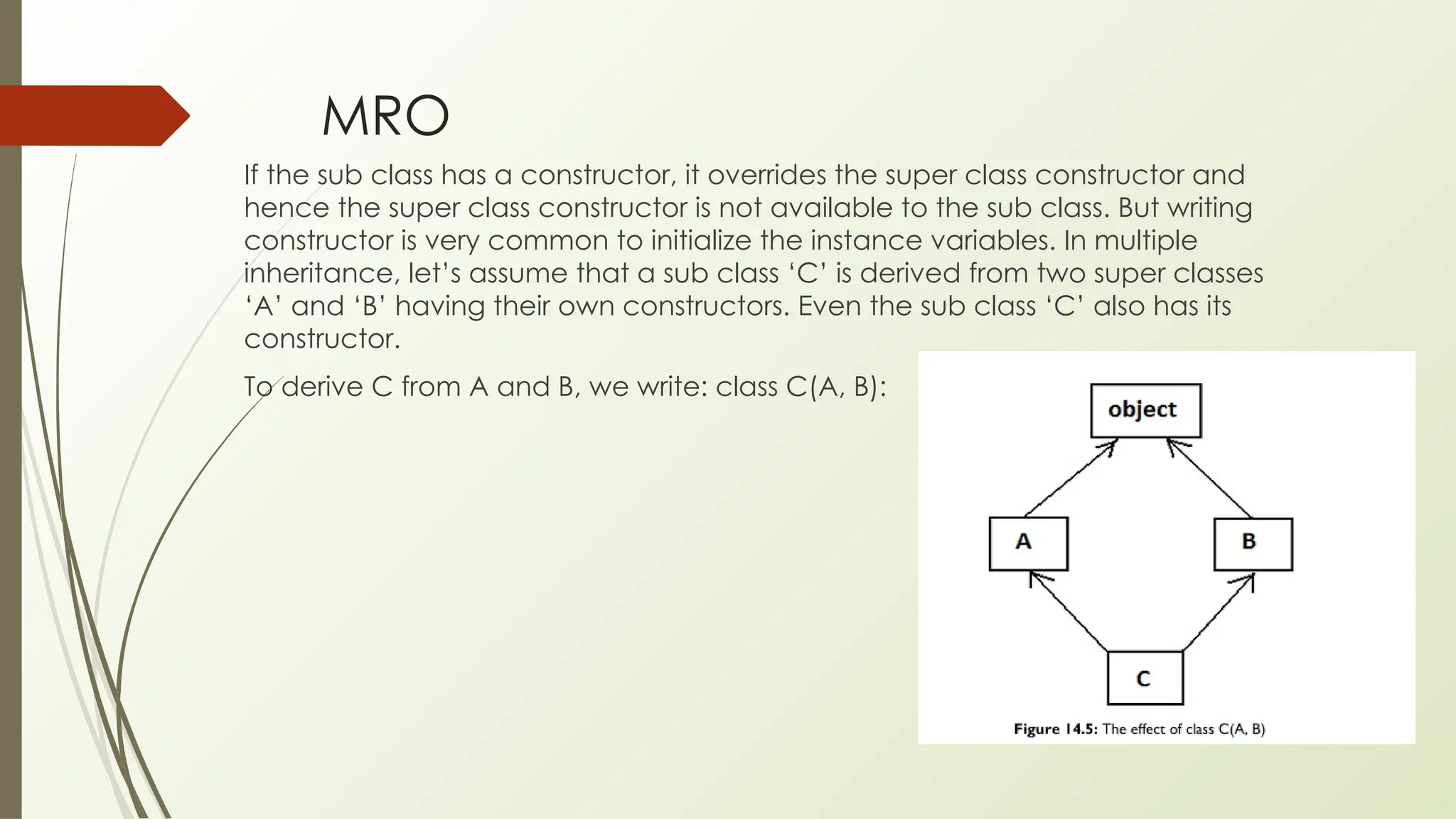
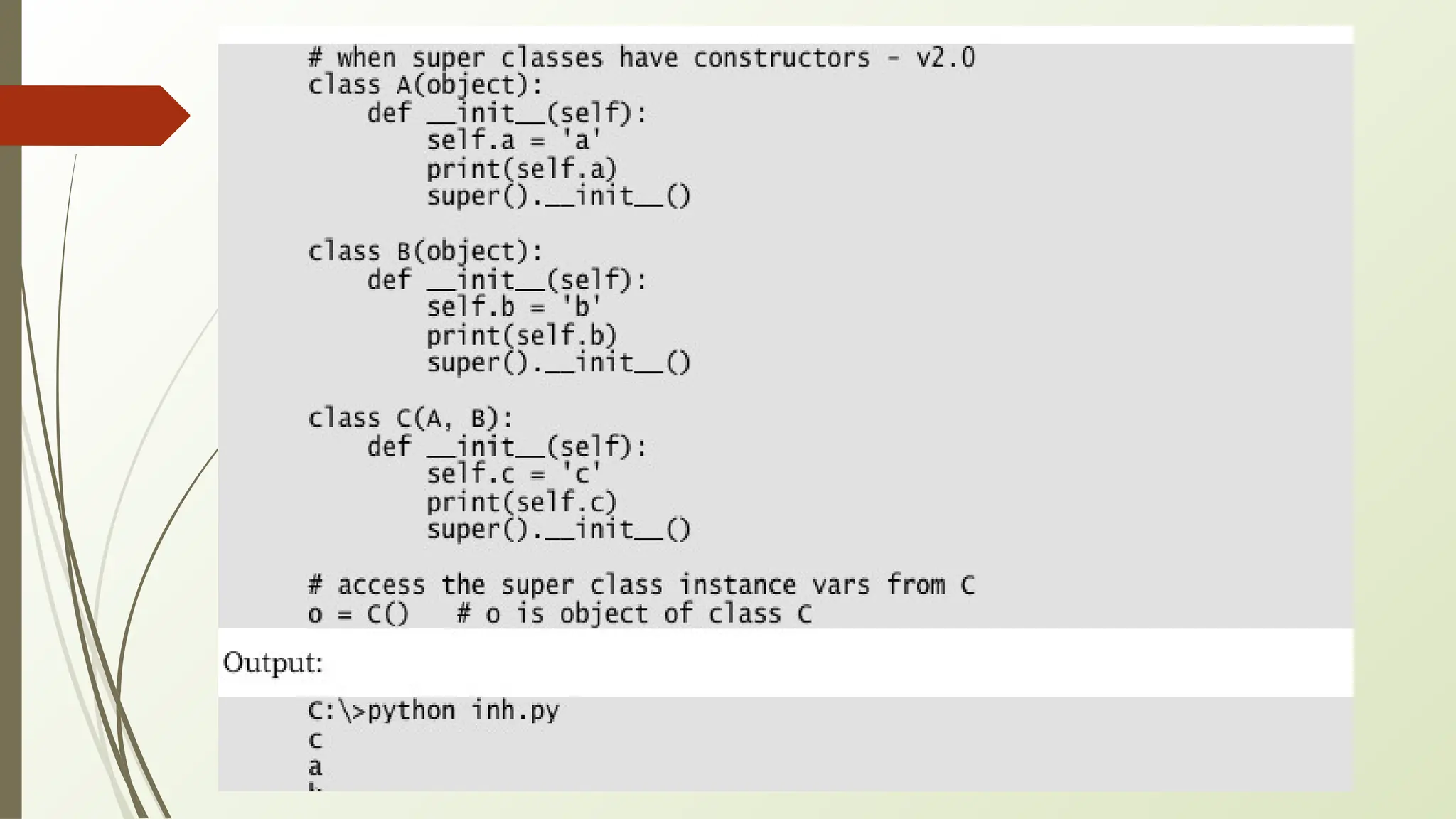
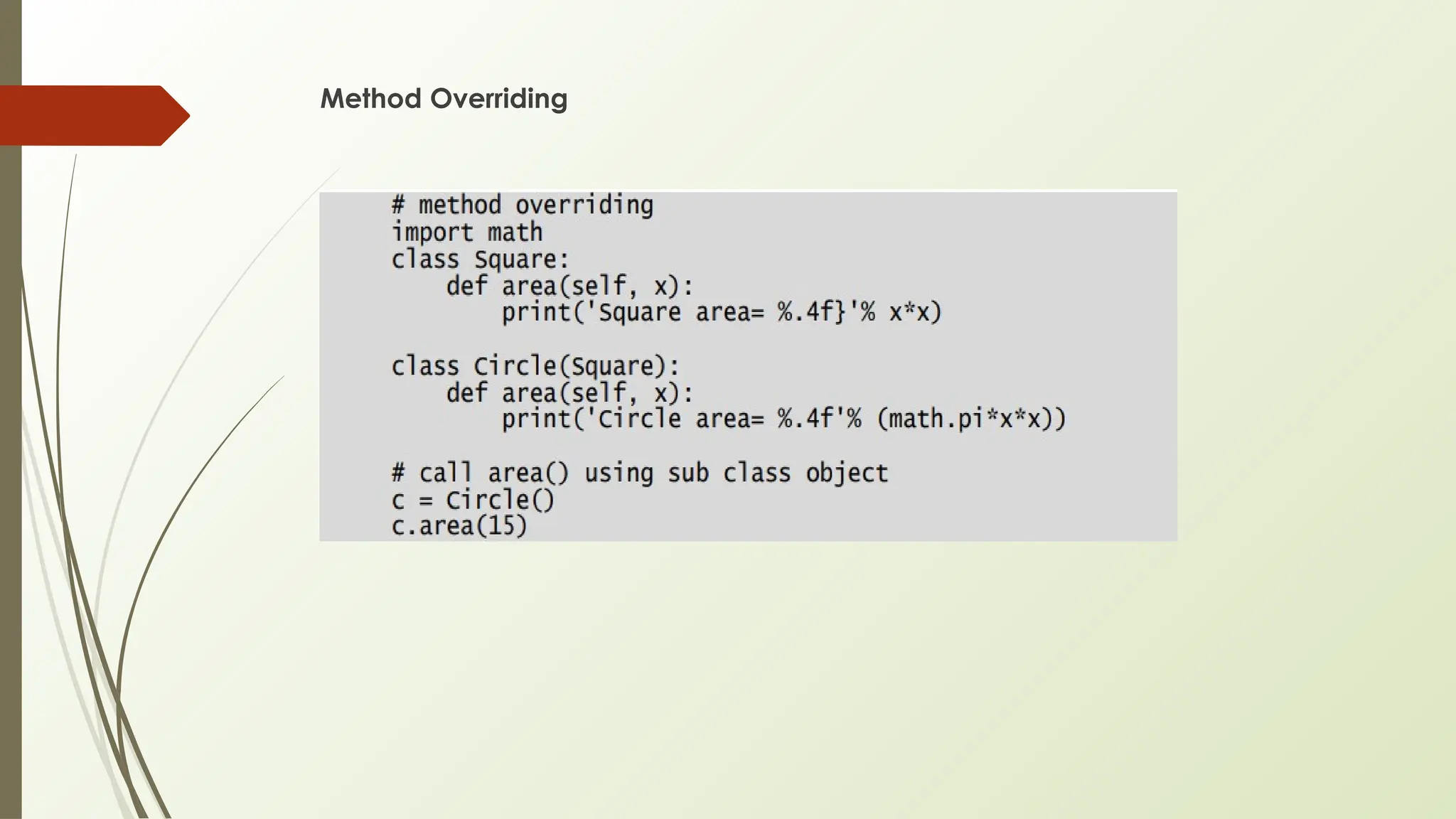
In Python, classes and objects define reusable blueprints for creating objects with attributes and behaviors, using concepts like constructors, self, and inner classes. OOP principles such as polymorphism (method overloading/overriding, abstract classes), encapsulation (private/protected members), inheritance (using super() and MRO), and abstraction (through abstract classes and interfaces) enable modular, reusable, and maintainable code.